Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
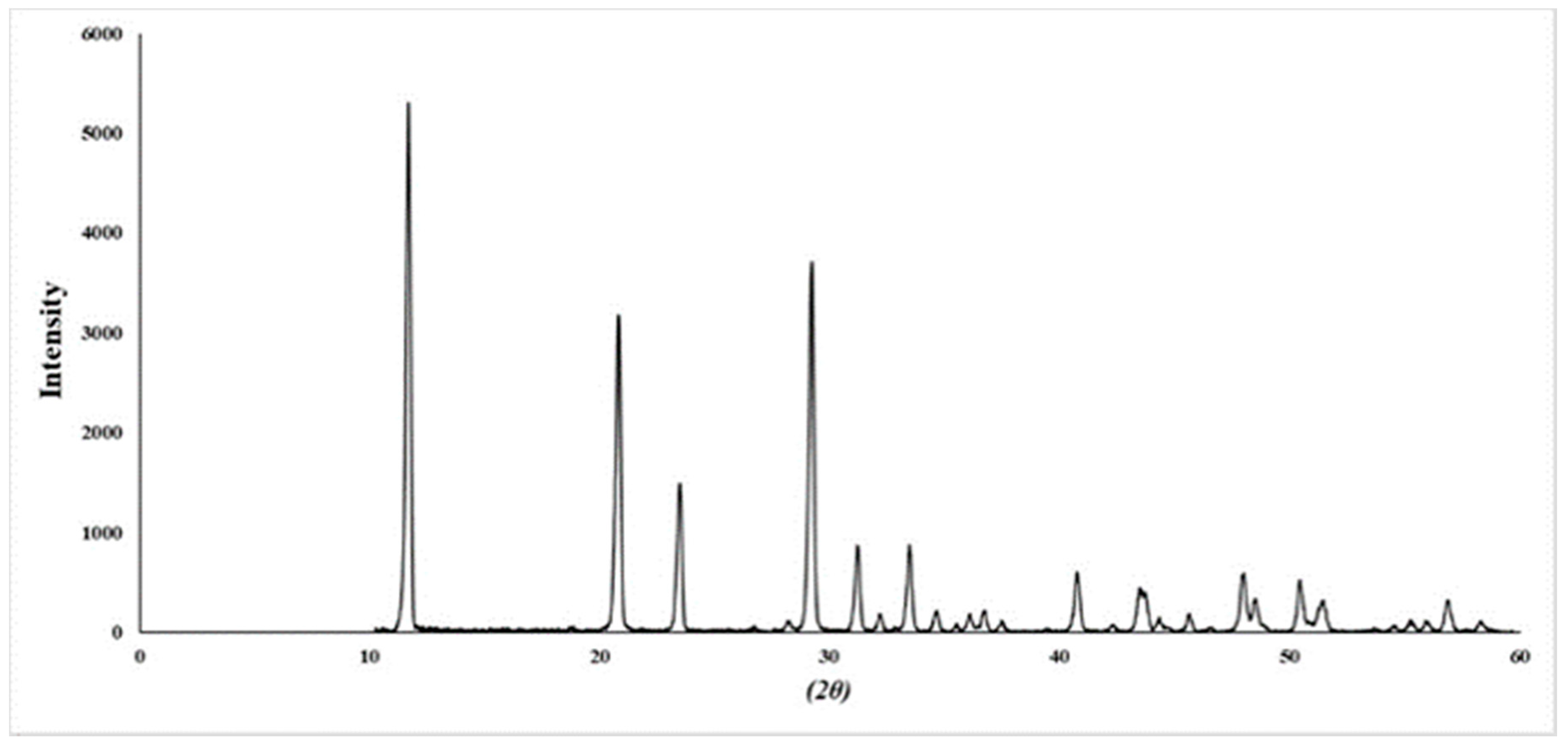
2.1. Identification of Ephedra sinica Stapf Extract (EHE) and Gypsum
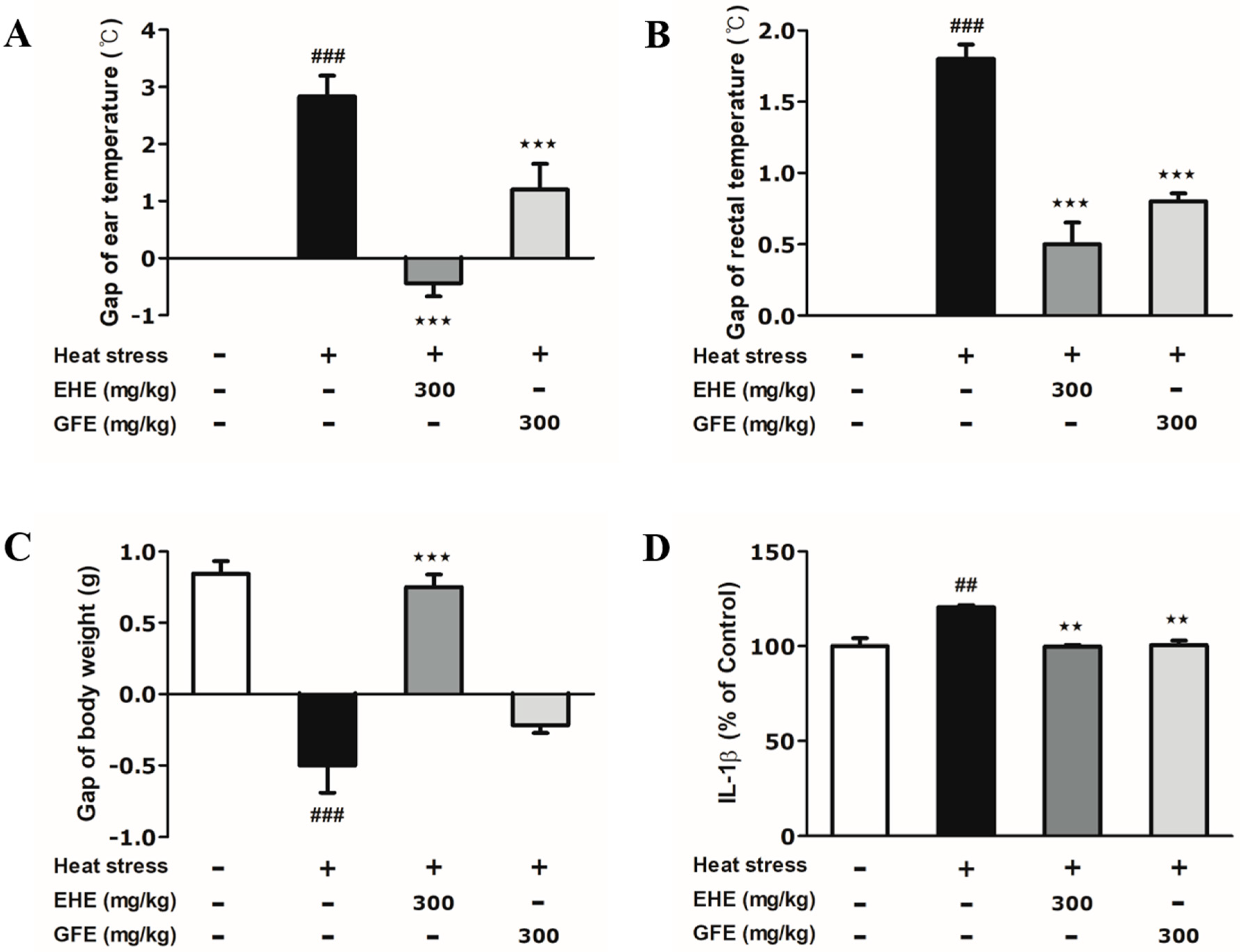
2.2. Effects of Ephedra sinica Stapf Extract and Gypsum Extract (GFE) on Heat-Induced Changes in the Body Temperature and Weight of Mice
2.3. Effects of EHE and GFE on Heat-Induced IL-1β Changes in the Hypothalamus
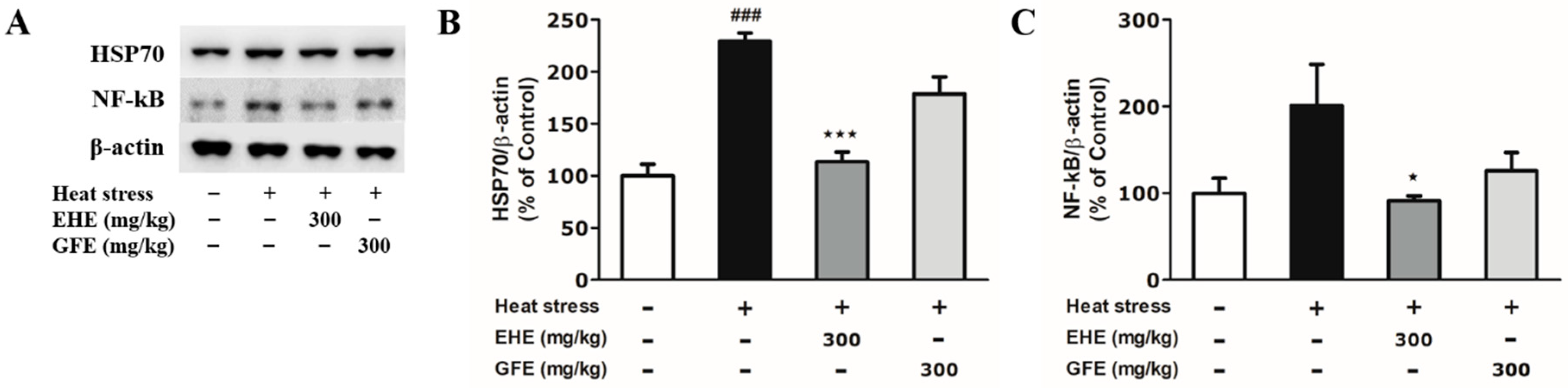
2.4. Effects of EHE and GFE on Heat-Induced Biochemical Changes in the Hypothalamus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of EH and GF
4.3. UPLC-PDA-ESI-MS Identification
4.4. XRD Analysis
4.5. Animals and Measurement
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. IL-1β Expression Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soni, M.G.; Carabin, I.G.; Griffiths, J.C.; Burdock, G.A. Safety of ephedra: Lessons learned. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 150, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, D. Toxicological risks of Chinese herbs. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; van der Heijden, R.; Spruit, S.; Hankermeier, T.; Chan, K.; van der Greef, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, M. Quality and safety of Chinese herbal medicines guided by a systems biology perspective. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.; Xing, X.F.; Tang, Q.F.; Chen, F.L.; Guo, Y.; Song, S.; Tan, X.M.; Luo, J.B. Antipyretic and anti-asthmatic activities of traditional Chinese herb-pairs, ephedra and gypsum. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 22, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Q.; Pan, C.S.; Yang, N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yan, L.; Sun, K.; Wei, X.H.; He, K.; Xiao, M.M.; Fan, J.Y.; et al. Posttreatment with ma-xing-shi-gan-tang, a Chinese medicine formula, ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung microvessel hyperpermeability and inflammatory reaction in rat. Microcirculation 2014, 21, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chang, C.W.; Wu, C.R. Antitussive, anti-pyretic and toxicological evaluation of ma-xing-gan-shi-tang in rodents. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Ni, Z.Y. Effect of ma-xin-shi-gan tang on the immune function in children with acute lower respiratory tract infection. Chin. J. Mod. Dev. Tradit. Med. 1990, 10, 600–602. [Google Scholar]
- Tansey, E.A.; Johnson, C.D. Recent advances in thermoregulation. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2015, 39, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Lu, J.; Chou, T.C.; Gooley, J. The hypothalamic integrator for circadian rhythms. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanovsky, A.A. Thermoregulation: Some concepts have changed. Functional architecture of the thermoregulatory system. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R37–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.; Huh, E.; Lee, W.; Song, E.J.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, T.H.; Oh, M.S. Coptidis rhizoma prevents heat stress-induced brain damage and cognitive impairment in mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Lee, W.; Choi, J.G.; Ju, I.G.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, T.H.; Oh, M.S. Inhibitory effects of aconiti lateralis radix preparata on chronic intermittent cold-induced inflammation in the mouse hypothalamus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 215, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Liu, T. Hypothalamic inflammation: A double-edged sword to nutritional diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1243, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhou, M.; Ma, X.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, D.; Bai, G. Mahuannin b an adenylate cyclase inhibitor attenuates hyperhidrosis via suppressing beta2-adrenoceptor/camp signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2017, 30, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Kim, Y.Y.; Christenson, H.K.; Meldrum, F.C. A new precipitation pathway for calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) via amorphous and hemihydrate intermediates. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood 2011, 117, 3720–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Moon, M.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, T.H.; Oh, M.S. Heat stress-induced memory impairment is associated with neuroinflammation in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.F.; Lo, C.W.; Liu, C.H.; Lin, S.; Yen, H.R.; Lin, T.Y.; Horng, J.T. Mechanism by which ma-xing-shi-gan-tang inhibits the entry of influenza virus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laye, S.; Parnet, P.; Goujon, E.; Dantzer, R. Peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide induces the expression of cytokine transcripts in the brain and pituitary of mice. Mol. Brain Res. 1994, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabellec, M.M.; Griffais, R.; Fillion, G.; Haour, F. Expression of interleukin 1 alpha, interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mrna in mouse brain: Regulation by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (lps) treatment. Mol. Brain Res. 1995, 31, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laye, S.; Gheusi, G.; Cremona, S.; Combe, C.; Kelley, K.; Dantzer, R.; Parnet, P. Endogenous brain il-1 mediates lps-induced anorexia and hypothalamic cytokine expression. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R93–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brobeck, J.R. Food and temperature. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1960, 16, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.A.; Ko, B.P. Effect of herbal ephedra sinica and evodia rutaecarpa on body composition and resting metabolic rate: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial in korean premenopausal women. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2008, 1, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Um, J.