Individual and Combined Effects of Fumonisin B1, Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on the Hepatic and Renal Membrane Lipid Integrity of Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bodyweight and Daily Feed Intake
2.2. Organ Weights (Absolute and Relative)
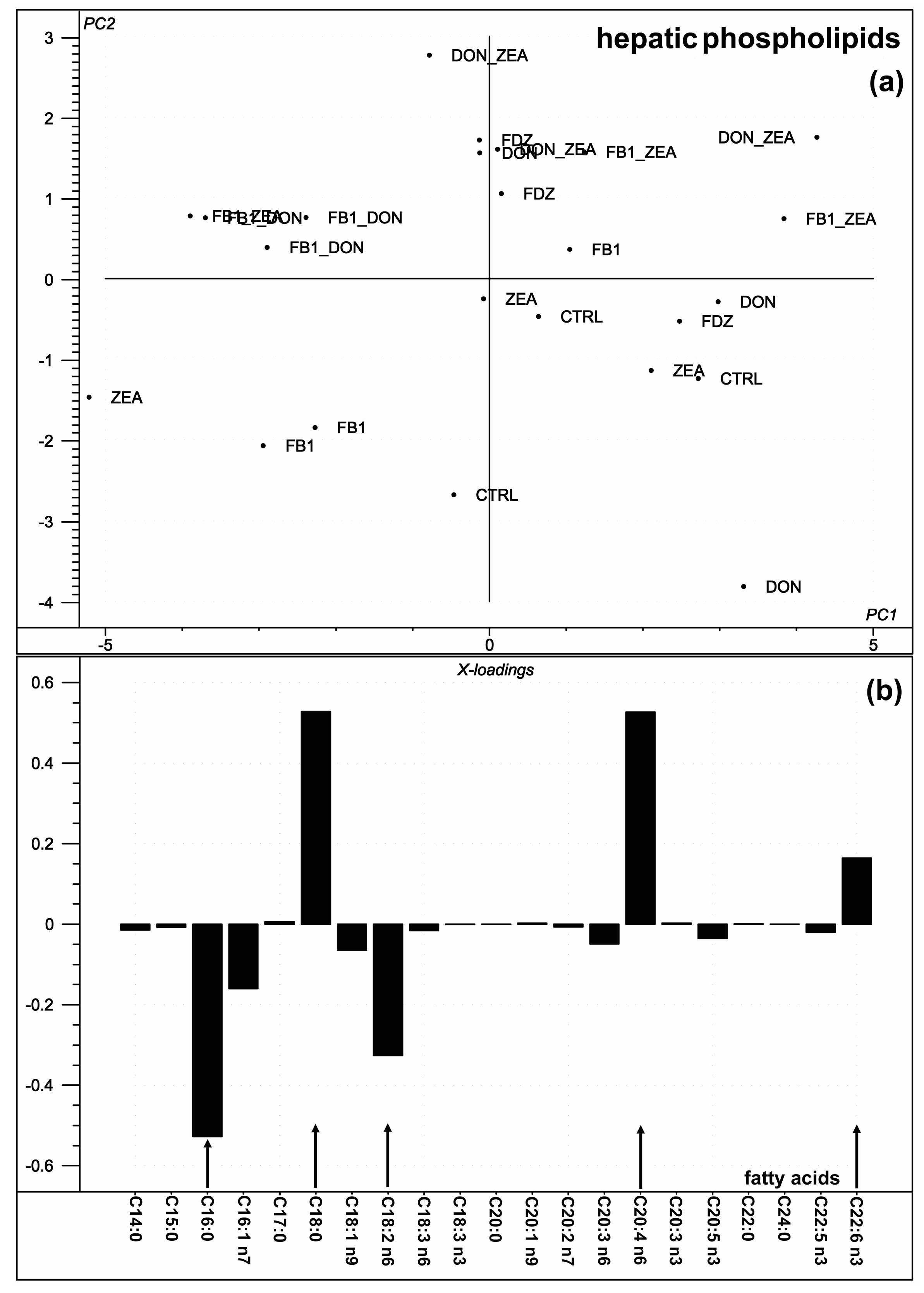
2.3. Hepatic Phospholipid Fatty Acid Composition
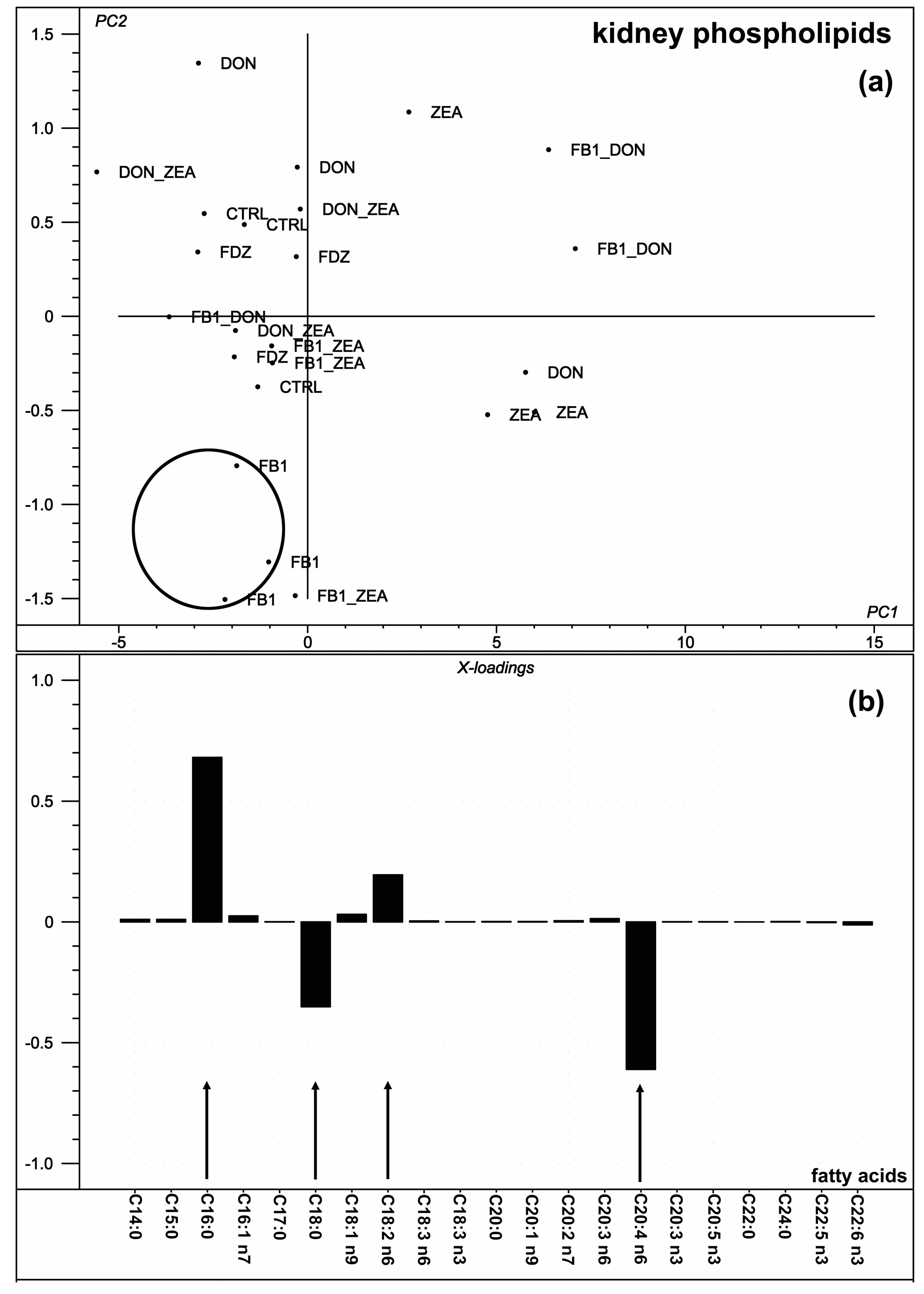
2.4. Kidney Phospholipid Fatty Acid Composition
2.5. Liver Antioxidant and Oxidative Parameters
2.6. Kidney Antioxidants and Oxidative Parameters
3. Discussion
3.1. Bodyweight and Daily Feed Intake
3.2. Organ Weights (Absolute and Relative)
3.3. Hepatic Phospholipid Fatty Acid Composition
3.4. Kidney Phospholipid Fatty Acid Composition
3.5. Liver Antioxidant and Oxidative Parameters
3.6. Kidney Antioxidants and oxidative Parameters
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals and Feeding
5.2. Lipid Analysis
5.3. Analysis of Lipid Peroxidation
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griessler, K.; Rodrigues, I.; Handl, J.; Hofstetter, U. Occurrence of mycotoxins in Southern Europe. World Mycotoxin J. 2010, 3, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Naehrer, K. A Three-Year Survey on the Worldwide Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Feedstuffs and Feed. Toxins 2012, 4, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOMIN Mycotoxin Survey, 2015: BIOMIN Holding GmbH, Getzersdorf, Austria. Available online: http://info.biomin.net/acton/attachment/14109/f-018d/1/-/-/l-0009/l-0009/MTX_Report2015_4S_EN_0316_SMS.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2017).
