Nutritional Factors and Food and Nutrition Insecurity in Patients with Tuberculosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting and Participant Population
2.2. Characterization of the Clinical and Sociodemographic Profile
2.3. Nutritional Status Assessment
2.3.1. Anthropometric Collection
2.3.2. Brazilian Food Insecurity Scale (EBIA)
2.3.3. Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
| M. tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| No | Number |
| FNS | Food and nutritional security |
| FNI | Food and nutrition insecurity |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| EBIA | Brazilian Food Insecurity Scale |
| FFQ | Food frequency questionnaire |
| ELSA-BRASIL | Estudo Longitudinal de Saúde do Adulto |
| POF | Household Budget Survey |
| TACO | Brazilian Food Composition Table |
| PHILIPPI | Food Composition Table |
| DRIs | Dietary Reference Intakes |
| EAR | Estimated Average Requirement |
| UL | Tolerable Upper Intake Level |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| p | Probability |
| CEP | Research Ethics Committee |
| CEUMA | University Center of Maranhão |
| ICF | Informed Consent Form |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| fa | Absolute frequency |
| f% | Percentage frequency |
| kg | Kilograms |
| m2 | Square meters |
| FAPEMA | Foundation for Research Support and Scientific and Technological Development of Maranhão |
References
- Ravimohan, S.; Kornfeld, H.; Weissman, D.; Bisson, G.P. Tuberculosis and lung damage: From epidemiology to pathophysiology. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahlwes, K.C.; Haapalainen, A.; Haney, C.; Boyce, K.; Jackson, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Virulence 2023, 14, 2150449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2021: Supplementary Material; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tabnet; Department of Informatics of SUS–DATASUS, Ministry of Health: Brasilia, Brazil, 2022. Available online: https://datasus.saude.gov.br/acesso-a-informacao/casos-de-tuberculose-desde-2001-sinan/ (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Ministry of Health. Brazil Free of Tuberculosis: National Plan to End Tuberculosis as a Public Health Problem: Strategies for 2021–2025; Department of Chronic Conditions Diseases and Sexually Transmitted Infections, Ministry of Health, Health Surveillance Secretariat: Brasilia, Brazil, 2021.
- Moreira, A.S.R.; Kritski, A.L.; Carvalho, A.C.C. Social determinants of health and catastrophic costs associated with the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2020, 6, e20200015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Han, J.; Shen, J.; Peng, X.; Zhou, L.; Yin, X. Diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis in adults with HIV. Medicine 2022, 101, e30405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnu, S.M.; Arora, V.K.; Anupama, N. Challenges in diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis in elderly. Indian J. Tuberc. 2022, 69, S205–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boadu, A.A.; Yeboah-Manu, M.; Osei-Wusu, S.; Yeboah-Manu, D. Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: The complexity of the comorbid interactions. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 146, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creates the National Food and Nutrition Security System (SISAN) with a View to Ensuring the Human Right to Adequate Food and Provides Other Measures; Official Gazette of the Union: Brasilia, Brazil, 2006; pp. 1–2.
