Effect of Lactobacilli on Paracellular Permeability in the Gut
Abstract
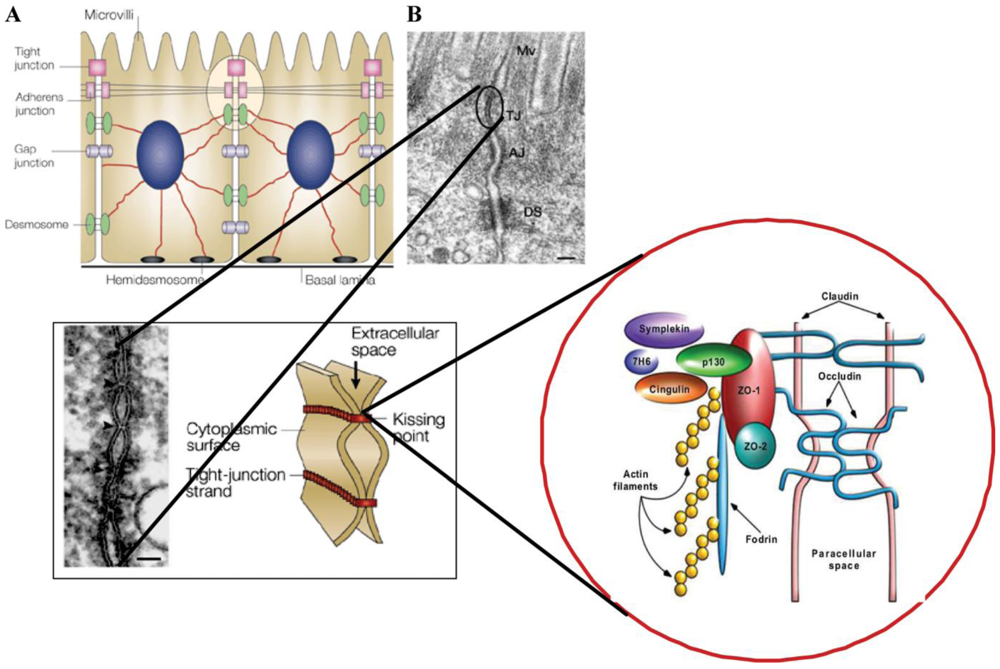
:1. Introduction
2. Effects in Animal Models
2.1. Methotrexate-Induced Colitis
2.2. Liver Injury Induced by D-Galactosamine
2.3. Dextran Sulfate-Induced Colitis
2.4. Alcohol-Induced Injury
2.5. Stress-Induced Models
2.6. Healthy Animals
3. Effects in Different Cell Systems
4. Effects in Human Studies
Clinical Trials
5. Conclusions
References
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S.P. Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Keita, Å.V.; Söderholm, J. The intestinal barrier and its regulation by neuroimmune factors. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 718–733. [Google Scholar]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Tapia, R.; Chamorro, D. Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 729–756. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Su, L.; Turner, J.R. Mechanisms and functional implications of intestinal barrier defects. Dig. Dis. 2009, 27, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Nusrat, A. Dynamic regulation of epithelial cell fate and barrier function by intercellular junctions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1165, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.E.; Griffiths, R.D.; Freestone, N.; Billington, D.; Atherton, S.T.; Macmillan, R.R. Intestinal permeability in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 1992, 18, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- O’Boyle, C.J.; MacFie, J.; Mitchell, C.J.; Johnstone, D.; Sagar, P.M.; Sedman, P.C. Microbiology of bacterial translocation in humans. Gut 1998, 42, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, G.; Velasco, D.; Waintre, C.; Castillo, L.; Bugedo, G.; Maiz, A.; Lopez, F.; Guzman, S.; Vargas, C. Gut mucosal atrophy after a short enteral fasting period in critically ill patients. J. Crit. Care 1999, 14, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Klarin, B. Using probiotics in intensive care with special reference to Lactobacillus plantarum 299 and 299v. October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.C.; Christou, N.V.; Meakins, J.L. The gastrointestinal tract. The “undrained abscess” of multiple organ failure. Ann. Surg. 1993, 218, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Meakins, J.L.; Marshall, J.C. The gastro-intestinal tract: the motor of multiple organ failure. Arch. Surg. 1986, 121, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Goris, R.J.A. The gut: the motor of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 1999, 2, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Gatt, M.; Reddy, B.S.; MacFie, J. Review article: bacterial translocation in the critically ill—evidence and methods of prevention. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 741–757. [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski, J.; Troost, F.J.; Konings, I.; Dekker, J.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.-J.M.; Wells, J.M. Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by Lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G851–G859. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, P.; Delos Santos, N.; Seth, A.; LaRusso, N.F.; Rao, R.K. Lipopolysaccharide disrupts tight junctions in cholangiocyte monolayers by c-Scc-, TLR4-, and LPB-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G308–G318. [Google Scholar]
- Laukoetter, M.G.; Nava, P.; Nusrat, A. Role of intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Förster, C. Tight junctions and the modulation of barrier function in disease. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 130, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Piche, T.; Barabara, G.; Aubert, P.; Bruley dês Varannes, S.; Dainese, R.; Nano, J.L.; Cremon, C.; Strangellini, V.; de Giorgio, R.; Galmiche, J.P.; Neunlist, M. Impaired intestinal barrier integrity in the colon of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: involvement of soluble mediators. Gut 2009, 58, 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Eutamene, H.; Bueno, L. Role of probiotics in correction abnormalities of colonic flora induced by stress. Gut 2007, 56, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrné, S.; Nobaek, S.; Jeppsson, B.; Adlerberth, I.; Wold, A.; Molin, G. The normal Lactobacillus flora of healthy human rectal and oral mucosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 85, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, J.; Rozing, A.; Sapone, A.; Lammers, K.; Fasano, A. Tight junctions, intestinal permeability and autoimmunity: celiac disease and type 1 diabetes paradigms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1165, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, T.; Miyasono, Y.; Ito, K.; Hamada, K.; Sekine, S.; Horie, T. Oxidative stress and enhanced permeability in the small intestine of methotrexate rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 65, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, P.; Basuroy, S.; Li, C.; Naren, A.P.; Rao, R.K. Role of phosphaditylinositol 3-kinase in oxidative stress-induced disruption of tight junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49239–49245. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.K.; Basuroy, S.; Rao, V.U.; Kamaky, K.J., Jr.; Gupta, A. Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occluding-ZO-1 and E-caderin-beta-catenin coplexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 471–481. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Nobaek, S.; Kasravi, B.; Adawi, D.; Stenram, U.; Molin, G.; Jeppsson, B. The effects of Lactobacillus strains and oat fiber on methotrexate-induced enterocolitis in the rats. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 334–344. [Google Scholar]
- Southcott, E.; Tooley, K.L.; Howart, G.S.; Davidsson, G.P.; Butler, R.N. Yoghurts containing probiotics reduce disruption of the small intestinal barrier in methotrexate-treated rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 1837–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer, B.L.; Waggoner, J.G.; Jones, E.A.; Gralnick, H.R.; Towne, D.; Butler, J.; Weise, V.; Kopin, I.; Walters, I.; Teychenne, P.F.; Goodman, D.G.; Berk, P.D. A model of fulminant hepatic failure in rabbit. Gastroenterology 1978, 74, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, V.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Galanos, C. Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Kasravi, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.-D.; Molin, G.; Bengmark, S.; Jeppsson, B. Bacterial translocation in acute liver injury induced by D-galactosamine. Hepatology 1996, 23, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, J.P. Endotoxin, reticuloendothelial function in liver injury. Hepatology 1981, 1, 458–465. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.-L.; Lv, S.; Liu, P. The roles of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in colon tight junction protein expression and intestinal mucosa structure in a mouse model of acute liver failure. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009, 9, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Ewaschuk, J.; Endersby, R.; Thiel, D.; Diaz, H.; Backer, J.; Ma, M.; Churchill, T.; Madsen, K. Probiotic bacteria prevent hepatic damage and maintain colonic barrier function in a mouse model of sepsis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 841–850. [Google Scholar]
- Adawi, D.; Kasravi, B.; Molin, G.; Jeppsson, B. Effect of Lactobacillus supplementation with and without arginine on liver damage and bacterial translocation in an acute liver injury model in the rat. Hepatology 1997, 25, 642–647. [Google Scholar]
- Adawi, D.; Molin, G.; Ahrné, S.; Jeppsson, B. Modulation of the colonic bacterial flora affects differently bacterial translocation and liver injury in an acute liver injury model. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1999, 11, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Poritz, L.S.; Garver, K.I.; Green, C.; Fitzpatrick, L.; Ruggiero, F.; Koltun, W.A. Loss of the tight junction protein ZO-1 in dextran sulfate sodium induced colitis. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 140, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dieleman, L.A.; Palmern, M.J.; Akol, H.; Bloemena, E.; Pena, A.S.; Meuwissen, S.G.; van Rees, E.P. Cronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 114, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Menningen, R.; Nolte, K.; Rijken, E.; Utech, M.; Loeffler, B.; Senninger, N.; Bruewer, M. Probiotic mixture VSL#3 protects the epithelial barrier by maintaining tight junction protein expression and preventing apoptosis in a murine model of colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1140–G1149. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, N.; Adawi, D.; Ahrné, S.; Jeppsson, B.; Molin, G. Modulation of the effect of dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis by the administration of different probiotic strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, N.; Adawi, D.; Ahrné, S.; Jeppsson, B.; Molin, G. Probiotics and blueberry attenuate the severity of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) induced colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2464–2473. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, N. Effects of probiotics and plant components on murine experimental colitis and acute liver failure. September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi, E.; Morita, H.; Tanabe, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus alleviates intestinal barrier dysfunction in part by increasing expression of zonula occludens-1 and myosin light chain kinase in vivo. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar]
