Effect of Bifidobacterium breve on the Intestinal Microbiota of Coeliac Children on a Gluten Free Diet: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
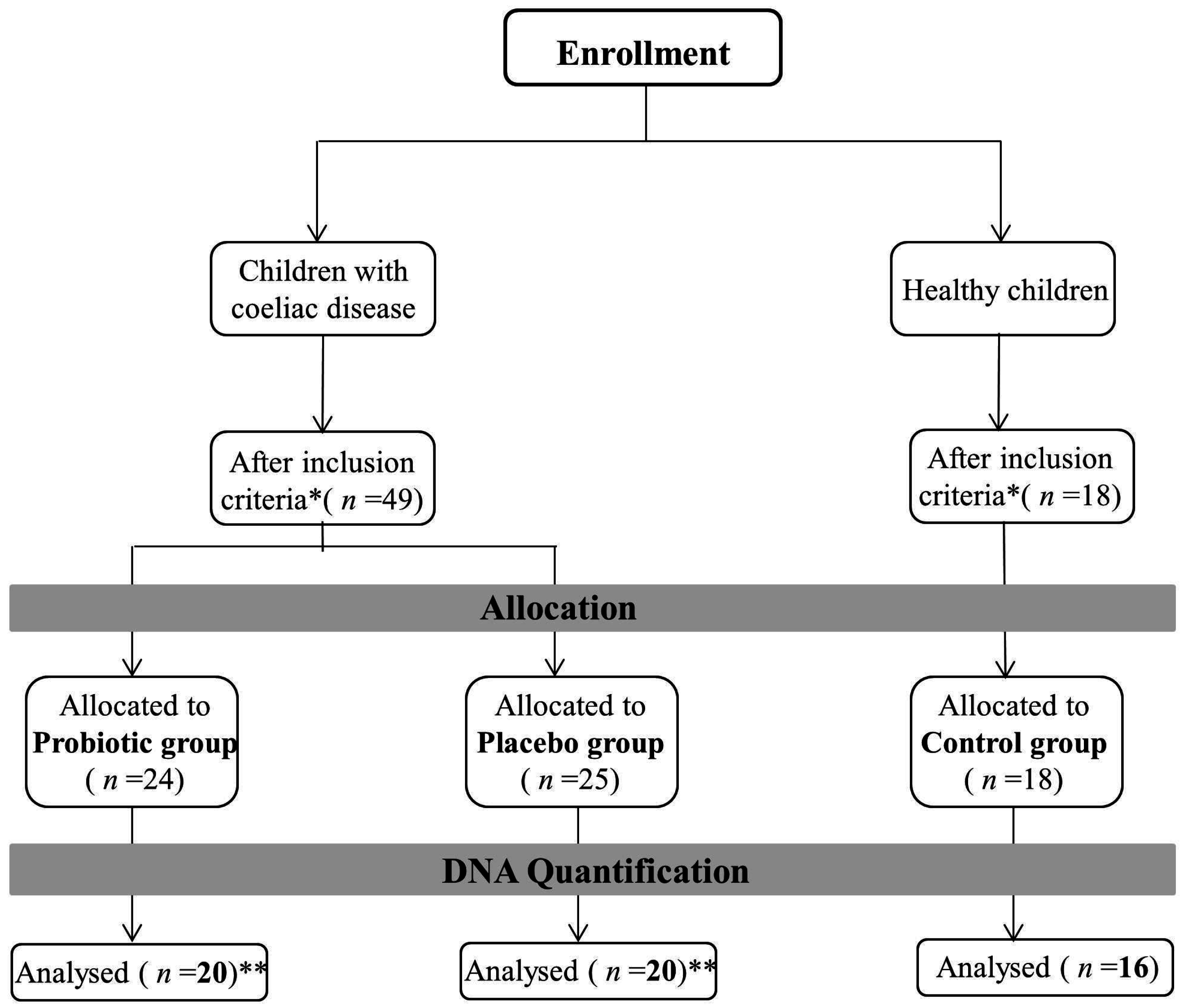
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Samples Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction from Faecal Samples
2.3. Preparation of DNA Libraries for Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses of NGS Experiment
2.5. Absolute Quantification of Selected Microbial Groups Using Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
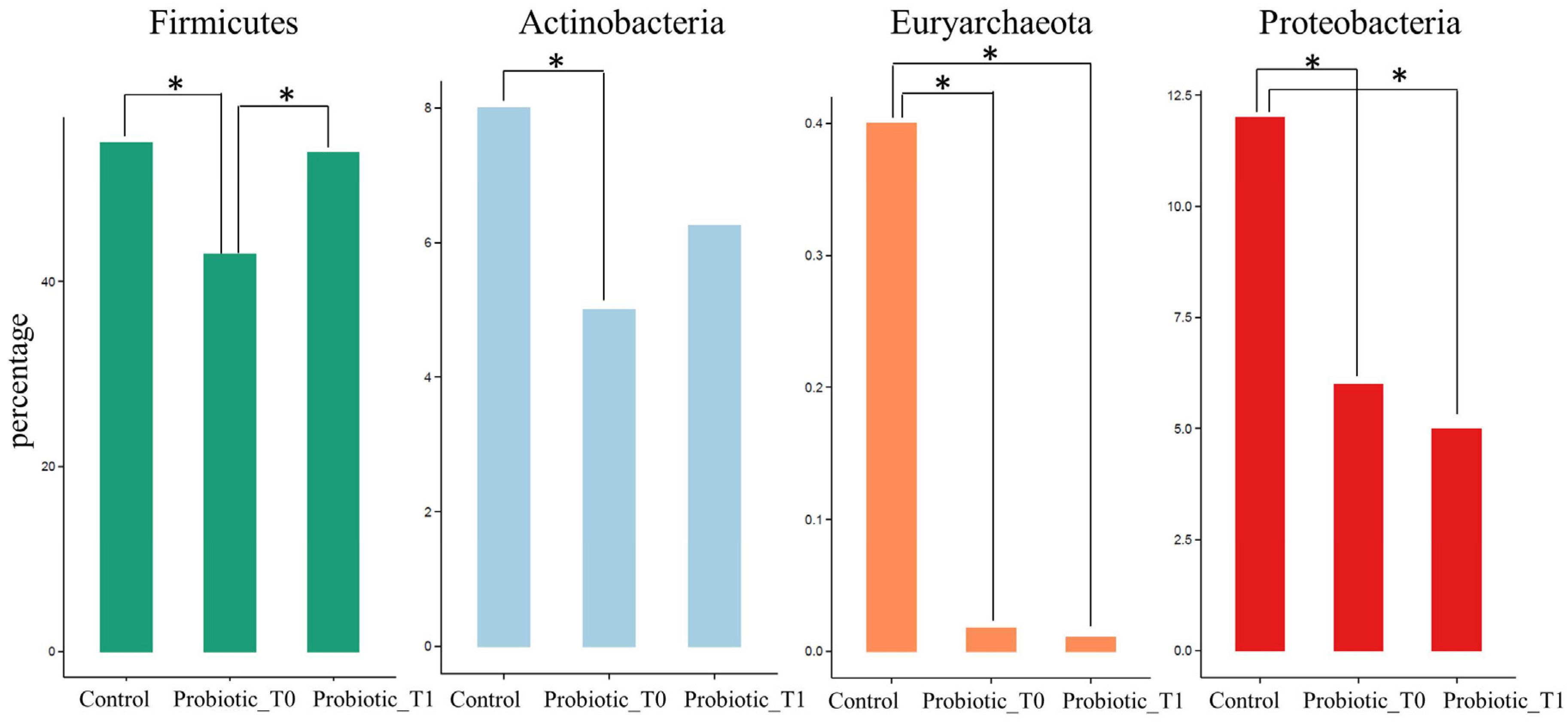
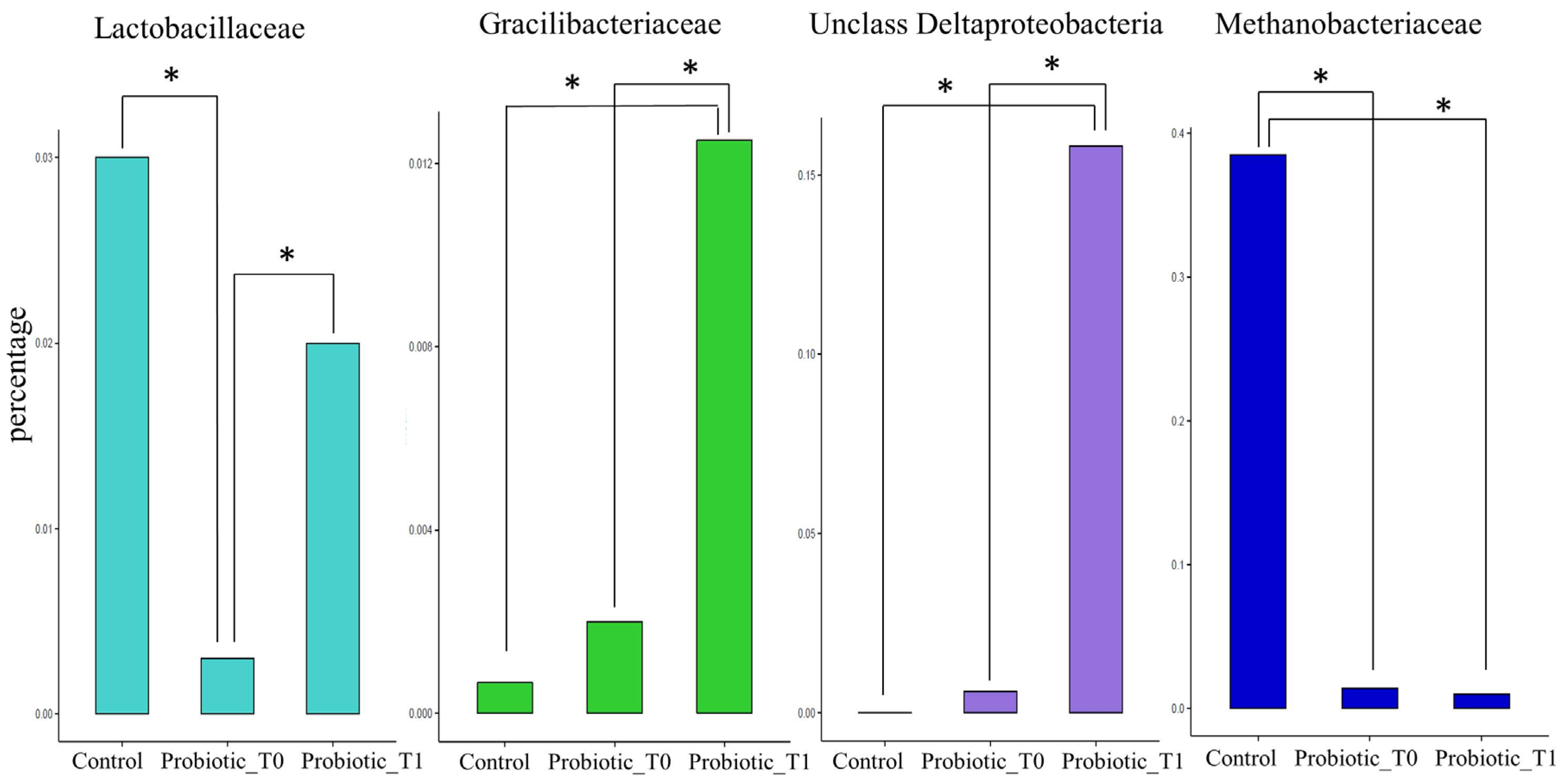
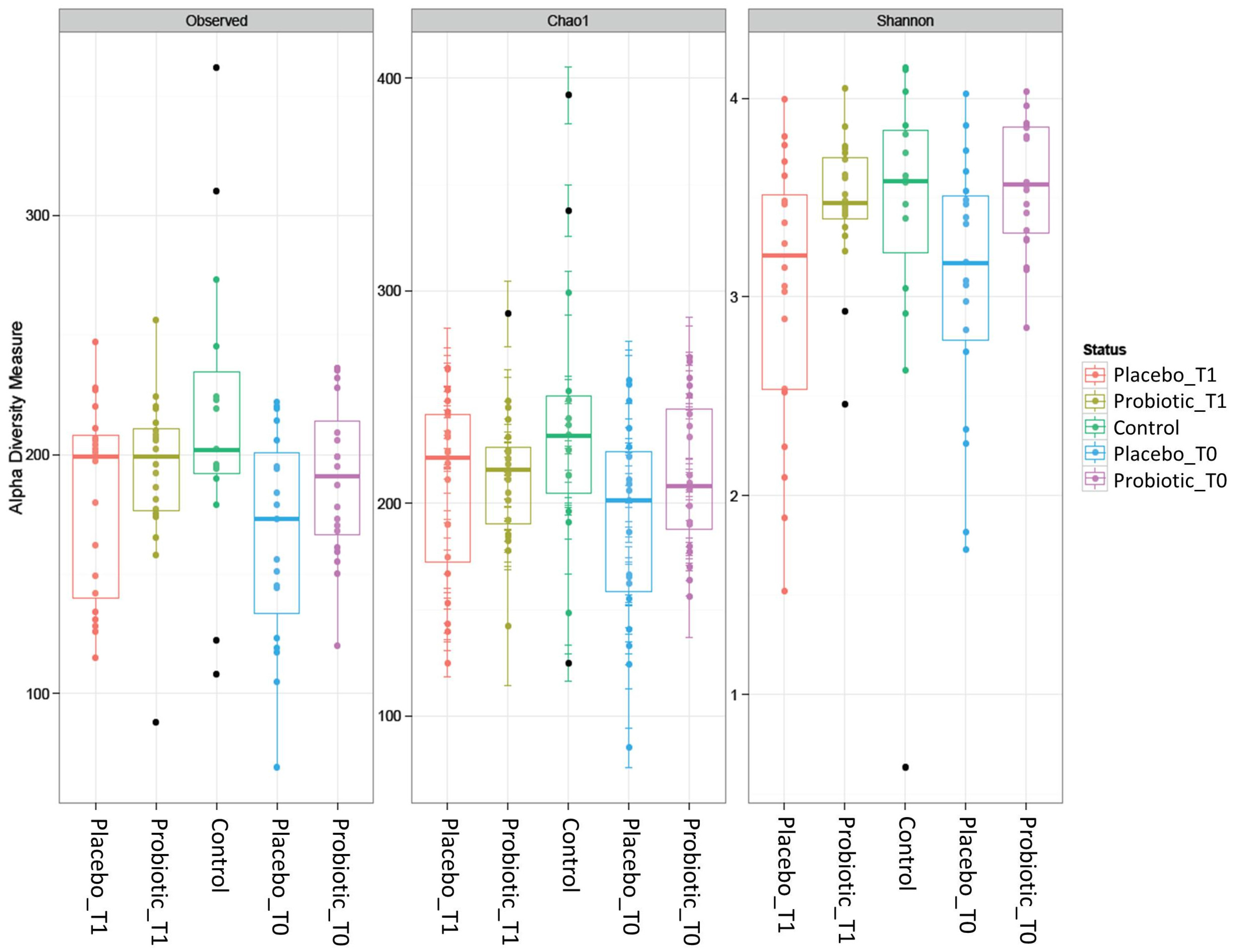
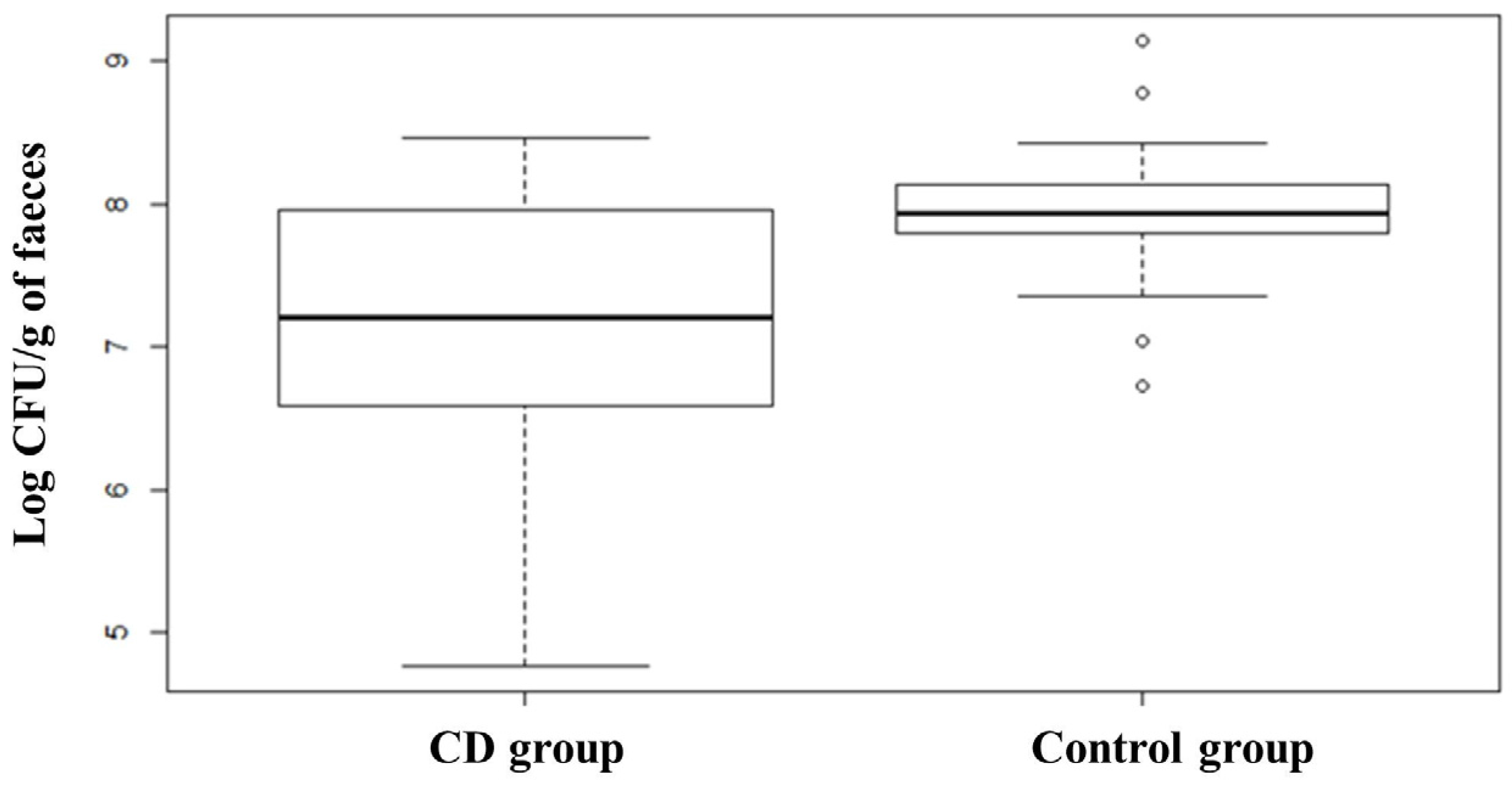
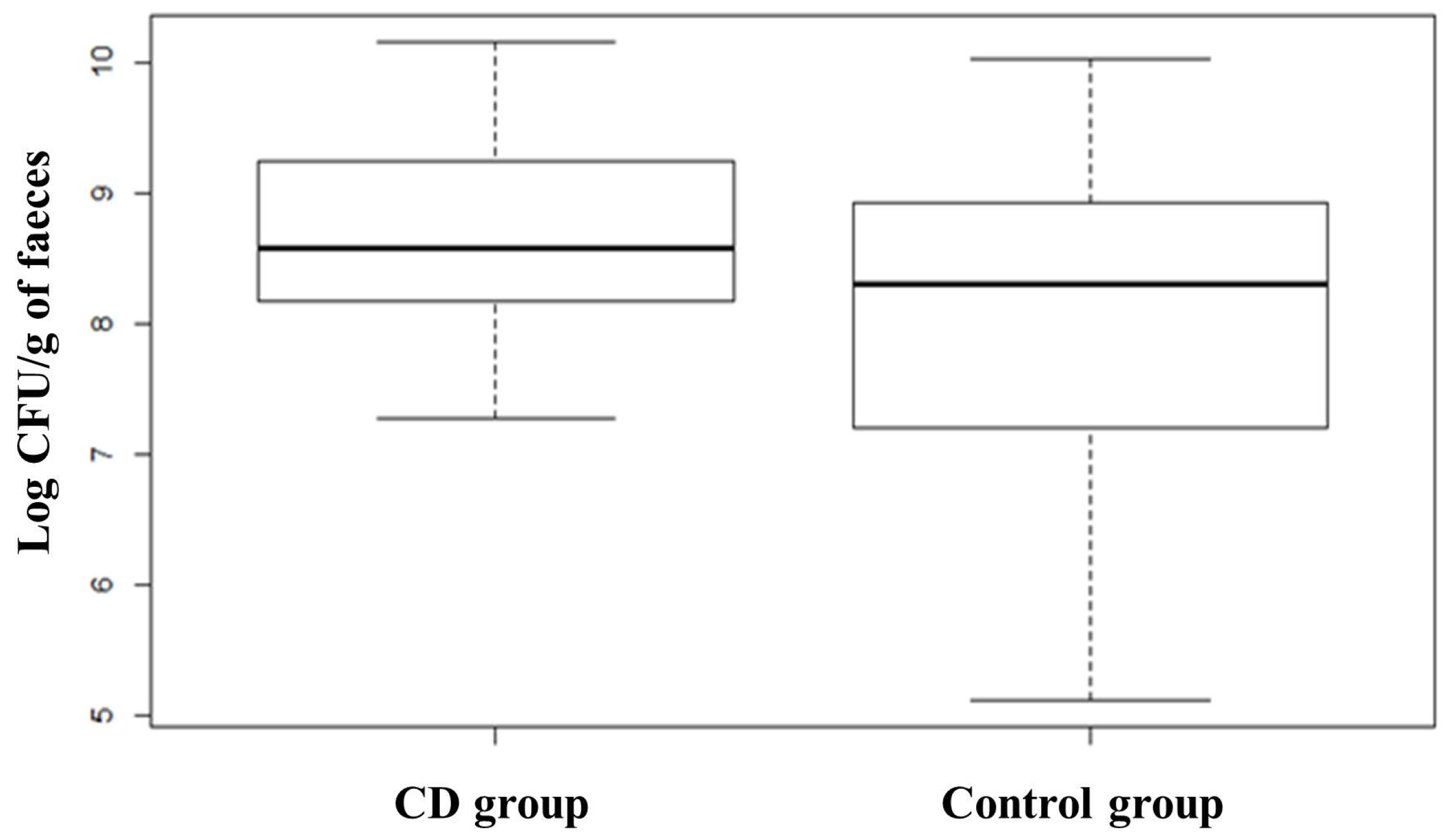
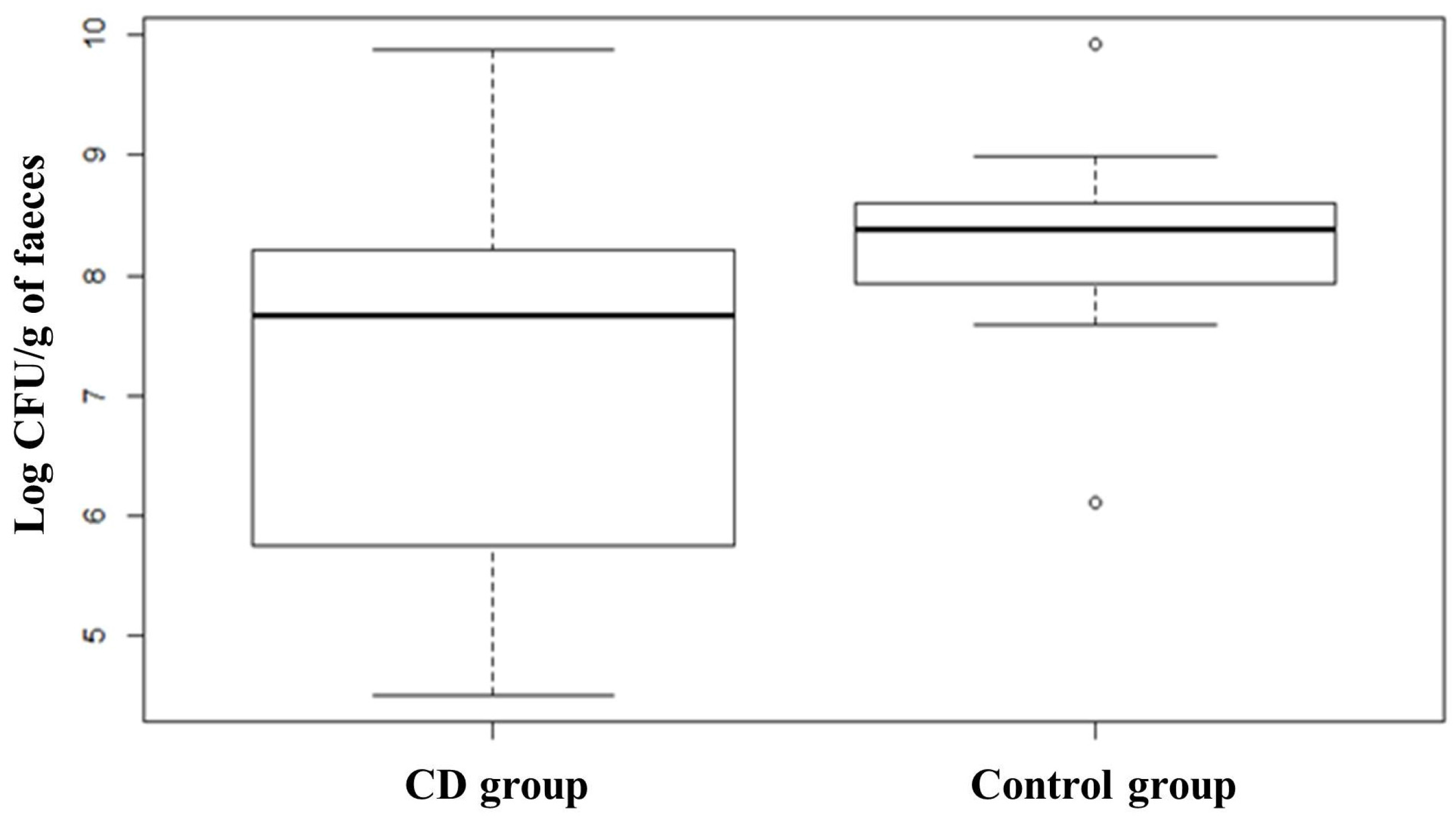
3. Results
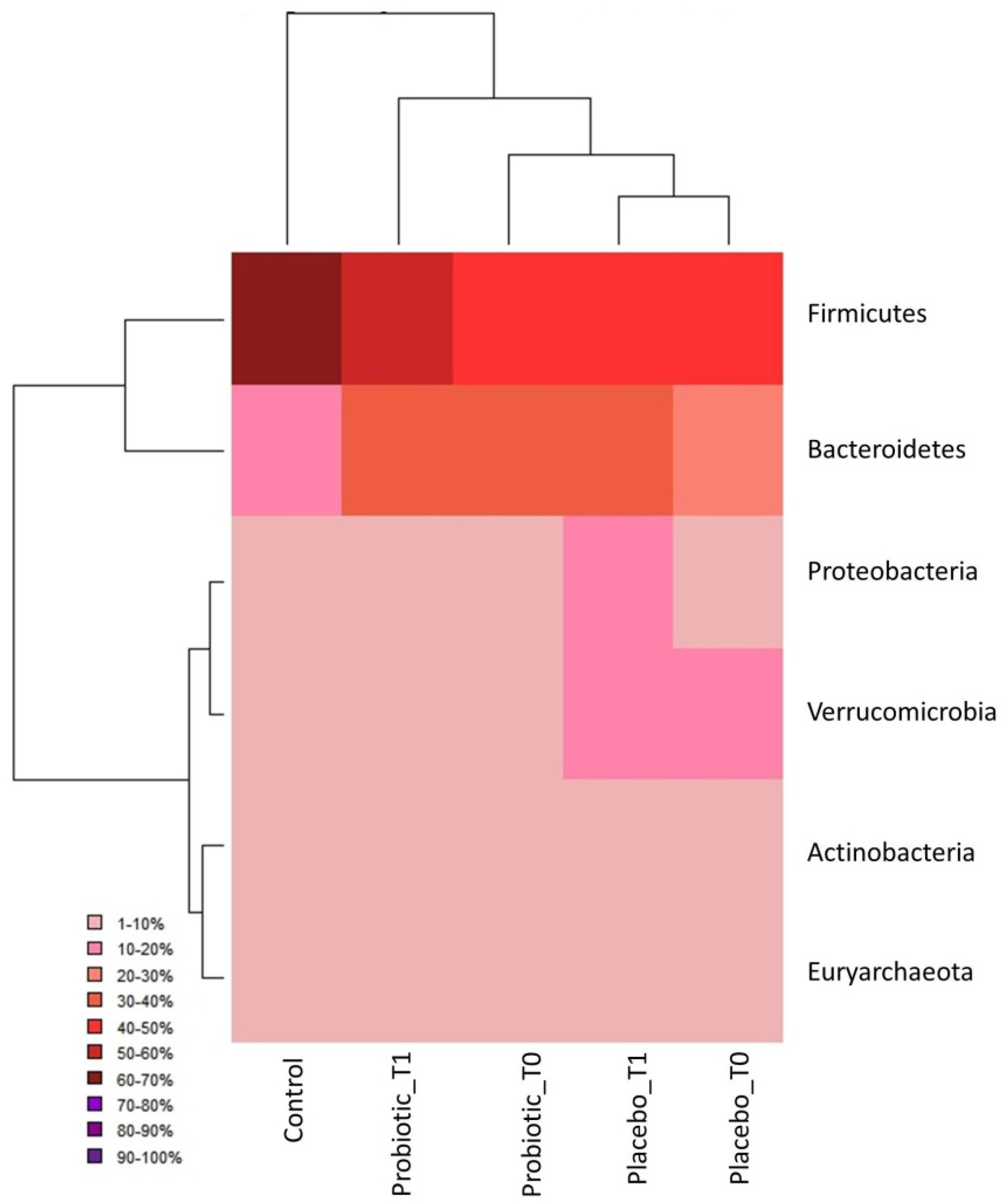
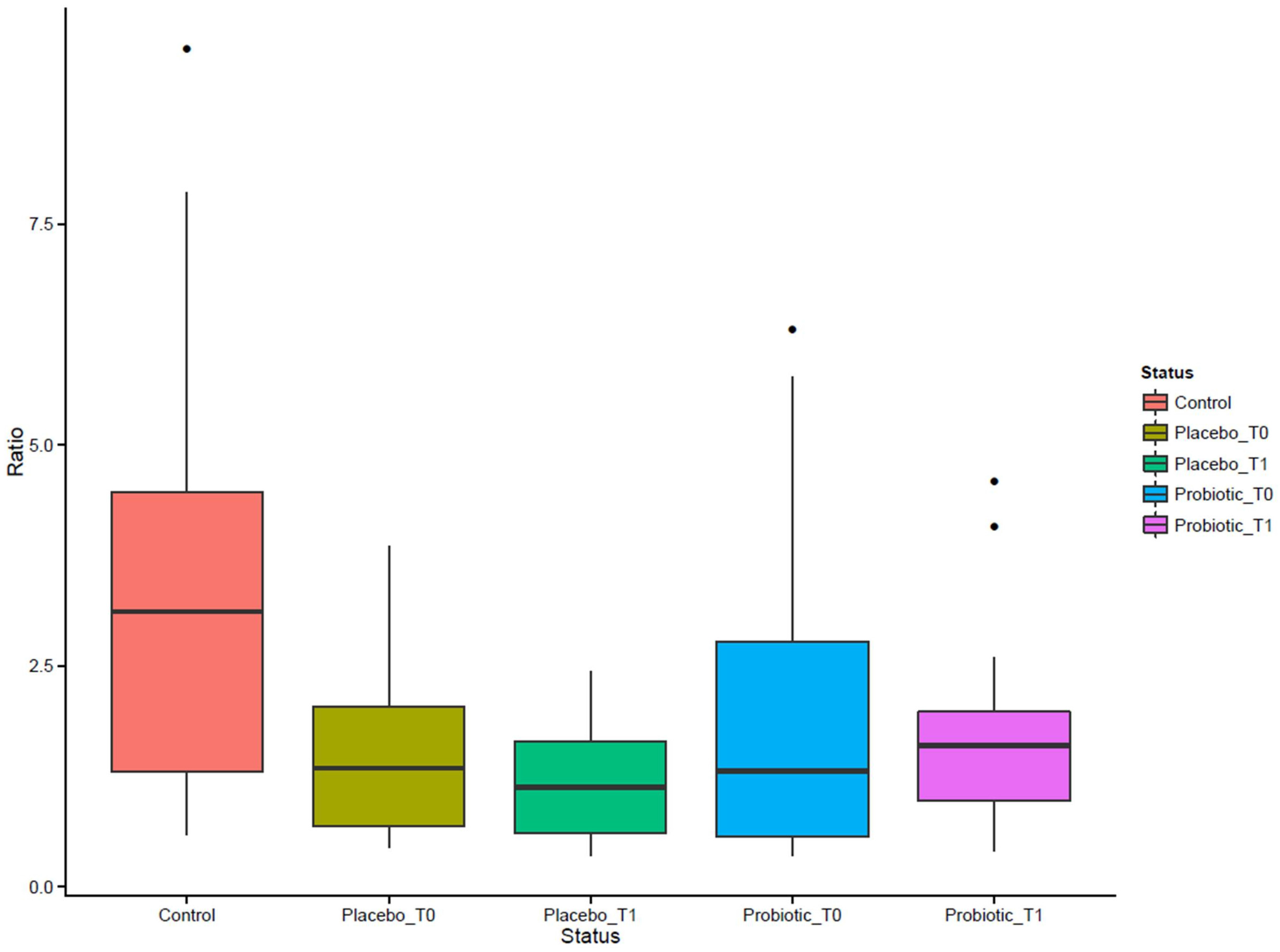
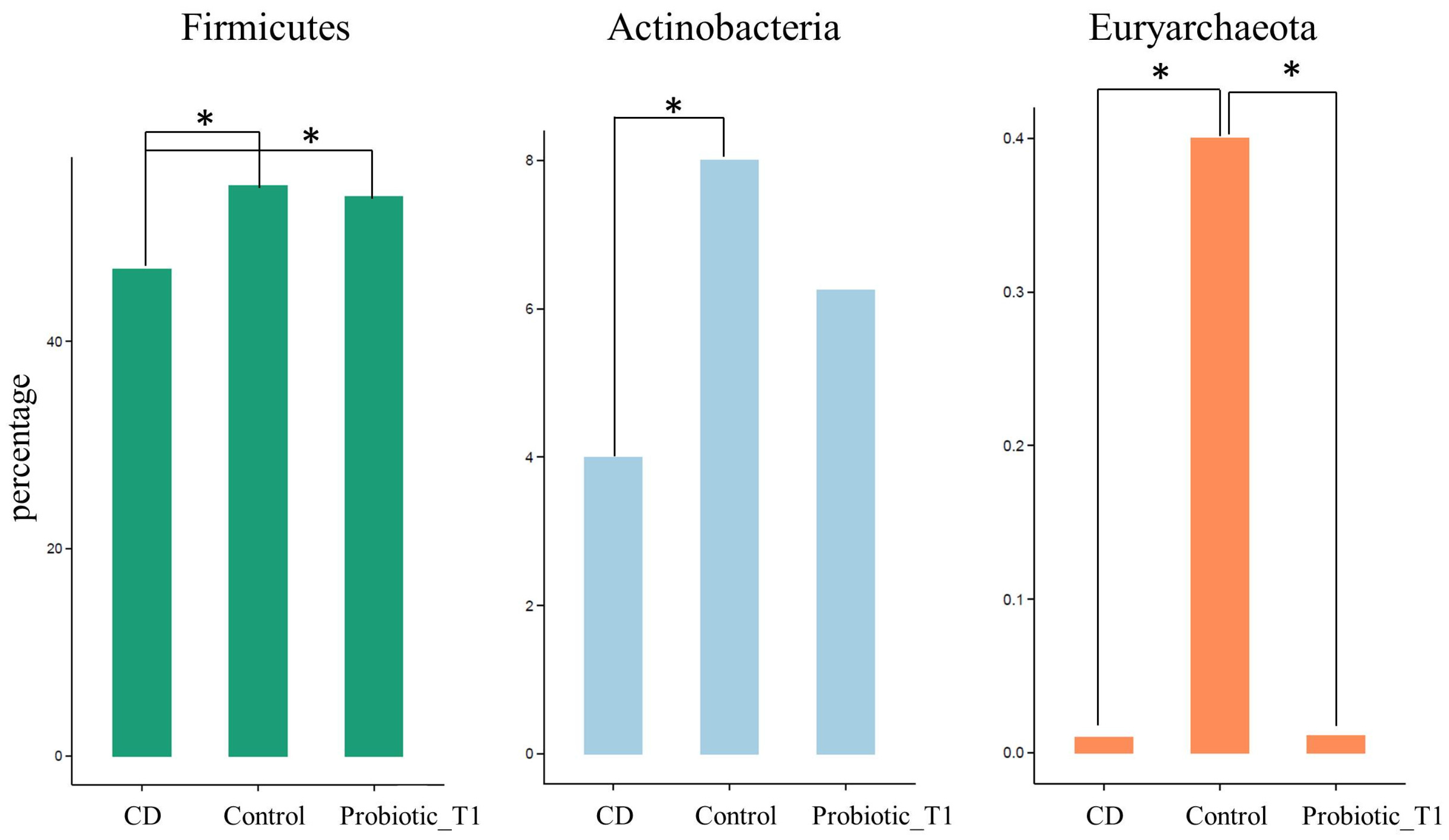
3.1. Metagenomic Analysis
