Exotic Snakebites Reported to Pennsylvania Poison Control Centers: Lessons Learned on the Demographics, Clinical Effects, and Treatment of These Cases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Original Data Extraction
2.2. Patient Demographics
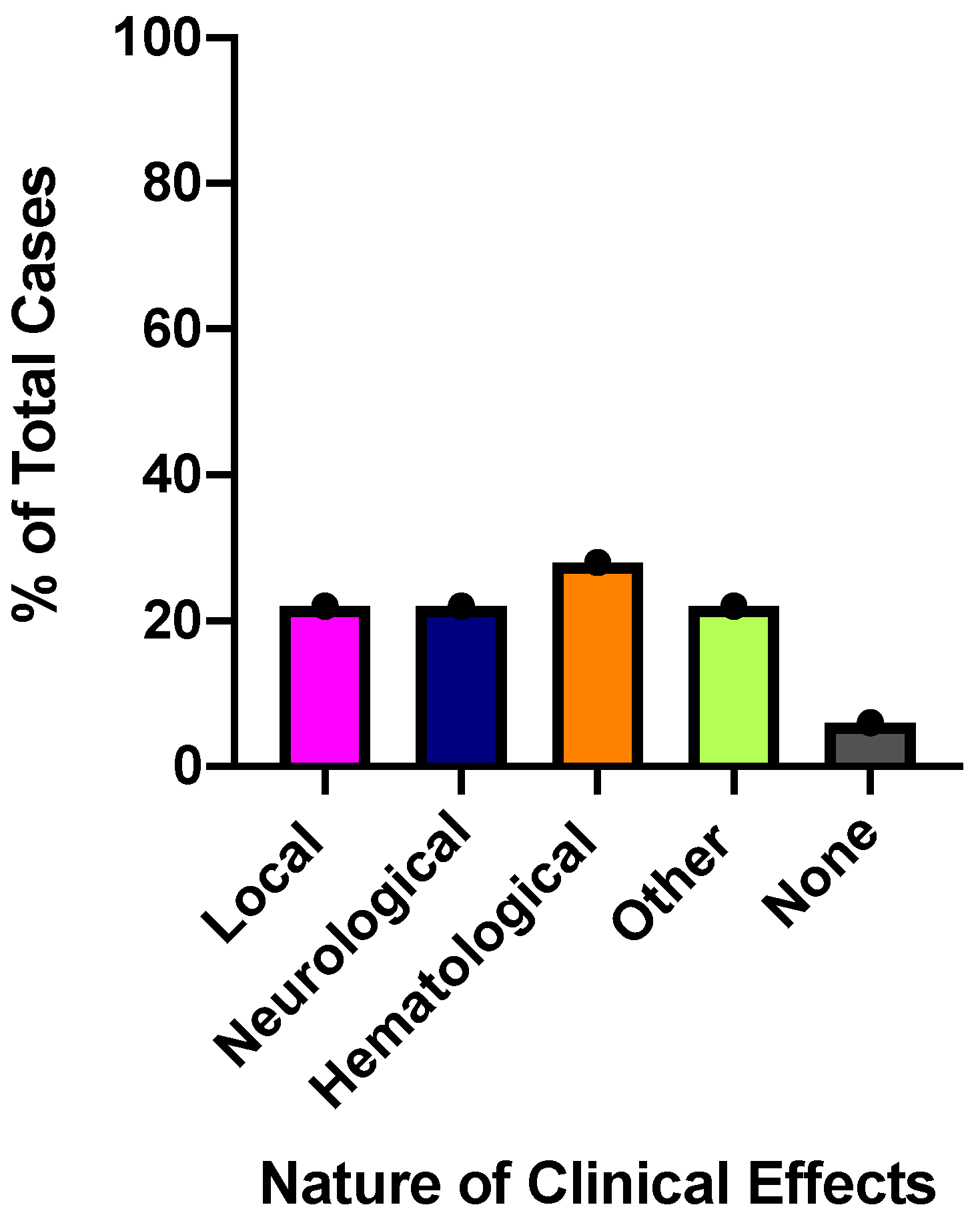
2.3. Clinical Envenomation Effects
2.3.1. Local Effects
2.3.2. Neurological Effects
2.3.3. Hematological Effects
2.3.4. Other Reported Clinical Effects
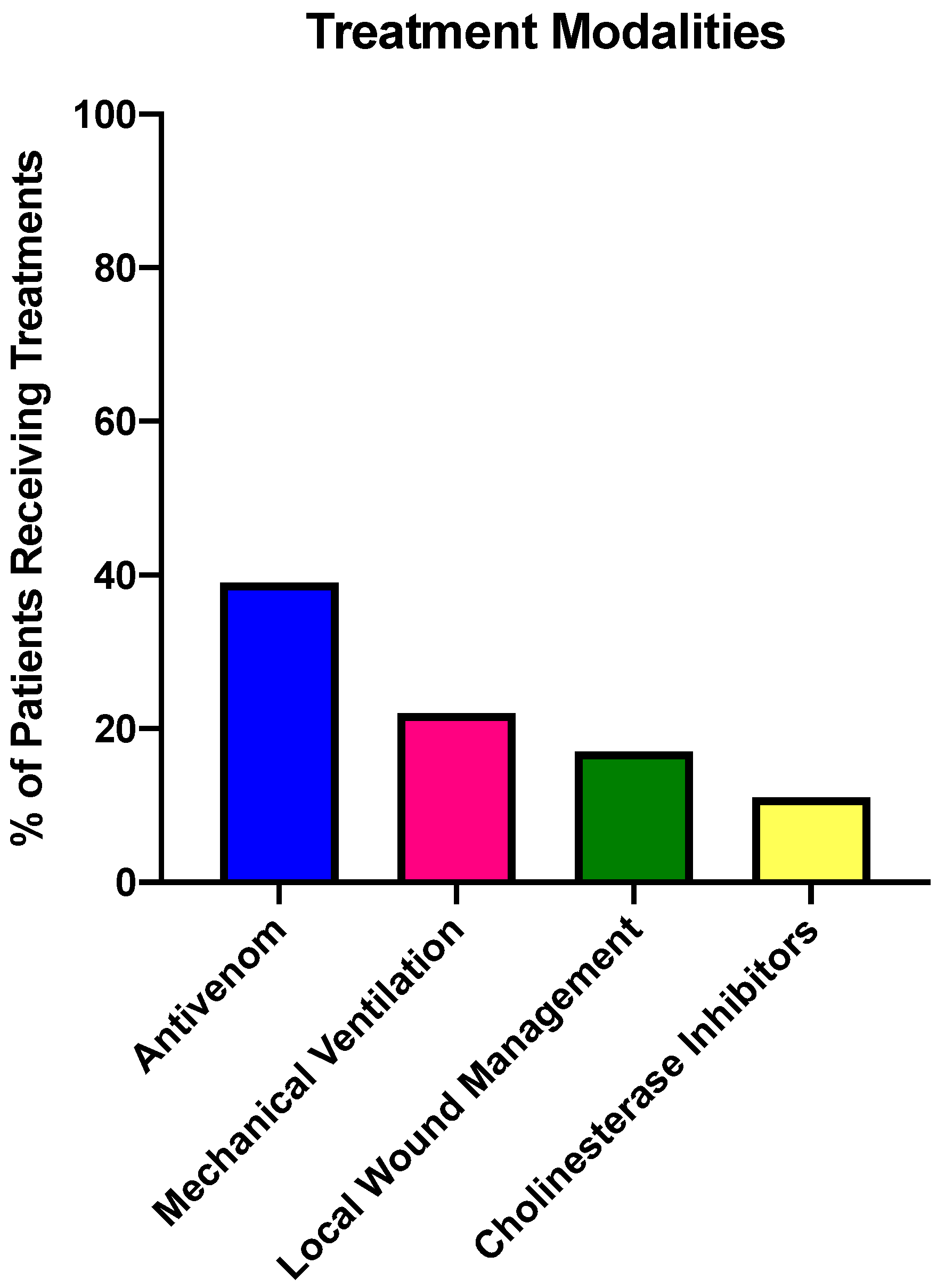
2.4. Treatments Provided for Exotic SBE
2.5. Time Spent in Health Care Facility
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chippaux, J.P. Snake-bites: Appraisal of the global situation. Bull. World Health Organ. 1998, 76, 515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, J.H. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longbottom, J.; Shearer, F.M.; Devine, M.; Alcoba, G.; Chappuis, F.; Weiss, D.J.; Ray, S.E.; Ray, N.; Warrell, D.A.; de Castañeda, R.R.; et al. Vulnerability to snakebite envenoming: A global mapping of hotspots. Lancet 2018, 392, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Ashokan, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Nattamaisundar, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Chandran, V.; Gajjeraman, P.; Baksh, M.F.; Gibbins, J.M.; et al. Snakebite and its socio-economic impact on the rural population of Tamil Nadu, India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, H.F.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Gajjeraman, P.; Hutchinson, G.; Gibbins, J.M.; Bicknell, A.B.; Vaiyapuri, S. Challenges in diagnosing and treating snakebites in a rural population of Tamil Nadu, India: The views of clinicians. Toxicon 2017, 130, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrish, H.M. Incidence of treated snakebites in the United States. Public Health Rep. 1966, 81, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.L.; Morrow, W.E. Deaths resulting from animal attacks in the United States. Wilderness Environ. Med. 1997, 8, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, S.A.; Boyer, L.V.; Benson, B.E.; Rogers, J.J. AAPCC database characterization of native U.S. venomous snake exposures, 2001–2005. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, B.J.; Boyer, L.V.; Seifert, S.A. Non-native (exotic) snake envenomations in the U.S., 2005–2011. Toxins 2014, 6, 2899–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seifert, S.A.; Oakes, J.A.; Boyer, L.V. Toxic Exposure Surveillance System (TESS)-based characterization of U.S. non-native venomous snake exposures, 1995–2004. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierink, F.; Bolon, I.; Durso, A.M.; de Castañeda, R.R.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Eskew, E.A.; Ray, N. Forty-four years of global trade in CITES-listed snakes: Trends and implications for conservation and public health. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 248, 108601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Knudsen, C.; Oliveira, I.S.; Rimbault, C.; Cerni, F.A.; Wen, F.H.; Sachett, J.D.G.; Sartim, M.A.; Laustsen, A.H.; Monteiro, W. Current Knowledge on Snake Dry Bites. Toxins 2020, 12, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, V.E.; Gerardo, C.J.; Rapp-Olsson, M.; Bush, S.P.; Mullins, M.E.; Greene, S.; Toschlog, E.A.; Quackenbush, E.; Rose, S.R.; Schwartz, R.B.; et al. Early administration of Fab antivenom resulted in faster limb recovery in copperhead snake envenomation patients. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, H.A.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Ranasinha, C.D.; Jayamanne, S.; Samarakoon, S.B.; Hittharage, A.; Kalupahana, R.; Ratnatilaka, G.A.; Uluwatthage, W.; Aronson, J.K.; et al. Low-Dose Adrenaline, Promethazine, and Hydrocortisone in the Prevention of Acute Adverse Reactions to Antivenom following Snakebite: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1000435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, S.A. Bites by non-native venomous snakes in the United States. Wilderness Environ. Med. 1996, 7, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, J.M.; Cooper, G.; Krishna, C.; Thompson, J.P. Snakebite enquiries to the UK National Poisons Information Service: 2004–2010. Emerg. Med. J. 2013, 30, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, V.C.; Lit, A.C.; Wong, O.F.; Tse, M.L.; Fung, H.T. Injuries and envenomation by exotic pets in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med. J. 2018, 24, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quarch, V.; Brander, L.; Cioccari, L. An Unexpected Case of Black Mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) Bite in Switzerland. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2017, 2017, 5021924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Thiyagarajan, N.; Hutchinson, E.G.; Gibbins, J.M. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of viper venom serine proteases. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittenbinder, M.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Brouw, B.O.D.; Youngman, N.J.; Dobson, J.S.; Naude, A.; Vonk, F.J.; Fry, B.G. Coagulotoxic Cobras: Clinical Implications of Strong Anticoagulant Actions of African Spitting Naja Venoms That Are Not Neutralised by Antivenom but Are by LY315920 (Varespladib). Toxins 2018, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eon, C.; Radvanyi, F.; Saliou, B.; Faure, G. Crotoxin: A Biochemical Analysis of Its Mode of Action. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1986, 5, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.A.H.; Pazin, W.M.; Dreyer, T.R.; Bicev, R.N.; Cavalcante, W.L.G.; Fortes-Dias, C.L.; Ito, A.S.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Fernandez, R.M.; Fontes, M.R. Biophysical studies suggest a new structural arrangement of crotoxin and provide insights into its toxic mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, J. Global Availability of Antivenoms: The Relevance of Public Manufacturing Laboratories. Toxins 2018, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Layfield, H.J.; Williams, H.F.; Ravishankar, D.; Mehmi, A.; Sonavane, M.; Salim, A.