- Choudry, M.A.; Rana, S.N.; Kavanaugh, M.J.; Kovacs, E.J.; Gamelli, R.L.; Sayed, M.M. Impaired intestinal immunity and barrier function: a cause for enhanced bacterial translocation in alcohol intoxication and burn injury. Alcohol 2004, 33, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Farhadi, A.; Jakate, S.M.; Tang, Y.; Shaikh, M.; Keshavarzian, A. Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banab, A.; Keshavarzian, A.; Zhang, L.; Shaikh, M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Tang, Y.; Fields, J.Z. NF-κB activation as a key mechanism in ethanol-induced disruption of the F-actin cytoskeleton and monolayer barrier integrity in intestinal epithelium. Alcohol 2007, 41, 447–460. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi, A.; Keshavarzian, A.; Ranjbaran, Z.; Fields, J.Z.; Banan, A. The role of protein kinase C isoforms in modulating injury and repair of the intestinal barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zareie, M.; Johnson-Henry, K.; Jury, J.; Yang, P.-C.; Ngan, B.-Y.; McKay, D.M.; Söderholm, J.D.; Perdue, M.H.; Sherman, P.M. Probiotics prevent translocation and improve intestinal barrier function in rats following chronic physiological stress. Gut 2006, 55, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Demaude, J.; Salvador-Cartier, C.; Fioramonti, J.; Ferrier, L.; Bueno, L. Phenotypic changes in colonocytes following acute stress or activation of mast cells in mice: implications for delayed epithelial barrier barrier dysfunction. Gut 2006, 55, 655–661. [Google Scholar]
- Gareau, M.G.; Jury, J.; MacQueen, G.; Sherman, P.M.; Perdue, M.H. Probiotic treatment of rat pups normalizes corticosterone release and ameliorates colonic dysfunction induced by maternal separation. Gut 2007, 56, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Bradesi, S.; Fioramonti, S.; Teodorou, V.; Bueno, L. Acute stress-induced hypersensitivity to colonic distension depends upon increases in paracellular permeability: role of myosin light chain kinase. Pain 2005, 113, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Eutamene, H.; Lamine, F.; Chabo, C.; Theodorou, V.; Rochat, F.; Bergoncelli, G.E.; Chorthésy-Theulaz, I.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L. Synergy between Lactobacillus paracasei and its bacterial products to counteract stress-induced gut permeability and sensitivity increase in rats. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Han, W.; Lamine, F.; Eutamene, H.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L.; Theodorou, V. Lactobacillus farciminis treatment suppresses stress induced visceral hypersensitivity: a possible action through interaction with epithelial cell cytoskeleton contraction. Gut 2006, 55, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Mangell, P.; Nejdfors, P.; Wang, M.; Ahrné, S.; Weström, B.; Thorlacius, H.; Jeppsson, B. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v inhibits Escherichia coli-induced intestinal permeability. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2002, 47, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Ma, J.; Juo, N.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, J. Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha disrupt epithelial barrier function by altering lipid composition in micro domains of tight junction. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzon, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Role of TNF-alpha in ileum tight junction alteration in a mouse model of restraint stress. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G1268–G1280. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.Y.; Iwamoto, G.K.; Hoa, N.T.; Akoti, V.; Pedram, A.; Boivin, M.A.; Said, H.M. TNF-alpha induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-kappa-B activation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G367–G376. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.Y.; Boivin, M.A.; Ye, D.; Pedram, A.; Said, H.M. Mechanism of TNF-α modulation of Caco-2 intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier: role of myosin light-chain kinase protein expression. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G422–G430. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.S.; Yang, H.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Seo, J.K. Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits epithelial barrier dysfunction and interleukin-8 secretion induced by tumor necrosis factor-α. World J.Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 1962–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.K.; Polk, D.B.; Seth, A.; Yan, F. Probiotics the good neighbor: Guarding the gut mucosal barrier. Am. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 5, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Philpott, D.J.; MaKay, D.M.; Sherman, P.M.; Perdue, M.H. Infection of T84 cells with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli alters barrier and transport functions. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 270, G634–G645. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhan, R.; Koutsouris, A.; Savkovic, S.D.; Hecht, G. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-induced MLC phosphorylation alters intestinal permeability. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar]
