Comparison of Glucose Monitoring Methods during Steady-State Exercise in Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Experimental Design
VO2peak Protocol (Day 1)
2.3. Steady-State Cycling Sessions
2.4. Measurements during Steady-State Cycling Tests
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Blood Glucose Analysis
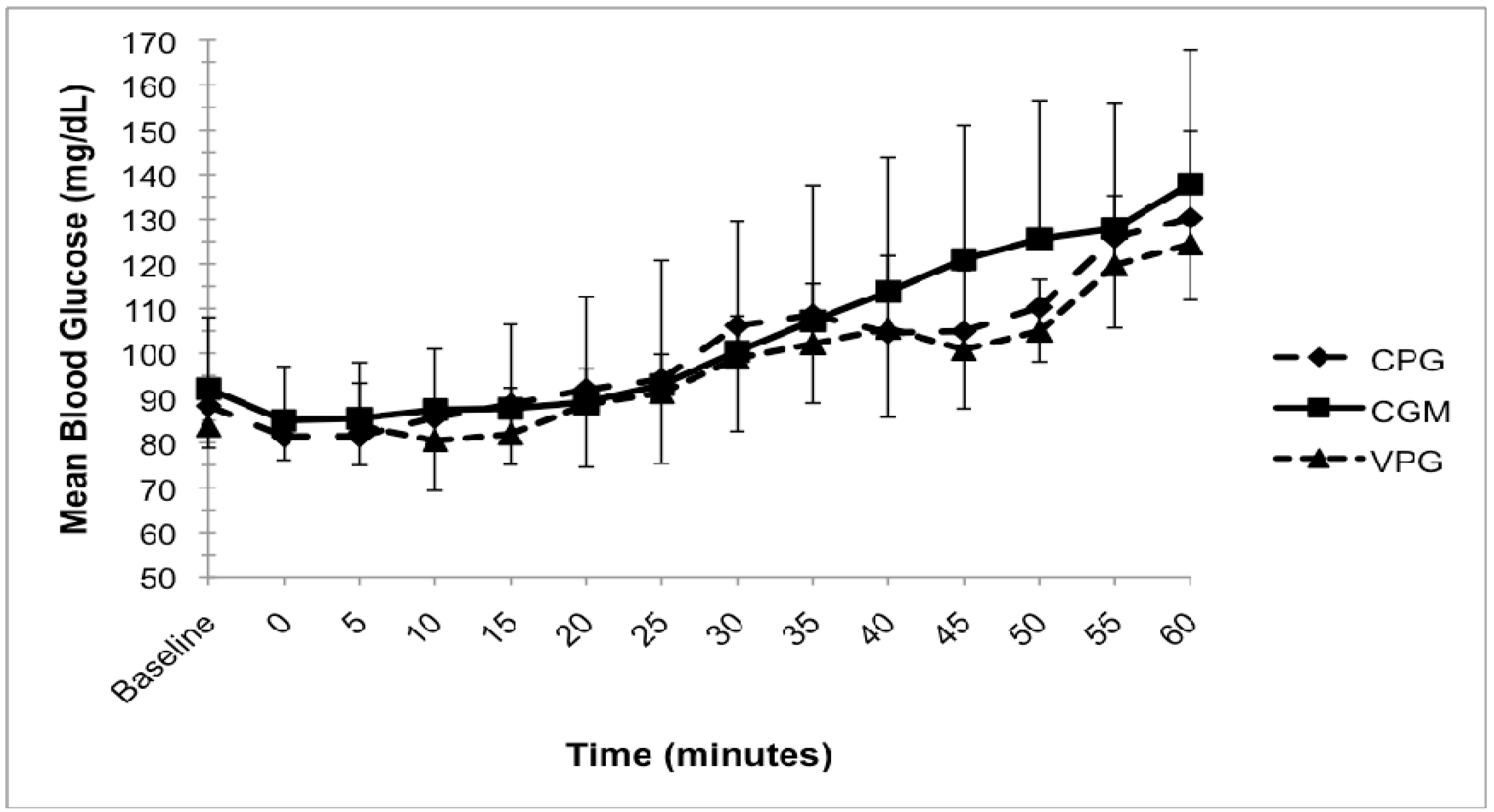
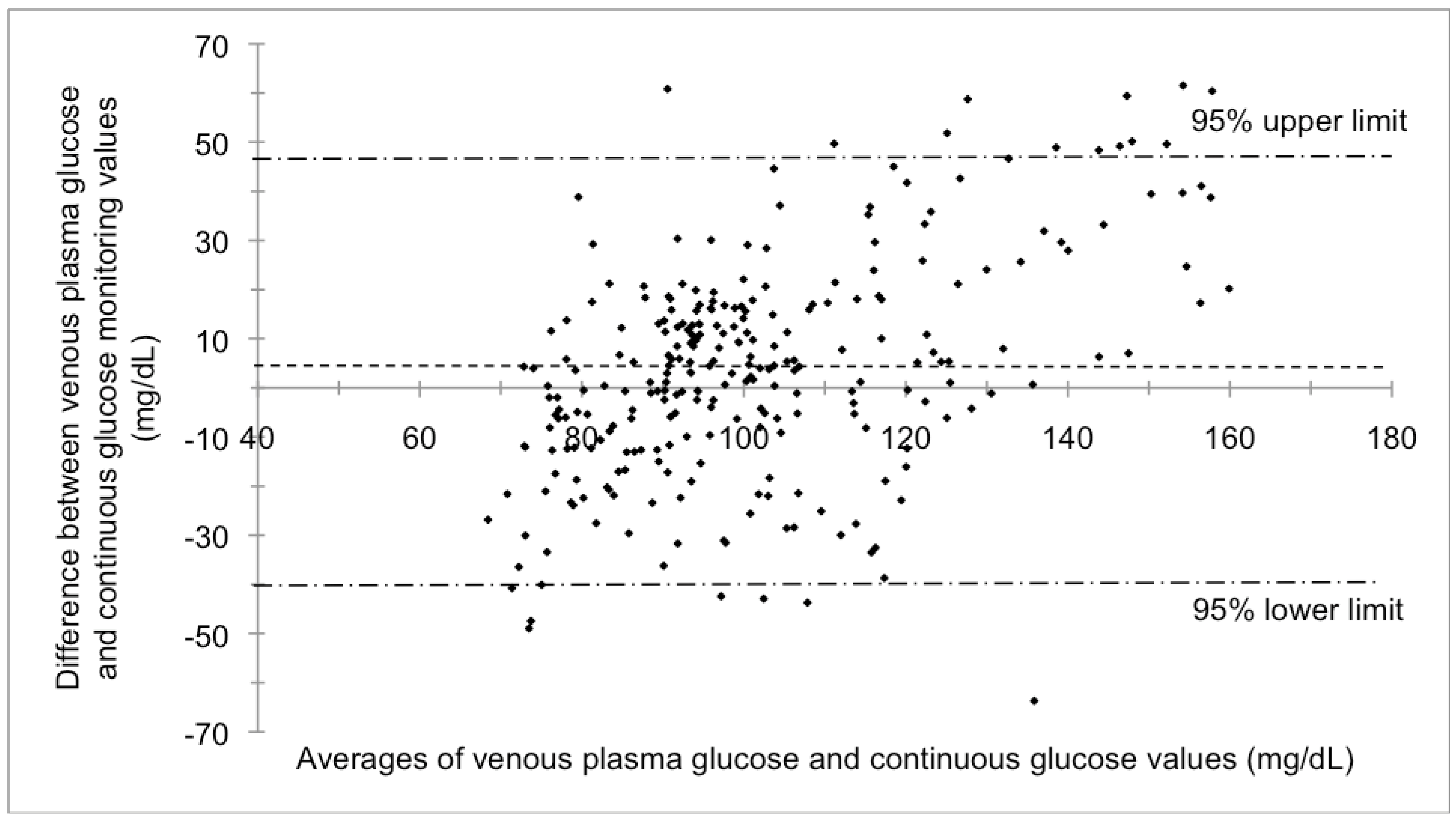
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Hornsby, W.G.; Chetlin, R.D. Management of Competitive Athletes. Diabetes Spectr. 2005, 18, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauza, E.; Hanusch-Enserer, U.; Strasser, B.; Ludvik, B.; Kostner, K.; Dunky, A.; Haber, P. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Diabetic Long Distance Runners. Int. J. Sports Med. 2005, 26, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, V.J.; Tate, D.B.; Davis, S.N. Type 1 Diabetes: Exercise and Hypoglycemia. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulve, E.A. Exercise and Glycemic Control in Diabetes: Benefits, Challenges, and Adjustments to Pharmacotherapy. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1297–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iscoe, K.E.; Campbell, J.E.; Jamnik, V.; Perkins, B.A.; Riddell, M.C. Efficacy of Continuous Real-Time Blood Glucose Monitoring during and after Prolonged High-Intensity Cycling Exercise: Spinning with a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2006, 8, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKnight, J.M.; Mistry, D.J.; Pastors, J.G.; Holmes, V.; Rynders, C.A. The Daily Management of Athletes with Diabetes. Clin. Sports Med. 2009, 28, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D.A.; Guy, D.L.; Richardson, M.A.; Ertl, A.C.; Davis, S.N. Effects of Low and Moderate Antecedent Exercise on Counterregulatory Responses to Subsequent Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEVEN® PLUS Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Users Guide, 7th ed; DexCom Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 60–77.
