Efficacy of Early Endoscopic Intervention for Restoring Normal Swallowing Function in Patients with Lateral Medullary Infarction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Review Methods
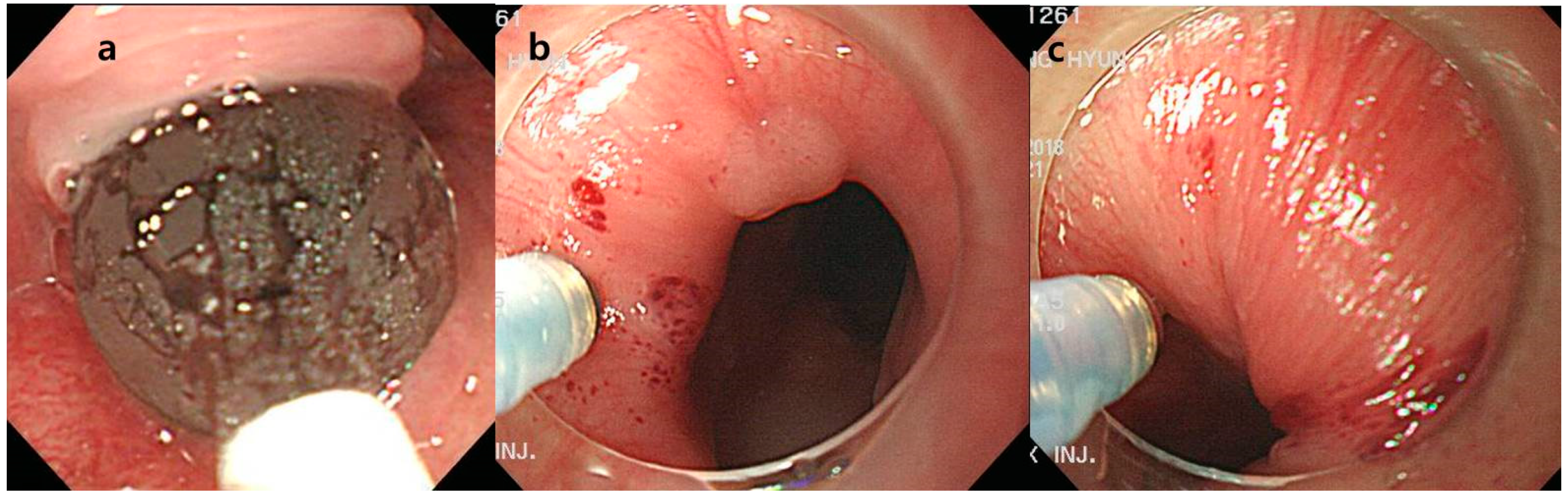
4.2. Endoscopic Procedure
4.3. Conventional Dysphagia Rehabilitation
4.4. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS)
4.5. Severity of Stoke
4.6. Dietary Level
4.7. Statistical Methods
4.8. Ethical Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.S. Pure lateral medullary infarction: Clinical-radiological correlation of 130 acute, consecutive patients. Brain 2003, 126, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Nam, H.; Hong, J.H.; Yeo, M.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, B.J.; Bae, H.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Dysphagia may be an independent marker of poor outcome in acute lateral medullary infarction. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydogdu, I.; Ertekin, C.; Tarlaci, S.; Turman, B.; Kiylioglu, N.; Secil, Y. Dysphagia in lateral medullary infarction (wallenberg’s syndrome): An acute disconnection syndrome in premotor neurons related to swallowing activity? Stroke 2001, 32, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasell, R.W.; McRae, M.; Heitzner, J.; Bhardwaj, A.; Finestone, H. Frequency of videofluoroscopic modified barium swallow studies and pneumonia in stroke rehabilitation patients: A comparative study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verin, E.; Leroi, A.M.; Marie, J.P. Restoration of normal swallowing function in wallenberg syndrome by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and surgery. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 59, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.A.; Koszewski, I.J.; Jaradeh, S.S.; Merati, A.L.; Blumin, J.H.; Bock, J.M. Botulinum toxin injection for the treatment of upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2013, 122, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murry, T.; Wasserman, T.; Carrau, R.L.; Castillo, B. Injection of botulinum toxin a for the treatment of dysfunction of the upper esophageal sphincter. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2005, 26, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenaz Bua, B.; Olsson, R.; Westin, U.; Rydell, R.; Ekberg, O. Treatment of cricopharyngeal dysfunction: A comparative pilot study. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, I.; Thumfart, W.F.; Pototschnig, C.; Eckel, H.E. Treatment of dysfunction of the cricopharyngeal muscle with botulinum a toxin: Introduction of a new, noninvasive method. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1994, 103, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Kaplan, D. Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest 2003, 124, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhara, V.; Koh, J.; Lattimer, L.; Dunbar, K.B.; Ravich, W.J.; Clarke, J.O. Endoscopic balloon catheter dilatation via retrograde or static technique is safe and effective for cricopharyngeal dysfunction. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 9, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonsi, E.; Restivo, D.A.; Cosentino, G.; De Icco, R.; Bertino, G.; Schindler, A.; Todisco, M.; Fresia, M.; Cortese, A.; Prunetti, P.; et al. Botulinum toxin is effective in the management of neurogenic dysphagia. Clinical-electrophysiological findings and tips on safety in different neurological disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzini, M.; Tehran, D.A.; Zanetti, G.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Hsp 90 and thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase enagle the catalytic activity of clostridial neurotoxins inside nerve terminals. Toxicon 2018, 147, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, R.; Kern, M.; Bardan, E.; Taylor, A.; Stewart, E.T.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Arndorfer, R.C.; Hofmann, C.; Bonnevier, J. Augmentation of deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter opening in the elderly by exercise. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, H. Effect of the Masako maneuver and neuromascular electrcal stimulation on the improvement of swallowing function in patients with dysphagia caused by stroke. J. Phy. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Logemann, J.A. Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders, 2nd ed.; PRO-ED: Austin, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schooling, T.L. Lessons from the National Outcomes Measurement System (NOMS). In Seminars in Speech and Language; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 24, pp. 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Brott, T.; Adams, H.P., Jr.; Olinger, C.P.; Marler, J.R.; Barsan, W.G.; Biller, J.; Spilker, J.; Holleran, R.; Eberle, R.; Hertzberg, V.; et al. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: A clinical examination scale. Stroke 1989, 20, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.T.; Hareendran, A.; Grant, M.; Baird, T.; Schulz, U.G.; Muir, K.W.; Bone, I. Improving the assessment of outcomes in stroke: Use of a structured interview to assign grades on the modified rankin scale. Stroke 2002, 33, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Endoscopic Group | Conventional Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| M:F | 8:1 | 3:6 | 0.01 * |
| Age (median, minimum to maximum) | 56 (46–77) | 67 (53–89) | 0.015 |
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL, median, minimum to maximum) | 13.7 (12.3–17.3) | 11.4 (8.7–13.9) | 0.010 |
| Albumin (g/dL, median, minimum to maximum) | 3.6 (2.9–4.6) | 3.3 (3–3.6) | 0.022 |
| VFSS (median, minimum to maximum) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–4) | 0.224 |
| Dietary level (median, minimum to maximum) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 1.000 |
| NIHSS (median, minimum to maximum) | 4 (1–5) | 7 (2–19) | 0.017 |
| MRS (median, minimum to maximum) | 4 (2–5) | 5 (3–5) | 0.064 |
| Characteristics | Endoscopic Group | Conventional Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (median, minimum to maximum) | 13.3 (11.5–17) | 11.8 (9.2–14.4) | 0.092 |
| Albumin (median, minimum to maximum) | 3.9 (3.1–4.4) | 3.4 (2.8–3.7) | 0.005 |
| VFSS (median, minimum to maximum) | 5 (3–6) | 5 (1–6) | 0.519 |
| Success of conversion from tube feeding to oral diet | 8/9 | 5/9 | 0.147 * |
| Dietary level (median, minimum to maximum) | 2 (0–3) | 1 (0–2) | 0.017 |
| Time interval from tube feeding to oral diet (days, median, minimum to maximum) | 16 (1–28) | 23 ((12–27) | 0.826 |
| NIHSS (median, minimum to maximum) | 1.5 (1–4) | 6 (0–10) | 0.209 |
| MRS (median, minimum to maximum) | 1.5 (1–4) | 4 (2–5) | 0.026 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Joo, J.S.; Eun, H.S.; Lee, E.S.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, J.K.; Lee, B.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; et al. Efficacy of Early Endoscopic Intervention for Restoring Normal Swallowing Function in Patients with Lateral Medullary Infarction. Toxins 2019, 11, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030144
Kang SH, Kim JS, Joo JS, Eun HS, Lee ES, Moon HS, Kim SH, Sung JK, Lee BS, Jeong HY, et al. Efficacy of Early Endoscopic Intervention for Restoring Normal Swallowing Function in Patients with Lateral Medullary Infarction. Toxins. 2019; 11(3):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030144
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sun Hyung, Ju Seok Kim, Jong Seok Joo, Hyuk Soo Eun, Eaum Seok Lee, Hee Seok Moon, Seok Hyun Kim, Jae Kyu Sung, Byung Seok Lee, Hyun Yong Jeong, and et al. 2019. "Efficacy of Early Endoscopic Intervention for Restoring Normal Swallowing Function in Patients with Lateral Medullary Infarction" Toxins 11, no. 3: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030144
APA StyleKang, S. H., Kim, J. S., Joo, J. S., Eun, H. S., Lee, E. S., Moon, H. S., Kim, S. H., Sung, J. K., Lee, B. S., Jeong, H. Y., Kim, Y., Sohn, M. K., & Jee, S. (2019). Efficacy of Early Endoscopic Intervention for Restoring Normal Swallowing Function in Patients with Lateral Medullary Infarction. Toxins, 11(3), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030144





