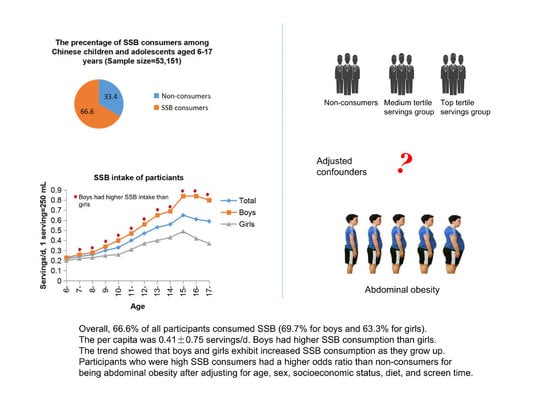
Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shields, M. Overweight and obesity among children and youth. Health Rep. 2006, 17, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.P.; Ma, Y.N.; Han, D.; Pan, C.W.; Xu, Y. Prevalence and trends in obesity among China’s children and adolescents, 1985–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, J. Understanding trends in blood pressure and their associations with body mass index in Chinese children, from 1985 to 2010: A cross-sectional observational study. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 2008, 117, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.S.; Mulder, C.; Twisk, J.W.; van Mechelen, W.; Chinapaw, M.J. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: A systematic review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.S.; Barlow, S.E.; Rao, G.; Inge, T.H.; Hayman, L.L.; Steinberger, J.; Urbina, E.M.; Ewing, L.J.; Daniels, S.R. Severe obesity in children and adolescents: Identification, associated health risks, and treatment approaches. Circulation 2013, 128, 1689–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.R.; Pratt, C.A.; Hayman, L.L. Reduction of risk for cardiovascular disease in children and adolescents. Circulation 2011, 124, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koplan, J.P.; Dietz, W.H. Caloric imbalance and public health policy. JAMA 1999, 282, 1579–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richelsen, B. Sugar-sweetened beverages and cardio-metabolic disease risks. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, M.B.; Kaar, J.L.; Welsh, J.A.; van Horn, L.V.; Feig, D.I.; Anderson, C.A.; Patel, M.J.; Cruz, M.J.; Krebs, N.F.; Xanthakos, S.A.; et al. Added sugars and cardiovascular disease risk in children: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 135, e1017–e1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kit, B.K.; Fakhouri, T.H.; Park, S.; Nielsen, S.J.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in sugar-sweetened beverage consumption among youth and adults in the United States: 1999–2010. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Miller, J.C.; Barclay, A.W. Declining consumption of added sugars and sugar-sweetened beverages in Australia: A challenge for obesity prevention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Pimienta, T.G.; Batis, C.; Lutter, C.K.; Rivera, J.A. Sugar-sweetened beverages are the main sources of added sugar intake in the Mexican population. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1888S–1896S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburto, T.C.; Pedraza, L.S.; Sánchez-Pimienta, T.G.; Batis, C.; Rivera, J.A. Discretionary foods have a high contribution and fruit, vegetables, and legumes have a low contribution to the total energy intake of the Mexican population. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1881S–1887S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guideline: Sugars Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, X.W.; Liu, A.L.