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, B.C. Beneficial effect of dietary ephedra sinica on obesity and glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M. Characterization and mechanism of fever induction by interleukin-1 beta. Pflugers Arch. 1991, 419, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor nf-kappab pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspec. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Yamakuni, T.; Yoshida, M.; Ohizumi, Y. Ephedorae herba decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxgenase-2 protein expression and nf-kappab-dependent transcription in c6 rat glioma cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 98, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
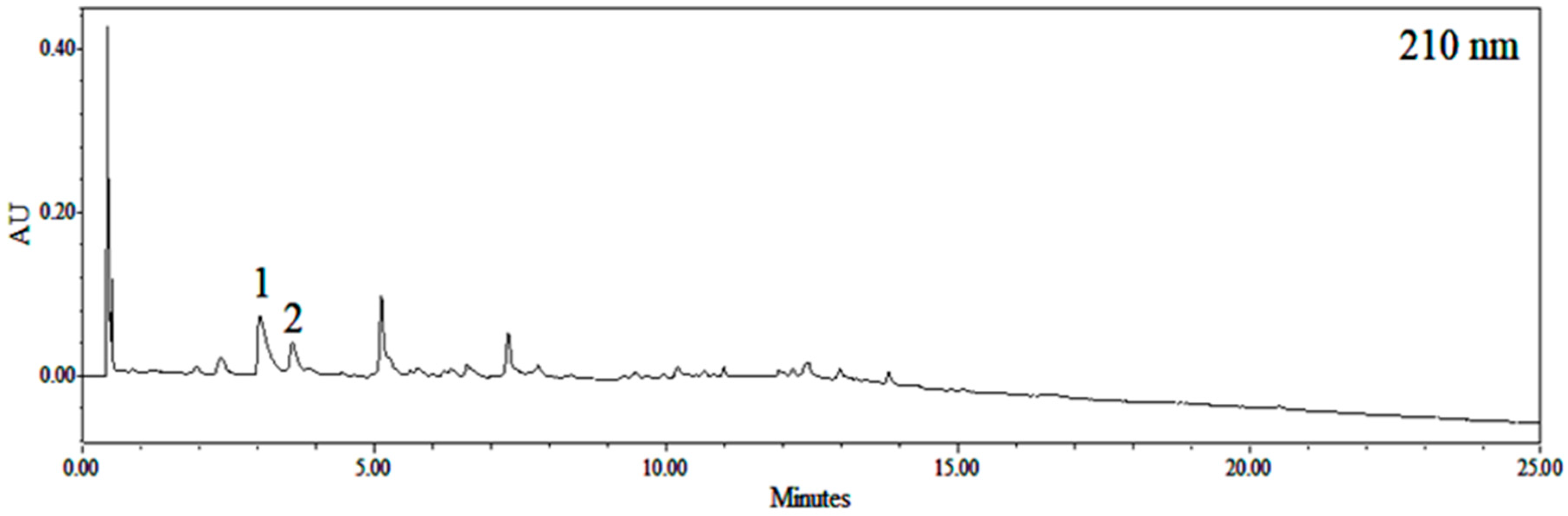
| Compound | Rt (min) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Molar Mass (g/mol) | λ max (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ephedrine | 2.84 | 166.11484 [M+H]+ 148.10664 [M−H2O+H]+ 133.08700 [M−H2O−CH3+H]+ | 165.115 | 206 |
| 2. Pseudoephedrine | 3.38 | 166.11544 [M+H]+ 148.10682 [M−H2O+H]+ 133.08706 [M−H2O−CH3+H]+ | 165.115 | 206 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Lee, W.; Huh, E.; Choi, E.; Jang, Y.P.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, T.-H.; Oh, M.S. Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice. Toxins 2020, 12, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010016
Kim W, Lee W, Huh E, Choi E, Jang YP, Kim Y-K, Lee T-H, Oh MS. Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice. Toxins. 2020; 12(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Wonnam, Wonil Lee, Eugene Huh, Eunjung Choi, Young Pyo Jang, Yun-Kyung Kim, Tae-Hee Lee, and Myung Sook Oh. 2020. "Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice" Toxins 12, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010016
APA StyleKim, W., Lee, W., Huh, E., Choi, E., Jang, Y. P., Kim, Y.-K., Lee, T.-H., & Oh, M. S. (2020). Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice. Toxins, 12(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010016







