Anabaenopeptins from Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Bodies of Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
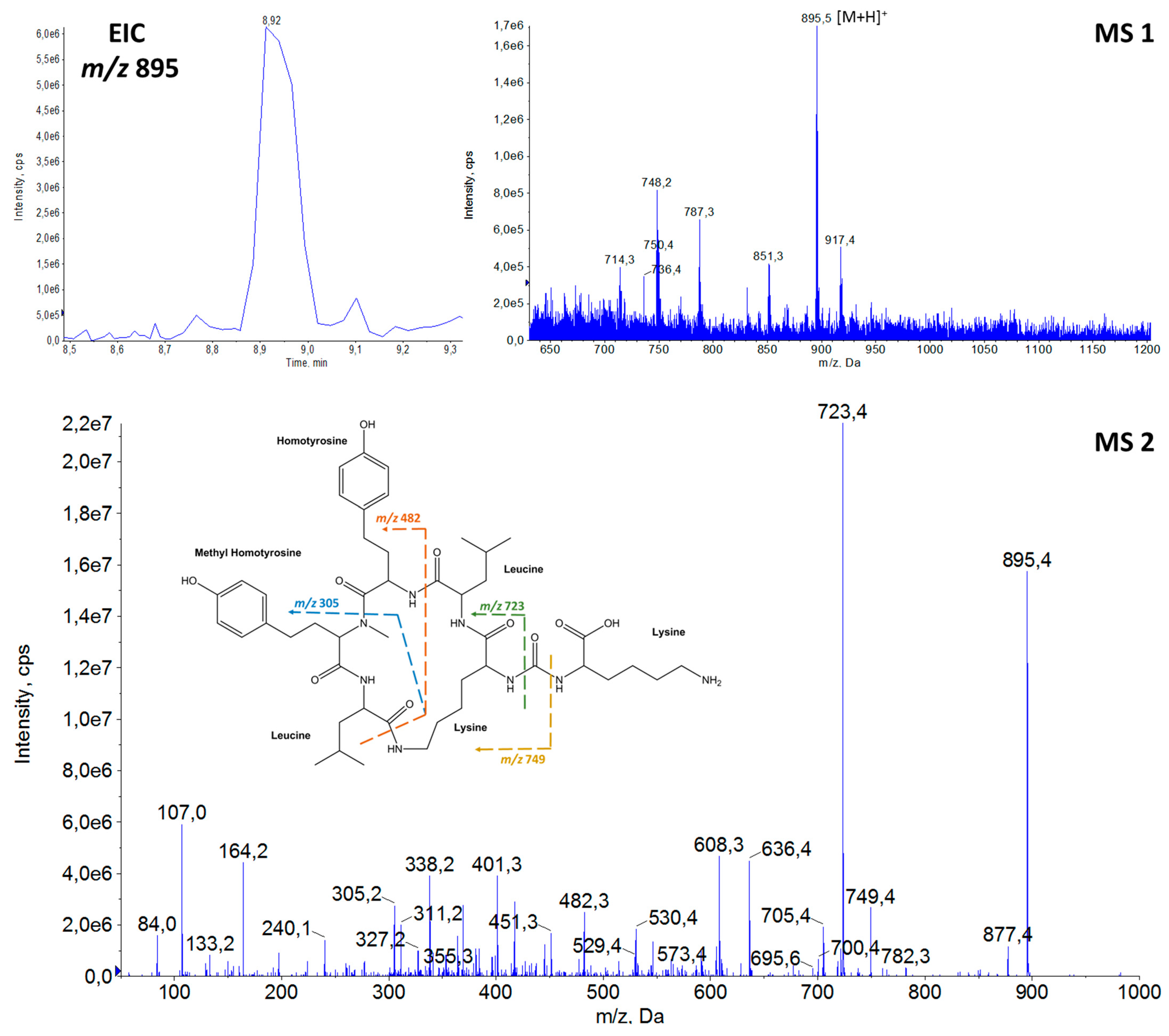
2.1. Structural Elucidation of Anabaenopeptins
2.2. Anabaenopeptins in Cyanobacterial Blooms from Greek Lakes
2.3. Anabaenopeptins in Cyanobacterial Strains Isolated from Greek Freshwaters
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cyanobacterial Bloom Samples
4.2. Source and Culture Conditions of Cyanobacterial Strains
4.3. Sample Preparation and LC–MS/MS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welker, M.; Von Döhren, H. Cyanobacterial peptides—Nature′s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 530–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodani, S.; Suzuki, S.; Ishida, K.; Murakami, M. Five new cyanobacterial peptides from water bloom materials of lake Teganuma (Japan). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 178, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, M.; Von Döhren, H.; Jungblut, P.R. Rapid identification of the new anabaenopeptin G from Planktothrix agardhii HUB 011 using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, M.; Flores, C.; Rivera, J.; Caixach, J. Determination of microcystin variants and related peptides present in a water bloom of Planktothrix (Oscillatoria) rubescens in a Spanish drinking water reservoir by LC/ESI-MS. Toxicon 2004, 44, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkelis, S.; Harjunpää, V.; Lanaras, T.; Sivonen, K. Diversity of hepatotoxic microcystins and bioactive anabaenopeptins in cyanobacterial blooms from Greek freshwaters. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.; Caixach, J. High Levels of Anabaenopeptins Detected in a Cyanobacteria Bloom from N.E. Spanish Sau-Susqueda-El Pasteral Reservoirs System by LC–HRMS. Toxins 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, R.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Cegłowska, M.; Ežerinskis, Ž.; Šapolaitė, J.; Mažeika, J.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Blooms of Toxic Cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena in Norwegian Fjords During Holocene Warm Periods. Toxins 2020, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Sutryk, K.; Hebel, A.; Hohlfeld, N.; Pietrasik, A.; Błaszczyk, A. Nodularia spumigena Peptides—Accumulation and Effect on Aquatic Invertebrates. Toxins 2015, 7, 4404–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spoof, L.; Błaszczyk, A.; Meriluoto, J.; Cegłowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Structures and Activity of New Anabaenopeptins Produced by Baltic Sea Cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanz, M.; Andreote, A.P.D.; Fiore, M.F.; Dörr, F.A.; Pinto, E. Structural Characterization of New Peptide Variants Produced by Cyanobacteria from the Brazilian Atlantic Coastal Forest Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3892–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Esposito, G.; Urajová, P.; Mareš, J.; Ewe, D.; Caso, A.; Macho, M.; Delawská, K.; Kust, A.; Hrouzek, P.; et al. Discovery of Unusual Cyanobacterial Tryptophan-Containing Anabaenopeptins by MS/MS-Based Molecular Networking. Molecules 2020, 25, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, P.R.; do Amaral, S.C.; Siqueira, A.S.; Xavier, L.P.; Santos, A.V. Anabaenopeptins: What We Know So Far. Toxins 2021, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, M.; Christiansen, G.; Von Döhren, H. Diversity of coexisting Planktothrix (cyanobacteria) chemotypes deduced by mass spectral analysis of microystins and other oligopeptides. Arch. Microbiol. 2004, 182, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrlack, T.; Skulberg, R.; Skulberg, O.M. Distribution of oligopeptide chemotypes of the cyanobacterium planktothrix and their persistence in selected lakes in fennoscandia. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Harada, K.-I.; Suzuki, M.; Kondo, F.; Ikai, Y.; Oka, H.; Carmichael, W.W.; Sivonen, K. Occurrence of novel cyclicpeptides together with microcystins from toxic cyanobacteria, Anabaena species. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 559–562. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Sivonen, K.; Nakano, T.; Harada, K.