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, X.Q.; Du, S.M.; Ma, J.; Xu, G.F.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.W.; Du, L.; et al. Report on childhood obesity in China (9): Sugar-sweetened beverages consumption and obesity. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Long, W.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y. Sugar-sweetened beverages consumption positively associated with the risks of obesity and hypertriglyceridemia among Children aged 7–18 years in South China. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 38570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, D.T.S.; Keller, A.; Laure, D.J.; Kruseman, M. Sugar-sweetened beverages and obesity risk in children and Adolescents: A systematic analysis on how methodological quality may influence conclusions. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 638–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, C.A.; Riddell, L.J.; Campbell, K.J.; Nowson, C.A. Dietary salt intake, sugar-sweetened beverage consumption, and obesity risk. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.H.; Akram, Y.; Shetty, S.; Malik, S.S.; Yanchou, N.V. Impact of sugar-sweetened beverages on blood pressure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Segal, M.S.; Sautin, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Feig, D.I.; Kang, D.H.; Gersch, M.S.; Benner, S.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G. Potential role of sugar (fructose) in the epidemic of hypertension, obesity and the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, D.S.; Peterson, K.E.; Gortmaker, S.L. Relation between consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks and childhood obesity: A prospective, observational analysis. Lancet 2001, 357, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.A.; Zavodny, M. Does the sale of sweetened beverages at school affect children’s weight? Soc. Sci. Med. 2011, 73, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laska, M.N.; Murray, D.M.; Lytle, L.A.; Harnack, L.J. Longitudinal associations between key dietary behaviors and weight gain over time: Transitions through the adolescent years. Obesity 2012, 20, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payab, M.; Kelishadi, R.; Qorbani, M.; Motlagh, M.E.; Ranjbar, S.H.; Ardalan, G.; Zahedi, H.; Chinian, M.; Asayesh, H.; Larijani, B.; et al. Association of junk food consumption with high blood pressure and obesity in Iranian children and adolescents: The CASPIAN-IV Study. J. Pediatr. 2015, 91, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, S.; Oliveira, A.; Pinto, E.; Moreira, P.; Barros, H.; Lopes, C. The influence of socioeconomic factors and family context on energy-dense food consumption among 2-year-old children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.B.; Arnberg, K.; Trolle, E.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Bro, R.; Pipper, C.B.; Molgaard, C. The effects of water and dairy drinks on dietary patterns in overweight adolescents. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBoer, M.D.; Scharf, R.J.; Demmer, R.T. Sugar-sweetened beverages and weight gain in 2- to 5-year-old children. Pediatrics 2013, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Pan, D.; et al. A national school-based health lifestyles interventions among Chinese children and adolescents against obesity: Rationale, design and methodology of a randomized controlled trial in China. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on public education. American academy of pediatrics: Children, adolescents, and television. Pediatrics 2001, 107, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Lyu, J.; He, P. Chinese guidelines for data processing and analysis concerning the International Physical Activity Questionnaire. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2014, 35, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group of China Obesity Task Force. Body mass index reference norm for screening overweight and obesity in Chinese children and adolescents. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2004, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.S.; Ji, C.Y.; Ma, J.; Mi, J.; Yt, S.R.; Xiong, F.; Yan, W.L.; Hu, X.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Du, S.M.; et al. Waist circumference reference values for screening cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese children and adolescents. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2010, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Wang, T.Y.; Meng, L.H. Development of blood pressure reference standards for Chinese children and adolescents. Chin. J. Evid. Based Pediatr. 2010, 5, 4–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, A.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and its association with overweight among young children from China. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Bleich, S.N.; Gortmaker, S.L. Increasing caloric contribution from sugar-sweetened beverages and 100% fruit juices among US children and adolescents, 1988–2004. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e1604–e1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorito, L.M.; Mitchell, D.C.; Smiciklas-Wright, H.; Birch, L.L. Dairy and dairy-related nutrient intake during middle childhood. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garriguet, D. Beverage consumption of children and teens. Health Rep. 2008, 19, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirmiran, P.; Yuzbashian, E.; Asghari, G. Consumption of sugar sweetened beverage is associated with incidence of metabolic syndrome in Tehranian children and adolescents. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.; Curhan, G.; Forman, J. Association of sweetened beverage intake with incident hypertension. J. Gen. Int. Med. 2012, 27, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayon-Orea, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Gea, A.; Alonso, A.; Pimenta, A.M.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Baseline consumption and changes in sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and the incidence of hypertension: The SUN project. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
