A Novel Hemp Seed Meal Protein Hydrolysate Reduces Oxidative Stress Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. In Vitro Antioxidant Assays
2.3. Animal Studies
2.4. Plasma Total Peroxides (TPx) Assay
2.5. Plasma Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) and Antioxidant Enzymes Assays
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of HMH
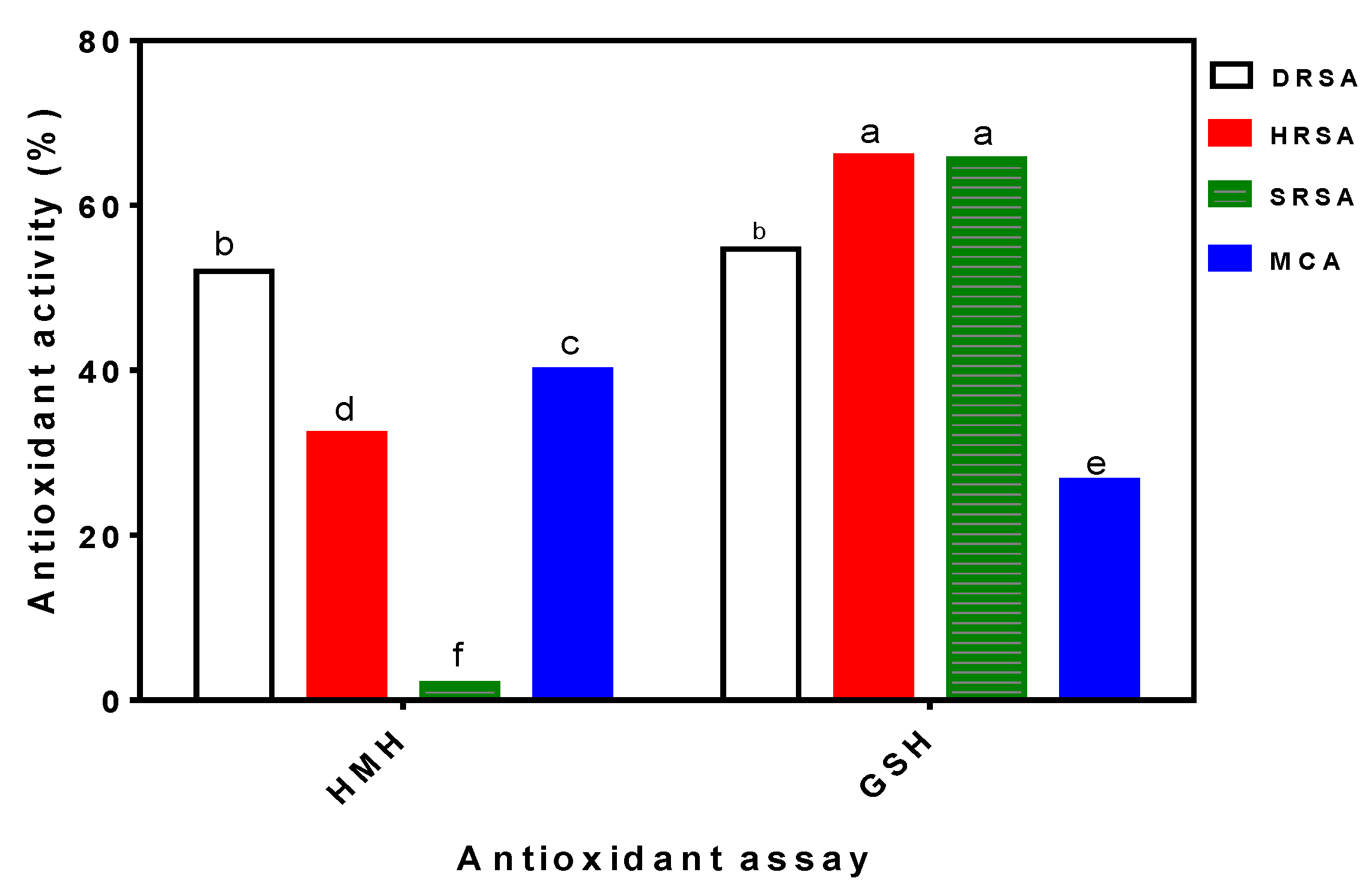
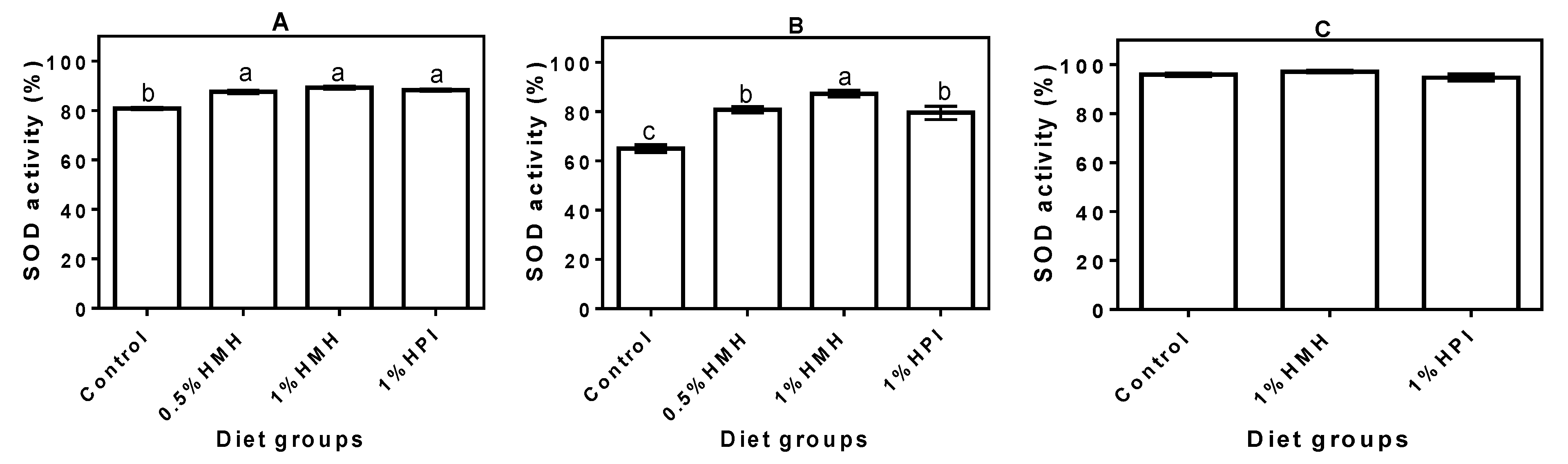
3.2. Plasma SOD Activity
3.3. Plasma CAT Activity

3.4. Plasma TAC
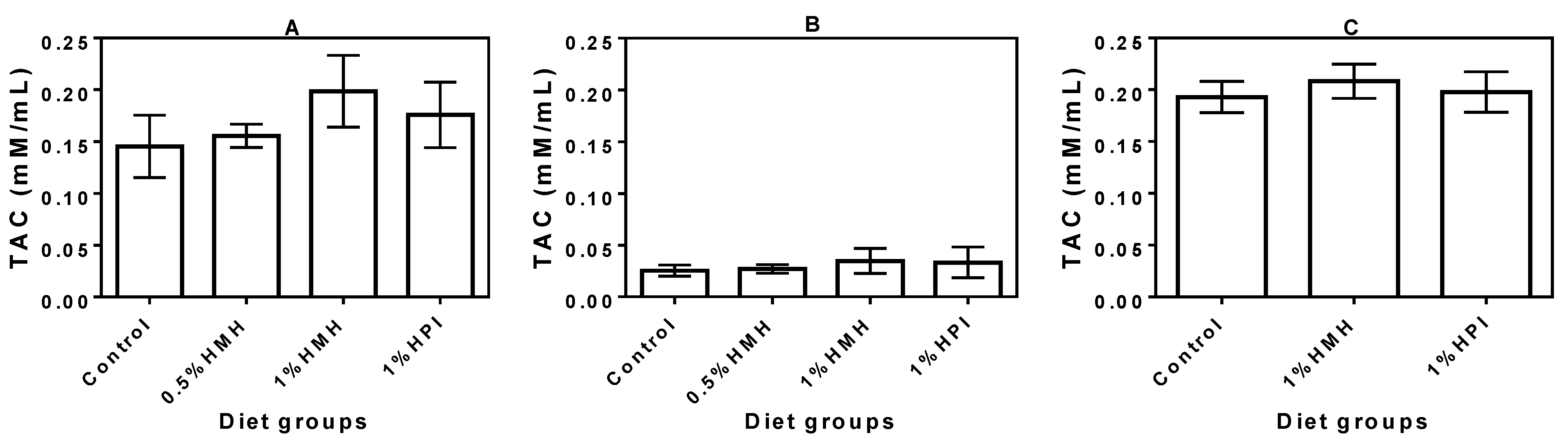

3.5. Plasma TPx
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callaway, J.C. Hempseed as a nutritional resource: An overview. Euphytica 2004, 140, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.W.; Tang, C.H.; Cao, J.S.; Hu, E.K.; Wen, Q.B.; Yang, X.Q. Effects of limited enzymatic hydrolysis with trypsin on the functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.S.; Tang, C.H.; Yang, X.Q.; Gao, W.R. Characterization, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) proteins. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.H.; Ten, Z.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, X.Q. Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, R.; FitzGerald, R.J. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins. In Bioactive Food Peptides in Health and Disease; Hernandez, B., Hsieh, C., Eds.; Intech Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 45–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pihlanto, A.; Mäkinen, S. Antihypertensive properties of plant protein derived peptides. In Bioactive Food Peptides in Health and Disease; Hernandez, B., Hsieh, C., Eds.; Intech Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 145–182. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, R.; Rana, S. Bioactive peptides: A review. Int. J. Bioautom. 2011, 15, 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Girgih, A.T.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. In vitro antioxidant properties of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysate fractions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.H.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, X.Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate by various proteases and antioxidant properties of the resulting hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Troudi, A.; Bouaziz, H.; Soudani, N.; Ben Amara, I.; Boudawara, T.; Touzani, H.; Lyoussi, B.; Zeghal, N. Neurotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by gibberellic acid in rats during late pregnancy and early postnatal periods: Biochemical and histological changes. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmadi, B.H.; Ismail, A. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: A review. Peptides 2010, 31, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Di Bernardini, R.; Harnedy, P.; Bolton, D.; Kerry, J.; O’Neill, E.; Mullen, A.M.; Hayes, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial peptidic hydrolysates from muscle protein sources and by-products. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chi, Y.J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Lv, L. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from egg white protein hydrolysate. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Faithong, N.; Benjakul, S.; Phatcharat, S.; Binsan, W. Chemical composition and antioxidative activity of Thai traditional fermented shrimp and krill products. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidative properties of milk protein-derived dipeptides and hydrolysates. Peptides 2013, 39, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Luo, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; Yao, L. Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide from porcine haemoglobin hydrolysate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.-J.; Lin, Y.-C.; Deng, J.-S.; Chen, H.-J.; Liao, J.-C.; Huang, S.-S.; Lin, Y.-H. A novel trypsin inhibitor from sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas Lam.) leaves and its synthesized peptides with antioxidant activities in vitro. Bot. Stud. 2012, 53, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) albumin hydrolysates. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, H. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from sunflower protein hydrolysate. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant and angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory properties of a flaxseed protein-derived high fischer ratio peptide mixture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4762–4768. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.R.; Qian, P.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X.H.; Chen, T.P.; He, J.F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J. Hempseed protein derived antioxidative peptides: Purification, identification and protection from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Nabha, L.; Garbern, J.C.; Buller, C.L.; Charpie, J.R. Vascular oxidative stress precedes high blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2005, 27, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Girgih, A.T.; Alashi, A.M.; He, R.; Malomo, S.A.; Aluko, R.E. Preventive and treatment effects of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) meal protein hydrolysate against high blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Aluko, R.E.; Monu, E. Functional and bioactive properties of quinoa seed protein hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar]
