Major Dietary Patterns in Relation to General and Central Obesity among Chinese Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Dietary Patterns
2.4. Assessment of Anthropometric Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
| Dietary Patterns | Overall Mean (SD) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Southern Dietary Pattern | Traditional Northern Dietary Pattern | Western/New Affluence Dietary Pattern | |||||
| Food group, day/week | |||||||
| Rice | 7.0 | + + | 1.4 | − − − | 5.6 | = | 5.3 (2.6) |
| Wheat | 1.7 | − − | 7.0 | + + + | 5.0 | + | 3.7 (2.9) |
| Other staple foods | 0.4 | − | 4.0 | + + + | 1.2 | − | 1.4 (2.3) |
| Meat | 3.9 | = | 1.4 | −− | 5.5 | + + | 3.7 (2.5) |
| Poultry | 0.8 | = | 0.1 | − − | 1.4 | + + | 0.8 (1.0) |
| Fish | 1.5 | = | 0.1 | − − | 2.3 | + + | 1.4 (1.6) |
| Eggs | 1.8 | − | 2.4 | = | 4.2 | + + | 2.5 (2.2) |
| Fresh vegetables | 6.9 | = | 6.6 | 7.0 | + | 6.8 (0.8) | |
| Soybean | 1.6 | = | 0.9 | − | 2.6 | + + | 1.7 (1.6) |
| Preserved vegetables | 2.3 | = | 1.5 | − | 2.5 | + | 2.2 (2.4) |
| Fresh fruit | 1.9 | − − | 1.3 | − − | 5.3 | + + + | 2.6 (2.5) |
| Dairy products | 0.2 | − − | 0.4 | − | 3.2 | + + + | 0.9 (2.1) |
| Beverage group, g/week | |||||||
| Beer | 1.2 | = | 0.9 | = | 14.4 | + | 4.1 (33.6) |
| Rice wine | 5.9 | = | <0.1 | = | 1.1 | = | 3.5 (35.3) |
| Wine | <0.1 | = | <0.1 | = | 0.4 | = | 0.1 (3.6) |
| Heavy spirit (≥40%) | 31.1 | = | 10.8 | − | 22.3 | = | 24.3 (113.0) |
| Light spirit (<40%) | 13.9 | = | 6.1 | = | 4.4 | = | 9.9 (68.4) |
| Green tea | 5.8 | = | 3.5 | − | 11.3 | + | 6.5 (15.9) |
| Oolong tea | 0.5 | = | <0.1 | = | 0.6 | = | 0.4 (4.5) |
| Black tea | 1.8 | + | <0.1 | − | 0.2 | − | 1.0 (7.6) |
| Other tea | <0.1 | = | <0.1 | = | <0.1 | = | 0.0 (0.7) |
3. Results
| Traditional Southern Dietary Pattern | Traditional Northern Dietary Pattern | Western/New Affluence Dietary Pattern | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 255,758 (53.9) | 110,962 (23.4) | 107,472 (22.7) |
| Female, % | 59.3 | 59.2 | 58.4 |
| Age, years | 51.7 ± 0.02 | 49.8 ± 0.03 | 50.4 ± 0.03 |
| Urban area, % | 40.1 | 6.8 | 85.2 |
| Southern area, % | 94.2 | 0.7 | 43.6 |
| Married, % | 93.0 | 92.9 | 93.6 |
| High school and above, % | 38.3 | 38.0 | 83.6 |
| Annual household income, % | |||
| <10,000 Yuan RMB | 24.2 | 56.5 | 8.3 |
| 10,000–19,999 Yuan RMB | 27.7 | 33.2 | 27.6 |
| ≥20,000 Yuan RMB | 48.1 | 10.3 | 64.1 |
| Current drinker, % | 8.1 | 3.2 | 10.3 |
| Current smoker, % | 13.3 | 11.4 | 8.8 |
| Physical activity, Met-hour/day | 22.7 ± 0.03 | 23.0 ± 0.04 | 18.9 ± 0.04 |
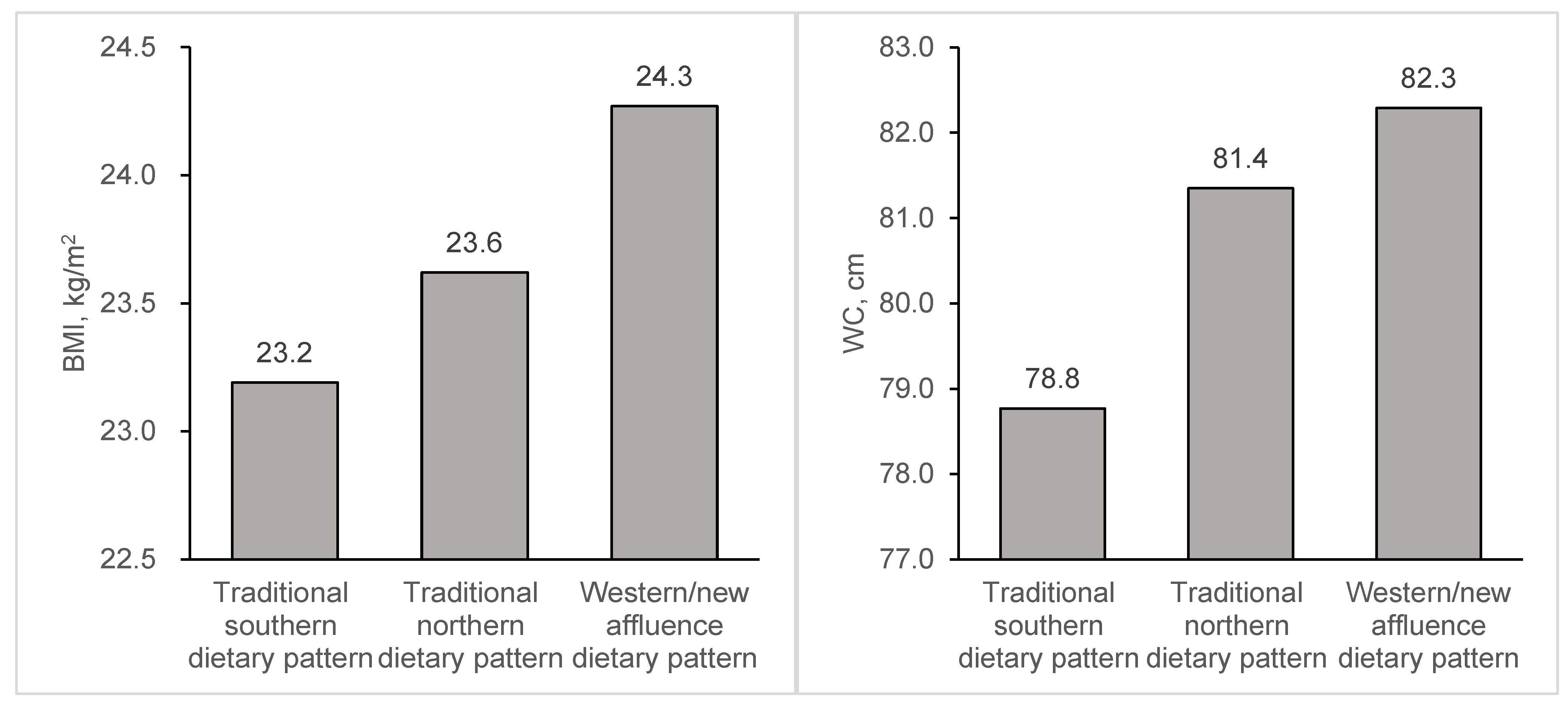
| Traditional Southern Dietary Pattern | Traditional Northern Dietary Pattern | Western/New Affluence Dietary Pattern | |
|---|---|---|---|
| General obesity | |||
| No. of cases (%) | 20,512 (8.02) | 12,404 (11.18) | 14,678 (13.66) |
| Crude | 1.00 | 1.39 (1.36–1.42) | 1.70 (1.67–1.74) |
| Model 1 | 1.00 | 1.41 (1.38–1.44) | 1.71 (1.68–1.75) |
| Model 2 | 1.00 | 1.05 (1.01–1.09) | 1.08 (1.05–1.10) |
| Model 3 | 1.00 | 1.05 (1.02–1.09) | 1.06 (1.03–1.08) |
| Central obesity | |||
| No. of cases (%) | 90,783 (35.50) | 47,694 (42.98) | 52,813 (49.14) |
| Crude | 1.00 | 1.21 (1.20–1.22) | 1.38 (1.37–1.40) |
| Model 1 | 1.00 | 1.24 (1.23–1.25) | 1.40 (1.39–1.41) |
| Model 2 | 1.00 | 1.17 (1.16–1.19) | 1.08 (1.07–1.10) |
| Model 3 | 1.00 | 1.17 (1.15–1.18) | 1.07 (1.06–1.08) |
| Traditional Southern Dietary Pattern | Traditional Northern Dietary Pattern | Western/New Affluence Dietary Pattern | P for Interaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General obesity | ||||
| Current drinker | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.04 (1.00–1.08) | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1.06 (1.02–1.10) | 1.19 (1.12–1.28) | 1.28 (1.23–1.34) | |
