Receptor Binding Domains of TcdB from Clostridioides difficile for Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 and Frizzled Proteins Are Functionally Independent and Additive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
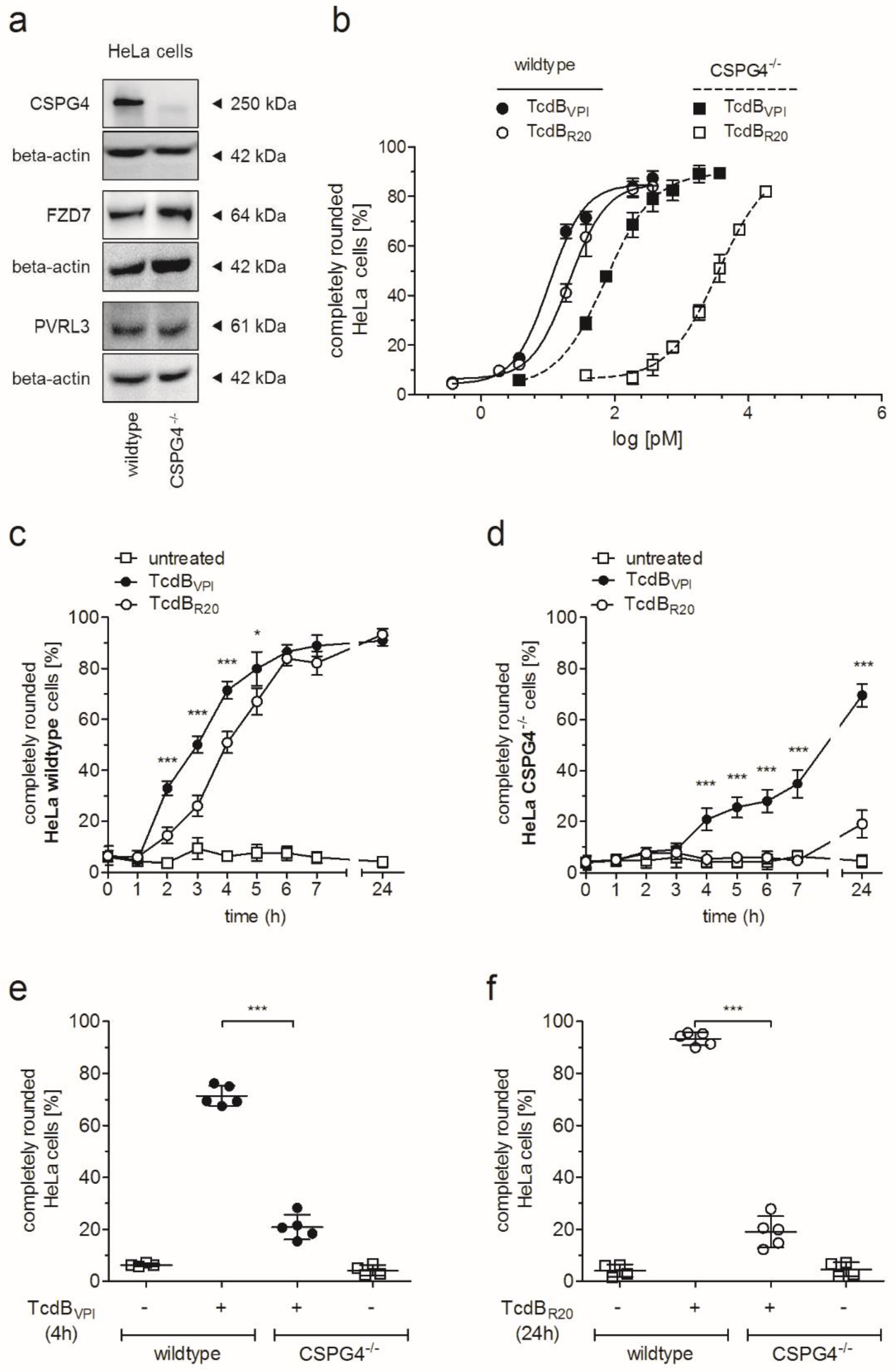
2.1. HeLa CSPG4−/− Cells Are Less Susceptible to Both TcdBVPI and TcdBR20
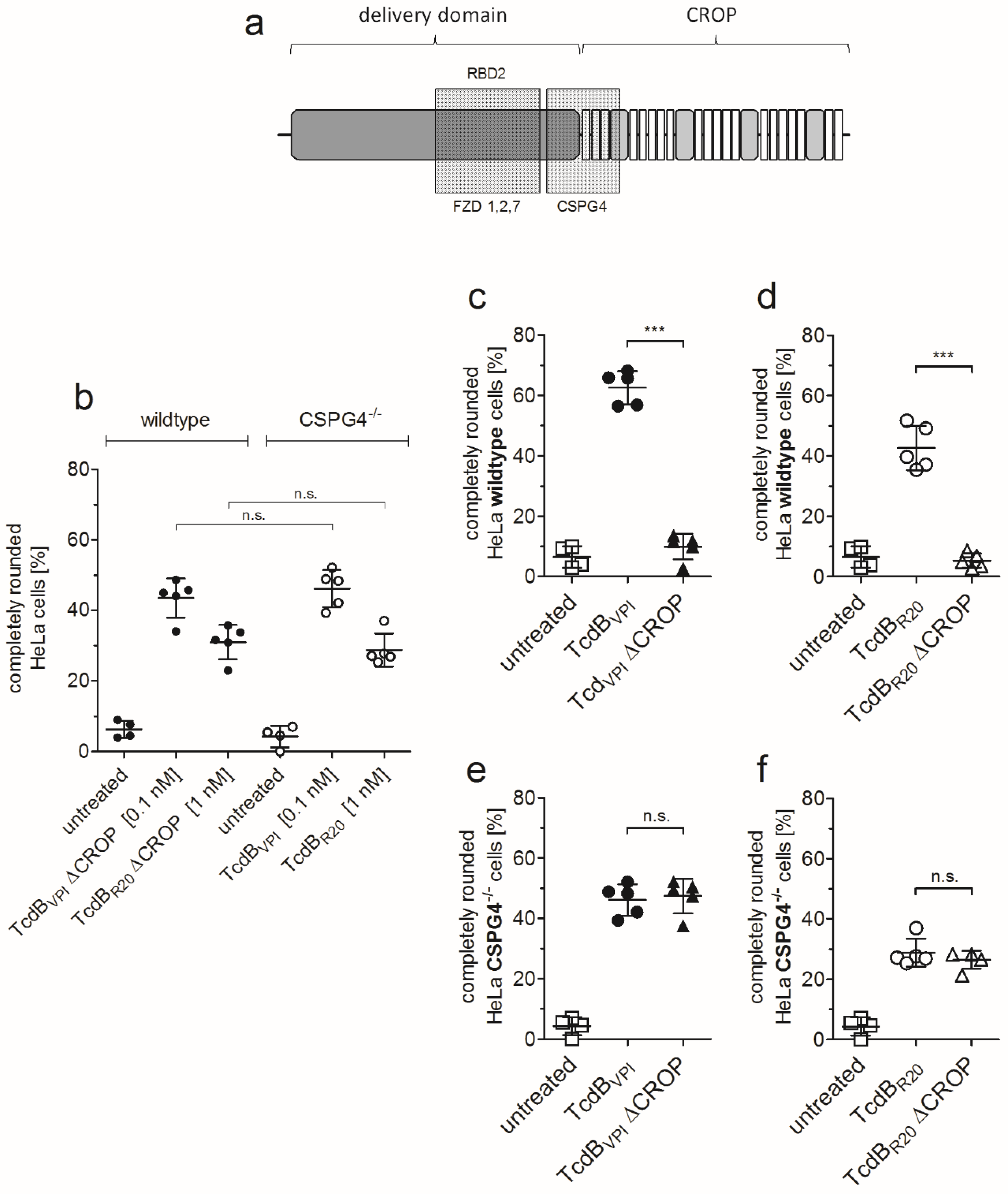
2.2. RBD2 Is Not Affected by CSPG4 Interaction or the CROP Domain
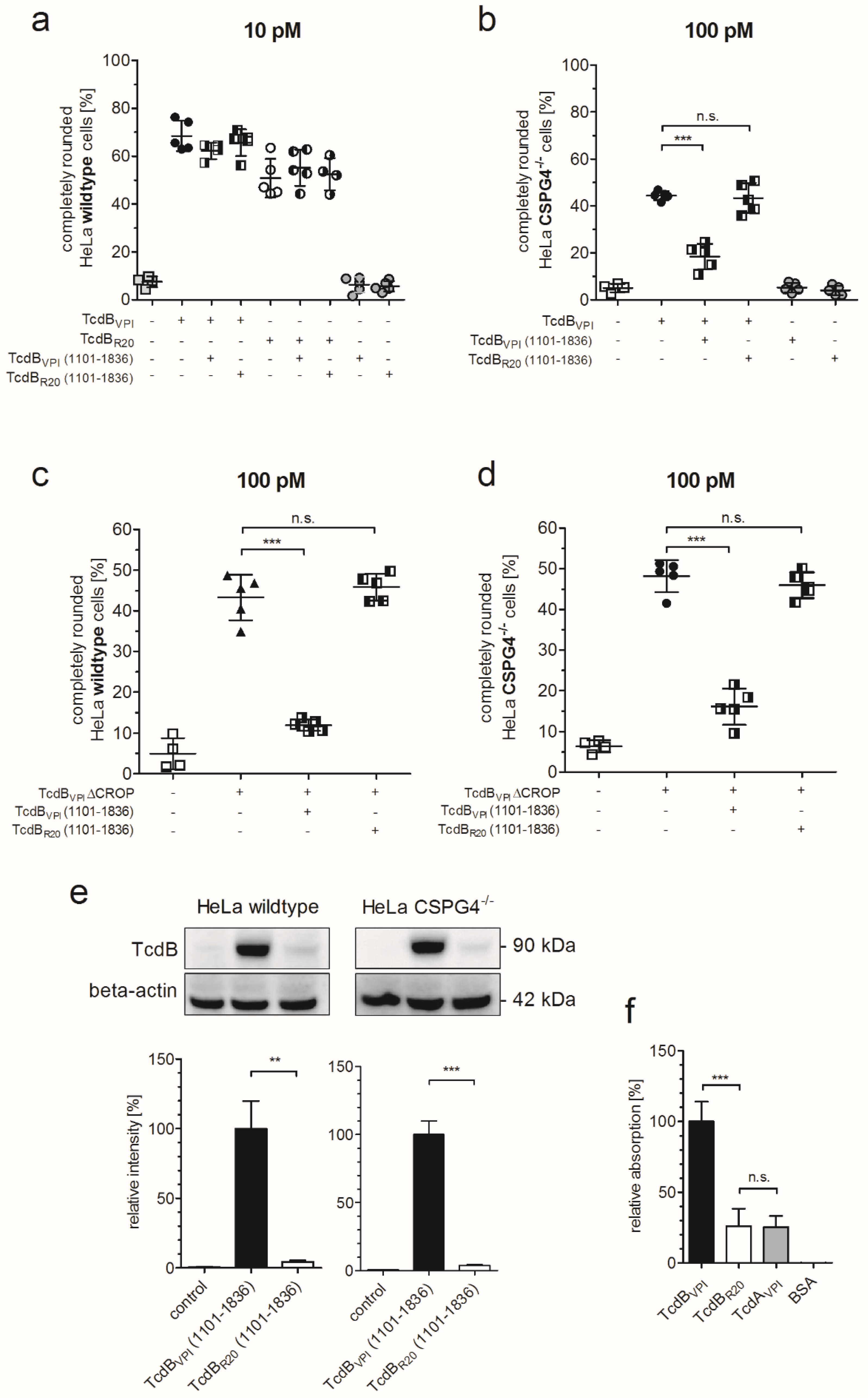
2.3. RBD2 of TcdBVPI But Not of TcdBR20 Binds to FZD1,2,7
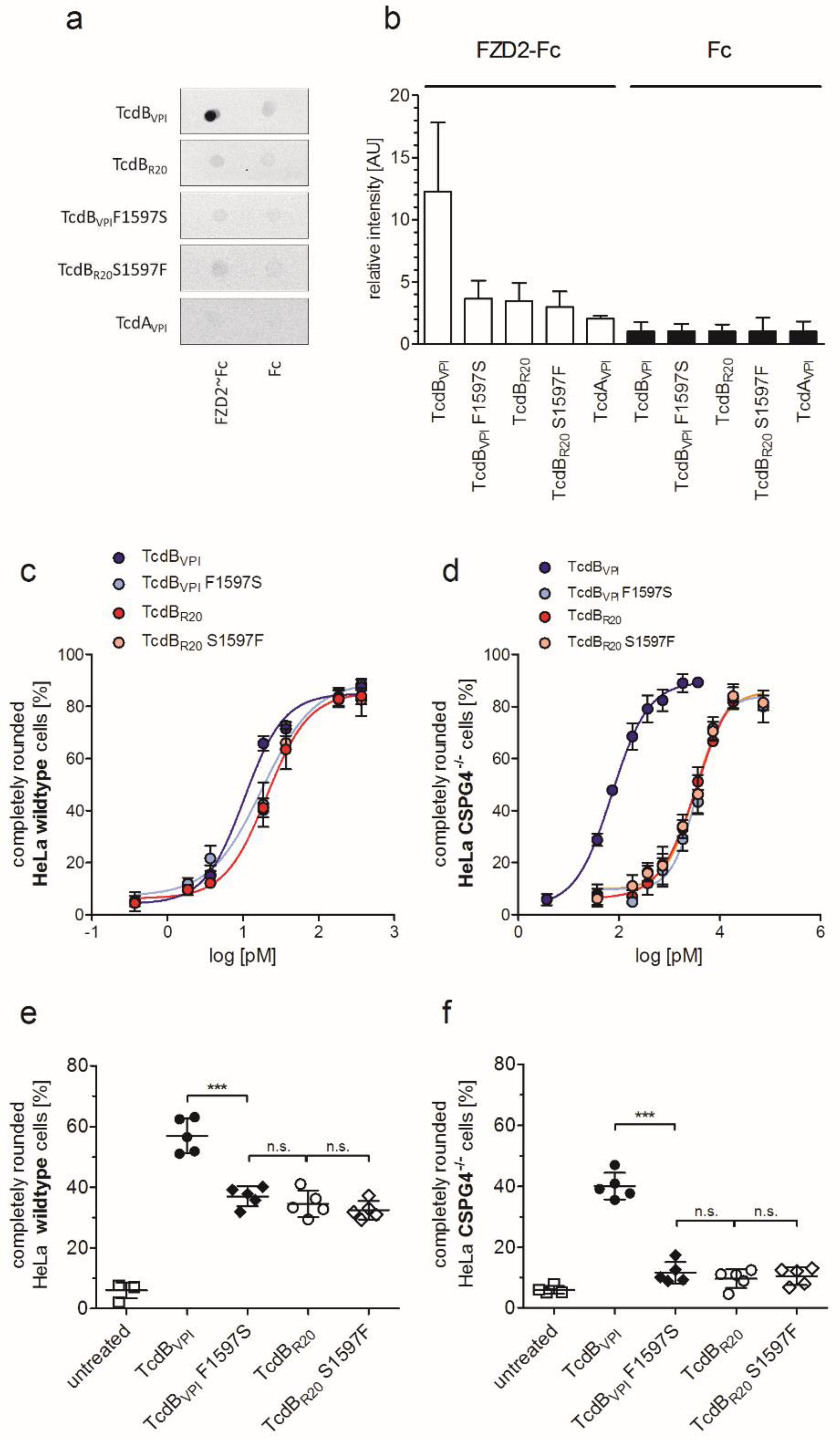
2.4. Exchange of Phenylalanine 1597 in TcdBVPI Abolishes Frizzled Binding
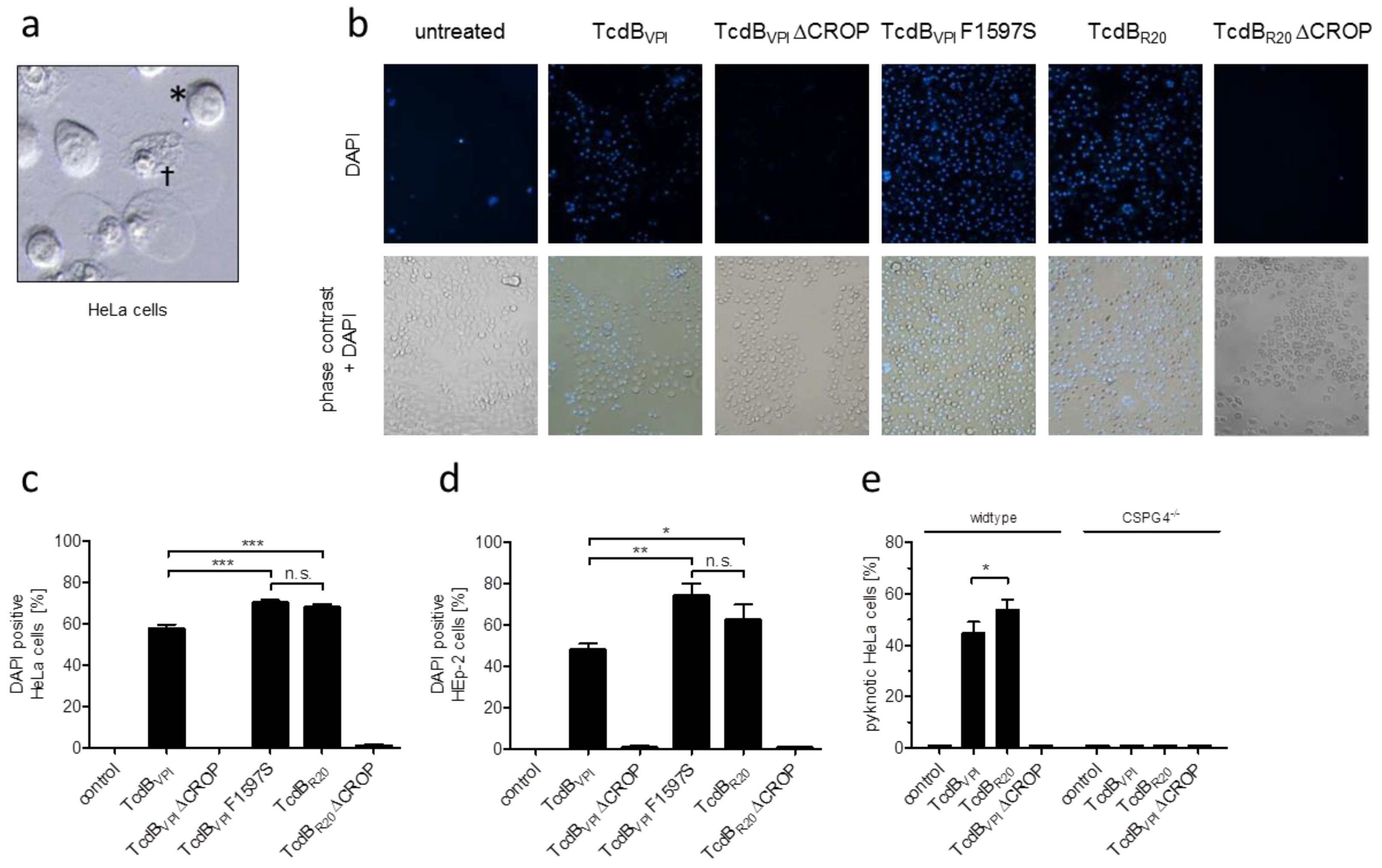
2.5. CSPG4 Is the Primary Receptor Facilitating Cytotoxic Effect of TcdB in HeLa cells
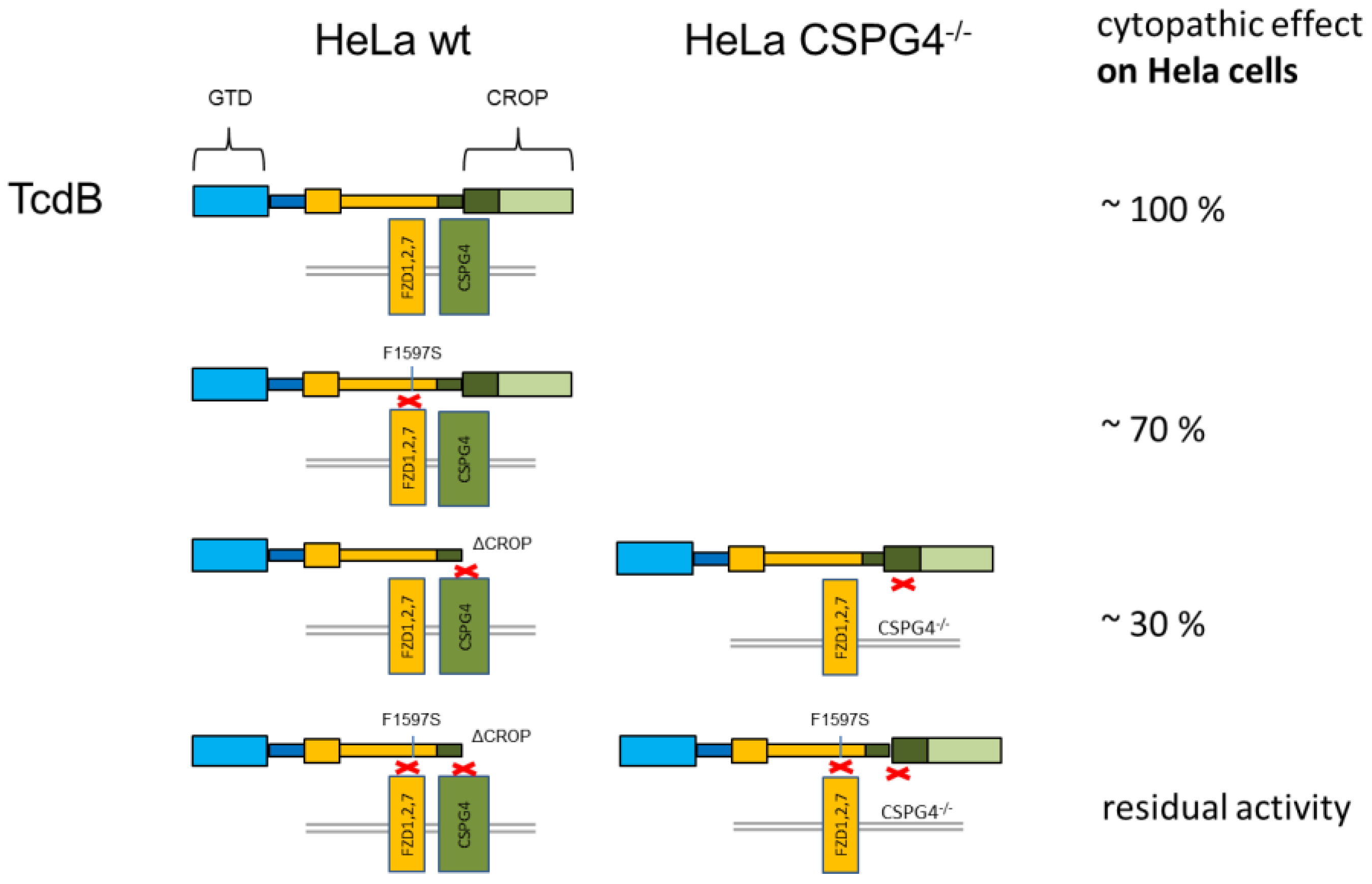
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expression and Site Directed Mutagenesis of Recombinant TcdB
4.2. Generation of HeLa CSPG4−/− Cells and Cell Culture
4.3. Immunoblot and Overlay Assay
4.4. Affinity Purification of Specific Anti-TcdB IgG
4.5. Binding Assay
4.6. ELISA
4.7. Evaluation of Cytopathic and Cytotoxic Effects
4.8. DAPI Incorporation Assay
4.9. Competition Assays
4.10. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voth, D.E.; Ballard, J.D. Clostridium difficile toxins: Mechanism of action and role in disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schorch, B.; Song, S.; van Diemen, F.R.; Bock, H.H.; May, P.; Herz, J.