- BIOMIN Mycotoxin Survey, 2016: BIOMIN Holding GmbH, Getzersdorf, Austria. Available online: https://info.biomin.net/acton/attachment/14109/f-0463/1/-/-/l-0009/l-0009/MAG_MTXsurveyReport_2016_EN_0117_PKO.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2017).
- Smith, M.-C.; Madec, S.; Coton, E.; Hymery, N. Natural Co-Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds and Their in vitro Combined Toxicological Effects. Toxins 2016, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, W.C.; Smuts, C.M.; Abel, S.; Snyman, S.D.; Van der Westhuizen, L.; Huber, W.W.; Swanevelder, S. Effect of fumonisin B1 on the levels and fatty acid composition of selected lipids in rat liver in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.J.; Zhou, H.-R.; Moon, Y.; Chung, Y.J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms for immune modulation by deoxynivalenol and other trichothecenes: Unraveling a paradox. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, K.; Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Zearalenone as an endocrine disruptor in humans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Sardjono; Yamashita, A.; Yoshizawa, T. Natural co-occurrence of aflatoxins and Fusarium mycotoxins (fumonisins, deoxynivalenol, nivalenol and zearalenone) in corn from Indonesia. Food Addit. Contam. 1998, 15, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeira, L.S.; Bryce, J.H.; Stewart, G.G.; Flannigan, B. The effect of combinations of Fusarium mycotoxins (deoxynivalenol, zearalenone and fumonisin B1) on growth of brewing yeasts. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Lei, M.; Zhang, N.Y.; Gao, X.; Li, C.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S. Individual and combined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone, deoxynivalenol and fumonisin B1 on BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicon 2015, 95, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentzel, J.F.; Lombard, M.J.; Du Plessis, L.H.; Zandberg, L. Evaluation of the cytotoxic properties, gene expression profiles and secondary signalling responses of cultured cells exposed to fumonisin B1, deoxynivalenol and zearalenone mycotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortinovis, C.; Caloni, F.; Schreiber, N.B.; Spicer, L.J. Effects of fumonisin B1 alone and combined with deoxynivalenol or zearalenone on porcine granulosa cell proliferation and steroid production. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.Y.M.; Woo, C.S.J.; Turner, P.C.; Wan, J.M.F.; El-Nezami, H. Individual and combined effects of Fusarium toxins on the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in swine jejunal epithelial cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, D.; De Luna, R.; Russo, R.; Severino, L. Effects of four Fusarium toxins (fumonisin B1, α-zearalenol, nivalenol and deoxynivalenol) on porcine whole-blood cellular proliferation. Toxicon 2008, 52, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Streit, E.; Schwab, C.; Sulyok, M.; Naehrer, K.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G. Multi-Mycotoxin Screening Reveals the Occurrence of 139 Different Secondary Metabolites in Feed and Feed Ingredients. Toxins 2013, 5, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, B.A.; Prelusky, D.B.; Pestka, J.J. Toxicology of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Deoxynivalenol in food and feed: Occurrence and exposure. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3379. Available online: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3379/epdf (accessed on 14 December 2017).
- Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Fébel, H.; Mézes, M.; Repa, I.; Kovács, M. Acute hepatic effects of low-dose fumonisin B1 in rats. Acta Vet. Hung. 2016, 64, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conková, E.; Laciaková, A.; Pástorová, B.; Seidel, H.; Kovác, G. The effect of zearalenone on some enzymatic parameters in rabbits. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 121, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueza, I.M.; Raspantini, P.C.F.; Raspantini, L.E.R.; Latorre, A.O.; Górniak, S.L. Zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin, is an immunotoxic compound. Toxins 2014, 6, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Fébel, H.; Romvári, R.; Kovács, M. Individual and combined haematotoxic effects of fumonisin B(1) and T-2 mycotoxins in rabbits. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzyn, A.; Górski, J. Ceramides and sphingomyelins in skeletal muscles of the rat: Content and composition. Effect of prolonged exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E277–E285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Pestka, J.J. Attenuation of mycotoxin-induced IgA nephropathy by eicosapentaenoic acid in the mouse: Dose response and relation to IL-6 expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2006, 17, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Pestka, J.J. Mechanisms for suppression of interleukin-6 expression in peritoneal macrophages from docosahexaenoic acid-fed mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, K.; Riebeling, C.; Bodennec, J.; Riezman, H.; Allegood, J.C.; Sullards, M.C.; Merrill, A.H.; Futerman, A.H. Upstream of Growth and Differentiation Factor 1 (uog1), a Mammalian Homolog of the Yeast Longevity Assurance Gene 1 (LAG1), Regulates N-Stearoyl-sphinganine (C18-(Dihydro)ceramide) Synthesis in a Fumonisin B1 -independent Manner in Mammalian Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35642–35649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, H.E.-D.M.; El Sawi, N.M.; Meki, A.-R.M.A. Acute Toxicity of the Mycotoxin Roridin E on Liver and Kidney of Rats. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 1997, 12, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, W.; Ayed-Boussema, I.; Oscoz, A.A.; De Cerain Lopez, A.; Bacha, H. The role of oxidative stress in zearalenone-mediated toxicity in Hep G2 cells: Oxidative DNA damage, gluthatione depletion and stress proteins induction. Toxicology 2007, 232, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, D.; Deng, J.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Individual and combined effects of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone on mouse kidney. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouadio, J.; Moukha, S.; Brou, K.; Gnakri, D. Lipid metabolism disorders, lymphocytes cells death, and renal toxicity induced by very low levels of deoxynivalenol and fumonisin B1 alone or in combination following 7 days oral administration to mice. Toxicol. Int. 2013, 20, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comission Recommendation 2006/576/EC—on the Presence of Deoxynivalenol, Zearalenone, Ochratoxin A, T-2 and HT-2 and Fumonisins in Products Intended for Animal Feeding. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:229:0007:0009:EN:PDF (accessed on 14 December 2017).
