Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Dissolved Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under Laboratory Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Accumulation of Dissolved OA and DTX1 from Seawater by Mussels
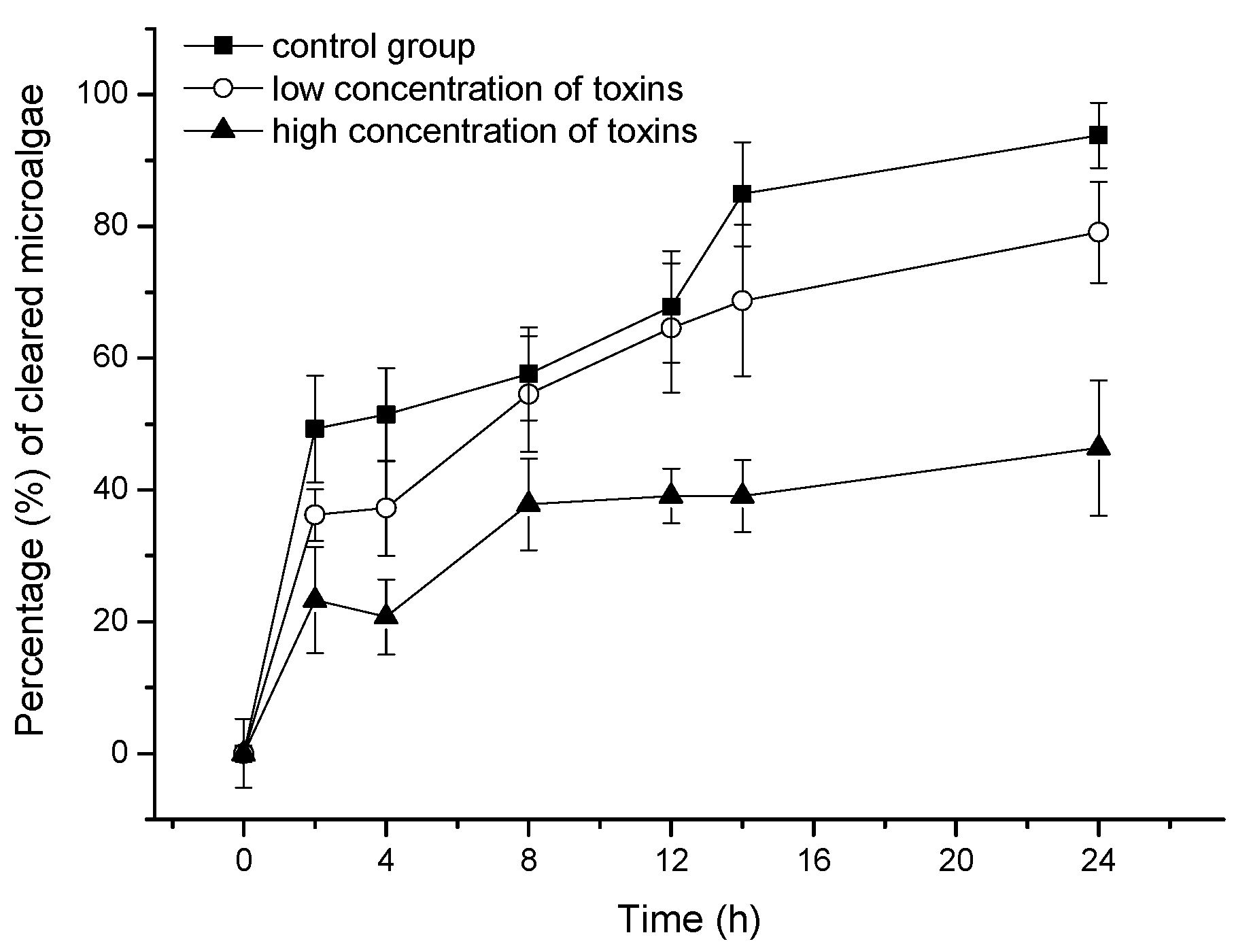
2.2. Effect of OA and DTX1 on the Feeding Ability of Mussels
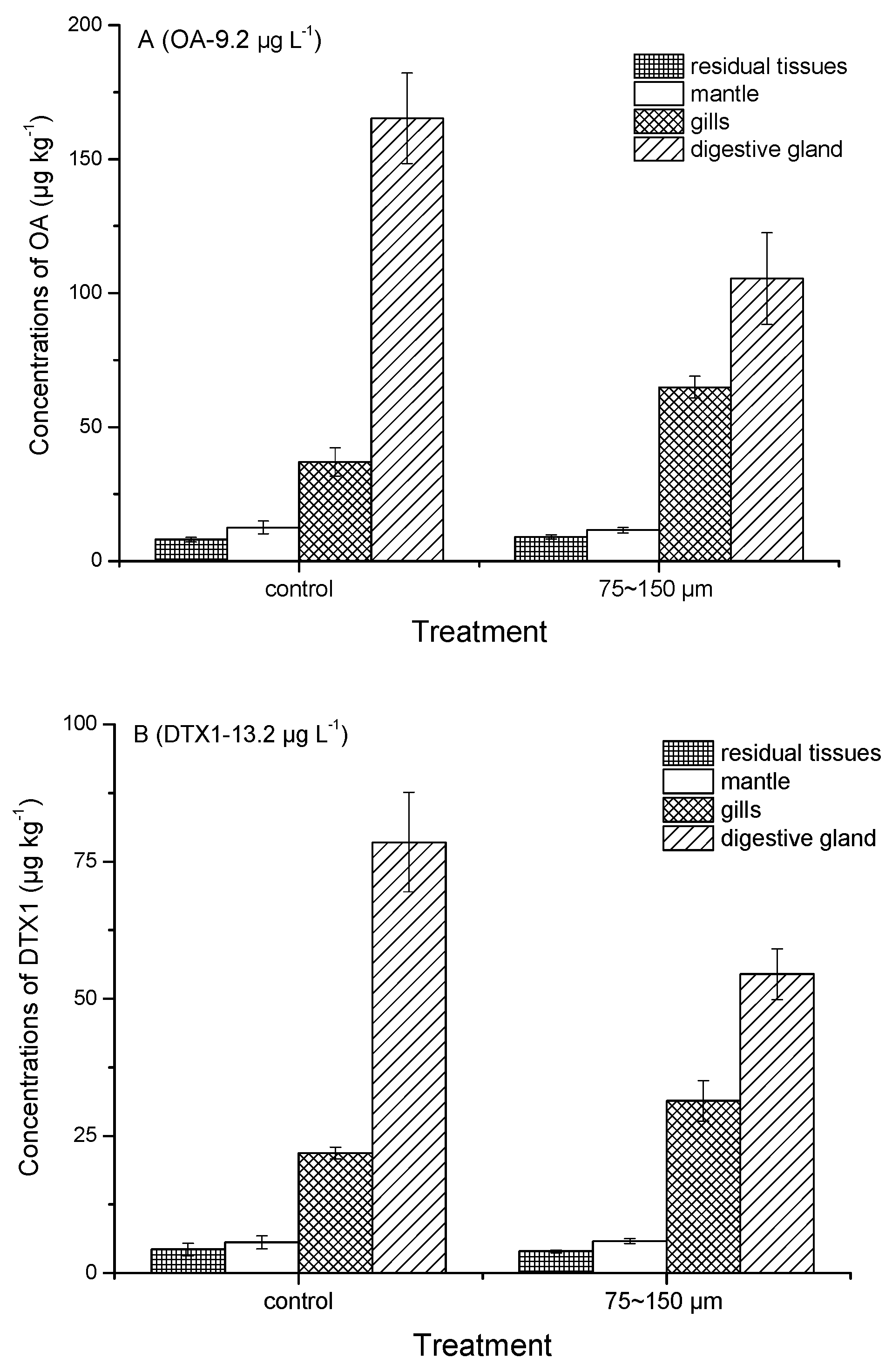
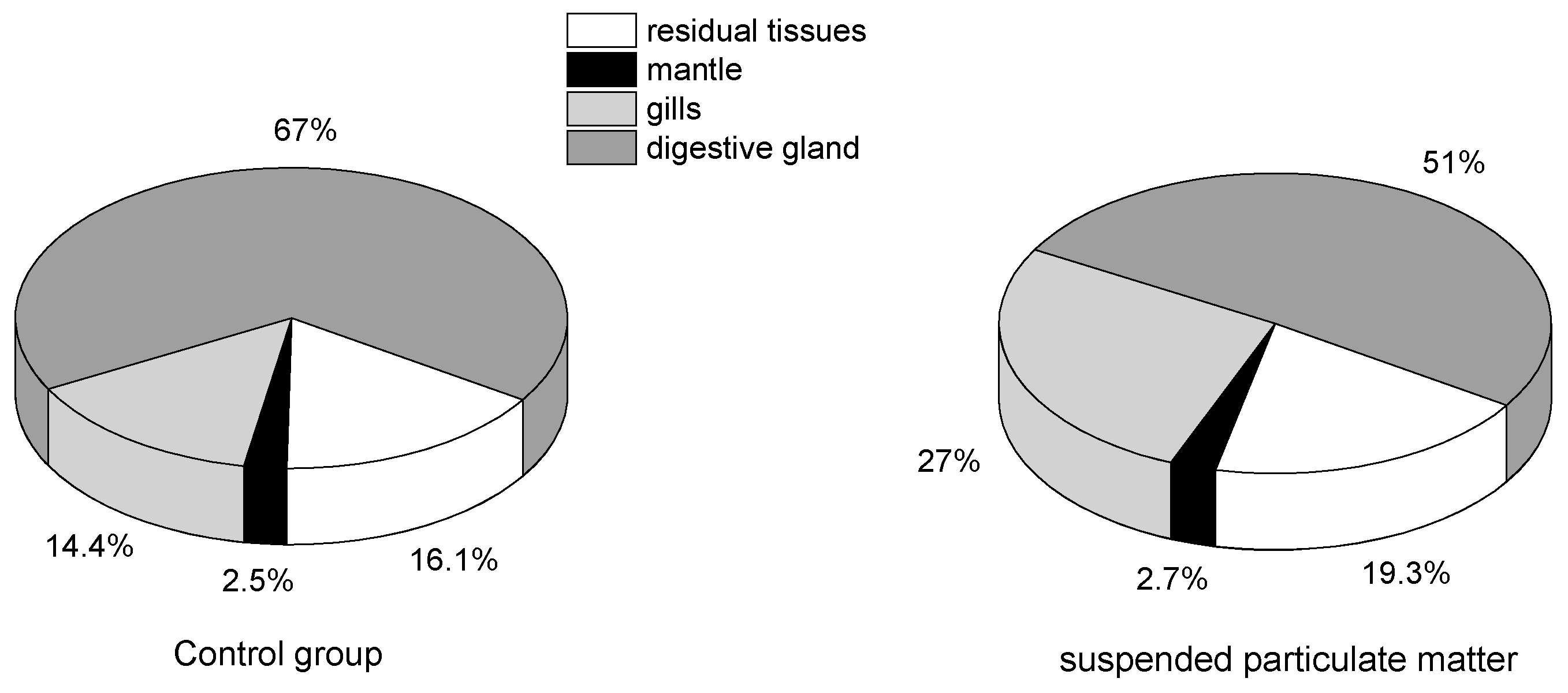
2.3. Tissue Distribution of Toxins Accumulated by Mussels
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals
5.2. Microalgae
5.3. Toxin Extraction and Purification
5.4. Preparation of Suspended Particulate Matter
5.5. Design of Mussel Feeding Experiments
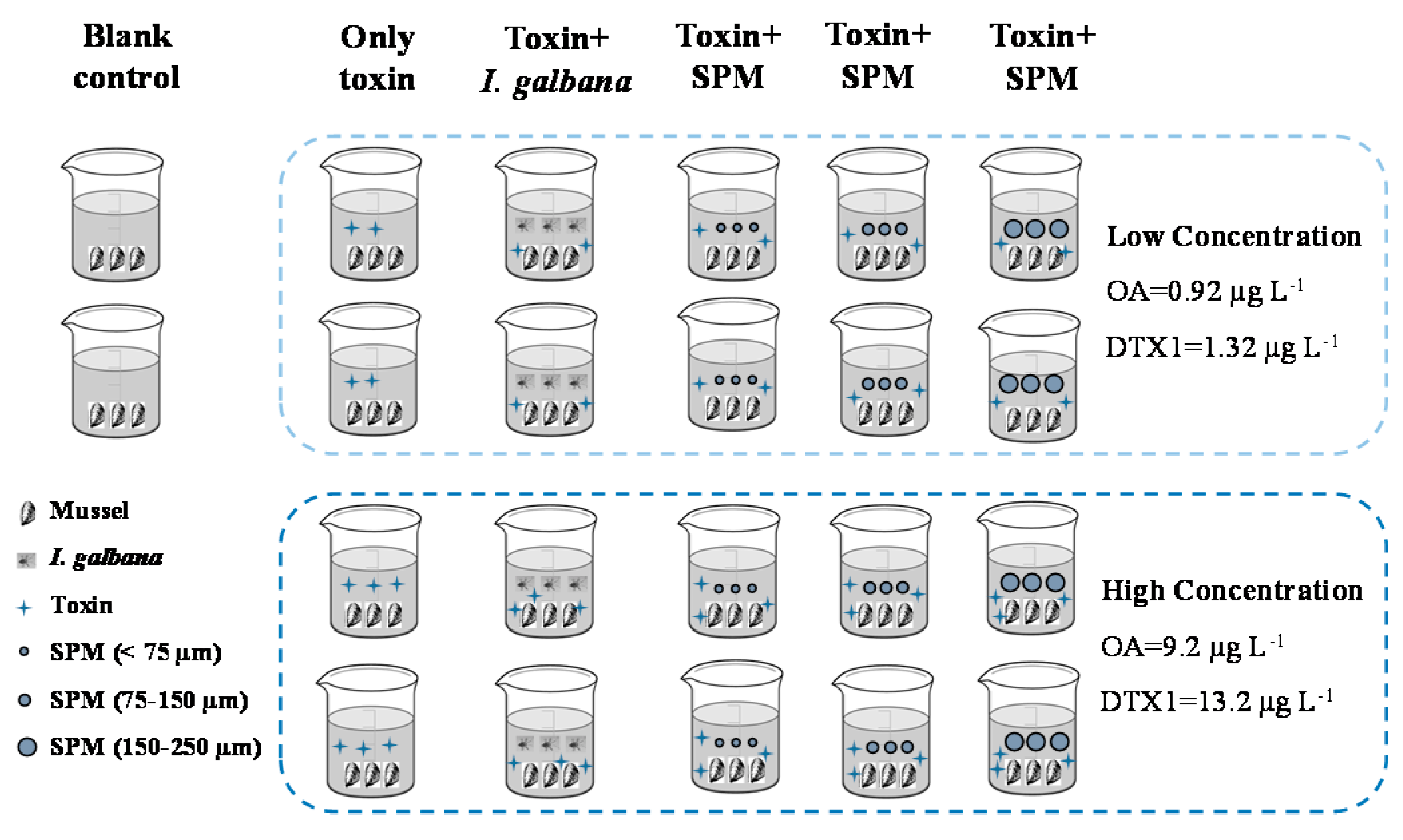
5.5.1. Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Toxins by Mussels
5.5.2. Effect of Toxins on Mussels Feeding Behaviors
5.5.3. Esterification and Distribution of OA and DTX1 in Mussels
5.6. Extraction of Toxins in Mussels
5.7. LC-MS/MS Analysis of OA and DTX1 Toxins
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marr, J.C.; Jackson, A.E.; McLachlan, J.L. Occurrence of Prorocentrum lima, a DSP toxin-producing species from the Atlantic coast of Canada. J. Appl. Phycol. 1992, 4, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, R.W.; Bobzin, S.C.; Faulkner, D.J.; Bencsath, Z.F.A.; Andrzejewski, D. Identification of okadaic acid from a Caribbean Dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum concayum. Toxicon 1990, 28, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.L.; Bomber, J.W.; Tindall, P.M. Environmental effects on the production of okadaic acid from Prorocentrum hoffmannianum Faust I. temperature, light, and salinity. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1994, 178, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Winshell, J.; Scorzetti, G.; Fell, J.W.; Rein, K.S. Identification of okadaic acid production in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum rhathymum from Florida Bay. Toxicon 2010, 55, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, P.A.; Efimova, K.V.; Rybin, V.G.; Orlova, T.Y. Detection of dinophysistoxin-1 in clonal culture of marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum foraminosum (Faust M.A., 1993) from the Sea of Japan. Toxins 2015, 7, 3947–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, B.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Raine, R.; Park, M.G. Harmful Dinophysis species: A review. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.J.; Carey, B.; O’Halloran, J.; Van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; Škrabáková, Z. Shellfish toxicity: Human health implications of marine algal toxins. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J. Okadaic acid induces morphological changes, apoptosis and cell cycle alterations in different human cell types. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terao, K.; Ito, E.; Yanagi, T.; Yasumoto, T. Histopathological studies on experimental marine toxin poisoning. I. Ultrastructural changes in the small intestine and liver of suckling mice induced by dinophysistoxin-1 and pectenotoxin-1. Toxicon 1986, 24, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a new type of toxic shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ma, J.; Cao, J.; McCarron, P. Toxins in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning episodes in China. Toxicon 2012, 60, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainer, V.L.; Moore, L.; Bill, B.D.; Adams, N.G.; Harrington, N.; Borchert, J.; da Silva, D.A.M.; Eberhart, B.T.L. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins and other polyether toxins of human health concern in Washington State. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1815–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; McIntyre, L.; Ritson, M.; Stone, J.; Bronson, R.; Bitzikos, O.; Rourke, W.; Galanis, E. Outbreak Investigation Team. Outbreak of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning associated with mussels, British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, L.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Beuzenberg, V.; Selwood, A.; Suzuki, T. Complex toxin profiles in phytoplankton and Greenshell mussels (Perna canaliculus), revealed by LC-MS/MS analysis. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinder, S.L.; Hays, G.C.; Brooks, C.J.; Davies, A.P.; Edwards, M.; Walne, A.W.; Gravenor, M.B. Toxic marine microalgae and shellfish poisoning in the British Isles: History, review of epidemiology, and future implications. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grattan, L.M.; Holobaugh, S.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Harmful algal blooms and public health. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgersen, T.; Wilkins, A.L.; Rundberget, T.; Miles, C.O. Characterization of fatty acid esters of okadaic acid and related toxins in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) from Norway. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; Goya, A.B. Occurrence and profiles of lipophilic toxins in shellfish harvested from Argentina. Toxicon 2015, 102, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, R.; Uchida, H.; Nagai, S.; Watanabe, R.; Kamio, M.; Nagai, H.; Kaneniwa, M.; Suzuki, T. Assimilation, accumulation, and metabolism of dinophysistoxins (DTXs) and pectenotoxins (PTXs) in the several tissues of Japanese scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Toxins 2015, 7, 5141–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A.M. First conformation of human diarrhoeic poisonings by okadaic acid esters ingestion of razor clams (Solen marginatus) and green crabs (Carcinus maenas) in Aveiro lagoon, Portugal and detection of okadaic acid esters in phytoplankton. Toxicon 2002, 40, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.; Scanlon, S.; Jensen, L.B. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxin esters in Danish blue mussels and surf clams. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, C.; Truan, D.; Lagos, M.; Santelices, J.P.; Diaz, J.C.; Lagos, N. Metabolic transformation of dinophysistoxin-3 into dinophysistoxin-1 causes human intoxication by consumption of O-acyl-derivates dinophysistoxins contaminated shellfish. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 30, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, E.; Ross, N.N.; Quilliam, M.A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of esterified diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins and pectenotoxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, A.C.; Alves, R.N.; Maulvault, A.L.; Barbosa, V.; Marques, A.; Costa, P.R. In vitro bioaccessibility of the marine biotoxin okadaic acid in shellfish. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 89, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgersen, T.; Miles, C.O.; Rundberget, T.; Wilkins, A.L. New esters of okadaic acid in seawater and blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9628–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request from the European Commission on Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins. EFSA J. 2009, 1306, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Selwood, A. Solid phase adsorption toxin tracking (SPATT): A new monitoring tool that simulates the biotoxin contamination of filter feeding bivalves. Toxicon 2004, 44, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundberget, T.; Gustad, E.; Samdal, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Miles, C.O. A convenient and cost-effective method for monitoring marine algal toxins with passive samplers. Toxicon 2009, 53, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Comparative accumulation and composition of lipophilic marine biotoxins in passive samplers and in mussels (M. edulis) on the West Coast of Ireland. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Z. Investigation of pectenotoxin profiles in the Yellow Sea (China) using passive sampling technique. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, L. In situ passive solid-phase adsorption of micro-algal biotoxins as a monitoring tool. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, G.; Moroño, Á.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Pazos, Y.; Reguera, B. Evaluation of passive samplers as a monitoring tool for early warning of Dinophysis toxins in shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3823–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, G.; Qiu, J.; Li, A. Occurrence and variation of lipophilic shellfish toxins in phytoplankton, shellfish and seawater samples from the aquaculture zone in the Yellow Sea, China. Toxicon 2017, 127, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Detection, occurrence and monthly variations of typical lipophilic marine toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in the coastal seawater of Qingdao City, China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in marine aquaculture environment using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauffrais, T.; Kilcoyne, J.; Herrenknecht, C.; Truquet, P.; Séchet, V.; Miles, C.O.; Hess, P. Dissolved azaspiracids are absorbed and metabolized by blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). Toxicon 2013, 65, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Fang, J.G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, L.L.; Wang, W. Studies on the effects of suspended sediment on the feeding physiology of three suspension-feeding bivalves. Mar. Fish. Res. 2006, 27, 21–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Hansen, P.J.; Krock, B.; Vismann, B. Accumulation, transformation and breakdown of DSP toxins from the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta in blue mussels, Mytilus edulis. Toxicon 2016, 117, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauffrais, T.; Contreras, A.; Herrenknecht, C.; Truquet, P.; Séchet, V.; Tillmann, U.; Hess, P. Effect of Azadinium spinosum on the feeding behaviour and azaspiracid accumulation of Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 124–125, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, P.A.; Imbs, A.B.; Orlova, T.Y. Distribution of DTX-3 in edible and non-edible parts of Crenomytilus grayanus from the Sea of Japan. Toxicon 2015, 98, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Kamiyama, T. Differences in the production and excretion kinetics of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1, and pectenotoxin-2 between cultures of Dinophysis acuminata and Dinophysis fortii isolated from western Japan. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Fux, E.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin production, retention, and extracellular release by Dinophysis acuminata during extended stationary phase and culture decline. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-de-Souza, C.; Varela, D.; Contreras, C.; LaIglesia, P.; Fernández, P.; Hipp, B.; Hernández, C.; Riobó, P.; Reguera, B.; Franco, J.M.; et al. Seasonal variability of Dinophysis spp. and Protoceratium reticulatum associated to lipophilic shellfish toxins in a strongly stratified Chilean fjord. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2014, 101, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Hargraves, P.E. Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 1993, 32, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ma, F.; Song, X.; Yu, R. Dynamic adsorption of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in passive sampling relates to pore size distribution of aromatic adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Sun, G.; Qiu, J.; Ma, Q.; Hess, P.; Li, A. Effect of seawater salinity on pore-size distribution on a poly(styrene)-based HP20 resin and its adsorption of diarrhetic shellfish toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1373, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Chen, H.; Qiu, J.; Lin, H.; Gu, H. Determination of multiple toxins in whelk and clam samples collected from the Chukchi and Bering seas. Toxicon 2016, 109, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzukia, T.; Otab, H.; Yamasakia, M. Direct evidence of transformation of dinophysistoxin-1 to 7-O-acyl-dinophysistoxin-1 (dinophysistoxin-3) in the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Toxicon 1999, 37, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.J.; McElhinney, M.A.; Boer, J. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of marine lipophilic toxins under alkaline conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
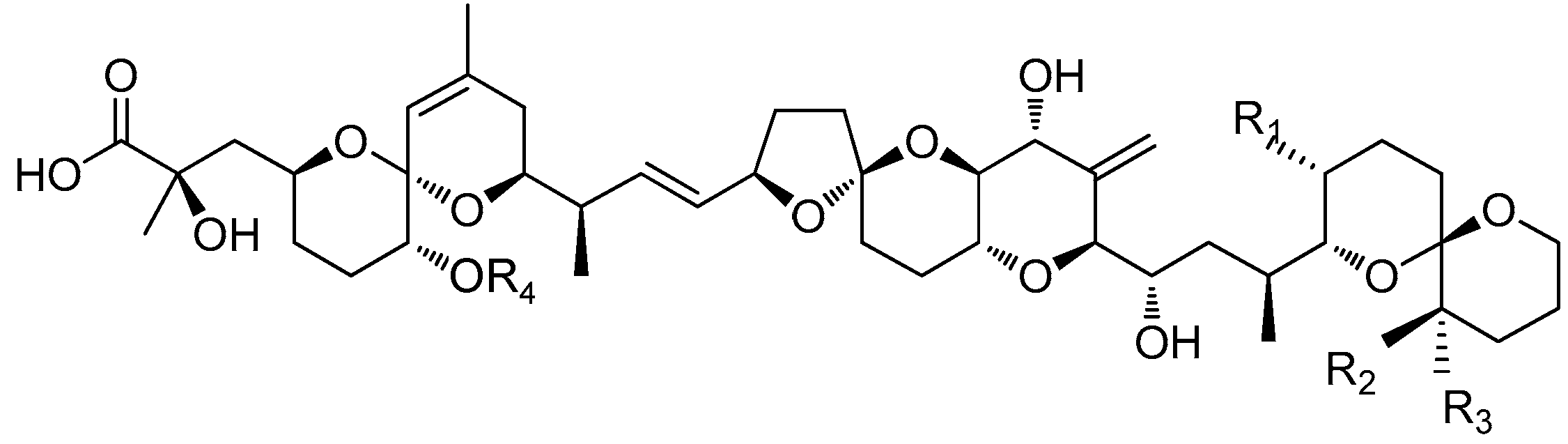
| DST | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | CH3 | H | H | H | 804.5 |
| DTX1 | CH3 | CH3 | H | H | 818.5 |
| DTX2 | H | H | CH3 | H | 804.5 |
| DTX3 | H or CH3 | H or CH3 | H or CH3 | Acyl | 1014~1082 |
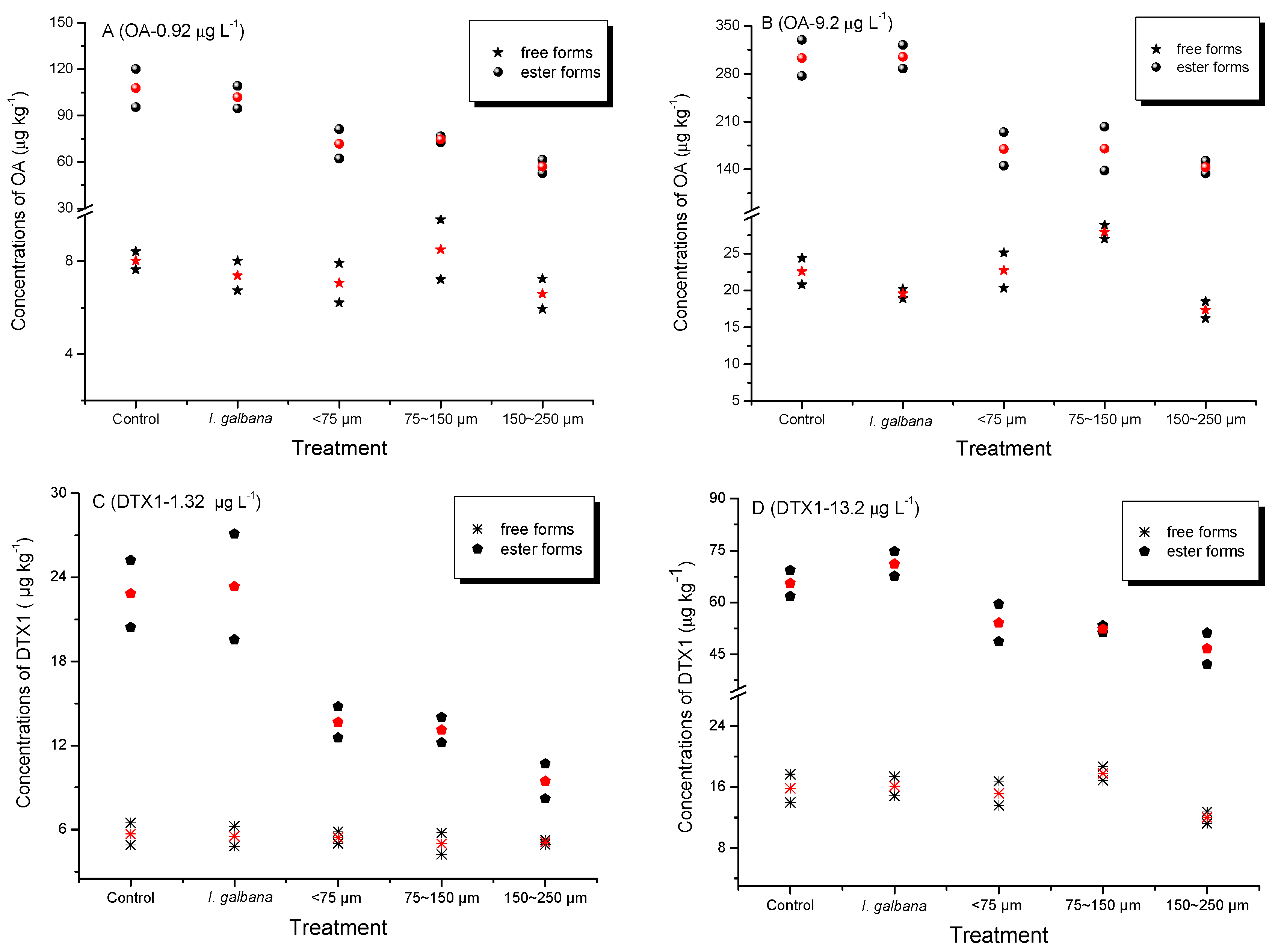
| Treatments | OA (µg L−1) | DTX1 (µg L−1) | OA:DTX1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.92 | 9.2 | 1.32 | 13.2 | Low Toxin Level | High Toxin Level | |
