The Adverse Effects of Alcohol on Vitamin A Metabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
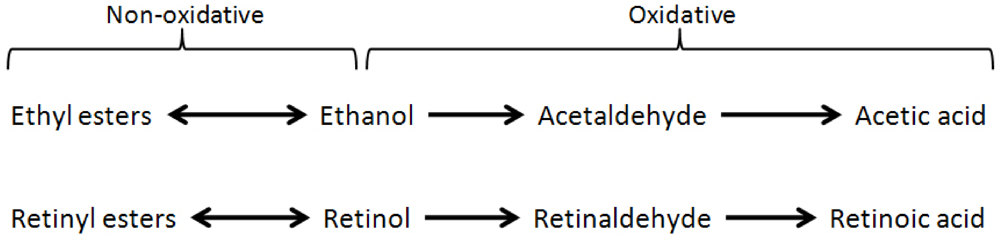
2. Vitamin A Deficiency and Alcoholism
3. Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Tissue Retinoid Levels
| Lead author (year of publication) [reference number] | Species (strain) | Hepatic retinoid status |
|---|---|---|
| Sato (1981) [18] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Leo (1986) [19] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Mobarhan (1986) [20] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Mobarhan (1991) [21] | Rat (Fischer 344) | Decreased # |
| Chapman (1992) [22] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Wang (1998) [23] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Chung (2001) [24] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Liu (2002) [25] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Chung (2009) [26] | Rat (Sprague-Dawley) | Decreased |
| Kane (2010) [27] | Mouse (C57BL/6) | Decreased |
| Luvizotto (2010) [28] | Rat (Fisher 344) | Decreased |
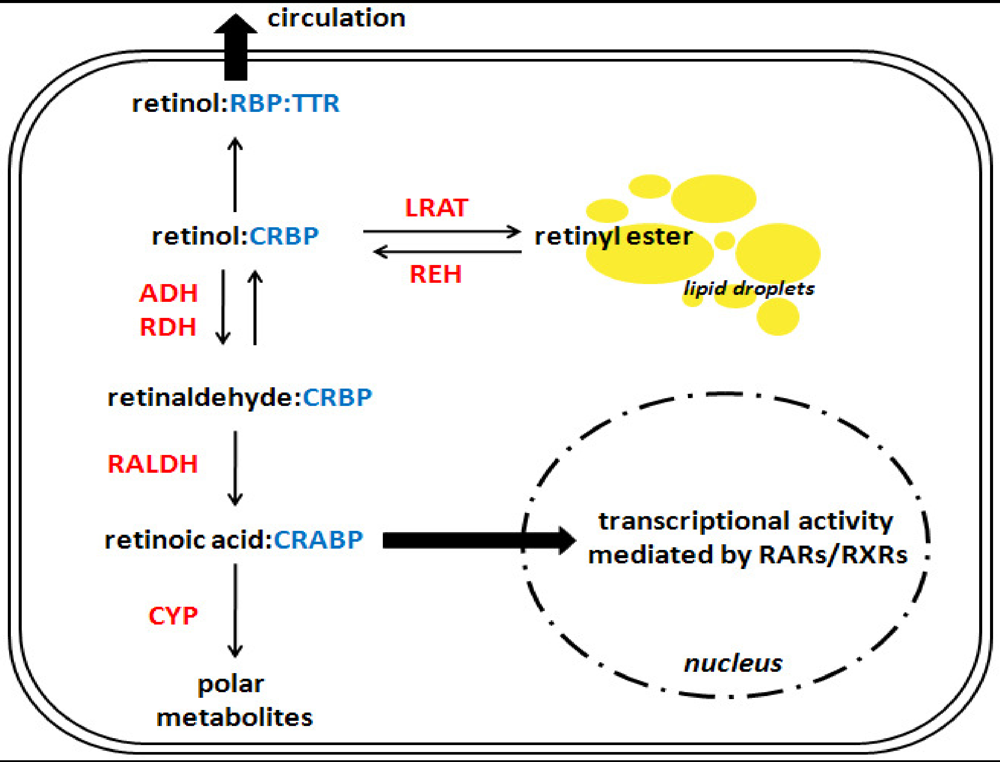
4. Interactions between Alcohol and Hepatic Retinoid Metabolism
4.1. Synthesis and Hydrolysis of Hepatic Retinyl Ester Stores
4.2. Synthesis of Retinoic Acid
4.3. Catabolism of Retinoic Acid
5. Effect of Altered Retinoid Homeostasis on Alcohol-Induced Disease
6. Summary
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Best, C.A.; Laposata, M. Fatty acid ethyl esters: Toxic non-oxidative metabolites of ethanol and markers of ethanol intake. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, e202–e217. [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson, A.; Walther, L.; Hansson, T.; Andersson, A.; Alling, C. Phosphatidylethanol in blood (b-peth): A marker for alcohol use and abuse. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Shirakami, Y.; Lee, S.A.; Clugston, R.D.; Blaner, W.S. Hepatic metabolism of retinoids and disease associations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 124–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zachman, R.D.; Grummer, M.A. The interaction of ethanol and vitamin A as a potential mechanism for the pathogenesis of fetal alcohol syndrome. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, M.S.; Sun, M.; Ko, J. Vitamin A, folate, and choline as a possible preventive intervention to fetal alcohol syndrome. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 78, 489–493. [Google Scholar]
- Lieber, C.S. Relationships between nutrition, alcohol use, and liver disease. Alcohol. Res. Health 2003, 27, 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Halsted, C.H. Nutrition and alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Patek, A.J.; Haig, C. The occurrence of abnormal dark adaptation and its relation to vitamin A metabolism in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J. Clin. Invest. 1939, 18, 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Halsted, J.A.; Smith, J.C., Jr. Letter: Night blindness and chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology 1974, 67, 193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, S.K.; Shaw, G.K.; Thomson, A.D. Vitamin A utilization status in chronic alcoholic patients. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1983, 53, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Roncone, D.P. Xerophthalmia secondary to alcohol-induced malnutrition. Optometry 2006, 77, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.C., Jr.; Brown, E.D.; White, S.C.; Finkelstein, J.D. Letter: Plasma vitamin A and zinc concentration in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet 1975, 1, 1251–1252. [Google Scholar]
