Absence of Cyanotoxins in Llayta, Edible Nostocaceae Colonies from the Andes Highlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
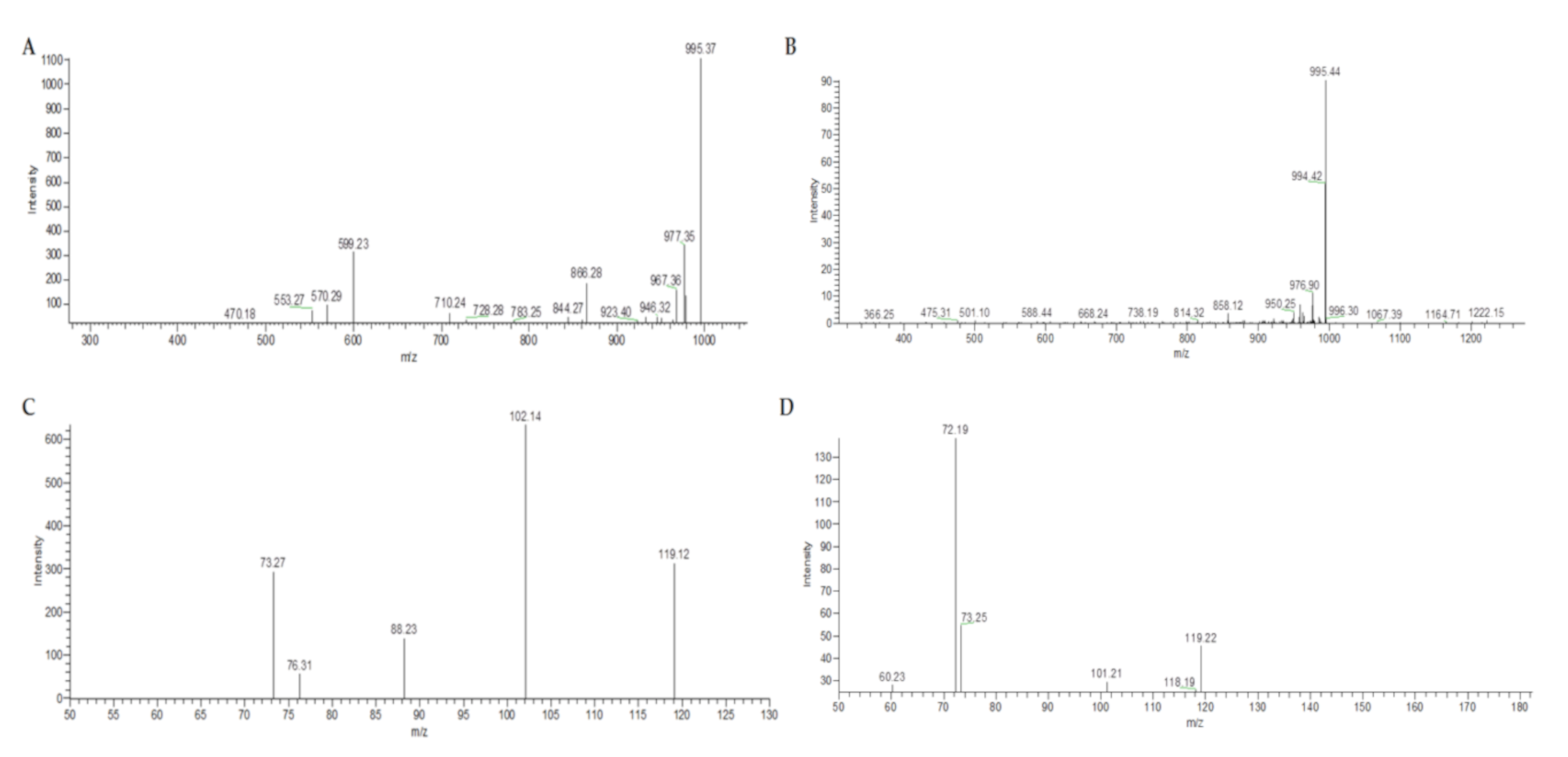
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welker, M.; von Dören, H. Cyanobacterial peptides—Nature’s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 530–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, H.; King, S.R.; Banack, S.A.; Webster, C.; Callanaupa, W.J.; Cox, P.A. Cyanobacteria (Nostoc commune) used as a dietary item in Peruvian highlands produce the neurotoxic amino acid BMAA. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.S.; Cianca, R.C.C.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Determination of the non protein amino acid β-N-methylamino-l-alanine in estuarine cyanobacteria by capillary electrophoresis. Toxicon 2011, 58, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, M.; Costa, M.; Moreira, C.; Vasconcelos, V.M.; Baptista, M.S. Screening of BMAA-producing cyanobacteria in cultured isolates and in in situ blooms. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirés, S.; Caser, M.C.; Quesada, A. Toxicity at the edge of life: A review on cyanobacterial toxins from extreme environments. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buono, S.; Langellitti, A.L.; Martello, A.; Rinna, F.; Fogliano, V. Functional ingredients from microalgae. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertonio, L. Vocabulario de la Lengua Aymara. Colección Biblioteca Nacional de Chile: Impreso en la Compañía de Jesús, Perú. 1612. Available online: http://www.memoriachilena.cl/602/w3-article-8656.html (accessed on 26 July 2019).
- Aldave-Pajares, A. Algas andino peruanas como recurso hidrobiológico alimentario. Bol. Lima 1985, 7, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Silva, B.; Mendizabal, C.; Tapia, I.; Olivares, H. Microalgas del norte de Chile. IV. Composición química de Nostoc commune Llaita. Rev. Invest. Cient. Tecnol. Cienc. Mar. 1994, 3, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Galetović, A.; Araya, J.; Gómez-Silva, B. Composición bioquímica y toxicidad de colonias comestibles de la cianobacteria andina Nostoc sp. Llayta. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2017, 44, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Galetović, A.; Licuime, R.; Benito Gómez-Silva, B. A microethnographic and ethnobotanical approach to Llayta consumption among the Andes feeding practices. Foods 2018, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasser, I.; Bukowska, A.; Humbert, J.F.; Haukka, K.; Fewer, D.P. Analysis of Toxigenic Cyanobacterial Communities through Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis. In Molecular Tools for the Detection and Quantification of Toxigenic Cyanobacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen, K.; Carmichael, W.; Namikoshi, K.; Rinehart, I.; Dahlem, A.M.; Niemela, S.I. Isolation and Characterization of Hepatotoxic Microcystin Homologs from the Filamentous Freshwater Cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. Strain 152. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2650–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, I.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Wahlsten, M.; Rikkinen, J.; Sivonen, K. Discovery of Rare and Highly Toxic Microcystins from Lichen-Associated Cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. Strain IO-102-I. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5756–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Solliec, M.; Sauvé, S.; Gagnon, C. A Data-Independent Methodology for the Structural Characterization of Microcystins and Anabaenopeptins Leading to the Identification of Four New Congeners. Toxins 2019, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouaïcha, N.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; Labidi, Z.; Djabri, A.; Benayache, N.Y.; Nguyen-Quang, T. Structural Diversity, Characterization and Toxicology of Microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikalsen, B.; Boison, G.; Skulberg, O.M.; Fastner, J.; William Davies, W.; Gabrielsen, T.M.; Rudi, K.; Jakobsen, K.S. Natural Variation in the Microcystin Synthetase Operon mcyABC and Impact on Microcystin Production in Microcystis Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2774–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via-Ordorika, L.; Fastner, J.; Kurmayer, R.; Hisbergues, M.; Dittmann, E.; Komarek, J.; Erhard, M.; Chorus, I. Distribution of Microcystin-Producing and Non-Microcystin-Producing Microcystis sp. in European Freshwater Bodies: Detection of Microcystins and Microcystin Genes in Individual Colonies. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmayer, R.; Christiansen, G. The genetic basis of toxin production in Cyanobacteria. Freshw. Rev. 2009, 2, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, A.; Fewer, D.P.; Hisbergues, M.; Rouhiainen, L.; Vaitomaa, J.; Börner, T.; Sivonen, K. Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Fan, H.; Ma, F.; McCarron, P.; Thomas, K.; Tanga, X.; Quilliam, M.A. Elucidation of matrix effects and performance of solid-phase extraction for LC-MS/MS analysis of b-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and 2,4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB) neurotoxins in cyanobacteria. Analyst 2012, 137, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, P.; Logan, A.C.; Giddings, S.D.; Quilliam, M.A. Analysis of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) in Spirulina-containing supplements by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Aquat. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, D.G.; Kerrin, E.S.; Giddings, S.D.; Quilliam, M.A.; McCarron, P. Differential Mobility-Mass Spectrometry Double Spike Isotope Dilution Study of Release of β-Methylaminoalanine and Proteinogenic Amino Acids during Biological Sample Hydrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saker, M.L.; Jungblut, A.-D.; Neilan, B.; Rawn, T.