Effects of Marine Oils, Digested with Human Fluids, on Cellular Viability and Stress Protein Expression in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Collection of Human Digestive Fluids
2.3. Marine Oils
2.4. In Vitro Digestion with Human Digests
2.5. Cell Line
2.6. Cell Experiments
2.7. Harvesting of Caco-2 Cells and Protein Analysis
2.8. Analysis of Peroxide Value (PV) and Aldehydes (HHE & MDA)
2.9. Human Cell Stress Array Analysis
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. MDA and HHE Formation during In Vitro Digestion with Human Digestive Fluids
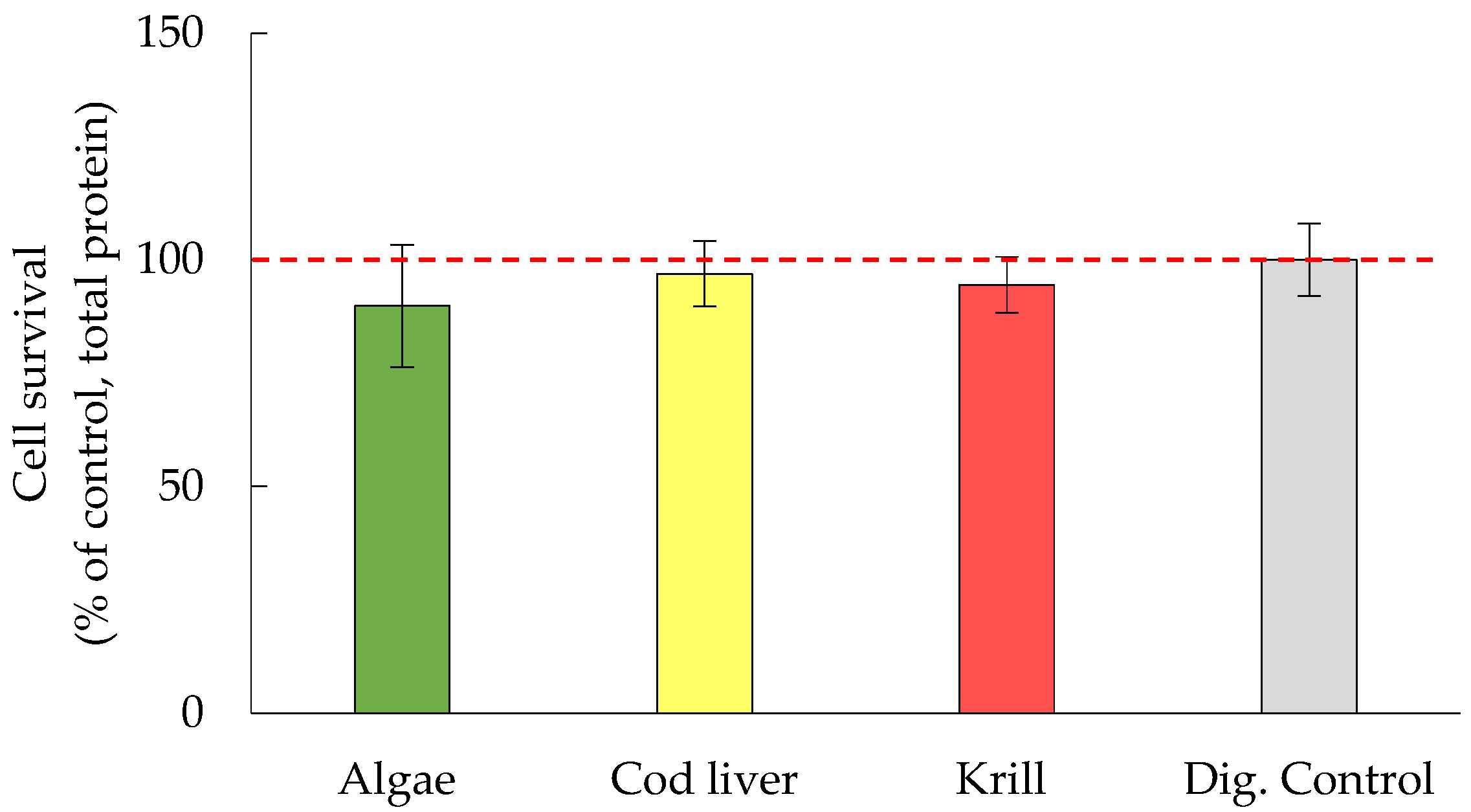
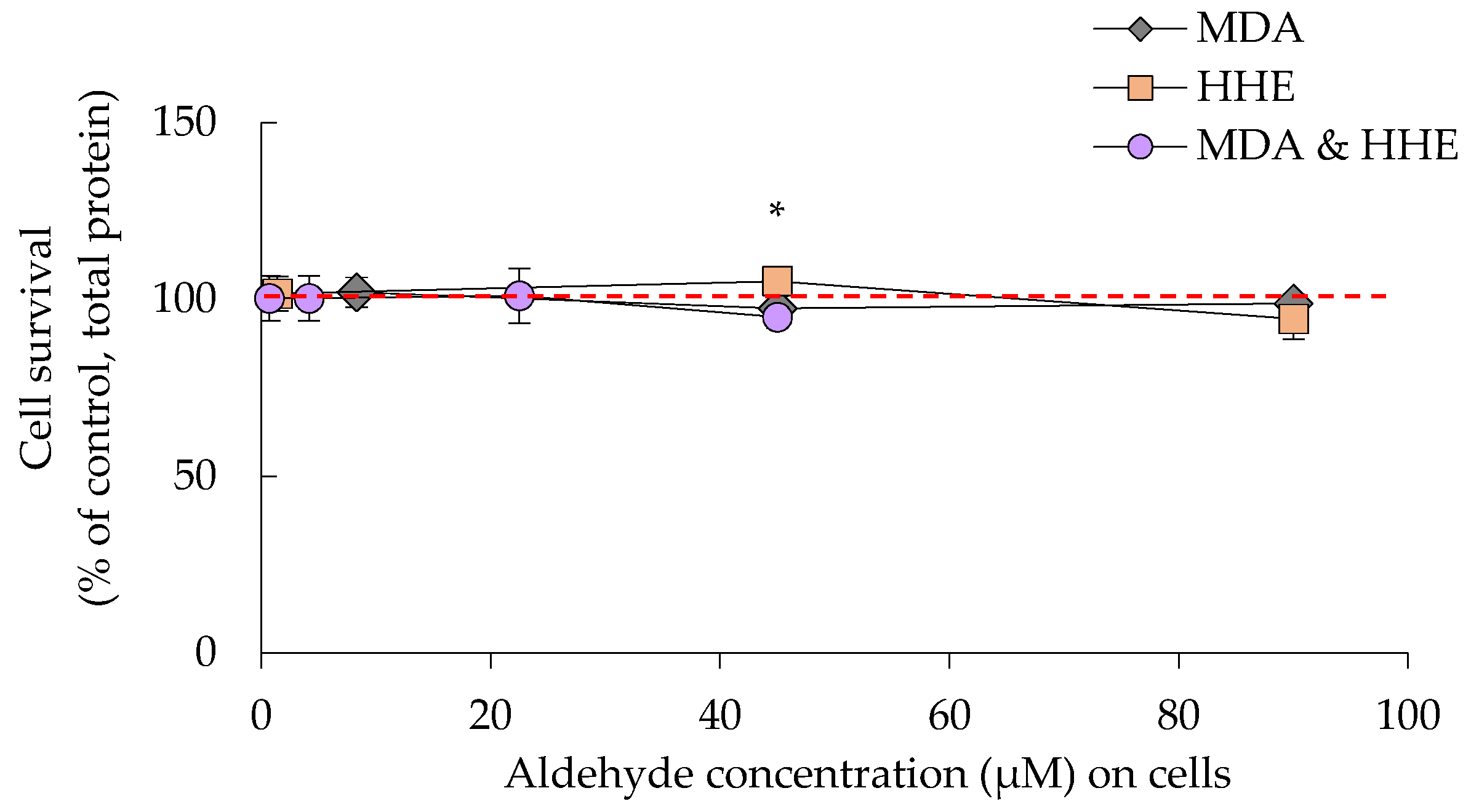
3.2. Cell Survival Was Not Significantly Affected by Either Oil Digests or HHE and MDA
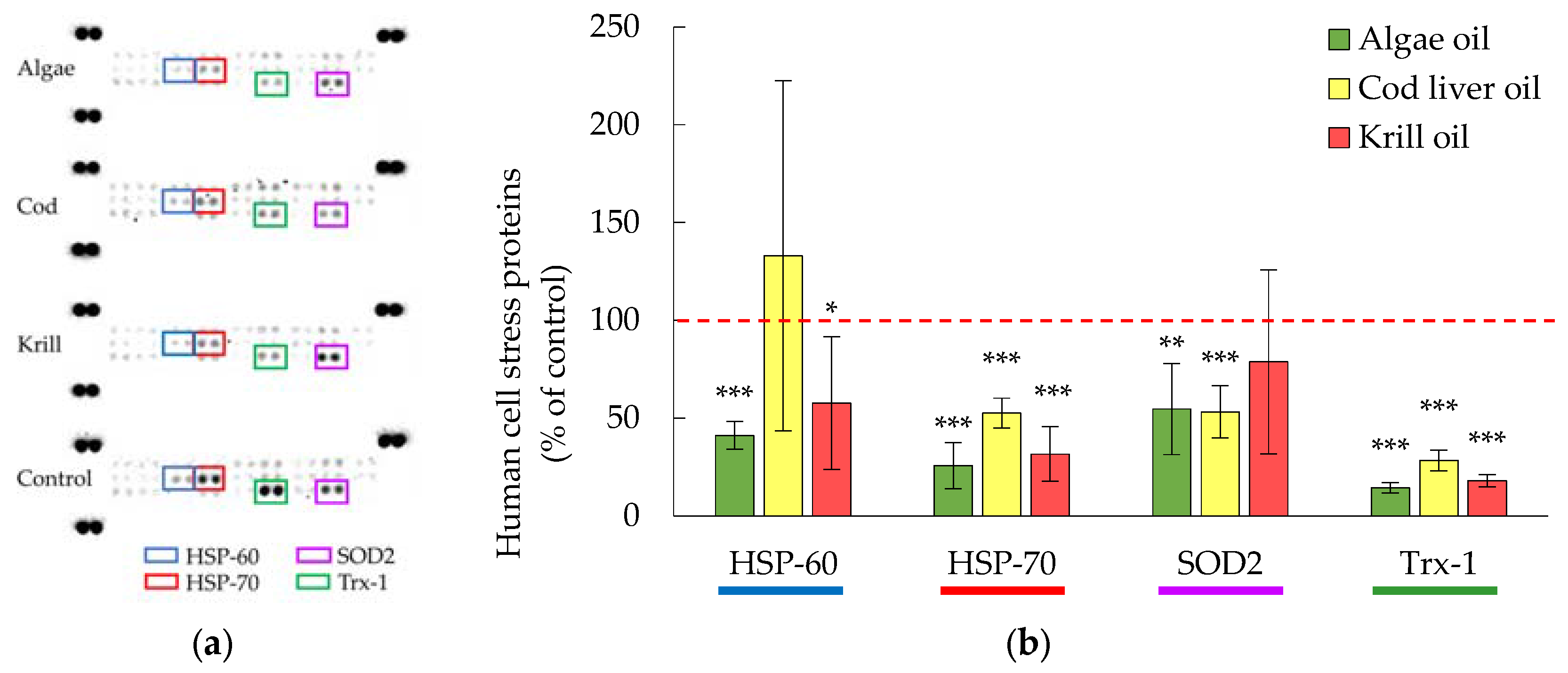
3.3. Cellular Levels of HSP-70 and Trx-1 Were Decreased in the Presence of Digested Marine Oils
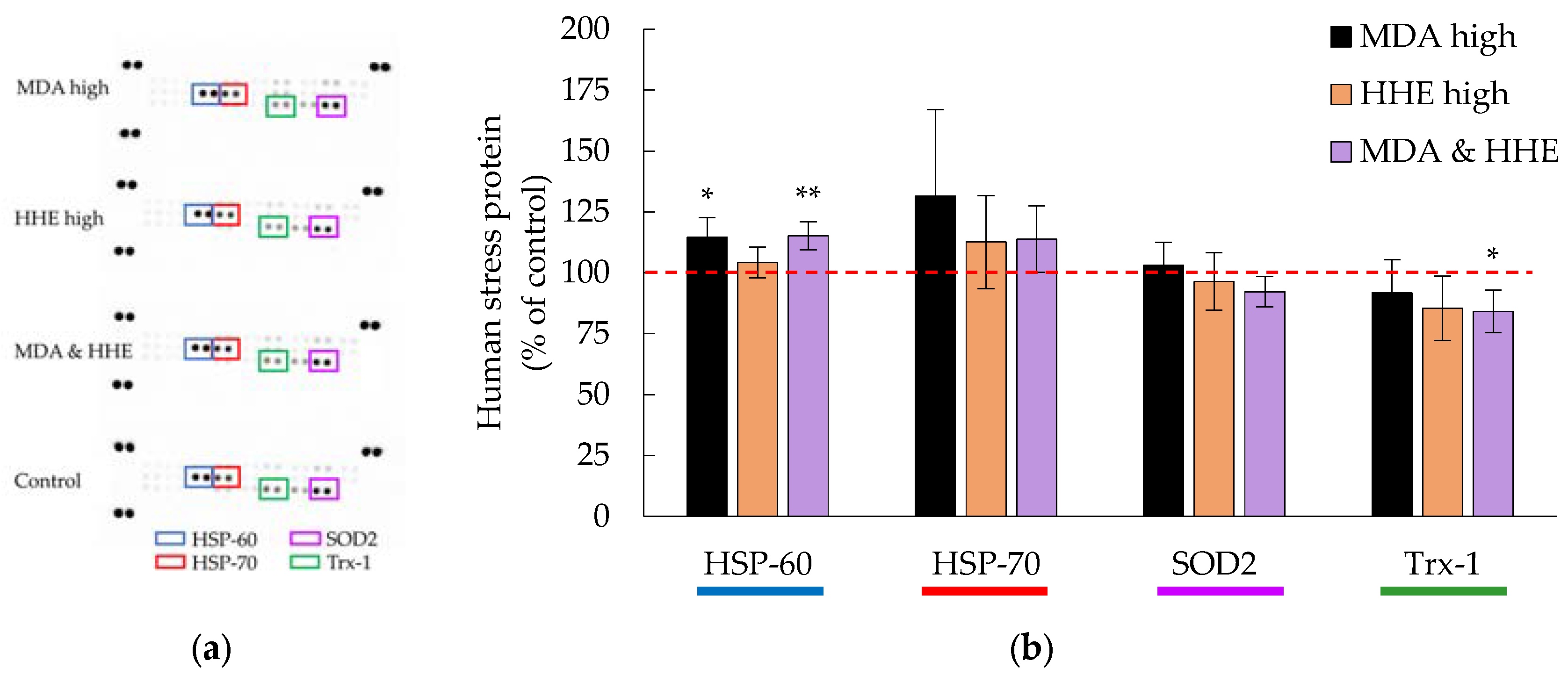
3.4. Cellular Hsp-70 and Trx-1 Levels Were Not Affected by Low MDA and HHE Levels (8.3 and 1.4 μM)
3.5. High Levels (90 μM) of MDA and HHE Did Not Affect the Cellular Levels of HSP-70 and Trx-1
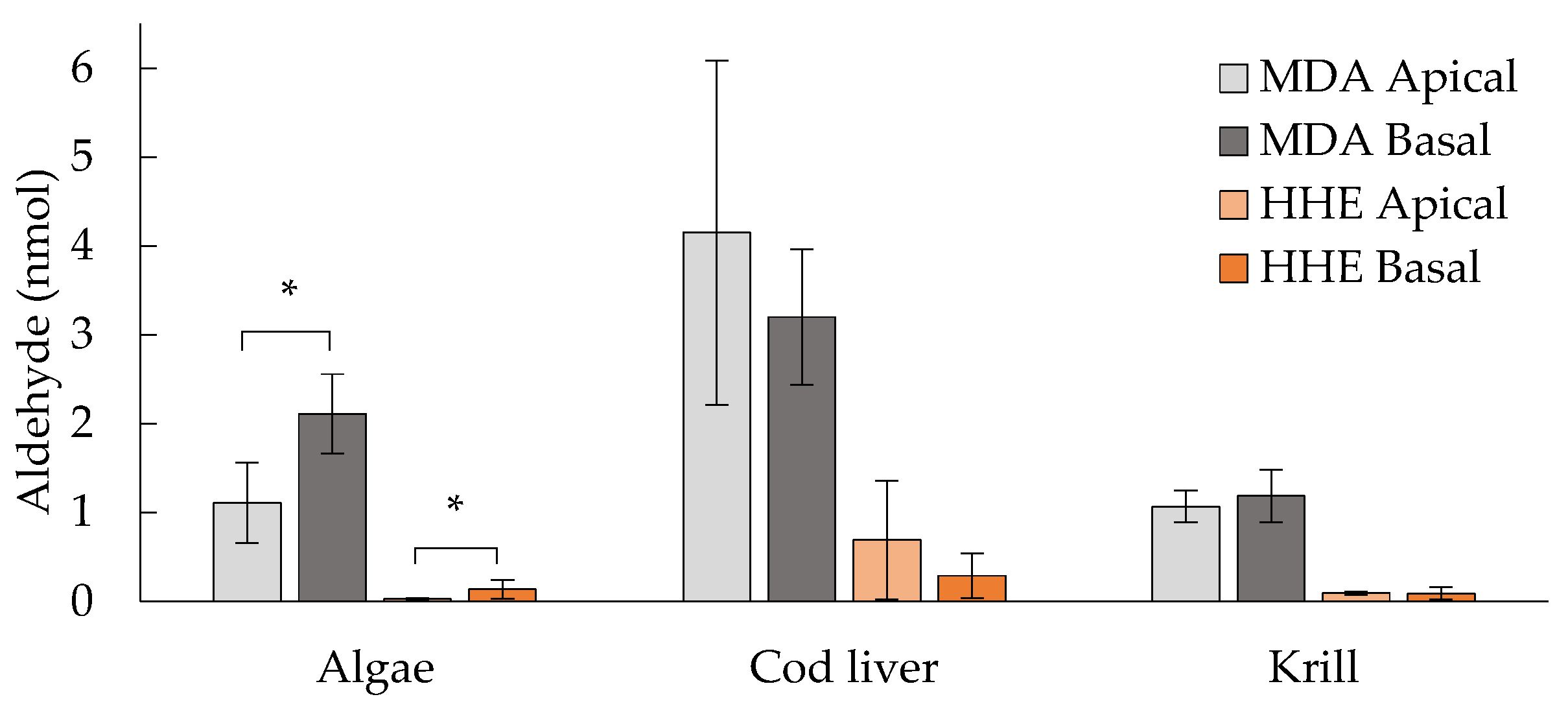
3.6. Levels of MDA and HHE on the Basal Side of the Epithelium
4. Discussion
4.1. Oxidation of the Oils during In Vitro Digestion
4.2. Human Digests of Marine Oils and the Aldehydes MDA and HHE Had No Adverse Effect on the Epithelium
4.3. Comparison of the Different Marine Oils
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V.; Mehra, M.R.; Ventura, H.O. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular diseases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Lista, J.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Perez-Jimenez, F. Long chain omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107 (Suppl. 2), S201–S213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, J.; Lapidot, T. The stomach as a bioreactor: Dietary lipid peroxidation in the gastric fluid and the effects of plant-derived antioxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; McLean, C.H.; Silvers, K.M. Are the health benefits of fish oils limited by products of oxidation? Nutr. Res. Rev. 2006, 19, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, B.B.