| Current smoker | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.10 (1.06–1.14) | 1.00 (0.97–1.03) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 0.69 (0.67–0.72) | 0.56 (0.53–0.60) | 0.92 (0.88–0.96) | |
| Physical activity | ||||
| T1 | 1.00 | 1.28 (1.23–1.33) | 1.20 (1.16–1.24) | <0.001 |
| T2 | 0.93 (0.90–0.96) | 0.98 (0.93–1.03) | 0.95 (0.91–0.98) | |
| T3 | 0.85 (0.82–0.87) | 0.59 (0.56–0.62) | 0.78 (0.74–0.81) | |
| Central adiposity | ||||
| Current drinker | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.11 (1.10–1.13) | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1.03 (1.01–1.04) | 1.19 (1.16–1.22) | 1.24 (1.22–1.26) | |
| Current smoker | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.19 (1.18–1.21) | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 0.81 (0.80–0.82) | 0.84 (0.82–0.86) | 1.07 (1.05–1.09) | |
| Physical activity | ||||
| T1 | 1.00 | 1.16 (1.14–1.17) | 1.10 (1.09–1.11) | <0.001 |
| T2 | 0.92 (0.90–0.93) | 1.11 (1.09–1.13) | 0.95 (0.94–0.97) | |
| T3 | 0.82 (0.81–0.83) | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.87 (0.85–0.88) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
China Kadoorie Biobank Collaborative Group
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2013, 309, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmienke, S.; Freitag, M.H.; Pischon, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Fankhaenel, T.; Goebel, H.; Gensichen, J. General and abdominal obesity parameters and their combination in relation to mortality: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Hao, T.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Changes in diet and lifestyle and long-term weight gain in women and men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B. Dietary pattern analysis: A new direction in nutritional epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2002, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNaughton, S.A.; Mishra, G.D.; Stephen, A.M.; Wadsworth, M.E. Dietary patterns throughout adult life are associated with body mass index, waist circumference, blood pressure, and red cell folate. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newby, P.K.; Muller, D.; Hallfrisch, J.; Qiao, N.; Andres, R.; Tucker, K.L. Dietary patterns and changes in body mass index and waist circumference in adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newby, P.K.; Muller, D.; Hallfrisch, J.; Andres, R.; Tucker, K.L. Food patterns measured by factor analysis and anthropometric changes in adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, R.M.; Grievink, L.; Ocke, M.C.; Feskens, E.J. Patterns of food consumption and risk factors for cardiovascular disease in the general dutch population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maskarinec, G.; Novotny, R.; Tasaki, K. Dietary patterns are associated with body mass index in multiethnic women. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 3068–3072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhai, F.Y.; Du, S.F.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.G.; Du, W.W.; Popkin, B.M. Dynamics of the Chinese diet and the role of urbanicity, 1991–2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhai, F.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, J.G.; Du, W.W.; Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.R.; Zhang, B. Secular trends in meat and seafood consumption patterns among Chinese adults, 1991–2011. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Liang, Y.; He, T.; Reilly, K.H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Mi, J. Secular trends in the prevalence of general and abdominal obesity among Chinese adults, 1993–2009. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Ma, G.; Zhai, F.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Feskens, E.J.; Yang, X. Dietary patterns and glucose tolerance abnormalities in Chinese adults. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, Y.; Lai, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Fu, P.; Yang, X.; Qi, L. Dietary patterns as compared with physical activity in relation to metabolic syndrome among Chinese adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Luan, D.; Zhai, F.; Yang, X.; Ma, G. Joint association of dietary pattern and physical activity level with cardiovascular disease risk factors among Chinese men: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, H.J.; Du, W.W.; Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.R.; Zhai, F.Y.; Zhang, B. Dietary patterns and their associations with general obesity and abdominal obesity among young Chinese women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Collins, R.; Guo, Y.; Peto, R.; Wu, F.; Li, L.; China Kadoorie Biobank Collaborative Group. China Kadoorie Biobank of 0.5 million people: Survey methods, baseline characteristics and long-term follow-up. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 1652–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lee, L.; Chen, J.; Collins, R.; Wu, F.; Guo, Y.; Linksted, P.; Peto, R. Cohort profile: The Kadoorie Study of chronic disease in China (KSCDC). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 34, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Bennett, D.; Li, L.; Whitlock, G.; Guo, Y.; Collins, R.; Chen, J.; Bian, Z.; Hong, L.S.; Feng, S.; et al. Physical activity and sedentary leisure time and their associations with BMI, waist circumference, and percentage body fat in 0.5 million adults: The China Kadoorie Biobank Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millwood, I.Y.; Li, L.; Smith, M.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Lewington, S.; Whitlock, G.; Sherliker, P.; Collins, R.; et al. Alcohol consumption in 0.5 million people from 10 diverse regions of China: Prevalence, patterns and socio-demographic and health-related correlates. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dagevos, H.; He, Y.; van der Lans, I.; Zhai, F. Consumption and corpulence in China: A consumer segmentation study based on the food perspective. Food Policy 2008, 33, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, Y.; Lai, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Fu, P.; Yang, X.; Qi, L. Dietary patterns are associated with stroke in Chinese adults. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.F. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults—Study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2002, 15, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barros, A.J.; Hirakata, V.N. Alternatives for logistic regression in cross-sectional studies: An empirical comparison of models that directly estimate the prevalence ratio. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2003, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skov, T.; Deddens, J.; Petersen, M.R.; Endahl, L. Prevalence proportion ratios: Estimation and hypothesis testing. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 27, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, I.K. Dietary pattern classifications and the association with general obesity and abdominal obesity in Korean women. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Yuan, B.; Hu, G.; Dai, Y.; Zuo, H.; Holmboe-Ottesen, G. Dietary pattern and weight change in a 5-year follow-up among Chinese adults: Results from the jiangsu nutrition study. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, K.; Gu, D.; Whelton, P.K.; Wu, X.; Duan, X.; Mo, J.; He, J.; For the InterASIA Collaborative Group. Prevalence and risk factors of overweight and obesity in China. Obesity 2007, 15, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Lin, X.; Haas, J.D.; Franco, O.H.; Rennie, K.L.