The Cytocidal Spectrum of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: From Insects to Human Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Leading Toxic Proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis and their Mechanism of Action
2.1. Cry Toxins
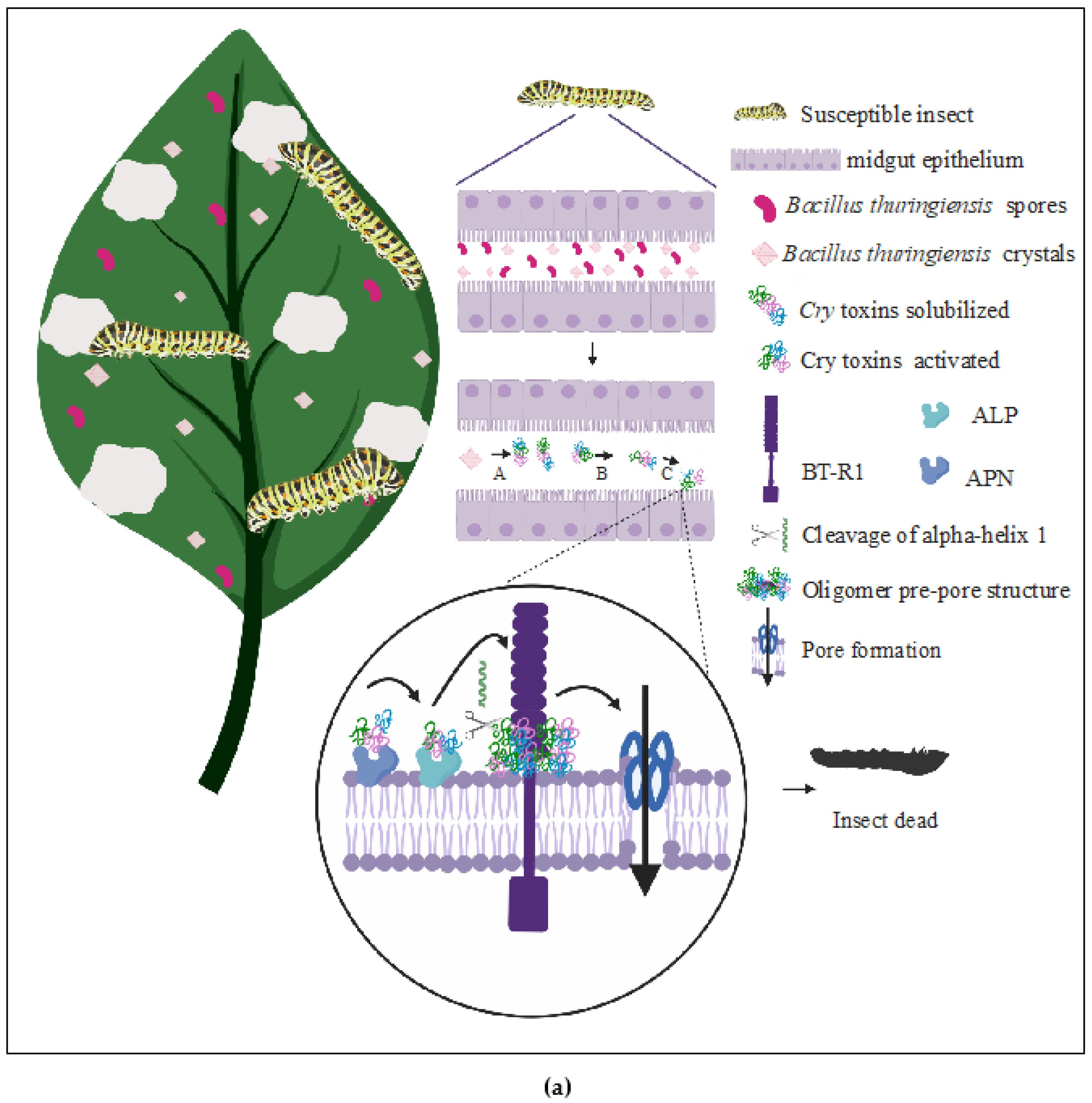
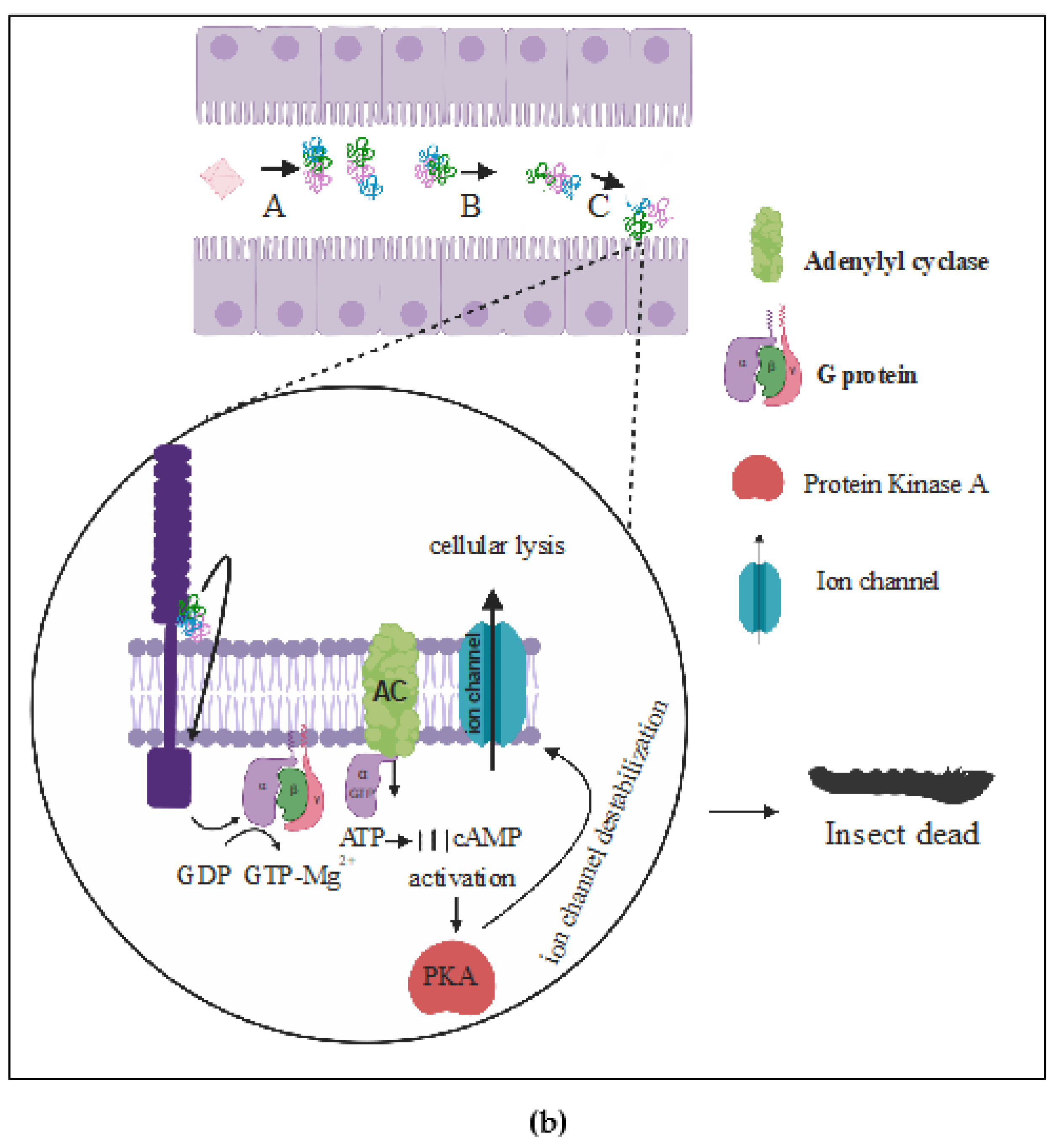
Mechanism of Action from Cry Toxins
(a) The Pore-Forming Model
(b) The Signaling Pathway Model
2.2. Cyt Family
Cyt Proteins Mechanism of Action
(a) The Pore-Formation Model
(b) The Detergent-Effect Model
2.3. Parasporins
2.3.1. Parasporin Classification
PS1 Family
PS2 Family
PS3 Family
PS4 Family
PS5 Family
PS6 Family
2.3.2. Mechanism of Action of Parasporins
2.4. S-Layer Proteins
2.5. Toxins Secreted by Bt
2.5.1. Vip Family
2.5.2. Sip Toxins
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knowles, B.H.; Dow, J.A.T. The crystal delta-endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis—Models for their mechanism of action on the insect gut. Bioessays 1993, 15, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.F.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Li, M.S.; Jin, B.R.; Je, Y.H. Bacillus thuringiensis as a specific, safe, and effective tool for insect pest control. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 17, 547–559. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, N. Bacterial control of vector-mosquitoes and black flies. In Entomopathogenic Bacteria: From Laboratory to Field Application; Charles, J.F., Delécluse, A., Nielsen-LeRoux, C., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, A.C.; Grady, J.O.; Gough, J.M.; Pearson, R.; Bagnall, N.H.; Kemp, D.H.; Akhurst, R.J. Toxicity of Bacillus Thuringiensis to Parasitic and Free-Living Life-Stages of Nematode Parasites of Livestock. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Mizuki, E.; Uemori, A. Parasporin, a new anticancer protein group from Bacillus thuringiensis. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, V.P.; Bravo, A.; Olmos, J. Identification of a Bacillus thuringiensis Surface Layer Protein with Cytotoxic Activity against MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, G.; Lei, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Qiqi, M.; Jianping, L.; Chenguang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Ziniu, Y.; Ming, S. A new group of parasporal inclusions encoded by the S-layer gene of Bacillus thuringiensis. FEMS. Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 282, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Boyd, S.D.; Bulla-Jr, L.A.; Winkler, D.D. The Defined Toxin-binding Region of the Cadherin G-protein Coupled Receptor, BT-R1, for the Active Cry1Ab Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Proteomics Bioinform. 2018, 11, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: An overview of their biocidal activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulla, L.A.; Kramer, K.J.; Cox, D.J.; Jones, B.L.; Davidson, L.I.; Lookhart, G.L. Purification and characterization of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 3000–3004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crickmore, N.; Zeigler, D.R.; Schnepf, E.; Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Bravo, A.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Nomenclature. Available online: http://www.lifesci.sussex.ac.uk/home/Neil_Crickmore/Bt/ (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Höfte, H.; Whiteley, H.R. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 5, 242–255. [Google Scholar]
- Van Frankenhuyzen, K. Insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 101, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiba, T.; Okumura, S. Parasporins 1 and 2: Their structure and activity. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 142, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sará, M.; Sleytr, U.B. S-Layer Proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, G.; Miranda-Rios, J.; de la Riva, G.; Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. A Bacillus thuringiensis S-layer protein involved in toxicity against Epilachna varivestis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, W.P.; Engleman, J.T.; Donovan, J.C.; Baum, J.A.; Bunkers, G.J.; Chi, D.J.; Clinton, W.P.; English, L.; Heck, G.R.; Ilagan, O.M.; et al. Discovery and characterization of Sip1A: A novel secreted protein from Bacillus thuringiensis with activity against coleopteran larvae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, M.; Banyuls, N.; Bel, Y.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Bacterial Vegetative Insecticidal Proteins (Vip) from Entomopathogenic Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Gomis-Cebolla, J.; Güneş, H.; Ferré, J. Characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis isolates by their insecticidal activity and their production of Cry and Vip3 proteins. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, O.; Capell, T.; Kohli, A.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Gatehouse, A.M. Recent developments and future prospects in insect pest control in transgenic crop. Trend Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Lopez, L.; Soberon, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, M.; Kough, J.; Vaituzis, Z.; Matthews, K. Are Bt crops safe? Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeis, J.; Meissle, M.; Bigler, F. Transgenic crops expressing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins and biological control. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, J.Z.; Collins, H.L.; Earle, E.D.; Cao, J.; Shelton, A.M. A critical assessment of the effects of Bt transgenic pants on parasitoids. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2284. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, A.L.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. Bacillus thuringiensis: Mechanism of action, resistance, and new applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischhoff, D.A.; Bowdish, K.S.; Perlak, F.J.; Marrone, P.G.; McCormick, S.M.; Niedermeyer, J.G.; Dean, D.A.; Kusano-Kretzmer, K.; Mayer, E.J.; Rochester, D.E.; et al. Insect tolerant transgenic tomato plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 1987, 5, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaek, M.; Reynaerts, A.; Hofte, A. Transgenic plants protected from insects. Nature 1987, 325, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.S.; Ward, J.M.; Levine, S.L.; Baum, G.A.; Vicini, J.L.; Hammond, B.G. The food and environmental safety of Bt crops. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 283–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Ellar, D.J.; Bishop, A.; Johnson, C.; Lin, S.; Hart, E.R. Characterization of a Bacillus thuringiensis delta endotoxin whic iIs toxic to insects in three orders. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 76, b131–b139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnepf, H.E.; Whiteley, H.R. Cloning and expression of the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 2893–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.J.; Morgan, J.A.; Whipps, J.M.; Saunders, J.R. Plasmid Transfer between the Bacillus thuringiensis Subspecies kurstaki and tenebrionis in Laboratory Culture and Soil and in Lepidopteran and Coleopteran Larvae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, I.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M.; Gómez, I. Role of alkaline phosphatase from Manduca sexta in the mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12497–12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.W.; Feil, S.C. Pore forming protein toxins: From structure to function. Progress. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2005, 88, 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Almazán, C.; Zavala, L.E.; Muñoz-Garay, C.; Jiménez-Juárez, N.; Pacheco, S.; Masson, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Dominant Negative Mutants of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab Toxin Function as Anti-Toxins: Demonstration of the Role of Oligomerization in Toxicity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maagd, R.A.; Bravo, A.; Crickmore, N. How Bacillus thuringiensis has evolved specific toxins to colonize the insect world. Trends Genet. 2001, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, F.; Hussain, S.R.A.; Cotrill, J.A.; Gould, F.; Dean, D.H. Mutations at domain II, loop 3, of Bacillus thuringiensis CryIAa and CryIAb δ-endotoxins suggest loop 3 is involved in initial binding to lepidopteran midguts. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 25220–25226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Rajamohan, F.; Jenkins, J.L.; Curtiss, A.S.; Dean, D.H. Role of two arginine residues in domain II, loop 2 of Cry1Ab and Cry1Ac Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin in toxicity and binding to Manduca sexta and Lymantria dispar aminopeptidase N. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maagd, R.A.; Bravo, A.; Berry, C.; Crickmore, N.; Schnepf, H.E. Structure, diversity, and evolution of protein toxins from spore-forming entomopathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2003, 37, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakey, J.H.; van der Goot, F.G.; Pattus, F. All in the family: The toxic activity of pore-forming toxins. Toxicology 1994, 87, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.; Green, J.; Artymiuk, P.J. Hemolysin E (HlyE, ClyA, SheA) and related toxins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 677, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kristan, K.C.; Viero, G.; Dalla-Serra, M.; Macek, P.; Anderluh, G. Molecular mechanism of pore formation by actinoporins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuMont, A.L.; Torres, V.J. Cell targeting by the Staphylococcus aureus pore-forming toxins: It’s not just about lipids. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovache, I.; Dal Peraro, M.; van der Goot, F.G. The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hotze, E.M.; Le, H.M.; Sieber, J.R.; Bruxvoort, C.; Mclnerney, M.J.; Tweten, R.K. Identification and characterization of the first cholesterol-dependent cytolysins from Gram-negative bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouaux, E. Channel-forming toxins: Tales of transformation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1997, 7, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, C.; Vecsey-Semjn, B.; Abrami, L.; Fivaz, M.; van der Goot, F.G. Membrane insertion: The strategy of toxins. Mol. Membrane Biol. 1997, 14, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovache, I.; Bischofberger, M.; van der Goot, F.G. Structure and assembly of pore-forming proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Peraro, M.; van der Goot, G. Pore-forming toxins: Ancient, but never really out of fashion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, L.A.; Heuck, A.P.; Hamman, B.D.; Rossjohn, J.; Parker, M.W.; Ryan, K.R.; Johnson, A.E.; Tweten, R.K. Identification of a membrane- spanning domain of the thiol-activated pore-forming toxin Clostridium perfringens perfringolysin O: An α-helical to β-sheet transition identified by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 14563–14574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.C.; Yu, Z.; Sun, M. Structural Insights into Bacillus thuringiensis Cry, Cyt and Parasporin Toxins. Toxins 2014, 6, 2732–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Oltean, D.I.; Gómez, I.; Pullikuth, A.K.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S. Heliothis virescens and Manduca sexta lipid rafts are involved in Cry1A toxin binding to the midgut epithelium and subsequent pore formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13863–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Gómez, I.; Conde, J.; Muñoz-Garay, C.; Sánchez, J.; Miranda, R.; Zhuang, M.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Oligomerization triggers binding of a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab pore-forming toxin to aminopeptidase N receptor leading to insertion into membrane microdomains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1667, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Soberón, M.; Gill, S.S. Bacillus thuringiensis Mechanisms and Use. Compr. Mol. Insect Sci. 2005, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-López, L.; Gómez, I.; Rausell, C.; Sánchez, J.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Structural changes of the Cry1Ac oligomeric pre-pore from Bacillus thuringiensis induced by N-acetylgalactosamine facilitates toxin membrane insertion. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10329–10336. [Google Scholar]
- Pigott, C.R.; Ellar, D.J. Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adang, M.J.; Crickmore, N.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxins and mechanism of action. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2014, 47, 39–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, I.; Oltean, D.I.; Gill, S.S.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. Mapping the epitope in cadherin-like receptors involved in Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxin interaction using phage display. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28906–28912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, I.; Miranda-Rios, J.; Rudiño-Piñera, E.; Oltean, D.I.; Gill, S.S.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. Hydropathic complementarity determines interaction of epitope (869) HITDTNNK (876) in Manduca sexta Bt-R(1) receptor with loop 2 of domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30137–30143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, I.; Dean, D.H.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. Molecular basis for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin specificity: Two structural determinants in the Manduca sexta Bt-R1 receptor interact with loops α8 and 2 in domain II of Cy1Ab toxin. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 10482–10489. [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch, J.A.; Candas, M.; Griko, N.B.; Maaty, W.S.A.; Midboe, E.G.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Bulla Jr, L.A. Cry1A toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis bind specifically to a region adjacent to the membrane-proximal extracellular domain of BT-R1 in Manduca sexta: Involvement of a cadherin in the entomopathogenicity of Bacillus thuringiensis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, I.; Sánchez, J.; Miranda, R.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. Cadherin-like receptor binding facilitates proteolytic cleavage of helix alpha-1 in domain I and oligomer pre-pore formation of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuadkitkan, A.; Smith, D.R.; Berry, C. Investigation of the Cry4B-prohibitin interaction in Aedes aegypti cells. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochulski, P.; Masson, L.; Borisova, S.; Pusztaicarey, M.; Schwartz, J.L.; Brousseau, R.; Cygler, M. Bacillus thuringiensis CrylA(a) insecticidal toxin: Crystal structure and channel formation. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, S.; Gómez, I.; Arenas, I.; Saab-Rincón, G.; Rodríguez-Almazán, C.; Gill, S.S.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. Domain II loop 3 of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin is involved in a “ping pong” binding mechanism with Manduca sexta aminopeptidase-N and cadherin receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32750–32757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelotl, J.; Sánchez, J.; Gómez, I.