Hidden Hunger in Pediatric Obesity: Redefining Malnutrition Through Macronutrient Quality and Micronutrient Deficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definitions and Guidelines for Pediatric Malnutrition
Assessing Nutritional Status Using Centile and Z-Score Charts
3. Screening and Diagnosis in Clinical Practice
- (a)
- The STRONGkids tool demonstrates high validity and reproducibility in detecting disease-related malnutrition by integrating clinical and dietary risk factors, making it suitable for both inpatient and outpatient settings.
- (b)
- The Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics (STAMP) has shown particular accuracy in critically ill children, where higher scores correlate with extended hospital stays and increased mortality.
- (c)
- The Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score (PYMS) exhibits strong sensitivity and specificity in specialized populations, such as pediatric oncology patients, facilitating early identification of those requiring targeted nutritional support.
4. Biological Mechanisms of Malnutrition in Obesity: Nutrient Deficiencies and Metabolic Dysfunction
4.1. Clinical Significance of Malnutrition in Obesity
4.1.1. Single Nutrient Models of Obesity
4.1.2. Insights from the Nutritional Geometry Framework (NGF)
4.2. Factors Contributing to Adolescent Obesity
4.2.1. Diet Quality
4.2.2. Body Weight and Macronutrients
5. Specific Macronutrient Deficiencies in Obesity
5.1. Protein
5.2. Carbohydrates
5.3. Fat
5.4. Fiber
6. Specific Micronutrient Deficiencies in Obesity
6.1. Vitamin D Deficiency
6.2. Calcium Deficiency
6.3. Iron Deficiency
6.4. Magnesium Deficiency
6.5. Zinc Deficiency
6.6. B Vitamins
6.7. Synthesis: The Nutritional Quality Deficit in Obesity
7. Advances in Biomarker Research
7.1. Genetic Damage
7.2. Adipose Tissue Biomarkers
7.3. Liver Biomarkers
7.4. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Biomarkers
8. Effect of Gut Microbiota on Obesity
8.1. Early-Life Determinants and Individual Variability
8.2. Microbial Signatures of Obesity
8.3. Microbiota Dysfunction in Obesity
8.4. Critical Appraisal of Microbiota Evidence
9. Precision Nutrition, Gut Microbiota, and Malnutrition in Obesity: Integrated Perspectives
10. Synthesis and Hierarchy of Evidence
10.1. Consensual and Well-Established Evidence
10.2. Probable and Plausible Mechanisms
10.3. Hypothesis-Level and Speculative Concepts
10.4. Critical Gaps in Pediatric Research
11. Limitations of the Research on Malnutrition in Pediatric Obesity
11.1. Inconsistent Prevalence Estimates for Pediatric Malnutrition
11.2. Limited Evidence for Diagnostic Accuracy of Malnutrition Criteria
11.3. Inconclusive Microbiota Modulation for Obesity Treatment
11.4. Inconsistent Evidence for Macronutrient Effects on Weight Gain
11.5. Unclear Role of the Microbiome in Obesity Causality
11.6. Inconsistent Evidence for Probiotics Mitigating Dietary Fat Effects
11.7. Over-Reliance on Observational Data and Short-Term Interventions
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| ASPEN | American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition |
| BAT | Brown Adipose Tissue |
| BCAA | Branched-Chain Amino Acids |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CD | Celiac Disease |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CIM | Carbohydrate–Insulin Model |
| EAR | Estimated Average Requirement |
| DGA | Dietary Guidelines for American |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| EBM | Energy Balance Model |
| FHO | Fructose Survival Hypothesis |
| GLIM | Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 |
| GI | Glycemic Index |
| GLUT4 | Glucose Transporter Type 4 |
| HEI | Healthy Eating Index |
| HFCS | High-Fructose Corn Syrup |
| hs-CRP | High-Sensitivity CRP |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IKK | IκB Kinase |
| IL-1 β | Interleukin 1 Beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| LMICs | Low- and Middle-Income Countries |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MUAC | Mid-Upper Arm Circumference |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated Fatty Acids |
| NCD | Non-Communicable Disease |
| NGF | Nutritional Geometry Framework |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| PLH | Protein Leverage Hypothesis |
| PPARG | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids |
| PYMS | Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score |
| RBC | Red Blood Cells |
| RDA | Recommended Dietary Allowance |
| SIBO | Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acid |
| STAMP | Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics |
| STRONGkids | Screening Tool for Risk on Nutritional Status and Growth |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| UACR | Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling Protein 1 |