3.2. Quantification of Selected Microbial Groups in Faecal Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reilly, N.R.; Fasano, A. Presentation of Celiac Disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; van Dyke, C.T.; Melton, L.J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Lahr, B.D.; Murray, J.A. Increasing incidence of celiac disease in a North American population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Hill, I.D.; Kelly, C.P.; Calderwood, A.H.; Murray, J.A. ACG clinical guidelines: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliari, D.; Urgesi, R.; Frosali, S.; Riccioni, M.E.; Newton, E.E.; Landolfi, R.; Pandolfi, F.; Cianci, R. The Interaction among Microbiota, Immunity, and Genetic and Dietary Factors Is the Condicio Sine Qua Non Celiac Disease Can Develop. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Maccaferri, S.; Turroni, S.; Brigidi, P. Intestinal microbiota is a plastic factor responding to environmental changes. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdu, E.F.; Galipeau, H.J.; Jabri, B. Novel players in coeliac disease pathogenesis: Role of the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Donat, E.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Calabuig, M.; Sanz, Y. Specific duodenal and faecal bacterial groups associated with paediatric coeliac disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, G.; Nadal, I.; Medina, M.; Donat, E.; Ribes-koninckx, C.; Calabuig, M.; Sanz, Y. Intestinal dysbiosis and reduced immunoglobulin-coated bacteria associated with coeliac disease in children. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cagno, R.; de Angelis, M.; de Pasquale, I.; Ndagijimana, M.; Vernocchi, P.; Ricciuti, P.; Gagliardi, F.; Laghi, L.; Crecchio, C.; Guerzoni, M.; et al. Duodenal and faecal microbiota of celiac children: Molecular, phenotype and metabolome characterization. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, I.; Donant, E.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Calabuig, M.; Sanz, Y. Imbalance in the composition of the duodenal microbiota of children with coeliac disease. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen, C.M.; Hernández, M. Identification and differentiation of Lactobacillus, Streptococcus and Bifidobacterium species in fermented milk products with bifidobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2007, 162, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preidis, G.A.; Versalovic, J. Targeting the Human Microbiome With Antibiotics, Probiotics, and Prebiotics: Gastroenterology Enters the Metagenomics Era. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2015–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.; de Palma, G.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Calabuig, M.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium strains suppress in vitro the pro-inflammatory milieu triggered by the large intestinal microbiota of coeliac patients. J. Inflamm. (Lond.) 2008, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindfors, K.; Blomqvist, T.; Juuti-Uusitalo, K.; Stenman, S.; Venalainen, J.; Maki, M.; Kaukinen, K. Live probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis bacteria inhibit the toxic effects induced by wheat gliadin in epithelial cell culture. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laparra, J.M.; Sanz, Y. Interactions of gut microbiota with functional food components and nutraceuticals. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Fasano, A.; Clemente, M.G.; Simone, C.; de Silano, M.; Vincenzi, M.; de Losito, I.; Gobbetti, M. VSL#3 probiotic preparation has the capacity to hydrolyze gliadin polypeptides responsible for Celiac Sprue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2006, 1762, 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Smecuol, E.; Hwang, H.J.; Sugai, E.; Corso, L.; Cherñavsky, A.C.; Bellavite, F.P.; González, A.; Vodánovich, F.; Moreno, M.L.; Vázquez, H.; et al. Exploratory, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study on the Effects of Bifidobacterium infantis Natren Life Start Strain Super Strain in Active Celiac Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, M.; Castillejo, G.; Varea, V.; Sanz, Y. Double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled intervention trial to evaluate the effects of Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7347 in children with newly diagnosed coeliac disease. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, T.D.; Alves, G.; Israel, P.; Lira, C.; de Lima, M.D.C. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium breve and Lactobacillus casei oral supplementation on necrotizing enterocolitis in very-low-birth-weight preterm infants: A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial 1–3. J. Clin. 2011, 93, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabbers, M.M.; de Milliano, I.; Roseboom, M.G.; Benninga, M.A. Is Bifidobacterium breve effective in the treatment of childhood constipation? Results from a pilot study. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M.; Nagata, S.; Saito, M.; Shimizu, T.; Yamashiro, Y.; Matsuki, T.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K. Effects of the enteral administration of Bifidobacterium breve on patients undergoing chemotherapy for pediatric malignancies. Support. Care Cancer 2010, 18, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Mearin, M.L.; Phillips, A.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Giersiepen, K.; Branski, D.; Catassi, C.; et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition guidelines for the diagnosis of coeliac disease. JPGN 2012, 54, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemenak, M.; Dolinšek, J.; Langerholc, T.; Di Gioia, D.; Mičetić-Turk, D. Administration of Bifidobacterium breve Decreases the Production of TNF-α in Children with Celiac Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 3386–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloisio, I.; Mazzola, G.; Corvaglia, L.T.; Tonti, G.; Faldella, G.; Biavati, B.; di Gioia, D. Influence of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis against group B Streptococcus on the early newborn gut composition and evaluation of the anti-Streptococcus activity of Bifidobacterium strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glockner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronest, E. Command-Line Tools for Processing Biological Sequencing Data, Ea-Utils. Available online: https://github.com/earonesty/ea-utils (accessed on 25 June 2015).