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Papatheodorou, P.; Aktories, K. Lrp1 is a receptor for clostridium perfringens tpel toxin indicating a two-receptor model of clostridial glycosylating toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6431–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olling, A.; Goy, S.; Hoffmann, F.; Tatge, H.; Just, I.; Gerhard, R. The repetitive oligopeptide sequences modulate cytopathic potency but are not crucial for cellular uptake of Clostridium difficile toxin. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivan, H.C.; Clark, G.F.; Smith, D.F.; Wilkins, T.D. Cell surface binding site for Clostridium difficile enterotoxin: Evidence for a glycoconjugate containing the sequence Gal alpha 1-3Gal beta 1-4GlcNac. Infect. Immun. 1986, 53, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Tian, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Robinson-McCarthy, L.; Miyashita, S.I.; Breault, D.T.; Gerhard, R.; Oottamasathien, S.; Whelan, S.P.J.; et al. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans and low-density lipoprotein receptor contribute to Clostridium difficile toxin a entry into cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Zeng, J.; Choi, M.Y.; Chen, H.; Gerhard, R.; Dong, M. Genome-wide crispr screen identifies semaphorin 6a and 6b as receptors for paeniclostridium sordellii toxin TCSL. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Beilhartz, G.L.; Kucharska, I.; Raman, S.; Cui, H.; Lam, M.H.Y.; Liang, H.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Schramek, D.; Julien, J.P.; et al. Recognition of semaphorin proteins by P. sordellii lethal toxin reveals principles of receptor specificity in clostridial toxins. Cell 2020, 182, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; He, R.; Li, C.; Guo, S.; Li, S.; et al. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 functions as the cellular receptor for Clostridium difficile toxin B. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhang, J.; Meraner, P.; Tovaglieri, A.; Wu, X.; Gerhard, R.; Zhang, X.; Stallcup, W.B.; Miao, J.; He, X.; et al. Frizzled proteins are colonic epithelial receptors for C. difficile toxin B. Nature 2016, 538, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFrance, M.E.; Farrow, M.A.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Sheng, J.; Rubin, D.H.; Lacy, D.B. Identification of an epithelial cell receptor responsible for Clostridium difficile TcdB-induced cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7073–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tao, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; He, A.; Lam, K.H.; Liu, Z.; He, X.; Perry, K.; Dong, M.; et al. Structural basis for recognition of frizzled proteins by Clostridium difficile toxin B. Science 2018, 360, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiman-Marangos, S.N.; Tam, J.; Raman, S.; Julien, J.P.; Kroh, H.K.; Lacy, D.B.; Murgolo, N.; Bekkari, K.; et al. Functional defects in Clostridium difficile tcdb toxin uptake identify CSPG4 receptor-binding determinants. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17290–17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manse, J.S.; Baldwin, M.R. Binding and entry of Clostridium difficile toxin B is mediated by multiple domains. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3945–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.Y.; Schottelndreier, D.; Tatge, H.; Fuhner, V.; Hust, M.; Beer, L.A.; Gerhard, R. The conserved cys-2232 in Clostridioides difficile toxin B modulates receptor binding. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Lam, K.H.; Liu, Z.; Mindlin, F.A.; Chen, B.; Gutierrez, C.B.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hamza, T.; Feng, H.; et al. Structure of the full-length Clostridium difficile toxin B. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Urena, D.; Orozco-Aguilar, J.; Chaves-Madrigal, Y.; Ramirez-Mata, A.; Villalobos-Jimenez, A.; Ost, S.; Quesada-Gomez, C.; Rodriguez, C.; Papatheodorou, P.; Chaves-Olarte, E. Toxin B variants from Clostridium difficile strains VPI 10463 and NAP1/027 share similar substrate profile and cellular intoxication kinetics but use different host cell entry factors. Toxins 2019, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlan, K.; Goy, S.; Olling, A.; Srivaratharajan, S.; Tatge, H.; Genth, H.; Gerhard, R. Pyknotic cell death induced by Clostridium difficile TcdB: Chromatin condensation and nuclear blister are induced independently of the glucosyltransferase activity. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1678–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, L.A.; Tatge, H.; Reich, N.; Tenspolde, M.; Olling, A.; Goy, S.; Rottner, K.; Alekov, A.K.; Gerhard, R. Early cell death induced by Clostridium difficile tcdb: Uptake and RAC1-glucosylation kinetics are decisive for cell fate. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, L.A.; Tatge, H.; Schneider, C.; Ruschig, M.; Hust, M.; Barton, J.; Thiemann, S.; Fuhner, V.; Russo, G.; Gerhard, R. The binary toxin CDT of Clostridium difficile as a tool for intracellular delivery of bacterial glucosyltransferase domains. Toxins 2018, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottelndreier, D.; Seeger, K.; Grassl, G.A.; Winny, M.R.; Lindner, R.; Genth, H. Expression and (lacking) internalization of the cell surface receptors of Clostridioides difficile toxin B. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallcup, W.B.; Dahlin, K.; Healy, P. Interaction of the NG2 chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with type VI collagen. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 111, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluschke, G.; Vanek, M.; Evans, A.; Dittmar, T.; Schmid, P.; Itin, P.; Filardo, E.J.; Reisfeld, R.A. Molecular cloning of a human melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9710–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaruzza, S.; Nicolosi, P.A.; Braghetta, P.; Pazzaglia, L.; Benassi, M.S.; Picci, P.; Lacrima, K.; Zanocco, D.; Rizzo, E.; Stallcup, W.B.; et al. NG2/CSPG4-collagen type VI interplays putatively involved in the microenvironmental control of tumour engraftment and local expansion. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 5, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, M.S.; Pazzaglia, L.; Chiechi, A.; Alberghini, M.; Conti, A.; Cattaruzza, S.; Wassermann, B.; Picci, P.; Perris, R. NG2 expression predicts the metastasis formation in soft-tissue sarcoma patients. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolih, V.; Barutello, G.; Iussich, S.; De Maria, R.; Quaglino, E.; Buracco, P.; Cavallo, F.; Riccardo, F. CSPG4: A prototype oncoantigen for translational immunotherapy studies. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tao, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, M.; Jin, R. Structural insight into wnt signaling inhibition by Clostridium difficile toxin B. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, M.A.; Chumbler, N.M.; Lapierre, L.A.; Franklin, J.L.; Rutherford, S.A.; Goldenring, J.R.; Lacy, D.B. Clostridium difficile toxin B-induced necrosis is mediated by the host epithelial cell NADPH oxidase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18674–18679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, N.; Ogita, H.; Komura, H.; Ozaki, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Majima, T.; Ijuin, T.; Takenawa, T.; Takai, Y. Involvement of the nectin-afadin complex in PDGF-induced cell survival. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.; Zhu, K.; Li, D.; Pan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Bian, Q.; He, L.; Song, X.; Zhen, Y.; Jin, D.; et al. Subtyping analysis reveals new variants and accelerated evolution of Clostridioides difficile toxin B. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileto, S.J.; Jarde, T.; Childress, K.O.; Jensen, J.L.; Rogers, A.P.; Kerr, G.; Hutton, M.L.; Sheedlo, M.J.; Bloch, S.C.; Shupe, J.A.; et al. Clostridioides difficile infection damages colonic stem cells via TcdB, impairing epithelial repair and recovery from disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8064–8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, R. Receptors and binding structures for Clostridium difficile toxins A and B. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 406, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.G.; Greco, A.; Rupnik, M.; Ng, K.K. Crystal structure of receptor-binding c-terminal repeats from Clostridium difficile toxin A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18373–18378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olling, A.; Huls, C.; Goy, S.; Muller, M.; Krooss, S.; Rudolf, I.; Tatge, H.; Gerhard, R. The combined repetitive oligopeptides of Clostridium difficile toxin A counteract premature cleavage of the glucosyl-transferase domain by stabilizing protein conformation. Toxins 2014, 6, 2162–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hamza, T.; Gao, S.; Feng, H. Masking autoprocessing of Clostridium difficile toxin A by the C-terminus combined repetitive oligo peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 459, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Base Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| TcdBR20 1102-sense | AAGGATCCGGAATTTCAGCAGGTATACCAAGTTTAG |
| TcdBR20 1830-antisense | AATGGATCCCATTCCAAAGTTATTAATATAAAATTTCTC |
| TcdBVPI F1597S-sense | GAATATAAAAAGTATTTTCGTTAATTCCTTACAATCTAATATTAAG |
| TcdBVPI F1597S-antisense | CTTAATATTAGATTGTAAGGAATTAACGAAAATACTTTTTATATTC |
| TcdBR20 S1597F-sense | GAATATAAAAAGTATTTTCATAAATTTCTTACAATCTAATACTAAG |
| TcdBR20 S1597F-antisense | CTTAGTATTAGATTGTAAGAAATTTATGAAAATACTTTTTATATTC |
| TcdBVPI 1101-1836-sense | AAGGATCCGGAATTTCAGCAGGTATACCAAGCTTAG |
| TcdBVPI 1101-1836-antisense | AAGGTACCTTAAGACACCATCATTCCAAAGTTATTAATATAAAATTTC |
