Molecular Modeling Studies on the Interactions of Aflatoxin B1 and Its Metabolites with Human Acetylcholinesterase. Part II: Interactions with the Catalytic Anionic Site (CAS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
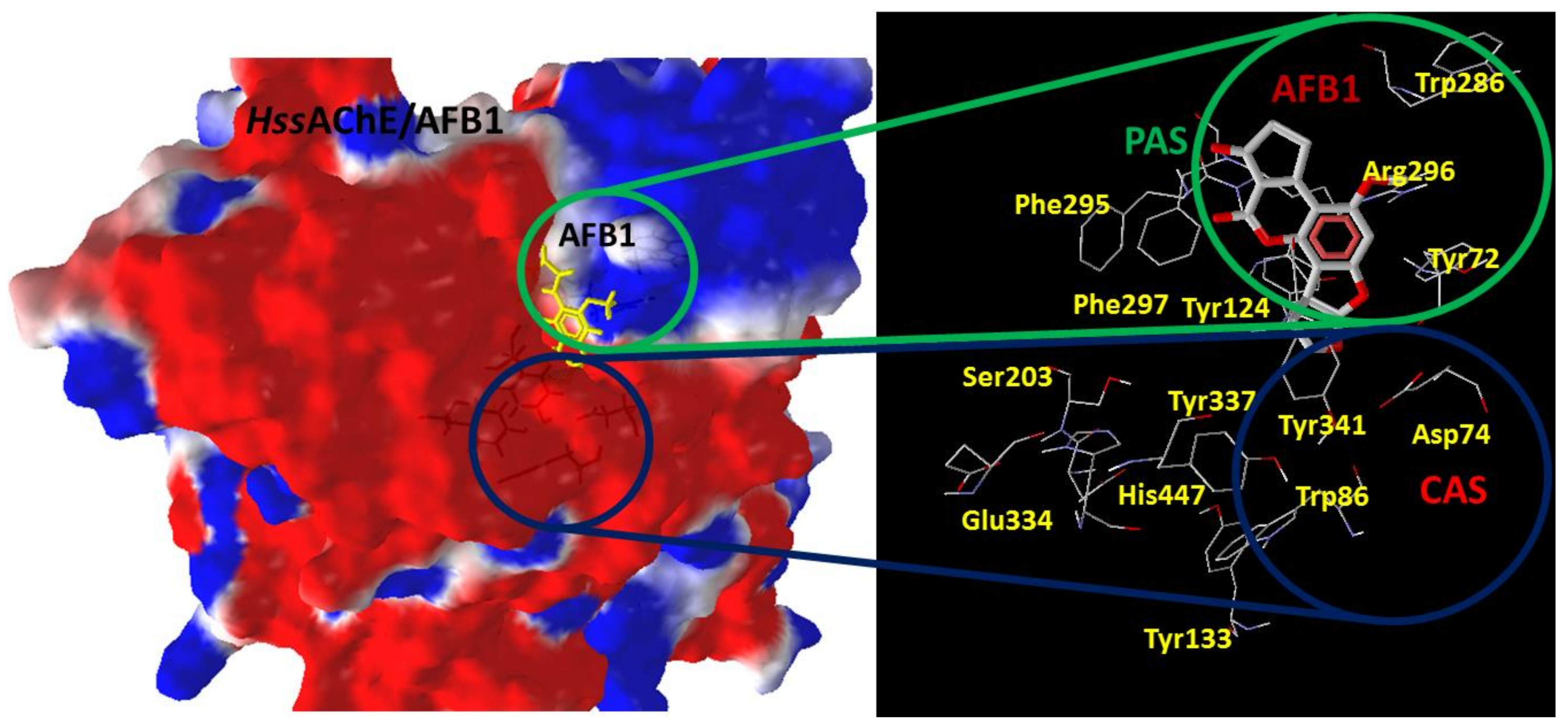
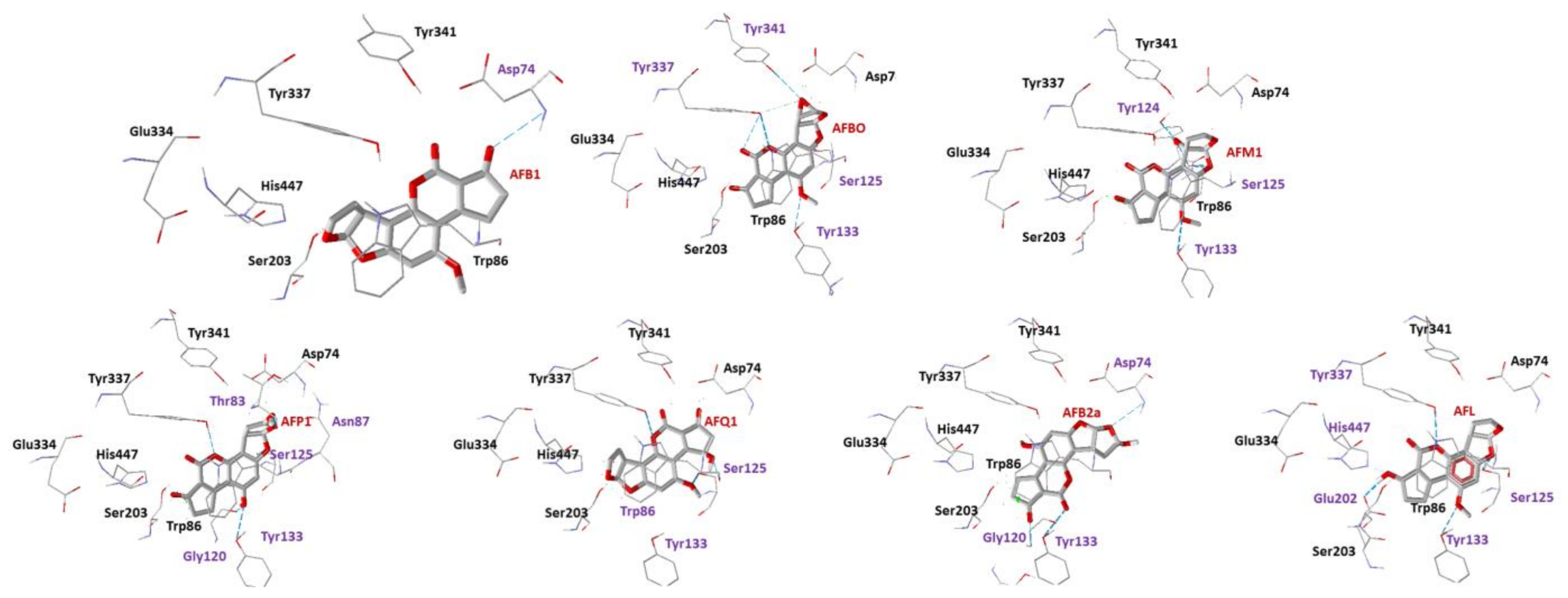
2.1. Docking Studies
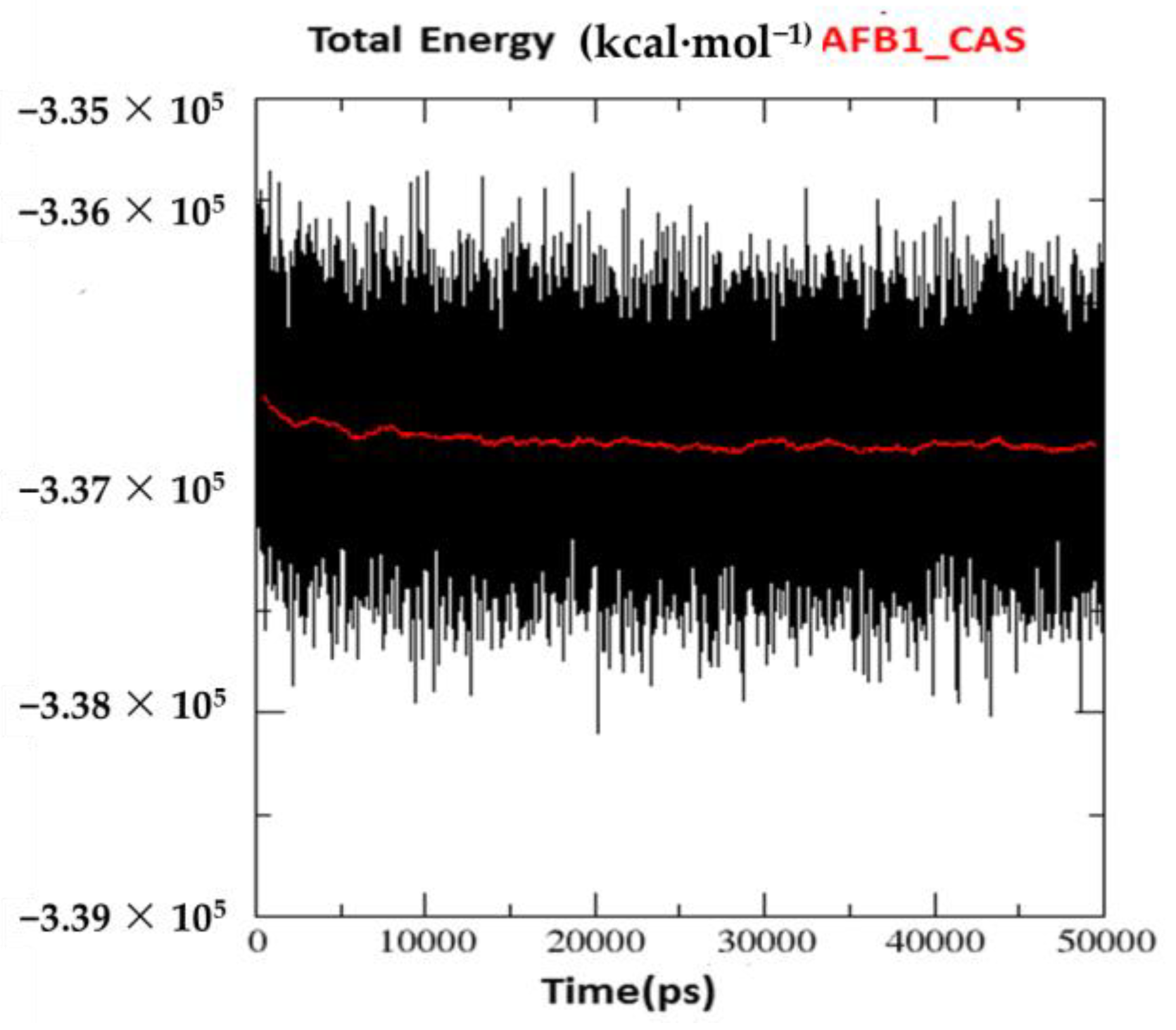
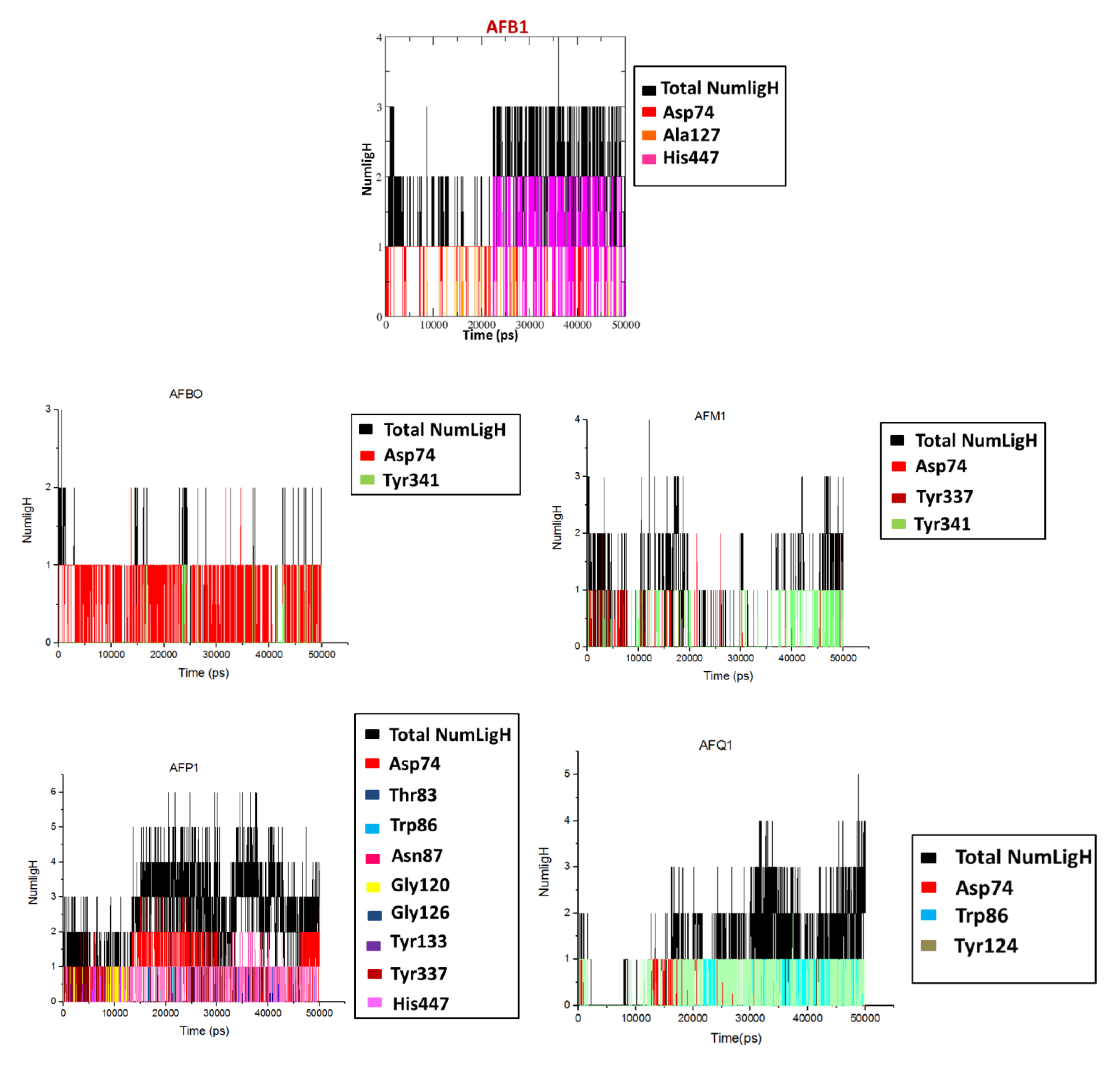
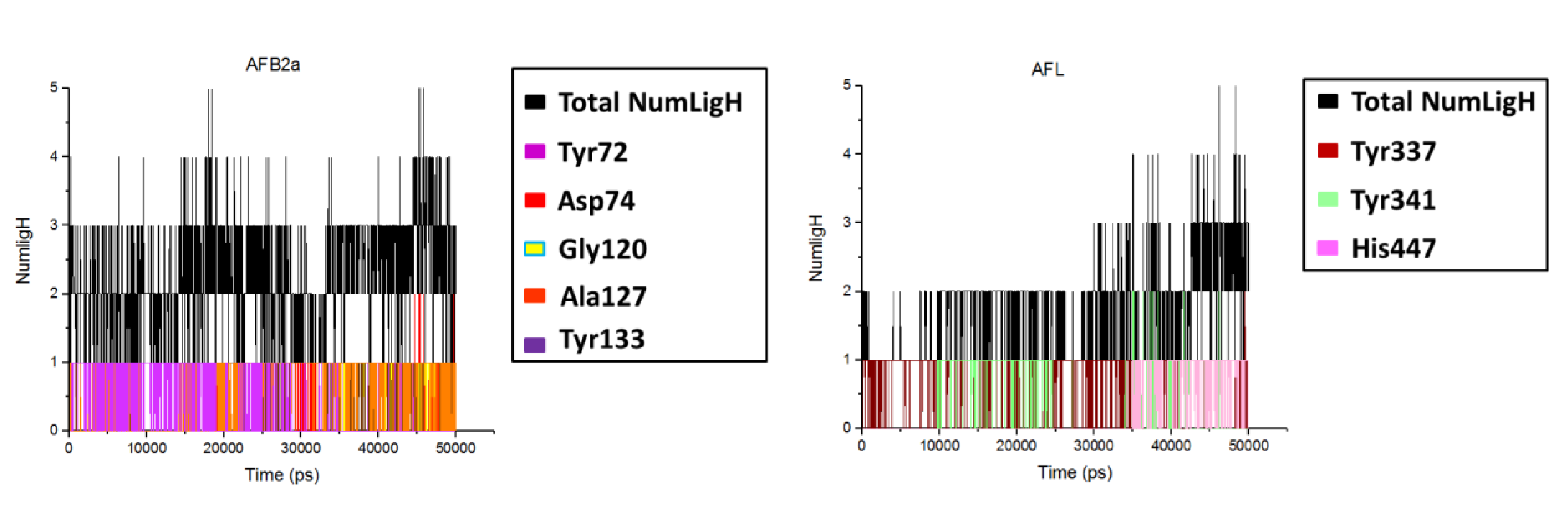
2.2. Molecular Dynamics
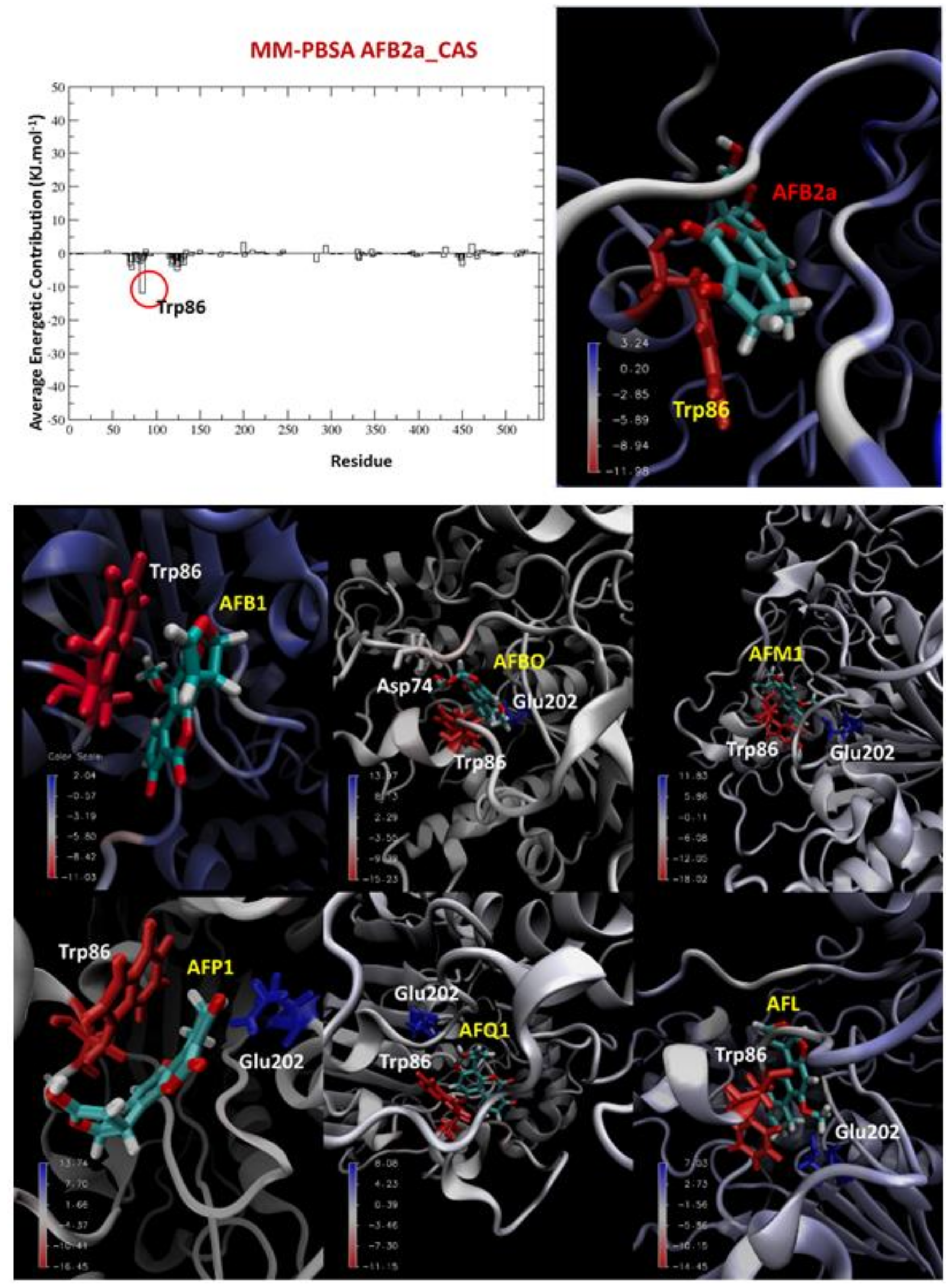
2.3. MM-PBSA Calculations
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Docking Energy Calculations
4.2. Molecular Dynamics and Free Energy Calculations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shotwell, O.L. Aflatoxins. Clin. Microbiol. News 1983, 5, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, R.A. Ranking animal carcinogens: A proposed regulatory approach. Science 1989, 214, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jezkova, A.; Yuan, Z.; Pavlikova, L.; Dohnal, V.; Kuca, K. Biological degradation of aflatoxins. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathway, D.E. Toxic action/toxicity. Biol. Rev. 2000, 75, 95–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohnal, V.