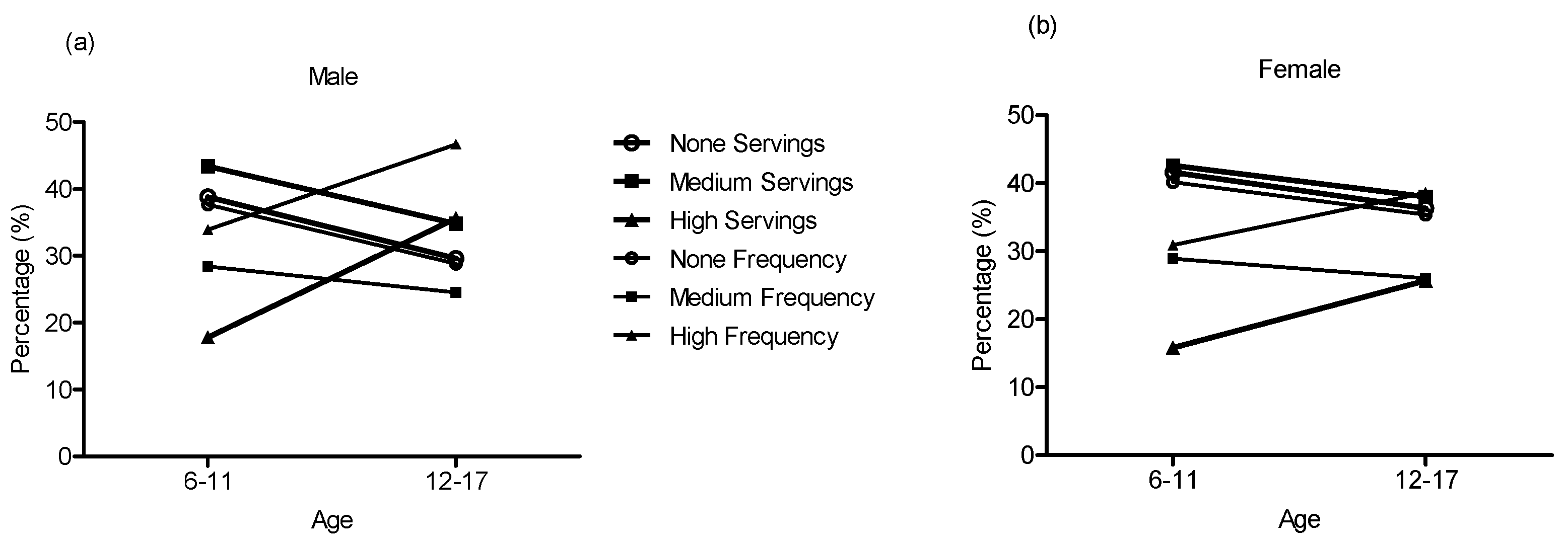
| Age (Years) | Average (Servings/Day) (Mean ± SD) | Servings/Day (%) | Average (Frequency/Week) (Mean ± SD) | Frequency/Week (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Boys | Girls | None Servings | Medium Servings | High Servings | Total | Boys | Girls | None Frequency | Medium Frequency | High Frequency | |
| 6–11 | 1.51 ± 2.81 | 1.59 ± 2.86 | 1.43 ± 2.76 * | 40.1 | 43.0 | 16.8 | 1.23 ± 1.48 | 1.27 ± 1.50 | 1.19 ± 1.45 | 38.9 | 28.6 | 32.5 |
| 12–17 | 2.95 ± 5.41 | 3.56 ± 6.24 | 2.32 ± 4.30 * | 32.8 | 36.4 | 30.8 | 1.28 ± 1.51 | 1.36 ± 1.55 | 1.21 ± 1.46 * | 37.5 | 28.8 | 33.7 |
| Total | 2.84 ± 5.26 | 3.40 ± 6.06 | 2.25 ± 4.20 * | 33.4 | 36.9 | 29.7 | 1.62 ± 1.78 | 1.80 ± 1.89 | 1.43 ± 1.63 * | 32.6 | 25.5 | 41.9 |
| Variables | None Servings/Week | Medium Servings/Week | High Servings/Week | p-Value | None Frequency/Week | Middle Frequency/Week | High Frequency/Week | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residence, n (%) | 0.981 | 0.04 | ||||||
| Urban | 11,209 (33.4) | 12,384 (36.9) | 9957 (29.7) | 11,209 (32.5) | 8947 (26.0) | 14,311 (41.5) | ||
| Rural | 6564 (33.5) | 7231 (36.9) | 5806 (29.6) | 6564 (32.7) | 4964 (24.7) | 8545 (42.6) | ||
| Paternal education, n (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Primary school or below | 1180 (34.6) | 1183 (34.7) | 1050 (30.7) | 1180 (33.7) | 889 (25.4) | 1433 (40.9) | ||
| Junior high school | 5481 (31.7) | 6441 (37.2) | 5389 (31.1) | 5481 (30.8) | 4531 (25.5) | 7783 (43.7) | ||
| High school | 4256 (32.3) | 5024 (38.1) | 3908 (29.6) | 4256 (31.4) | 3515 (26.0) | 5770 (42.6) | ||
| Junior college or above | 5278 (38.2) | 5204 (37.7) | 3317 (24.1) | 5278 (37.5) | 3706 (26.3) | 5102 (36.2) | ||
| Maternal education, n (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Primary school or below | 1579 (33.6) | 1680 (35.7) | 1443 (30.7) | 1579 (32.6) | 1237 (25.5) | 2033 (41.9) | ||
| Junior high school | 5709 (32.0) | 6586 (36.9) | 5553 (31.1) | 5709 (31.2) | 4556 (24.9) | 8056 (43.9) | ||
| High school | 4059 (32.5) | 4803 (38.5) | 3620 (29.0) | 4059 (31.7) | 3404 (26.6) | 5333 (41.7) | ||
| Junior college or above | 4792 (38.1) | 4764 (37.9) | 3022 (24.0) | 4792 (37.3) | 3418 (26.6) | 4647 (36.1) | ||
| Family income, RMB/month, n (%) | 0.037 | 0.001 | ||||||
| 2000 or below | 1194 (36.1) | 1179 (35.7) | 932 (28.2) | 1194 (35.3) | 874 (25.8) | 1318 (38.9) | ||
| 2000–5000 | 3635 (33.4) | 4105 (37.7) | 3138 (28.9) | 3635 (32.5) | 3033 (27.2) | 4500 (40.3) | ||
| 5000–8000 | 2744 (33.0) | 3188 (38.3) | 2395 (28.7) | 2744 (32.2) | 2255 (26.4) | 3529 (41.4) | ||
| 8000 or above | 3175 (34.4) | 3545 (38.5) | 2499 (27.1) | 3175 (33.7) | 2408 (25.6) | 3829 (40.7) | ||
| Don’t know or no answer | 4624 (35.3) | 4859 (37.1) | 3626 (27.6) | 4624 (34.3) | 3341 (24.8) | 5501 (40.9) | ||
| Screen time, n (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| <2 h | 11,631 (37.0) | 11,874 (37.8) | 7940 (25.3) | 11,631 (36.1) | 8381 (26.0) | 12,195 (37.9) | ||