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A Simple Method for the Isolation And Purification of Total Lipides From Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leray, C.; Andriamampandry, M.; Gutbier, G.; Cavadenti, J.; Klein-Soyer, C.; Gachet, C.; Cazenave, J.P. Quantitative analysis of vitamin E, cholesterol and phospholipid fatty acids in a single aliquot of human platelets and cultured endothelial cells. J. Chromatogr. B. 1997, 696, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, W.W. A simple procedure for rapid transmethylation of glycerolipids and cholesteryl esters. J. Lipid Res. 1982, 23, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Placer, Z.A.; Cushman, L.L.; Johnson, B.C. Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehyde) in biochemical systems. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 16, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.A.; Burk, R.F. Species, tissue and subcellular distribution of non Se-dependent glutathione peroxidase activity. J. Nutr. 1978, 108, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- SPSS for Windows ver. 20, SPSS, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2012.
- Bliss, C.I. The toxicity of poisons applied jointly. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1939, 26, 585–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multivariate Analysis Software, CAMO Software AS. Nedre Vollgate 8, N-0158, The Unscrambler®: Oslo, Norway, 2006.
| Group | Control | FB1 | DON | ZEA | FD | FZ | DZ | FDZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Somatic traits | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| BW initial (g) | 307.2 ± 14.9 | 306.4 ± 9.49 | 299.6 ± 4.20 | 317.9 ± 15.9 | 304.3 ± 1.56 | 307.5 ± 10.8 | 289.7 ± 23.3 | 296.8 ± 11.6 |
| BW final (g) | 326.9 ± 19.9 | 361.2 ± 13.8 | 344.5 ± 44.2 | 392.7 ± 27.5 | 350.0 ± 8.59 | 357.7 ± 28.9 | 348.7 ± 40.8 | 331.9 ± 35.6 |
| BW gain (total in 14 days) | 19.7 ± 10.6 | 54.9 ± 6.86 | 44.9 ± 44.8 | 74.9 ± 17.2 | 45.7 ± 8.61 | 50.2 ± 19.5 | 59.0 ± 34.6 | 35.1 ± 25.7 |
| BW gain (g/day) | 1.41 ± 0.76 | 3.92 ± 0.49 | 3.21 ± 3.20 | 5.35 ± 1.23 | 3.26 ± 0.61 | 3.59 ± 1.40 | 4.22 ± 2.47 | 2.50 ± 1.83 |
| liver weight (g) | 11.3 ± 0.85 ab | 13.5 ± 0.38 ab | 10.2 ± 2.06 a | 14.8 ± 1.27 b | 12.7 ± 1.33 ab | 12.8 ± 1.25 ab | 13.1 ± 2.08 ab | 11.5 ± 2.54 ab |
| kidney weight (g) | 2.17 ± 0.12 ab | 2.23 ± 0.12 ab | 2.23 ± 0.06 ab | 2.63 ± 0.23 b | 2.20 ± 0.10 ab | 2.30 ± 0.26 ab | 2.37 ± 0.31 ab | 2.07 ± 0.12 a |
| spleen weight (g) | 0.67 ± 0.06 a | 0.77 ± 0.12 ab | 0.67 ± 0.06 a | 0.93 ± 0.06 ab | 0.83 ± 0.15 ab | 0.83 ± 0.06 b | 0.97 ± 0.12 ab | 0.70 ± 0.10 ab |
| relative liver weight (%) | 3.45 ± 0.09 ab | 3.75 ± 0.23 | 2.93 ± 0.23 a | 3.78 ± 0.14 b | 3.61 ± 0.29 b | 3.59 ± 0.13 ab | 3.76 ± 0.20 b | 3.45 ± 0.39 ab |
| relative kidney weight (%) | 0.67 ± 0.07 | 0.62 ± 0.05 | 0.66 ± 0.08 | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 0.65 ± 0.10 | 0.68 ± 0.08 | 0.63 ± 0.04 |
| relative spleen weight (%) | 0.20 ± 0.01 ab | 0.21 ± 0.03 ab | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 0.24 ± 0.03 ab | 0.24 ± 0.04 ab | 0.23 ± 0.04 b | 0.28 ± 0.02 b | 0.21 ± 0.03 ab |
| Σ feed intake (g/14 days/ind.) | 336.1 ± 6.41 | 405.8 ± 40.0 | 358.4 ± 43.1 | 448.7 ± 67.3 | 359.2 ± 2.71 | 382.2 ± 44.3 | 395.4 ± 69.1 | 363.7 ± 39.9 |
| Group | Control | FB1 | DON | ZEA | FD | FZ | DZ | FDZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL FA profile of the LIVER | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| C14:0 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.07 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.07 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.06 |
