Hypocholesterolaemic Activity of Lupin Peptides: Investigation on the Crosstalk between Human Enterocytes and Hepatocytes Using a Co-Culture System Including Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Peptic and Tryptic Peptide Mixtures
2.3. Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.4. Cell Treatments with Lupin Peptides
2.5. Cell Monolayer Integrity and Differentiation Evaluation
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Quantification of Excreted PCSK9 in Cell Culture Experiments by ELISA
2.8. Statistically Analysis
3. Results
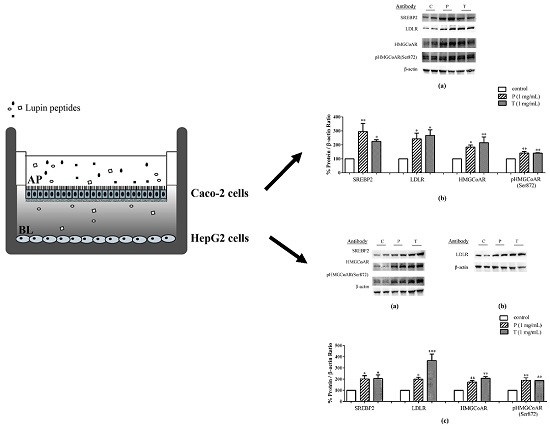
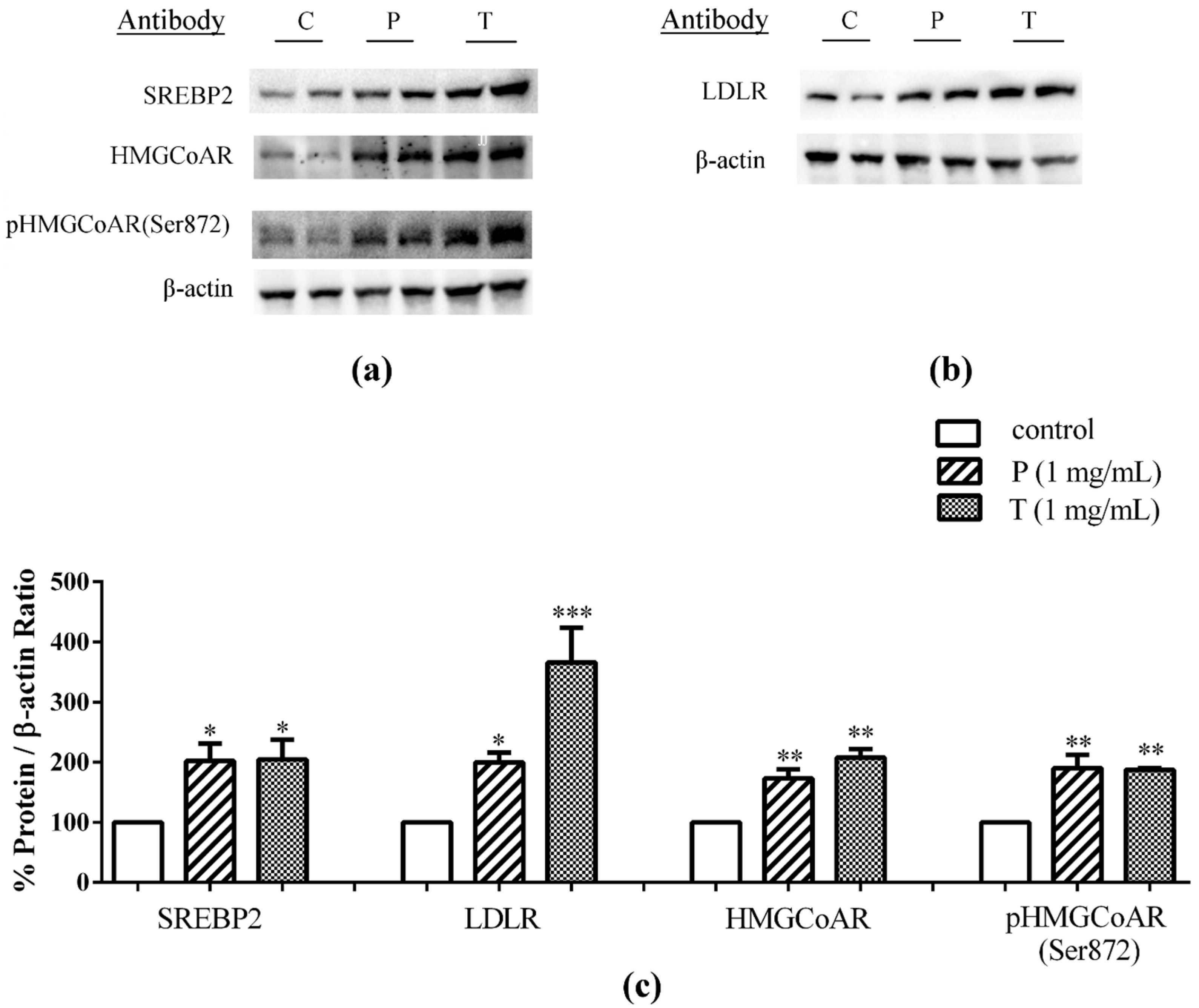
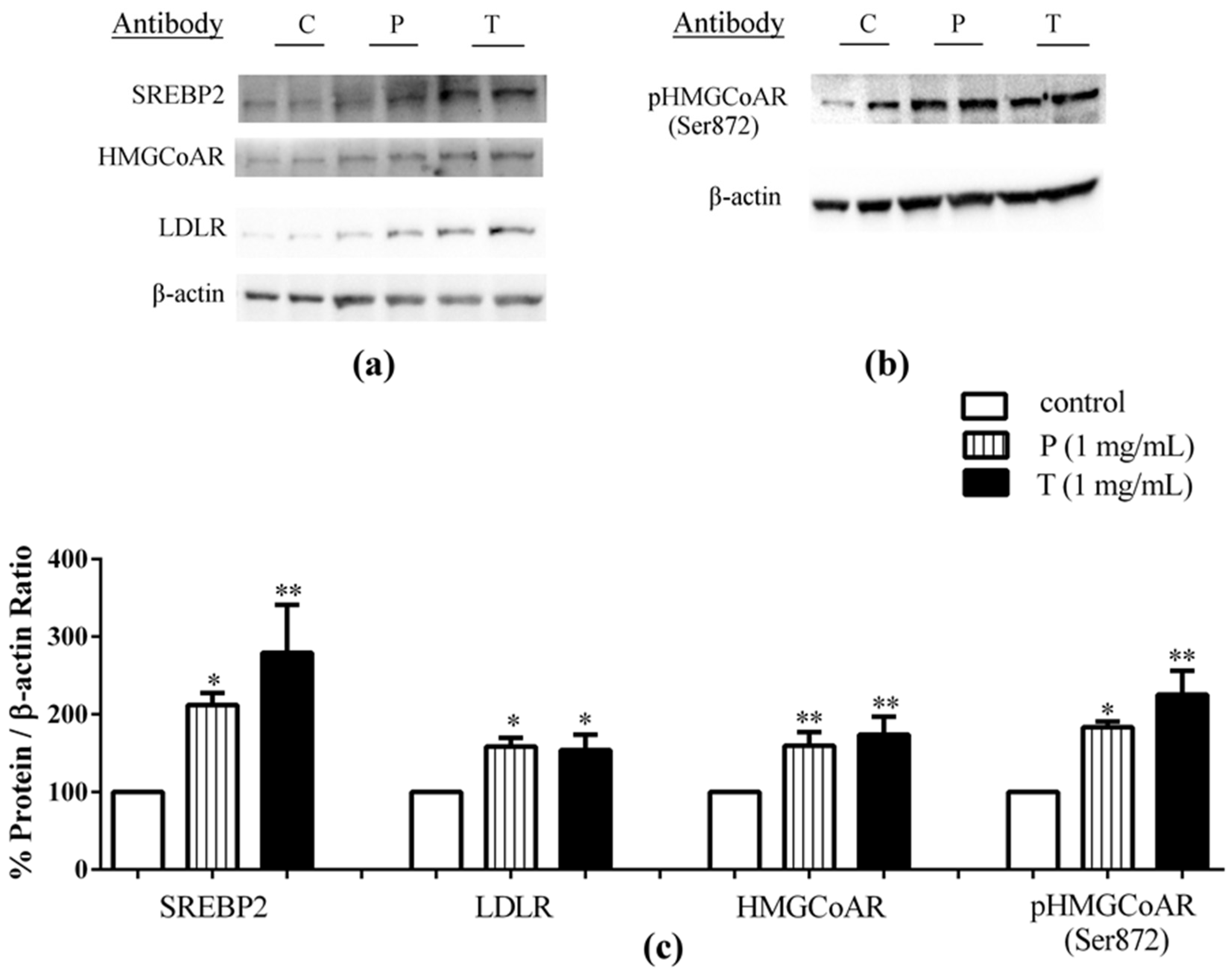
3.1. Absorbed Lupin Peptides Maintain the Capacity to Induce the Up-Regulation of LDLR-SREBP2 Pathway in HepG2 Cells
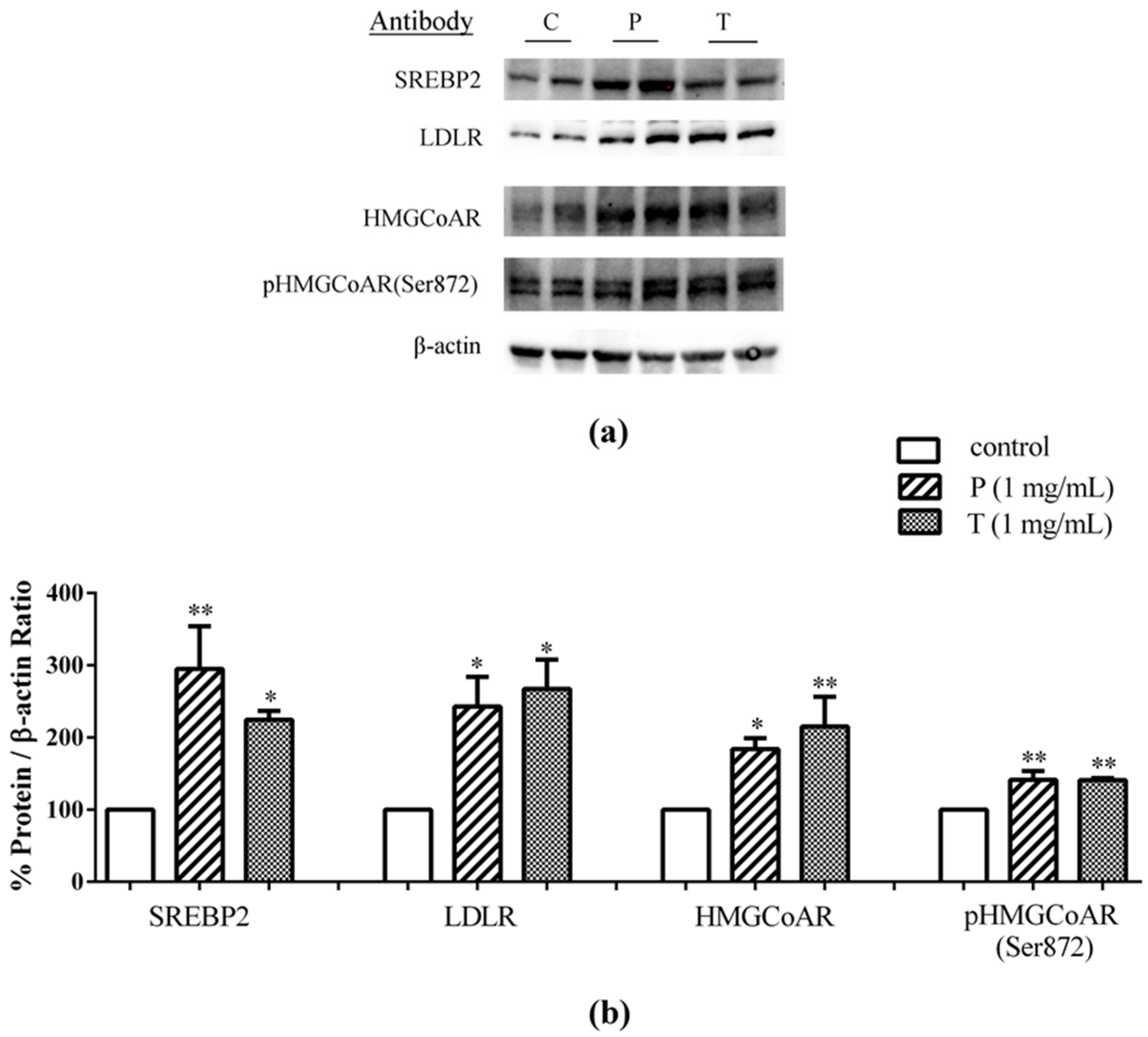
3.2. Lupin Peptides Mediate the Up-Regulation of LDLR-SREBP2 in Human Intestinal Cells
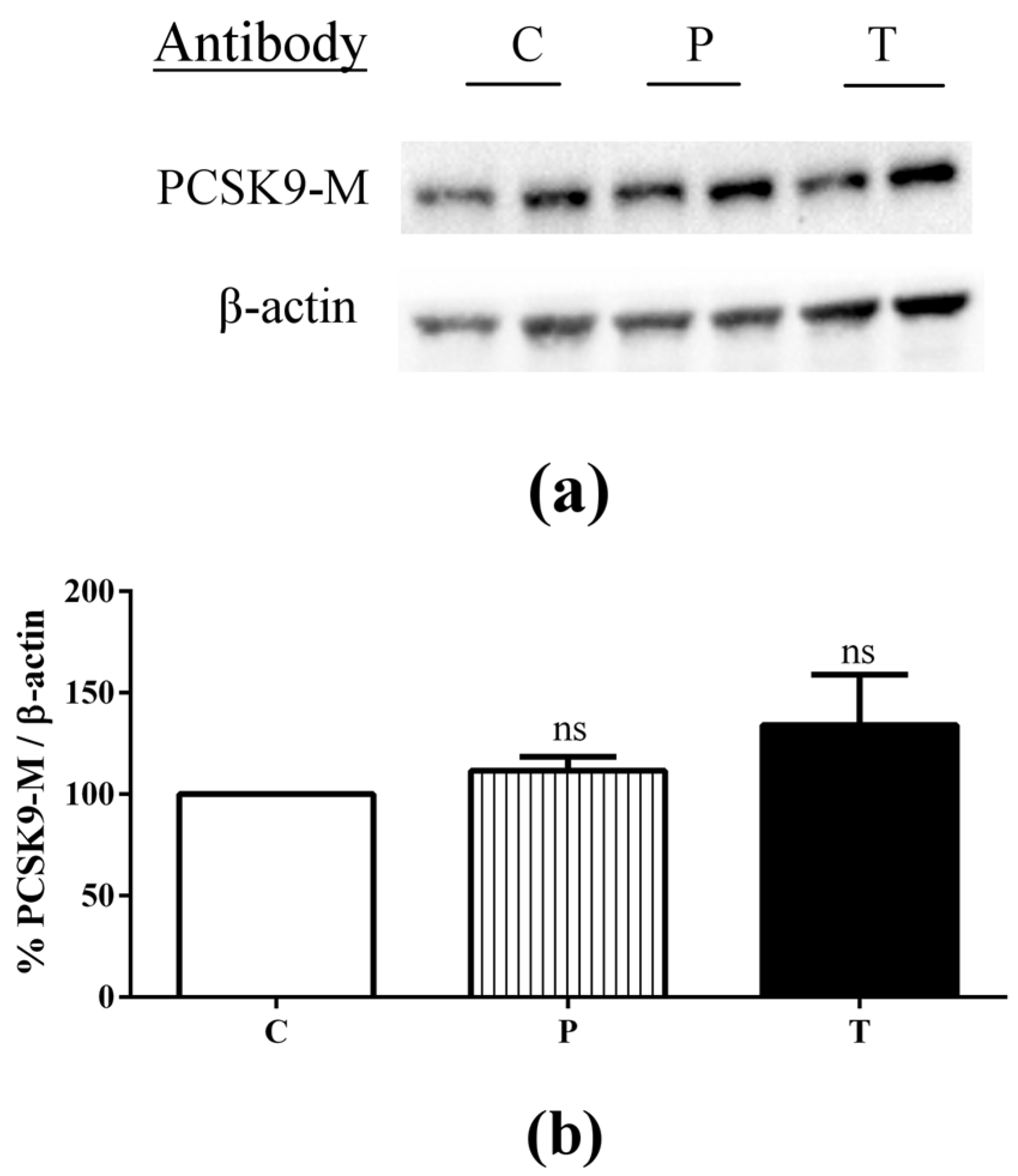
3.3. Lupin Peptides Decrease the Ability of Caco-2 Cells to Secrete PCSK9 in the BL Medium
4. Discussion
4.1. Absorbed Lupin Peptides Maintain Their Hypocholesterolaemic Activity on Human Hepatic HepG2 Cells Grown in a Co-Culture System
4.2. Role of Lupin Peptides in the Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism in Human Intestinal Cells
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMPK | 5′-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| AP | apical |
| BL | basolateral |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FBS | Foetal bovine serum |
| HMGCoAR | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase |
| HNF-1 | alpha hepatic nuclear factor 1 alpha |
| LDL | low density lipoprotein |
| LDLR | low density lipoprotein receptor |
| NPC1L1 | Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 |
| PCSK9 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 |
| SREBP-2 | sterol regulatory element binding proteins 2 |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulphate—polyacrylamide |