| ≥2 h | 3669 (24.5) | 5409 (36.2) | 5884 (39.3) | 3669 (24.5) | 3739 (24.4) | 7909 (51.6) | ||
| Physical activity, MET (min/week), Mean ± SE | 3064.3 ± 28.9 | 3289.1 ± 27.3 | 3805.9 ± 37.5 | <0.001 | 3064.3 ± 28.9 | 3343.6 ± 34.0 | 3624.6 ± 29.0 | <0.001 |
| Dietary consumption (times/week), Mean ± SE | ||||||||
| Fruit | 1.28 ± 0.01 | 1.23 ± 0.01 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | 1.28 ± 0.01 | 1.26 ± 0.01 | 1.29 ± 0.01 | 0.037 |
| Vegetables | 1.87 ± 0.01 | 1.72 ± 0.01 | 1.81 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | 1.77 ± 0.01 | 1.76 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Meat | 4.91 ± 0.02 | 4.89 ± 0.02 | 5.24 ± 0.02 | <0.001 | 4.91 ± 0.02 | 4.79 ± 0.02 | 5.19 ± 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Milk | 4.61 ± 0.02 | 4.57 ± 0.02 | 4.37 ± 0.02 | <0.001 | 4.61 ± 0.02 | 4.49 ± 0.02 | 4.46 ± 0.02 | <0.001 |
| High-energy food | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 1.99 ± 0.01 | 2.80 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 1.80 ± 0.01 | 2.66 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Fried food | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.01 | 1.88 ± 0.01 | <0.001 | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 1.73 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Anthropometry, Mean ± SE | ||||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.24 ± 0.03 | 18.39 ± 0.03 | 19.36 ± 0.03 | <0.001 | 18.24 ± 0.03 | 18.32 ± 0.03 | 19.08 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 63.65 ± 0.08 | 64.15 ± 0.08 | 67.59 ± 0.09 | <0.001 | 63.65 ± 0.08 | 63.92 ± 0.09 | 66.62 ± 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 75.61 ± 0.09 | 76.01 ± 0.08 | 80.85 ± 0.10 | <0.001 | 75.61 ± 0.09 | 75.72 ± 0.10 | 79.47 ± 0.08 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 103.44 ± 0.09 | 103.91 ± 0.09 | 106.23 ± 0.10 | <0.001 | 103.44 ± 0.09 | 103.71 ± 0.10 | 105.56 ± 0.08 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 65.80 ± 0.07 | 65.90 ± 0.06 | 67.04 ± 0.07 | <0.001 | 65.80 ± 0.07 | 65.79 ± 0.07 | 66.73 ± 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Total n (%) | None Servings/Week | Medium Servings/Week | High Servings/Week | None Frequency/Week | Middle Frequency/Week | High Frequency/Week |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | |||||||
| Underweight, n (%) | 4284 (6.9) | 1262 (7.1) | 1282 (6.6) | 1040 (6.6) | 1262 (7.1) | 925 (6.6) | 1485 (6.5) |
| Normal, n (%) | 43,607 (69.8) | 12,392 (69.7) | 13,581 (69.2) | 10,905 (69.2) | 12,392 (69.7) | 9578 (68.9) | 15,906 (69.6) |
| Overweight, n (%) | 8000 (12.8) | 2214 (12.5) | 2596 (13.2) | 2113 (13.4) | 2214 (12.5) | 1845 (13.3) | 3032 (13.3) |
| Obesity, n (%) | 6626 (10.6) | 1905 (10.7) | 2156 (11.0) | 1705 (10.8) | 1905 (10.7) | 1563 (11.2) | 2433 (10.6) |
| p-value | 0.009 | 0.009 | |||||
| Abdominal obesity | |||||||
| No, n (%) | 44,425 (78.1) | 12,520 (78.4) | 13,715 (77.6) | 11,461(76.7) | 12,520 (78.4) | 9224 (77.6) | 15,952 (76.9) |
| Yes, n (%) | 12,460 (21.9) | 3443 (21.6) | 3962 (22.4) | 3489 (23.3) | 3443 (21.6) | 2659 (22.4) | 4792 (23.1) |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.002 | |||||