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Pang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Obesity related metabolic abnormalities: Distribution and geographic differences among middle-aged and older Chinese populations. Prev. Med. 2009, 48, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Taylor, A.W.; Hu, G.; Gill, T.; Wittert, G.A. Rice intake, weight change and risk of the metabolic syndrome development among Chinese adults: The jiangsu nutrition study (JIN). Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 21, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mittendorfer, B.; Sidossis, L.S. Mechanism for the increase in plasma triacylglycerol concentrations after consumption of short-term, high-carbohydrate diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondo, I.; Funahashi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Ojima, T.; Yoshita, K.; Nakamura, Y. Association between food group intake and serum total cholesterol in the Japanese population: NIPPON DATA 80/90. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, S576–S581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, O.P.; Ronquillo, D.; Caamano Mdel, C.; Camacho, M.; Long, K.Z.; Rosado, J.L. Zinc, vitamin A, and vitamin C status are associated with leptin concentrations and obesity in Mexican women: Results from a cross-sectional study. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaugh, M.A.; Herrick, J.S.; Sweeney, C.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Guiliano, A.R.; Byers, T.; Slattery, M.L. Diet composition and risk of overweight and obesity in women living in the Southwestern United States. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, V.; Sieri, S.; Masala, G.; Palli, D.; Panico, S.; Vineis, P.; Sacerdote, C.; Mattiello, A.; Galasso, R.; Salvini, S.; et al. Associations between dietary pattern and lifestyle, anthropometry and other health indicators in the elderly participants of the EPIC-Italy cohort. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidari, F.; Shirbeigi, E.; Cheraghpour, M.; Mohammadshahi, M. Association of dietary patterns with body mass index, waist circumference, and blood pressure in an adult population in Ahvaz, Iran. Saudi Med. J. 2014, 35, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.A.; Shin, A.; Kim, J. Dietary patterns are associated with body mass index in a Korean population. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, A.M.; Godin, G.; Perusse, L.; Vohl, M.C. Associations between dietary patterns and obesity phenotypes. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaillzadeh, A.; Azadbakht, L. Major dietary patterns in relation to general obesity and central adiposity among Iranian women. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vergnaud, A.C.; Norat, T.; Romaguera, D.; Mouw, T.; May, A.M.; Travier, N.; Luan, J.; Wareham, N.; Slimani, N.; Rinaldi, S.; et al. Meat consumption and prospective weight change in participants of the EPIC-PANACEA study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, W.; Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Popkin, B.M. Fatty and lean red meat consumption in China: Differential association with Chinese abdominal obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Shaper, A.G.; Whincup, P.H. Alcohol and adiposity: Effects of quantity and type of drink and time relation with meals. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, H.; Morales-Molina, J.A.; Bermejo, S.; Barral, D.; Mandoli, E.S.; Grau, M.; Guxens, M.; de Jaime Gil, E.; Alvarez, M.D.; Marrugat, J. Relationship of abdominal obesity with alcohol consumption at population scale. Eur. J. Nutr. 2007, 46, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasiewicz, E.; Mennen, L.I.; Bertrais, S.; Arnault, N.; Preziosi, P.