Interacting Environmental Stress Factors Affects Targeted Metabolomic Profiles in Stored Natural Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
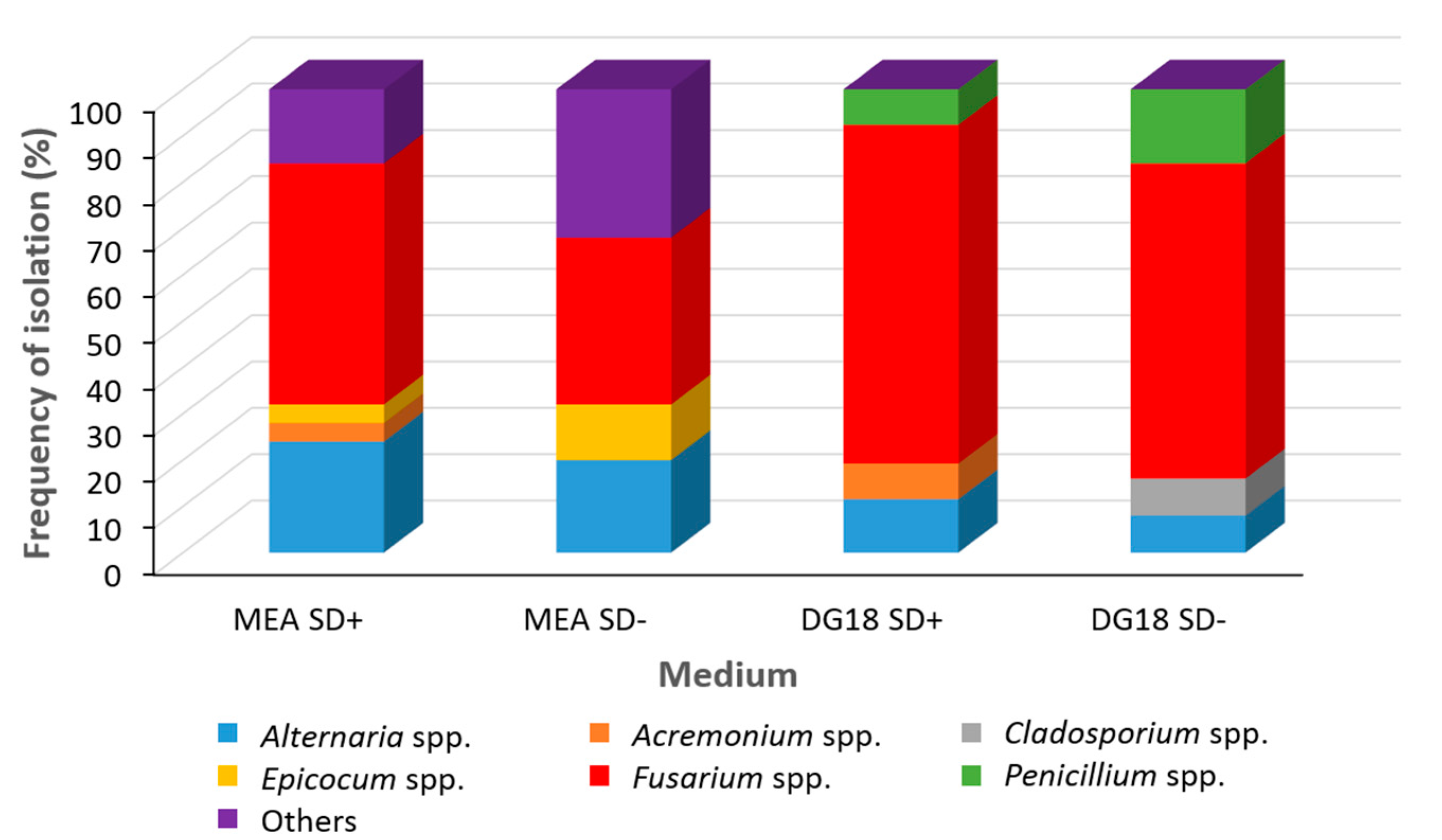
2.1. Natural Fungal Contamination
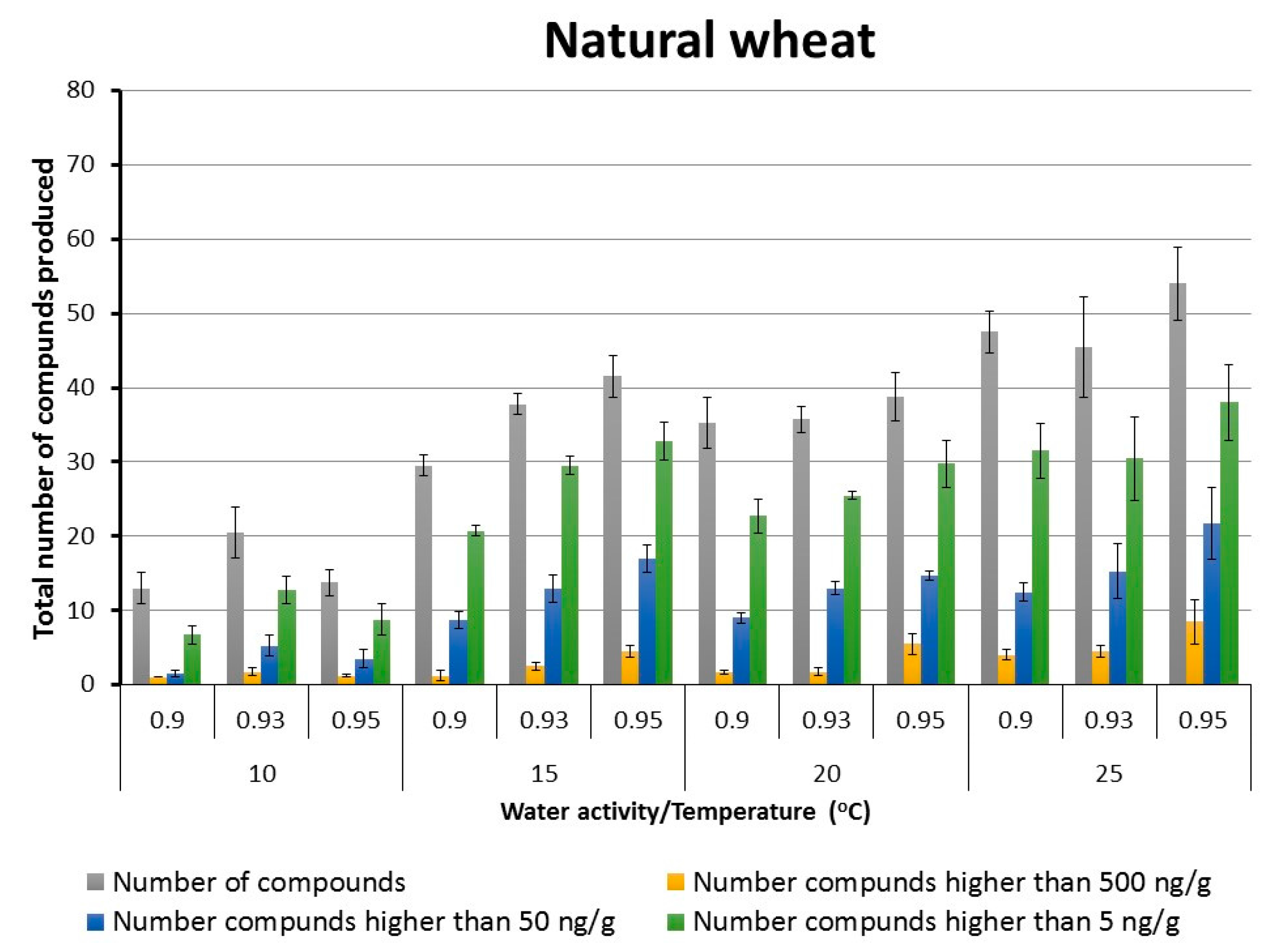
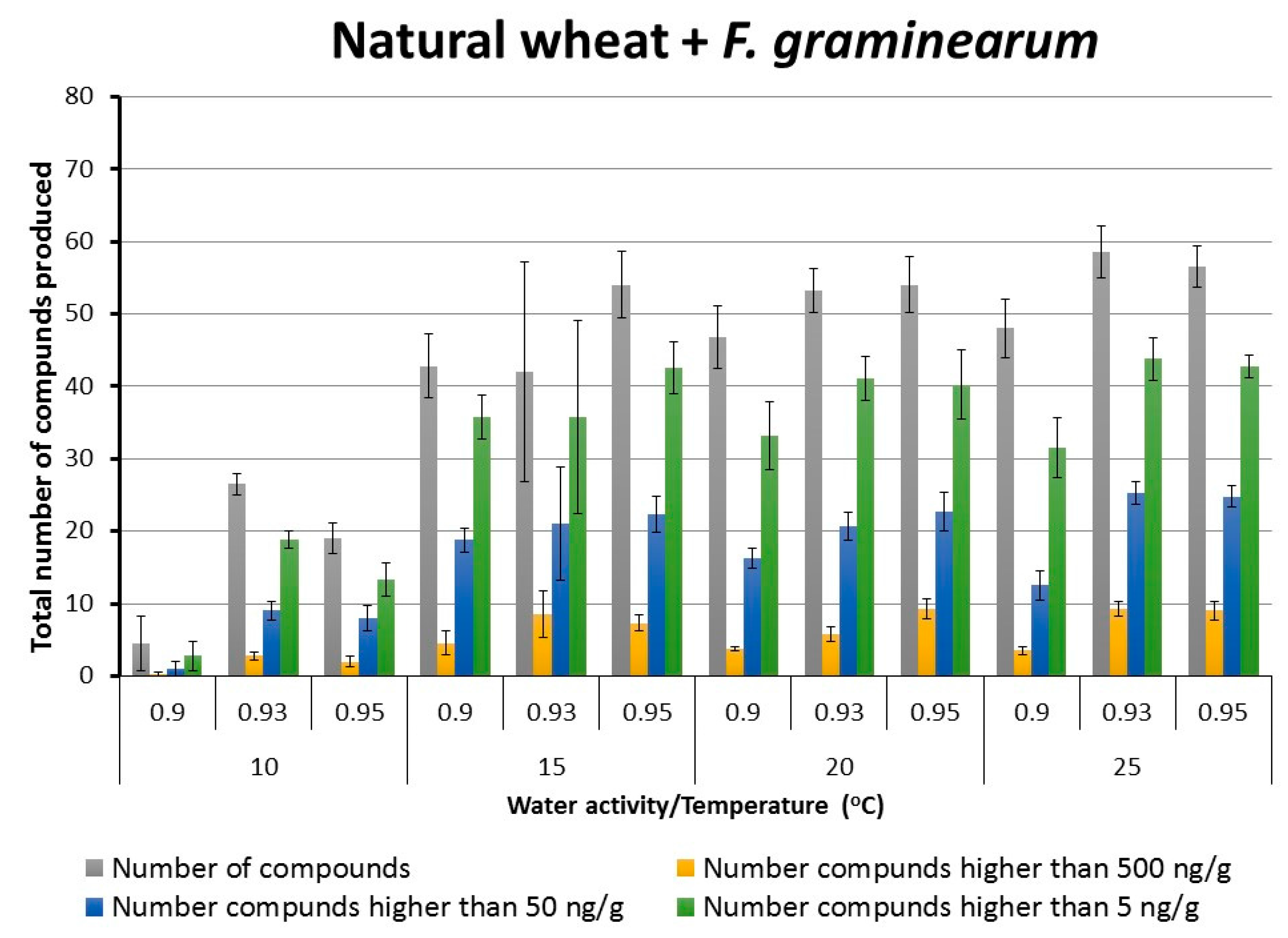
2.2. Patterns of Total Targeted Metabolite Production in Relation to Interacting Environmental Factors in Naturally Stored Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum
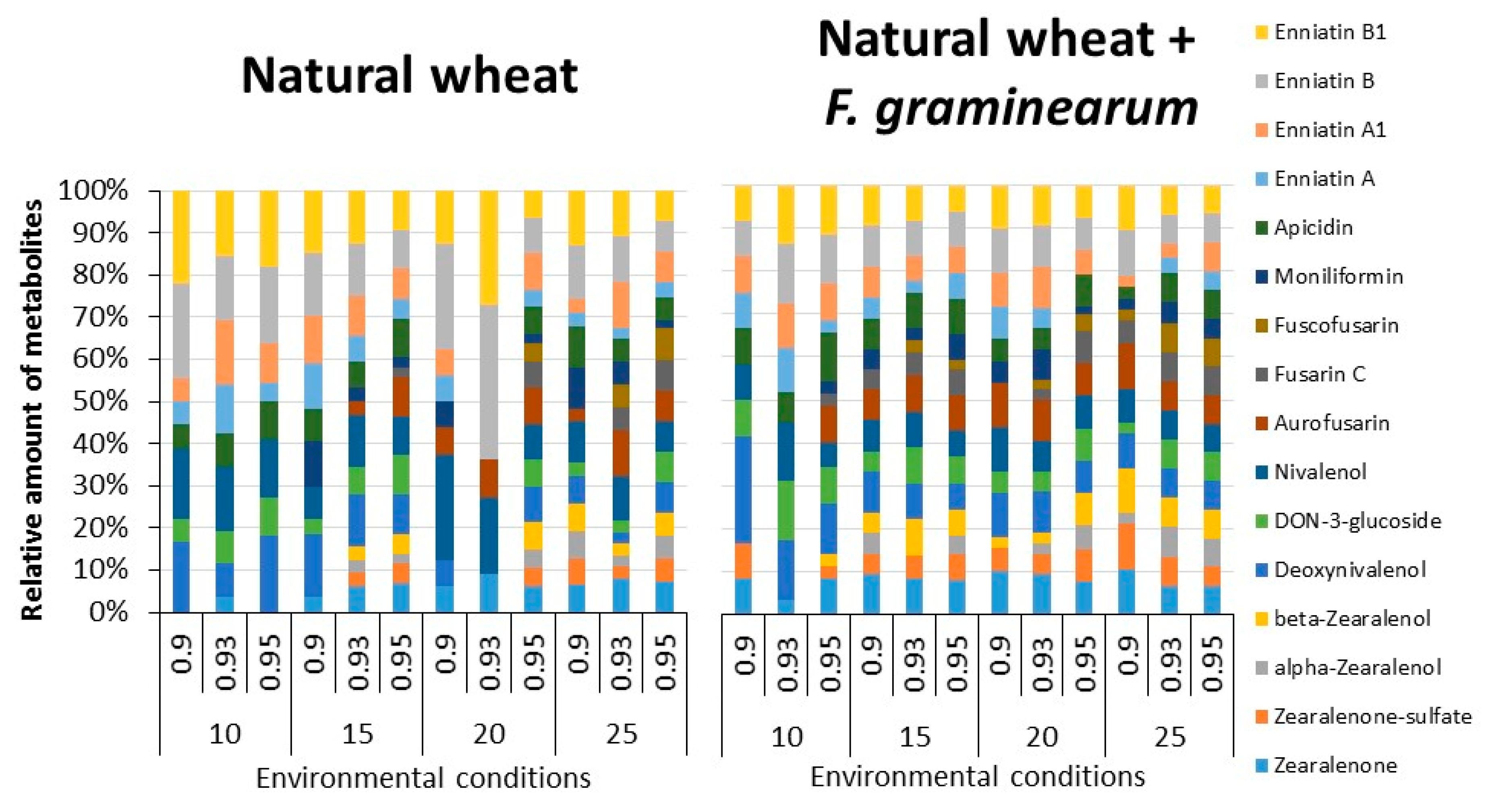
2.3. Trichothecenes, Zearalenone and Related Fusarium Metabolites in Naturally Stored Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungal Cultures
4.2. Natural Fungal Contamination
4.2.1. Enumeration of Fungi
4.2.2. Fungal Identification
4.3. Wheat Grain Moisture Content and Water Activity Adjustment
4.4. Grain Inoculation and Incubation
4.5. Secondary Metabolite Analyses
4.5.1. Sample Preparation
4.5.2. LC-MS/MS Parameters
4.6. Statistical Analysis and Modelling the Results
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | altersolanol |
| ATX-I | altertoxin-I |
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| ENNs | enniatins |
| LDA | linear discriminant analysis |
| MON | moniliformin |
| NIV | nivalenol |
| SMs | secondary metabolites |
| TEN | tentoxin |
| TCTs-B | trichothecenes type B |
| VOCs | volatile organic compounds |
| alpha-ZOL | alpha-Zearalenol |
| beta-ZOL | beta-Zearalenol |
| ZEN | zearalenone |
References
