Development and Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-HR-MS Method for the Determination of Fumonisin B1 and Its Hydrolysed Metabolites and Fumonisin B2 in Broiler Chicken Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
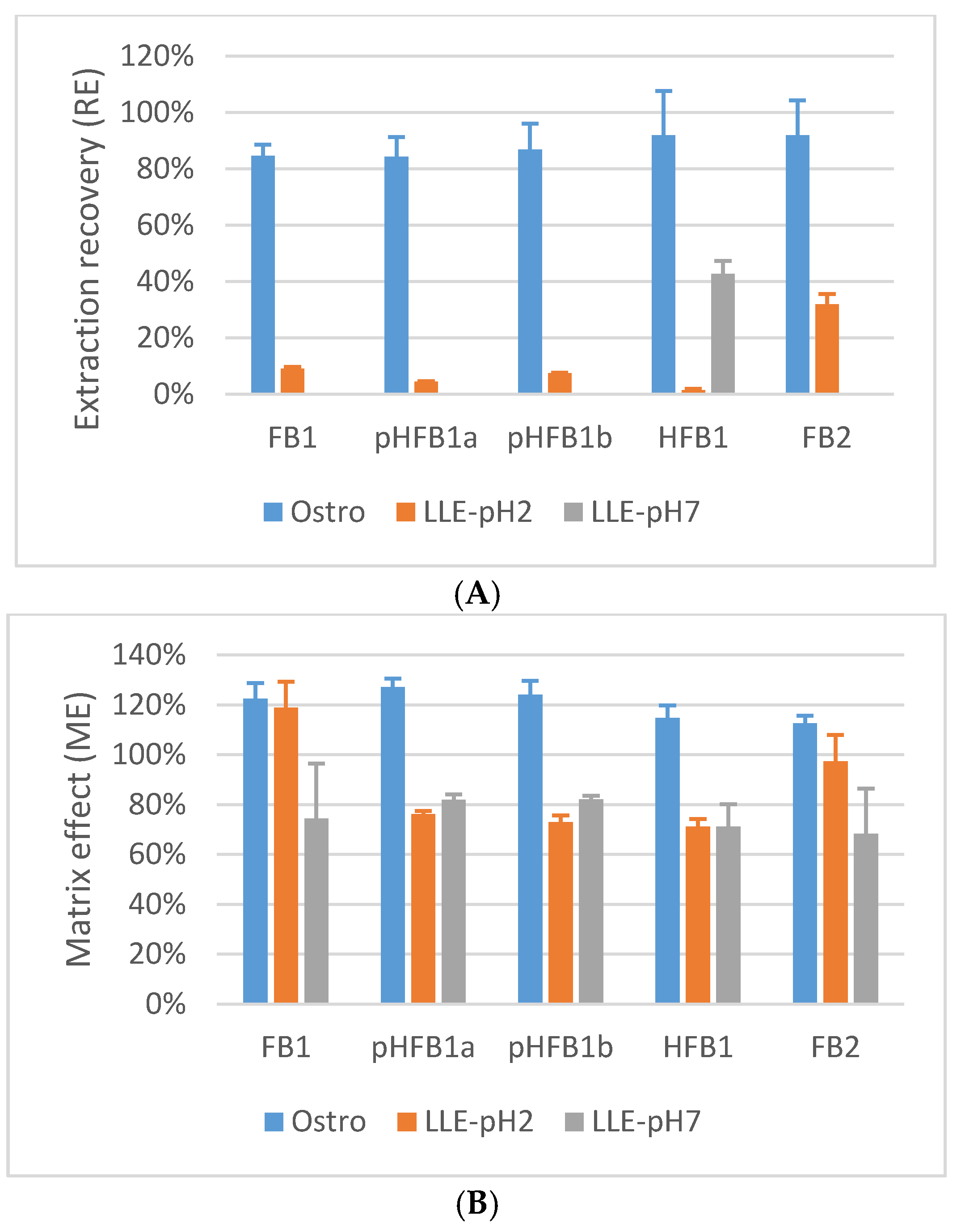
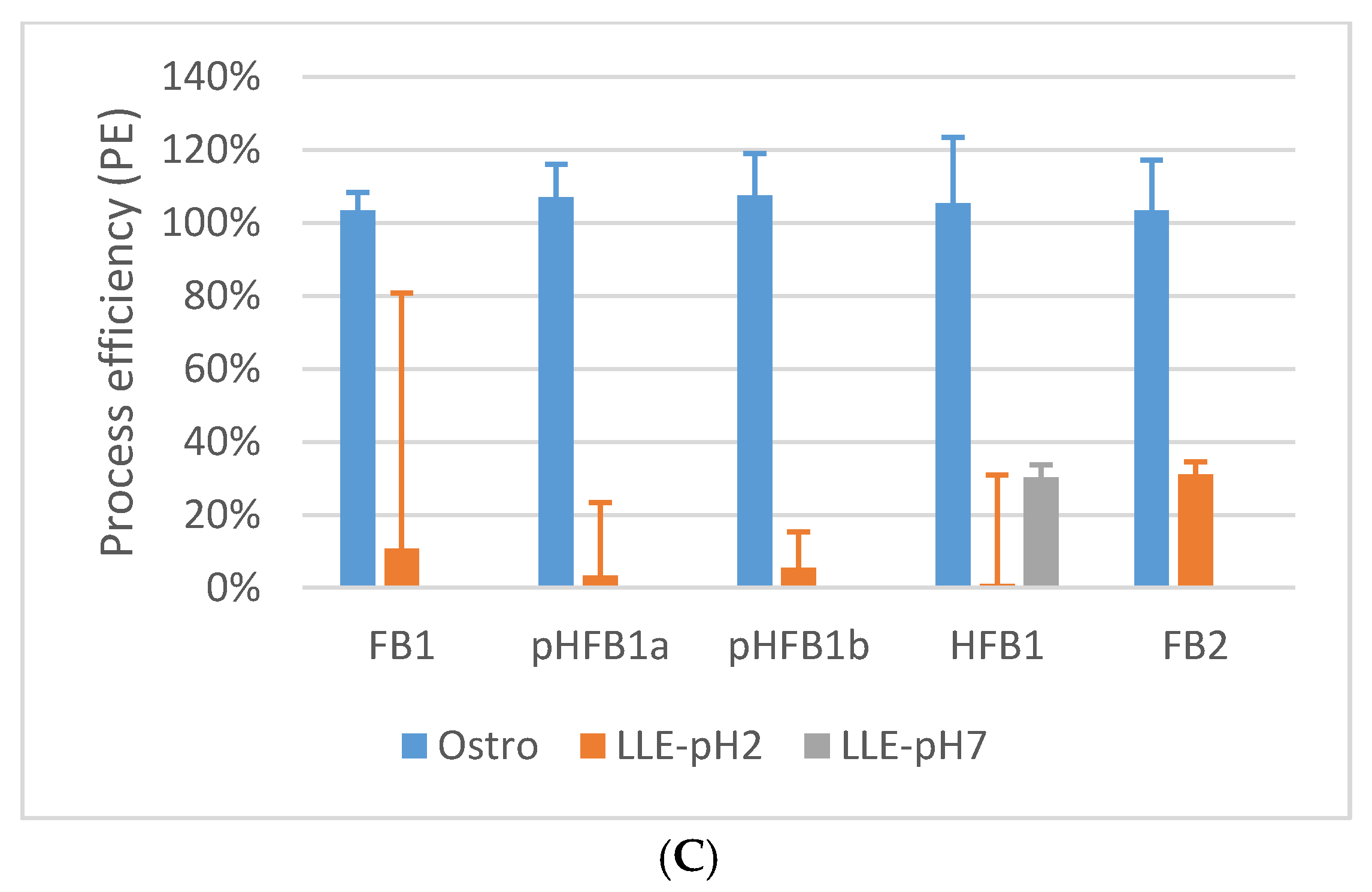
2.1. Sample Preparation
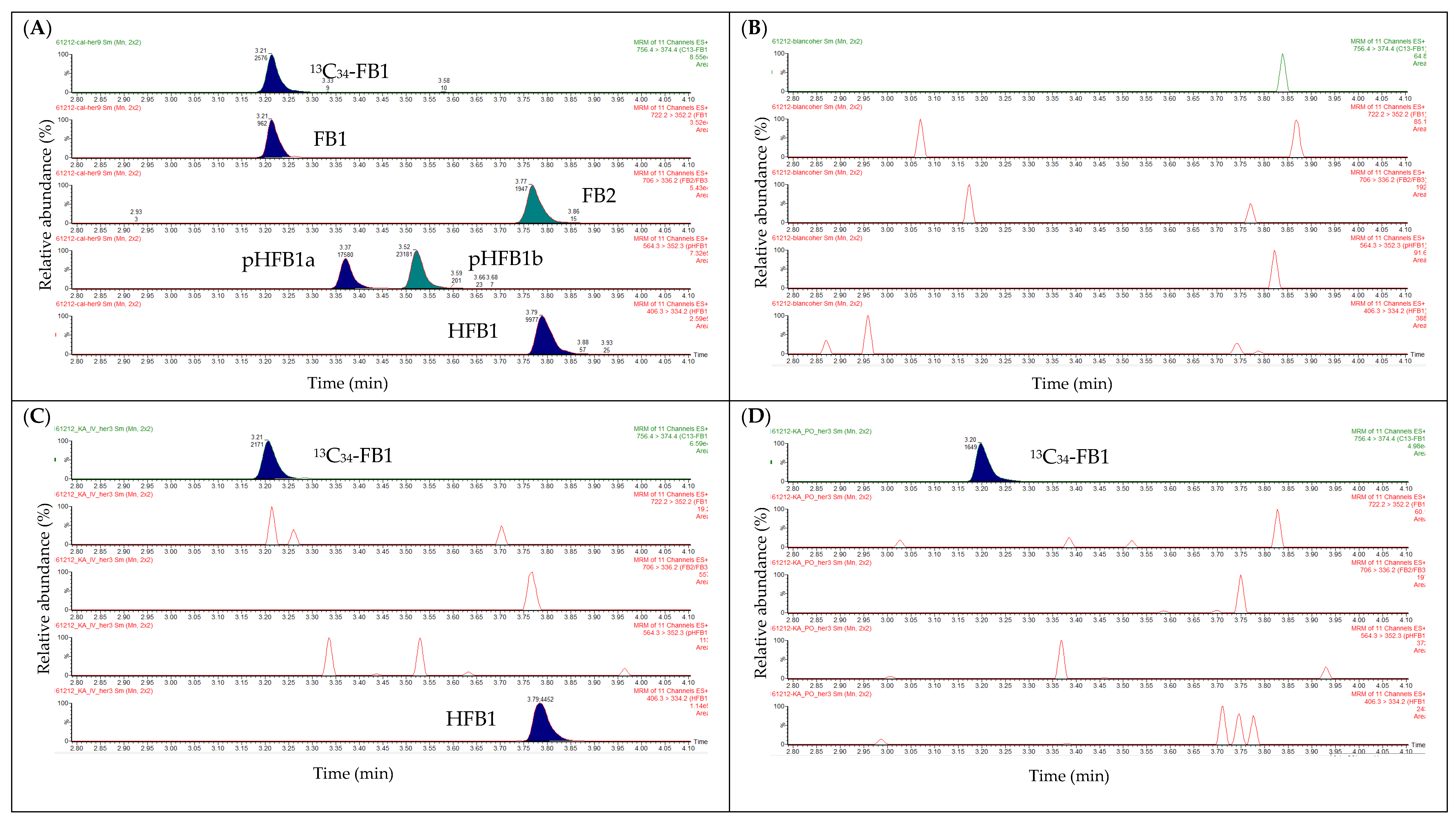
2.2. Liquid Chromatography
2.3. Mass Spectrometry
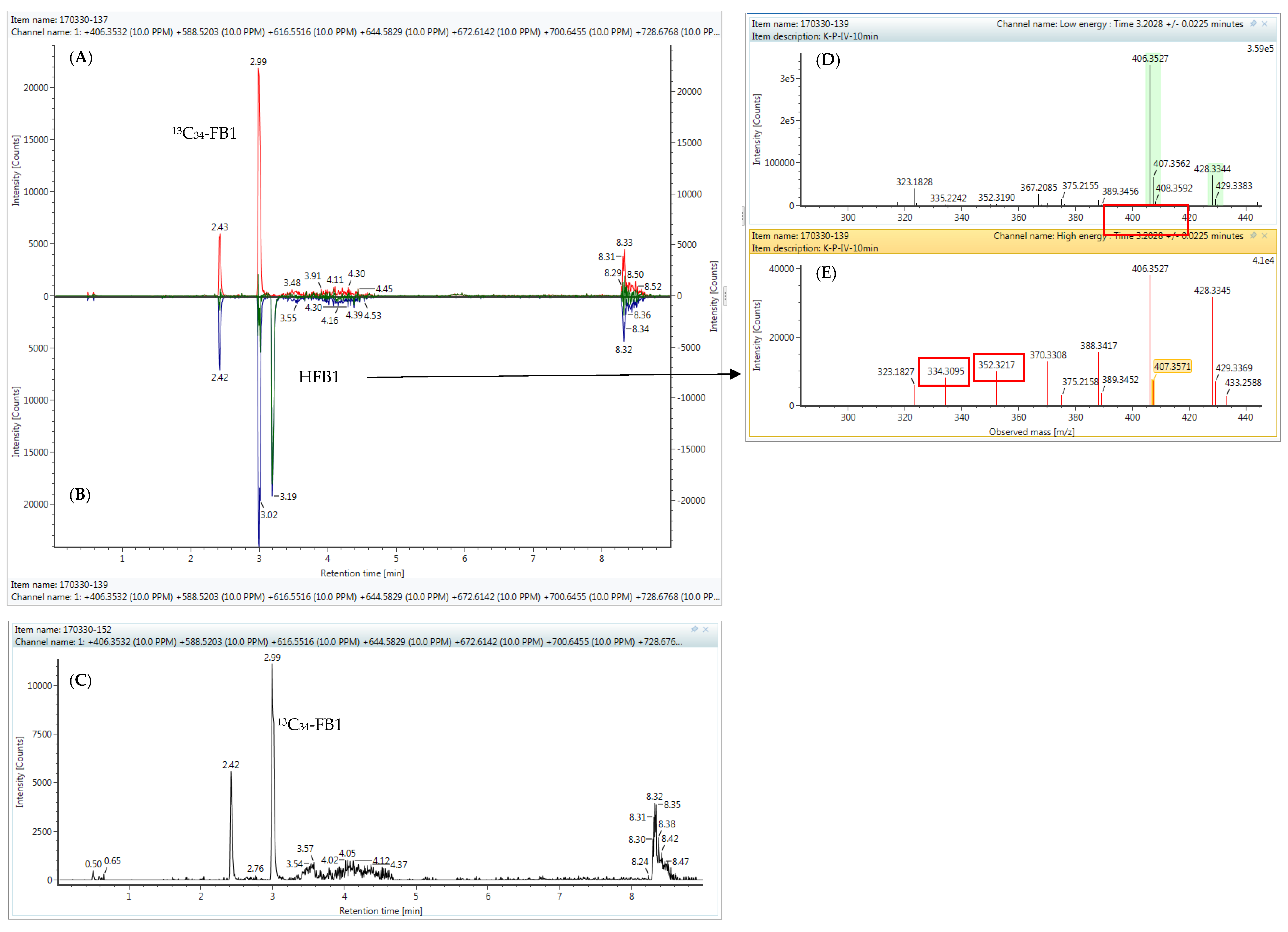
2.4. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
2.5. Method Validation
2.5.1. Linearity
2.5.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.5.3. LOQ and LOD
2.5.4. Carry-Over
2.5.5. Matrix Effects and Process Efficiency
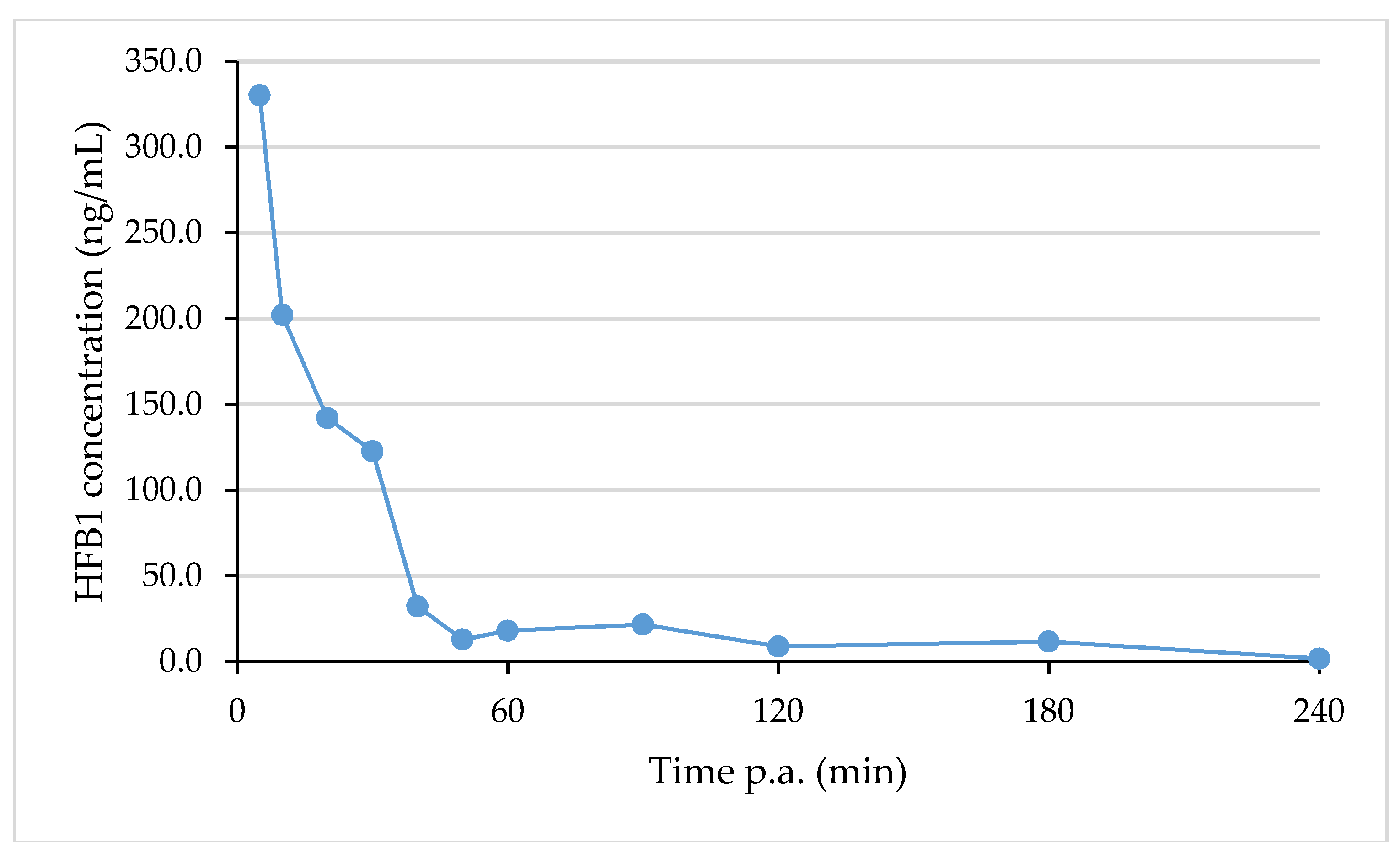
2.6. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
4.3. Biological Samples
4.4. Sample Pre-Treatment
4.4.1. Final Procedure
4.4.2. Liquid–Liquid Extraction Procedure
4.5. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis for Quantification
4.6. UPLC-HR-MS Analysis for Identification
4.7. Method Validation
4.7.1. Calibration Curves
4.7.2. Accuracy and Precision
4.7.3. LOQ and LOD
4.7.4. Carry-Over
4.7.5. Extraction Recovery, Matrix Effects and Process Efficiency
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escriva, L.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. In vivo toxicity studies of fusarium mycotoxins in the last decade: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, I.; Nagl, V.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Varga, E.; Schwarz, C.; Slavik, V.; Reisinger, N.; Malachova, A.; Cirlini, M.; Generotti, S.; et al. Effects of orally administered fumonisin B1 (FB1), partially hydrolysed FB1, hydrolysed FB1 and N-(1-deoxy-D-fructos-1-yl) FB1 on the sphingolipid metabolism in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrer, H.; Laviad, E.L.; Humpf, H.