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. ABCC2 is associated with Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin oligomerization and membrane insertion in diamondback moth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, D.G. Learning the ABCs of Bt: ABC transporters and insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis provide clues to a crucial step in toxin mode of action. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 104, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberón, M.; Pardo-Lopez, L.; Lopez, I.; Gómez, I.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Bravo, A. Engineering modified Bt toxins to counter insect resistance. Science 2007, 318, 1640–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, H.; Jimenez, G.; Cordoba, E.; Leon, P.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Tobacco plants expressing the Cry1AbMod toxin suppress tolerance to Cry1Ab toxin of Manduca sexta cadherin-silenced larvae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Huang, F.; Ghimire, M.N.; Leonard, B.R.; Siegfried, B.D.; Rangasamy, M.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gahan, L.J.; Heckel, D.G.; et al. Efficacy of genetically modified Bt toxins against insects with different mechanisms of resistance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, T.J.; Davis, T.; Granados, R.R.; Shuler, M.L.; Wood, H.A. Screening of insect cell lines for the production of recombinant proteins and infectious virus in the baculovirus expression system. Biotechnol. Prog. 1992, 8, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castella, C.; Pauron, D.; Hilliou, F.; Trang, V.T.; Zucchini-Pascal, N.; Gallet, A.; Barbero, P. Transcriptomic analysis of Spodoptera frugiperda Sf9 cells resistant to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ca toxin reveals that extracellular Ca2+, Mg2+ and production of cAMP are involved in toxicity. Biol. Open 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, M.S.G.; de Maagd, R.A.; Stiekema, W.J.; Vlak, J.M.; Bosh, D. Toxicity and binding properties of the Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin Cry1C to cultured insect cells. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1998, 71, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Candas, M.; Griko, N.B.; Taissing, R.; Bulla, L.A., Jr. A mechanism of cell death involving an adenylyl cyclase/PKA signaling pathway is induced by the Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9897–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Koni, P.A.; Ellar, D.J. Structure of the mosquitocidal delta-endotoxin CytB from Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kyushuensis and implications for membrane pore formation. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 257, 129–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, G.; Adang, M.J. Effects and mechanisms of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxins for mosquito larvae. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 714–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.; O’Neil, S.; Ben-Dov, E.; Jones, A.F.; Murphy, L.; Quail, M.A.; Holden, M.T.; Harris, D.; Zaritsky, A.; Parkhill, J. Complete sequence and organization of pBtoxis, the toxin-coding plasmid of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5082–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butko, P. Cytolytic toxin Cyt1A and its mechanism of membrane damage: Data and hypotheses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.E.; Ellar, D.J. Bacillus thuringiensis var. israeliensis crystal delta-endotoxin: Effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 1983, 60, 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- Chogule, N.P.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Linz, L.B.; Narva, K.E.; Meade, T.; Bonning, B.C. Retargeting of the Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cyt2Aa against hemipteran insect pests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8465–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Lo, Y.C.; Lin, J.Y.; Liaw, Y.C. Crystal structures and electron micrographs of fungal volvatoxin A2. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Jeng, T.W.; Chen, C.C.; Shi, G.Y.; Tung, T.C. Isolation of a new cardiotoxic protein from the edible mushroom, Volvariella volvacea. Nature 1973, 246, 524–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manasherob, R.; Itsko, M.; Sela-Baranes, N.; Ben-Dov, E.; Berry, C.; Cohen, S.; Zaritsky, A. Cyt1Ca from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: Production in Escherichia coli and comparison of its biological activities with those of other Cyt-like proteins. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Martínez de Castro, D.; Sánchez, J.; Cantón, P.E.; Mendoza, G.; Gómez, I.; Pacheco, S.; García-Gómez, B.I.; Onofre, J.; Ocelotl, J.; et al. Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins and their use in the control of insect pests. In Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins, 4th ed.; Alouf, J.E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 858–873. [Google Scholar]