- Magan, N.; Aldred, D.; Mylona, K.; Lambert, R.J.M. Limiting mycotoxions in wheat. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, A.; Akbar, A.; Baazeem, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Magan, N. Climate change, food security and mycotoxins: Do we know enough? Fungal Biol. Rev. 2017, 31, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skaar, I.; Sulyok, M.; Liu, X.; Rao, M.; Taylor, J.W. The Microbiome and Metabolites in Fermented Pu-erh Tea as Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing and Quantitative Multiplex Metabolite Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adetunji, M.; Atanda, O.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Sulyok, M.; Warth, B.; Beltrán, E.; Krska, R.; Obadina, O.; Bakare, A.; Chilaka, C.A. Fungal and bacterial metabolites of stored maize (Zea mays L.) from five agro-ecological zones of Nigeria. Mycotoxin Res. 2014, 30, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, J.M.; Sulyok, M.; van der Westhuizen, L.; Shephard, G.S.; Frisvada, J.C.; Thrane, U.; Krska, R.; Nielsen, K.F. Single-kernel analysis of fumonisins and other fungal metabolites in maize from South African subsistence farmers. Food Addit. Contam. 2011, 28, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Britzi, M.; Zakin, V.; Kostyukovsky, M.; Trostanetsky, A.; Quinn, E.; Sionov, E. Rapid Detection and Identification of Mycotoxigenic Fungi and Mycotoxins in Stored Wheat Grain. Toxins 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laddomada, B.; Del Coco, L.; Durante, M.; Presicce, D.S.; Siciliano, P.A.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Logrieco, A.F. Volatile Metabolite Profiling of Durum Wheat Kernels Contaminated by Fusarium poae. Metabolites 2014, 4, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshri, G.; Magan, N. Detection and differentiation between mycotoxigenic and non-mycotoxigenic