| C15:0 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| C16:0 | 18.7 ± 0.88 | 20.3 ± 0.80 | 18.4 ± 1.08 | 20.1 ± 1.67 | 21.5 ± 0.47 | 19.4 ± 2.25 | 19.40 ± 1.41 | 19.3 ± 1.04 |
| C16:1 n7 | 0.77 ± 0.35 | 1.28 ± 0.38 | 0.80 ± 0.54 | 1.75 ± 0.81 | 1.57 ± 0.22 | 1.54 ± 0.60 | 1.11 ± 0.31 | 1.00 ± 0.48 |
| C17:0 | 0.42 ± 0.10 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 0.35 ± 0.07 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.11 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.03 |
| C18:0 | 24.4 ± 1.22 | 23.1 ± 1.28 | 24.2 ± 1.74 | 22.9 ± 2.38 | 20.9 ± 0.40 | 22.2 ± 2.30 | 21.92 ± 1.42 | 22.8 ± 1.13 |
| C18:1 n9c | 2.52 ± 0.33 | 2.75 ± 0.39 | 2.60 ± 0.43 | 3.04 ± 0.70 | 2.62 ± 0.10 | 2.86 ± 0.35 | 2.52 ± 0.31 | 2.50 ± 0.10 |
| C18:2 n6c | 12.0 ± 1.90 | 12.3 ± 1.61 | 11.2 ± 1.34 | 11.6 ± 1.51 | 12.0 ± 0.31 | 10.2 ± 1.34 | 9.73 ± 0.98 | 10.7 ± 0.52 |
| C18:3 n6 | 0.13 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.11 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.07 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.04 |
| C18:3 n3 | 0.13 ± 0.07 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.04 |
| C20:0 | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab |
| C20:1 n9 | 0.11 ± 0.05 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| C20:2 n7 | 0.38 ± 0.09 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.29 ± 0.12 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.37 ± 0.05 | 0.37 ± 0.09 | 0.42 ± 0.07 | 0.36 ± 0.08 |
| C20.3 n6 | 0.72 ± 0.33 | 0.83 ± 0.09 | 0.69 ± 0.51 | 1.01 ± 0.18 | 0.96 ± 0.03 | 1.25 ± 0.25 | 1.02 ± 0.31 | 0.83 ± 0.41 |
| C20:4 n6 | 30.9 ± 1.94 | 29.9 ± 1.02 | 32.4 ± 1.81 | 30.4 ± 1.87 | 30.1 ± 0.70 | 31.9 ± 1.88 | 32.97 ± 1.82 | 31.9 ± 0.78 |
| C20:3 n3 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| C20:5 n3 | 0.18 ± 0.09 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.16 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.37 ± 0.13 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.26 ± 0.15 |
| C22:0 | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.01 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab |
| C24:0 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| C22:5 n3 | 1.00 ± 0.22 ab | 1.14 ± 0.11 ab | 0.95 ± 0.22 a | 1.11 ± 0.14 ab | 1.38 ± 0.14 b | 1.33 ± 0.05 ab | 1.29 ± 0.13 ab | 1.25 ± 0.12 ab |
| C22:6 n3 | 7.23 ± 0.99 | 6.66 ± 1.66 | 7.20 ± 2.21 | 6.10 ± 1.00 | 7.07 ± 0.22 | 7.28 ± 0.99 | 8.11 ± 1.07 | 7.91 ± 0.40 |
| saturated | 43.9 ± 1.55 | 44.2 ± 1.04 | 43.3 ± 0.84 | 43.7 ± 0.84 | 43.2 ± 0.26 | 42.4 ± 0.38 | 42.14 ± 0.27 | 42.9 ± 0.12 |
| MUFA | 3.40 ± 0.07 | 4.11 ± 0.79 | 3.48 ± 0.65 | 4.86 ± 1.50 | 4.27 ± 0.32 | 4.50 ± 0.80 | 3.74 ± 0.63 | 3.58 ± 0.37 |
| PUFA | 52.7 ± 1.60 | 51.6 ± 1.12 | 53.2 ± 0.19 | 51.4 ± 1.47 | 52.5 ± 0.06 | 53.1 ± 1.12 | 54.12 ± 0.37 | 53.5 ± 0.41 |
| n6 | 43.7 ± 2.75 | 43.1 ± 1.57 | 44.4 ± 2.63 | 43.3 ± 0.89 | 43.2 ± 0.42 | 43.5 ± 0.76 | 43.87 ± 1.00 | 43.6 ± 0.87 |
| n3 | 8.62 ± 1.24 | 8.22 ± 1.64 | 8.48 ± 2.50 | 7.79 ± 0.95 | 8.97 ± 0.37 | 9.15 ± 0.83 | 9.83 ± 1.15 | 9.61 ± 0.41 |
| n6/n3 | 5.16 ± 1.02 | 5.40 ± 1.18 | 5.70 ± 2.34 | 5.61 ± 0.71 | 4.83 ± 0.25 | 4.78 ± 0.45 | 4.51 ± 0.59 | 4.54 ± 0.28 |
| UI | 204.1 ± 3.52 ab | 199.1 ± 8.40 a | 207.7 ± 6.77 ab | 198.9 ± 8.33 a | 204.4 ± 0.55 ab | 210.2 ± 8.04 ab | 216.4 ± 3.62 b | 211.8 ± 0.36 ab |