-U.; Futerman, A.H. Identification of N-acyl-fumonisin B1 as new cytotoxic metabolites of fumonisin mycotoxins. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrer, H.; Humpf, H.-U.; Voss, K.A. In vivo formation of N-acyl-fumonisin B1. Mycotoxin Res. 2015, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiferlein, M.; Humpf, H.-U.; Voss, K.A.; Sullards, M.C.; Allegood, J.C.; Wang, E.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Hydrolyzed fumonisins HFB1 and HFB2 are acylated in vitro and in vivo by ceramide synthase to form cytotoxic N-acyl-metabolites. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.F.X.; Sprando, R.L.; Black, T.N.; Olejnik, N.; Eppley, R.M.; Shackelford, M.E.; Howard, P.C.; Rorie, J.I.; Bryant, M.; Ruggles, D.I. Effects of aminopentol on in utero development in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzotti, T.; Zironi, E.; Lugoboni, B.; Barbarossa, A.; Piva, A.; Pagliuca, G. Analysis of fumonisins B1, B2 and their hydrolysed metabolites in pig liver by LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloni, F.; Spotti, M.; Auerbach, H.; Op den Camp, H.; Fink Gremmels, J.; Pompa, G. In vitro metabolism of fumonisin B1 by ruminal microflora. Vet. Res. Commun. 2000, 24, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinl, S.; Hartinger, D.; Themhesl, M.; Vekiru, E.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.-D.; Grabherr, R. Degradation of fumonisin B1 by consecutive action of two bacterial enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 145, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliuca, G.; Zironi, E.; Ceccolini, A.; Matera, R.; Serrazanetti, G.P.; Piva, A. Simple method for the simultaneous isolation and determination of fumonisin B1 and its metabolite aminopentol-1 in swine liver by liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 819, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Girolamo, A.; Lattanzio, V.M.T.; Schena, R.; Visconti, A.; Pascale, M. Use of liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry for isolation and characterization of hydrolyzed fumonisins and relevant analysis in maize-based products. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, J.; Balogh, K.; Weber, M.; Mézes, M.; Kametler, L.; Pósa, R.; Mamet, R.; Bauer, J.; Horn, P.; Kovács, F.; et al. Absorption, distribution and elimination of fumonisin B1 metabolites in weaned piglets. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2008, 25, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humpf, H.-U.; Schmelz, E.-M.; Meredithi, F.I.; Vesper, H.; Vales, T.R.; Wang, E.; Menaldino, D.S.; Liotta, D.C.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Acylation of Naturally Occurring and Synthetic 1-Deoxysphinganines by Ceramide Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 19060–19064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shephard, G.S.; Thiel, P.G.; Sydenham, E.W. Determination of fumonisin B1 in plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1992, 574, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, M.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Quantitative determination of several toxicological important mycotoxins in pig plasma using multi-mycotoxin and analyte-specific high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1257, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Luan, L.; Wu, Y. A reliable isotope dilution method for simultaneous determination of fumonisins B1, B2, B3 in traditional Chinese medicines by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.T.; Torres, O.; Showker, J.L.; Zitomer, N.C.; Matute, J.; Voss, K.A.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.; Maddox, J.R.; Gregory, S.G.; Ashley-Koch, A.E. The kinetics of urinary fumonisin B1 excretion in humans consuming maize-based diets. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilkin, P.; Direito, G.; Simas, M.M.S.; Mallmann, C.A.; Corrêa, B. Toxicokinetics and toxicological effects of single oral dose of fumonisin B1 containing Fusarium verticillioides culture material in weaned piglets. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 185, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baere, S.; Devreese, M.; Watteyn, A.; Wyns, H.; Plessers, E.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography–tandemmass spectrometry method for the quantitative determination of gamithromycin in animal plasma, lung tissue and pulmonaryepithelial lining fluid. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1398, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlazzo, A.M.; Bruschetta, G.; Di Pietro, P.; Medica, P.; Notti, A.; Rotondo, E. Phospholipid composition of plasma and erythrocyte membranes in animal species by 31P NMR. Vet. Res. Commun. 2011, 35, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.; Wagrowski-Diehl, D.M.; Lu, Z.; Mazzea, J.R. Systemic and comprehensive strategy for reducing matrix effects in LC-MS/MS analyses. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Mohr, K.; Bauer, J.; Horn, P.; Kovács, M. Residue formation of fumonisin B1 in porcine tissues. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baere, S.; Goossens, J.; Osselaere, A.; Devreese, M.; Vandenbroucke, V.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Quantitative determination of T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, deoxynivalenol and deepoxy-deoxynivalenol in animal body fluids using LC-MS/MS detection. J. Chrom. B 2011, 879, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, J.; Stork, G. Percentage and logarithmic procedures for calculation of calibration curves. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1974, 270, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.M.; Castel-Branco, M.M.; Falcão, A.C. Linear regression for calibration lines revisited: Weighting schemes for bioanalytical methods. J. Chromatogr. B. 2002, 774, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. VICH GL49(R): Guidance for Industry. Studies to Evaluate the Metabolism and Residue Kinetics of Veterinary Drugs in Food-Producing Animals: Validation of Analytical Methods Used in Residue Depletion Studies, Revision at Step 9 for Implementation at Step 7; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Veterinary Medicine: Rockvill, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonissen, G.; De Baere, S.; Novak, B.; Bichl, G.; Devreese, M.; Croubels, S. Toxicokinetics of hydrolyzed fumonisin B1 in broiler chickens fed a control or a fumonisins contaminated diet. 2018; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Decision 2002/657/EC, implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performances of analytical methods and interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2002, L221, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Heitzman, R.J. Veterinary Drug Residues; Report Eur. 14126-EN; Commision of the EC: Brussels, Belgium; Luxembourg, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hopmans, E.C.; Hauck, C.C.; Hendrich, S.; Murphy, P.A. Excretion of Fumonisin B1, Hydrolyzed Fumonisin B1, and the Fumonisin B1-Fructose Adduct in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | TCA | TCA | OH | OH | H |
| FB2 | TCA | TCA | H | OH | H |
| FB3 | TCA | TCA | OH | H | H |
| pHFB1a | TCA | H | OH | OH | H |
| pHFB1b | H | TCA | OH | OH | H |
| HFB1 | H | H | OH | OH | H |
| NAHFB1 | H | H | OH | OH | NA |