strains of Fusarium spp. using volatile production profiles and hydrolytic enzymes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanes, F.J.; Sahgal, N.; Magan, N. Early discrimination of fungal species responsible of ochratoxin a contamination of wine and other grape products using an electronic nose. Mycotoxin Res. 2009, 25, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, R.D.; Saei, W.; Westphal, K.R.; Klitgarrd, C.S.; Nielsen, K.L.; Lysoe, E.; Gardiner, D.M.; Wimmer, R.; Sondergaard, T.E.; Sorensen, J.L. Chrysogine biosynthesis is mediated by a two-module nonribosomal peptide synthetase. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2131–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlig, S.; Eriksen, G.S.; Hofgaard, I.S.; Krska, R.; Beltrán, E.; Sulyok, M. Faces of a Changing Climate: Semi-Quantitative Multi-Mycotoxin Analysis of Grain Grown in Exceptional Climatic Conditions in Norway. Toxins 2013, 5, 1682–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusztahelyi, T.; Holb, I.J.; Pócsi, I. Secondary metabolites in fungus-plant interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collemare, J.; Billard, A.; Böhnert, H.U.; Lebrun, M.-H. Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthegrisea: The role of hybrid PKS-NRPS in pathogenicity. Mycol. Res. 2008, 112, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Magan, N.; Geisen, R. Stress induction of mycotoxin biosynthesis genes in relation to abiotic factors. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 284, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Parra, R.; Geisen, R.; Magan, N. Modelling the relationship between environmental factors, transcriptional genes and deoxynivalenol mycotoxin production by two Fusarium species. J. R. Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magan, N.; Aldred, D.; Hope, R.; Mitchell, D. Environmental factors and interactions with mycoflora of grain and grapes: Effects on growth and deoxynivalenol and ochratoxin a production by Fusarium culmorum and Aspergillus carbonarius. Toxins 2010, 2, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magan, N.; Aldred, D. Environmental fluxes and fungal interactions: Maintaining a competitive edge. In Stress in Yeasts and Filamentous Fungi; Van West, P., Avery, S., Stratford, M., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Magan, N.; Aldred, D. Why to fungi produce mycotoxins? In Food Mycology: A Multifaceted Approach to Fungi and Food; Dijksterhuis, J., Samson, R.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad, M.; Johnsson, P.; Jonsson, N.; Lindqvist, R.; Olsen, M. Predicting non-compliant levels of ochratoxin A in cereal grain from Penicillium verrucosum counts. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.A.; Houbraken, J.; Thrane, U.; Frisvad, J.C.; Anderson, B. Food and Indoor Fungi; CBS, Fungal Biodiversity Centre: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Malachová, A.; Sulyok, M.; Beltrán, E.; Berthiller, F.; Krska, R. Optimization and validation of a quantitative liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric method covering 295 bacterial and fungal metabolites including all regulated mycotoxins in four model food matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malachova, A.; Michael, S.; Beltran, E.; Berthiller, F.; Krska, R. Multi-Toxin Determination in Food—The Power of Dilute and Shoot Approaches in LC–MS–MS. LCGC Eur. 2015, 28, 542–555. [Google Scholar]
