Establishment of a Novel Oral Murine Model of Ricin Intoxication and Efficacy Assessment of Ovine Ricin Antitoxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
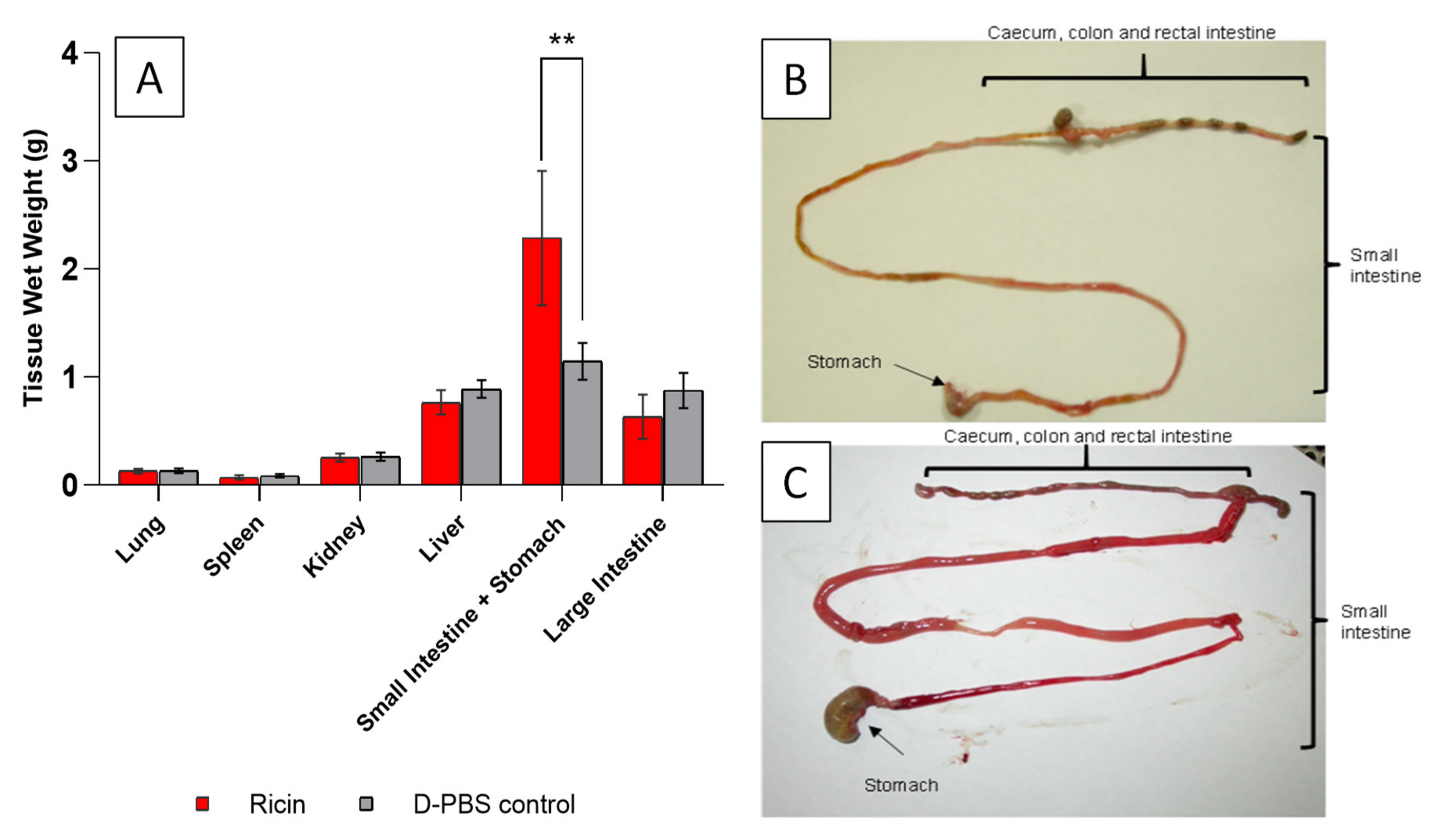
2.1. A Food Withdrawal Time of 8 h Minimizes Variability in Stomach Contents
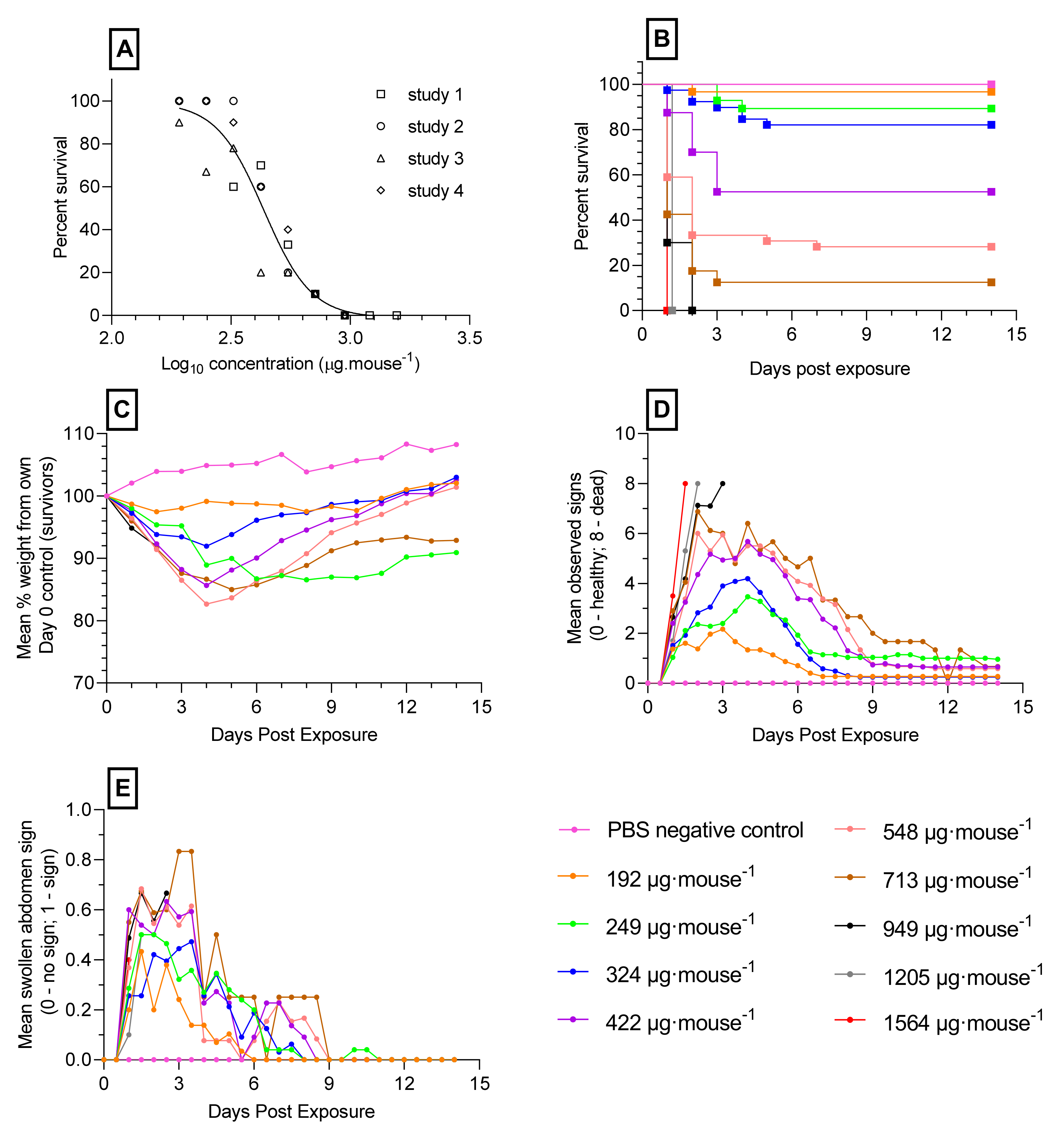
2.2. Toxicity of Orally Administered Ricin
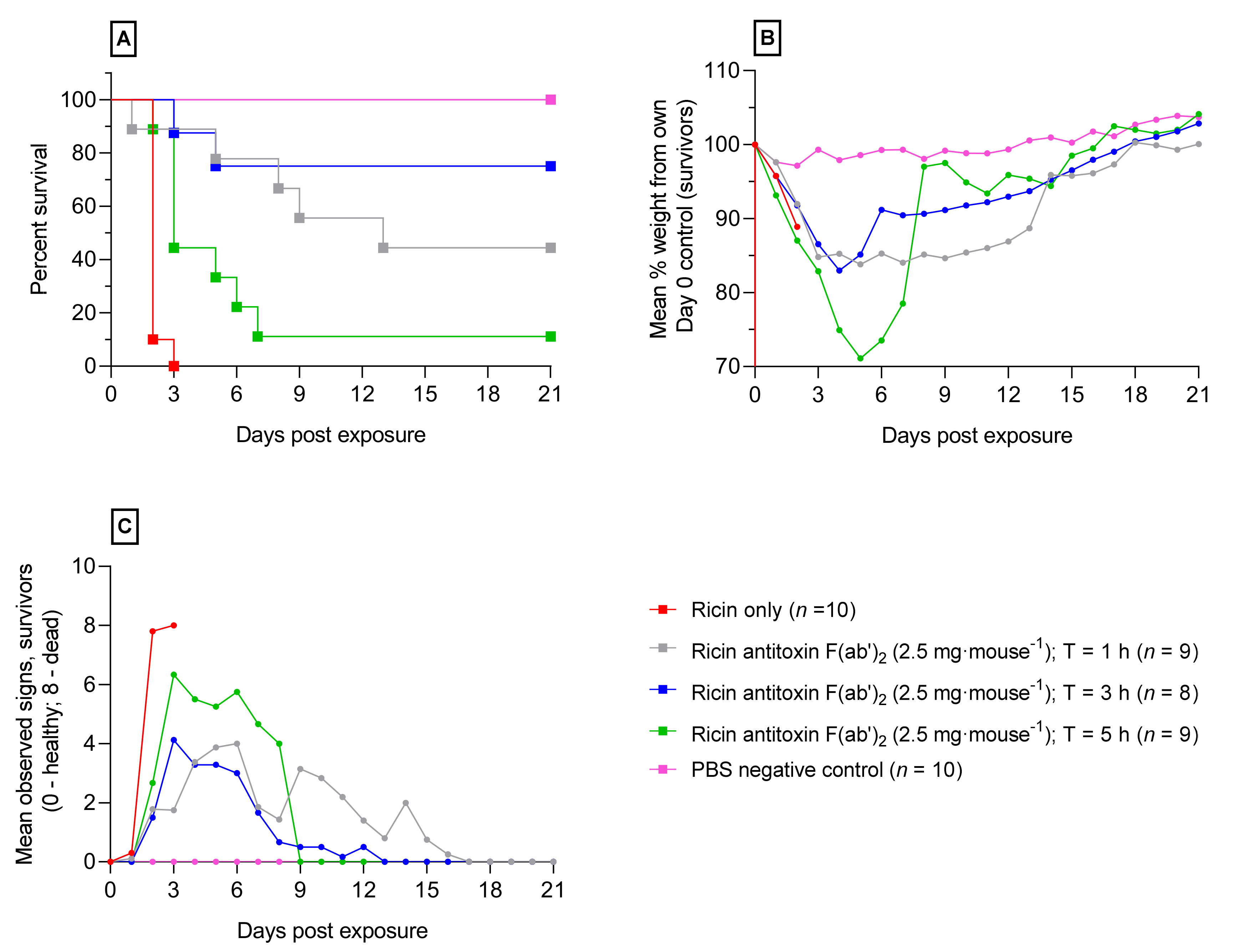
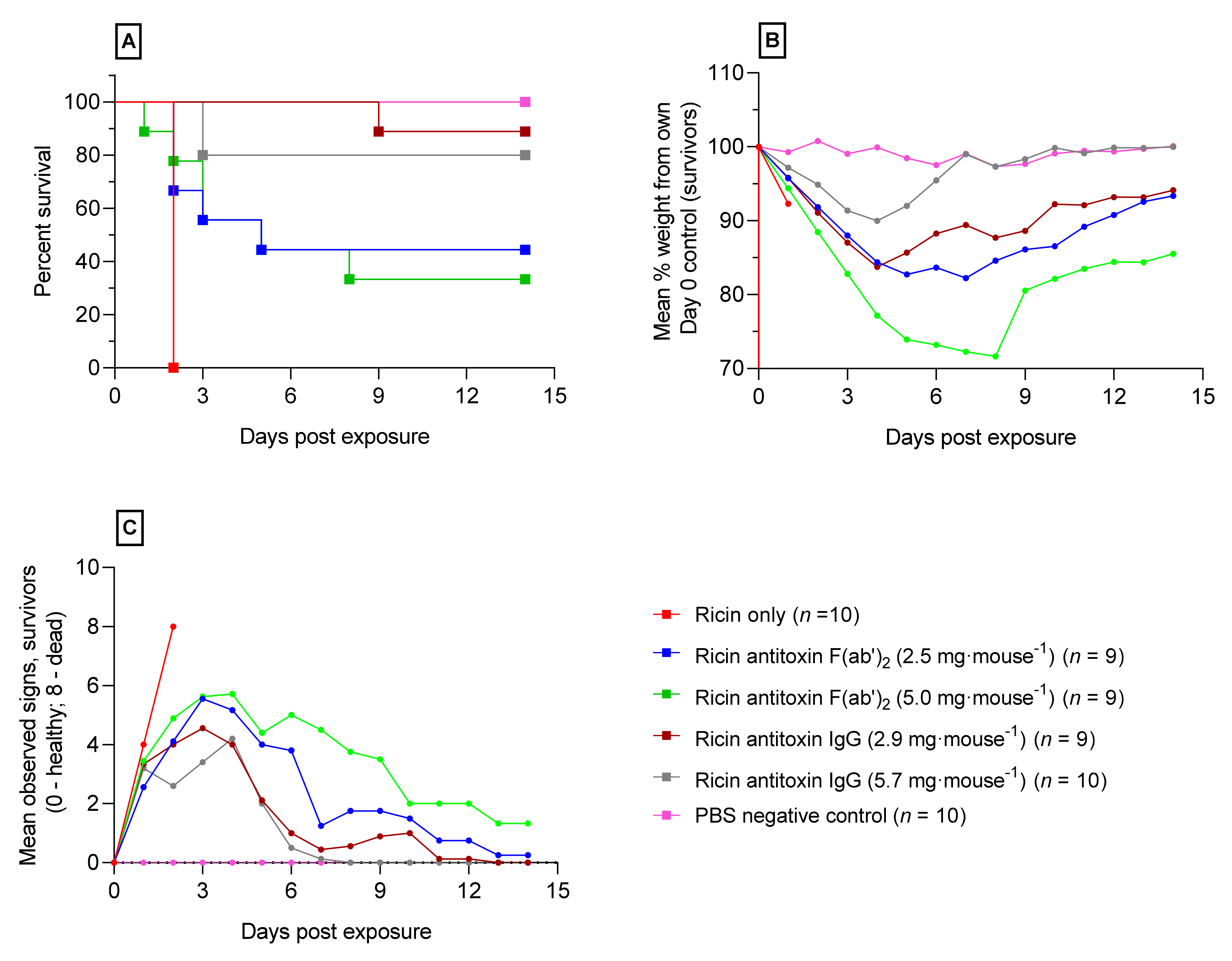
2.3. Ricin Antitoxin Increases Survival and Reduces Morbidity Following Orally Administered Ricin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ricin Toxin
4.2. Preparation of Ricin Antitoxins
4.3. Animal Husbandry
4.4. Minimisation of Variability after Oral Gavage into the Digestive Tract
4.5. Lethal Oral Model of Ricin Intoxication
4.6. Determination of Oral Toxicity of Ricin in Mice
4.7. Confirmation of Ricin Challenge Dose for Use in Antitoxin Efficacy Studies
4.8. Efficacy of Ricin Antitoxins against Lethal Oral Ricin Challenge
4.9. Data and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coppock, R.W.; Dziwenka, M. Potential Agents That Can Cause Contamination of Animal Feedstuffs and Terror. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Millard, C.B.; LeClaire, R.D. Ricin and Related Toxins: Review and Perspective. In Chemical Warfare Agents: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutics, 2nd ed.; Romano, J.A., Jr., Lukey, B.