| Analyte | Chemical Formula | MM a (g/mol) | Precursor Ion (m/z) b | Product Ions (m/z) | CE c (eV) | Cone (V) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | C34H59NO15 | 721.3885 | 722.2 | 334.2 | 33 | 40 | 3.29 |
| 352.2 d | 33 | 40 | |||||
| pHFB1a | C28H53NO10 | 563.3669 | 564.3 | 334.3 | 27 | 40 | 3.42 |
| 352.3 d | 27 | 40 | |||||
| pHFB1b | C28H53NO10 | 563.3669 | 564.3 | 334.3 | 27 | 40 | 3.56 |
| 352.3 d | 27 | 40 | |||||
| HFB1 | C22H47NO5 | 405.3454 | 406.3 | 334.2 d | 25 | 40 | 3.80 |
| 352.3 | 25 | 40 | |||||
| FB2 | C34H59NO14 | 705.3936 | 706.0 | 336.2 d | 35 | 40 | 3.84 |
| 354.2 | 35 | 40 | |||||
| FB3 | C34H59NO14 | 705.3936 | 706.0 | 336.2 d | 35 | 40 | 3.59 |
| 354.2 | 35 | 40 | |||||
| 13C34-FB1 | 13C34H59NO15 | 755.5025 | 756.4 | 356.4 | 35 | 40 | 3.28 |
| 374.4 d | 35 | 40 |
| Component | Chemical Formula | Chemical Formula N-acyl Chain | Theoretical Exact Mass (g/mol) | Theoretical Exact Mass Protonated Molecular Ion [M-H]+ (m/z) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFB1 | C22H47O5N | 405.3454 | 406.3532 | |
| C12-HFB1 | C34H69O6N | +C12H22O | 587.5125 | 588.5203 |
| C14-HFB1 | C36H73O6N | +C14H26O | 615.5438 | 616.5516 |
| C16-HFB1 | C38H77O6N | +C16H30O | 643.5751 | 644.5829 |
| C18-HFB1 | C40H81O6N | +C18H34O | 671.6064 | 672.6142 |
| C20-HFB1 | C42H85O6N | +C20H38O | 699.6377 | 700.6455 |
| C22-HFB1 | C44H89O6N | +C22H42O | 727.6690 | 728.6768 |
| C24-HFB1 | C46H93O6N | +C24H46O | 755.7003 | 756.7081 |
| C26-HFB1 | C48H97O6N | +C26H50O | 783.7316 | 784.7394 |
| C24:1-HFB1 | C46H91O6N | +C24H44O | 753.6846 | 754.6925 |
| C26:1-HFB1 | C48H95O6N | +C26H48O | 781.7159 | 782.7238 |
| Component | Calibration Range (ng/mL) | Spike Levels (ng/mL) | A a | b a | gof a (%) | r a | LOQ (ng/mL) | LOD c (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | 1–500 | 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500 | 0.00869 ± 0.00026 | −0.00207 ± 0.00722 | 5.25 ± 1.18 | 0.99825 ± 0.00085 | 1.0 (S/N b = 20.1) | 0.15 |