- Butko, P.; Huang, F.; Pusztai-Carey, M.; Surewicz, W.K. Membrane permeabilization induced by cytolytic delta-endotoxin CytA from Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 11355–11360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.C.; Dlécluse, A.; Walton, W.E. Cyt1Ab1 and Cyt2Ba1 from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. medellin and B. thuringiensis subsp. israelensis synergize Bacillus sphaericus against Aedes aegypti and Resistant Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3280–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soberón, M.; Lopez-Díaz, J.A.; Bravo, A. Cyt toxins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis: A protein fold conserved in several pathogenic microorganisms. Peptides 2013, 41, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, C.; Fernández, L.E.; Sun, J.; Folch, J.L.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cyt1Aa synergizes Cry11Aa toxin by functioning as a membrane-bound receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18303–18308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.H.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.K.; Yuan, Z.M. Cytolytic Toxin Cyt1aa of Bacillus thuringiensis Synergizes the Mosquitocidal Toxin Mtx1 of Bacillus sphaericus. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2006, 70, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-quintero, M.C.; Gómez, I.; Pacheco, S.; Sánchez, J.; Flores, H.; Osuna, J.; Mendoza, G.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Engineering Bacillus thuringiensis Cyt1Aa toxin specificity from dipteran to lepidopteran toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Aizawa, K. Insect toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from soils of Japan. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1986, 47, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubika, T.; Girija, D.; Deepa, K.; Salini, S.; Meera, N.; Raghavamenon, A.; Divya, M.; Babu, T. A parasporin from Bacillus thuringiensis native to Peninsular India induces apoptosis in cancer cells through intrinsic pathway. J. Biosci. 2018, 43, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Akao, T.; Yamashita, S.; Saitoh, H.; Park, Y.S. Unique activity associated with non-insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal inclusions: In vitro cell-killing action on human cancer cells. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, S.; Ohba, M.; Mizuki, E.; Crickmore, N.; Côté, J.C.; Nagamatsu, Y.; Kitada, S.; Sakai, H.; Harata, K.; Shin, T. Parasporin nomenclature. 2010. Available online: http://parasporin.fitc.pref.fukuoka.jp/list.html (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Kim, H.S.; Yamashita, S.; Akao, T.; Saitoh, H.; Higuchi, K.; Park, Y.S.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M. In vitro cytotoxicity of non-Cyt inclusion proteins of a Bacillus thuringiensis isolate against human cells, including cancer cells. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Akao, T.; Yamashita, S.; Katayama, H.; Maeda, M.; Saitoh, H.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M. Noninsecticidal parasporal proteins of a Bacillus thuringiensis serovar shandongiensis isolate exhibit a preferential cytotoxicity against human leukemic T cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 272, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuki, E.; Park, Y.S.; Saitoh, H.; Yamashita, S.; Akao, T.; Higuchi, K.; Ohba, M. Parasporin, a human leukemic cell-recognizing parasporal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Saitoh, H.; Higuchi, K.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Ohba, M. Characterization of the anti-cancer-cell parasporal proteins of a Bacillus thuringiensis isolate. Can. J. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Katayama, H.; Akao, T.; Maeda, M.; Tanaka, R.; Yamashita, S.; Saitoh, H.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M. A 28-kDa protein of the Bacillus thuringiensis serovar shandongiensis isolate 89-T-34-22 induces a human leukemic cell-specific cytotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1547, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagiwa, M.; Namba, A.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Sakai, H. Cytotoxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein against mammalian cells. Mem. Fac. Eng. Okayama Univ. 2002, 36, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Namba, A.; Yamagiwa, M.; Amano, H.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Sakai, H. The cytotoxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. coreanensis A1519 strain against the human leukemic T cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1622, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Abe, Y.; Kitada, S.; Kusaka, Y.; Ito, A.; Ichimatsu, T.; Katayama, H.; Akao, T.; Higuchi, K.; Mizuki, E.; et al. Crystallization of parasporin-2, a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein with selective cytocidal activity against human cells. Acta Cryst. 2004, D60, 2355–2357. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, A.; Sasaguri, Y.; Kitada, S.; Kusaka, Y.; Kuwano, K.; Masutomi, K.; Mizuki, E.; Akao, T.; Ohba, M. Selective cytocidal action of a crystal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis on human cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21282–21286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, S.; Akao, T.; Higuchi, K.; Saitoh, H.