| TcdBR20 1101-1836-sense | AAGGATCCGGAATTTCAGCAGGTATACCAAGTTTAG |
| TcdBR20 1101-1836-antisense | AAGGTACCTTAAGATACCATCATTCCAAAGTTATTAATATAAAATTTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henkel, D.; Tatge, H.; Schöttelndreier, D.; Tao, L.; Dong, M.; Gerhard, R. Receptor Binding Domains of TcdB from Clostridioides difficile for Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 and Frizzled Proteins Are Functionally Independent and Additive. Toxins 2020, 12, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120736
Henkel D, Tatge H, Schöttelndreier D, Tao L, Dong M, Gerhard R. Receptor Binding Domains of TcdB from Clostridioides difficile for Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 and Frizzled Proteins Are Functionally Independent and Additive. Toxins. 2020; 12(12):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120736
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenkel, Daniel, Helma Tatge, Dennis Schöttelndreier, Liang Tao, Min Dong, and Ralf Gerhard. 2020. "Receptor Binding Domains of TcdB from Clostridioides difficile for Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 and Frizzled Proteins Are Functionally Independent and Additive" Toxins 12, no. 12: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120736
APA StyleHenkel, D., Tatge, H., Schöttelndreier, D., Tao, L., Dong, M., & Gerhard, R. (2020). Receptor Binding Domains of TcdB from Clostridioides difficile for Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 and Frizzled Proteins Are Functionally Independent and Additive. Toxins, 12(12), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120736





