Interrelations of Leptin and Interleukin-6 in Vitamin D Deficient and Overweight Orthodox Nuns from Northern Greece: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Dietary Patterns
2.4. Anthropometric Measurements and Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popkin, B.M. Does global obesity represent a global public health challenge? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máčová, L.; Bičíková, M. Vitamin D: Current Challenges between the Laboratory and Clinical Practice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paspala, I.; Katsiki, N.; Kapoukranidou, D.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Tsiligiroglou-Fachantidou, A. The role of psychobiological and neuroendocrine mechanisms in appetite regulation and obesity. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2012, 6, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkorakis, M.; Katsarou, A.; Katsiki, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Milestones in the journey towards addressing obesity; Past trials and triumphs, recent breakthroughs, and an exciting future in the era of emerging effective medical therapies and integration of effective medical therapies with metabolic surgery. Metabolism 2023, 148, 155689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antuna-Puente, B.; Feve, B.; Fellahi, S.; Bastard, J.P. Adipokines: The missing link between insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, I.; Zelzer, S.; Raggam, R.B.; Prüller, F.; Truschnig-Wilders, M.; Meinitzer, A.; Schnedl, W.J.; Horejsi, R.; Möller, R.; Weghuber, D.; et al. Link between leptin and interleukin-6 levels in the initial phase of obesity related inflammation. Transl. Res. 2012, 159, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, M.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Neyestani, T. Vitamin D and serum leptin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naini, A.E.; Vahdat, S.; Hedaiati, Z.P.; Shahzeidi, S.; Pezeshki, A.H.; Nasri, H. The effect of vitamin D administration on serum leptin and adiponectin levels in end-stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis with vitamin D deficiency: A placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. J. Res. Med Sci. 2016, 21, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Arunabh, S.; Pollack, S.; Yeh, J.; Aloia, J.F. Body fat content and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in healthy women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamycheva, E.; Joakimsen, R.M.; Jorde, R. Intakes of calcium and vitamin D predict body mass index in the population of Northern Norway. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortsman, J.; Matsuoka, L.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Lu, Z.; Holick, M.F. Decreased bioavailability of vitamin D in obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, A.L.; Akinyemi, O.A.; Elliott, J.; Sier, J.; Hunt, J.; Lanham-New, S.; Blackbourn, D. The effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on Interleukin-6 concentrations in healthy South Asian and Caucasian women: Preliminary analysis of the D2-D3 study. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, E240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepanowski, J.F.; Bloomer, R.J. The impact of religious fasting on human health. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, K.O.; Linardakis, M.K.; Bervanaki, F.N.; Tzanakis, N.E.; Kafatos, A.G. Greek Orthodox fasting rituals: A hidden characteristic of the Mediterranean diet of Crete. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Antonopoulou, V.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Mitrofanova, E.; Mulrooney, H.; Petróczi, A.; Zebekakis, P.; et al. Effects of orthodox religious fasting versus combined energy and time restricted eating on body weight, lipid concentrations and glycaemic profile. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Polyzos, S.A.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Similar late effects of a 7-week orthodox religious fasting and a time restricted eating pattern on anthropometric and metabolic profiles of overweight adults. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Effects of Christian Orthodox Fasting Versus Time-Restricted Eating on Plasma Irisin Concentrations among Overweight Metabolically Healthy Individuals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Makedou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Kotsa, K. Implementation of Christian Orthodox fasting improves plasma adiponectin concentrations compared with time-restricted eating in overweight premenopausal women. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greek National Dietary Guidelines for Adults. Available online: http://www.fao.org/nutrition/education/food-dietary-guidelines/regions/countries/greece/en/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation 2014, 129, S102–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Global Database on Body Mass Index. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/topic-details/GHO/body-mass-index (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Tanita Academy. Understanding Your Measurements. Available online: http://tanita.eu/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Petróczi, A.; Folkerts, D.; Kypraiou, M.; Mulrooney, H.; Naughton, D.P.; Persynaki, A.; Zebekakis, P.; Skoutas, D.; et al. Christian Orthodox fasting in practice: A comparative evaluation between Greek Orthodox general population fasters and Athonian monks. Nutrition 2019, 59, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, S.N.; Persynaki, A.; Petróczi, A.; Barkans, E.; Mulrooney, H.; Kypraiou, M.; Tzotzas, T.; Tziomalos, K.; Kotsa, K.; Tsioudas, A.; et al. Health benefits and consequences of the Eastern Orthodox fasting in monks of Mount Athos: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N.; Teede, H.; Scragg, R.; de Courten, B. Vitamin D supplementation for improvement of chronic low-grade inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.J.; Mousa, A.; Ebeling, P.R.; Scott, D.; de Courten, B. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory markers in heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinca, M.; Serban, M.C.; Sahebkar, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Toth, P.P.; Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Blüher, M.; Gurban, C.; Penson, P.; et al. Does vitamin D supplementation alter plasma adipokines concentrations? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, T.; Lange, J.K.; LeBoff, M.S.; Gorska, A.; Luu, S.; Zhou, S.; Glowacki, J.J. Obesity and leptin influence vitamin D metabolism and action in human marrow stromal cells. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 198, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimitphong, H.; Guo, W.; Holick, M.F.; Fried, S.K.; Lee, M.J. Vitamin D Inhibits Adipokine Production and Inflammatory Signaling Through the Vitamin D Receptor in Human Adipocytes. Obesity 2021, 29, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Different patterns of changes in free 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations during intermittent fasting among meat eaters and non-meat eaters and correlations with amino acid intake. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 74, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Popovic, D.S.; Adamidou, L.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Mediterranean Eating Pattern Combining Energy and Time-Restricted Eating Improves Vaspin and Omentin Concentrations Compared to Intermittent Fasting in Overweight Individuals. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Popovic, D.S.; Kotsa, K. Changes in dietary intake of aspartic acid during and after intermittent fasting correlate with an improvement in fasting glucose in overweight individuals. J. Diabetes 2023, 15, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppold, D.A.; Breinlinger, C.; Hanslian, E.; Kessler, C.; Cramer, H.; Khokhar, A.R.; Peterson, C.M.; Tinsley, G.; Vernieri, C.; Bloomer, R.J.; et al. International consensus on fasting terminology. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1779–1794.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed Khaja, A.; Binsaleh, N.K.; Beg, M.M.A.; Ashfaq, F.; Khan, M.I.; Almutairi, M.G.; Qanash, H.; Saleem, M.; Ginawi, I.A.M. Clinical importance of cytokine (IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10) and vitamin D levels among patients with Type-1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batún-Garrido, J.A.J.; Salas-Magaña, M.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E. Association between leptin and IL-6 concentrations with cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Mârza, S.M.; Papuc, I. The immunomodulatory effects of vitamins in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1464329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraphin, G.; Rieger, S.; Hewison, M.; Capobianco, E.; Lisse, T.S. The impact of vitamin D on cancer: A mini review. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 231, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, S.M.d.M.; Schmitt, E.G.; dos Santos, L.S.; Schreiner, G.E.; Malheiros, R.T.; Klock, C.; Petry, C.C.; Gonçalves, I.L.; Manfredini, V. Vitamin D supplementation: Biochemical and inflammatory effects in non-pathological Wistar rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
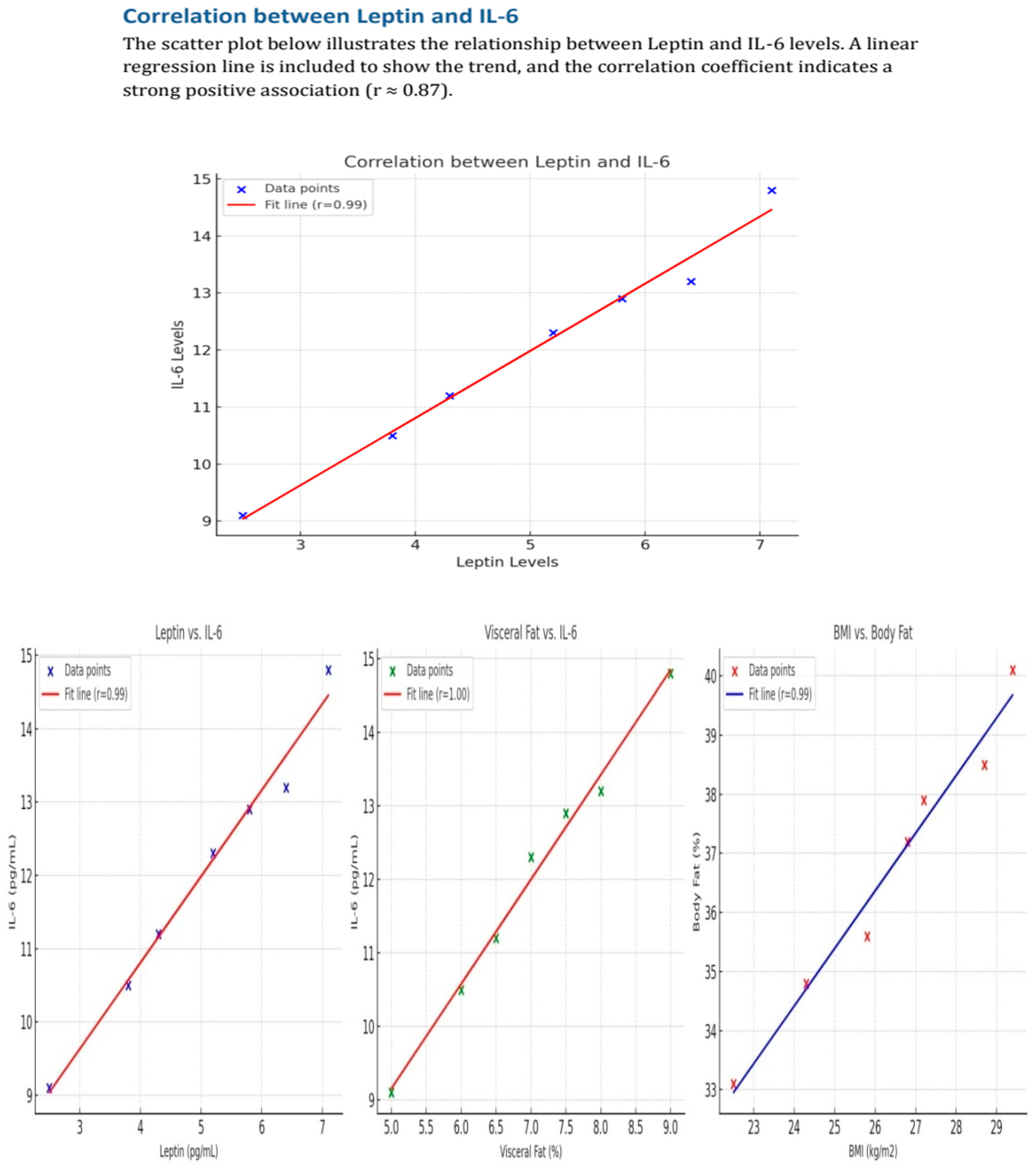
| Variables | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.4 ± 17.1 |
| Monastery stay (years) | 17 (1–55) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.8 (21.5–48.5) |
| Body fat (%) | 37.2 ± 7.1 |
| Visceral fat (%) | 7 (1–21) |
| Muscular mass (kg) | 43.4 (35.3–58.3) |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | 9.44 (2.51–38.45) |
| Leptin (pg/mL) | 19.632 (5.179–75.859 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 2.27 (1.0–22.1) |
| Ca (mg/dL) | 9.39 (8.8–11.1) |
| PTH (pg/mL) | 46.4 (26.6–103.0) |
| 25(OH)D (ng/mL) | 23.0 ± 9.9 |
| Variables | Pearson (r)/Spearman (rho) Coefficient | p |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| Age—monastery stay | r = 0.615 | <0.001 |
| Age—body fat | r = 0.425 | 0.006 |
| Age—visceral fat | rho = 0.791 | <0.001 |
| Age—muscular mass | rho = −0.368 | 0.018 |
| Age—leptin | rho = 0.447 | 0.007 |
| Age—IL-6 | rho = 0.647 | <0.001 |
| Monastery stay | ||
| Monastery stay—age | r = 0.615 | <0.001 |
| Monastery stay—BMI | rho= 0.334 | 0.003 |
| Monastery stay—body fat | rho = 0.463 | 0.002 |
