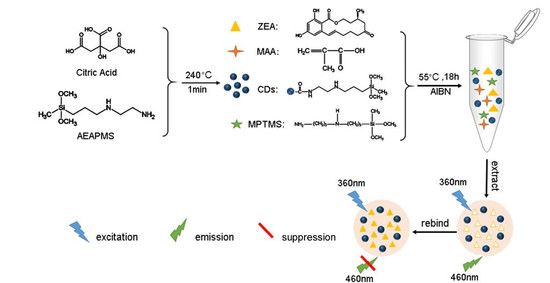
Carbon Quantum Dots Encapsulated Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Quenching Particles for Sensitive Detection of Zearalenone in Corn Sample
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
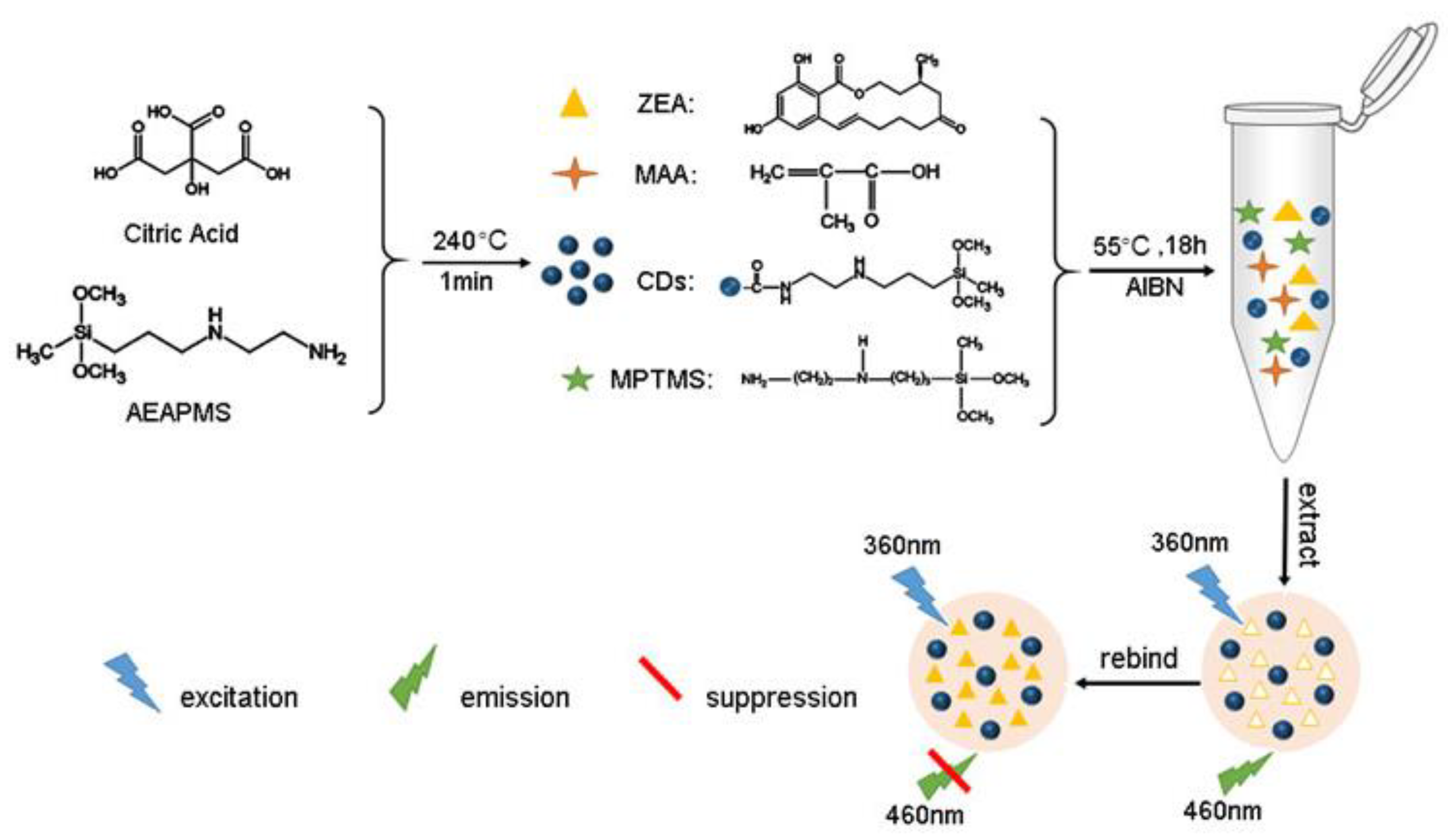
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of CDs
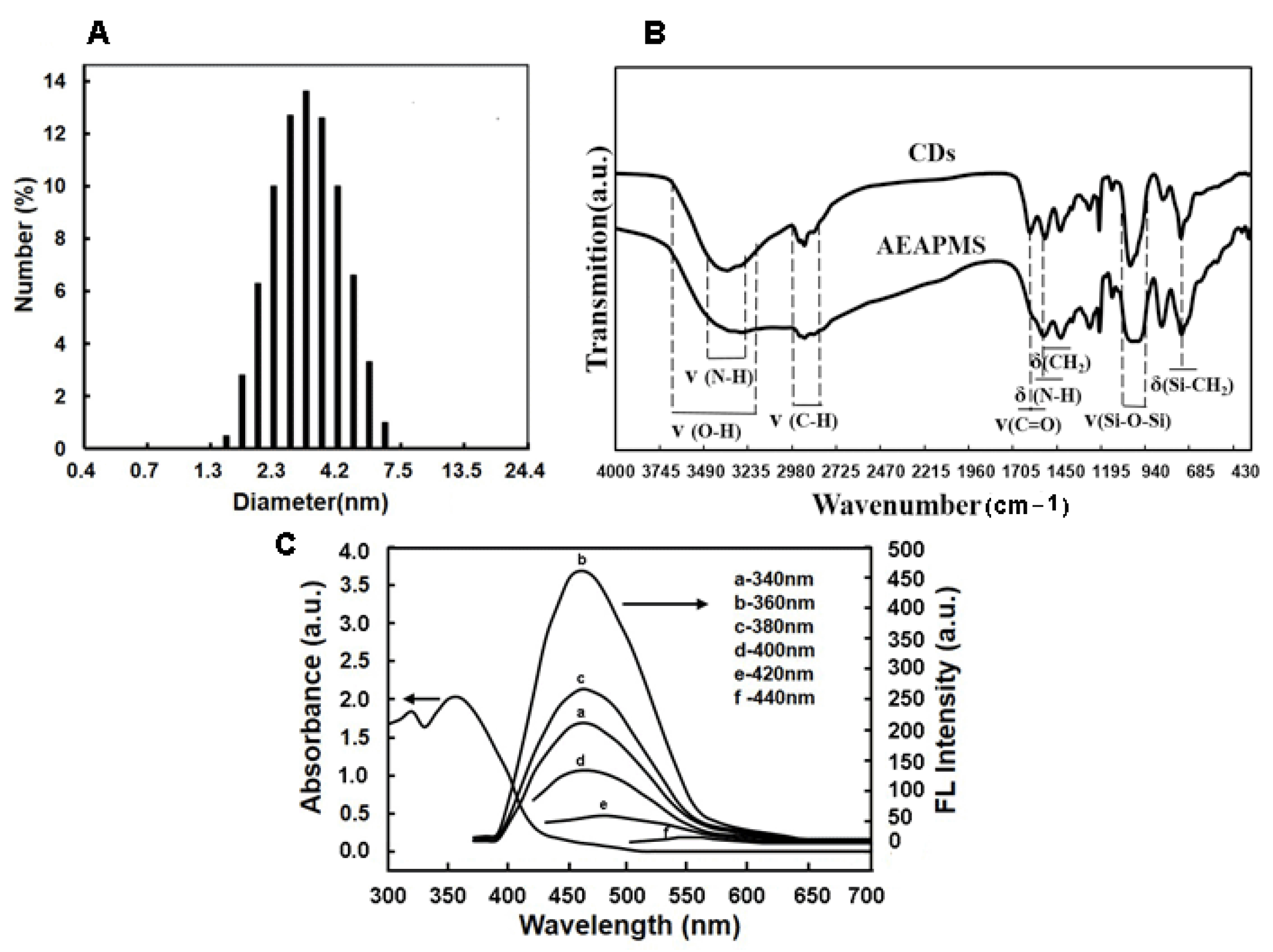
2.2. MIFQP Preparation and Characterization
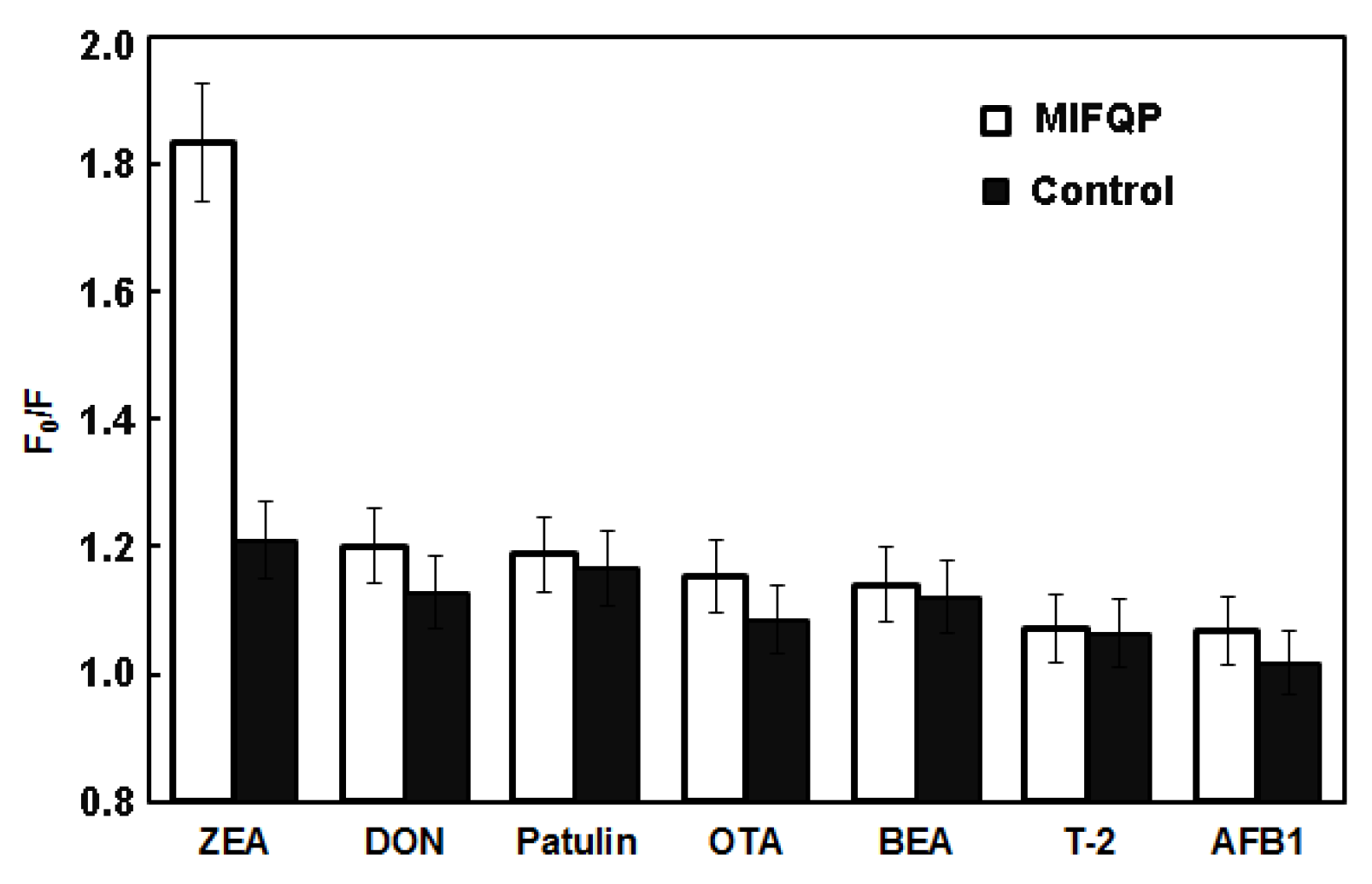
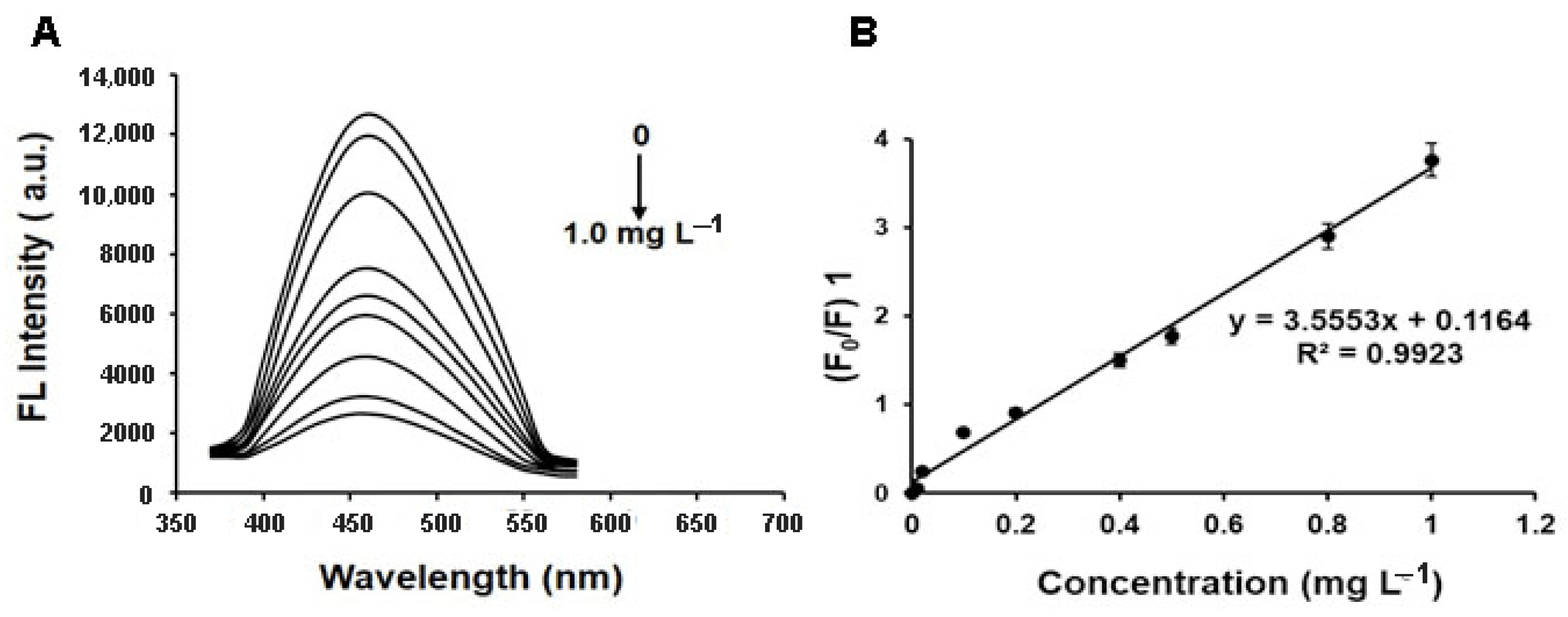
2.3. Selectivity and Sensitivity of MIFQP Experiments
2.4. Validation and Application of MIFQP
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instruments and Measurements
4.3. CDs and MIFQP Synthesis
4.4. FL Measurements
4.5. Sample Pretreatment
4.6. Method Validation and Quality Assurance
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, S.; Huang, X.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y. Novel fluorescent ELISA for the sensitive detection of zearalenone based on H2O2-sensitive quantum dots for signal transduction. Talanta 2016, 158, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, S.; Foster, J.S.; Bukovsky, A.; Wimalasena, J. Signal transduction through the Ras/Erk pathway is essential for the mycoestrogen zearalenone-induced cell-cycle progression in MCF-7 cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2001, 30, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañes, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shier, W.T.; Xie, W.M.C.; Shier, A.C. Structure-activity relationships for human estrogenic activity in zearalenone mycotoxins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiani, M.R.; Yazdanpanah, H.; Ghazikhansari, M.; Cheraghali, A.M.; Goodarzi, M. Survey of the natural occurrence of zearalenone in maize from northern Iran by thin-layer chromatography densitometry. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.C.; Lee, W.J.; Zhang, G.P.; Hu, X.F.; Eremin, S.A.; Zhang, L.J. Development of anti-zearalenone monoclonal antibody and detection of zearalenone in corn products from China by ELISA. Food Control 2013, 31, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, H.E.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, M.; Chun, H.S. HPLC and UPLC methods for the determination of zearalenone in noodles, cereal snacks and infant formula. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songsermsakul, P.; Sontag, G.; Cichnamarkl, M.; Zentek, J.; Razzazifazeli, E. Determination of zearalenone and its metabolites in urine, plasma and faeces of horses by HPLC-APCI-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 843, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Guo, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Yue, T. Development and application of a method for the analysis of 9 mycotoxins in maize by HPLC-MS/MS. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.W.; Subrahmanyam, S.; Piletsky, S.A. Analytical methods for determination of mycotoxins: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Han, D.; Li, F.; Niu, L. Efficient one-pot synthesis of molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded carbon dots for fluorescent dopamine optosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.R.; Ni, Y.L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, J. Detection of glycoprotein through fluorescent boronic acid-based molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Papageorgiou, M.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Preparation of molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction fiber for the selective removal and extraction of the antiviral drug abacavir in environmental and biological matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 913, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltini, A.; Scalabrini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Sturini, M.; Profumo, A. Newest applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of