- Burge, M.R.; Mitchell, S.; Sawyer, A.; Schade, D.S. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: The Future of Diabetes Management. Diabetes Spectr. 2008, 21, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manders, R.J.F.; van Dijk, J.M.; van Loon, L.J.C. Low-Intensity Exercise Reduces the Prevalence of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, T.S.; Zisser, H.C.; Garg, S.K. Reduction in Hemoglobin A1c with Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Results from a 12-week Observational Study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2007, 9, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiss, D.; Bolinder, J.; Riveline, J.; Battelino, T.; Bosi, E.; Tubiana-Rufi, N.; Kerr, D.; Phillip, M. Improved Glycemic Control in Poorly Controlled Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Using Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2730–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiss, D.; Hartmann, R.; Hoeffe, J.; Kordonouori, O. Assessment of Glycemic Control by Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in 50 Children with Type 1 Diabetes Starting on Insulin Pump Therapy. Pediatr Diabetes 2004, 5, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Jovanovic, L. Relationship of Fasting and Hourly Blood Glucose Levels to HbA1c Values. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2644–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Zisser, H.; Schwartz, S.; Bailey, T.; Kaplan, R.; Ellis, S.; Jovanovic, L. Improvement in Glycemic Excursions with a Transcutaneous, Real-Time Continuous Glucose Sensor. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.; Hanas, R. Continuous Subcutaneous Glucose Monitoring Improved Metabolic Control in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Controlled Crossover Study. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauza, E.; Hanusch-Enserer, U.; Strasser, B.; Kostner, S.K.; Dunky, A.; Haber, P. Strength and Endurance Training Lead to Different Post Exercise Glucose Profiles in Diabetic Participants Using a Continuous Subcutaneous Glucose Monitoring System. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 35, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.L.; Philp, A.; Harrison, M.; Bone, A.J.; Watt, P.W. Monitoring Exercise-Induced Changes in Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyne, M.S.; Silver, D.M.; Kaplan, J.; Saudek, C.D. Timing of Changes in Interstitial and Venous Blood Glucose Measured with a Continuous Subcutaneous Glucose Sensor. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2790–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassin, L.J.; Wilinska, M.E.; Hovorka, R. Intense Exercise in Type 1 Diabetes: Exploring the Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2007, 1, 570–573. [Google Scholar]
- Monsod, T.P.; Flanagan, D.E.; Rife, F.; Saenz, R.; Caprio, S.; Sherwin, R.S.; Tamborlane, W.V. Do Sensor Glucose Levels Accurately Predict Plasma Glucose Concentrations during Hypoglycemia and Hyperinsulinemia? Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.N.; Mynark, R. Balance Deficits in Recreational Athletes within Chronic Ankle Instability. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- American College of Sports Medicine, Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 8th ed; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; p. 81.