| T (°C) | aw | Natural Wheat | Natural Wheat + F. graminearum | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZEN 1 | Alpha-ZOL 2 | Beta-ZOL 3 | Total Sum | ZEN 1 | Alpha-ZOL 2 | Beta-ZOL 3 | Total Sum | ||
| 10 | 0.9 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0 |
| 0.93 | 6.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 6.0 | 25.5 | <LOD | <LOD | 25.5 | |
| 0.95 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.0 | 1.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 1.0 | |
| 15 | 0.9 | 16.7 | <LOD | <LOD | 16.7 | 195.9 | 2.6 | 12.0 | 210.4 |
| 0.93 | 18.5 | 1.1 | 3.6 | 23.1 | 551.8 | 2.7 | 7.4 | 561.9 | |
| 0.95 | 131.9 | 1.2 | 6.7 | 139.7 | 241.9 | 2.9 | 8.2 | 252.9 | |
| 20 | 0.9 | 0.5 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.5 | 110.9 | <LOD | 3.2 | 114.1 |
| 0.93 | 1.0 | <LOD | <LOD | 1.0 | 11.4 | <LOD | <LOD | 11.4 | |
| 0.95 | 777.5 | 13.3 | 51.9 | 842.6 | 810.2 | 9.1 | 35.7 | 855.1 | |
| 25 | 0.9 | 112.5 | 2.8 | 16.3 | 131.6 | 382.6 | 8.5 | 16.4 | 407.5 |
| 0.93 | 1536.9 | 19.9 | 84.9 | 1641.7 | 1489.7 | 13.3 | 81.5 | 1584.5 | |
| 0.95 | 1167.8 | 15.6 | 59.7 | 1243.1 | 1461.4 | 11.4 | 78.3 | 1551.1 | |
| T (°C) | aw | Natural Wheat | Natural Wheat + F. graminearum | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DON 1 | DON-3-Glucoside 2 | NIV 3 | Total TCTs-B 4 | DON 1 | DON-3-Glucoside 2 | NIV 3 | Total TCTs-B 4 | ||
| 10 | 0.9 | 26.2 | 5.2 | 15.1 | 46.5 | 11.5 | 0.5 | 9.9 | 22.0 |
| 0.93 | 105.8 | 1.2 | 23.9 | 130.9 | 112.3 | 4.7 | 31.2 | 148.2 | |
| 0.95 | 25.4 | 3.9 | 14.4 | 43.7 | 257.8 | 29.7 | 23.0 | 310.5 | |