| TEER | trans-epithelial electrical resistance |
| TICE | trans-intestinal cholesterol efflux |
Appendix A

References
- Sujak, A.; Kotlarz, A.; Strobel, W. Compositional and nutritional evaluation of several lupin seeds. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschin, G.; Arnoldi, A. Legumes are valuable sources of tocopherols. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siger, A.; Czubinski, J.; Kachlicki, P.; Dwiecki, K.; Lampart-Szczapa, E.; Nogala-Kalucka, M. Antioxidant activity and phenolic content in three lupin species. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 25, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, Y.; Ibrahim, R.K.; Tahara, S. HPLC analysis of white lupin isoflavonoids. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoldi, A.; Boschin, G.; Zanoni, C.; Lammi, C. The health benefits of sweet lupin seed flours and isolated proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, C.; Sessa, F.; Accardo, E.; Vanoni, M.; Morazzoni, P.; Scarafoni, A.; Duranti, M. Conglutin gamma, a lupin seed protein, binds insulin in vitro and reduces plasma glucose levels of hyperglycemic rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoglio, J.C.; Calvo, M.A.; Hancke, J.L.; Burgos, R.A.; Riva, A.; Morazzoni, P.; Ponzone, C.; Magni, C.; Duranti, M. Hypoglycemic effect of lupin seed γ-conglutin in experimental animals and healthy human subjects. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschin, G.; Scigliuolo, G.M.; Resta, D.; Arnoldi, A. ACE-inhibitory activity of enzymatic protein hydrolysates from lupin and other legumes. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.P.; Mori, T.A.; Puddey, I.B.; Sipsas, S.; Ackland, T.R.; Beilin, L.J.; Hodgson, J.M. Effects of lupin kernel flour-enriched bread on blood pressure: A controlled intervention study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R.; Lovati, M.R.; Manzoni, C.; Castiglioni, S.; Duranti, M.; Magni, C.; Morandi, S.; D’Agostina, A.; Arnoldi, A. Proteins of white lupin seed, a naturally