Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract and Fish Oil Improves Memory in Mice via Modulation of Anti-Oxidative Stress and Regulation of BDNF/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PSE, FO and MPF
2.2. Neurite Outgrowth Assay
2.3. Animal Study and Experimental Design
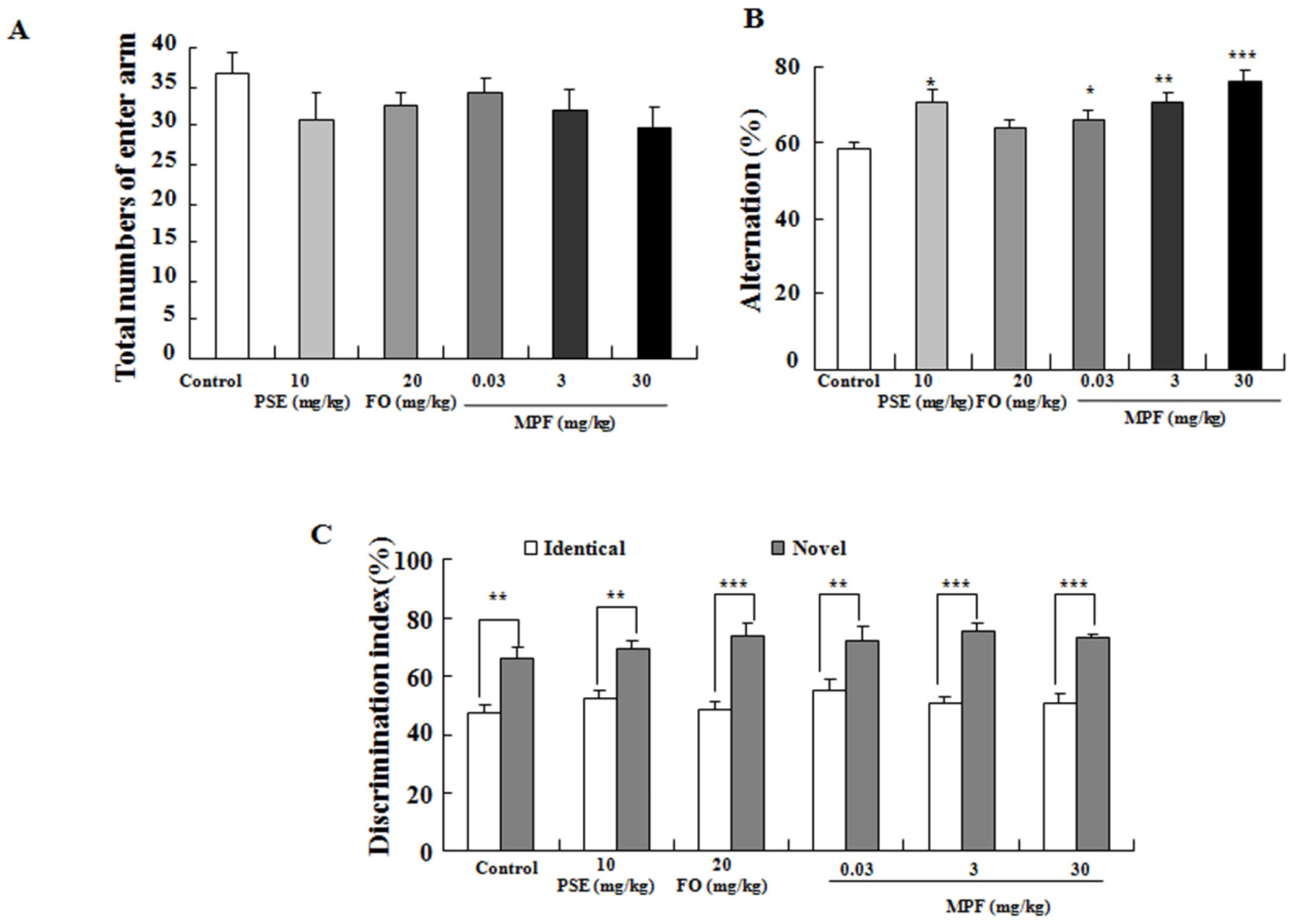
2.3.1. Y-Maze Memory Test
2.3.2. NOR Memory Tasks
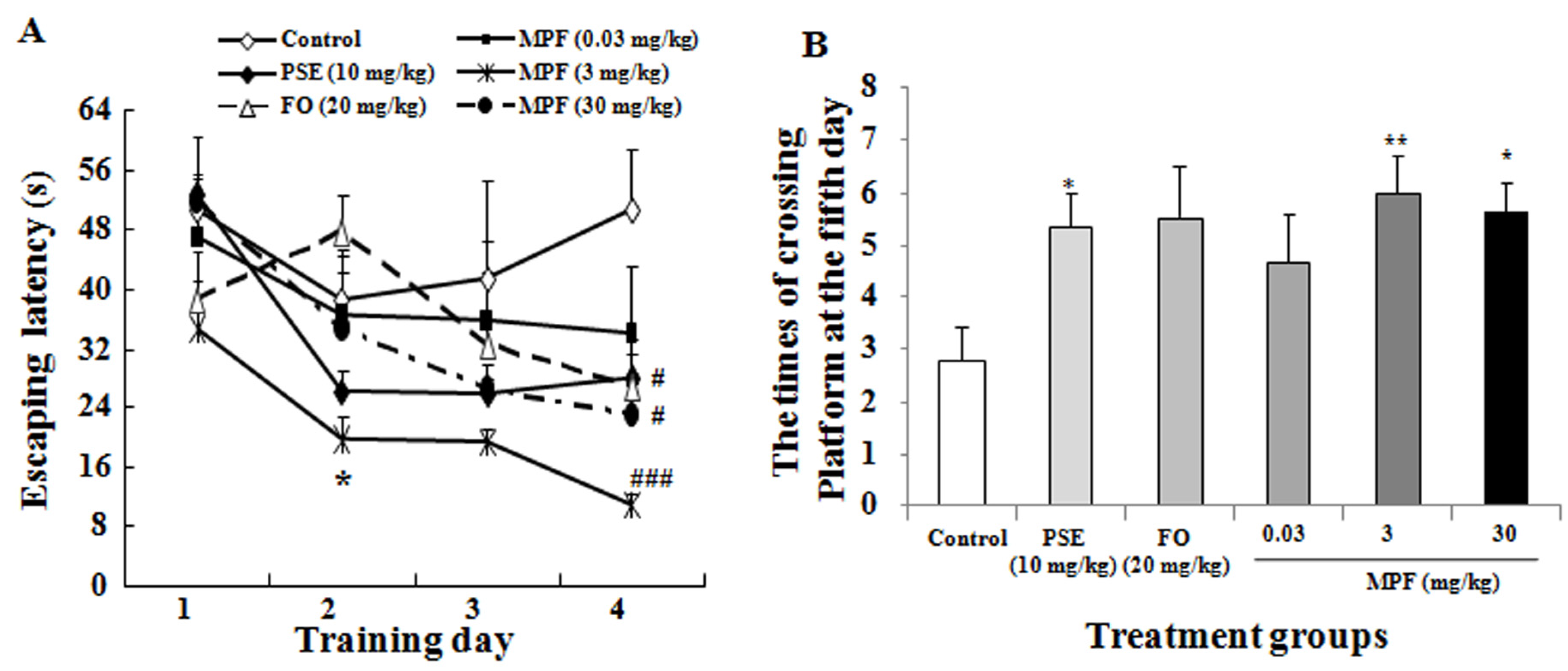
2.3.3. Morris Water Maze Test
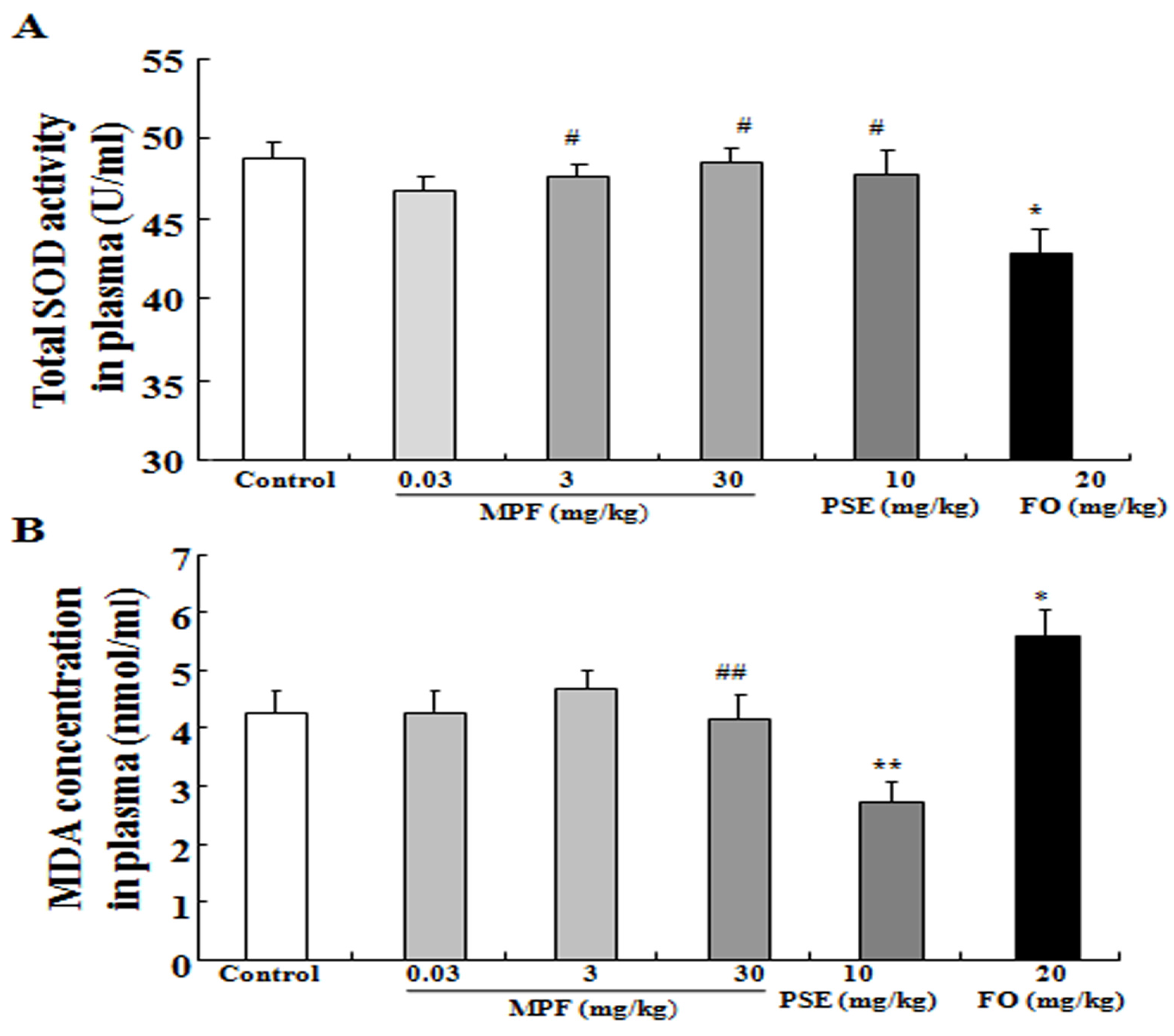
2.4. SOD Activity and MDA Level in the Plasma, the Cerebral Cortex and the Hippocampus
2.5. Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
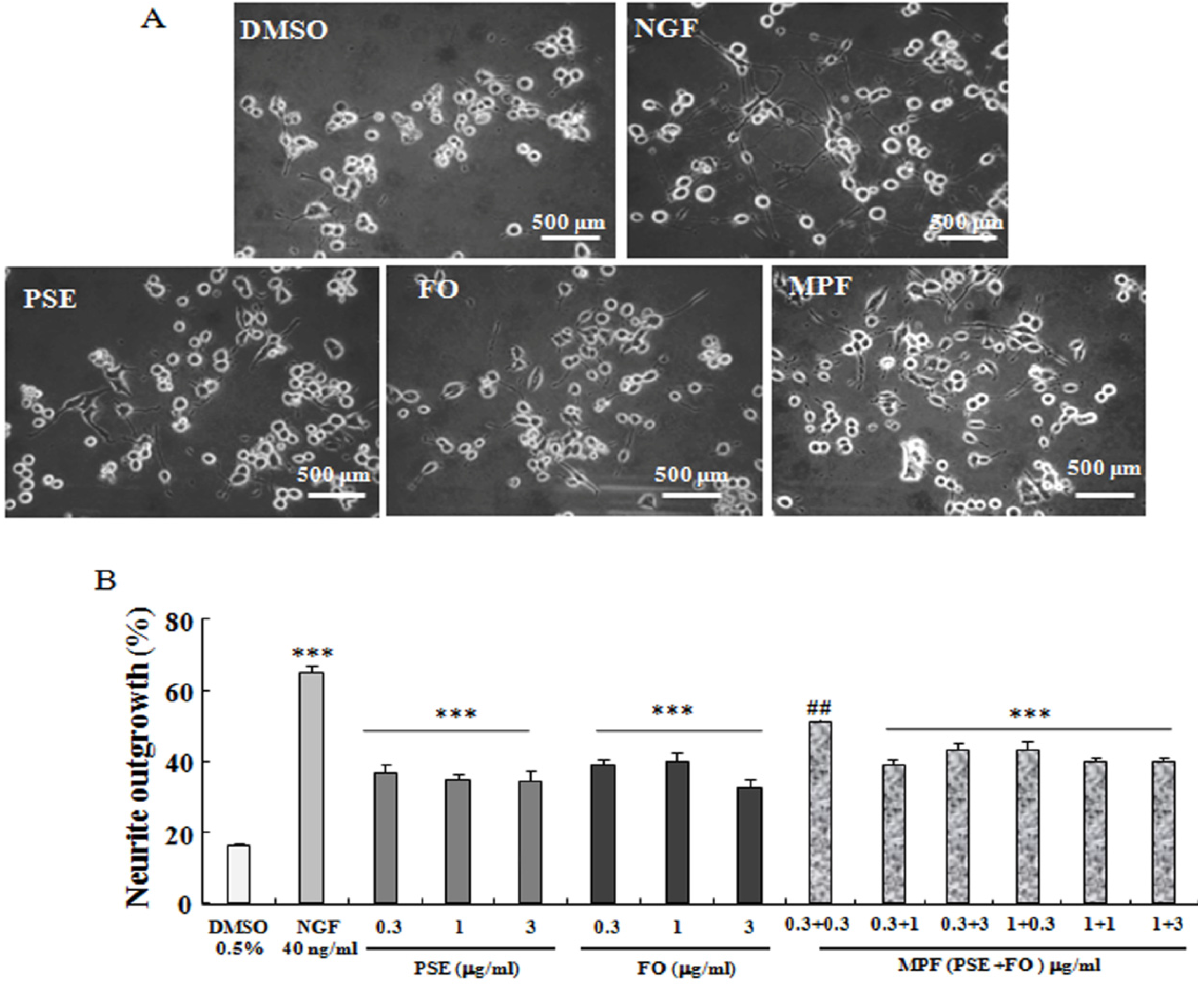
3.1. NGF-Mimicking Effects of PSE, FO, and MPF on PC12 Cells
3.2. MPF Improves Learning Ability and Spatial Memory
3.3. MPF Can Rescue SOD Activity Reduction and Reduce MDA Production Induced by FO in the Plasma
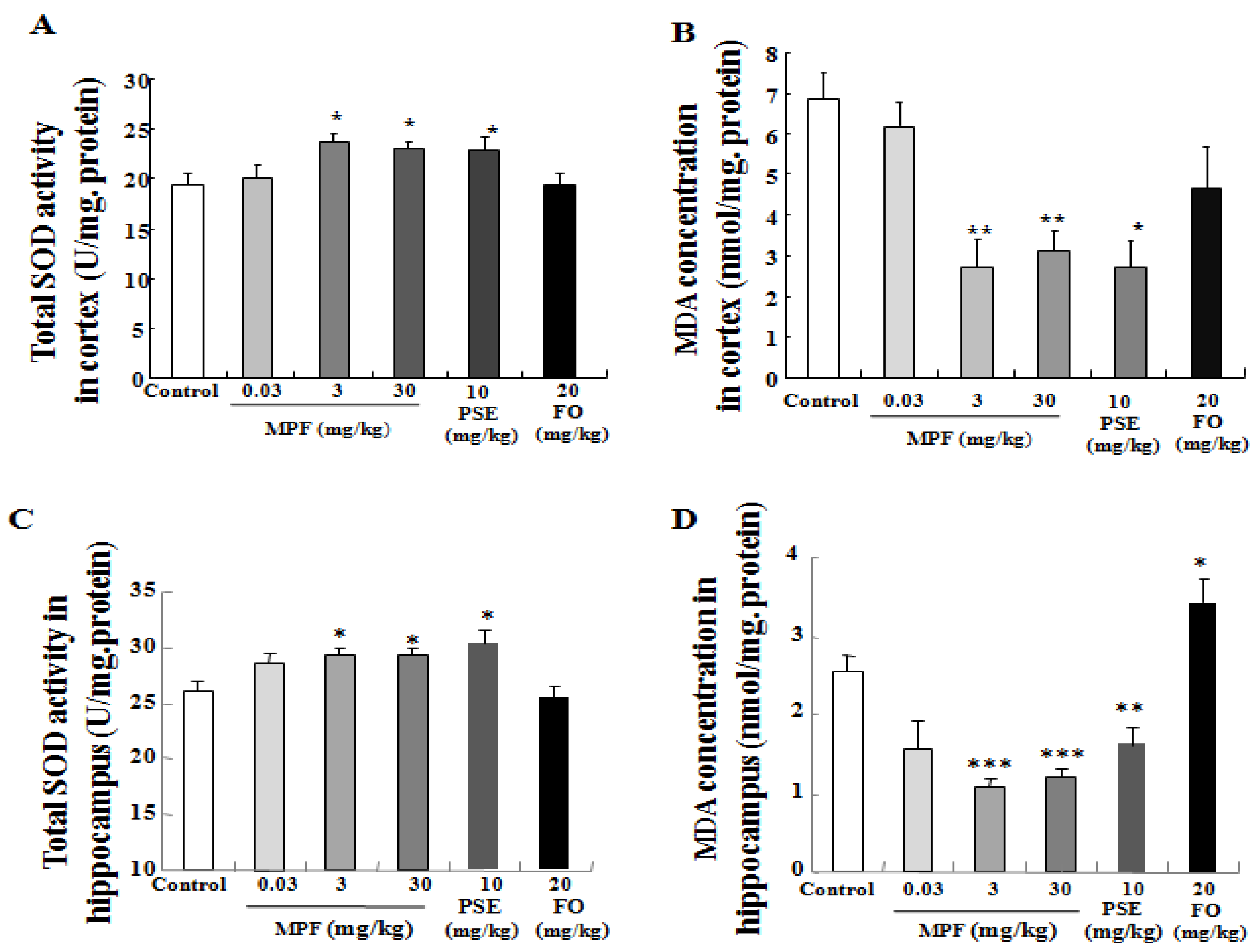
3.4. MPF Increases SOD Activity and Lowers MDA Production in the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus
3.5. MPF Increases BDNF and CREB Gene Expression Levels in the Cerebral Cortex and the Hippocampus
3.6. MPF Increases Phosphorylation of AKT, ERK and CREB in the Hippocampus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| ARC | Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein |
| BCL-X1 | B-cell lymphoma-X1 |
| BDNF | Brain derived-neurophic factor |
| CREB | cAMP responsive element-binding protein |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| DI | Discrimination index |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FO | Fish oil |
| ICR | Institute of Cancer Research |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MDA | Malonyldialdehyde |
| MPF | Mixture of peanut skin extract and fish oil |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| NOR | Novel object recognition |