- Grada, A.; Phillips, T.J. Nutrition and Cutaneous Wound Healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 40, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Ford, K.L.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Murnane, L.C.; Gillis, C.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Morrison, C.A.; Lobo, D.N. Nascent to novel methods to evaluate malnutrition and frailty in the surgical patient. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 47, S54–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, B.; Mrowiec, S. Nutritional Status and Its Detection in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuls, C.; de Marañon, A.M.; Veses, S.; Castro-Vega, I.; López-Domènech, S.; Salom-Vendrell, C.; Orden, S.; Álvarez, Á.; Rocha, M.; Victor, V.; et al. Malnutrition impairs mitochondrial function and leukocyte activation. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrest, L.; Wilthagen, E.A.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Dorlo, T.P.C. Influence of Malnutrition on the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs Used in the Treatment of Poverty-Related Diseases: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 1149–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolina, K.; Iwona, M.-C.; Cyuńczyk, M.; Witkowska, A.M. Malnutrition Risk in Older Adults: Evaluating the Diagnostic Relevance of Serum Biomarkers: SIRT-1, CCK-8, Melatonin, and Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC). Nutrients 2025, 17, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, P.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q. Associations between nutritional and immune status and clinicopathologic factors in patients with tuberculosis: A comprehensive analysis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 888727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Davis, J.; Saag, L.; Wanke, C.; Salgame, P.; Mesick, J.; Horsburgh, C.R.; Hochberg, N.S. Undernutrition and tuberculosis: Public health implications. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, A.K.; Zehra, S.; Zubair, H.; Imran, S. Main nutritional deficiencies. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2022, 63 (Suppl. S3), E93–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podell, B.K.; Ackart, D.F.; Obregon-Henao, A.; Richardson, M.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Basaraba, R.J. The impact of vitamin A deficiency on tuberculosis progression. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipschitz, D.A. Screening for nutritional status in the elderly. Prim. Care 1994, 21, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry: Report of a WHO Expert Committee; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, M.S.; Santos, R.O.; Santos, A.A.; Teixeira, D.S.; Mello, R.L. Food and nutritional insecurity in Brazil and its correlation with vulnerability markers. Cien Saude Colet. 