| Control | 53 | 15 | 9.1 | 2.7 | 5.82 | 5.56 |
| Isochrysis galbana | 50 | 15 | 9.2 | 2.9 | 5.43 | 5.17 |
| SPM < 75 μm | 36 | 8.8 | 6.1 | 2.4 | 5.90 | 3.67 |
| SPM 75–150 μm | 38 | 9.1 | 5.8 | 2.4 | 6.55 | 3.79 |
| SPM 150–250 μm | 29 | 7.4 | 4.6 | 2.0 | 6.30 | 3.70 |
| Treatments | OA (µg L−1) | DTX1 (µg L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.92 | 9.2 | 1.32 | 13.2 | |
| Control | 93 | 93 | 80 | 81 |
| Isochrysis galbana | 93 | 94 | 81 | 82 |
| SPM < 75 μm | 91 | 88 | 72 | 78 |
| SPM 75–150 μm | 90 | 86 | 72 | 75 |
| SPM 150–250 μm | 90 | 89 | 65 | 80 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, A.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Song, J.; Ji, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Che, Y. Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Dissolved Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under Laboratory Conditions. Toxins 2018, 10, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070273
Li A, Li M, Qiu J, Song J, Ji Y, Hu Y, Wang S, Che Y. Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Dissolved Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under Laboratory Conditions. Toxins. 2018; 10(7):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Aifeng, Meihui Li, Jiangbing Qiu, Jialiang Song, Ying Ji, Yang Hu, Shuqin Wang, and Yijia Che. 2018. "Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Dissolved Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under Laboratory Conditions" Toxins 10, no. 7: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070273
APA StyleLi, A., Li, M., Qiu, J., Song, J., Ji, Y., Hu, Y., Wang, S., & Che, Y. (2018). Effect of Suspended Particulate Matter on the Accumulation of Dissolved Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under Laboratory Conditions. Toxins, 10(7), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070273