-I. Structural elucidation of cyanobacterial peptides encoded by peptide synthetase gene in Anabaena species. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6863–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach-Pogrebinsky, O.; Carmeli, S. Three novel anabaenopeptins from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 10233–10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonk, L.; Welker, M.; Huisman, J.; Visser, P.M. Production of cyanopeptolins, anabaenopeptins, and microcystins by the harmful cyanobacteria Anabaena 90 and Microcystis PCC 7806. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Von Döhren, H. Determination of Oligopeptide Diversity within a Natural Population of Microcystis spp. (Cyanobacteria) by Typing Single Colonies by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5069–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welker, M.; Brunke, M.; Preussel, K.; Lippert, I.; von Döhren, H. Diversity and distribution of Microcystis (cyanobacteria) oligopeptide chemotypes from natural communities studies by single-colony mass spectrometry. Microbiology 2004, 150, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beresovsky, D.; Hadas, O.; Livne, A.; Sukenik, A.; Kaplan, A.; Carmeli, S. Toxins and biologically active secondary metabolites of Microcystis sp. isolated from Lake Kinneret. Isr. J. Chem. 2006, 46, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Maršálek, B.; Šejnohová, L.; von Döhren, H. Detection and identification of oligopeptides in Microcystis (cyanobacteria) colonies: Toward an understanding of metabolic diversity. Peptides 2006, 27, 2090–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, M.; Kiss-Szikszai, A.; Gonda, S.; Boros, G.; Vitál, Z.; Borsodi, A.K.; Krett, G.; Borics, G.; Ujvárosi, A.Z.; Vasas, G. Microcystis chemotype diversity in the alimentary tract of bigheaded carp. Toxins 2019, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shishido, T.K.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Wahlsten, M.; Fiore, M.F.; Sivonen, K. Simultaneous Production of Anabaenopeptins and Namalides by the Cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. CENA543. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, M.; Kiss-Szikszai, A.; Gonda, S.; Parizsa, P.; Deák, B.; Török, P.; Valkó, O.; Felföldi, T.; Vasas, G. Chemotyping of terrestrial Nostoc-like isolates from alkali grassland areas by non-targeted peptide analysis. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Shin, H.J.; Matsuda, H.; Ishida, K.; Yamaguchi, K. A cyclic peptide, anabaenopeptin B, from the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Kaya, K. Oscillamide Y, a chymotrypsin inhibitor from toxic Oscillatoria agardhii. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 5933–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Matsuda, H.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, K. Anabaenopeptins E and F, two new cyclic peptides from the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii (NIES-204). J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itou, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Ishida, K.; Murakami, M. Anabaenopeptins G and H, Potent Carboxypeptidase A inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii (NIES-595). Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Usui, T.; Ueda, K.; Osada, H.; Kaya, K. Isolation of new protein phosphatase inhibitors from two cyanobacteria species, Planktothrix spp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosol, S.; Schmidt, J.; Kurmayer, R. Variation in peptide net production and growth among strains of the toxic cyanobacterium Planktothrix spp. Eur. J. Phycol. 2009, 44, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okumura, H.S.; Philmus, B.; Portmann, C.; Hemscheidt, T.K. Homotyrosine-containing cyanopeptolins 880 and 960 and anabaenopeptins 908 and 915 from Planktothrix agardhii CYA 126/8. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grach-Pogrebinsky, O.; Sedmak, B.; Carmeli, S. Protease inhibitors from a Slovenian Lake Bled toxic waterbloom of the cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 8329–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Erhard, M. Consistency between chemotyping of single filaments of Planktothrix rubescens (cyanobacteria) by MALDI-TOF and the peptide patterns of strains determined by HPLC-MS. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.-I.; Fujii, K.; Shimada, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sano, H.; Adachi, K.; Carmichael, W.W. Two cyclic peptides, anabaenopeptins, a third group of bioactive compounds from the cyanobacteriumAnabaena flos-aquae NRC 525-17. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Agha, R.; Cirés, S.; Lezcano, M.Á.; Sánchez-Contreras, M.; Waara, K.-O.; Utkilen, H.; Quesada, A. Effects of harmful cyanobacteria on the freshwater pathogenic free-living amoeba Acanthamoeba castellanii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130–131, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, M.L.; Fastner, J.; Dittmann, E.; Christiansen, G.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Variation between strains of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa isolated from a Portuguese river. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.; Saker, M.L.; Moreira, C.; Welker, M.; Fastner, J.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Peptide diversity in strains of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa isolated from Portuguese water supplies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiv, S.; Carmeli, S. Protease Inhibitors from Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom Material Collected from the Dalton Reservoir, Israel. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhiainen, L.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Urmann, M.; Sivonen, K. Two Alternative Starter Modules for the Non-Ribosomal Biosynthesis of Specific Anabaenopeptin Variants in Anabaena (Cyanobacteria). Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, M.; Suzuki, S.; Itou, Y.; Kodani, S.; Ishida, K. New anabaenopeptins, carboxypeptidaze-A inhibitors from the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Sivonen, K.; Adachi, K.; Noguchi, K.; Sano, H.; Hirayama, K.; Suzuki, M.; Harada, K.-I. Comparative study of toxic and non-toxic cyanobacterial products: Novel peptides from toxic Nodularia spumigena AV1. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 5525–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.; Wilson, N.; Tabudravu, J.N.; Edwards, C.; Lawton, L.A.; Motti, C.; Wright, A.D.; Diederich, M.; Jaspars, M. New nodulopeptins from Nodularia spumigena KAC 66. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Kaczkowska, M.J.; Blaszczyk, A.; Akcaalan, R.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J. Diversity of Peptides Produced by Nodularia spumigena from Various Geographical Regions. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Bertos-Fortis, M.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Fidor, A.; Legrand, C. Chemical and Genetic Diversity of Nodularia spumigena from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bober, B.; Lechowski, Z.; Bialczyk, J. Determination of some cyanopeptides synthesized by Woronichinia naegeliana (Chroococcales, Cyanophyceae). Phycol. Res. 2011, 59, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, B.; Chrapusta-Srebrny, E.; Bialczyk, J. Novel cyanobacterial metabolites, cyanopeptolin 1081 and anabaenopeptin 899, isolated from an enrichment culture dominated by Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin. Eur. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggqvist, K.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Błaszczyk, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Meriluoto, J. Morphologic, Phylogenetic and Chemical Characterization of a Brackish Colonial Picocyanobacterium (Coelosphaeriaceae) with Bioactive Properties. Toxins 2016, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zi, J.; Lantvit, D.D.; Swanson, S.M.; Orjala, J. Lyngbyaureidamides A and B, two anabaenopeptins from the cultured freshwater cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. (SAG 36.91). Phytochemistry 2012, 74, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthew, S.; Ross, C.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Pompanopeptins A and B, new cyclic peptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoides. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, V.; Carmeli, S. Schizopeptin 791, a New Anabeanopeptin-like Cyclic Peptide from the Cyanobacterium Schizothrix sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1187–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Krick, A.; Kehraus, S.; Mehner, C.; Hart, M.; Küpper, F.C.; Saxena, K.; Prinz, H.; Schwalbe, H.; Janning, P.; et al. Brunsvicamides A−C: Sponge-Related Cyanobacterial Peptides with Mycobacterium tuberculosis Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitory Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4871–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.I.; Sato, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Shigemori, H.; Nakamura, T.; Ohizumi, Y. Keramamide A, a novel peptide from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1991, 10, 2609–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Sato, M.; Murayama, T.; Ishibashi, M.; Wälchi, M.R.; Kanai, M.; Shoji, J.; Ohizumi, Y. Konbamide, a novel peptide with calmodulin antagonistic activity from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1991, 15, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemoto, H.; Yahiro, Y.; Shigemori, H.; Tsuda, M.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y.; Kobayashi, J.I. Keramamides K and L, new cyclic peptides containing unusual tryptophan residue from Theonella sponge. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 6719–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Keffer, J.L.; Lloyd, J.R.; Colin, P.L.; Bewley, C.A. Paltolides A-C, anabaenopeptin-type peptides from the Palau sponge theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.J.; Tenney, K.; Yee, D.F.; Martinez, L.; Media, J.E.; Valeriote, F.A.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Crews, P. Probing the Bioactive Constituents from Chemotypes of the Sponge Psammocinia aff. bulbosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.W.; Harper, M.K.; Faulkner, D.J. Mozamides A and B, Cyclic Peptides from a Theonellid Sponge from Mozambique. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Craig, M.; Holmes, C.F.B.; Andersen, R.J. Ferintoic Acids A and B, New Cyclic Hexapeptides from the Freshwater Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rounge, T.B.; Rohrlack, T.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Kristensen, T.; Jakobsen, K.S. A genome-wide analysis of nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene clusters and their peptides in a Planktothrix rubescens strain. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christiansen, G.; Philmus, B.; Hemscheidt, T.; Kurmayer, R. Genetic variation of adenylation domains of the anabaenopeptin synthesis operon and evolution of substrate promiscuity. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3822–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Entfellner, E.; Frei, M.; Christiansen, G.; Deng, L.; Blom, J.; Kurmayer, R. Evolution of Anabaenopeptin Peptide Structural Variability in the Cyanobacterium Planktothrix. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanobacterial peptides beyond microcystins—A review on co-occurrence, toxicity, and challenges for risk assessment. Water Res. 2019, 151, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, H.; Kurita, K.L.; Pan, L.; Wahome, P.G.; He, H.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Carter, G.T.; Linington, R.G. Discovery of anabaenopeptin 679 from freshwater algal bloom material: Insights into the structure–activity relationship of anabaenopeptin protease inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrir-Ilan, E.; Carmeli, S. Eight novel serine proteases inhibitors from a water bloom of the cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 9194–9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubik, A.; Sedmak, B.; Novinec, M.; Lenarčič, B.; Lah, T.T. Cytotoxic and peptidase inhibitory activities of selected non-hepatotoxic cyclic peptides from cyanobacteria. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmak, B.; Eleršek, T.; Grach-Pogrebinsky, O.; Carmeli, S.; Sever, N.; Lah, T.T. Ecotoxicologically relevant cyclic peptides from cyanobacterial bloom (Planktothrix rubescens)—A threat to human and environmental health. Radiol. Oncol. 