The Southeast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) Partnership: Addressing Data Gaps in Harmful Algal Bloom Monitoring and Shellfish Safety in Southeast Alaska
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
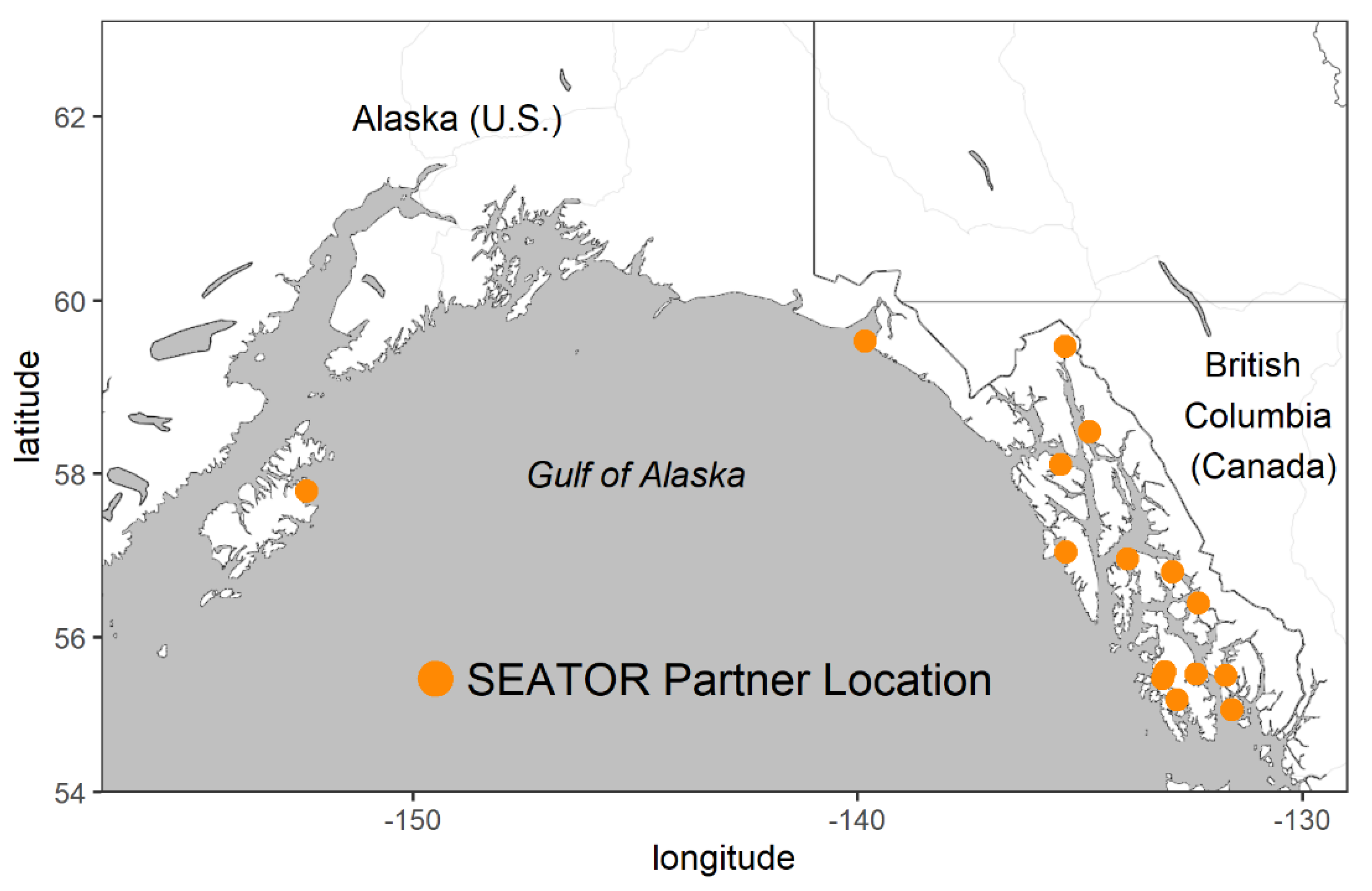
2.1. HAB and Oceanographic Observations
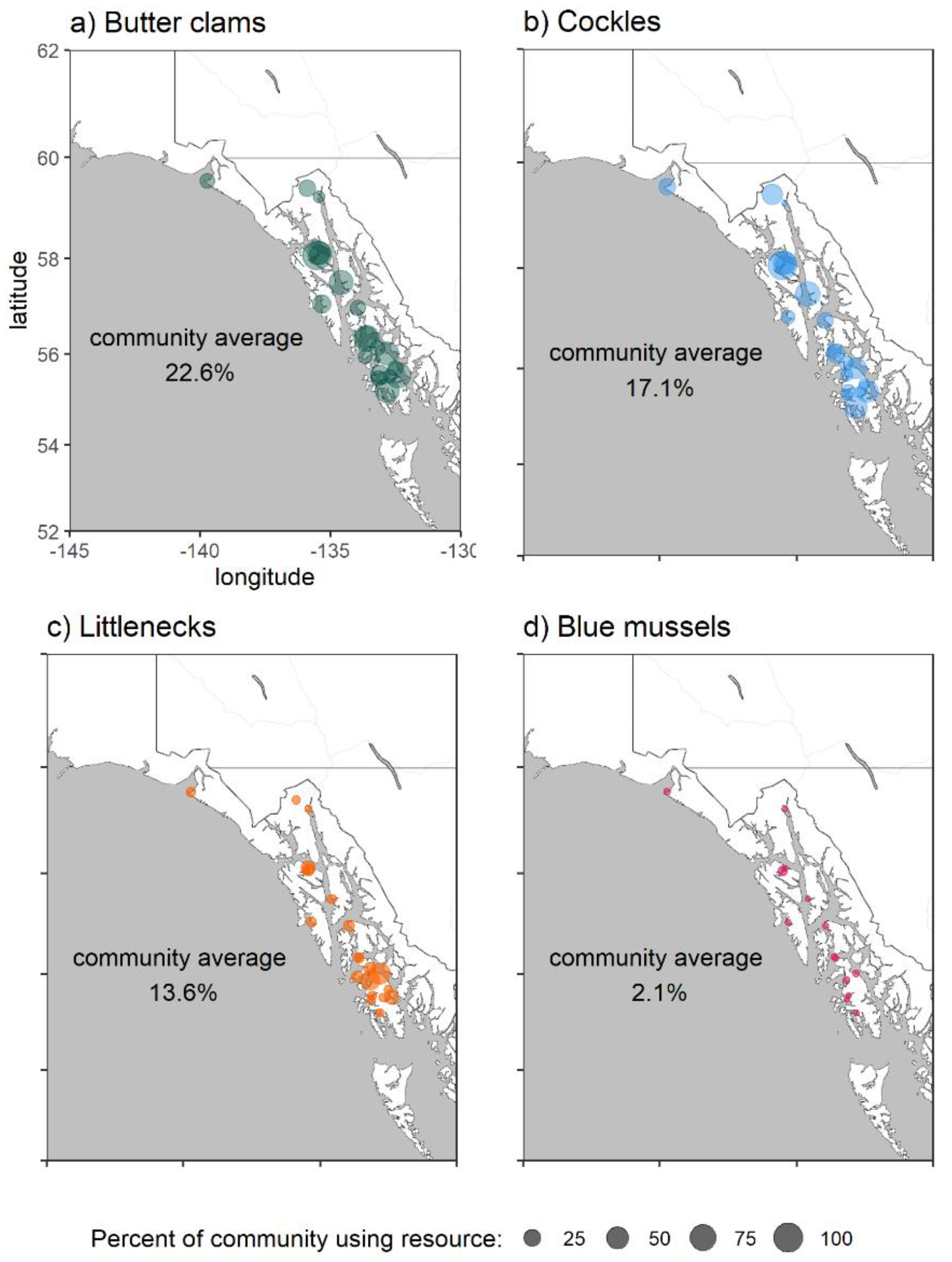
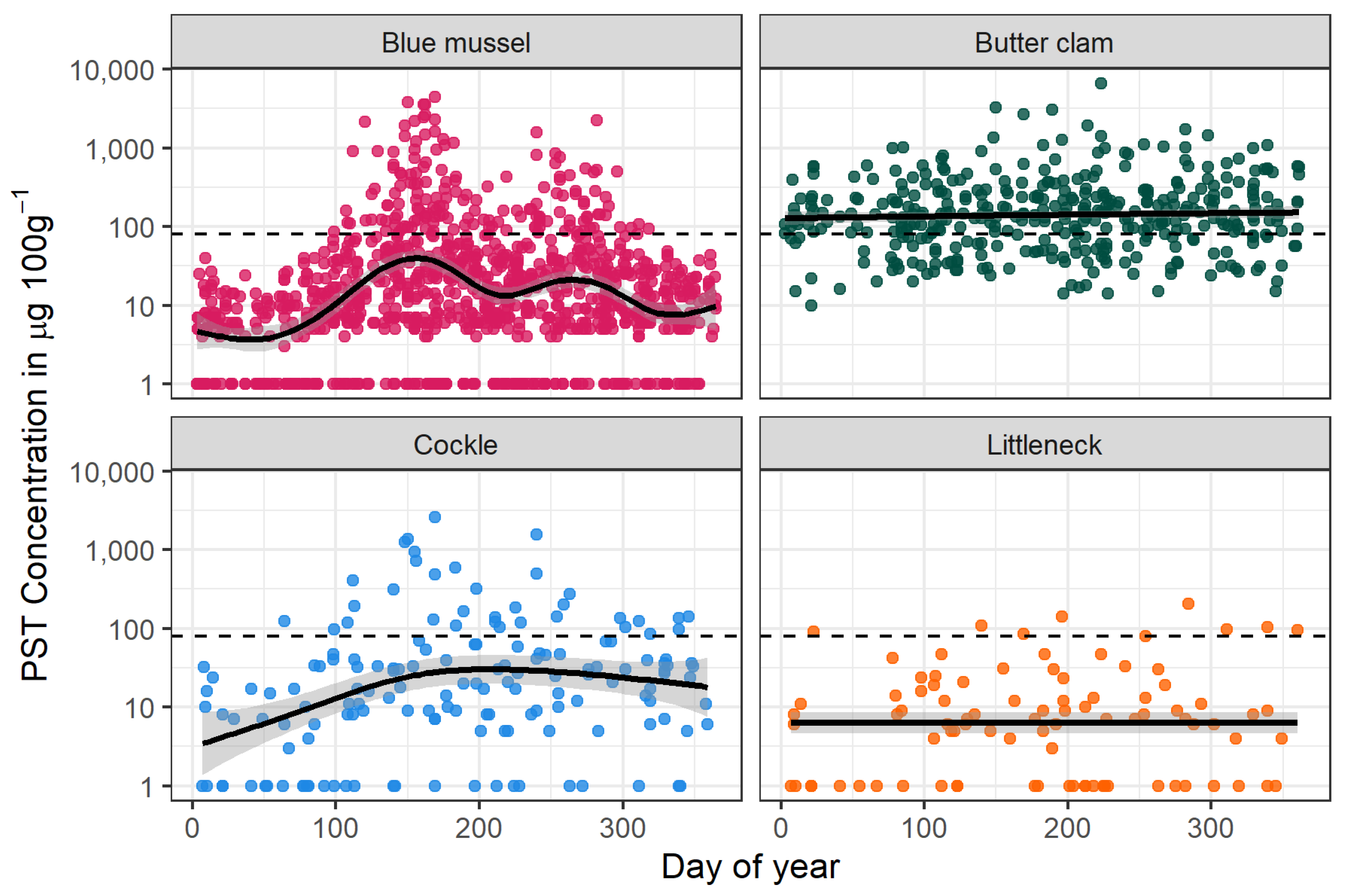
2.2. PSTs in Southeast Alaska Shellfish
2.3. Value of These Data as a Platform for Modeling Efforts
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.X.; Tatters, A.O.; Hutchins, D.A. A Global change and the future of harmful algal blooms in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 470, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, L.M.; Holobaugh, S.; Morris, J.G. Harmful algal blooms and public health. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.J.; Carey, B.; O’halloran, J.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; Škrabáková, Z. Shellfish toxicity: Human health implications of marine algal toxins. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Doherty, O.M.; Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Griffith, A.W.; Kang, Y.; Litaker, R.W. Ocean warming since 1982 has expanded the niche of toxic algal blooms in