| DBP | |||||||
| Normal, n (%) | 52,623 (84.5) | 15,046 (85.1) | 16,532 (85.2) | 13,241 (84.3) | 15,046 (85.1) | 11,805 (85.2) | 19,267 (84.6) |
| Pre-hypertension, n (%) | 4902 (7.9) | 1275 (7.2) | 1469 (7.5) | 1494 (9.5) | 1275 (7.2) | 991 (7.2) | 2055 (9.0) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 4721 (7.6) | 1367 (7.7) | 1431 (7.3) | 968 (6.2) | 1367 (7.7) | 1062 (7.7) | 1442 (6.3) |
| p-value | 0.282 | 0.713 | |||||
| SBP | |||||||
| Normal, n (%) | 49,941 (80.3) | 14,366 (81.2) | 15,787 (80.8) | 12,183 (77.6) | 14,366 (81.2) | 11,254 (81.2) | 17,881 (78.6) |
| Pre-hypertension, n (%) | 6697 (10.8) | 1701 (9.6) | 1953 (10.0) | 2155 (13.7) | 1701 (9.6) | 1327 (9.6) | 2901 (12.7) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 5585 (9.0) | 1622 (9.2) | 1790 (9.2) | 1366 (8.7) | 1622 (9.2) | 1281 (9.2) | 1977 (8.7) |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| Hypertension | |||||||
| Normal, n (%) | 46,690 (75.1) | 13,470 (76.2) | 14,836 (76.0) | 11,440 (72.9) | 13,470 (76.2) | 10,568 (76.3) | 16,800 (73.9) |
| Pre-hypertension, n (%) | 7633 (12.3) | 1957 (11.1) | 2213 (11.3) | 2446 (15.6) | 1957 (11.1) | 1510 (10.9) | 3288 (14.5) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 7856 (12.6) | 2249 (12.7) | 2464 (12.6) | 1805 (11.5) | 2249 (12.7) | 1771 (12.8) | 2654 (11.7) |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| BMI, n (%) | Abdominal Obesity, n (%) | Hypertension, n (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Underweight | Normal | Overweight | Obesity | No | Yes | Normal | Pre-Hypertension | Hypertension |
| Paternal education | |||||||||
| Primary school or below | 260 (7.1) | 2689 (73.0) | 436 (11.8) | 299 (8.1) | 2874 (81.9) | 637 (18.1) | 2668 (72.8) | 549 (15.0) | 450 (12.3) |
| Junior high school | 1193 (6.4) | 13,163 (71.0) | 2252 (12.2) | 1922 (10.4) | 13,593 (79.2) | 3578 (20.8) | 13,321 (72.2) | 2599 (14.1) | 2526 (13.7) |
| High school | 905 (6.4) | 9656 (68.3) | 1908 (13.5) | 1611 (11.8) | 9750 (76.1) | 3062 (23.9) | 10,613 (75.6) | 1611 (11.5) | 1821 (13.0) |
| Junior college or above | 1039 (7.1) | 9653 (65.5) | 2182 (14.8) | 1862 (12.6) | 9674 (74.7) | 3268 (25.3) | 11,652 (79.5) | 1404 (9.6) | 1601 (10.9) |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Maternal education | |||||||||
| Primary school or below | 364 (7.2) | 3739 (73.7) | 552 (10.9) | 421 (8.3) | 3936 (82.1) | 860 (7.9) | 3681 (72.9) | 729 (14.4) | 639 (12.7) |
| Junior high school | 1242 (6.5) | 13,472 (70.6) | 2353 (12.3) | 2012 (10.5) | 13,958 (78.9) | 3724 (21.1) | 13729 (72.3) | 2690 (14.2) | 2576 (13.6) |
| High school | 841 (6.3) | 9010 (67.5) | 1861 (13.9) | 1636 (12.3) | 9097 (75.4) | 2969 (24.6) | 10,059 (75.8) | 1455 (11.0) | 1761 (13.3) |
| Junior college or above | 944 (7.0) | 8848 (65.7) | 1998 (14.8) | 1686 (12.5) | 8778 (74.5) | 2998 (25.5) | 10,704 (79.9) | 1280 (9.6) | 1411 (10.5) |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Family income, RMB /month | |||||||||