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Metabolism of aflatoxins: Key enzymes and interindividual as well as interspecies differences. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldatkin, O.O.; Burdak, O.S.; Sergeyeva, T.A.; Arkhypova, V.M.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Acetylcholinesterase-based conductometric biosensor for determination of aflatoxin B1. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2013, 188, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepurska, K.V.; Soldatkin, O.O.; Arkhypova, V.M.; Soldatkin, A.P.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Dzyadevych, S.V. Development of novel enzyme potentiometric biosensor based on pH-sensitive field-effect transistors for aflatoxin B1 analysis in real samples. Talanta 2015, 144, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egnibuke, G.N.; Ikegwuonu, F.I. Effect of aflatoxicosis on acetylcholinesterase activity in the brain and adenohypophysis on male rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 52, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Cometa, M.F.; Lorenzinia, P.; Fortunaa, S.; Volpea, M.T.; Meneguza, A.; Palmeryb, M. In vitro inhibitory effect of aflatoxin B1 on acetylcholinesterase activity in mouse brain. Toxicology 2005, 206, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansmann, T.; Sanson, B.; Stojan, J.; Weik, M.; Marty, J.; Fournier, D. Kinetic insight into mechanism of cholinesterase inhibition by aflatoxin B1 to develop biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.S.F.D.; Cavalcante, S.F.A.; Dolezal, R.; Kuca, K.; Musilek, K.; Jun, D.; França, T.C.C. Molecular modeling studies on the interactions of aflatoxin B1 and its metabolites with the pheripheral anionic site (PAS) of human acetylcholinesterase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Sanson, B.; Colletier, J.; Xu, Y.; Lang, P.T.; Jiang, H.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L.; Weik, M. Backdoor opening mechanism in acetylcholinesterase based on X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulations. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Bursthteyn, M.S.