| PC12 cells | Rat pheochromocytoma cells |
| PSE | Peanut skin extract |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
References
- Schirmer, S.H.; Werner, C.M.; Binder, S.B.; Faas, M.E.; Custodis, F.; Böhm, M.; Laufs, U. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on postprandial triglycerides and monocyte activation. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, G.M.; Lim, G.P.; Yang, F.; Teter, B.; Begum, A.; Ma, Q.; Harris-White, M.E.; Frautschy, S.A. Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Omega-3 fatty acid and phenolic anti-oxidant interventions. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 133S–136S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, D.S. Omega-3 fatty acids in anti-inflammation (pro-resolution) and GPCRs. Prog. Lipid Res. 2012, 51, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iagher, F.; de Brito Belo, S.R.; Souza, W.M.; Nunes, J.R.; Naliwaiko, K.; Sassaki, G.L.; Bonatto, S.J.; de Oliveira, H.H.; Brito, G.A.; de Lima, C.; et al. Anti-tumor and anti-cachectic effects of shark liver oil and fish oil: Comparison between independent or associative chronic supplementation in walker 256 tumor-bearing rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S. Lifestyle-related diseases and anti-aging ophthalmology: Suppression of retinal and choroidal pathologies by inhibiting renin-angiotensin system and inflammation. Nihon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 2009, 113, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albert, B.B.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Oxidation of marine omega-3 supplements and human health. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 464921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shibata, T.; Hisaka, S.; Kawai, Y.; Osawa, T. DHA hydroperoxides as a potential inducer of neuronal cell death: A mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated pathway. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2008, 43, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Enns, J.E.; Yeganeh, A.; Zarychanski, R.; Abou-Setta, A.M.; Friesen, C.; Zahraska, P.; Taylor, C.G. The impact of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on the incidence of cardiovascular events and complications in peripheral arterial disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C.D.; Pistell, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Johnson, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; White, C.L.; Purpera, M.N.; Uranga, R.M.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; et al. High fat diet increases hippocampal oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in aged mice: Implications for decreased Nrf2 signaling. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, C.E.; Winocur, G. High-fat diets, insulin resistance and declining cognitive function. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, S42–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistell, P.J.; Morrison, C.D.; Gupta, S.; Knight, A.G.; Keller, J.N.; Ingram, D.K.; Bruce-Keller, A.J. Cognitive impairment following high fat diet consumption is associated with brain inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 219, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, T.H.; McMichael, R.W.; Hendrix, K.W., Jr. Occurrence of resveratrol in edible peanuts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, V.; Ananga, A.; Tsolova, V. Recent advances and uses of grape flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Nutrients 2014, 6, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Khymenets, O.; Urpí-Sardà, M.; Tulipani, S.