Serum Retinol Levels in Pregnant Adolescents and Their Relationship with Habitual Food Intake, Infection and Obstetric, Nutritional and Socioeconomic Variables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Characteristics
2.2. Evaluation of Serum Retinol Levels
2.3. Evaluation of Food Intake
2.4. Other Study Variables
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clagett-Dame, M.; Knutson, D. Vitamin A in reproduction and development. Nutrients 2011, 3, 385–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Supplementation Vitamin A in Pregnant Women; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44625/1/9789241501781_eng.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2016).
- Carlson, B.M. Human Embryology and Developmental Biology, 5rd ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, A.B.F.; Pereira, R.A.; Queiroz, J.; Saunders, C. Energy and nutrient intakes and low birth weight: Cohort study with pregnant adolescents. Rev. Nutr. 2013, 26, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Populations at Risk 1995–2005: WHO Global Database on Vitamin A Deficiency; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cediel, G.; Olivares, M.; Brito, A.; de Romana, D.L.; Cori, H.; La Frano, M.R. Interpretation of serum retinol data from Latin America and the Caribbean. Food Nutr. Bull. 2015, 36, S98–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.A.; Bennett, J.E.; Hennocq, Q.; Lu, Y.; De-Regil, L.M.; Rogers, L.; Danaei, G.; Li, G.; White, R.A.; Flaxman, S.R.; et al. Trends and mortality effects of vitamin A deficiency in children in 138 low-income and middle-income countries between 1991 and 2013: A pooled analysis of population-based surveys. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e528–e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuralli, D.; Tumer, L.; Hasanoglu, A.; Biberoglu, G.; Pasaoglu, H. Vitamin A status and factors associated in healthy school-age children. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kositamongkol, S.; Suthutvoravut, U.; Chongviriyaphan, N.; Feungpean, B.; Nuntnarumit, P. Vitamin A and E status in very low birth weight infants. J. Perinatol. 2011, 31, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citelli, M.; Bittencourt, L.L.; Da Silva, S.V.; Pierucci, A.P.T.; Pedrosa, C. Vitamin A modulates the expression of genes involved in iron bioavailability. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 149, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, S. The effect of vitamin A deficiency during pregnancy on anorectal malformations. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustino, J.F.; Ribeiro-Silva, A.; Dalto, R.F.; Souza, M.M.D.; Furtado, J.M.F.; Rocha, G.D.M.; Rocha, E.M.; Alves, M.; Rocha, E.M. Vitamin A and the eye: An old tale for modern times. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2016, 79, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kæstel, P.; Martinussen, T.; Aaby, P.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Friis, H. Serum retinol is associated with stage of pregnancy and the acute phase response in pregnant women in Guinea-Bissau. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, S.; Ahmed, A.; Randhawa, M.A.; Atukorala, S.; Arlappa, N.; Ismail, T.; Ali, Z. Prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in South Asia: Causes, outcomes, and possible remedies. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2013, 31, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, C.; Lyden, E.; Abresch, C.; Anderson-Berry, A. Serum retinol concentrations, race, and socioeconomic status in of women of childbearing age in the United States. Nutrients 2016, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Newsletter Nutritional Deficiencies: Vitamin A Deficiency; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2009.
- Garcêz, L.S.; Teles, L.D.F.D.S.; Brito, A.N.M.D.; Lima, G.D.S.P.; Paiva, A.D.A. Vitamin “A” food consumption by pregnant women in Brazil: A systematic review. Braz. J. Health Promot. 2015, 28, 452–462. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano, A.R.; Neilson, E.M.; Kelly, B.E.; Canfield, L.M. Simultaneous quantitation and separation of carotenoids and retinol in human milk by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 213, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dimenstein, R.; Trugo, N.M.F.; Donangelo, C.M.; Trugo, L.C.; Anastacio, A.S. Effect of subadequate maternal vitamin-A status on placental transfer of retinol and beta-carotene to the human fetus. Neonatology 1996, 69, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Indicators for Assessing Vitamin A Deficiency and Their Application in Monitoring and Evaluating Intervention Programmes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Verly, E., Jr.; Castro, M.A.; Fisberg, R.M.; Marchioni, D.M.L. Precision of usual food intake estimates according to the percentage of individuals with a second dietary measurement. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verly Junior, E.; Cesar, C.L.G.; Fisberg, R.M.; Marchioni, D.M.L. Within-person variance of the energy and nutrient intake in adolescents: Data adjustment in epidemiological studies. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2013, 16, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Support Program Nutrition–NutWin, version 1.5; Anção, M.S.; Cuppari, L.; Draibe, A.S.; Sigulem, D. (Eds.) Computer Program; Department of Health Informatics-Unifesp/EPM: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002.