contaminants from environmental and food matrices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechichi, A.; Cristallini, C.; Vitale, U.; Ciardelli, G.; Barbani, N.; Vozzi, G.; Giusti, P. New biomedical devices with selective peptide recognition properties. Part 1: Characterization and cytotoxicity of molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, I.; Chiono, V.; Vozzi, G.; Ciardelli, G.; Silvestri, D.; Giusti, P. Molecularly imprinted submicronspheres for applications in a novel model biosensor-film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habimana, J.D.D.; Ji, J.; Pi, F.; Karangwa, E.; Sun, J.; Guo, W.; Cui, F.; Shao, J.; Ntakirutimana, C.; Sun, X. A Class-specific Artificial Receptor-Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated Quantum Dot centers for the Detection of signaling molecules, N-Acyl-homoserine Lactones Present in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1031, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñezsedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical sensors based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.B.; Tang, Q.; Gong, C.B.; Lam, M.H. Review of the recent progress in photoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymers containing azobenzene chromophores. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 900, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Mosbach, K. Influence of mobile phase composition and cross-linking density on the enantiomeric recognition properties of molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 888, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.Z.; Tan, J.; Yan, X.P. An ion-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique combined with a sol-gel process for selective solid-phase extraction of cadmium(II). Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.L.; Carlson, C.A.; Edmiston, P.L. Development and characterization of molecularly imprinted sol-gel materials for the selective detection of DDT. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.F.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Yan, X.P.; Gao, R.Y.; Zheng, J.Y. A Room Temperature Ionic Liquid (RTIL)-Mediated, Non-Hydrolytic Sol–Gel Methodology to Prepare Molecularly Imprinted, Silica-Based Hybrid Monoliths for Chiral Separation. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3266–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lei, Y. Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2Nd, P.T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.H. Quantum dots in diagnostics and detection: Principles and paradigms. Analyst 2014, 139, 2968–2981. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisavljevic, M.; Krizkova, S.; Vaculovicova, M.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Quantum dots-fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based nanosensors and their application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foubert, A.; Beloglazova, N.V.; Saeger, S.D. Comparative study of colloidal gold and quantum dots as labels for multiplex screening tests for multi-mycotoxin detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 955, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himaja, A.L.; Karthik, P.S.; Singh, S.P. Carbon Dots: The Newest Member of the Carbon Nanomaterials Family. Chem. Rec. 2015, 15, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosconi, D.; Mazzier, D.; Silvestrini, S.; Privitera, A.; Marega, C.; Franco, L.; Moretto, A. Synthesis and Photochemical Applications of Processable Polymers Enclosing Photoluminescent Carbon Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4156–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Pang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Kreiter, M.; Liu, C. One-Step Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Carbon Dots in Noncoordinating Solvents. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4528–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, Z.B.