| ACL | 18.57 ± 0.05 | 18.49 ± 0.10 | 18.60 ± 0.05 | 18.48 ± 0.12 | 18.50 ± 0.01 | 18.59 ± 0.13 | 18.65 ± 0.05 | 18.62 ± 0.03 |
| Group | Control | FB1 | DON | ZEA | FD | FZ | DZ | FDZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL FA profile of the KIDNEY | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| C14:0 | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.20 ± 0.02 ab | 0.19 ± 0.04 ab | 0.24 ± 0.03 ab | 0.26 ± 0.07 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 ab | 0.18 ± 0.03 ab | 0.19 ± 0.02 ab |
| C15:0 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.03 |
| C16:0 | 22.1 ± 0.45 | 21.6 ± 0.68 | 24.1 ± 2.58 | 26.2 ± 0.62 | 25.56 ± 4.32 | 22.2 ± 0.35 | 21.7 ± 1.92 | 21.9 ± 1.05 |
| C16:1 n7 | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 0.61 ± 0.09 | 0.69 ± 0.13 | 0.69 ± 0.17 | 0.69 ± 0.29 | 0.80 ± 0.07 | 0.59 ± 0.15 | 0.66 ± 0.11 |
| C17:0 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.10 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.09 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.33 ± 0.08 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.29 ± 0.07 |
| C18:0 | 22.3 ± 0.12 ab | 22.9 ± 0.30 b | 21.0 ± 1.28 ab | 19.9 ± 0.66 a | 20.2 ± 2.28 ab | 21.9 ± 0.66 ab | 22.3 ± 0.72 ab | 21.9 ± 0.39 ab |
| C18:1 n9c | 5.23 ± 0.37 | 5.08 ± 0.35 | 5.63 ± 0.26 | 5.38 ± 0.64 | 5.10 ± 0.45 | 5.36 ± 0.31 | 4.95 ± 0.18 | 5.50 ± 0.39 |
| C18:2 n6c | 7.15 ± 0.50 ab | 8.02 ± 0.48 ab | 7.58 ± 1.09 ab | 8.76 ± 0.42 b | 8.45 ± 1.04 ab | 7.88 ± 0.41 ab | 6.94 ± 0.38 a | 7.36 ± 0.27 ab |
| C18:3 n6 | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 ab | 0.07 ± 0.02 ab | 0.11 ± 0.01 b | 0.10 ± 0.03 ab | 0.08 ± 0.02 ab | 0.08 ± 0.00 ab | 0.08 ± 0.01 ab |
| C18:3 n3 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| C20:0 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.01 |
| C20:1 n9 | 0.08 ± 0.02 ab | 0.09 ± 0.02 ab | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.02 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 ab | 0.09 ± 0.02 ab | 0.09 ± 0.01 ab |
| C20:2 n7 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.29 ± 0.07 | 0.29 ± 0.03 |
| C20.3 n6 | 0.85 ± 0.21 | 0.98 ± 0.12 | 0.92 ± 0.29 | 1.12 ± 0.22 | 1.03 ± 0.13 | 1.14 ± 0.09 | 1.06 ± 0.08 | 0.95 ± 0.22 |
| C20:4 n6 | 37.5 ± 0.68 | 36.5 ± 0.51 | 36.0 ± 3.33 | 33.5 ± 1.71 | 34.5 ± 3.46 | 36.2 ± 0.82 | 38.0 ± 1.88 | 37.3 ± 0.79 |
| C20:3 n3 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| C20:5 n3 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.06 |
| C22:0 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| C24:0 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| C22:5 n3 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.06 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.03 |
| C22:6 n3 | 2.46 ± 0.08 | 2.30 ± 0.23 | 2.21 ± 0.32 | 2.24 ± 0.12 | 2.28 ± 0.13 | 2.49 ± 0.27 | 2.50 ± 0.10 | 2.42 ± 0.26 |
| saturated | 45.2 ± 0.42 | 45.4 ± 0.81 | 45.9 ± 1.44 | 47.2 ± 0.80 | 46.8 ± 2.45 | 45.0 ± 0.85 | 44.9 ± 1.25 | 44.7 ± 0.81 |
| MUFA | 5.84 ± 0.49 | 5.78 ± 0.45 | 6.40 ± 0.40 | 6.19 ± 0.80 | 5.86 ± 0.51 | 6.25 ± 0.38 | 5.63 ± 0.29 | 6.25 ± 0.31 |
| PUFA | 48.9 ± 0.08 | 48.8 ± 0.58 | 47.7 ± 1.84 | 46.7 ± 1.03 | 47.3 ± 2.60 | 48.7 ± 0.79 | 49.4 ± 1.52 | 49.1 ± 1.01 |
| n6 | 45.5 ± 0.17 | 45.6 ± 0.76 | 44.6 ± 2.10 | 43.5 ± 1.19 | 44.1 ± 2.55 | 45.3 ± 1.00 | 46.1 ± 1.61 | 45.7 ± 0.82 |