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehre, W.J.; Deppmeier, B.J.; Klunzinger, P.E. PC Spartan Pro molecular modeling for desktop. Chem. Eng. News 1999, 77, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, G.B.; Freire, R.O.; Simas, A.M.; Stewart, J.J.P. RM1: A Reparameterization of AM1 for H, C, N, O, P, S, F, Cl, Br, and I. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A New Technique for High-Accuracy Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1996, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Pall, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. Softw. X 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.W.S.; Vranken, W.F. ACPYPE—Antechamber Python Parser Interface. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranken, W.F.; Boucher, W.; Stevens, T.J.; Vogh, R.H.; Pajon, A.; Llinas, M.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Ionides, J.; Laue, E.D. The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: Development of a software pipeline. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 59, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.A.S.T.; Horta, B.A.C.; de Alencastro, R.B. MKTOP: A program for automatic construction of molecular topologies. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 1433–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.S.F.D.; Cuya Guizado, T.R.; Guimarães, A.P.; Ramalho, T.C.; Gonçalves, A.S.; de Koning, M.C.; França, T.C.C. Docking and molecular dynamics studies of peripheral site ligand-oximes as reactivators of sarin-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 2632–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD-Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; DeLano Scientific: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Lynn, A. g_mmpbsa—A GROMACS Tool for High-Throughput MM-PBSA Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
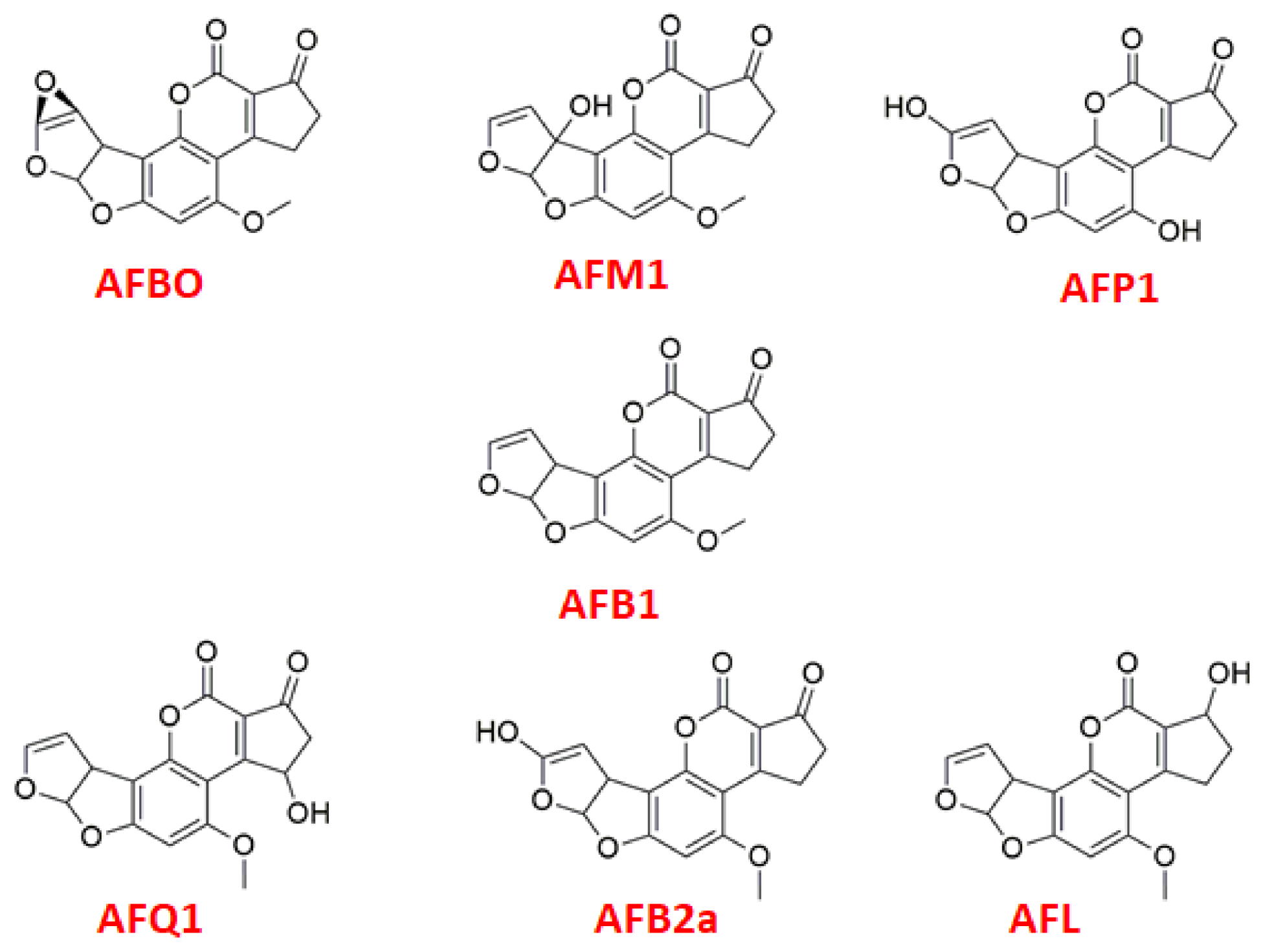


| Ligand | EInteraction (kcal·mol−1) CAS | H-Bond Interactions CAS | EH-Bond (kcal·mol−1) CAS | EInteraction (kcal·mol−1) PAS [12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | −141.95 | Asp74 | −0.77 | −56.68 |
| AFBO | −137.73 | Ser125 Tyr133 Tyr337 Tyr341 | −8.82 | −107.68 |
| AFM1 | −140.00 | Tyr124 Ser125 Tyr133 | −8.63 | −117.75 |
| AFP1 | −146.87 | Asp74 Thr83 Asn87 Gly120 Ser125 Tyr133 Tyr337 | −15.21 | −96.47 |