| 2000 or below | 254 (6.5) | 2843 (72.4) | 448 (11.4) | 380 (9.7) | 2967 (79.8) | 752 (20.2) | 2759 (71.5) | 542 (13.9) | 572 (14.6) |
| 2000–5000 | 833 (6.5) | 8938 (69.8) | 1642 (12.8) | 1385 (10.8) | 9349 (78.5) | 2568 (21.5) | 9238 (71.7) | 1751 (13.7) | 1849 (14.5) |
| 5000–8000 | 621 (6.5) | 6584 (68.7) | 1261 (13.2) | 1119 (11.7) | 6708 (77.2) | 1978 (22.8) | 7044 (73.9) | 1171 (12.3) | 1318 (13.8) |
| 8000 or above | 685 (6.7) | 6886 (67.4) | 1457 (14.3) | 1190 (11.6) | 6834 (75.9) | 2165 (24.1) | 7975 (78.5) | 1007 (9.9) | 1173 (11.6) |
| Don’t know or no answer | 1072 (7.2) | 10,426 (69.6) | 1874 (12.5) | 1605 (10.7) | 10,524 (77.9) | 2987 (22.1) | 11,245 (75.5) | 1822 (12.2) | 1835 (12.3) |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Meat | |||||||||
| Low | 1676 (6.3) | 18,562 (69.9) | 3346 (12.6) | 2959 (11.1) | 19,072 (77.6) | 5519 (22.4) | 19,129 (72.4) | 3608 (13.7) | 2806 (10.6) |
| High | 2013 (7.1) | 19,459 (68.9) | 3775 (13.4) | 2982 (10.6) | 19,758 (77.7) | 5676 (22.3) | 21,858 (77.8) | 3172 (11.3) | 2359 (8.4) |
| p-value | 0.128 | 0.734 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Fried food | |||||||||
| Low | 1617 (6.9) | 16,174 (69.3) | 3051 (13.1) | 2485 (10.7) | 16,465 (77.8) | 4706 (22.2) | 17,798 (76.7) | 2649 (11.4) | 2753 (11.9) |
| High | 2022 (6.5) | 21,515 (69.5) | 4032 (13.0) | 3409 (11.0) | 22,015 (77.4) | 6412 (22.6) | 22,827 (74.0) | 4098 (13.3) | 3906 (12.7) |
| p-value | 0.122 | 0.387 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Screen time | |||||||||
| <2 h | 2222 (6.9) | 22,177 (68.6) | 4353 (13.5) | 3584 (11.1) | 22,405 (76.7) | 6820 (23.3) | 24,428 (75.9) | 3895 (12.1) | 3857 (12.0) |
| ≥2 h | 973 (6.3) | 10,655 (69.2) | 1982 (12.9) | 1792 (11.6) | 11,206 (77.6) | 3239 (22.4) | 11,483 (74.9) | 1933 (12.6) | 1909 (12.5) |
| p-value | 0.262 | 0.033 | 0.022 | ||||||
| Physical activity, MET (min/week) | |||||||||
| 1413.0 or below | 1085 (6.7) | 11,186 (69.5) | 2072 (12.9) | 1750 (10.9) | 11,082 (77.7) | 3176 (22.3) | 12,788 (79.9) | 1721 (10.7) | 1505 (9.4) |
| 1413.0–3399.5 | 1117 (6.8) | 11,320 (69.3) | 2134 (13.1) | 1765 (10.8) | 11,577 (77.3) | 3409 (22.7) | 13,018 (80.0) | 1782 (10.9) | 1475 (9.1) |
| 3399.5 or above | 1047 (6.5) | 11,156 (68.9) | 2193 (13.5) | 1795 (11.1) | 11,888 (77.2) | 3502 (22.8) | 12,750 (79.7) | 1879 (11.7) | 1486 (9.2) |
| p-value | 0.444 | 0.533 | 0.074 | ||||||
| Overweight OR (95% CI) | Obesity OR (95% CI) | Abdominal Obesity OR (95% CI) | Pre-Hypertension OR (95% CI) | Hypertension OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSB | |||||
| SSB Servings/week | |||||
| Model 1 | |||||
| None Servings | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Servings | 1.070 (1.006–1.138) * | 1.033 (0.966–1.103) | 1.050 (0.998–1.106) | 1.027 (0.962–1.096) | 0.995 (0.935–1.058) |
| High Servings | 1.085 (1.016–1.157) * | 1.017 (0.948–1.091) | 1.107 (1.049–1.168) *** | 1.472 (1.380–1.570) *** | 0.945 (0.884–1.010) |
| Model 2 | |||||
| None Servings | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Servings | 1.054 (0.990–1.121) | 1.017 (0.951–1.088) | 1.053 (1.000–1.109) | 1.000 (0.935–1.069) | 0.992 (0.933–1.056) |