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Inouye, K. Bacillus thuringiensis serovar shandongiensis strain 89-T-34-22 produces multiple cytotoxic proteins with similar molecular masses against human cancer cell. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, H.; Yamagiwa, M.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Sakai, H. A novel 29-kDa crystal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis induces caspase activation and cell death of Jurkat T cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Katayama, H.; Yokota, H.; Akao, T.; Nakamura, O.; Ohba, M.; Mekada, E.; Mizuki, E. Parasporin-1, a novel cytotoxic protein to human cells from non-insecticidal parasporal inclusions of Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Biochem. 2005, 137, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, S.; Saitoh, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Wasano, N.; Yamashita, S.; Kusumoto, K.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Inouye, K. Identification of a Novel Cytotoxic Protein, Cry45Aa, from Bacillus thuringiensis A1470 and Its Selective Cytotoxic Activity against Various Mammalian Cell Lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6313–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Katayama, H.; Saitoh, H.; Akao, T.; Park, Y.S.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M.; Ito, A. Typical three-domain Cry proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis strain A1462 exhibit cytocidal activity on limited human cancer cells. J. Biochem. 2005, 138, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, S.; Saitoh, H.; Wasano, N.; Katayama, H.; Higuchi, K.; Mizuki, E.; Inouye, K. Efficient Solubilization, activation and purification of recombinant Cry45Aa of Bacillus thuringiensis expressed as an Escherichia coli inclusion body. Protein Expres. Purif. 2006, 47, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, H.; Okumura, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M. Investigation of a novel Bacillus thuringiensis gene encoding a parasporal protein, parasporin-4, that preferentially kills leukaemic T cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2935–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Kanagawa, R.; Kotani, Y.; Kimura, M.; Yamagiwa, M.; Yamane, Y.; Takebe, S.; Sakai, H. Parasporin-2Ab, a newly isolated cytotoxic crystal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, K.; Okumura, S.; Mizuki, E. Parasporin-4, A Novel Cancer Cell-killing Protein Produced by Bacillus thuringiensis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, S.; Saitoh, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Mizuki, E.; Inouye, K. Identification and characterization of a novel cytotoxic protein, parasporin-4, produced by Bacillus thuringiensis A1470 strain. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2008, 14, 225–252. [Google Scholar]
- Uemori, A.; Ohgushi, A.; Yasutake, K.; Maeda, M.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M. Parasporin-1Ab, a Novel Bacillus thuringiensis Cytotoxin Preferentially Active on Human Cancer Cells In Vitro. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagamatsu, Y.; Okamura, S.; Saitou, H.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E. Three Cry toxins in two types from Bacillus thuringiensis strain M019 preferentially kill human hepatocyte cancer and uterus cervix cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, S.; Begum, A.; Saga, M.; Hirao, A.; Mizuki, E.; Sakai, H.; Hayakawa, T. Parasporin 1Ac2, a Novel Cytotoxic Crystal Protein Isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis B0462 Strain. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Saitoh, H.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E. Identification of a second cytotoxic protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis A1470. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekino, K.; Okumura, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Kitada, S.; Saitoh, H.; Akao, T.; Oka, T.; Nomura, Y.; Ohba, M.; Shin, T.; et al. Cloning and Characterization of a Unique Cytotoxic Protein Parasporin-5 Produced by Bacillus thuringiensis A1100 Strain. Toxins 2014, 6, 1882–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasutake, K.; Binh, N.D.; Kagoshima, K.; Uemori, A.; Ohgushi, A.; Maeda, M.; Mizuki, E.; Yu, Y.M.; Ohba, M. Occurrence of parasporin-producing Bacillus thuringiensis in Vietnam. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutake, K.; Uemori, A.; Binh, N.D.; Mizuki, E.; Ohba, M. Identification of parasporin genes in Vietnamese isolates of Bacillus thuringiensis. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C 2008, 63, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenina, N.K.; Naveenkuma, A.; Sozhavendan, A.E.; Balakrishnan, N.; Balasubramani, V.; Udayasuriyan, V. Characterization of parasporin gene harboring Indian isolates of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biotech 2014, 4, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nadarajah, V.D.; Ting, D.; Chan, K.K.; Mohamed, S.M.; Kanakeswary, K.; Lee, H.L. Selective cytotoxic activity against leukemic cell lines from mosquitocidal Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal inclusions. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Shi, Y. Apoptosis of HL-60 cells induced by crystal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis Bt9875. Wei Sheng Wu xue Bao 2008, 48, 690–694. [Google Scholar]