- Pollock, M.L.; Schmidt, D.H.; Jackson, A.S. Measurement of Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Composition in the Clinical Setting. Compr. Ther. 1980, 6, 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical Bases of Perceived Exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Maud, P.J.; Foster, C. Physiological Assessment of Human Fitness, 2nd ed; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2006; pp. 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fayolle, C.; Brun, J.F.; Bringer, J.; Mercier, J.; Renard, E. Accuracy of Continuous Subcutaneous Glucose Monitoring with the GlucoDay in Type 1 Diabetic Patients Treated by Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion during Exercise of Low vs. High Intensity. Diabetes Metab. 2006, 32, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, M.J.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Performance Metrics for Continuous Interstitial Glucose Monitoring; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2008.
- Young, J.K.; Ellison, J.M.; Marshall, R. Performance Evaluation of a New Blood Glucose Monitor that Requires No Coding: The OneTouch® Vita™ System. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 814–818. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, A.; Mahalingam, B.J. Analysis of Time Lags and Other Sources of Error of the DexCom SEVEN Continuous Glucose Monitor. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2009, 11, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, R.L.; Schwartz, S.L.; Brazg, R.L.; Bugler, J.R.; Peyser, T.A.; McGarraugh, G.V. Accuracy of the 5-Day FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar]
- McGowan, K.; Thomas, W.; Moran, A. Spurious Reporting of Nocturnal Hypoglycemia by CGMS in Patients with Tightly Controlled Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, E.; Tamborlane, W.V. A Tale of Two Compartments: Interstitial Blood Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Techol. Ther. 2009, 11, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, B.; Forst, S.; Weber, M.M.; Larbig, M.; Pfützner, A.; Forst, T. Evaluation of CGMS® during Rapid Blood Glucose Changes in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2006, 8, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalkoff, S.R.; Polychronakos, C. Evaluation of Conventional Blood Glucose Monitoring as an Indicator of Integrated Glucose Values Using a Continuous Subcutaneous Sensor. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, B.; Gross, K.; Rikalo, N.; Schwartz, S.; Wahl, T.; Page, C.; Gross, T.; Mastrototaro, J. Alarms Based on Real—Time Sensor Glucose Values Alert Patients to Hypo—and Hyperglycemia: The Guardian Continuous Monitoring System. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2004, 6, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrington, S.J.; Gee, D.L.; Dow, S.D.; Monosky, K.A.; Davis, E.; Pritchett, K.L. Comparison of Glucose Monitoring Methods during Steady-State Exercise in Women. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1282-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4091282
Herrington SJ, Gee DL, Dow SD, Monosky KA, Davis E, Pritchett KL. Comparison of Glucose Monitoring Methods during Steady-State Exercise in Women. Nutrients. 2012; 4(9):1282-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4091282
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrington, Stefanie J., David L. Gee, Shireen D. Dow, Keith A. Monosky, Erika Davis, and Kelly L. Pritchett. 2012. "Comparison of Glucose Monitoring Methods during Steady-State Exercise in Women" Nutrients 4, no. 9: 1282-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4091282
APA StyleHerrington, S. J., Gee, D. L., Dow, S. D., Monosky, K. A., Davis, E., & Pritchett, K. L. (2012). Comparison of Glucose Monitoring Methods during Steady-State Exercise in Women. Nutrients, 4(9), 1282-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4091282