2008, 42, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkelis, S.; Lanaras, T.; Sivonen, K. The presence of microcystins and other cyanobacterial bioactive peptides in aquatic fauna collected from Greek freshwaters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder, H.; Liesum, A.; Lönze, P.; Stump, H.; Hoffmann, H.; Schiell, M.; Kurz, M.; Toti, L.; Bauer, A.; Kallus, C.; et al. Isolation, Co-Crystallization and Structure-Based Characterization of Anabaenopeptins as Highly Potent Inhibitors of Activated Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFIa). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenz, K.A.; Miller, T.R.; Ma, H. Anabaenopeptins and cyanopeptolins induce systemic toxicity effects in a model organism the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Toporowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Effects of secondary metabolites produced by different cyanobacterial populations on the freshwater zooplankters Brachionus calyciflorus and Daphnia pulex. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11793–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedmak, B.; Carmeli, S.; Eleršek, T. “Non-toxic” cyclic peptides induce lysis of cyanobacteria—An effective cell population density control mechanism in cyanobacterial blooms. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 56, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstvedt, C.B.; Rohrlack, T.; Ptacnik, R.; Edvardsen, B. On the effect of abiotic environmental factors on production of bioactive oligopeptides in field populations of Planktothrix spp. (Cyanobacteria). J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohrlack, T.; Edvardsen, B.; Skulberg, R.; Halstvedt, C.B.; Utkilen, H.C.; Ptacnik, R.; Skulberg, O.M. Oligopeptide chemotypes of the toxic freshwater cyanobacterium Planktothrix can form sub-populations with dissimilar ecological traits. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, M.; Kobos, J.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Non-ribosomal peptides produced by Planktothrix agardhii from Siemianówka Dam Reservoir SDR (northeast Poland). Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toporowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Pawlik-Skowrońska, B. The Effects of Cyanobacterial Bloom Extracts on the Biomass, Chl-a, MC and Other Oligopeptides Contents in a Natural Planktothrix agardhii Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kust, A.; Řeháková, K.; Vrba, J.; Maicher, V.; Mareš, J.; Hrouzek, P.; Chiriac, M.-C.; Benedová, Z.; Tesařová, B.; Saurav, K. Insight into Unprecedented Diversity of Cyanopeptides in Eutrophic Ponds Using an MS/MS Networking Approach. Toxins 2020, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, H.I.; Jüttner, F. Inter-annual stability of oligopeptide patterns of Planktothrix rubescens blooms and mass mortality of Daphnia in Lake Hallwilersee. Limnologica 2008, 38, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, C.; Caixach, J. An integrated strategy for rapid and accurate determination of free and cell-bound microcystins and related peptides in natural blooms by liquid chromatography–electrospray-high resolution mass spectrometry and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight mass spectrometry using both positive and negative ionization modes. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1407, 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ferranti, P.; Fabbrocino, S.; Cerulo, M.G.; Bruno, M.; Serpe, L.; Gallo, P. Characterisation of biotoxins produced by a cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Averno using two LC–MS-based techniques. Food Addit. Contam.—Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferranti, P.; Nasi, A.; Bruno, M.; Basile, A.; Serpe, L.; Gallo, P. A peptidomic approach for monitoring and characterising peptide cyanotoxins produced in Italian lakes by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogialli, S.; Bortolini, C.; Di Gangi, I.M.; Di Gregorio, F.N.; Lucentini, L.; Favaro, G.; Pastore, P. Liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometric methods for the surveillance monitoring of cyanotoxins in freshwaters. Talanta 2017, 170, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerasino, L.; Capelli, C.; Salmaso, N. A comparative study of the metabolic profiles of common nuisance cyanobacteria in southern perialpine lakes. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2017, 8, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Pofi, G.; Favero, G.; Nigro Di Gregorio, F.; Ferretti, E.; Viaggiu, E.; Lucentini, L. Multi-residue Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-High resolution mass spectrometric method for the analysis of 21 cyanotoxins in surface water for human consumption. Talanta 2020, 211, 120738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Solliec, M.; Sauvé, S.; Gagnon, C. A Data-Independent Methodology for the Structural Characterization of Microcystins and Anabaenopeptins Leading to the Identification of Four New Congeners. Toxins 2019, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Solliec, M.; Sauvé, S.; Gagnon, C. Evaluation of ELISA-based method for total anabaenopeptins determination and comparative analysis with on-line SPE-UHPLC-HRMS in freshwater cyanobacterial blooms. Talanta 2021, 223, 121802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, D.; Jones, M.R.; Haley, J.A.; Núñez, O.; Farré, M.; Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanobacteria and their secondary metabolites in three freshwater reservoirs in the United Kingdom. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesner-Apter, S.; Carmeli, S. Three novel metabolites from a bloom of the cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 6628–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, L.R.; Pipole, F.; Werner, V.R.; Laughinghouse Iv, H.D.; De Camargo, A.C.M.; Rangel, M.; Konno, K.; Sant Anna, C.L. A toxic cyanobacterial bloom in an urban coastal lake, Rio Grande do Sul State, southern Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Vo Duy, S.; Munoz, G.; Dinh, Q.T.; Bahl, E.; Simon, D.F.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of multiclass cyanotoxins (microcystins, anabaenopeptins, cylindrospermopsin and anatoxins) in lake waters using on-line SPE liquid chromatography high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5289–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, S.L.; Brunner, S.L.; Klump, J.V.; Houghton, E.M.; Miller, T.R. Spatial analysis of toxic or otherwise bioactive cyanobacterial peptides in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Miller, T.R. Variable cyanobacterial toxin and metabolite profiles across six eutrophic lakes of differing physiochemical characteristics. Toxins 2017, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Rude, K.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Seaman, M.; Kozik, C.; Biese, P.; Gosz, T.; Suha, M.; Stempa, C.; et al. Analysis of cyanobacterial metabolites in surface and raw drinking waters reveals more than microcystin. Water Res. 2018, 140, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Bartlett, S.L.; Weirich, C.A.; Hernandez, J. Automated Subdaily Sampling of Cyanobacterial Toxins on a Buoy Reveals New Temporal Patterns in Toxin Dynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5661–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddick, J.; Prinsep, M.R. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of Cyanobacteria: A global approach to the discovery of novel secondary metabolites. Chem. N. Z. 2008, 72, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Anahas, A.M.P.; Gayathri, M.; Muralitharan, G. Isolation and characterization of microcystin-producing microcystis aeruginosa MBDU 626 from a freshwater bloom sample in Tamil Nadu, South India. In Microbiological Research in Agroecosystem Management; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Skafi, M.; Vo Duy, S.; Munoz, G.; Dinh, Q.T.; Simon, D.F.; Juneau, P.; Sauvé, S. Occurrence of microcystins, anabaenopeptins and other cyanotoxins in fish from a freshwater wildlife reserve impacted by harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Toxicon 2021, 194, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkelis, S.; Lanaras, T.; Sivonen, K. Cyanobacterial Toxic and Bioactive Peptides in Freshwater Bodies of Greece: Concentrations, Occurrence Patterns, and Implications for Human Health. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6319–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zervou, S.-K.; Moschandreou, K.; Paraskevopoulou, A.; Christophoridis, C.; Grigoriadou, E.; Kaloudis, T.; Triantis, T.M.; Tsiaoussi, V.; Hiskia, A. Cyanobacterial Toxins and Peptides in Lake Vegoritis, Greece. Toxins 2021, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkobi-Peer, S.; Carmeli, S. New Prenylated Aeruginosin, Microphycin, Anabaenopeptin and Micropeptin Analogues from a Microcystis Bloom Material Collected in Kibbutz Kfar Blum, Israel. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2347–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferranti, P.; Fabbrocino, S.; Chiaravalle, E.; Bruno, M.; Basile, A.; Serpe, L.; Gallo, P. Profiling microcystin contamination in a water reservoir by MALDI-TOF and liquid chromatography coupled to Q/TOF tandem mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Pinto, E.; Torres, M.A.; Dörr, F.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Szubert, K.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; et al. CyanoMetDB, a comprehensive public database of secondary metabolites from cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkelis, S.; Panou, M. Capturing biodiversity: Linking a cyanobacteria culture collection to the “scratchpads” virtual research environment enhances biodiversity knowledge. Biodivers Data J. 2016, 6, e7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shishido, T.K.; Jokela, J.; Humisto, A.; Suurnäkki, S.; Wahlsten, M.; Alvarenga, D.O.; Sivonen, K.; Fewer, D.P. The Biosynthesis of Rare Homo-Amino Acid Containing Variants of Microcystin by a Benthic Cyanobacterium. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Manach, S.; Duval, C.; Marie, A.; Djediat, C.; Catherine, A.; Edery, M.; Bernard, C.; Marie, B. Global Metabolomic Characterizations of Microcystis spp. Highlights Clonal Diversity in Natural Bloom-Forming Populations and Expands Metabolite Structural Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkelis, S.; Panou, M.; Chronis, I.; Zervou, S.-K.; Christophoridis, C.; Manolidi, K.; Ntislidou, C.; Triantis, T.M.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A.; et al. Monitoring a newly re-born patient: Water quality and cyanotoxin occurrence in a reconstructed shallow Mediterranean lake. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2017, 8, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vardaka, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Cook, C.M.; Lanaras, T. Cyanobacterial blooms and water quality in Greek waterbodies. J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkelis, S.; Tussy, P.F.; Zaoutsos, N. Isolation and preliminary characterization of cyanobacteria strains from freshwaters of Greece. Open Life Sci. 2014, 10, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkelis, S.; Panou, M.; Konstantinou, D.; Apostolidis, P.; Kasampali, A.; Papadimitriou, S.; Kati, D.; Di Lorenzo, G.M.; Ioakeim, S.; Zervou, S.-K.; et al. Diversity, Cyanotoxin Production, and Bioactivities of Cyanobacteria Isolated from Freshwaters of Greece. Toxins 2019, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
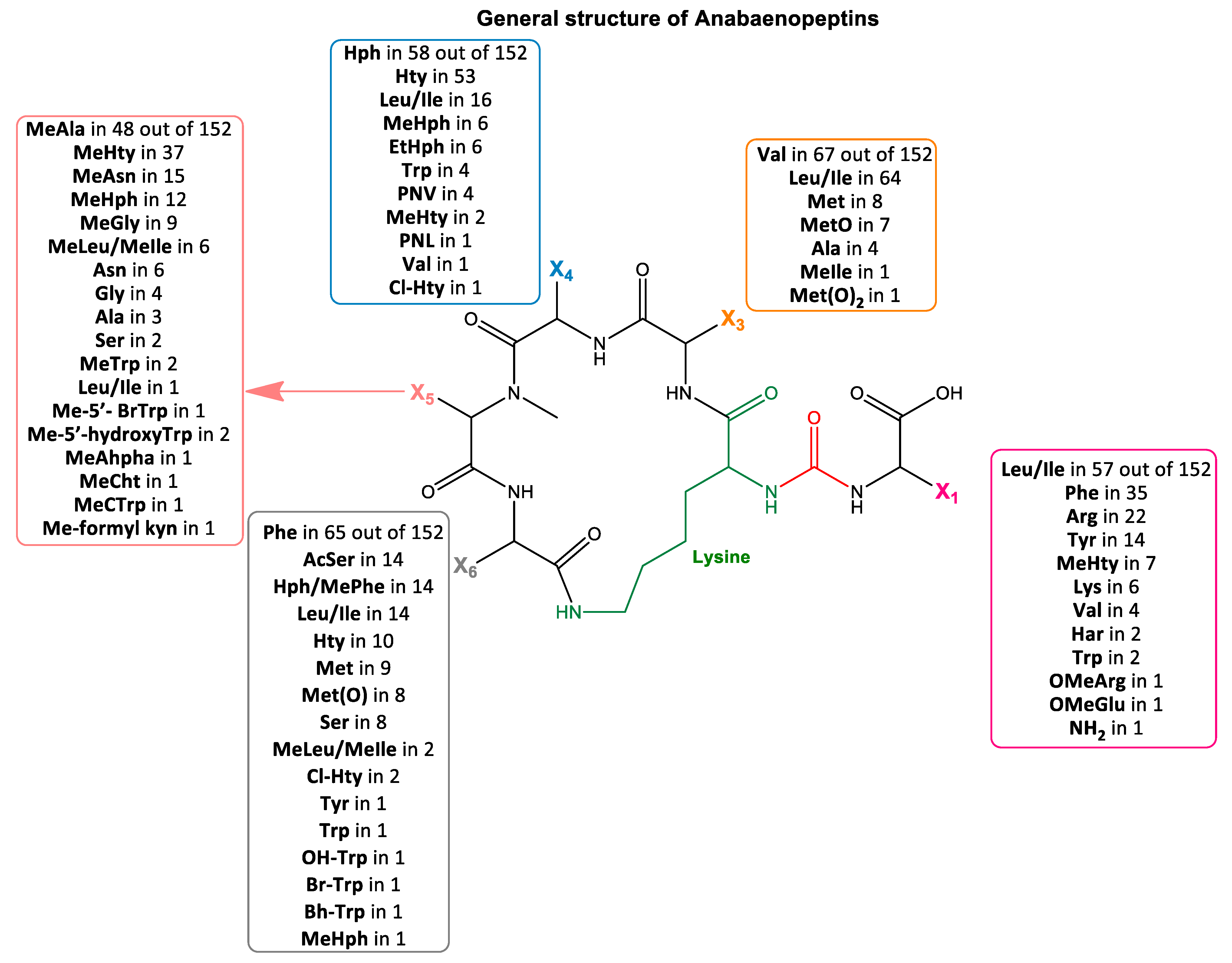


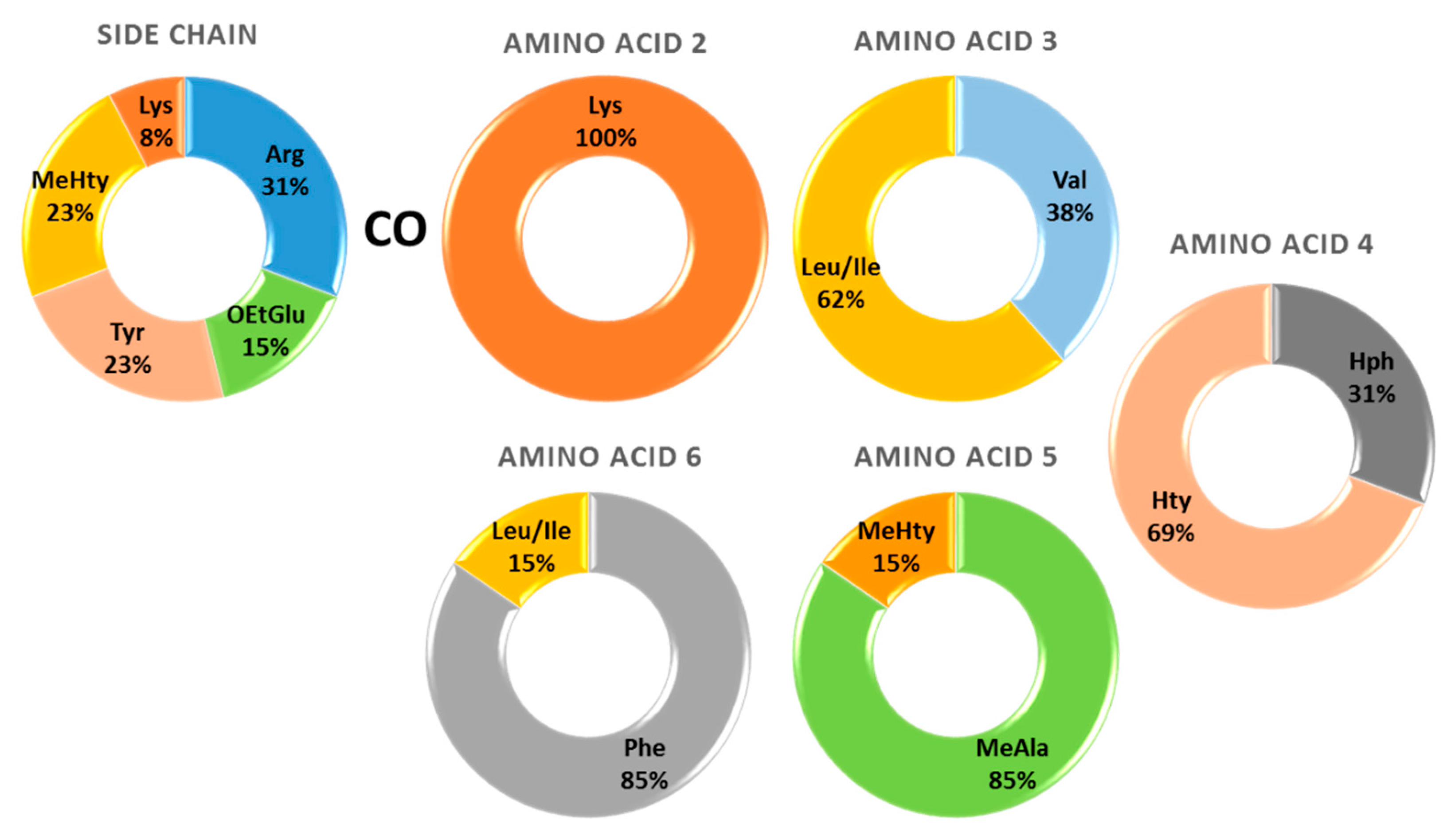
| m/z [M + H]+ | tR (min) | Name | Amino Acid Sequence | Ref. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Side Chain) | Ureido Linkage | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||
| 1 | 821.2 | 9.4 | AP 820 | Agr | CO | Lys | Val | Hph | MeAla | Phe | [22] |
| 2 | 837.4 | 7.9 | AP B | Arg | CO | Lys | Val | Hty | MeAla | Phe | [35] |
| 3 | 838.3 | 9.2 | AP 837 | EtOGlu | CO | Lys | Val | Hty | MeAla | Phe | This study |
| 4 | 842.3 | 10.6 | AP 842 | Tyr | CO | Lys | Ile | Hph | MeAla | Phe | [23] |
| 5 | 844.2 | 9.9 | AP A | Tyr | CO | Lys | Val | Hty | MeAla | Phe | [35] |
| 6 | 851.3 | 8.8 | AP F | Arg | CO | Lys | Ile | Hty | MeAla | Phe | [28] |
| 7 | 852.2 | 9.4 | AP 851 | EtOGlu | CO | Lys | Leu/Ile | Hty | MeAla | Phe | This study |
| 8 | 858.4 | 10.0 | Osc Y | Tyr | CO | Lys | Ile | Hty | MeAla | Phe | [27] |
| 9 | 870.4 | 10.8 | AP 870 | MeHty | CO | Lys | Leu/Ile | Hph | MeAla | Phe | [23] |
| 10 | 872.3 | 10.1 | AP 872 | MeHty | CO | Lys | Val | Hty | MeAla | Phe | [23] |
| 11 | 886.4 | 10.2 | AP 886 | MeHty | CO | Lys | Leu/Ile | Hty | MeAla | Phe | [23] |
| 12 | 895.6 | 8.9 | AP 894 | Lys | CO | Lys | Leu/Ile | Hty | MeHty | Leu/Ile | This study |
| 13 | 907.3 | 9.5 | AP KB906 | Arg | CO | Lys | Ile | Hph | MeHty | Ile | [101] |