| FB2 | 1–500 | 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500 | 0.013669 ± 0.00152 | −0.00506 ± 0.00395 | 6.22 ± 1.14 | 0.99757 ± 0.00106 | 1.0 (S/N = 33.3) | 0.09 |
| pHFB1a | 0.86–860 | 0.86, 1.72, 4.3, 8.6, 17.2, 43, 86, 172, 430, 860 | 0.06929 ± 0.00767 | −0.01107 ± 0.00632 | 5.72 ± 1.82 | 0.99798 ± 0.00105 | 0.86 (S/N = 69.5) | 0.04 |
| pHFB1b | 0.72–1430 | 0.72, 1.43, 2.86, 7.15, 14.3, 28.6, 71.5, 143, 286, 715, 1430 | 0.05665 ± 0.00702 | −0.01758 ± 0.00927 | 4.30 ± 3.78 | 0.99831 ± 0.00161 | 0.72 (S/N = 70.3) | 0.03 |
| HFB1 | 2.5–2500 | 2.5, 5, 12.5, 25, 50, 125, 250, 500, 1250, 2500 | 0.01240 ± 0.00285 | −0.00280 ± 0.00362 | 5.99 ± 0.85 | 0.99795 ± 0.00058 | 2.5 (S/N = 45.4) | 0.17 |
| Component | Theoretical Concentration (ng/mL) | Mean Concentration ± SD (ng/mL) | Precision, RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | 1.0 a | 1.01 ± 0.11 | 10.7 | 1.2 |
| 2.5 a | 2.4 ± 0.39 | 16.4 | −3.5 | |
| 2.5 b | 2.4 ± 0.58 | 24.7 | −5.5 | |
| 25.0 a | 25.2 ± 1.82 | 7.2 | 0.7 | |
| 25.0 b | 23.6 ± 1.66 | 7.1 | −5.8 | |
| 250.0 a | 243.8 ± 10.19 | 4.2 | −2.5 | |
| 250.0 b | 251.0 ± 8.20 | 3.3 | 0.4 | |
| FB2 | 1.0 a | 0.77 ± 0.15 | 19.0 | −23.0 |
| 2.5 a | 2.2 ± 0.40 | 18.0 | −12.2 | |
| 2.5 b | 2.3 ± 0.21 | 9.1 | −9.9 | |
| 25.0 a | 24.0 ± 1.11 | 4.6 | −4.0 | |
| 25.0 b | 24.2 ± 2.80 | 11.6 | −3.3 | |
| 250.0 a | 246.5 ± 9.75 | 4.0 | −1.4 | |
| 250.0 b | 253.1 ± 16.91 | 6.7 | 1.3 | |
| pHFB1a | 0.86 a | 1.02 ± 0.05 | 5.3 | 19.1 |
| 4.3 a | 4.1 ± 0.28 | 6.9 | −4.7 | |
| 4.3 b | 4.0 ± 0.33 | 8.2 | −7.6 | |
| 43.0 a | 34.4 ± 3.49 | 10.2 | −20.0 | |
| 43.0 b | 39.1 ± 1.97 | 5.0 | −9.1 | |
| 430.0 a | 387.8 ± 38.24 | 9.9 | −9.8 | |
| 430.0 b | 425.7 ± 16.00 | 3.8 | −1.0 | |
| pHFB1b | 0.72 a | 0.77 ± 0.13 | 16.4 | 7.0 |
| 7.2 a | 6.3 ± 0.32 | 5.0 | −11.7 | |
| 7.2 b | 6.5 ± 0.31 | 4.7 | −8.6 | |