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Oxidation of marine omega-3 supplements and human health. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 464921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristinova, V.; Storrø, I.; Rustad, T. Influence of human gastric juice on oxidation of marine lipids—In vitro study. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3859–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestre, R.; Douglass, J.D.; Kodukula, S.; Medina, I.; Storch, J. Alterations in the intestinal assimilation of oxidized pufas are ameliorated by a polyphenol-rich grape seed extract in an in vitro model and caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullberg, C.; Larsson, K.; Carlsson, N.G.; Comi, I.; Scheers, N.; Vegarud, G.; Undeland, I. Formation of reactive aldehydes (MDA, HHE, HNE) during the digestion of cod liver oil: Comparison of human and porcine in vitro digestion models. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, K.; Harrysson, H.; Havenaar, R.; Alminger, M.; Undeland, I. Formation of malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (HHE) and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in fish and fish oil during dynamic gastrointestinal in vitro digestion. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1176–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awada, M.; Soulage, C.O.; Meynier, A.; Debard, C.; Plaisancie, P.; Benoit, B.; Picard, G.; Loizon, E.; Chauvin, M.A.; Estienne, M.; et al. Dietary oxidized n-3 PUFA induce oxidative stress and inflammation: Role of intestinal absorption of 4-HHE and reactivity in intestinal cells. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutteridge, J.M. Free-radical damage to lipids, amino acids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids determined by thiobarbituric acid reactivity. Int. J. Biochem. 