| Lake | Sampling Date | Dominant Cyanobacterial Species | Anabaenopeptins Amino Acid Sequences Are Listed in Table 1 | Number of Congeners |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amvrakia | 10 August 1999 | Microcystis spp., Dolichospermum viguieri | AP F, Osc Y, AP 872, AP 886 | 4 |
| Amvrakia * | 19 August 1999 | Dolichospermum perturbatum, Microcystis spp. | AP F | 1 |
| Amvrakia * | 19 August 1999 | Dolichospermum perturbatum | AP F, Osc Y, AP 886 | 3 |
| Kastoria * | 5 October 1995 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis novacekii, Microcystis wesenbergii | AP B, AP 842, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 886 | 6 |
| Kastoria * | 5 October 1995 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis novacekii, Microcystis wesenbergii | AP 820, AP B, AP 842, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 872, AP 886 | 8 |
| Kastoria | 3 July 2000 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis novacekii | AP B, AP F, Osc Y | 3 |
| Kastoria | 20 September 2000 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis flos-aquae | AP B, AP F, Osc Y, AP 872 | 4 |
| Kastoria | 18 September 2014 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis flos-aquae, Microcystis spp., Pseudanabaena mucicola | AP B, AP F, Osc Y, AP 886 | 4 |
| Kastoria | 6 October 2015 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis flos-aquae, Microcystis novacekii, Microcystis ichthyoblabe | AP B, AP F, Osc Y | 3 |
| Kerkini | 3 August 1999 | Microcystis spp., Microcystis wesenbergii | AP B, AP 842, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 870, AP 872, AP 886 | 8 |
| Kerkini | 26 August 1999 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Dolichospermumspiroides | AP B, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 872, AP 894 | 6 |
| Mikri Prespa | 5 August 1999 | Microcystis spp., Microcystis wesenbergii | AP B, AP F, Osc Y, AP 870, AP 872, AP 886 | 6 |
| Mikri Prespa | 4 November 2014 | Microcystis aeruginosa | AP B, AP 837, AP A, AP F, AP 851, Osc Y | 6 |
| Pamvotida | 22 July 1999 | Microcystis aeruginosa | AP B, AP 842, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 886 | 6 |
| Pamvotida | 18 August 1999 | Dolichospermum flos-aquae, Microcystisaeruginosa | AP F, Osc Y, AP 886 | 3 |
| Pamvotida | 5 August 2000 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Dolichospermum flos-aquae | Osc Y | 1 |
| Pamvotida | 17 August 2000 | Dolichospermum flos-aquae, Microcystis spp. | AP F, Osc Y, AP 886 | 3 |
| Pamvotida * | 18 August 2000 | Microcystis spp., Dolichospermum flos-aquae | AP B, AP F, Osc Y, AP 870, AP 872, AP 886 | 6 |
| Pamvotida * | 18 August 2000 | Microcystis spp., Dolichospermum flos-aquae | AP B, AP 842, AP F, Osc Y, AP 872, AP 886 | 6 |
| Vistonida | 2 August 1999 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis spp. | AP B, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 872, AP 886 | 6 |
| Zazari | 5 August 1999 | Microcystis aeruginosa, Microcystis spp. | AP B, AP 842, AP A, AP F, Osc Y, AP 872, AP 894, AP KB906 | 8 |
| Karla | 1 July 2015 | Anabaenopsis elenkinii, Raphidiopsis (Cylindrospermopsis) raciborskii, Planktothrix cf. agardhii, Pseudanabaena limnetica | - | 0 |
| Marathonas | 26 October 2010 | Microcystis flos-aquae, Microcystis viridis, Pseudanabaena raphidioides, Planktolyngbya limnetica | - | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zervou, S.-K.; Kaloudis, T.; Gkelis, S.; Hiskia, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Anabaenopeptins from Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Bodies of Greece. Toxins 2022, 14, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010004
Zervou S-K, Kaloudis T, Gkelis S, Hiskia A, Mazur-Marzec H. Anabaenopeptins from Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Bodies of Greece. Toxins. 2022; 14(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleZervou, Sevasti-Kiriaki, Triantafyllos Kaloudis, Spyros Gkelis, Anastasia Hiskia, and Hanna Mazur-Marzec. 2022. "Anabaenopeptins from Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Bodies of Greece" Toxins 14, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010004
APA StyleZervou, S.-K., Kaloudis, T., Gkelis, S., Hiskia, A., & Mazur-Marzec, H. (2022). Anabaenopeptins from Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Bodies of Greece. Toxins, 14(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010004