- McLaren, D.S.; Kraemer, K. Interaction of vitamin A and other micronutrients. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 103, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silion, Vandadium, Zinc; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.nap.edu/read/10026/chapter/1 (accessed on 25 February 2016).
- The Multiple Source Method (MSM). Available online: https://msm.dife.de (accessed on 20 March 2016).
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Ministry of Planning, Budget and Management. Summary of Social Indicators-An Analysis of the Living Conditions of the Population in 2012; Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012.
- Ramalho, R.A.; Flores, H.; Accioly, E.; Saunders, C. Association between maternal and newborn vitamin A status and economic stratum in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Braz. Med. Assoc. 2006, 52, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurro, H.; Konichezky, S.; Fonseca, D.; Caldeyro-Barcia, R. A simplified method for diagnosis of gestational age in the newborn infant. J. Pediatr. 1978, 93, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Prenatal Care: Technical Manual; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2000.
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Attention to Prenatal Low Risk; Ministry of Health: Brasília, Brazil, 2012.
- World Health Organization. WHO Reference 2007: Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dati, F.; Schumann, G.; Thomas, L.; Aguzzi, F.; Baudner, S.; Bienvenu, J.; Blaadjerg, O.; Blirup-Jensen, S.; Carlström, A.; Hyltoft-Petersen, P.; et al. Consensus of a group of professional societies and diagnostic companies on guidelines for interim reference ranges for 14 proteins in serum based on the standardization against the IFCC/BCR/CAP reference material (CRM 470). Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1996, 34, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mei, Z.; Li, H.; Serdula, M.K.; Flores-Ayala, R.C.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.M.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. C-reactive protein increases with gestational age during pregnancy among Chinese women. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2016, 28, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olang, B.; Abdollahi, Z.; Neshati, R.; Ali, M.A.; Naghavi, M.; Yngve, A. Vitamin A Status in Pregnant Women in Iran in 2001 and Its Relationship with Province and Gestational Age. Available online: http://www.foodandnutritionresearch.net/index.php/fnr/article/view/25707 (accessed on 18 June 2016).
- Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Yun, C.; Piao, J.; Yang, X. Prevalence and influence factors of vitamin A deficiency of Chinese pregnant women. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, P.F.; Leal, M.J.; Amaya, D.C.; Mejías, L.C. Deficiencia de vitamina A em adolescentes no gestantes y gestantes de Maracaibo, Venezuela. Rev. Chil. Obstet. Ginecol. 2011, 75, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Fernandes, T.F.; Andreto, L.M.; Dos Santos Vieira, C.S.; De Arruda, I.K.G.; Da Silva Diniz, A. Serum retinol concentrations in mothers and newborns at delivery in a public maternity hospital in Recife, Northeast Brazil. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2014, 32, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Miglioli, T.C.; Fonseca, V.M.; Junior, G.; Clair, S.; Lira, P.I.C.D.; Batista Filho, M. Vitamin a deficiency in mothers and children in the state of Pernambuco. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2013, 18, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.M. Changes in serum immunity during pregnancy. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2009, 21, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andert, C.U.; Sanchaisuriya, P.; Sanchaisuriya, K.; Schelp, F.P.; Schweigert, F.J. Nutritional status of pregnant women in Northeast Thailand. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 15, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pena, E.; Sánchez, A.; Portillo, Z.; Solano, L. Dietary evaluation of pregnant adolescents during first, second and third trimester. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2003, 53, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, I.O.; Eka, O.U.; Essien, E.U. Vitamin A status of pregnant women in Calabar metropolis, Nigeria. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreselassie, S.G.; Gase, F.E.; Deressa, M.U. Prevalence and correlates of prenatal vitamin A deficiency in rural Sidama, Southern Ethiopia. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2013, 31, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureano, G.H.C.; Torman, V.B.L.; Crispim, S.P.; Dekkers, A.L.M.; Camey, S.A. Comparison of the ISU, NCI, MSM, and SPADE methods for estimating usual intake: A simulation study of nutrients consumed daily. Nutrients 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
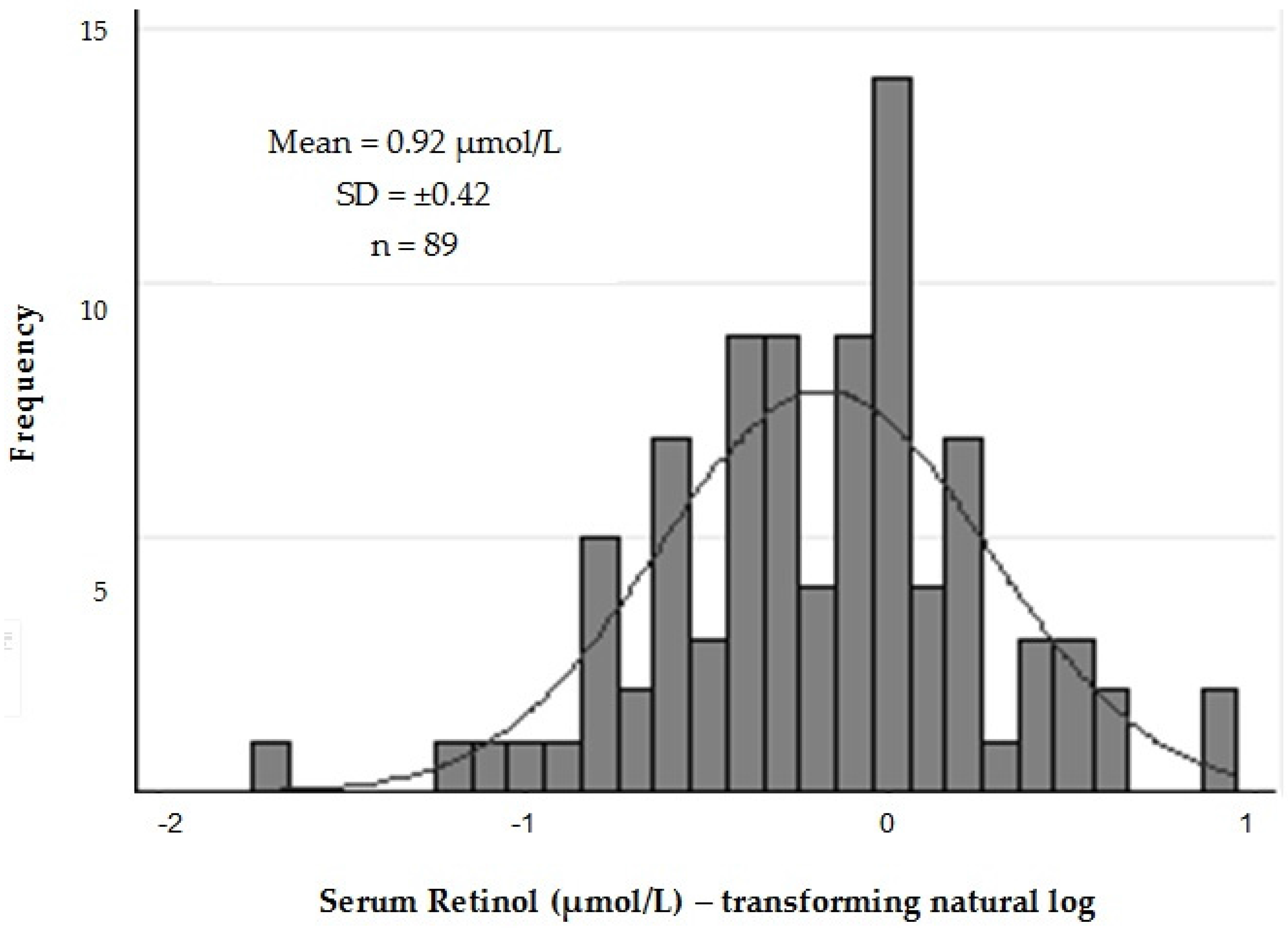
| Variables | N (%) | Mean (CI 95%) | Median | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic | ||||
| Age (years) | ||||
| ≤14 | 11 (12.4) | 0.73 (0.60–0.86) | 0.70 | |
| >14 to ≤16 | 40 (44.9) | 0.87 (0.74–1.00) | 0.87 | 0.115 * |
| >16 | 38 (42.7) | 1.02 (0.87–1.18) | 0.93 | |
| Schooling (years) | ||||
| <8 | 21 (23.6) | 0.79 (0.63–0.95) | 0.73 | 0.091 ** |
| ≥8 | 68 (76.4) | 0.96 (0.86–1.06) | 0.91 | |
| Per capita income | ||||
| ≤0.25 SM | 17 (19.1) | 1.07 (0.86–1.30) | 1.01 | |