1982, 14, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, E.N.; Neff, W.E. Formation of malonaldehyde from lipid oxidation-products. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 754, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schaur, R.J.; Zollner, H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 81–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, D.; Stewart, A.J.; Pellegrini, N. A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2005, 15, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, K. Role of reactive aldehyde in cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoPachin, R.M.; Gavin, T. Molecular mechanisms of aldehyde toxicity: A chemical perspective. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kuijk, F.J.; Holte, L.L.; Dratz, E.A. 4-hydroxyhexenal: A lipid peroxidation product derived from oxidized docosahexaenoic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1043, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichardant, M.; Bacot, S.; Moliere, P.; Lagarde, M. Hydroxy-alkenals from the peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids and urinary metabolites. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 75, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awada, M.; Meynier, A.; Soulage, C.O.; Hadji, L.; Geloen, A.; Viau, M.; Ribourg, L.; Benoit, B.; Debard, C.; Guichardant, M.; et al. N-3 PUFA added to high-fat diets affect differently adiposity and inflammation when carried by phospholipids or triacylglycerols in mice. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2013, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, N.K.; Ross, A.B.; Scheers, N.; Savolainen, O.I.; Nookaew, I.; Gabrielsson, B.G.; Sandberg, A.S. Splenic immune response is down-regulated in C57BL/6J mice fed eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid enriched high fat diet. Nutrients 2017, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.; Morbini, M.; Borghi, C. Do we need ‘new’ omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids formulations? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adarme-Vega, T.C.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Schenk, P.M. Towards sustainable sources for omega-3 fatty acids production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 26, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassis, N.M.; Gigliotti, J.C.; Beamer, S.K.; Tou, J.C.; Jaczynski, J. Characterization of lipids and antioxidant capacity of novel nutraceutical egg products developed with omega-3-rich oils. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tou, J.C.; Jaczynski, J.; Chen, Y.C. Krill for human consumption: Nutritional value and potential health benefits. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, H.; Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, L. The oxidative stability of microalgae oil (Schizochytrium aggregatum) and its antioxidant activity after simulated gastrointestinal digestion: Relationship with constituents. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1928–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulleberg, E.K.; Comi, I.; Holm, H.; Herud, E.B.; Jacobsen, M.; Vegarud, G.E. Human gastrointestinal juices intended for use in in vitro digestion models. Food Dig. 2011, 2, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, H.; Krogdahl, A.; Hanssen, L.E. High and low inhibitor soybean meals affect human duodenal proteinase activity differently: In vitro comparison of proteinase inhibition. J. Nutr. 1988, 118, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykkesfeldt, J. Determination of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography using subtraction methods: Reliable reduction with tris[2-carboxyethyl]phosphine hydrochloride. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 282, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrikson, M.; Carlsson, N.G.; Almgren, A.; Sandberg, A.S. Simultaneous and sensitive analysis of Cu, Ni, Zn, Co, Mn, and Fe in food and biological samples by ion chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jónsdóttir, R.; Geirsdottir, M.; Hamaguchi, P.Y.; Jamnik, P.