2020, 25, 3833–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chor, D.; Alves, M.G.; Giatti, L.; Cade, N.V.; Nunes, M.A.; Molina Mdel, C.; Bensenor, I.M.; Aquino, E.M.L.; Passos, V.; Santos, S.M.; et al. ELSA-Brasil questionnaire: Challenges in the elaboration of a multidimensional instrument. Rev. Saude Publica 2013, 47, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.C.O.R.; Meneguci, J.; Figueiredo, R.O.; de Assis, M.M. Validation of a questionnaire on the frequency of food consumption for pregnant women attended at basic health units. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 2020, 30, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes: Applications in Dietary Planning; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes: Applications in Dietary Assessment; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Slash, S.S.; Hase, N.K.; Jamge, S.S.; Jamge, S.; Supe, S. Assessment of oxidative stress biomarkers and body mass index in pulmonary tuberculosis patients: A case-control study. Niger. Med. J. 2021, 62, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, S.V.M.A.; dos Santos, A.D.; Duque, A.M.; Goes, M.A.d.O.; Peixoto, M.V.d.S.; Araújo, D.d.C.; Ribeiro, C.J.N.; Santos, M.B.; de Araújo, K.C.G.M.; Nunes, M.A.P. Spatial and temporal analysis of tuberculosis in an area of social inequality in Northeast Brazil. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyu, H.H.; Maddison, E.R.; Henry, N.J.; Mumford, J.E.; Barber, R.; Shields, C.; Brown, J.C.; Nguyen, G.; Carter, A.; Wolock, T.M.; et al. The global burden of tuberculosis: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018, 18, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Melo, F.R.; Carneiro, M.; Ramos, A.N., Jr.; Heukelbach, J.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Werneck, G.L. The burden of tuberculosis and attributable risk factors in Brazil, 1990–2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Popul. Health Metr. 2020, 18, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, C.R.; Conceição, E.C.; Monteiro, L.H.M.T.; da Silva, O.M.; Lima, L.N.G.C.; de Oliveira, R.A.C.; de Brito, A.C.; Guimarães, R.J.d.P.S.e.; Lima, K.V.B. A clinical-epidemiological and geospatial study of tuberculosis in a neglected area in the Amazonian region highlights the urgent need for control measures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussien, B.; Workicho, A.; Tafa, B.; Dube, L.; Leta, S. Nutritional deficiency and associated factors among new pulmonary tuberculosis patients of Bale Zone Hospitals, southeast Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Saqib, S.E.; Atiq, M. Health-related quality of life of tuberculosis patients and the role of socioeconomic factors: A mixed-method study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 106, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Khokhar, A. Risk factors and perceptions about coronavirus disease among tuberculosis psatients in Delhi, India: A cross-sectional study. Indian J. Tuberc. 