- Lan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cole, J.R.; Rosen, G.L. Using the RDP classifier to predict taxonomic novelty and reduce the search space for finding novel organisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Waste Not, Want Not: Why Rarefying Microbiome Data Is Inadmissible. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.M.P.; Bussema, C.; Schmidt, T.M. rrn DB: Documenting the number of rRNA and tRNA genes in bacteria and archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinttila, T.; Kassinen, A.; Malinen, E.; Krogius, L.; Palva, A. Development of an extensive set of 16S rDNA-targeted primers for quantification of pathogenic and indigenous bacteria in faecal samples by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, M.; Martín-Orúe, S.M.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Badiola, I.; Martín, M.; Gasa, J. Quantification of total bacteria, enterobacteria and lactobacilli populations in pig digesta by real-time PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 114, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penders, J.; Thijs, C.; Vink, C.; Stelma, F.F.; Snijders, B.; Kummeling, I.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Stobberingh, E.E. Factors influencing the composition of the intestinal microbiota in early infancy. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, S.; Fite, A.; Macfarlane, G.T.; McMurdo, M.E.T. Characterization of Bacterial Communities in Feces from Healthy Elderly Volunteers and Hospitalized Elderly Patients by Using Real-Time PCR and Effects of Antibiotic Treatment on the Fecal Microbiota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Liu, C.; McTeague, M.; Summanen, P.; Finegold, S. Clostridium bartlettii sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Anaerobe 2004, 10, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloisio, I.; Santini, C.; Biavati, B.; Dinelli, G.; Cencič, A.; Chingwaru, W.; Mogna, L.; di Gioia, D. Characterization of Bifidobacterium spp. strains for the treatment of enteric disorders in newborns. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, L.; de Vecchi, E.; Gabrieli, A.; de Grandi, R.; Toscano, M. Immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus salivarius LS01 and Bifidobacterium breve BR03, alone and in combination, on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of allergic asthmatics. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogna, L.; del Piano, M.; Mogna, G. Capability of the two microorganisms Bifidobacterium breve B632 and Bifidobacterium breve BR03 to colonize the intestinal microbiota of children. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, S37–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, Y. Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult humans. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, G.; Capilla, A.; Nova, E.; Castillejo, G.; Varea, V.; Pozo, T.; Garrote, J.A.; Polanco, I.; López, A.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; et al. Influence of milk-feeding type and genetic risk of developing coeliac disease on intestinal microbiota of infants: The PROFICEL study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I. A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host-archaeal-bacterial mutualism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10011–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.M.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Kober, O.I.; Juge, N.; Avershina, E.; Rudi, K.; Narbad, A.; Jenmalm, M.C.; et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Hosaka, A.; Kaneko, N.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Yamashiro, Y. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve supplementation on intestinal flora of low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Int. 2004, 46, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuka, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Izumi, H.; Namura, M.; Ikeda, T.; Ikuse, T.; Baba, Y.; Kudo, T.; Suzuki, R.; Shimizu, T. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve on inflammatory gene expression in neonatal and weaning rat intestine. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 71, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servin, A.L. Antagonistic activities of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 405–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, M.; Girardin, S.E.; Regnault, B.; le Bourhis, L.; Dillies, M.; Coppée, J.; Bourdet-sicard, R.; Sansonetti, P.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of lactobacillus casei on shigella-infected human intestinal epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 176, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Microorganisms | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) | References | Annealing Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium spp. | 243 | [32] | 55 °C | |
| BifTOT-F | TCGCGTCYGGTGTGAAAG | |||
| BifTOT-R | CCACATCCAGCRTCCAC | |||
| Lactobacillus spp. | 349 | [33] | 60 °C | |
| Lac-F | GCAGCAGTAGGGAATCTTCCA | |||
| Lac-R | GCATTYCACCGCTACACATG | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis group | 92 | [34] | 58 °C | |
| Bfra-F | CGGAGGATCCGAGCGTTA | |||
| Bfra-R | CCGCAAACTTTCACAACTGACTTA | |||
| Enterobacteria | 195 | [35] | 63 °C | |
| Eco 1457F | CATTGACGTTACCCGCAGAAGAAGC | |||
| Eco 1652R | CTCTACGAGACTCAAGCTGC | |||
| Clostridium cluster I | 232 | [36] | 52 °C | |
| CI-F1 | TACCHRAGGAGGAAGCCAC | |||
| CI-F2 | GTTCTTCCTAATCTCTACGCAT |
| Target Microorganisms | Initial Denaturation | Denaturation | Annealing | Cycles | Fw nM | Rev nM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium spp. BifTOT F/BifTOT-R | 95 °C, 20 s | 95 °C–30 s | 60 °C–30 s | 40 | 200 | 300 |
| Lactobacillus spp. LAC-F/LAC-R | 95 °C, 20 s | 95 °C–30 s | 63.5 °C–30 s | 40 | 200 | 200 |
| Bacteroides fragilis group Bfra-F/Bfra-R | 95 °C, 20 s | 95 °C–30 s | 60 °C–30 s | 40 | 300 | 300 |
| Enterobacteria Eco-F/Eco-R | 95 °C, 20 s | 95 °C–30 s | 60 °C–30 s | 40 | 400 | 400 |
| Clostridium cluster I CI-F1/CI-F2 | 95 °C, 20 s | 95 °C–30 s | 60 °C–30 s | 40 | 200 | 200 |
| Target | Log No. CFU/g of Faeces | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotic Group | Placebo Group | Control Group | |||
| T0 | T1 | T0 | T1 | T0 | |
| Bifidobacterium spp. | 7.64 ± 1.01 | 8.06 ± 0.98 | 7.82 ± 0.80 | 7.74 ± 0.73 | 7.26 ± 0.92 |
| Lactobacillus spp. | 6.87 ± 1.08 | 6.92 ± 0.95 | 7.21 ± 0.80 | 7.04 ± 0.97 | 7.84 ± 0.58 |
| B. fragilis group | 8.73 ± 0.79 | 8.71 ± 0.77 | 8.74 ± 0.76 | 8.84 ± 1.03 | 7.46 ± 1.47 |
| Enterobacteria | 7.10 ± 1.24 | 6.75 ± 1.29 | 7.25 ± 1.81 | 7.63 ± 1.48 | 8.29 ± 0.80 |
| Clostridium sensu stricto | 5.97 ± 0.96 | 5.83 ± 0.87 | 6.17 ± 0.95 | 6.19 ± 0.81 | 5.86 ± 0.80 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quagliariello, A.; Aloisio, I.; Bozzi Cionci, N.; Luiselli, D.; D’Auria, G.; Martinez-Priego, L.; Pérez-Villarroya, D.; Langerholc, T.; Primec, M.; Mičetić-Turk, D.; et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium breve on the Intestinal Microbiota of Coeliac Children on a Gluten Free Diet: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100660
Quagliariello A, Aloisio I, Bozzi Cionci N, Luiselli D, D’Auria G, Martinez-Priego L, Pérez-Villarroya D, Langerholc T, Primec M, Mičetić-Turk D, et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium breve on the Intestinal Microbiota of Coeliac Children on a Gluten Free Diet: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2016; 8(10):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100660
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuagliariello, Andrea, Irene Aloisio, Nicole Bozzi Cionci, Donata Luiselli, Giuseppe D’Auria, Llúcia Martinez-Priego, David Pérez-Villarroya, Tomaž Langerholc, Maša Primec, Dušanka Mičetić-Turk, and et al. 2016. "Effect of Bifidobacterium breve on the Intestinal Microbiota of Coeliac Children on a Gluten Free Diet: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 8, no. 10: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100660
APA StyleQuagliariello, A., Aloisio, I., Bozzi Cionci, N., Luiselli, D., D’Auria, G., Martinez-Priego, L., Pérez-Villarroya, D., Langerholc, T., Primec, M., Mičetić-Turk, D., & Di Gioia, D. (2016). Effect of Bifidobacterium breve on the Intestinal Microbiota of Coeliac Children on a Gluten Free Diet: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 8(10), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100660