- Moazamian, E.; Bahador, N.; Azarpira, N.; Rasouli, M. Anti-cancer Parasporin Toxins of New Bacillus thuringiensis Against Human Colon (HCT-116) and Blood (CCRF-CEM) Cancer Cell Lines. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboul-Soud, M.; Al-Amri, M.Z.; Kumar, A.; Al-Sheikh, Y.A.; Ashour, A.E.; El-Kersh, T.A. Specific Cytotoxic Effects of Parasporal Crystal Proteins Isolated from Native Saudi Arabian Bacillus thuringiensis Strains against Cervical Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.C.; Mizuki, E.; Côte, J.C. Isolation and characterization of a novel Bacillus thuringiensis strain expressing a novel crystal protein with cytocidal activity against human cancer cells. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, E.; Granados, J.C.; Short, J.D.; Ammons, D.R.; Rampersad, J. Parasporins from a Caribbean Island: Evidence for a Globally dispersed Bacillus thuringiensis strain. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, S.; Saitoh, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Inouye, K.; Mizuki, E. Mode of action of parasporin-4, a cytocidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H.; Kusaka, Y.; Mizuk, E. Parasporin-1 Receptor and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 20110038880 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.H.; Jackson, S.; Seaman, M.; Brown, K.; Kempkes, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; Levine, B. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 1999, 402, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S.; Abe, Y.; Shimada, H.; Kusaka, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Katayama, H.; Okumura, S.; Akao, T.; Mizuki, E.; Kuge, O.; et al. Cytocidal actions of parasporin-2, an anti-tumor crystal toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26350–26360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Abe, Y.; Kitada, S.; Kusaka, Y.; Ito, A.; Ichimatsu, T.; Katayama, H.; Akao, T.; Higuchi, K.; Mizuki, E.; et al. Crystal structure of the parasporin-2 Bacillus thuringiensis toxin that recognizes cancer cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 13, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Inoue, H.; Ashida, H.; Maeda, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Kitada, S. Glycan region of GPI anchored-protein is required for cytocidal oligomerization of an anticancer parasporin-2, Cry46Aa1 protein, from Bacillus thuringiensis strain 3. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 142, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, K.; Auger, P.; Asselin, E.; Parent, S.; Côte, J.C.; Sirois, M. Parasporin-2 from a New Bacillus thuringiensis 4R2 Strain Induces Caspases Activation and Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazes, B. The (QxW)3 domain: A flexible lectin scaffold. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, V.; Domanska, B.; Elhigazi, A.; Afolabi, F.; West, M.J.; Crickmore, N. The human cancer cell active toxin Cry41Aa from Bacillus thuringiensis acts like its insecticidal counterparts. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniatte, M.; van der Goot, F.G.; Buckley, J.T.; Pattus, F.; van Dorsselaer, A. Characterisation of the heptameric pore-forming complex of the Aeromonas toxin aerolysin using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. FEBS Lett. 1996, 384, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, S.; Abe, Y.; Maeda, T.; Shimada, H. Parasporin-2 requires GPI-anchored proteins for the efficient cytocidal action to human hepatoma cells. Toxicology 2009, 264, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Messner, P.; Pum, D.; Sára, M. Crystalline bacterial cell surface layers. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 10, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Shuster, B.; Egelseer, E.M.; Pum, D. S-layers: Principles and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 823–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, W.; Yuan, M.; Tang, M.; Chen, J.; Pang, Y. Expression of vip1/vip2 genes in Escherichia coli and Bacillus thuringiensis and the analysis of their signal peptides. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, C.; Crickmore, N.; Wang, Q.; Du, L.; Song, F.; Zhang, J. Genomic sequencing identifies novel Bacillus thuringiensis Vip1/Vip2 binary and Cry8 toxins that have high toxicity to Scarabaeoidea larvae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.W. Vegetative insecticidal proteins: Novel proteins for control of corn pests. In Advances in Insect Control, the Role of Transgenic Plants; Carozzi, N.B., Koziel, M., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 1997; pp. 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Maiti, M.K. Molecular characterization of a novel vegetative insecticidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis effective against sap-sucking insect pest. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucovic, M.; Walters, F.S.; Warren, G.W.; Palekar, N.V.; Chen, J.S. From enzyme to zymogen: Engineering Vip2, an ADP-ribosyltransferase from Bacillus cereus, for conditional toxicity. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2008, 21, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuber, M.; Orlik, F.; Schiffler, B.; Sickmann, A.; Benz, R. Vegetative insecticidal protein (Vip1Ac) of Bacillus thuringiensis HD201: Evidence for oligomer and channel formation. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, H.; Aktories, K.; Popoff, M.R.; Stiles, B.G. Binary bacterial toxins: Biochemistry, biology, and applications of common Clostridium and Bacillus proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 373–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel, Y.; Banyuls, N.; Chakroun, M.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Insights into the Structure of the Vip3Aa Insecticidal Protein by Protease Digestion Analysis. Toxins 2017, 4, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkefi-Mesrati, L.; Boukedi, H.; Chakroun, M.; Kamoun, F.; Azzouz, H.; Tounsi, S.; Rouis, S.; Jaoua, S. Investigation of the steps involved in the difference of susceptibility of Ephesitia kuehniella and Spodoptera littoralis to the Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa16 toxin. J. Invertebr. Path. 2011, 107, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, G.; Portillo, A.; Arias, E.; Ribas, R.M.; Olmos, J. New Combinations of Cry Genes From Bacillus Thuringiensis Strains Isolated From Northwestern Mexico. Int. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Almanza, G.; Rocha-Zavaleta, L.; Aguilar-Zacarías, C.; Ayala-Luján, J.; Olmos, S.J. Cry1A Proteins are Cytotoxic to HeLa but not to SiHa Cervical Cancer Cells. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
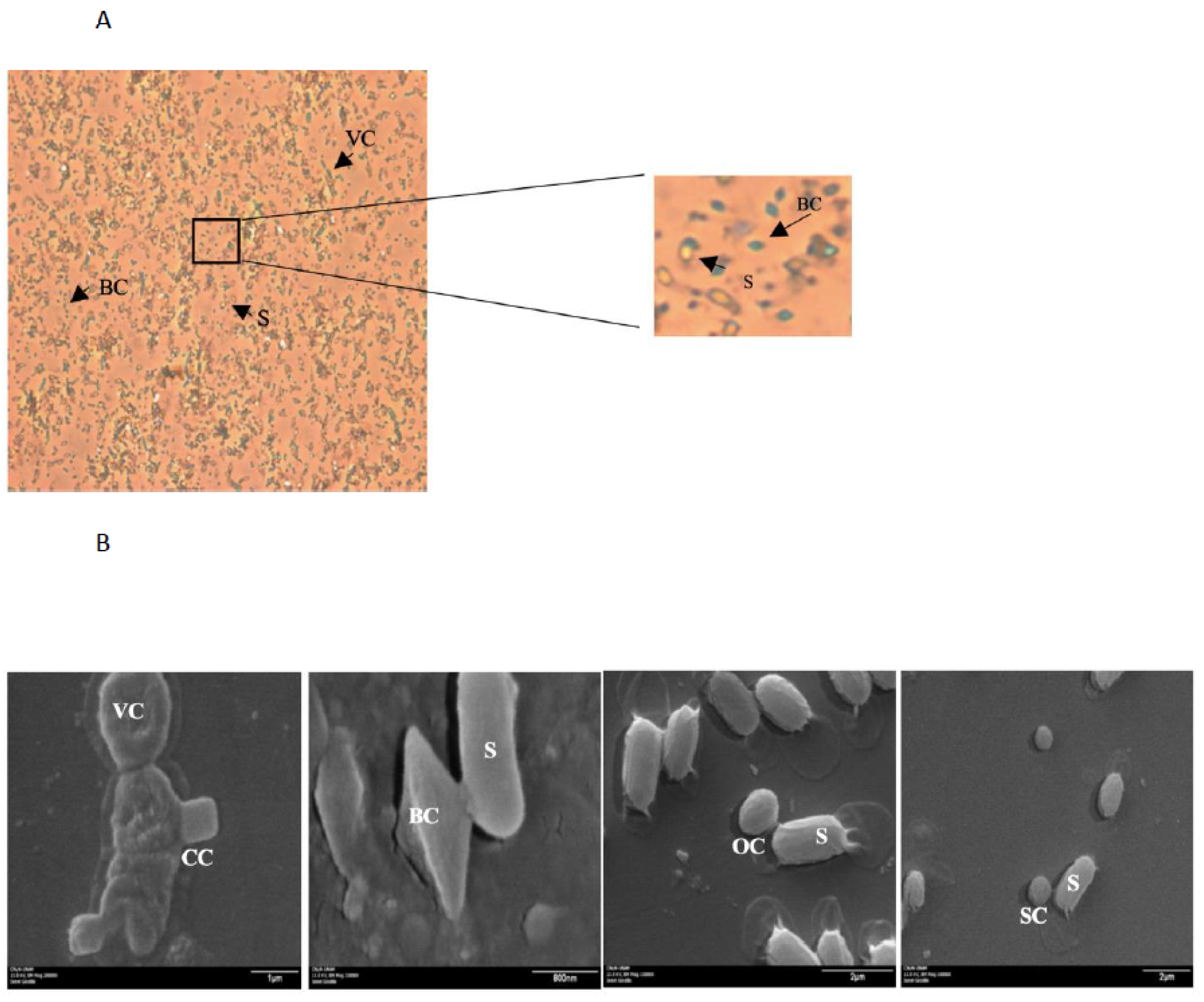

| Aedes spp. | Culex spp. | Anopheles spp. |
|---|---|---|
| Cyt1Aa, Cyt2Ba | Cyt1Aa, Cyt2Ba | Cyt1Aa, Cyt2Aa |
| Cry4Aa | Cry4Aa | Cry4Aa |
| Cry4Ba | Cry4Ba | Cry10Aa |
| Cry10Aa | Cry10Aa | Cry11Aa |
| Cry11Aa | Cry11Aa |
| PS | Bt Strain | Cry Gene | Protoxin (kDa) | Active Toxin (kDa) | Protease Activation | Main Cellular Target | EC50 [µg/mL] | Mechanism Action | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS1Aa1 | A1190 | Cry31Aa1 | 81 | 15, 56 | Trypsin | HeLa | 0.12 | Apoptosis | Japan | [99] |
| PS1Aa2 | M15 | Cry31Aa2 | 83 | 55, 70 | Trypsin | Jurkat HepG2 | 0.02 0.02 | ND | Canada | [128] |
| PS1Aa3 | B195 | Cry31Aa3 | 81 | 56 | Trypsin | HeLa | 14.7 | ND | Japan | [116] |
| PS1Aa4 | Bt79-25 | Cry31Aa4 | 81 | NP | Proteinase K | ND | ND | ND | Vietnam | [122] |
| PS1Aa5 | Bt92-10 | Cry31Aa5 | 81 | NP | Proteinase K | ND | ND | ND | Vietnam | [122] |
| PS1Aa6 | M019, 64-1-94 | Cry31Aa6 | 70 | 15, 55 | Trypsin | HepG2 | 0.52 | ND | Japan, Caribbean | [117,129] |
| PS1Ab1 | B195 | Cry31Ab1 | 82 | 56 | Trypsin | HeLa | 14.7 | ND | Japan | [116] |
| PS1Ab2 | Bt31-5 | Cry31Ab2 | 82 | NP | Proteinase K | ND | ND | ND | Vietnam | [122] |
| PS1Ac1 | Bt87-29 | Cry31Ac1 | 87 | NP | Proteinase K | ND | ND | ND | Vietnam | [122] |
| PS1Ac2 | B0462 | Cry31Ac2 | 81 | 15, 60 | Proteinase K | HeLa | 2 | Apoptosis | Japan | [118] |
| PS1Ad1 | 64-1-94, M15, M019 | Cry31Ad1 | 73 | 14, 59 | Trypsin | HepG2 | 0.52 | ND | Caribbean, Canada, Japan | [117,128,129] |
| PS2Aa1 | A1547 | Cry46Aa1 | 37 | 30 | Proteinase K | HepG2 | 0.023 | Pore-forming | Japan, USA | [105] |
| PS2Aa2 | A1470 | Cry31Aa2 | 30 | 28 | Proteinase K | MOLT-4 | 0.041 | ND | Japan | [119] |
| PS2Ab1 | TK-E6 | Cry31Ab1 | 33 | 29 | Proteinase K | Jurkat | 0.545ng/ml | ND | Japan | [113] |
| PS3Aa1 | A1462 | Cry41Aa1 | 88 | 64 | Proteinase K | HL60 | 1.32 | ND | Japan | [100] |
| PS3Ab1 | A1462 | Cry41Ab1 | 88 | 64 | Proteinase K | HL60 | 1.25 | ND | Japan | [100] |
| PS4Aa1 | A1470 | Cry45Aa1 | 31 | 28 | Proteinase K | CaCo2 | 0.124 | Pore-forming | Japan | [111] |
| PS5Aa1 | A1100 | Cry64Aa1 | 33 | 30 | Proteinase K | TCS | 0.046 | ND | Japan | [120] |
| PS6Aa1 | M019, 64-1-94 | Cry63Aa1 | 85 | 14, 59 | Trypsin | HepG2 | 2.3 | ND | Japan, Caribbean | [117,129] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Almanza, G.; Esparza-Ibarra, E.L.; Ayala-Luján, J.L.; Mercado-Reyes, M.; Godina-González, S.; Hernández-Barrales, M.; Olmos-Soto, J. The Cytocidal Spectrum of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: From Insects to Human Cancer Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050301
Mendoza-Almanza G, Esparza-Ibarra EL, Ayala-Luján JL, Mercado-Reyes M, Godina-González S, Hernández-Barrales M, Olmos-Soto J. The Cytocidal Spectrum of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: From Insects to Human Cancer Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(5):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050301
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Almanza, Gretel, Edgar L. Esparza-Ibarra, Jorge L. Ayala-Luján, Marisa Mercado-Reyes, Susana Godina-González, Marisa Hernández-Barrales, and Jorge Olmos-Soto. 2020. "The Cytocidal Spectrum of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: From Insects to Human Cancer Cells" Toxins 12, no. 5: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050301
APA StyleMendoza-Almanza, G., Esparza-Ibarra, E. L., Ayala-Luján, J. L., Mercado-Reyes, M., Godina-González, S., Hernández-Barrales, M., & Olmos-Soto, J. (2020). The Cytocidal Spectrum of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: From Insects to Human Cancer Cells. Toxins, 12(5), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050301