2022, 69, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M. Risk Factors of Tuberculosis Destroyed Lung in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Structural Lung Diseases: A Retrospective Observational Study. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2024, 17, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.J.; Zhang, X.F.; Su, C.P.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, H. Prevalence and prognostic significance of malnutrition risk in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: A hospital-based cohort study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1039661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswal, N.; Thangavel, H.; Lizardo, K.; Dhanyalayam, D.; Sidrat, T.; Salgame, P.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Diets Differently Regulate Pulmonary Pathogenesis and Immune Signaling in Mice during Acute and Chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Life 2023, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Ngo, M.D.; Bartlett, S.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Keshvari, S.; Hasnain, S.Z.; Donovan, M.L.; Kling, J.C.; Blumenthal, A.; Chen, C.; et al. Pre-Diabetes Increases Tuberculosis Disease Severity, While High Body Fat Without Impaired Glucose Tolerance Is Protective. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 691823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiraveetil, R.; Sarkar, S.; Chinnakali, P.; Jeyashree, K.; Vijayageetha, M.; Thekkur, P.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; Knudsen, S.; Hochberg, N.S.; Horsburgh, C.R.; et al. Household food insecurity among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and its associated factors in South India: A cross-sectional analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, T.; Amissah Essandoh, H.; Anyiam, F.E.; Hagan, G.N.; Fenenga, C. HIV, tuberculosis, and food insecurity in Africa—A syndemics-based scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wu, S.Y.; Li, H.; Ren, Y.J. Analysis of Dietary and Nutritional Status of Tuberculosis Patients in Hulunbuir Region. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2024, 17, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, D.B.; de Seixas Maciel, E.M.G.; Brazil, P.E.A.A.; Braga, J.U. Tuberculosis incidence inequalities and its social determinants in Manaus from 2007 to 2016. Int. J. Equity Health 2018, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis-Santos, B.; Locatelli, R.; Oliosi, J.; Sales, C.M.; Prado, T.N.D.; Shete, P.B.; Riley, L.W.; Maciel, E.L. A matter of inclusion: A cluster-randomized trial to assess the effect of food vouchers versus traditional treatment on tuberculosis outcomes in Brazil. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimni, V.; Shasty, B.A.; Madhyastha, S.P.; Shetty, G.V.; Acharya, R.V.; Bekur, R.; Doddamani, A. Association of vitamin D deficiency and newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis. Pulm Med. 2021, 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A.B.K.; Garcia-Perdomo, H.A. Effectiveness of micronutrients supplement in patients with active tuberculosis on treatment: Systematic review/Meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Pellegrino, C.; Ricciardi, A.; Novara, R.; Cotugno, S.; Papagni, R.; Guido, G.; Totaro, V.; De Iaco, G.; Romanelli, F.; et al. Potential Role of Vitamins A, B, C, D and E in TB Treatment and Prevention: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xiao, W.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y. Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces host autophagic ferritin degradation for enhanced iron bioavailability and bacterial growth. Autophagy 2023, 20, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Yuan, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Li, X. Iron Metabolism and Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 816282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairz, M.; Weiss, G. Iron in infection and immunity. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, C.; Liu, K.; Chen, B. Association of variant vitamin statuses and tuberculosis development: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2396566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.M.; Shenkin, A.; Schweinlin, A.; Amrein, K.; Augsburger, M.; Biesalski, H.K.; Bischoff, S.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Gundogan, K.; Lepp, H.-L.; et al. ESPEN micronutrient guideline. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2022, 41, 1357–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Omage, S.O.; Börmel, L.; Kluge, S.; Schubert, M.; Wallert, M.; Lorkowski, S. Vitamin E and Metabolic Health: Relevance of Interactions with Other Micronutrients. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioboata, R.; Vasile, C.M.; Bălteanu, M.A.; Georgescu, D.E.; Toma, C.; Dracea, A.S.; Nicolosu, D. Evaluating Serum Calcium and Magnesium Levels as Predictive Biomarkers for Tuberculosis and COVID-19 Severity: A Romanian Prospective Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Associating the blood vitamin A, C, D and E status with tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4825–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, S.; Aryal, B.B.; Shrestha, B.M.; Adhikari, S.; Kafle, S. Association of vitamin D deficiency with pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2021, 13, e17885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.O.; Santos, C.A.; Oliviera, I.S.; Silva, R.P.; Lopes, I.M.; Rocha, I.F. Food insecurity and micronutrient deficiency in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
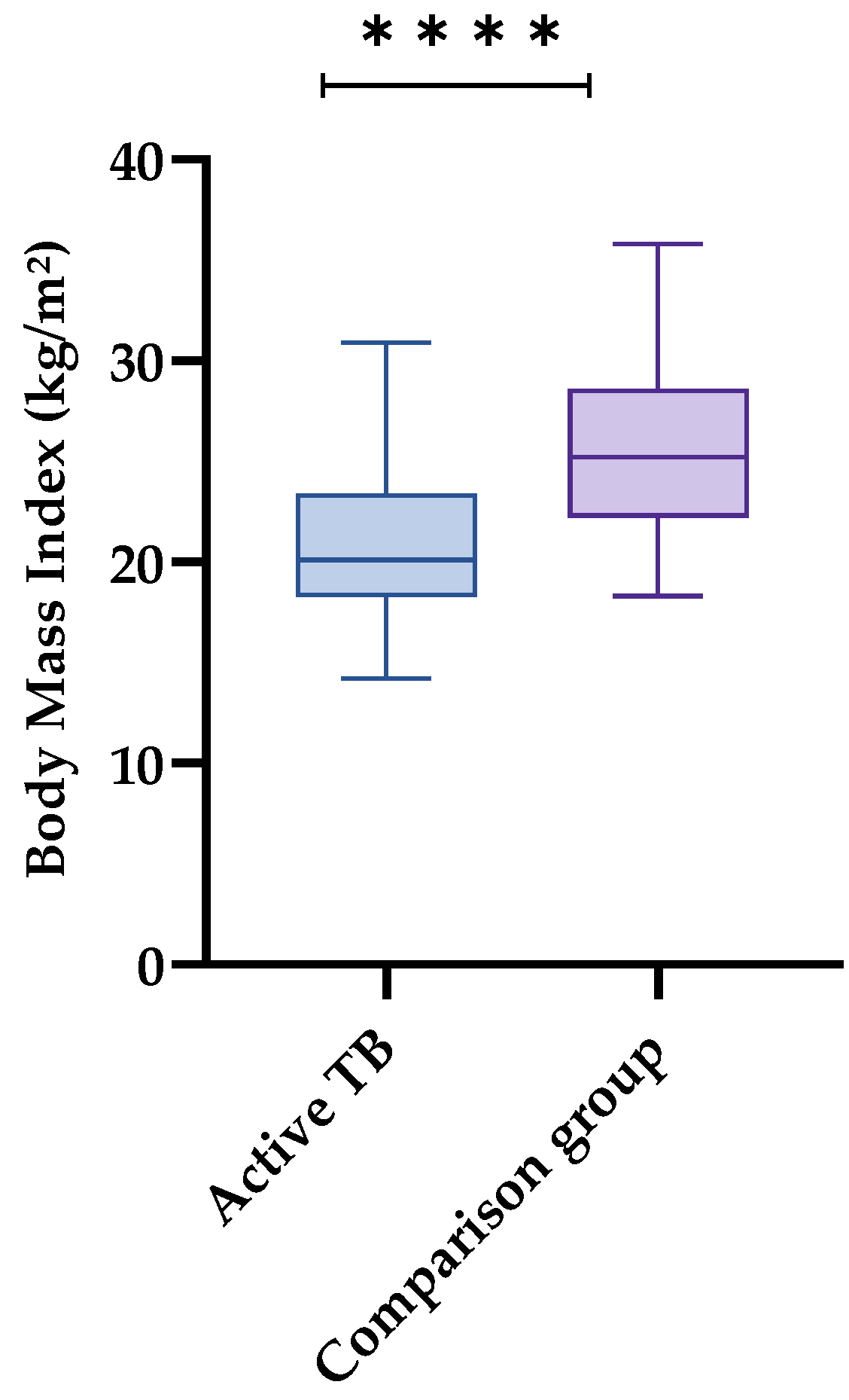

| Variables | Total | Active | Control | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fa | f% | fa | f% | fa | f% | ||
