Effects of Nutrient Limitation on the Synthesis of N-Rich Phytoplankton Toxins: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
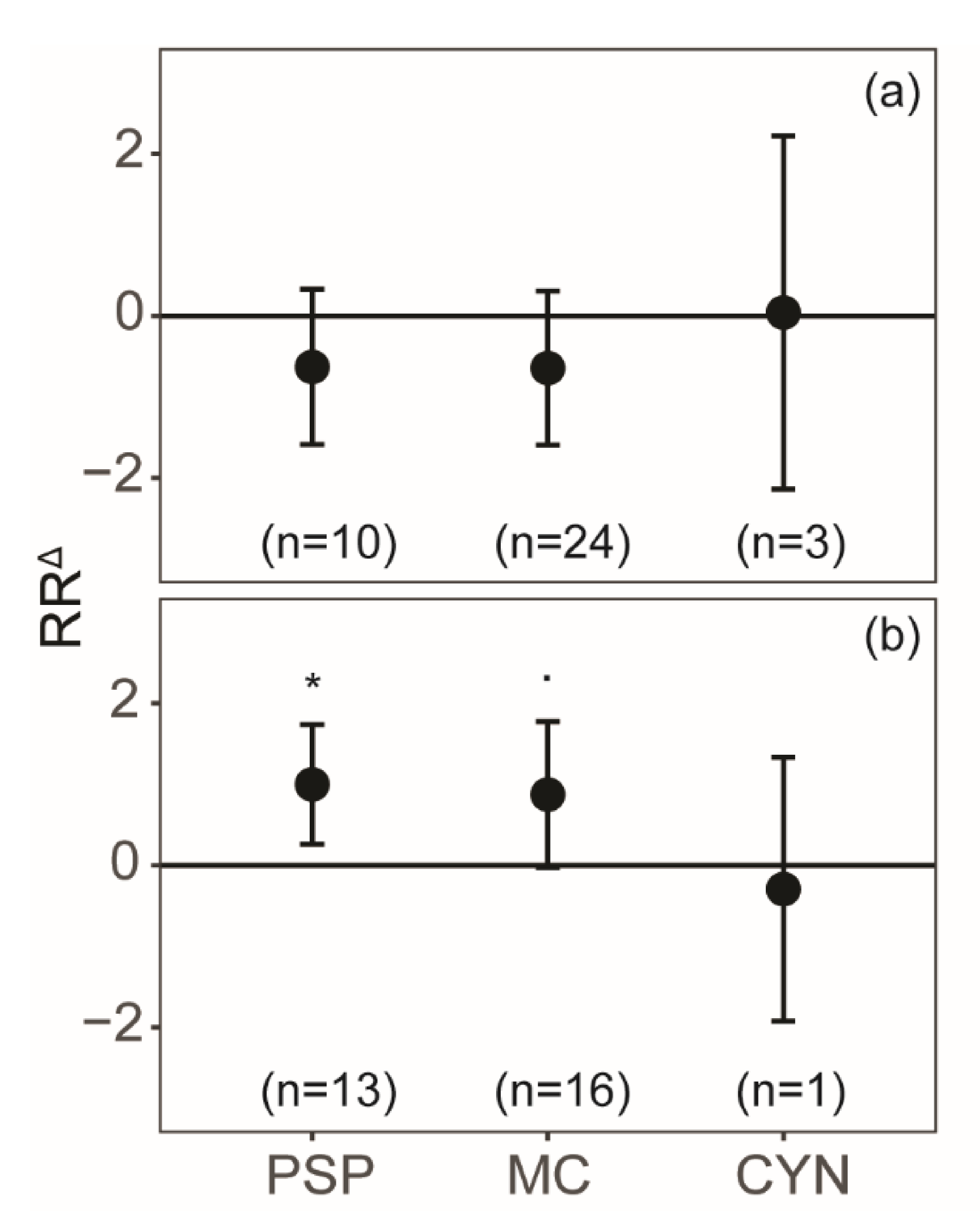
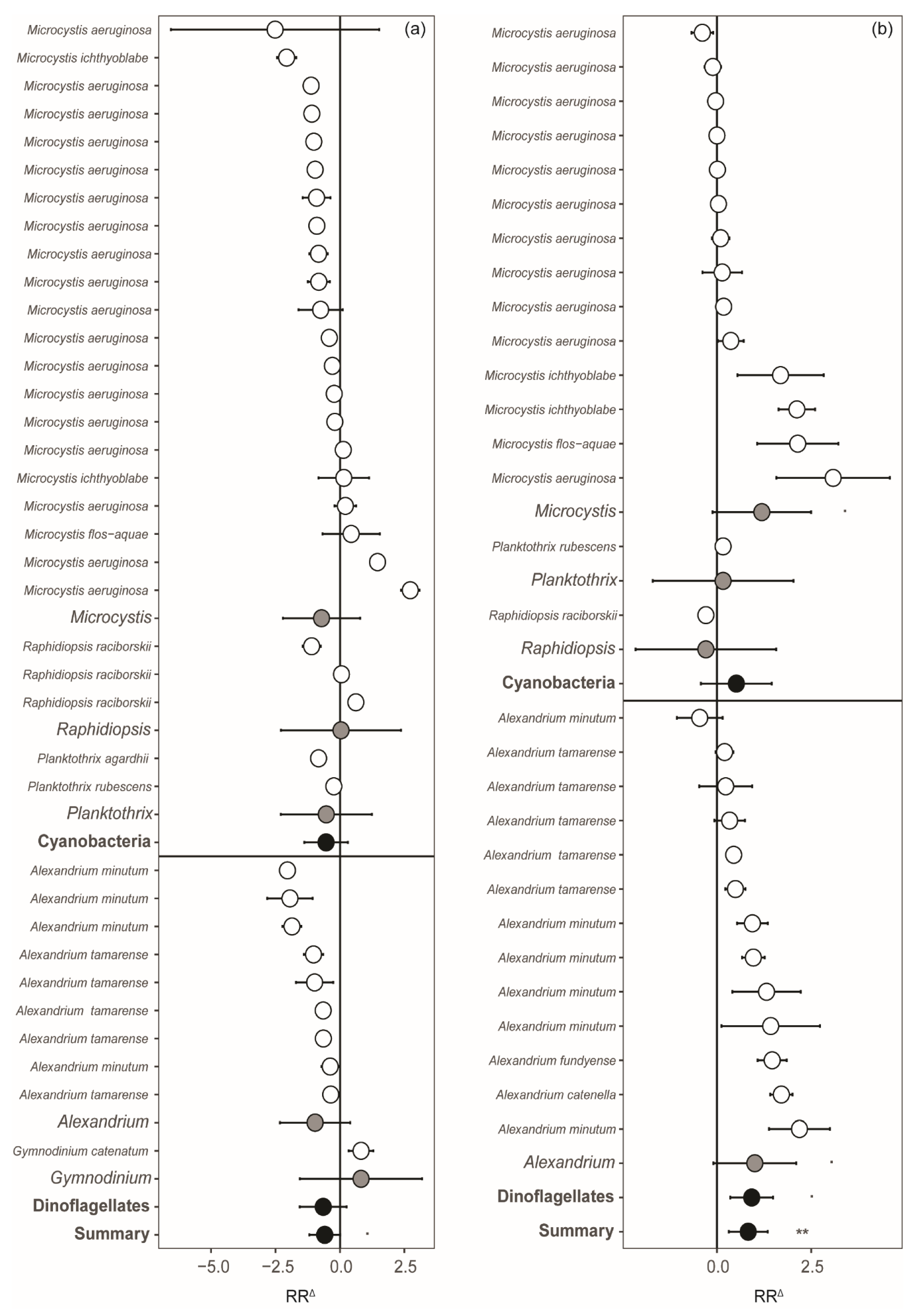
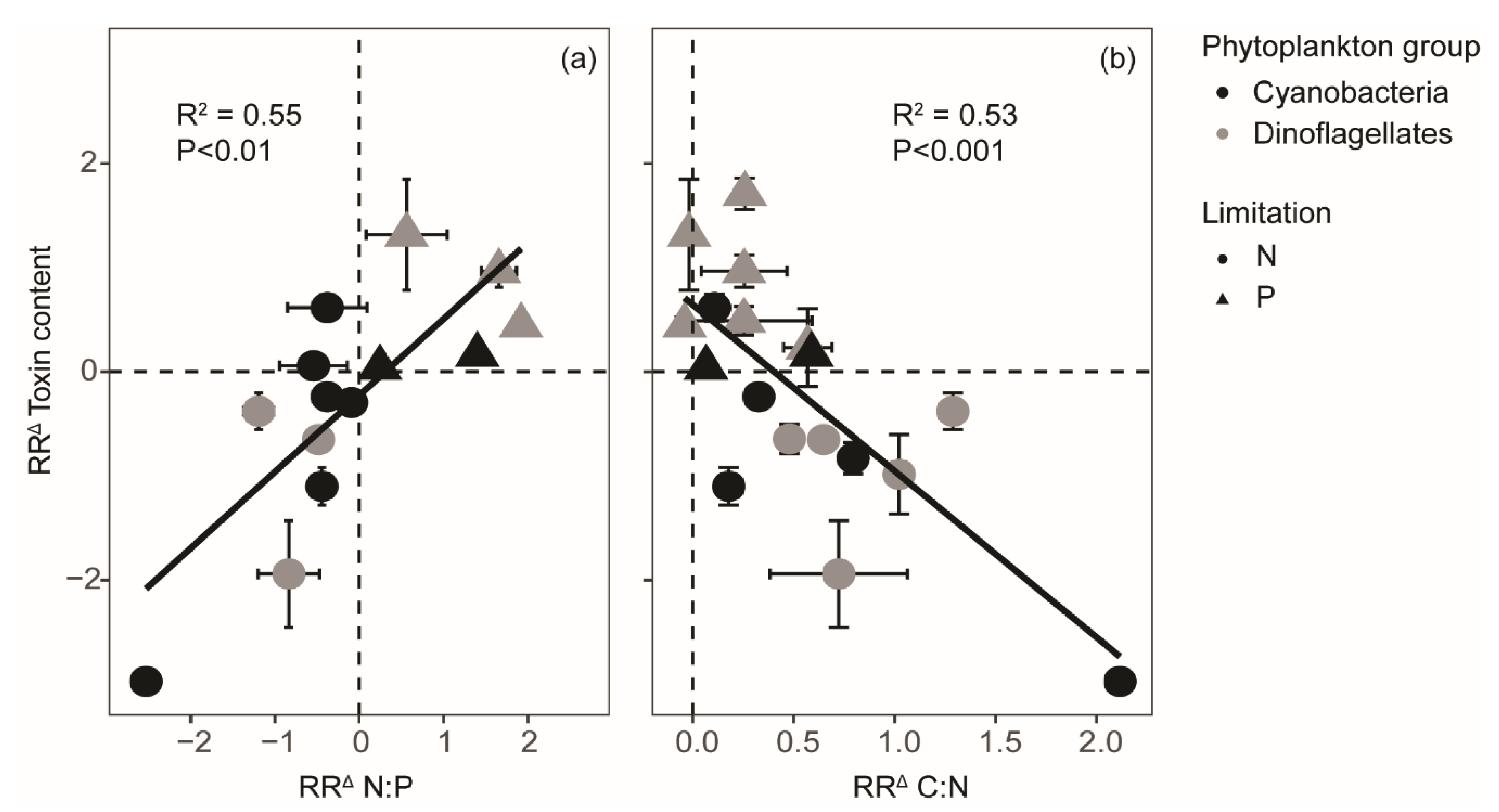
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Response Ratios
4.3. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Cochlan, W.P.; Glibert, P.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Kudela, R.; Parsons, M.L.; Jack, J.E.; Townsend, D.W.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the United States. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: Paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibert, P.M.; Seitzinger, S.; Heil, C.; Burkholder, J.M.; Parrow, M.; Codispoti, L.; Kelly, V. The role of eutrophication in the global proliferation of harmful algal blooms. Oceanography 2005, 18, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. The complex relationships between increases in fertilization of the earth, coastal eutrophication and proliferation of harmful algal blooms. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Graneli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 189, pp. 341–354. ISBN 978-3-540-32209-2. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.L.; Dortch, Q. Sedimentological evidence of an increase in Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) abundance in response to coastal eutrophication. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, K.; Schreider, M.; McArthur, L.; Schreider, S. Changes in the water quality characteristics during a macroalgal bloom in a coastal lagoon. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 118, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Scott, J.T.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Hoffman, D.K.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. It takes two to tango: When and where dual nutrient (N & P) reductions are needed to protect lakes and downstream ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10805–10813. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J. Harmful algal blooms: Their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, E.; Teegarden, G.; Campbell, R.; Cembella, A.; Baumgartner, M.F.; Mate, B.R. North Atlantic right whales, Eubalaena glacialis, exposed to paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins via a zooplankton vector, Calanus finmarchicus. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Lewis, N.I.; Bauder, A.G.; Aversano, C.D.; Thomas, K.; Jellett, J.; Cusack, R.R. The toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense as the probable cause of mortality of caged salmon in Nova Scotia. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, G.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Martin, J.L.; Michaud, J.; Cole, T.V.N.; Rolland, R.M. Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins in North Atlantic right whales Eubalaena glacialis and their zooplankton prey in the Bay of Fundy, Canada. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 306, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunda, W.G.; Graneli, E.; Gobler, C.J. Positive feedback and the development and persistence of ecosystem disruptive algal blooms. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bláha, L.; Babica, P.; Maršálek, B. Toxins produced in cyanobacterial water blooms—Toxicity and risks. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga-Cervera, B.; García Balboa, C.; Costas, E.; Lopez-Rodas, V. Why cyanobacteria produce toxins? Evolutionary game theory suggests the key. Int. J. Biol. 2014, 7, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Gowen, R.J.; Harrison, P.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Hoagland, P.; Moschonas, G. Anthropogenic nutrients and harmful algae in coastal waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z. Neurotoxins from marine dinoflagellates: A brief review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M. Toxic algae blooms and red tides: A global perspective. In Red Tides: Biology, Environmental Science and Toxicology; Okaichi, T., Anderson, D.M., Nemoto, T., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Diversity of marine and freshwater algal toxins. In Seafood Toxicology: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Luis M. Botana: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, G. Bioaccumulation of the hepatotoxic microcystins in various organs of a freshwater snail from a subtropical Chinese Lake, Taihu Lake, with dense toxic Microcystis blooms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, J.; López-Rodas, V.; Costas, E. Microcystins from tap water could be a risk factor for liver and colorectal cancer: A risk intensified by global change. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 72, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; WHO: London, UK, 1999; ISBN 9781317436980. [Google Scholar]
- Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Simeunović, J.; Baltić, V.; Stanić, D.; Svirčev, Z. Human exposure to cyanotoxins and their effects on health. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2013, 64, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton Univeristy Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Geider, R.J.; La Roche, J. Redfield revisited: Variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical basis. Eur. J. Phycol. 2002, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Steinert, G.; Boersma, M.; Malzahn, A. Goldman revisited: Faster-growing phytoplankton has lower N:P and lower stoichiometric flexibility. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 2076–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Van de Waal, D.B. Biological stoichiometry of oleaginous microalgal lipid synthesis: The role of N:P supply ratios and growth rate on microalgal elemental and biochemical composition. Algal Res. 2018, 32, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Pančić, M.; Andersen, K.H.; Kiørboe, T. The cost of toxin production in phytoplankton: The case of PST producing dinoflagellates. ISME J. 2019, 13, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Smith, V.H.; Declerck, S.A.J.; Stam, E.C.M.; Elser, J.J. Stoichiometric regulation of phytoplankton toxins. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Tillmann, U.; Zhu, M.M.; Koch, B.P.; Rost, B.; John, U. Nutrient pulse induces dynamic changes in cellular C:N:P, amino acids, and paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in Alexandrium tamarense. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 493, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D. Ecophysiology and metabolism of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine microalgae. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Graneli, E.; Johansson, N.; Panosso, R. Cellular toxin contents in relation to nutrient conditions for different groups of phycotoxins. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; IOC-UNESCO; pp. 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, N.D.; Osburn, F.S.; Wang, J.; Taylor, R.B.; Boedecker, A.R.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W.; Scott, J.T. Biological stoichiometry regulates toxin production in Microcystis aeruginosa (UTEX 2385). Toxins 2019, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hutchins, D.A.; Feng, Y.; Seubert, E.L.; Caron, D.A.; Fu, F.X. Effects of changing pCO2 and phosphate availability on domoic acid production and physiology of the marine harmful bloom diatom Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Lürling, M.; Van Donk, E.; Visser, P.M.; Huisman, J. The ecological stoichiometry of toxins produced by harmful cyanobacteria: An experimental test of the carbon-nutrient balance hypothesis. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström-Öst, J.; Hogfors, H.; El-Shehawy, R.; De Stasio, B.; Vehmaa, A.; Gorokhova, E. Toxin-producing cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena, potential competitors and grazers: Testing mechanisms of reciprocal interactions. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkvist, J.; Selander, E.; Pavia, H. Induction of toxin production in dinoflagellates: The grazer makes a difference. Oecologia 2008, 156, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selander, E.; Thor, P.; Toth, G.; Pavia, H. Copepods induce paralytic shellfish toxin production in marine dinoflagellates. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 273, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, X. Interactions between Microcystis aeruginosa and coexisting bisphenol A at different nitrogen levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.A.; Jankowiak, J.G.; Kramer, B.J.; Goleski, J.A.; Huang, I.S.; Zimba, P.V.; do Carmo Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.; Gobler, C.J. Succession and toxicity of Microcystis and Anabaena (Dolichospermum) blooms are controlled by nutrient-dependent allelopathic interactions. Harmful Algae 2018, 74, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Jia, P.; Dai, R. Evaluation of changes in Microcystis aeruginosa growth and microcystin production by urea via transcriptomic surveys. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graneli, E.; Flynn, K. Chemical and physical factors influencing toxin content. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Graneli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 189, pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Verspagen, J.M.H.; Van de Waal, D.B.; Finke, J.F.; Visser, P.M.; Huisman, J. Contrasting effects of rising CO2 on primary production and ecological stoichiometry at different nutrient levels. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, T.; Van de Waal, D.B.; Brandenburg, K.M.; John, U.; Voss, M.; Achterberg, E.P.; Rost, B. Interactive effects of ocean acidification and nitrogen limitation on two bloom-forming dinoflagellate species. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 443, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Arrayás, M.; Ebert, U.; Sommeijer, B. How do sinking phytoplankton species manage to persist? Am. Nat. 2002, 159, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, J.S.M.; Giani, A. Microcystin production and regulation under nutrient stress conditions in toxic Microcystis. Strains 2014, 80, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, H.P.; Pearson, L.A.; Neilan, B.A. NtcA from Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 is autoregulatory and binds to the microcystin promoter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4362–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrlack, T.; Dittmann, E.; Henning, M.; Börner, T.; Kohl, J.G. Role of microcystins in poisoning and food ingestion inhibition of Daphnia galeata caused by the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, F.M.; Thomson, C.; Metcalf, J.S.; Lucocq, J.M.; Codd, G.A. Immunogold localisation of microcystins in cryosectioned cells of Microcystis. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkilen, H.; Gjolme, N. Iron-stimulated toxin production in Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, D.; Keren, Y.; Vardi, A.; Sukenik, A.; Carmeli, S.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E.; Kaplan, A. Towards clarification of the biological role of microcystins, a family of cyanobacterial toxins. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexova, R.; Fujii, M.; Birch, D.; Cheng, J.; Waite, T.D.; Ferrari, B.C.; Neilan, B.A. Iron uptake and toxin synthesis in the bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa under iron limitation. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Yu, S.; Sun, Z.; Xie, X.; Liu, W.; Fu, Z. Effects of copper sulfate, hydrogen peroxide and N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on oxidative stress and the expression of genes involved photosynthesis and microcystin disposition in Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Ruiz, M.; Zhang, C.C. Oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.; Adams, M.P.; Chuang, A.W.; Orr, P.T.; O’Brien, K.R.; Burford, M.A. Constitutive toxin production under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes of three ecotypes of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii ((Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju). Harmful Algae 2015, 47, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, V.S.; Stomp, M.; Rosso, C.; Van Beusekom, S.A.M.; Emmerich, B.; Stal, L.J.; Huisman, J. Low temperature delays timing and enhances the cost of nitrogen fixation in the unicellular cyanobacterium Cyanothece. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Sullivan, J.J.; Hall, S.; Lee, C. Dynamics of physiology of saxitoxin production by the dinoflagellates Alexandrium spp. Mar. Biol. 1990, 104, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teegarden, G.J. Copepod grazing selection and particle discrimination on the basis of PSP toxin content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 181, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.P.; Dam, H.G. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense on the copepod Acartia hudsonica: A test of the mechanisms that reduce ingestion rates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 248, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D. Chemical ecolgy of eukaryotic microalgae in marine ecosystems. Phycologia 2003, 42, 420–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Oshima, Y. Response of Gymnodinium catenatum to increasing levels of nitrate: Growth patterns and toxicity. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.M.; Morris, R.; Zimmerman, W. Cyanophycin granule polypeptide protease in a unicellular cyanobacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 138, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verschoor, A.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Van Donk, E.; Huisman, J. Climate-driven changes in the ecological stoichiometry of aquatic ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ru, J.; Hou, Y. Relationship of energy charge and toxin content of Microcystis aeruginosa in nitrogen-limited or phosphorous-limited cultures. Toxicon 2008, 51, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, N.H.; Chan, S.L.; Trevor, A.J. Production of saxitoxin by cultures of Gonyaulax catenella. Toxicon 1975, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroncher-Oldenburg, G.