- McClain, C.J.; van Thiel, D.H.; Parker, S.; Badzin, L.K.; Gilbert, H. Alterations in zinc, vitamin A, and retinol-binding protein in chronic alcoholics: A possible mechanism for night blindness and hypogonadism. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1979, 3, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Hepatic vitamin A depletion in alcoholic liver injury. New Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 597–601. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Sato, M.; Lieber, C.S. Effect of hepatic vitamin A depletion on the liver in humans and rats. Gastroenterology 1983, 84, 562–572. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, H.; Nilsson, A.; Norum, K.R.; Pedersen, L.B.; Raknerud, N.; Rasmussen, M. Retinol and retinyl esters in patients with alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 1989, 8, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, S.; Moriwaki, H.; Muto, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Fukutomi, Y.; Shimazaki, M.; Okuno, M.; Ninomiya, M. Reduced retinoid content in hepatocellular carcinoma with special reference to alcohol consumption. Hepatology 1991, 14, 776–780. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Lieber, C.S. Hepatic vitamin A depletion after chronic ethanol consumption in baboons and rats. J. Nutr. 1981, 111, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Kim, C.; Lieber, C.S. Increased vitamin A in esophagus and other extrahepatic tissues after chronic ethanol consumption in the rat. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1986, 10, 487–492. [Google Scholar]
- Mobarhan, S.; Layden, T.J.; Friedman, H.; Kunigk, A.; Donahue, P. Depletion of liver and esophageal epithelium vitamin A after chronic moderate ethanol consumption in rats: Inverse relation to zinc nutriture. Hepatology 1986, 6, 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- Mobarhan, S.; Seitz, H.K.; Russell, R.M.; Mehta, R.; Hupert, J.; Friedman, H.; Layden, T.J.; Meydani, M.; Langenberg, P. Age-related effects of chronic ethanol intake on vitamin A status in fisher 344 rats. J. Nutr. 1991, 121, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, K.; Prabhudesai, M.; Erdman, J.W., Jr. Effects of ethanol and carbon tetrachloride upon vitamin A status of rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1992, 16, 764–768. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D.; Liu, C.; Chung, J.; Stickel, F.; Seitz, H.K.; Russell, R.M. Chronic alcohol intake reduces retinoic acid concentration and enhances ap-1 (c-jun and c-fos) expression in rat liver. Hepatology 1998, 28, 744–750. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Liu, C.; Smith, D.E.; Seitz, H.K.; Russell, R.M.; Wang, X.D. Restoration of retinoic acid concentration suppresses ethanol-enhanced c-jun expression and hepatocyte proliferation in rat liver. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chung, J.; Seitz, H.K.; Russell, R.M.; Wang, X.D. Chlormethiazole treatment prevents reduced hepatic vitamin A levels in ethanol-fed rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Veeramachaneni, S.; Liu, C.; Mernitz, H.; Russell, R.M.; Wang, X.D. Vitamin E supplementation does not prevent ethanol-reduced hepatic retinoic acid levels in rats. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 664–670. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, M.A.; Folias, A.E.; Wang, C.; Napoli, J.L. Ethanol elevates physiological all-trans-retinoic acid levels in select loci through altering retinoid metabolism in multiple loci: A potential mechanism of ethanol toxicity. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 823–832. [Google Scholar]
- Luvizotto, R.A.; Nascimento, A.F.; Veeramachaneni, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.D. Chronic alcohol intake upregulates hepatic expression of carotenoid cleavage enzymes and ppar in rats. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Blaner, W.S.; O’Byrne, S.M.; Wongsiriroj, N.; Kluwe, J.; D’Ambrosio, D.M.; Jiang, H.; Schwabe, R.F.; Hillman, E.M.; Piantedosi, R.; Libien, J. Hepatic stellate cell lipid droplets: A specialized lipid droplet for retinoid storage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, M.; Blomhoff, R.; Helgerud, P.; Solberg, L.A.; Berg, T.; Norum, K.R. Retinol and retinyl esters in parenchymal and nonparenchymal rat liver cell fractions after long-term administration of ethanol. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Cottalasso, D.; Bassi, A.M.; Canepa, C.; Maloberti, G.; Casu, A.; Nanni, G. Chronic ethanol treatment: Dolichol and retinol distribution in isolated rat liver cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Arai, M.; Sato, M.; Lieber, C.S. Hepatotoxicity of vitamin A and ethanol in the rat. Gastroenterology 1982, 82, 194–205. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Hepatic fibrosis after long-term administration of ethanol and moderate vitamin A supplementation in the rat. Hepatology 1983, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, W.F.; Bosma, A.; Hendriks, H.F.; Blaner, W.S.; van Leeuwen, R.E.; van Thiel-de Ruiter, G.C.; Wilson, J.H.; Knook, D.L.; Brouwer, A. Chronic administration of ethanol with high vitamin A supplementation in a liquid diet to rats does not cause liver fibrosis. 2. Biochemical observations. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bosma, A.; Seifert, W.F.; Wilson, J.H.; Roholl, P.J.; Brouwer, A.; Knook, D.L. Chronic administration of ethanol with high vitamin A supplementation in a liquid diet to rats does not cause liver fibrosis. 1. Morphological observations. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Chavez, P.R.; Russell, R.M.; Wang, X.D. Retinoic acid inhibits hepatic jun n-terminal kinase-dependent signaling pathway in ethanol-fed rats. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Dan, Z.; Fu, Y.; Tang, W.; Lin, J. Low-dose atra supplementation abolishes PRM formation in rat liver and ameliorates ethanol-induced liver injury. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2006, 26, 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Kim, C.; Lowe, N.; Lieber, C.S. Interaction of ethanol with beta-carotene: Delayed blood clearance and enhanced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 1992, 15, 883–891. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Aleynik, S.I.; Aleynik, M.K.; Lieber, C.S. Beta-carotene beadlets potentiate hepatotoxicity of alcohol. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Kim, C.I.; Lieber, C.S. Increased vitamin A in esophagus and lungs after moderate ethanol consumption. Drug Nutr. Interact. 1988, 5, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Lieber, C.S. Changes in vitamin A status after acute ethanol administration in the rat. J. Nutr. 1982, 112, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, K.M.; Prabhudesai, M.; Erdman, J.W., Jr. Effects of acute ethanol doses or dietary phenobarbitol with carbon tetrachloride exposure on vitamin A status of rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1993, 17, 637–642. [Google Scholar]
- Balmer, J.E.; Blomhoff, R. Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1773–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, J.L. Effects of ethanol on physiological retinoic acid levels. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Lieber, C.S. Increased metabolism of retinoic acid after chronic ethanol consumption in rat liver microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1982, 213, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Molotkov, A.; Duester, G. Retinol/ethanol drug interaction during acute alcohol intoxication in mice involves inhibition of retinol metabolism to retinoic acid by alcohol dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22553–22557. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvant, P.; Sapin, V.; Abergel, A.; Schmidt, C.K.; Blanchon, L.; Alexandre-Gouabau, M.C.; Rosenbaum, J.; Bommelaer, G.; Rock, E.; Dastugue, B.; et al. Pav-1, a new rat hepatic stellate cell line converts retinol into retinoic acid, a process altered by ethanol. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, G. Tissue-specific increases in endogenous all-trans retinoic acid: Possible contributing factor in ethanol toxicity. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Alcohol, vitamin A, and beta-carotene: Adverse interactions, including hepatotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Stryker, W.S.; Kaplan, L.A.; Stein, E.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Sober, A.; Willett, W.C. The relation of diet, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption to plasma beta-carotene and alpha-tocopherol levels. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 127, 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.J.; Peters, T.J. The antioxidant status of patients with either alcohol-induced liver damage or myopathy. Alcohol Alcohol. 