| Distal Level: Sociodemographic | |||||||
| Sex | 0.127 | ||||||
| Male | 93 | 67.3 | 48 | 73.8 | 45 | 61.6 | |
| Female | 45 | 32.6 | 17 | 26.2 | 28 | 38.4 | |
| Race | 0.002 * | ||||||
| Black | 32 | 23.7 | 16 | 25.8 | 16 | 21.9 | |
| Mixed ancestry | 80 | 59.2 | 43 | 69.4 | 37 | 50.7 | |
| White | 23 | 17.0 | 3 | 4.8 | 20 | 27.4 | |
| Education level | 0.000 * | ||||||
| Higher education | 62 | 46.2 | 5 | 8.2 | 57 | 78.1 | |
| Middle school | 44 | 32.8 | 31 | 50.8 | 13 | 17.8 | |
| Elementary School | 28 | 20.9 | 25 | 22.6 | 3 | 4.1 | |
| Occupation | 0.000 * | ||||||
| Employee | 113 | 83.7 | 43 | 69.4 | 70 | 95.9 | |
| Retired | 8 | 5.9 | 5 | 8.1 | 3 | 4.1 | |
| Unemployed | 14 | 10.3 | 14 | 22.6 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| Household income | 0.000 * | ||||||
| >3 Minimum Wages | 47 | 37.9 | 4 | 7.8 | 43 | 58.9 | |
| ≤3 Minimum Wages | 77 | 62.1 | 47 | 92.2 | 30 | 41.1 | |
| Intermediate Level: Nutritional aspects | |||||||
| EBIA | 0.115 | ||||||
| Mon. Feed | 59 | 43.0 | 23 | 35.9 | 36 | 49.3 | |
| Insg. Food (Mild, Moderate or Severe) | 78 | 56.9 | 41 | 64.1 | 37 | 50.7 | |
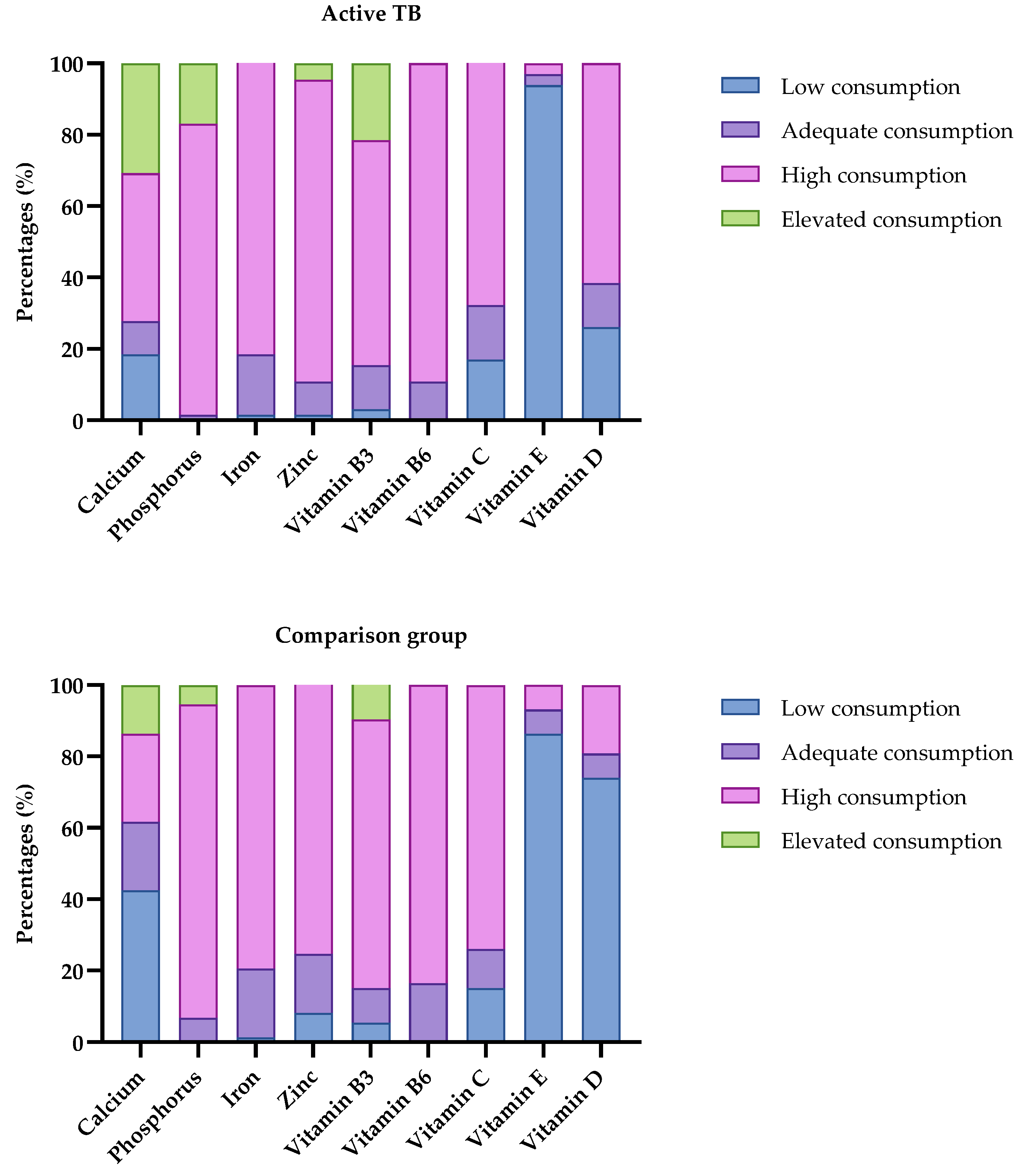
| Calcium | 0.001 * | ||||||
| Low consumption | 43 | 31.16 | 12 | 18.46 | 31 | 42.47 | |
| Adequate consumption | 20 | 14.49 | 6 | 9.23 | 14 | 19.18 | |
| High consumption | 45 | 32.61 | 27 | 47.54 | 18 | 24.66 | |
| Elevated consumption | 30 | 21.74 | 20 | 30.77 | 10 | 13.70 | |
| Vitamin D | 0.000 * | ||||||
| Low consumption | 71 | 51.45 | 17 | 26.15 | 54 | 73.97 | |
| Adequate consumption | 13 | 9.42 | 8 | 12.31 | 5 | 6.85 | |
| High consumption | 54 | 39.13 | 40 | 61.54 | 14 | 19.18 | |
| Vitamin E | 0.342 | ||||||
| Low consumption | 124 | 89.86 | 61 | 93.85 | 63 | 86.3 | |
| Adequate consumption | 7 | 5.07 | 2 | 3.08 | 5 | 6.85 | |
| High consumption | 7 | 5.07 | 2 | 3.08 | 5 | 6.85 | |
| Zinc | |||||||
| Low consumption | 7 | 5.07 | 1 | 14.29 | 6 | 8.22 | 0.043 * |
| Adequate consumption | 18 | 16.44 | 6 | 9.23 | 12 | 16.44 | |
| High consumption | 110 | 75.34 | 55 | 84.62 | 55 | 75.34 | |
| Elevated consumption | 3 | 4.62 | 3 | 4.62 | 0 | 0 | |
| Iron | |||||||
| Low consumption | 2 | 1.45 | 1 | 1.54 | 1 | 1.37 | 0.941 |
| Adequate consumption | 25 | 18.12 | 11 | 16.92 | 14 | 19.18 | |
| High consumption | 111 | 80.43 | 53 | 81.54 | 58 | 79.45 | |
| Phosphorus | |||||||
| Adequate consumption | 6 | 4.35 | 1 | 1.54 | 5 | 6.85 | |
| High consumption | 117 | 84.78 | 53 | 81.54 | 64 | 87.67 | |
| Elevated consumption | 15 | 10.87 | 11 | 16.92 | 4 | 5.48 | |
| Proximal Level: Anthropometric aspect | |||||||
| BMI | 0.000 * | ||||||
| Eutrophy | 72 | 52.1 | 37 | 56.9 | 35 | 48.0 | |
| Low weight | 18 | 13.0 | 17 | 26.1 | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Overweight and obesity | 48 | 34.7 | 11 | 16.9 | 37 | 50.7 | |