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Monagas, M.; Mora-Cubillos, X.; Llorach, R.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Cocoa polyphenols and inflammatory markers of cardiovascular disease. Nutrients 2014, 6, 844–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravishankar, D.; Rajora, A.K.; Greco, F.; Osborn, H.M. Flavonoids as prospective compounds for anti-cancer therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oršolić, N.; Sirovina, D.; Gajski, G.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V.; JazvinšćakJembrek, M.; Kosalec, I. Assessment of DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in diabetic mice: Effects of propolis and epigallocatechingallate (EGCG). Mutat. Res. 2013, 757, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Herrera, I.; Martín, M.Á.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Cocoa flavonoids attenuate high glucose-induced insulin signalling blockade and modulate glucose uptake and production in human HepG2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 64, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnoski, P.J.; Johnson, J.V.; Reed, K.A.; Tanko, J.M.; O’Keefe, S.F. Separation and characterization of proanthocyanidins in Virginia type peanut skins by LC-MS. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansode, R.R.; Randolph, P.; Hurley, S.; Ahmedna, M. Evaluation of hypolipidemic effects of peanut skin-derived polyphenols in rats on a western-diet. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalan, U.; Fernandez-Castillejo, S.; Angles, N.; Morello, J.R.; Yebras, M.; Solà, R. Inhibition of the transcription factor c-Jun by the MAPK family, and not the NF-κB pathway, suggests that peanut extract has anti-inflammatory properties. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 52, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.J.; Xiang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G.F.; Li, J.Y.; Qi, J.H. Gentisides, C.-K: Nine new neuritogenic compounds from the traditional Chinese medicine Gentiana rigescens Franch. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6995–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppe, G.J.; Dongmo, A.B.; Foyet, H.S.; Tsabang, N.; Olteanu, Z.; Cioanca, O.; Hancianu, M.; Dimo, T.; Hritcu, L. Memory-enhancing activities of the aqueous extract of Albiziaadianthifolialeaves in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesion rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.F.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J.H. Leu452His mutation in lipoprotein lipase gene transfer associated with hypertriglyceridemia in mice in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Katakura, M.; Tanabe, Y. n-3 fatty acids effectively improve the reference memory-related learning ability associated with increased brain docosahexaenoic acid-derived docosanoids in aged rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Cognitive-enhancing and antioxidant activities of iridoid glycosides from Scrophularia buergeriana in scopolamine-treated mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 588, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, M.; Ernesto, C.; Thomas, R.G.; Klauber, M.R.; Schafer, K.; Grundman, M. A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-to copherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nade, V.S.; Kanhere, S.V.; Kawale, L.A.; Yadav, A.V. Cognitive enhancing and antioxidant activity of ethyl acetate soluble fraction of the methanol extract of Hibiscus rosa sinensis in scopolamine-induced amnesia. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piche, L.A.; Draper, H.H.; Cole, P.D. Malondialdehyde excretion by subjects consuming cod liver oil vs. a concentrate of n-3 fatty acids. Lipids 1988, 23, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Cammarota, M.; Katche, C.; Slipczuk, L.; Rossato, J.I.; Goldin, A.; Izquierdo, I.; Medina, J.H. BDNF is essential to promote persistence of long-term memory storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restivo, L.; Vetere, G.; Bontempi, B.; Ammassari-Teule, M. The formation of recent and remote memory is associated with time-dependent formation of dendritic spines in the hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8206–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramham, C.R.; Alme, M.N.; Bittins, M.; Kuipers, S.D.; Nair, R.R.; Pai, B.; Panja, D.; Schubert, M.; Soule, J.; Tiron, A.; et al. The Arc of synaptic memory. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 200, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.B.; Yang, Z.Y.; An, R.; Ding, S.H. Effects of special brain area cerebral blood flow abnormal perfusion on learning and memory function and its molecular mechanism in rats. Front. Biol. China 2008, 3, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Medina, J.H.; Pozzo-Miller, L. ERK1/2 activation is necessary for BDNF to increase dendritic spine density in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Learn. Mem. 2004, 11, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Yamada, K.; Olariu, A.; Nawa, H.; Nabeshima, T. Involvement of brain-derived neuotrophic factor in spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test in rats. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7116–7121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.C.; Gean, P.W. Regulation of amygdata-dependent learning by brain-derived neurotrophic factor is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidyliostiol-3-kinase. Neuopsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, L.; Cao, X.-L.; Xing, T.-Y.; Mori, D.; Tang, R.-Q.; Li, J.; Gao, L.-J.; Qi, J.-H. Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract and Fish Oil Improves Memory in Mice via Modulation of Anti-Oxidative Stress and Regulation of BDNF/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2016, 8, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050256
Xiang L, Cao X-L, Xing T-Y, Mori D, Tang R-Q, Li J, Gao L-J, Qi J-H. Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract and Fish Oil Improves Memory in Mice via Modulation of Anti-Oxidative Stress and Regulation of BDNF/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways. Nutrients. 2016; 8(5):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050256
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Lan, Xue-Li Cao, Tian-Yan Xing, Daisuke Mori, Rui-Qi Tang, Jing Li, Li-Juan Gao, and Jian-Hua Qi. 2016. "Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract and Fish Oil Improves Memory in Mice via Modulation of Anti-Oxidative Stress and Regulation of BDNF/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways" Nutrients 8, no. 5: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050256
APA StyleXiang, L., Cao, X.-L., Xing, T.-Y., Mori, D., Tang, R.-Q., Li, J., Gao, L.-J., & Qi, J.-H. (2016). Mixture of Peanut Skin Extract and Fish Oil Improves Memory in Mice via Modulation of Anti-Oxidative Stress and Regulation of BDNF/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways. Nutrients, 8(5), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050256