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Vallance, T.M.; Bicknell, A.B.; et al. Repurposing Cancer Drugs Batimastat and Marimastat to Inhibit the Activity of a Group I Metalloprotease from the Venom of the Western Diamondback Rattlesnake, Crotalus atrox. Toxins 2020, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Chaves, F.; León, G.; Franceschi, A.; Ovadia, M.; Escalante, T.; Cury, Y. Inhibition of local hemorrhage and dermonecrosis induced by Bothrops asper snake venom: Effectiveness of early in situ administration of the peptidomimetic metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat and the chelating agent CaNa2EDTA. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 63, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albulescu, L.-O.; Xie, C.; Ainsworth, S.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Dawson, C.A.; Softley, R.; Bartlett, K.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Kool, J.; et al. Casewelet al. A therapeutic combination of two small molecule toxin inhibitors provides pancontinental preclinical efficacy against viper snakebite. bioRxiv 2020. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.13.094599v1.full (accessed on 28 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. Inhibition of Naja naja Venom. Hyaluronidase by Plant.-Derived Bioactive Components and Polysaccharides. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaramakrishnan, V.; Ilamathi, M.; Girish, K.; Kemparaju, K.; Rangappa, K.S.; Dhananjaya, B.L. Viper venom hyaluronidase and its potential inhibitor analysis: A multipronged computational investigation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickler, P.E. Amplification of Snake Venom. Toxicity by Endogenous Signaling Pathways. Toxins 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubich, C.; Krenzelok, E.P. Exotic snakes are not always found in exotic places: How poison centres can assist emergency departments. Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2007, 24, 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.F.; Mellows, B.A.; Mitchell, R.; Sfyri, P.; Layfield, H.J.; Salamah, M.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Collins-Hooper, H.; Bicknell, A.B.; Matsakas, A.; et al. Mechanisms underpinning the permanent muscle damage induced by snake venom metalloprotease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elashry, M.I.; Collins-Hooper, H.; Vaiyapuri, S.; Patel, K. Characterisation of connective tissue from the hypertrophic skeletal muscle of myostatin null mice. J. Anat. 2012, 220, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamah, M.F.; Ravishankar, D.; Kodji, X.; Moraes, L.A.; Williams, H.F.; Vallance, T.M.; Albadawi, D.A.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Watson, K.; Gibbins, J.M.; et al. The endogenous antimicrobial cathelicidin LL37 induces platelet activation and augments thrombus formation. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2973–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.I.; Sage, T.; Moraes, L.A.; Vaiyapuri, S.; Hussain, U.; Tucker, K.L.; Barrett, N.E.; Gibbins, J.M. Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Inhibits Platelet Response to Thrombin and von Willebrand Factor by Regulating the Internalization of Glycoprotein Ib via AKT/Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3/Dynamin and Integrin αIIbβ3. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Hutchinson, E.G.; Ali, M.S.; Dannoura, A.; Stanley, R.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Bicknell, A.B.; Gibbins, J.M. Rhinocetin, a Venom-derived Integrin-specific Antagonist Inhibits Collagen-induced Platelet and Endothelial Cell Functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26235–26244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Snake Species | Age (Years) | Gender | Location of Bite | Clinical Effects | Antivenom (Yes/No) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspidelaps lubricus | 44 | M | Hand | Severe | No |
| Atheris chlorechis | 17 | M | Finger | Unknown | No |
| Atheris squamigera | 30 | M | Finger | Moderate | No |
| Bitis arietans | 50 | F | Face | Severe | Yes * |
| Bothrops schlegelii | 42 | M | Finger | Minor | Yes |
| Crotalus durissus terrificus | 36 | M | Finger | Moderate | Yes |
| Naja kaouthia | 23 | F | Buttocks | Severe | Yes |
| Naja kaouthia | 24 | M | Forearm | Unknown | No |
| Naja kaouthia | 31 | M | Finger | None | No |
| Naja kaouthia | 33 | M | Unknown | Severe | Yes * |
| Naja kaouthia ** | Unknown | M | Unknown | Unknown | No |
| Naja melanoleuca | 63 | F | Unknown | Minor | No |
| Naja pallida | 16 | M | Hand | Moderate | Yes * |
| Naja siamensis | 38 | M | Finger | Moderate | Yes * |
| Naja sumatrana | 55 | M | Ocular | Minor | No |
| Trimeresurus albolabris | 24 | M | Finger | Minor | No |
| Trimeresurus albolabris | 28 | M | Hand | Moderate | No |
| Trimeresurus purpureomaculatus | 23 | M | Finger | Moderate | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, S.W.; Osterhoudt, K.C.; Korenoski, A.S.; Patel, K.; Vaiyapuri, S. Exotic Snakebites Reported to Pennsylvania Poison Control Centers: Lessons Learned on the Demographics, Clinical Effects, and Treatment of These Cases. Toxins 2020, 12, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120755
Miller SW, Osterhoudt KC, Korenoski AS, Patel K, Vaiyapuri S. Exotic Snakebites Reported to Pennsylvania Poison Control Centers: Lessons Learned on the Demographics, Clinical Effects, and Treatment of These Cases. Toxins. 2020; 12(12):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120755
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Stephen W., Kevin C. Osterhoudt, Amanda S. Korenoski, Ketan Patel, and Sakthivel Vaiyapuri. 2020. "Exotic Snakebites Reported to Pennsylvania Poison Control Centers: Lessons Learned on the Demographics, Clinical Effects, and Treatment of These Cases" Toxins 12, no. 12: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120755
APA StyleMiller, S. W., Osterhoudt, K. C., Korenoski, A. S., Patel, K., & Vaiyapuri, S. (2020). Exotic Snakebites Reported to Pennsylvania Poison Control Centers: Lessons Learned on the Demographics, Clinical Effects, and Treatment of These Cases. Toxins, 12(12), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120755