1992, 27, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Interactions between alcohol and beta-carotene in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, M.R.; Beecher, G.R.; Lanza, E.; Reichman, M.E.; Graubard, B.I.; Campbell, W.S.; Marr, T.; Yong, L.C.; Judd, J.T.; Taylor, P.R. Effect of alcohol consumption on plasma carotenoid concentrations in premenopausal women: A controlled dietary study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Fukao, A.; Tsubono, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Ido, T.; Akazawa, N.; Tsuji, I.; Komatsu, S.; Minami, Y.; Hisamichi, S. The independent association of smoking and drinking with serum beta-carotene levels among males in miyagi, japan. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 25, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ambrosio, D.N.; Clugston, R.D.; Blaner, W.S. Vitamin A metabolism: An update. Nutrients 2011, 3, 63–103. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, H.; Mobarhan, S.; Hupert, J.; Lucchesi, D.; Henderson, C.; Langenberg, P.; Layden, T.J. In vitro stimulation of rat liver retinyl ester hydrolase by ethanol. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 269, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Herr, F.M.; Ong, D.E. Differential interaction of lecithin-retinol acyltransferase with cellular retinol binding proteins. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 6748–6755. [Google Scholar]
- Boerman, M.H.; Napoli, J.L. Cholate-independent retinyl ester hydrolysis. Stimulation by apo-cellular retinol-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 22273–22278. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sandell, L.L.; Trainor, P.A.; Koentgen, F.; Duester, G. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases: Retinoid metabolic effects in mouse knockout models. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, J.L. Physiological insights into all-trans-retinoic acid biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.L.; Liao, C.S.; Wu, C.W.; Hwong, C.L.; Lee, A.R.; Yin, S.J. Contribution to first-pass metabolism of ethanol and inhibition by ethanol for retinol oxidation in human alcohol dehydrogenase family—implications for etiology of fetal alcohol syndrome and alcohol-related diseases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 254, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Parlesak, A.; Menzl, I.; Feuchter, A.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C. Inhibition of retinol oxidation by ethanol in the rat liver and colon. Gut 2000, 47, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Kedishvili, N.Y.; Gough, W.H.; Davis, W.I.; Parsons, S.; Li, T.K.; Bosron, W.F. Effect of cellular retinol-binding protein on retinol oxidation by human class iv retinol/alcohol dehydrogenase and inhibition by ethanol. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 249, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, D.E.; Kakkad, B.; MacDonald, P.N. Acyl-coa-independent esterification of retinol bound to cellular retinol-binding protein (type II) by microsomes from rat small intestine. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, M.A.; Kim, C.I.; Lowe, N.; Lieber, C.S. Increased hepatic retinal dehydrogenase activity after phenobarbital and ethanol administration. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1989, 38, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.C.; Zolfaghari, R. Regulation of hepatic retinol metabolism: Perspectives from studies on vitamin A status. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, S269–S275. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.C.; Zolfaghari, R. Cytochrome p450s in the regulation of cellular retinoic acid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2011, 31, 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Russell, R.M.; Seitz, H.K.; Wang, X.D. Ethanol enhances retinoic acid metabolism into polar metabolites in rat liver via induction of cytochrome p4502e1. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Koop, D.R.; Tierney, D.J. Multiple mechanisms in the regulation of ethanol-inducible cytochrome p450IIE1. Bioessays 1990, 12, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D. Alcohol, vitamin A, and cancer. Alcohol 2005, 35, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, U.E.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ryle, P.R.; Hodges, A.; Thomson, A.D. Inhibition of ethanol induced hepatic vitamin A depletion by administration of n,n′-diphenyl-p-phenylene-diamine (DPPD). Life Sci. 1986, 38, 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Wong, K.; Jui, L.; Nanji, A.A.; Mendenhall, C.S.; French, S.W. Effect of dietary fat on ito cell activation by chronic ethanol intake: A long-term serial morphometric study on alcohol-fed and control rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1991, 15, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, Z.; Popov, Y.; Patsenker, E.; Preimel, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.D.; Seitz, H.K.; Schuppan, D.; Stickel, F. Hepatotoxicity of alcohol-induced polar retinol metabolites involves apoptosis via loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 845–847. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, M.; Reitz, R.C.; Morin, R.J.; Nguyen, K.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; French, S.W. CYP-2E1 inhibitors partially ameliorate the changes in hepatic fatty acid composition induced in rats by chronic administration of ethanol and a high fat diet. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 2953–2964. [Google Scholar]
- Gouillon, Z.; Lucas, D.; Li, J.; Hagbjork, A.L.; French, B.A.; Fu, P.; Fang, C.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; French, S.W. Inhibition of ethanol-induced liver disease in the intragastric feeding rat model by chlormethiazole. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 2000, 224, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- Schutze, M.; Boeing, H.; Pischon, T.; Rehm, J.; Kehoe, T.; Gmel, G.; Olsen, A.; Tjonneland, A.M.; Dahm, C.C.; Overvad, K.; et al. Alcohol attributable burden of incidence of cancer in eight european countries based on results from prospective cohort study. BMJ 2011, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.M.; Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Ethanol potentiates squamous metaplasia of the rat trachea caused by vitamin A deficiency. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1984, 97, 210–221. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, K.M.; Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Potentiation by ethanol consumption of tracheal squamous metaplasia caused by vitamin A deficiency in rats. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1987, 79, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, K.M.; Leo, M.A.; Lieber, C.S. Effect of ethanol and vitamin A deficiency on epithelial cell proliferation and structure in the rat esophagus. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 362–370. [Google Scholar]
- van Thiel, D.H.; Gavaler, J.; Lester, R. Ethanol inhibition of vitamin A metabolism in the testes: Possible mechanism for sterility in alcoholics. Science 1974, 186, 941–942. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, E.R.; Gavaler, J.S.; van Thiel, D.H. Lipid peroxidation: A mechanism for alcohol-induced testicular injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1989, 7, 569–577. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Clugston, R.D.; Blaner, W.S. The Adverse Effects of Alcohol on Vitamin A Metabolism. Nutrients 2012, 4, 356-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4050356
Clugston RD, Blaner WS. The Adverse Effects of Alcohol on Vitamin A Metabolism. Nutrients. 2012; 4(5):356-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4050356
Chicago/Turabian StyleClugston, Robin D., and William S. Blaner. 2012. "The Adverse Effects of Alcohol on Vitamin A Metabolism" Nutrients 4, no. 5: 356-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4050356
APA StyleClugston, R. D., & Blaner, W. S. (2012). The Adverse Effects of Alcohol on Vitamin A Metabolism. Nutrients, 4(5), 356-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu4050356