| High Servings | 1.052 (0.984–1.125) | 1.057 (0.983–1.137) | 1.124 (1.063–1.187) *** | 1.052 (0.983–1.126) | 0.975 (0.910–1.044) |
| Model 3 | |||||
| None Servings | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Servings | 1.008 (0.934–1.187) | 1.012 (0.934–1.096) | 1.029 (0.966–1.096) | 1.039 (0.957–1.128) | 0.973 (0.902–1.050) |
| High Servings | 1.072 (0.986–1.166) | 1.055 (0.964–1.154) | 1.126 (1.051–1.206) ** | 1.088 (0.998–1.186) | 0.996 (0.915–1.084) |
| Model 4 | |||||
| None Servings | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Servings | 1.039 (0.964–1.120) | 0.992 (0.913–1.078) | 1.028 (0.963–1.096) | 0.994 (0.912–1.083) | 0.926 (0.854–1.004) |
| High Servings | 1.076 (0.989–1.170) | 1.042 (0.948–1.144) | 1.133 (1.054–1.217) ** | 1.025 (0.936–1.123) | 0.927 (0.845–1.016) |
| SSB Frequency/week | |||||
| Model 1 | |||||
| None Frequency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Frequency | 1.078 (1.008–1.153) * | 1.062 (0.988–1.141) | 1.036 (0.980–1.097) | 0.983 (0.915–1.057) | 1.004 (0.938–1.074) |
| High Frequency | 1.067 (1.005–1.132) * | 0.995 (0.933–1.061) | 1.092 (1.039–1.147) *** | 1.347 (1.268–1.431) * | 0.946 (0.891–1.005) |
| Model 2 | |||||
| None Frequency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Frequency | 1.056 (0.987–1.130) | 1.035 (0.962–1.113) | 1.039 (0.982–1.100) | 0.972 (0.903–1.046) | 0.997 (0.932–1.067) |
| High Frequency | 1.042 (0.980–1.107) | 1.019 (0.954–1.089) | 1.102 (1.048–1.158) *** | 1.034 (0.971–1.101) | 0.966 (0.909–1.028) |
| Model 3 | |||||
| None Frequency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Frequency | 1.029 (0.950–1.114) | 1.023 (0.941–1.113) | 1.014 (0.949–1.084) | 0.991 (0.907–1.081) | 0.991 (0.916–1.073) |
| High Frequency | 1.055 (0.981–1.134) | 1.015 (0.940–1.097) | 1.092 (1.028–1.159) * | 1.064 (0.986–1.149) | 0.990 (0.920–1.065) |
| Model 4 | |||||
| None Frequency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium Frequency | 1.033 (0.952–1.120) | 0.995 (0.913–1.084) | 1.009 (0.943–1.079) | 0.961 (0.879–1.051) | 0.954 (0.880–1.035) |
| High Frequency | 1.063 (0.985–1.148) | 0.992 (0.915–1.076) | 1.094 (1.027–1.165) * | 1.049 (0.968–1.136) | 0.963 (0.892–1.040) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gui, Z.-H.; Zhu, Y.-N.; Cai, L.; Sun, F.-H.; Ma, Y.-H.; Jing, J.; Chen, Y.-J. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121302
Gui Z-H, Zhu Y-N, Cai L, Sun F-H, Ma Y-H, Jing J, Chen Y-J. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients. 2017; 9(12):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121302
Chicago/Turabian StyleGui, Zhao-Huan, Yan-Na Zhu, Li Cai, Feng-Hua Sun, Ying-Hua Ma, Jin Jing, and Ya-Jun Chen. 2017. "Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis" Nutrients 9, no. 12: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121302
APA StyleGui, Z.-H., Zhu, Y.-N., Cai, L., Sun, F.-H., Ma, Y.-H., Jing, J., & Chen, Y.-J. (2017). Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients, 9(12), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121302