the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.L.; Karlson, B.; Wulff, A.; Kudela, R.; Trick, C.; Asnaghi, V.; Berdalet, E.; Cochlan, W.; Davidson, K.; De Rijcke, M.; et al. Future HAB science: Directions and challenges in a changing climate. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Sullivan, K.; Eberhart, B.-T.L.; Shuler, A.; Hignutt, E.; Kiser, J.; Eckert, G.L.; Shumway, S.E.; Morton, S.L. Enhancing Shellfish Safety in Alaska through Monitoring of Harmful Algae and Their Toxins. J. Shellfish Res. 2014, 33, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, B.D.; Middaugh, J.P. Paralytic shellfish poisoning in Alaska: A 20-year retrospective analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 141, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrodale, L. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning—Alaska, 1993–2014; State of Alaska Epidemiology Bulletin; Department of Health and Social Services: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2015.
- Trainer, V.L.; Hardy, F.J. Integrative Monitoring of Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae in Washington State for Public Health Protection. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 1206–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.; Moss, M. The Subsistence Lifeway of the Tlingit People: Excerpts of Oral Interviews; U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, Alaska Region: Juneau, AK, USA, 1984.
- Sill, L.A.; Koster, D. The Harvest and Use of Wild Resources in Haines, Hoonah, Angoon, Whale Pass, and Hydaburg, Alaska, 2012; Alaska Department of Fish and Game Division of Subsistence: Juneau, AK, USA, 2017; Technical Paper No. 399.
- Alaska Department of Fish and Game Community Subsistence Information System (CSIS). Available online: https://www.adfg.alaska.gov/sb/CSIS/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Moss, M.L. Shellfish, Gender, and Status on the Northwest Coast: Reconciling Archeological, Ethnographic, and Ethnohistorical Records of the Tlingit. Am. Anthropol. 1993, 95, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnis, S.; Krstic, N.; McIntyre, L.; Nelson, T.A.; Henderson, S.B. Spatiotemporal patterns of paralytic shellfish toxins and their relationships with environmental variables in British Columbia, Canada from 2002 to 2012. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valbi, E.; Ricci, F.; Capellacci, S.; Casabianca, S.; Scardi, M.; Penna, A. A model predicting the PSP toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum occurrence in the coastal waters of the NW Adriatic Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.K.; Mantua, N.J.; Hickey, B.M.; Trainer, V.L. Recent trends in paralytic shellfish toxins in Puget Sound, relationships to climate, and capacity for prediction of toxic events. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Z. Implementation of the Gulf of Maine Operational Forecast System (GOMOFS) and the Semi-Operational Nowcast/forecast Skill Assessment; NOS CO-OPS; Center for Operational Oceanographic Products and Services: Spring, MD, USA, 2018.
- Tobin, E.D.; Wallace, C.L.; Crumpton, C.; Johnson, G.; Eckert, G.L. Environmental drivers of paralytic shellfish toxin producing Alexandrium catenella blooms in a fjord system of northern Southeast Alaska. Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, T.; Eisner, L.; Eckert, G.L.; Danielson, S.; Bellwood, D. Southeast Alaska: Oceanographic Habitats and Linkages. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, B.D.; Moore, S.K.; Hay, L.R.; Anderson, D.M.; Trainer, V.L. Effects of temperature and salinity on the growth of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) isolates from the Salish Sea. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, H.E.; McLain, D.R.; Wing, B.L. Annual Physical and Chemical Oceanographic Cycles of Auke Bay, Southeastern Alaska; NMFS SSRF; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1977.