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 423–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hayoun, M.A.; Kong, E.L.; Smith, M.E.; King, K.C. Ricin Toxicity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, Y.; Mitsui, K.; Motizuki, M.; Tsurigi, T. Mechanism of Action of Ricin and related Toxic Lectins on Eukaryotic ribosomes. J. Biochem. 1987, 262, 5908–5912. [Google Scholar]
- Spooner, R.A.; Lord, J.M. Ricin trafficking in cells. Toxins 2015, 7, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audi, J.; Benson, M.; Patel, M.; Schier, J.; Osterloh, J. Ricin poisoning: A comprehensive Review. JAMA 2005, 9, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowa-Rogzinska, N.; Sominka, H.; Nowakowska-Golacka, J.; Sandvig, K.; Slominska-Wojewodzka, M. Intracellular transport and cytotoxicity of the protein toxin ricin. Toxins 2019, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worbs, S.; Kohler, K.; Pauly, D.; Avondet, H.A.; Schaer, M.; Dorner, M.B.; Dorner, B.G. Ricinus communis intoxication in humans and veterinary medicine—A summary of real cases. Toxins 2011, 3, 1332–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankova, M.; Handlos, P.; Svidrnoch, M.; Maier, V. Fatal intoxication by intravenous injection of caster bean (Ricinus communis L) extract- a case study. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamor, M.; Gharbi, E.; Bouzid, S.; Chakroun-Walha, O.; Rekik, N. Ricin poisoning after oral ingestion of castor beans: A case report and literature review. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2020. In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G.; Calafato, G.; Bolognesi, A. Ricin: An Ancient Story for a Timeless Plant Toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, O.F.L.; Pizon, A.F.; Tamara, K. Ricin poisoning after oral ingestion of castor beans—A case report and review of literature and lab testing. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 53, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallshaw, J.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Vitetta, E.S. RiVax, a recombinant ricin subunit vaccine, protects mice against ricin delivered by gavage or aerosol. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7459–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradberry, S. Ricin and Abrin. Chem. Terrorism. 2016, 44, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, S.J.; Griffiths, G.; Jenner, D.; Gwyther, R.J.; Stahl, F.M.; Cork, L.; Holley, J.L.; Green, A.C.; Clark, G. Production, Characterisation and Testing of an Ovine Antitoxin against Ricin; Efficacy, Potency and Mechanisms of Action. Toxins 2017, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyke, G.; Ehrbar, D.; Doering, J.; Yates, J.; Vitetta, E.; Donini, O.; Mantis, N. Endpoint and epitope-specific antibody responses as correlates of vaccine-mediated protection of mice against ricin toxin. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6721–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falach, R.; Sapoznikov, A.; Evgy, Y.; Aftalion, M.; Makovitzki, A.; Agami, A.; Mimran, A.; Lerer, E.; Ben David, A.; Zichel, R.; et al. Post-Exposure Anti-Ricin Treatment Protects Swine Against Lethal Systemic and Pulmonary Exposures. Toxins 2020, 12, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nydegger, U.E.; Sturzenegger, M. Adverse effects of intravenous immunoglobulinum therapy. Drug Saf. 1999, 21, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Pauly, M.; Guthals, A. A humanised monoclonal antibody cocktail to prevent Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication. Toxins 2020, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshigaro, M.; Nakashima, H.; Tanabe, S.; Sakakibara, R. Interaction of toxic lectin Ricin with epithelial cells of rat small intestine in vitro. J. Pharm. Dyn. 1992, 40, 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Alyssa, D.F.; Teel, L.D.; Smith, M.A.; Sinclair, J.F.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; O’Brien, A.D. Ricin Crosses Polarized Human Intestinal Cells and Intestines of Ricin-Gavaged Mice without Evident Damage and Then Disseminates to Mouse Kidneys. PLoS ONE 2013, 17, e69706. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, D.R.; Jaax, N.K. Ricin toxin. In Medical Aspects of Chemical and Biological Warfare; Borden Institute, Walter Reed Army Medical Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Chapter 32; pp. 631–642. [Google Scholar]
- Balint, G.A. Ricin: The toxic protein of castor oil seeds. Toxicology 1974, 2, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covell, D.G.; Barebt, J.; Holton, O.D.; Black, C.D.V.; Parker, R.J.; Weinstein, J.N. Pharmacokinetics of Monoclonal Immunoglobulin IgG1, F(ab′)2 and Fab′ in Mice. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar]