| n3 | 3.15 ± 0.10 | 2.96 ± 0.20 | 2.82 ± 0.40 | 2.88 ± 0.15 | 2.95 ± 0.18 | 3.20 ± 0.27 | 3.09 ± 0.08 | 3.10 ± 0.33 |
| n6/n3 | 14.5 ± 0.52 | 15.5 ± 1.36 | 16.1 ± 2.90 | 15.2 ± 1.20 | 15.0 ± 1.13 | 14.3 ± 1.50 | 14.9 ± 0.90 | 14.8 ± 1.52 |
| UI | 191.1 ± 1.33 | 188.4 ± 1.21 | 185.1 ± 9.08 | 178.3 ± 4.23 | 181.5 ± 12.15 | 189.1 ± 1.88 | 193.1 ± 6.26 | 191.5 ± 4.53 |
| ACL | 18.43 ± 0.02 | 18.41 ± 0.01 | 18.34 ± 0.11 | 18.26 ± 0.04 | 18.29 ± 0.17 | 18.40 ± 0.01 | 18.45 ± 0.08 | 18.43 ± 0.05 |
| Group | Control | FB1 | DON | ZEA | FD | FZ | DZ | FDZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peroxidation traits, LIVER | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| GSH (micromol/g protein) | 2.11 ± 0.09 a | 2.60 ± 0.26 abc | 2.42 ± 0.52 ab | 3.34 ± 0.33 bc | 3.52 ± 0.13 c | 3.24 ± 0.35 bc | 3.38 ± 0.46 bc | 3.27 ± 0.43 bc |
| GSHPx (IU/g protein) | 0.99 ± 0.28 a | 1.53 ± 0.57 ab | 1.79 ± 0.55 ab | 1.70 ± 0.34 ab | 2.33 ± 0.29 b | 1.81 ± 0.22 ab | 1.82 ± 0.56 ab | 1.58 ± 0.39 ab |
| MDA (micromol/g) | 16.2 ± 0.34 | 17.6 ± 2.91 | 15.6 ± 3.99 | 15.6 ± 1.89 | 16.6 ± 1.52 | 15.0 ± 1.35 | 13.47 ± 0.71 | 16.0 ± 1.85 |
| Peroxidation traits, KIDNEY | ||||||||
| GSH (micromol/g protein) | 1.49 ± 0.24 | 1.76 ± 0.80 | 2.14 ± 0.50 | 1.98 ± 0.31 | 1.88 ± 0.25 | 1.99 ± 0.96 | 1.30 ± 0.32 | 1.92 ± 0.74 |
| GSHPx (IU/g protein) | 0.44 ± 0.11 | 0.59 ± 0.42 | 0.54 ± 0.15 | 0.42 ± 0.44 | 0.91 ± 0.57 | 0.93 ± 0.27 | 0.37 ± 0.23 | 0.73 ± 0.47 |
| MDA (micromol/g) | 4.13 ± 0.58 ab | 4.41 ± 0.35 ab | 5.78 ± 1.50 b | 5.02 ± 0.97 ab | 4.31 ± 0.30 ab | 3.67 ± 0.14 a | 3.49 ± 0.49 a | 4.44 ± 0.26 ab |
| Chemical Composition | |
|---|---|
| Dry matter (%) | 88.4 |
| Crude protein (%) | 19 |
| Crude fat (%) | 3.5 |
| Crude fiber (%) | 3.6 |
| Crude ash (%) | 6.5 |
| N free extract (%) | 55.9 |
| Gross energy (MJ/kg) | 16.4 |
| Metab. energy (MJ/kg) | 13.4 |
| Fatty Acid Composition | Weight % |
| C14:0 | 0.01 |
| C16:0 | 0.49 |
| C16:1 n7 | 0.01 |
| C18:0 | 0.08 |
| C18:1 n9 | 0.65 |
| C18:2 n6 | 1.9 |
| C18:3 n3 | 0.25 |
| C20:0 | 0.01 |
| C20:1 n9 | 0.02 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Fébel, H.; Mézes, M.; Balogh, K.; Bázár, G.; Kocsó, D.; Ali, O.; Kovács, M. Individual and Combined Effects of Fumonisin B1, Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on the Hepatic and Renal Membrane Lipid Integrity of Rats. Toxins 2018, 10, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010004
Szabó A, Szabó-Fodor J, Fébel H, Mézes M, Balogh K, Bázár G, Kocsó D, Ali O, Kovács M. Individual and Combined Effects of Fumonisin B1, Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on the Hepatic and Renal Membrane Lipid Integrity of Rats. Toxins. 2018; 10(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, András, Judit Szabó-Fodor, Hedvig Fébel, Miklós Mézes, Krisztián Balogh, György Bázár, Dániel Kocsó, Omeralfaroug Ali, and Melinda Kovács. 2018. "Individual and Combined Effects of Fumonisin B1, Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on the Hepatic and Renal Membrane Lipid Integrity of Rats" Toxins 10, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010004
APA StyleSzabó, A., Szabó-Fodor, J., Fébel, H., Mézes, M., Balogh, K., Bázár, G., Kocsó, D., Ali, O., & Kovács, M. (2018). Individual and Combined Effects of Fumonisin B1, Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on the Hepatic and Renal Membrane Lipid Integrity of Rats. Toxins, 10(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010004