| >0.25 to ≤0.5 SM | 47 (52.8) | 0.86 (0.74–0.98) | 0.77 | 0.109 * |
| >0.5 SM | 25 (28.1) | 0.93 (0.75–1.10) | 0.80 | |
| Water supply | ||||
| Public with internal connections | 84 (94.4) | 1.03 (0.36–1.69) | 0.91 | 0.701 ** |
| Public without indoor plumbing and others | 5 (5.6) | 0.91 (0.82–1.00) | 0.86 | |
| Garbage collection | ||||
| Regular | 70 (78.6) | 0.93 (0.82–1.04) | 0.86 | 0.888 ** |
| Irregular | 19 (21.4) | 0.88 (0.73–1.04) | 0.87 | |
| Sewer connect to the public network or existence of septic tank | ||||
| Yes | 54 (60.7) | 0.96 (0.85–1.08) | 0.91 | 0.134 ** |
| No | 35 (39.3) | 0.89 (0.76–1.02) | 0.79 | |
| Basic sanitation | ||||
| Adequate | 52 (58.4) | 0.99 (0.88–1.11) | 0.91 | 0.033 ** |
| Inadequate | 37 (41.6) | 0.87 (0.74–0.99) | 0.77 | |
| Obstetric | ||||
| Parity (number of pregnancies) | ||||
| 1 | 77 (86.5) | 0.93 (0.84–1.02) | 0.87 | 0.330 ** |
| ≥2 | 12 (13.5) | 0.87 (0.53–1.20) | 0.66 | |
| Trimester at the time of blood collection | ||||
| First (≤14 weeks) | 46 (51.7) | 1.01 (0.91–1.12) | 0.96 | 0.002 ** |
| Second (>14 to ≤20 weeks) | 43 (48.3) | 0.82 (0.68–0.96) | 0.73 | |
| Nutritional | ||||
| Pre-gestational nutritional status (BMI/age) | ||||
| Low weight | 73 (82.0) | 0.92 (0.83–1.01) | 0.87 | |
| Adequate | 05 (5.6) | 0.57 (0.31–0.82) | 0.45 | 0.063 * |
| Pre-Obesity/Obesity | 11 (12.4) | 1.06 (0.67–1.45) | 1.05 | |
| Gestational nutritional status (BMI) | ||||
| Low weight | 50 (56.2) | 0.95 (0.83–1.07) | 0.87 | |
| Adequate | 30 (37.7) | 0.84 (0.71–0.97) | 0.82 | 0.466 * |
| Pre-Obesity/Obesity | 09 (10.1) | 1.04 (0.58–1.49) | 0.94 | |
| Infection (CRP ≥ 5 mg/L) | ||||
| Yes | 73 (82.0) | 0.90 (0.81–1.00) | 0.84 | 0.716 ** |
| No | 16 (18.0) | 0.99 (0.72–1.26) | 0.90 |
| Nutrient | Mean (±SD) |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A (µg) | 636.4 (±240.9) ** |
| Estimated Average Requirement (µg/day) | 530.0 (±0.0) |
| Zinc (mg) | 10.5 (±3.2) |
| Estimated Average Requirement (mg/day) | 10.5 (±0.0) |
| Iron (mg) | 14.10 (±5.0) ** |
| Estimated Average Requirement (mg/day) | 23.0 (±0.0) |
| Variables | R | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic | ||
| Age (years) | 0.125 | 0.243 |
| Schooling (years) | 0.118 | 0.267 |
| Per capita income (real) | −0.080 | 0.441 |
| Water supply | 0.061 | 0.565 |
| Garbage collection | 0.008 | 0.935 |
| Sewer connect to the public network or existence of septic tank | 0.162 | 0.128 |
| Basic sanitation | 0.226 | 0.033 |
| Obstetric | ||
| Parity (number of pregnancies) | −0.125 | 0.243 |
| Trimester at the time of blood collection | −0.317 | 0.002 |
| Nutritional | ||
| Pre-gestational nutritional status (BMI/age) * | 0.276 | 0.008 |
| Gestational nutritional status (BMI) * | 0.246 | 0.019 |