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Undeland, I. The ability of in vitro antioxidant assays to predict the efficiency of a cod protein hydrolysate and brown seaweed extract to prevent oxidation in marine food model systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavonius, L.R.; Carlsson, N.-G.; Undeland, I. Quantification of total fatty acids in microalgae: Comparison of extraction and transesterification methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7313–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazeer, R.; Gao, H.; Howell, N.K. Cytotoxicity of oxidised lipids in cultured colonal human intestinal cancer cells (caco-2 cells). Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 180, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undeland, I.; Hultin, H.O.; Richards, M.P. Added triacylglycerols do not hasten hemoglobin-mediated lipid oxidation in washed minced cod muscle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6847–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.; Martinus, R.D. Hyperglycaemia and oxidative stress upregulate HSP60 & HSP70 expression in hela cells. Springerplus 2013, 2, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibowitz, G.; Ktorza, A.; Cerasi, E. The role of txnip in the pathophysiology of diabetes and its vascular complications: A concise review. Medicographia 2014, 36, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, K.; Tullberg, C.; Alminger, M.; Havenaar, R.; Undeland, I. Malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal are formed during dynamic gastrointestinal in vitro digestion of cod liver oils. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3458–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppeler, C.; Haugen, J.-E.; Rødbotten, R.; Kirkhus, B. Formation of malondialdehyde, 4-hydroxynonenal, and 4-hydroxyhexenal during in vitro digestion of cooked beef, pork, chicken, and salmon. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikado, A.; Morino, K.; Nishio, Y.; Nakagawa, F.; Mukose, A.; Sono, Y.; Yoshioka, N.; Kondo, K.; Sekine, O.; Yoshizaki, T.; et al. 4-hydroxy hexenal derived from docosahexaenoic acid protects endothelial cells via Nrf2 activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Sethi, S. Oxidized omega-3 fatty acids inhibit NF-κB activation via a PPARα-dependent pathway. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, J.; Galano, J.M.; Durand, T.; Le Guennec, J.Y.; Lee, J.C. Physiological role of reactive oxygen species as promoters of natural defenses. FASEB J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.R.; Duryee, M.J.; Shurmur, S.W.; Um, J.Y.; Bussey, W.D.; Hunter, C.D.; Garvin, R.P.; Sayles, H.R.; Mikuls, T.R.; Klassen, L.W.; et al. Unique antibody responses to malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde (MAA)-protein adducts predict coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayathilake, A.G.; Senior, P.V.; Su, X.Q. Krill oil extract suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.; Cesi, V.; Prete, E.; Negroni, A.; Palone, F.; Cucchiara, S.; Oliva, S.; Leter, B.; Stronati, L. Krill oil reduces intestinal inflammation by improving epithelial integrity and impairing adherent-invasive escherichia coli pathogenicity. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobraico, J.M.; DiLello, L.C.; Butler, A.D.; Cordisco, M.E.; Petrini, J.R.; Ahmadi, R. Effects of krill oil on endothelial function and other cardiovascular risk factors in participants with type 2 diabetes, a randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2015, 3, e000107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nr | Analyte | Nr | Analyte |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ADAMTS1 | 14 | IDO |
| 2 | Bcl-2 | 15 | Phospho-JNK PAN (T183/Y185) |
| 3 | Carbonic Anhydrase IX | 16 | NFκB1 |
| 4 | Cited-2 | 17 | p21/CIP1 |
| 5 | COX-2 | 18 | p27 |
| 6 | Cytochrome C (Cyt C) | 19 | Phospho-p38a (T180/Y182) |
| 7 | Dickkopf-4 (Dkk-4) | 20 | Phospho-p53 (S46) |