isoflavone-poor legume, reduce cholesterolemia in rats and increase LDL receptor activity in HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bettzieche, A.; Brandsch, C.; Schmidt, M.; Weisse, K.; Eder, K.; Stangl, G. Differing effect of protein isolates from different cultivars of blue lupin on plasma lipoproteins of hypercholesterolemic rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 3114–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, M.; Parolini, C.; Diani, E.; Rigamonti, E.; Cornelli, L.; Arnoldi, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Chiesa, G. Hypolipidaemic and anti-atherosclerotic effects of lupin proteins in a rabbit model. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanari, G.G.; Batistuti, J.; da Cruz, R.; Saldiva, P.; Areas, J. Cholesterol-lowering effect of whole lupin (Lupinus albus) seed and its protein isolate. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähr, M.; Fechner, A.; Kiehntopf, M.; Jahreis, G. Consuming a mixed diet enriched with lupin protein beneficially affects plasma lipids in hypercholesterolemic subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R.; Triolo, M.; Bosisio, R.; Bondioli, A.; Calabresi, L.; De Vergori, V.; Gomaraschi, M.; Mombelli, G.; Pazzucconi, F.; Zacherl, C.; et al. Hypocholesterolaemic effects of lupin protein and pea protein/fibre combinations in moderately hypercholesterolaemic individuals. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Scigliuolo, G.M.; D’Amato, A.; Arnoldi, A. Lupin Peptides Lower Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Cholesterol through an Up-regulation of the LDL Receptor/Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 2 (SREBP2) Pathway at HepG2 Cell Line. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7151–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.M.; Zhang, D.W. Hypercholesterolemia, low density lipoprotein receptor and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin-type 9. J. Biomed. Res. 2015, 29, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.A.; Raal, F.J. Lipid-lowering drug therapy for CVD prevention: Looking into the future. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Song, K.; Zhu, M.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) in lipid metabolism, atherosclerosis and ischemic stroke. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunzioni, I.; Tavori, H. New developments in atherosclerosis: Clinical potential of PCSK9 inhibition. Vasc. Health Risk. Manag. 2015, 11, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Calabresi, L.; Arnoldi, A. Lupin protein exerts cholesterol-lowering effects targeting PCSK9: From clinical evidences to elucidation of the in vitro molecular mechanism using HepG2 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzza, S.; Scarino, M.L.; Gambling, L.; Natella, F.; Sambuy, Y. Biphasic effect of iron on human intestinal Caco-2 cells: Early effect on tight junction permeability with delayed onset of oxidative cytotoxic damage. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-Grand) 2003, 49, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, M.; Grootaert, C.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.C.; Van Camp, J.; Toldra, F. Transepithelial transport of dry-cured ham peptides with ACE inhibitory activity through a Caco-2 cell monolayer. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Aiello, G.; Vistoli, G.; Zanoni, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Sambuy, Y.; Ferruzza, S.; Ranaldi, G. A multidisciplinary investigation on the bioavailability and activity of peptides from lupin protein. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havekes, L.; van Hinsbergh, V.; Kempen, H.J.; Emeis, J. The metabolism in vitro of human low-density lipoprotein by the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. Biochem. J. 1983, 214, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitt, N.B. Hep G2 cells as a resource for metabolic studies: Lipoprotein, cholesterol, and bile acids. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vrins, C.L. From blood to gut: Direct secretion of cholesterol via transintestinal cholesterol efflux. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5953–5957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Veen, J.N.; van Dijk, T.H.; Vrins, C.L.; van Meer, H.; Havinga, R.; Bijsterveld, K.; Tietge, U.J.; Groen, A.K.; Kuipers, F. Activation of the liver X receptor stimulates trans-intestinal excretion of plasma cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19211–19219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Velde, A.E.; Vrins, C.L.; van den Oever, K.; Kunne, C.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Kuipers, F.; Groen, A.K. Direct intestinal cholesterol secretion contributes significantly to total fecal neutral sterol excretion in mice. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natoli, M.; Leoni, B.D.; D’Agnano, I.; D’Onofrio, M.; Brandi, R.; Arisi, I.; Zucco, F.; Felsani, A. Cell growing density affects the structural and functional properties of Caco-2 differentiated monolayer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzza, S.; Rossi, C.; Scarino, M.L.; Sambuy, Y. A protocol for differentiation of human intestinal Caco-2 cells in asymmetric serum-containing medium. Toxicol. in Vitro 2012, 26, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.T. Optimizing lipid lowering in patients at risk. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 27, III22–III26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Transcriptional mediators of lipid homeostasis. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2002, 67, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.A.; Tabor, D.; Kast, H.R.; Venkateswaran, A. Regulation of gene expression by SREBP and SCAP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1529, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.; Ben Djoudi Ouadda, A.; Spahis, S.; Sane, A.T.; Garofalo, C.; Grenier, É.; Emonnot, L.; Yara, S.; Couture, P.; Beaulieu, J.F.; et al. PCSK9 plays a significant role in cholesterol homeostasis and lipid transport in intestinal epithelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Yokode, M.; Hammer, R.E.; Hofmann, S.L.