| 15 | 0.9 | 75.4 | 1.7 | 35.2 | 112.3 | 102.8 | 13.5 | 17.9 | 134.1 |
| 0.93 | 98.7 | 9.0 | 15.7 | 123.4 | 1266.2 | 28.2 | 78.7 | 1373.1 | |
| 0.95 | 718.4 | 10.7 | 77.7 | 806.8 | 1325.1 | 53.5 | 49.2 | 1427.8 | |
| 20 | 0.9 | 4.6 | <LOD | 15.0 | 19.6 | 100.2 | 3.3 | 20.1 | 123.6 |
| 0.93 | <LOD | <LOD | 32.9 | 32.9 | 89.1 | 18.4 | 11.2 | 118.6 | |
| 0.95 | 806.2 | 33.7 | 34.3 | 874.2 | 2003.1 | 77.9 | 122.0 | 2203.1 | |
| 25 | 0.9 | 113.6 | 5.8 | 8.8 | 128.2 | 26.5 | 3.2 | 15.5 | 45.3 |
| 0.93 | 117.3 | 5.2 | 23.3 | 145.8 | 761.6 | 25.5 | 85.5 | 872.5 | |
| 0.95 | 619.6 | 18.8 | 213.8 | 852.2 | 1265.6 | 53.7 | 261.3 | 1580.6 | |
| T (°C) | aw | Natural Wheat | Natural Wheat + F. graminearum | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENN A 1 | ENN A1 2 | ENN B 3 | ENN B1 4 | Total ENNs 5 | ENN A 1 | ENN A1 2 | ENN B 3 | ENN B1 4 | Total ENNs | ||
| 10 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 3.0 | <LOD | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 2.9 |
| 0.93 | 0.5 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 7.7 | 16.0 | 0.8 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 7.5 | 15.7 | |
| 0.95 | 10.3 | 32.3 | 5.1 | 21.7 | 69.3 | <LOD | 0.7 | 15.9 | 4.7 | 21.2 | |
| 15 | 0.9 | 6.1 | 76.0 | 64.8 | 145.8 | 292.7 | 13.4 | 100.6 | 74.9 | 175.9 | 364.8 |
| 0.93 | 0.6 | 3.9 | 5.6 | 9.4 | 19.4 | 2.0 | 18.4 | 36.0 | 52.9 | 109.3 | |
| 0.95 | 2.6 | 22.9 | 26.3 | 49.7 | 101.5 | 2.0 | 27.2 | 37.5 | 62.9 | 129.6 | |
| 20 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 5.3 | 1.2 | 5.8 | 12.8 | 0.3 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 7.2 | 13.5 |
| 0.93 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 4.6 | 16.4 | 19.4 | 40.8 | |