| AFQ1 | −146.17 | Trp86 Ser125 Tyr337 | −7.09 | −104.67 |
| AFB2a | −140.39 | Asp74 Gly120 Tyr133 | −3.48 | −94.32 |
| AFL | −137.98 | Ser125 Tyr133 Glu202 Tyr337 His447 | −7.60 | −102.69 |
| Ligand | Number of H-Bonds (Average) | H-Bond Observed during MD Simulations | Average Distance between Mass Centers (nm) | H-Bonds Observed in the Docking Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | 3 | Asp74 Ala127 His447 | -- | Asp74 |
| AFBO | 1 | Asp74 Tyr341 | 0.86, 1.14 | Tyr133 Tyr337, Tyr341 |
| AFM1 | 2 | Asp74 Tyr337 Tyr341 | 0.91, 0.83, 0.77 | Tyr124 Ser125 Tyr133 |
| AFP1 | 5 | Asp74 Thr83 Trp86 Asn87 Gly120 Gly126 Tyr133 Tyr337 His447 | 0.84, 0.74, 0.40 0.78, 0.80, 0.67 1.07, 0.92, 0.91 | Asp74 Thr83 Asn87 Gly120 Ser125 Tyr133 Tyr337 |
| AFQ1 | 3 | Asp74 Trp86 Tyr124 | 0.93, 0.49, 0.70 | Trp86 Ser125 Tyr337 |
| AFB2a | 3 | Tyr72 Asp74 Gly120 Ser125 Ala127 Tyr133 | 1.04, 0.99, 0.68, 0.62, 0.74, 1.02 | Asp74 Gly120 Tyr133 |
| AFL | 3 | Tyr337 Tyr341His447 | 1.02, 0.84, 0.97 | Ser125 Tyr133 Tyr337 |