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S. Alcohol intake in relation to body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio: The importance of type of alcoholic beverage. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dare, S.; Mackay, D.F.; Pell, J.P. Relationship between smoking and obesity: A cross-sectional study of 499,504 middle-aged adults in the UK general population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Yin, X.M.; Wang, Y. The association between amount of cigarettes smoked and overweight, central obesity among Chinese adults in Nanjing, China. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weinsier, R.L.; Hunter, G.R.; Heini, A.F.; Goran, M.I.; Sell, S.M. The etiology of obesity: Relative contribution of metabolic factors, diet, and physical activity. Am. J. Med. 1998, 105, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankinson, A.L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Bouchard, C.; Carnethon, M.; Lewis, C.E.; Schreiner, P.J.; Liu, K.; Sidney, S. Maintaining a high physical activity level over 20 years and weight gain. JAMA 2010, 304, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Fung, T.T.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Dietary patterns and changes in body weight in women. Obesity 2006, 14, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottai, M.; Frongillo, E.A.; Sui, X.; O’Neill, J.R.; McKeown, R.E.; Burns, T.L.; Liese, A.D.; Blair, S.N.; Pate, R.R. Use of quantile regression to investigate the longitudinal association between physical activity and body mass index. Obesity 2014, 22, E149–E156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layman, D.K.; Boileau, R.A.; Erickson, D.J.; Painter, J.E.; Shiue, H.; Sather, C.; Christou, D.D. A reduced ratio of dietary carbohydrate to protein improves body composition and blood lipid profiles during weight loss in adult women. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clifton, P.M.; Condo, D.; Keogh, J.B. Long term weight maintenance after advice to consume low carbohydrate, higher protein diets—A systematic review and meta analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, D.S. Dietary glycemic index and obesity. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 280s–283s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lucan, S.C.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. How calorie-focused thinking about obesity and related diseases may mislead and harm public health. An alternative. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Shi, Z.; Lv, J.; Du, H.; Qi, L.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Chang, L.; Tang, X.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Major Dietary Patterns in Relation to General and Central Obesity among Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5834-5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075253
Yu C, Shi Z, Lv J, Du H, Qi L, Guo Y, Bian Z, Chang L, Tang X, Jiang Q, et al. Major Dietary Patterns in Relation to General and Central Obesity among Chinese Adults. Nutrients. 2015; 7(7):5834-5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075253
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Canqing, Zumin Shi, Jun Lv, Huaidong Du, Lu Qi, Yu Guo, Zheng Bian, Liang Chang, Xuefeng Tang, Qilian Jiang, and et al. 2015. "Major Dietary Patterns in Relation to General and Central Obesity among Chinese Adults" Nutrients 7, no. 7: 5834-5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075253
APA StyleYu, C., Shi, Z., Lv, J., Du, H., Qi, L., Guo, Y., Bian, Z., Chang, L., Tang, X., Jiang, Q., Mu, H., Pan, D., Chen, J., Chen, Z., & Li, L. (2015). Major Dietary Patterns in Relation to General and Central Obesity among Chinese Adults. Nutrients, 7(7), 5834-5849. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075253