| 8 | Fatty acid-binding protein 1 (FABP-1) | 21 | Paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) |
| 9 | HIF-1a | 22 | Paraoxonase-2 (PON-2) |
| 10 | HIF-2a | 23 | Paraoxonase-3 (PON-3) |
| 11 | Phospho-HSP27 (S78/S82) | 24 | Thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) |
| 12 | Heat Shock Protein-60 (HSP-60) | 25 | Deacetylase Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) |
| 13 | Heat Shock Protein-70 (HSP-70) | 26 | Superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) |
| Marine Oil | MDA μM ± SD | HHE μM ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Algae oil | 4.45 ± 1.81 | 0.13 ± 0.039 |
| Cod liver oil | 16.6 ± 7.74 | 2.77 ± 2.66 |
| Krill oil | 4.29 ± 0.70 | 0.38 ± 0.061 |
| HHE (nmol) Added | HHE (nmol), BM |
|---|---|
| 0.7 | 0.0080 ± 0.0042 |
| 0.0325 | 0.0035 ± 0.0011 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tullberg, C.; Vegarud, G.; Undeland, I.; Scheers, N. Effects of Marine Oils, Digested with Human Fluids, on Cellular Viability and Stress Protein Expression in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111213
Tullberg C, Vegarud G, Undeland I, Scheers N. Effects of Marine Oils, Digested with Human Fluids, on Cellular Viability and Stress Protein Expression in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Nutrients. 2017; 9(11):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111213
Chicago/Turabian StyleTullberg, Cecilia, Gerd Vegarud, Ingrid Undeland, and Nathalie Scheers. 2017. "Effects of Marine Oils, Digested with Human Fluids, on Cellular Viability and Stress Protein Expression in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells" Nutrients 9, no. 11: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111213
APA StyleTullberg, C., Vegarud, G., Undeland, I., & Scheers, N. (2017). Effects of Marine Oils, Digested with Human Fluids, on Cellular Viability and Stress Protein Expression in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Nutrients, 9(11), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111213