| Ligand | MM-PBSA Average Binding Energy (kcal·mol−1) | Van Der Waals/Electrostatic Energy (kcal·mol−1) | Polar Solvation Energy (kcal·mol−1) | Apolar Solvation Energy (kcal·mol−1) | Molecular Docking Energy (kcal·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | −29.23 | −47.35 | 22.14 | 4.03 | −141.95 |
| AFBO | −26.82 | −42.91 | 19.78 | −3.69 | −137.73 |
| AFM1 | −26.11 | −48.42 | 26.65 | −4.35 | −140.00 |
| AFP1 | −27.93 | −51.32 | 27.35 | −3.96 | −144.50 |
| AFQ1 | −26.67 | −47.57 | 25.04 | −4.14 | −146.17 |
| AFB2a | −32.36 | −59.09 | 30.83 | −4.09 | −140.39 |
| AFL | −26.28 | −47.83 | 25.67 | −4.12 | −137.98 |
| Ligand | Favorable Energetic Contributions | Unfavorable Energetic Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | Trp86 | - |
| AFBO | Trp86 Asp74 | Glu202 |
| AFM1 | Trp86 | Glu202 |
| AFP1 | Trp86 | Glu202 |
| AFQ1 | Trp86 | Glu202 |
| AFB2a | Trp86 | - |
| AFL | Trp86 | Glu202 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Almeida, J.S.F.D.; Dolezal, R.; Krejcar, O.; Kuca, K.; Musilek, K.; Jun, D.; França, T.C.C. Molecular Modeling Studies on the Interactions of Aflatoxin B1 and Its Metabolites with Human Acetylcholinesterase. Part II: Interactions with the Catalytic Anionic Site (CAS). Toxins 2018, 10, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100389
De Almeida JSFD, Dolezal R, Krejcar O, Kuca K, Musilek K, Jun D, França TCC. Molecular Modeling Studies on the Interactions of Aflatoxin B1 and Its Metabolites with Human Acetylcholinesterase. Part II: Interactions with the Catalytic Anionic Site (CAS). Toxins. 2018; 10(10):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100389
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Almeida, Joyce S. F. D., Rafael Dolezal, Ondrej Krejcar, Kamil Kuca, Kamil Musilek, Daniel Jun, and Tanos C. C. França. 2018. "Molecular Modeling Studies on the Interactions of Aflatoxin B1 and Its Metabolites with Human Acetylcholinesterase. Part II: Interactions with the Catalytic Anionic Site (CAS)" Toxins 10, no. 10: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100389
APA StyleDe Almeida, J. S. F. D., Dolezal, R., Krejcar, O., Kuca, K., Musilek, K., Jun, D., & França, T. C. C. (2018). Molecular Modeling Studies on the Interactions of Aflatoxin B1 and Its Metabolites with Human Acetylcholinesterase. Part II: Interactions with the Catalytic Anionic Site (CAS). Toxins, 10(10), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100389