| 0.95 | 4.3 | 16.4 | 14.0 | 38.4 | 73.1 | 14.1 | 63.1 | 116.2 | 205.9 | 399.3 | |
| 25 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 4.6 | 2.0 | 3.6 | 10.6 | <LOD | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.9 |
| 0.93 | 0.9 | 4.3 | 9.5 | 15.8 | 30.5 | 11.9 | 105.1 | 62.9 | 71.6 | 251.4 | |
| 0.95 | 38.9 | 174.3 | 125.7 | 304.4 | 643.3 | 2.5 | 37.1 | 185.6 | 177.5 | 402.7 | |
| T (°C) | aW | Natural Wheat | Natural Wheat + F. graminearum | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apicidin | MON 1 | Aurofusarin | Fusarin C | 5-Hydroxy Culmorin | Chrysogine | Apicidin | MON 1 | Aurofusarin | Fusarin C | 5-Hydroxy Culmorin | Chrysogine | ||
| 10 | 0.9 | 0.9 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.2 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 7.9 |
| 0.93 | 2.9 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 13.3 | 17.0 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 29.7 | |
| 0.95 | 9.5 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 12.4 | 4.7 | <LOD | 254.0 | 18.7 | 254.1 | 7.1 | |
| 15 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 183.2 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 7.2 | 12.3 | 16.4 | 628.2 | 38.5 | <LOD | 24.4 |
| 0.93 | 13.7 | 18.6 | 914.3 | <LOD | <LOD | 24.9 | 27.1 | 276.6 | 3402.0 | 46.0 | 430.7 | 20.2 | |
| 0.95 | 12.2 | 68.5 | 2945.7 | 25.0 | 677.6 | 20.4 | 25.5 | 11.3 | 11,672.0 | 43.8 | 708.4 | 16.8 | |
| 20 | 0.9 | <LOD | 2.9 | 91.2 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 6.0 | 12.2 | 1343.6 | <LOD | <LOD | 71.4 |
| 0.93 | <LOD | <LOD | 61.0 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 13.2 | 19.7 | 1107.4 | <LOD | <LOD | 65.4 | |