| 71.5 a | 57.6 ± 5.19 | 9.0 | −19.5 | |
| 71.5 b | 63.7 ± 1.64 | 2.6 | −10.9 | |
| 715.0 a | 682.4 ± 51.44 | 7.5 | −4.6 | |
| 715.0 b | 714.9 ± 29.66 | 4.1 | 0.0 | |
| HFB1 | 2.5 a | 2.4 ± 0.40 | 16.6 | −3.1 |
| 12.5 a | 12.5 ± 0.81 | 6.4 | −0.1 | |
| 12.5 b | 11.3 ± 1.59 | 14.0 | −9.7 | |
| 125.0 a | 115.9 ± 7.15 | 6.2 | −7.3 | |
| 125.0 b | 122.2 ± 10.9 | 8.9 | −2.3 | |
| 1250.0 a | 1225.9 ± 57.79 | 4.7 | −1.9 | |
| 1250.0 b | 1253.6 ± 97.29 | 7.8 | 0.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Baere, S.; Croubels, S.; Novak, B.; Bichl, G.; Antonissen, G. Development and Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-HR-MS Method for the Determination of Fumonisin B1 and Its Hydrolysed Metabolites and Fumonisin B2 in Broiler Chicken Plasma. Toxins 2018, 10, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020062
De Baere S, Croubels S, Novak B, Bichl G, Antonissen G. Development and Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-HR-MS Method for the Determination of Fumonisin B1 and Its Hydrolysed Metabolites and Fumonisin B2 in Broiler Chicken Plasma. Toxins. 2018; 10(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Baere, Siegrid, Siska Croubels, Barbara Novak, Gerlinde Bichl, and Gunther Antonissen. 2018. "Development and Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-HR-MS Method for the Determination of Fumonisin B1 and Its Hydrolysed Metabolites and Fumonisin B2 in Broiler Chicken Plasma" Toxins 10, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020062
APA StyleDe Baere, S., Croubels, S., Novak, B., Bichl, G., & Antonissen, G. (2018). Development and Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-HR-MS Method for the Determination of Fumonisin B1 and Its Hydrolysed Metabolites and Fumonisin B2 in Broiler Chicken Plasma. Toxins, 10(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020062