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Detection of microcystin synthethase genes in health food supplements containing the freshwater cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Toxicon 2005, 46, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rellan, S.; Osswald, J.; Saker, M.; Gago, A.; Vasconcelos, V.M. First detection of anatoxin-a in human and animal dietary supplements containing cyanobacteria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisbergues, M.; Christiansen, G.; Rouhiainen, L.; Sivonen, K.; Borner, T. PCR-based identification of microcystin-producing genotypes of different cyanobacterial genera. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 180, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Neilan, B.A. Molecular identification and evolution of the cyclic peptide hepatotoxins, microcystin and nodularin, synthetase genes in three orders of cyanobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 185, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihali, T.K.; Kellmann, R.; Muenchhoff, J.; Barrow, K.D.; Neilan, B.A. Characterization of the gene cluster responsible for cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casero, M.C.; Ballot, A.; Agha, R.; Quesada, A.; Cirés, S. Characterization of saxitoxin production and release and phylogeny of sxt genes in paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin-producing Aphanizomenon gracile. Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Gene | Primer Pair | Target Group Producers | Size (bps) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mcyA | mcyA-Cd1F/mcyA-Cd1R | Microcystin | 297 | [26] |
| mcyE | HEPF/HEPR | Microcystin and nodularin | 472 | [27] |
| cyrJ | cynsulF; cylnamR | Cylindrospermopsin | 586 | [28] |
| anaC | anaC-genF/anaC-genR | Anatoxin | 366 | [28] |
| sxtA | sxtAF/sxtAR | Saxitoxin | 683 | [29] |
| sxtG | sxtGF/sxtGR | Saxitoxin | 893 | [29] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galetović, A.; Azevedo, J.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Oliveira, F.; Gómez-Silva, B.; Vasconcelos, V. Absence of Cyanotoxins in Llayta, Edible Nostocaceae Colonies from the Andes Highlands. Toxins 2020, 12, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060382
Galetović A, Azevedo J, Castelo-Branco R, Oliveira F, Gómez-Silva B, Vasconcelos V. Absence of Cyanotoxins in Llayta, Edible Nostocaceae Colonies from the Andes Highlands. Toxins. 2020; 12(6):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060382
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaletović, Alexandra, Joana Azevedo, Raquel Castelo-Branco, Flavio Oliveira, Benito Gómez-Silva, and Vitor Vasconcelos. 2020. "Absence of Cyanotoxins in Llayta, Edible Nostocaceae Colonies from the Andes Highlands" Toxins 12, no. 6: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060382
APA StyleGaletović, A., Azevedo, J., Castelo-Branco, R., Oliveira, F., Gómez-Silva, B., & Vasconcelos, V. (2020). Absence of Cyanotoxins in Llayta, Edible Nostocaceae Colonies from the Andes Highlands. Toxins, 12(6), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060382