- Bazin-Redureau, M.I.; Renard, C.B.; Scherrmann, J.M. Pharmacokinetics of heterologous and homologous immunoglobulin G, F(ab′)2 and Fab after intravenous administration in the rat. J. Pharm. Pharm. 1997, 49, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.L.; Kiersgaard, M.K.; Sørensen, D.B.; Mikkelsen, L.F. Fasting of mice: A review. Lab. Anim. 2013, 47, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strubelt, O.; Dost-Kempf, E.; Siegers, C.P.; Younes, M.; Volpel, M.; Preuss, U.; Dreckmann, J.G. The influence of fasting on the susceptibility of mice to hepatotoxic injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1981, 60, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedric, H.J.; Bullock, G.R. The Laboratory Mouse; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, M.; Igarashi, S.; Kume, E.; Saito, N.; Arakawa, K. Fasting induces impairment of gastric mucosal integrity in non-insulin-dependent diabetic (db/db) mice. Aliment. Pharm. 2000, 14, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellacott, K.L.J.; Morton, G.J.; Woods, S.C.; Tso, P.; Schwartz, M.W. Assessment of feeding behaviour in laboratory mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froy, O.; Miskin, R. Interrelations among feeding, circadian rhythms and ageing. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Michihata, T.; Nakamura, W.; Takumi, T.; Shimizu, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Ikeda, M.; Ohmiya, Y.; Nakajima, Y. Dual-colour luciferase mouse directly demonstrates coupled expression of two clock genes. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8053–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© Crown copyright (2020), Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl). This material is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit (http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3).
Share and Cite
Whitfield, S.J.; Padgen, D.B.; Knight, S.; Gwyther, R.J.; Holley, J.L.; Clark, G.C.; Green, A.C. Establishment of a Novel Oral Murine Model of Ricin Intoxication and Efficacy Assessment of Ovine Ricin Antitoxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120784
Whitfield SJ, Padgen DB, Knight S, Gwyther RJ, Holley JL, Clark GC, Green AC. Establishment of a Novel Oral Murine Model of Ricin Intoxication and Efficacy Assessment of Ovine Ricin Antitoxins. Toxins. 2020; 12(12):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120784
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhitfield, Sarah J., Debbie B. Padgen, Simon Knight, Robert J. Gwyther, Jane L. Holley, Graeme C. Clark, and A. Christopher Green. 2020. "Establishment of a Novel Oral Murine Model of Ricin Intoxication and Efficacy Assessment of Ovine Ricin Antitoxins" Toxins 12, no. 12: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120784
APA StyleWhitfield, S. J., Padgen, D. B., Knight, S., Gwyther, R. J., Holley, J. L., Clark, G. C., & Green, A. C. (2020). Establishment of a Novel Oral Murine Model of Ricin Intoxication and Efficacy Assessment of Ovine Ricin Antitoxins. Toxins, 12(12), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120784