| 0.95 | 45.8 | 5.4 | 9759.3 | 117.4 | <LOD | 10.5 | 53.9 | 245.3 | 6795.0 | 33.7 | <LOD | 46.5 | |
| 25 | 0.9 | 7.6 | 11.5 | 6.3 | <LOD | <LOD | 14.9 | 4.3 | <LOD | 337.3 | 71.6 | <LOD | 10.5 |
| 0.93 | 15.4 | 15.4 | 686.0 | 165.0 | <LOD | 32.5 | 9.9 | 65.7 | 9126.7 | 293.7 | <LOD | 24.8 | |
| 0.95 | 4.6 | 104.8 | 6912.1 | 797.2 | <LOD | 8.8 | 132.0 | 225.8 | 17,405.3 | 748.2 | <LOD | 24.7 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Cela, E.; Kiaitsi, E.; Medina, A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Magan, N. Interacting Environmental Stress Factors Affects Targeted Metabolomic Profiles in Stored Natural Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum. Toxins 2018, 10, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020056
Garcia-Cela E, Kiaitsi E, Medina A, Sulyok M, Krska R, Magan N. Interacting Environmental Stress Factors Affects Targeted Metabolomic Profiles in Stored Natural Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum. Toxins. 2018; 10(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Cela, Esther, Elisavet Kiaitsi, Angel Medina, Michael Sulyok, Rudolf Krska, and Naresh Magan. 2018. "Interacting Environmental Stress Factors Affects Targeted Metabolomic Profiles in Stored Natural Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum" Toxins 10, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020056
APA StyleGarcia-Cela, E., Kiaitsi, E., Medina, A., Sulyok, M., Krska, R., & Magan, N. (2018). Interacting Environmental Stress Factors Affects Targeted Metabolomic Profiles in Stored Natural Wheat and That Inoculated with F. graminearum. Toxins, 10(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020056