- Parassol, N.; Freita, M.; Thoreaux, K.; Dalmasso, G.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Rampal, P. Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 inhibits the increase in paracellular permeability of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-infected T84 cells. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 156, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Michail, S.; Abernathy, F. Lactobacillus plantarum reduces the in vitro secretory response of intestinal epithelial cells to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. 2002, 35, 350–355. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hang, X.; Jiang, Y. L. plantarum prevents enteroinvasive Escherichia coli-induced tight junction proteins changes in intestinal epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 63. [Google Scholar]
- McCracken, V.J.; Chun, T.; Baldeón, M.E.; Ahrné, S.; Molin, G.; Mackie, R.; Gaskins, H.R. TNF-α sensitizes HT-29 colonic epithelial cells to intestinal lactobacilli. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 227, 665–670. [Google Scholar]
- Mangell, P.; Lennernäs, P.; Wang, M.; Olsson, C.; Ahrné, S.; Molin, G.; Thorlacius, H.; Jeppsson, B. Adhesive capability of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v is important for preventing bacterial translocation in endotoxaemic rats. APMIS 2006, 114, 611–618. [Google Scholar]
- Mack, D.R.; Michail, S.; Wei, S.; McDougall, L.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Probiotics inhibit enteropathogenic E. coli adherence in vitro by inducing intestinal mucin gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, G941–G950. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mack, D.R.; Ahrné, S.; Hyde, L.; Wei, S.; Hollingworth, M.A. Extracellular MUC3 mucin secretion follows adherence of Lactobacillus strains to intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Gut 2003, 52, 827–833. [Google Scholar]
- McNaught, C.E.; Woodcook, N.P.; Andersson, A.D.G.; MacFie, J. A prospective randomized trial of probiotics in critically ill patients. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Klarin, B.; Wullt, M.; Palmquist, I.; Molin, G.; Larsson, A.; Jeppsson, B. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v reduces colonization of Clostridium difficile in critically ill patients treated with antibiotics. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Nobaek, S.; Johansson, M.-L.; Molin, G.; Ahrné, S.; Jeppsson, B. Alteration of intestinal microflora is associated with reduction in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Niedzielin, K.; Kordecki, H.; Birkenfeld, B. A controlled double-blind randomized study on the efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 13, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeldt, V.; Benfeldt, E.; Valerus, N.H.; Paerregaard, A.; Michaelsen, K.F. Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal symptoms and small intestinal permeability in children with atopic dermatitis. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 612–616. [Google Scholar]
- Sentongo, T.A.; Cohran, V.; Korff, S.; Sullivan, C.; Iyer, K.; Zheng, X. Intestinal permeability and effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in children with short bowel syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 46, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahrne, S.; Johansson Hagslatt, M.-L. Effect of Lactobacilli on Paracellular Permeability in the Gut. Nutrients 2011, 3, 104-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3010104
Ahrne S, Johansson Hagslatt M-L. Effect of Lactobacilli on Paracellular Permeability in the Gut. Nutrients. 2011; 3(1):104-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3010104
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhrne, Siv, and Marie-Louise Johansson Hagslatt. 2011. "Effect of Lactobacilli on Paracellular Permeability in the Gut" Nutrients 3, no. 1: 104-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3010104
APA StyleAhrne, S., & Johansson Hagslatt, M.-L. (2011). Effect of Lactobacilli on Paracellular Permeability in the Gut. Nutrients, 3(1), 104-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3010104