| Monastery stay—visceral fat | rho = 0.641 | <0.001 |
| Monastery stay—leptin | rho = 0.383 | 0.023 |
| Monastery stay—IL-6 | rho = 0.393 | 0.024 |
| BMI | ||
| BMI—monastery stay | rho = 0.334 | 0.003 |
| BMI—body fat | rho = 0.745 | <0.001 |
| BMI—visceral fat | rho = 0.696 | <0.001 |
| BMI—leptin | rho = 0.399 | 0.017 |
| BMI—IL-6 | rho = 0.622 | <0.001 |
| Body fat | ||
| Body fat—age | r = 0.425 | 0.006 |
| Body fat—monastery stay | rho = 0.463 | 0.002 |
| Body fat—BMI | rho = 0.745 | <0.001 |
| Body fat—visceral fat | rho = 0.858 | <0.001 |
| Body fat—leptin | rho = 0.538 | <0.001 |
| Body fat—IL-6 | rho = 0.675 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat | ||
| Visceral fat—age | rho = 0.791 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat—monastery stay | rho = 0.641 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat—BMI | rho = 0.696 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat—body fat | rho = 0.858 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat—insulin | rho = 0.440 | 0.008 |
| Visceral fat—leptin | rho = 0.613 | <0.001 |
| Visceral fat—IL-6 | rho = 0.741 | <0.001 |
| Insulin | ||
| Insulin—visceral fat | rho = 0.440 | 0.008 |
| Insulin—leptin | rho = 0.662 | <0.001 |
| Insulin—IL-6 | rho = 0.368 | 0.035 |
| Leptin | ||
| Leptin—age | rho = 0.447 | 0.007 |
| Leptin—monastery stay | rho = 0.383 | 0.023 |
| Leptin—BMI | rho = 0.399 | 0.017 |
| Leptin—body fat | rho = 0.538 | <0.001 |
| Leptin—visceral fat | rho = 0.613 | <0.001 |
| Leptin—insulin | rho = 0.662 | <0.001 |
| Leptin—IL-6 | rho = 0.507 | 0.003 |
| IL-6 | ||
| IL-6-age | rho = 0.647 | <0.001 |
| IL-6-monastery stay | rho = 0.393 | 0.024 |
| IL-6- BMI | rho = 0.622 | <0.001 |
| IL-6-body fat | rho = 0.675 | <0.001 |
| IL-6-visceral fat | rho = 0.741 | <0.001 |
| IL-6-insulin | rho = 0.368 | 0.035 |
| IL-6-leptin | rho = 0.507 | 0.003 |
| 25(OH)D | ||
| 25(OH)D—PTH | rho = −0.380 | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karras, S.N.; Michalakis, K.; Katsiki, N.; Kypraiou, M.; Vlastos, A.; Anemoulis, M.; Koukoulis, G.; Mouslech, Z.; Talidis, F.; Tzimagiorgis, G.; et al. Interrelations of Leptin and Interleukin-6 in Vitamin D Deficient and Overweight Orthodox Nuns from Northern Greece: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071144
Karras SN, Michalakis K, Katsiki N, Kypraiou M, Vlastos A, Anemoulis M, Koukoulis G, Mouslech Z, Talidis F, Tzimagiorgis G, et al. Interrelations of Leptin and Interleukin-6 in Vitamin D Deficient and Overweight Orthodox Nuns from Northern Greece: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071144
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarras, Spyridon N., Konstantinos Michalakis, Niki Katsiki, Maria Kypraiou, Antonios Vlastos, Marios Anemoulis, Georgios Koukoulis, Zadalla Mouslech, Filotas Talidis, Georgios Tzimagiorgis, and et al. 2025. "Interrelations of Leptin and Interleukin-6 in Vitamin D Deficient and Overweight Orthodox Nuns from Northern Greece: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071144
APA StyleKarras, S. N., Michalakis, K., Katsiki, N., Kypraiou, M., Vlastos, A., Anemoulis, M., Koukoulis, G., Mouslech, Z., Talidis, F., Tzimagiorgis, G., Haitoglou, C., Georgios, Μ., Papanikolaou, E. G., Dimitrios, S., & Georgopoulos, N. (2025). Interrelations of Leptin and Interleukin-6 in Vitamin D Deficient and Overweight Orthodox Nuns from Northern Greece: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 17(7), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071144