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Coupling of saxitoxin biosynthesis to the G1 phase of the cell cycle in the dinoflagellate Alexandriun fundyense: Temperature and nutrient effects. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H. Effects of nitrate and phosphate on grazer-induced toxin production in Alexandrium minutum. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenken, T.; Wierenga, J.; Gsell, A.S.; van Donk, E.; Rohrlack, T.; Van de Waal, D.B. Changes in N:P supply ratios affect the ecological stoichiometry of a toxic cyanobacterium and its fungal parasite. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowe, M.A.D.; Abbas, F.; Porojan, C.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Lim, R.P.; Furey, A.; Yeo, D.C.J. Roles of nitrogen and phosphorus in growth responses and toxin production (using LC-MS/MS) of tropical Microcystis ichthyoblabe and M. flos-aquae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Skelton, H.M. Mixotrophy, a major mode of nutrition for harmful algal species in eutrophic waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.K. Mixotrophy among Dinoflagellates. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, D.M.; Anderson, D.M. Widespread phagocytosis of ciliates and other protists by marine mixotrophic and heterotrophic thecate dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebyk, D.; Bechemin, C.; Ward, C.J.; Verite, C.; Codd, G.A.; Maestrini, S.Y. Effects of salinity and two coastal waters on the growth and toxin content of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.M.; Munoz, M.G.; Contreras, A.M. Temperature as a factor regulating growth and toxin content in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström-Öst, J.; Repka, S.; Mikkonen, M. Interactions between plankton and cyanobacterium Anabaena with focus on salinity, growth and toxin production. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedaria, A.I.; Luckas, B.; Reinhardt, K.; Azanza, R.V. Growth response and toxin concentration of cultured Pyrodinium bahamense var. compressum to varying salinity and temperature conditions. Toxicon 2007, 50, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Sano, T.; Li, R.; Watanabe, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Kaya, K. Microcystin production of Microcystis viridis (cyanobacteria) under different culture conditions. Phycol. Res. 1998, 46, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatters, A.O.; Flewelling, L.J.; Fu, F.; Granholm, A.A.; Hutchins, D.A. High CO2 promotes the production of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins by Alexandrium catenella from Southern California waters. Harmful Algae 2013, 30, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, A.M.; Rücker, J.; Pick, F.R.; Fastner, J.; Rohrlack, T.; Mischke, U.; Wiedner, C. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: The influence of nitrogen versus phosphorus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, N.L.; Manderville, R.A. Toxic mechanisms of microcystins in mammals. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P. New saxitoxin analogues in the marine environment: Developments in toxin chemistry, detection and biotransformation during the 2000s. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y. Toxigenesis and biosynthesis of saxitoxin analogues. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Burkholder, J.A.M.; Davis, T.W.; Harke, M.J.; Johengen, T.; Stow, C.A.; Van de Waal, D.B. The dual role of nitrogen supply in controlling the growth and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinehart, K.L.; Namikoshi, M.; Choi, B.W. Structure and biosynthesis of toxins from blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). J. Appl. Phycol. 1994, 6, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Nagashima, Y.; Taguchi, S. N:P ratios controlling the growth of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense: Content and composition of paralytic shellfish poison. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.; Muftakhidinov, B.; Winchen, T. Engauge Digitizer, version 4.1; Github: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lajeunesse, M.J. Bias and correction for the log response ratio in ecological meta-analysis. Ecology 2015, 96, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Toxin (Short Name) | (Full Name) | C:N Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| PSP | Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins | 1.5 |
| CYN | Cylindrospermopsin | 3.0 |
| MC | Microcystin (MC-LR; MC-RR) | 4.3 |
| NOD | Nodularin | 5.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandenburg, K.; Siebers, L.; Keuskamp, J.; Jephcott, T.G.; Van de Waal, D.B. Effects of Nutrient Limitation on the Synthesis of N-Rich Phytoplankton Toxins: A Meta-Analysis. Toxins 2020, 12, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040221
Brandenburg K, Siebers L, Keuskamp J, Jephcott TG, Van de Waal DB. Effects of Nutrient Limitation on the Synthesis of N-Rich Phytoplankton Toxins: A Meta-Analysis. Toxins. 2020; 12(4):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040221
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandenburg, Karen, Laura Siebers, Joost Keuskamp, Thomas G. Jephcott, and Dedmer B. Van de Waal. 2020. "Effects of Nutrient Limitation on the Synthesis of N-Rich Phytoplankton Toxins: A Meta-Analysis" Toxins 12, no. 4: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040221
APA StyleBrandenburg, K., Siebers, L., Keuskamp, J., Jephcott, T. G., & Van de Waal, D. B. (2020). Effects of Nutrient Limitation on the Synthesis of N-Rich Phytoplankton Toxins: A Meta-Analysis. Toxins, 12(4), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040221