| Infection (CRP ≥ 5 mg/L) | −0.068 | 0.527 |
| Nutrient intake | ||
| Vitamin A (µg) * | 0.046 | 0.666 |
| Zinc (mg) * | 0.048 | 0.654 |
| Iron (mg) * | 0.001 | 0.986 |
| Coefficient | Standard Error | CI 95% | p ** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 ** | |||||
| Sewer connect to the public network or existence of septic tank | −0.079 | 0.151 | −0.379 | 0.221 | 0.603 |
| Basic sanitation | 0.300 | 0.149 | 0.003 | 0.597 | 0.048 |
| Trimester at the time of blood collection | −0.296 | 0.087 | −0.469 | -0.123 | 0.001 |
| Pre-gestacional nutritional status (BMI/age) * | 1.275 | 0.620 | 0.042 | 2.509 | 0.043 |
| Gestational nutritional status (BMI) * | −0.542 | 0.699 | −1.933 | 0.849 | 0.441 |
| Model 2 *** | |||||
| Basic sanitation | 0.235 | 0.086 | 0.064 | 0.406 | 0.008 |
| Trimester at the time of blood collection | −0.279 | 0.084 | −0.447 | −0.111 | 0.001 |
| Pre-gestacional nutritional status (BMI/age) * | 0.853 | 0.273 | 0.311 | 1.396 | 0.002 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spíndola Garcêz, L.; De Sousa Paz Lima, G.; De Azevedo Paiva, A.; Maria Rebêlo Sampaio da Paz, S.; Lázaro Gomes, E.I.; Nunes, V.S.; Cotta de Faria, E.; De Barros-Mazon, S. Serum Retinol Levels in Pregnant Adolescents and Their Relationship with Habitual Food Intake, Infection and Obstetric, Nutritional and Socioeconomic Variables. Nutrients 2016, 8, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110669
Spíndola Garcêz L, De Sousa Paz Lima G, De Azevedo Paiva A, Maria Rebêlo Sampaio da Paz S, Lázaro Gomes EI, Nunes VS, Cotta de Faria E, De Barros-Mazon S. Serum Retinol Levels in Pregnant Adolescents and Their Relationship with Habitual Food Intake, Infection and Obstetric, Nutritional and Socioeconomic Variables. Nutrients. 2016; 8(11):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110669
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpíndola Garcêz, Laís, Geania De Sousa Paz Lima, Adriana De Azevedo Paiva, Suzana Maria Rebêlo Sampaio da Paz, Erica Ivana Lázaro Gomes, Valéria Sutti Nunes, Eliana Cotta de Faria, and Sílvia De Barros-Mazon. 2016. "Serum Retinol Levels in Pregnant Adolescents and Their Relationship with Habitual Food Intake, Infection and Obstetric, Nutritional and Socioeconomic Variables" Nutrients 8, no. 11: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110669
APA StyleSpíndola Garcêz, L., De Sousa Paz Lima, G., De Azevedo Paiva, A., Maria Rebêlo Sampaio da Paz, S., Lázaro Gomes, E. I., Nunes, V. S., Cotta de Faria, E., & De Barros-Mazon, S. (2016). Serum Retinol Levels in Pregnant Adolescents and Their Relationship with Habitual Food Intake, Infection and Obstetric, Nutritional and Socioeconomic Variables. Nutrients, 8(11), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110669