- De Avellar, I.G.J.; Magalhães, M.M.M.; Silva, A.B.; Souza, L.L.; Leitão, A.C.; Hermes-Lima, M. Reevaluating the role of 1,10-phenanthroline in oxidative reactions involving ferrous ions and DNA damage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2004, 1675, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, X. Mechanism of pyrogallol autoxidation and determination of superoxide dismutase enzyme activity. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1998, 45, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Antioxidant activity of peptides isolated from alfalfa leaf protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T.; Mu, W.; Liu, J. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of chickpea protein hydrolysate (CPH). Food Chem. 2008, 106, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, L.-M.; Chen, J.-K.; Huang, S.-S.; Lee, R.-S.; Su, M.-J. Cardioprotective effect of resveratrol, a natural antioxidant derived from grapes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 47, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Young, I.S.; Woodside, J.V. Antioxidants in health and disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 176–186. [Google Scholar]
- Girgih, A.T.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. Reverse-phase HPLC separation of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysate produced peptide fractions with enhanced antioxidant capacity. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 2013, 68, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Moure, A.; Domínguez, H.; Parajó, J.C. Antioxidant properties of ultrafiltration-recovered soy protein fractions from industrial effluents and their hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Simão, S.; Gomes, P.; Pinto, V.; Silva, E.; Amaral, J.S.; Igreja, B.; Alfonso, J.; Serrão, M.P.; Pinho, M.J.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Age-related changes in renal expression of oxidant and antioxidant enzymes and oxidative stress markers in male SHR and WKY rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, S.K.; Lennon, S.L. Analysis of cellular responses to free radicals: Focus on exercise and skeletal muscle. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1999, 58, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Kregel, K.C.; Zhang, H.J. An integrated view of oxidative stress in aging: Basic mechanisms, functional effects, and pathological considerations. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, 18–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, V.; Amaral, J.; Silva, E.; Simão, S.; Cabral, J.M.; Afonso, J.; Serrão, M.P.; Gomes, P.; Pinho, M.J.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Age-related changes in the renal dopaminergic system and expression of renal amino acid transporters in WKY and SHR rats. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2011, 132, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, R.H.; Regenstein, J.M. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) peptides prepared by papain digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7948–7953. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Khaled, H.; Ghlissi, Z.; Chtourou, Y.; Hakim, A.; Ktari, N.; Fatma, M.A.; Barkia, A.; Sahnoun, Z.; Nasri, M. Effect of protein hydrolysates from sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) on the oxidative status and blood lipid profile of cholesterol-fed rats. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Young, I.S. Measurement of total antioxidant capacity. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 339–340. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, P.L.; Chen, B.H.; Yang, F.L.; Lu, Y.F. Effects of deep-frying oil on blood pressure and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Nutrition 2010, 26, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Winczura, A.; Zdzalik, D.; Tudek, B. Damage of DNA and proteins by major lipid peroxidation products in genome stability. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 442–459. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimitsu, T.; Tobian, L.; Sugimoto, K.; Everson, T. High potassium diets reduce vascular and plasma lipid peroxides in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1996, 18, 659–673. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Girgih, A.T.; Alashi, A.M.; He, R.; Malomo, S.A.; Raj, P.; Netticadan, T.; Aluko, R.E. A Novel Hemp Seed Meal Protein Hydrolysate Reduces Oxidative Stress Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5652-5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6125652
Girgih AT, Alashi AM, He R, Malomo SA, Raj P, Netticadan T, Aluko RE. A Novel Hemp Seed Meal Protein Hydrolysate Reduces Oxidative Stress Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients. 2014; 6(12):5652-5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6125652
Chicago/Turabian StyleGirgih, Abraham T., Adeola M. Alashi, Rong He, Sunday A. Malomo, Pema Raj, Thomas Netticadan, and Rotimi E. Aluko. 2014. "A Novel Hemp Seed Meal Protein Hydrolysate Reduces Oxidative Stress Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats" Nutrients 6, no. 12: 5652-5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6125652
APA StyleGirgih, A. T., Alashi, A. M., He, R., Malomo, S. A., Raj, P., Netticadan, T., & Aluko, R. E. (2014). A Novel Hemp Seed Meal Protein Hydrolysate Reduces Oxidative Stress Factors in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients, 6(12), 5652-5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6125652