| Initial Model | Final Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Final OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Distal Level: Sociodemographic | ||||
| Race | ||||
| White | 0.34 (0.34–3.40) | 0.358 * | ||
| Education level | ||||
| Middle school | 30.76 (5.52–171.44) | 0.000 * | 34.92 (7.29–167.02) | 0.07 |
| Elementary School | 83.53 (9.46–737.14) | 0.000 * | 119.98 (17.19–836.97) | 0.00 * |
| Occupation | ||||
| Retired | 0.65 (0.084–5.08) | 0.684 | ||
| Income | ||||
| ≥Minimum Wages | 2.20 (0.394–12.255) | 0.369 | ||
| Intermediate Level: Nutritional aspects | ||||
| EBIA | ||||
| Inseg. Food (Mild. Moderate or Severe) | 1.99 (0.639–6.205) | 0.235 | ||
| Calcium | ||||
| Adequate consumption | 0.62 (0.17–2.29) | 0.470 | ||
| High consumption | 0.31 (0.05–1.83) | 0.195 | ||
| Elevated consumption | 0.17 (0.02–1.49) | 0.110 | ||
| Vitamin D | ||||
| Adequate consumption | 10.56 (1.80–61.93) | 0.01 * | 7.13 (0.83–61.21) | 0.07 |
| High consumption | 26.45 (4.28–163.52) | 0.00 * | 16.85 (3.72–76.20) | 0.00 * |
| Proximal Level: Anthropometric aspect | ||||
| BMI | ||||
| Low weight | 5.89 (0.57–60.73) | 0.136 | 4.21 (0.42–41.71) | 0.16 |
| Overweight/obesity | 0.08 (0.18–0.41) | 0.002 * | 0.065 (0.012–0.33) | 0.00 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendes, Y.C.; Dourado, A.L.L.; de Oliveira, P.V.; Rezende, A.d.O.; Sales, A.C.d.S.; de Sousa, G.P.; Pereira, E.d.A.; Sousa, E.L.C.; Lindoso, M.C.C.M.; Júnior, R.d.M.R.; et al. Nutritional Factors and Food and Nutrition Insecurity in Patients with Tuberculosis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050878
Mendes YC, Dourado ALL, de Oliveira PV, Rezende AdO, Sales ACdS, de Sousa GP, Pereira EdA, Sousa ELC, Lindoso MCCM, Júnior RdMR, et al. Nutritional Factors and Food and Nutrition Insecurity in Patients with Tuberculosis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(5):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050878
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendes, Yasmim Costa, Ana Larysse Lacerda Dourado, Patricia Vieira de Oliveira, Aline de Oliveira Rezende, Amanda Caroline de Souza Sales, Gabriel Pereira de Sousa, Elaíne de Araújo Pereira, Elane Luiza Costa Sousa, Maria Cecília Cruz Morais Lindoso, Roberdilson de Melo Rodrigues Júnior, and et al. 2025. "Nutritional Factors and Food and Nutrition Insecurity in Patients with Tuberculosis" Nutrients 17, no. 5: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050878
APA StyleMendes, Y. C., Dourado, A. L. L., de Oliveira, P. V., Rezende, A. d. O., Sales, A. C. d. S., de Sousa, G. P., Pereira, E. d. A., Sousa, E. L. C., Lindoso, M. C. C. M., Júnior, R. d. M. R., Fernandes, L. R., Santana, L. C., Goiano, M. F., da Silva, L. C. N., Martins, R. F. M., de Sousa, E. M., & Zagmignan, A. (2025). Nutritional Factors and Food and Nutrition Insecurity in Patients with Tuberculosis. Nutrients, 17(5), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050878