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Shi, G. A novel composite of graphene quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer for fluorescent detection of paranitrophenol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zor, E.; Morales-Narvaez, E.; Zamora-Galvez, A.; Bingol, H.; Ersoz, M.; Merkoci, A. Graphene Quantum Dots-based Photoluminescent Sensor: A Multifunctional Composite for Pesticide Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20272–20279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Valcarcel, M. Semiconductor and carbon-based fluorescent nanodots: The need for consistency. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Zou, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhan, Z.; Zhao, S. Green preparation of fluorescent carbon dots from lychee seeds and their application for the selective detection of methylene blue and imaging in living cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6783–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gao, N.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Recent advances in bioapplications of C-dots. Carbon 2015, 85, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.G. Highly Luminescent Organosilane-Functionalized Carbon Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhuang, J.; Guan, S.; Yang, W. Synthesis of robust water-soluble ZnS:Mn/SiO 2 core/shell nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Lu, F.; Meziani, M.J.; Li, H.; Qi, G.; Zhou, B.; Harruff, B.A.; Kermarrec, F.; Sun, Y.P. Photoinduced electron transfers with carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2009, 46, 3774–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.F.; He, Y.; Ji, T.R.; Yan, X.P. Surface molecular imprinting on Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for room-temperature phosphorescence optosensing of pentachlorophenol in water. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H. Mesoporous structured MIPs@CDs fluorescence sensor for highly sensitive detection of TNT. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ren, S.; Shao, M.; De Saeger, S.; Song, S.; Yan, L. A competitive immunoassay for zearalenone with integrated poly(dimethysiloxane) based microarray assay. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4036–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Concentration of ZEA (mg L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSDr | RSDR | LOD (mg L−1) | LOQ (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 105.1 | 13.3 | 16.3 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 78.2 | 10.1 | 14.1 | ||
| 3 | 0.8 | 90.7 | 8.7 | 12.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, M.; Yao, M.; Saeger, S.D.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Carbon Quantum Dots Encapsulated Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Quenching Particles for Sensitive Detection of Zearalenone in Corn Sample. Toxins 2018, 10, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110438
Shao M, Yao M, Saeger SD, Yan L, Song S. Carbon Quantum Dots Encapsulated Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Quenching Particles for Sensitive Detection of Zearalenone in Corn Sample. Toxins. 2018; 10(11):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110438
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Manyu, Ming Yao, Sarah De Saeger, Liping Yan, and Suquan Song. 2018. "Carbon Quantum Dots Encapsulated Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Quenching Particles for Sensitive Detection of Zearalenone in Corn Sample" Toxins 10, no. 11: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110438
APA StyleShao, M., Yao, M., Saeger, S. D., Yan, L., & Song, S. (2018). Carbon Quantum Dots Encapsulated Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Quenching Particles for Sensitive Detection of Zearalenone in Corn Sample. Toxins, 10(11), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110438