- Reverdin, G.; Morisset, S.; Boutin, J.; Martin, N. Rain-induced variability of near sea-surface T and S from drifter data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.M.; Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Gulland, F.M.; Thomson, R.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trainer, V.L. An unprecedented coastwide toxic algal bloom linked to anomalous ocean conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs: Occurrence, Transfer Kinetics, and Biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Ruus, A.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis spp.) as sentinel organisms in coastal pollution monitoring: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvitek, R.G.; Beitler, M.K. Relative insensitivity of butter clam neurons to saxitoxin: A pre-adaptation for sequestering paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins as a chemical defense. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 69, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Green, D.; Hickey, B.M.; Jacobs, J.M.; Lanerolle, L.W.J.; Moore, S.; Schwab, D.J.; Trainer, V.L.; Trtanj, J.; Turner, E.; et al. Towards operational forecasts of algal blooms and pathogens. In Environmental Tracking for Public Health Surveillance; Morain, S.A., Budge, A.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 11, pp. 345–368. [Google Scholar]
- Alaska Ocean Observing System. Available online: https://aoos.org/ (accessed on 17 March 2020).
- Campbell, J.L.; Rustad, L.E.; Porter, J.H.; Taylor, J.R.; Dereszynski, E.W.; Shanley, J.B.; Gries, C.; Henshaw, D.L.; Martin, M.E.; Sheldon, W.M. Quantity is nothing without quality: Automated QA/QC for streaming environmental sensor data. BioScience 2013, 63, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Fire, S.E.; Leighfield, T.A.; Mikulski, C.M.; Doucette, G.J. Determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish by receptor binding assay: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.; Claassen, L.; Borchert, J.; Trainer, V. SoundToxins: A Puget Sound Harmful Algae Monitoring Partnership. Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (2018: Seattle, Wash). Available online: cedar.wwu.edu/ssec/2018ssec/allsessions/269/ (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Washington Sea Grant. SoundToxins Manual; Washington Sea Grant: Seattle, WA, USA, 2016; p. 36. [Google Scholar]



| Species | Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| Blue mussel | 916 | 3791 | 2243 | 4412 |
| (M. trossulus) | ||||
| Butter clam | 723 | 6624 | 1712 | 3081 |
| (S. gigantea) | ||||
| California mussel | NT | NT | 24 | 29 |
| (Mytilus californianus) | ||||
| Cockle | 202 | 1367 | 1565 | 2603 |
| (C. nuttallii) | ||||
| Eastern softshell | 15 | 6 | 8 | 21 |
| (Mya arenaria) | ||||
| Horse clam | 13 | BDL | 42 | 37 |
| (Tresus capax) | ||||
| Littleneck clam | 24 | 47 | 206 | 142 |
| (Leukoma staminea) | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harley, J.R.; Lanphier, K.; Kennedy, E.G.; Leighfield, T.A.; Bidlack, A.; Gribble, M.O.; Whitehead, C. The Southeast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) Partnership: Addressing Data Gaps in Harmful Algal Bloom Monitoring and Shellfish Safety in Southeast Alaska. Toxins 2020, 12, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060407
Harley JR, Lanphier K, Kennedy EG, Leighfield TA, Bidlack A, Gribble MO, Whitehead C. The Southeast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) Partnership: Addressing Data Gaps in Harmful Algal Bloom Monitoring and Shellfish Safety in Southeast Alaska. Toxins. 2020; 12(6):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060407
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarley, John R., Kari Lanphier, Esther G. Kennedy, Tod A. Leighfield, Allison Bidlack, Matthew O. Gribble, and Christopher Whitehead. 2020. "The Southeast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) Partnership: Addressing Data Gaps in Harmful Algal Bloom Monitoring and Shellfish Safety in Southeast Alaska" Toxins 12, no. 6: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060407
APA StyleHarley, J. R., Lanphier, K., Kennedy, E. G., Leighfield, T. A., Bidlack, A., Gribble, M. O., & Whitehead, C. (2020). The Southeast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) Partnership: Addressing Data Gaps in Harmful Algal Bloom Monitoring and Shellfish Safety in Southeast Alaska. Toxins, 12(6), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060407