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Anderson, R.G. Tissue-specific sorting of the human LDL receptor in polarized epithelia of transgenic mice. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 111, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 1990, 343, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallottini, V.; Martini, C.; Pascolini, A.; Cavallini, G.; Gori, Z.; Bergamini, E.; Incerpi, S.; Trentalance, A. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase deregulation and age-related hypercholesterolemia: A new role for ROS. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005, 126, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, Y.P.; Davies, S.P.; Hardie, D.G. Analysis of the specificity of the AMP-activated protein kinase by site-directed mutagenesis of bacterially expressed 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, using a single primer variant of the unique-site-elimination method. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidah, N.G.; Awan, Z.; Chrétien, M.; Mbikay, M. PCSK9: A key modulator of cardiovascular health. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, S.; Tavori, H.; Brown, P.E.; Linton, M.F.; He, J.; Giunzioni, I.; Fazio, S. Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 promotes intestinal overproduction of triglyceride-rich apolipoprotein B lipoproteins through both low-density lipoprotein receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Circulation 2014, 130, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le May, C.; Kourimate, S.; Langhi, C.; Chétiveaux, M.; Jarry, A.; Comera, C.; Collet, X.; Kuipers, F.; Krempf, M.; Cariou, B.; et al. Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 null mice are protected from postprandial triglyceridemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le May, C.; Berger, J.M.; Lespine, A.; Pillot, B.; Prieur, X.; Letessier, E.; Hussain, M.M.; Collet, X.; Cariou, B.; Costet, P. Transintestinal cholesterol excretion is an active metabolic process modulated by PCSK9 and statin involving ABCB1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | C | Peptic Peptides | Tryptic Peptides |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secreted PCSK9 in BL solution (ng/mL) | 4.82 ± 0.35 | 4.10 ± 0.46 * | 3.20 ± 0.25 ** |
| Secreted PCSK9 in AP solution (ng/mL) | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Ferruzza, S.; Ranaldi, G.; Sambuy, Y.; Arnoldi, A. Hypocholesterolaemic Activity of Lupin Peptides: Investigation on the Crosstalk between Human Enterocytes and Hepatocytes Using a Co-Culture System Including Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2016, 8, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070437
Lammi C, Zanoni C, Ferruzza S, Ranaldi G, Sambuy Y, Arnoldi A. Hypocholesterolaemic Activity of Lupin Peptides: Investigation on the Crosstalk between Human Enterocytes and Hepatocytes Using a Co-Culture System Including Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients. 2016; 8(7):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070437
Chicago/Turabian StyleLammi, Carmen, Chiara Zanoni, Simonetta Ferruzza, Giulia Ranaldi, Yula Sambuy, and Anna Arnoldi. 2016. "Hypocholesterolaemic Activity of Lupin Peptides: Investigation on the Crosstalk between Human Enterocytes and Hepatocytes Using a Co-Culture System Including Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells" Nutrients 8, no. 7: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070437
APA StyleLammi, C., Zanoni, C., Ferruzza, S., Ranaldi, G., Sambuy, Y., & Arnoldi, A. (2016). Hypocholesterolaemic Activity of Lupin Peptides: Investigation on the Crosstalk between Human Enterocytes and Hepatocytes Using a Co-Culture System Including Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients, 8(7), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070437