| UCP2 | Uncoupling Protein 2 |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- United Nations Children’s Fund; World Health Organization; World Bank Group. Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition: UNICEF/WHO/The World Bank Group Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates: Key Findings of the 2016 Edition; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Govender, I.; Rangiah, S.; Kaswa, R.; Nzaumvila, D. Malnutrition in Children under the Age of 5 Years in a Primary Health Care Setting. S. Afr. Fam. Pract. 2021, 63, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulungan, A.B.; Puteri, H.A.; Ratnasari, A.F.; Hoey, H.; Utari, A.; Darendeliler, F.; Al-Zoubi, B.; Joel, D.; Valiulis, A.; Cabana, J.; et al. Childhood Obesity as a Global Problem: A Cross-Sectional Survey on Global Awareness and National Program Implementation. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2024, 16, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Zhao, Y.; Slivka, L.; Wang, Y. Double Burden of Diseases Worldwide: Coexistence of Undernutrition and Overnutrition-Related Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates (JME) (UNICEF-WHO-WB). Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/joint-child-malnutrition-estimates-unicef-who-wb (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- De Sanctis, V.; Soliman, A.; Alaaraj, N.; Ahmed, S.; Alyafei, F.; Hamed, N. Early and Long-Term Consequences of Nutritional Stunting: From Childhood to Adulthood. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal-Herrera, A.; Kigen, B.; Kapanga, E.; Samia, A.; Nabwera, H.; Samia, P. The Impact of Undernutrition and Overnutrition on Early Brain Development. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2025, 55, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A. The Determinants of Food Insecurity among Developing Countries: Are There Any Differences? Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, F.; Salam, R.A.; Lassi, Z.S.; Das, J.K. The Intertwined Relationship Between Malnutrition and Poverty. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, F.S.; Jani, B.D. Emerging Trends and Future Research on the Role of Socioeconomic Status in Chronic Illness and Multimorbidity. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e128–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Salemi, J.; Phillips, W.; Wong Vega, M.; Swanson, J.; Becker, P.J.; Salemi, J.L. Malnutrition among Hospitalized Children in the United States: A 2012-2019 Update of Annual Trends. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet 2023, 123, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.A.; Patton, G.C.; Cini, K.I.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbas, N.; Abd Al Magied, A.H.A.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Abdoun, M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity, 1990–2021, with Forecasts to 2050: A Forecasting Study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 785–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Park, T.; Khoury, C.K.; Béné, C. Changing Diets and the Transformation of the Global Food System. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1478, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monda, A.; de Stefano, M.I.; Villano, I.; Allocca, S.; Casillo, M.; Messina, A.; Monda, V.; Moscatelli, F.; Dipace, A.; Limone, P.; et al. Ultra-Processed Food Intake and Increased Risk of Obesity: A Narrative Review. Foods 2024, 13, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiledengle, B.; Atlaw, D.; Mwanri, L.; Petrucka, P.; Kumie, A.; Tekalegn, Y.; Desta, F.; Zenbaba, D.; Mesfin, T.; Gomora, D.; et al. Burden of Childhood Diarrhea and Its Associated Factors in Ethiopia: A Review of Observational Studies. Int. J. Public Health 2024, 69, 1606399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.; Galmiche, M.; Déchelotte, P. Dysbiotic Gut Bacteria in Obesity: An Overview of the Metabolic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives of Next-Generation Probiotics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Aréstegui, A.; Porter, C.; Sánchez, A.; Singhal, S. The Long Shadow of Conflict on Human Capital: Intergenerational Evidence from Peru. J. Dev. Econ. 2025, 174, 103468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Definitions and Terminology of Clinical Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, D.S.; Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Astrup, A.; Cantley, L.C.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Johnson, J.D.; King, J.C.; Krauss, R.M.; et al. Competing Paradigms of Obesity Pathogenesis: Energy Balance versus Carbohydrate-Insulin Models. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, T. Protein Leverage Hypothesis: A Role for Stress and Protein Digestibility? Med. Hypotheses 2025, 202, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P.; Carney, L.N.; Corkins, M.R.; Monczka, J.; Smith, E.; Smith, S.E.; Spear, B.A.; White, J.V.; Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. Consensus Statement of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics/American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Indicators Recommended for the Identification and Documentation of Pediatric Malnutrition (Undernutrition). Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, M.A.; Albassam, E.M.; Aldajani, E.A.; Alaskar, R.A.; Devol, E.B. Implementation of New Indicators of Pediatric Malnutrition and Comparison to Previous Indicators. Int. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2022, 9, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H. da S. Anthropometric Assessment of Children’s Nutritional Status: A New Approach Based on an Adaptation of Waterlow’s Classification. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullimore, M.A.; Cheng, X.; Brennan, N.A. The Limitations of Centile Curves for Evaluating Myopic Eye Growth. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2025, 102, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, J. Why and When You Should Avoid Using Z-Scores in Graphs Displaying Profile or Group Differences. J. Pers. Oriented Res. 2025, 11, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Millana, A.; Hulst, J.M.; Boon, M.; Witters, P.; Fernandez-Llatas, C.; Asseiceira, I.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Basagoiti, I.; Traver, V.; De Boeck, K.; et al. Optimisation of Children Z-Score Calculation Based on New Statistical Techniques. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachal, C.V.; Fernández-González, S.M.; Moreno-Álvarez, A.; Solar-Boga, A. Nutritional Screening Tools in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serón-Arbeloa, C.; Labarta-Monzón, L.; Puzo-Foncillas, J.; Mallor-Bonet, T.; Lafita-López, A.; Bueno-Vidales, N.; Montoro-Huguet, M. Malnutrition Screening and Assessment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheean, P.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Prado, C.M.; McKeever, L.; Hall, A.M.; Braunschweig, C.A. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Clinical Guidelines: The Validity of Body Composition Assessment in Clinical Populations. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 12–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C. Clinical Analysis and Management of Long-Stay Patients. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattavelli, E.; Verduci, E.; Mascheroni, A.; Corradi, E.; Da Prat, V.; Ammoni, E.; Cereda, D.; Scardoni, A.; Amorosi, A.; Caccialanza, R. Toward a Pragmatic Multidisciplinary Management of Nutritional Risk in Hospitalized Patients: Initiatives and Proposals of the Clinical Nutrition Network of Lombardy Region. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltramo, E.; Berrone, E.; Tarallo, S.; Porta, M. Effects of Thiamine and Benfotiamine on Intracellular Glucose Metabolism and Relevance in the Prevention of Diabetic Complications. Acta Diabetol. 2008, 45, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, V.A.; Rossi, E.; Lauriola, C.; D’Oria, R.; Palma, G.; Borrelli, A.; Caccioppoli, C.; Giorgino, F.; Cignarelli, A. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Obesity-Related Male Hypogonadism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Franco, A.; Castañé, H.; Martínez-Navidad, C.; Placed-Gallego, C.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Samarra, I.; Canela-Capdevila, M.; Arenas, M.; Zorzano, A.; et al. Metabolic Adaptations in Severe Obesity: Insights from Circulating Oxylipins before and after Weight Loss. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability, and Systemic Inflammation: A Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanakis, K.; Upadhyay, J.; Ramirez-Cisneros, A.; Patel, N.; Sahai, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin Physiology and Pathophysiology in Energy Homeostasis, Immune Function, Neuroendocrine Regulation and Bone Health. Metabolism 2024, 161, 156056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vici, G.; Belli, L.; Biondi, M.; Polzonetti, V. Gluten Free Diet and Nutrient Deficiencies: A Review. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.M.; Murray, J.A.; Pimentel, M. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampela, I.; Sakelliou, A.; Vallianou, N.; Christodoulatos, G.-S.; Magkos, F.; Dalamaga, M. Vitamin D and Obesity: Current Evidence and Controversies. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristancho, C.; Mogensen, K.M.; Robinson, M.K. Malnutrition in Patients with Obesity: An Overview Perspective. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2024, 39, 1300–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, D.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Fan, Z.; Wang, G.; Xu, W.; Zhu, G.; Xin, Z.; et al. The Impact of Dietary Fat and Fatty Acid Consumption on Human Health: A Comprehensive Review of Meta-Analyses and the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 160, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.; Melchor, J.; Carr, R.; Karjoo, S. Obesity and Malnutrition in Children and Adults: A Clinical Review. Obes. Pillars 2023, 8, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T.; Gao, L.; Yao, Z.; Shao, S.; Wang, X.; Proud, C.G.; Zhao, J. Hepatic Selective Insulin Resistance at the Intersection of Insulin Signaling and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 947–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Farooqi, I.S.; Friedman, J.M.; Klein, S.; Loos, R.J.F.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M.; Ryan, D.H.; et al. The Energy Balance Model of Obesity: Beyond Calories in, Calories Out. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.A. Nutrition, Insulin Resistance and Dysfunctional Adipose Tissue Determine the Different Components of Metabolic Syndrome. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 483–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthanont, P.; Jensen, M.D. Does Basal Metabolic Rate Predict Weight Gain? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastías-Pérez, M.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L. Dietary Options for Rodents in the Study of Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geidl-Flueck, B.; Gerber, P.A. Fructose Drives de Novo Lipogenesis Affecting Metabolic Health. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 257, e220270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Cicerchi, C.; Li, N.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Le, M.; Garcia, G.E.; Thomas, J.B.; Rivard, C.J.; et al. Uric Acid Stimulates Fructokinase and Accelerates Fructose Metabolism in the Development of Fatty Liver. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozma, A.I.; Sievenpiper, J.L. The Role of Fructose, Sucrose and High-Fructose Corn Syrup in Diabetes. Eur. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A. Commentary on: The Fructose Survival Hypothesis as a Mechanism for Unifying the Various Obesity Hypotheses. Obesity 2024, 32, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Hepatic Consequence of Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, E.E.J.G.; Abete, I.; Astrup, A.; Martinez, J.A.; van Baak, M.A. Starches, Sugars and Obesity. Nutrients 2011, 3, 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, J.A.; Ni, D.; Facey, H.J.W.; Dodgson, T.; Pulpitel, T.J.; Senior, A.M.; Raubenheimer, D.; Macia, L.; Simpson, S.J. Determining the Metabolic Effects of Dietary Fat, Sugars and Fat-Sugar Interaction Using Nutritional Geometry in a Dietary Challenge Study with Male Mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulconbridge, L.F.; Hayes, M.R. Regulation of Energy Balance and Body Weight by the Brain: A Distributed System Prone to Disruption. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 34, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Guo, F. Impacts of Essential Amino Acids on Energy Balance. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummen, M.; Tischmann, L.; Gatta-Cherifi, B.; Adam, T.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M. Dietary Protein and Energy Balance in Relation to Obesity and Co-Morbidities. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.J.; Geisler, C.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Recent Advances in Understanding Body Weight Homeostasis in Humans. F1000Res 2018, 7, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Jeong, J.-H.; Hong, S.-C. The Impact of Sleep and Circadian Disturbance on Hormones and Metabolism. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 591729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Sparks, L.M. Metabolic Flexibility in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efeyan, A.; Comb, W.C.; Sabatini, D.M. Nutrient-Sensing Mechanisms and Pathways. Nature 2015, 517, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsmuth, H.R.; Weninger, S.N.; Duca, F.A. Role of the Gut-Brain Axis in Energy and Glucose Metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, J.; von Essen, G.; Cannon, B. Brown Adipose Tissue: Can It Keep Us Slim? A Discussion of the Evidence for and against the Existence of Diet-Induced Thermogenesis in Mice and Men. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solon-Biet, S.M.; McMahon, A.C.; Ballard, J.W.O.; Ruohonen, K.; Wu, L.E.; Cogger, V.C.; Warren, A.; Huang, X.; Pichaud, N.; Melvin, R.G.; et al. The Ratio of Macronutrients, Not Caloric Intake, Dictates Cardiometabolic Health, Aging, and Longevity in Ad Libitum-Fed Mice. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, K.; Hegsted, D.M. Efficiency of Utilization of Various Sources of Energy for Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4866–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, J.A.; Milner, A.J.; Luk, A.W.S.; Pulpitel, T.J.; Dodgson, T.; Facey, H.J.W.; Wahl, D.; Kebede, M.A.; Senior, A.M.; Sullivan, M.A.; et al. Impact of Dietary Carbohydrate Type and Protein-Carbohydrate Interaction on Metabolic Health. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanhope, K.L.; Schwarz, J.-M.; Havel, P.J. Adverse Metabolic Effects of Dietary Fructose: Results from the Recent Epidemiological, Clinical, and Mechanistic Studies. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, M.; Song, M.; Shan, Z.; Hu, F.; Rosner, B.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Willett, W.C. Reproducibility and Validity of Diet Quality Scores Derived from Food-Frequency Questionnaires. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, N.; Dwyer, J.; Terry, A.; Moshfegh, A.; Johnson, C. Update on NHANES Dietary Data: Focus on Collection, Release, Analytical Considerations, and Uses to Inform Public Policy. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, P.M.; Reedy, J.; Krebs-Smith, S.M. Development of the Healthy Eating Index-2005. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Reedy, J.; Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Pannucci, T.E.; Subar, A.F.; Wilson, M.M.; Lerman, J.L.; Tooze, J.A. Applications of the Healthy Eating Index for Surveillance, Epidemiology, and Intervention Research: Considerations and Caveats. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.D.; Zuelch, M.L.; Dimitratos, S.M.; Scherr, R.E. Adolescent Obesity: Diet Quality, Psychosocial Health, and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Nutrients 2019, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Guenther, P.M.; Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Dodd, K.W. Americans Do Not Meet Federal Dietary Recommendations1. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, H.; Ruiz-Carnicer, Á.; Segura, V.; Comino, I.; Sousa, C. Challenges of Monitoring the Gluten-Free Diet Adherence in the Management and Follow-Up of Patients with Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, E.C.; Liu, Y.; Davis, J.S.; Chang, S.; Frazier-Wood, A.C. Poor Adherence to US Dietary Guidelines for Children and Adolescents in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Population. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorson, B.A.; Melgar-Quinonez, H.R.; Taylor, C.A. Correlates of Fruit and Vegetable Intakes in US Children. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Tucker, K.L. Dietary Quality of the US Child and Adolescent Population: Trends from 1999 to 2012 and Associations with the Use of Federal Nutrition Assistance Programs12. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreiro, A.L.; Dhillon, J.; Gordon, S.; Higgins, K.A.; Jacobs, A.G.; McArthur, B.M.; Redan, B.W.; Rivera, R.L.; Schmidt, L.R.; Mattes, R.D. The Macronutrients, Appetite, and Energy Intake. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 73–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, X.; Duan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gong, S.; Han, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Q.; et al. Role of Brain-Gut-Muscle Axis in Human Health and Energy Homeostasis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 947033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Theodoulou, A.; Oke, J.L.; Butler, A.R.; Bastounis, A.; Dunnigan, A.; Byadya, R.; Cobiac, L.J.; Scarborough, P.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; et al. Long-Term Effect of Weight Regain Following Behavioral Weight Management Programs on Cardiometabolic Disease Incidence and Risk: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2023, 16, e009348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stice, E.; Burger, K.S.; Yokum, S. Relative Ability of Fat and Sugar Tastes to Activate Reward, Gustatory, and Somatosensory Regions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sclafani, A. Oral and Postoral Determinants of Food Reward. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 81, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.-R.; Lenard, N.R.; Shin, A.C. Food Reward, Hyperphagia, and Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R1266–R1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.C.; Sedgmond, J.; Maizey, L.; Chambers, C.D.; Lawrence, N.S. Food Addiction: Implications for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Overeating. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkamp, R.F. The Role of Fatty Acids and Their Endocannabinoid-like Derivatives in the Molecular Regulation of Appetite. Mol. Aspects Med. 2018, 64, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Burden of Carbohydrates in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhorst, M.A.B.; Westerterp, K.R.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Gluconeogenesis and Protein-Induced Satiety. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, G.; Puig-Parnau, I.; Serrano, J.C.E.; Martin-Gari, M.; Rodríguez-Palmero, M.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.A.; Tibau, J.; Kádár, E. Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Arc Expression Are Enhanced in High-Fat Fed Prepubertal Female Pigs by a Diet Including Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Bifidobacterium Breve CECT8242. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, A.; Laposky, A.D.; Ramsey, K.M.; Estrada, C.; Joshu, C.; Kobayashi, Y.; Turek, F.W.; Bass, J. High-Fat Diet Disrupts Behavioral and Molecular Circadian Rhythms in Mice. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.R.; Hawley, J.A. Update on the Effects of Physical Activity on Insulin Sensitivity in Humans. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maljaars, P.W.J.; Peters, H.P.F.; Mela, D.J.; Masclee, A.A.M. Ileal Brake: A Sensible Food Target for Appetite Control. A Review. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 95, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viroli, G.; Kalmpourtzidou, A.; Cena, H. Exploring Benefits and Barriers of Plant-Based Diets: Health, Environmental Impact, Food Accessibility and Acceptability. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.; Slavin, J. Perspective: Defining Carbohydrate Quality for Human Health and Environmental Sustainability. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnie, M.; Hooker, E.; Brunstrom, J.M.; Corfe, B.M.; Green, M.A.; Watson, A.W.; Williams, E.A.; Stevenson, E.J.; Penson, S.; Johnstone, A.M. Protein for Life: Review of Optimal Protein Intake, Sustainable Dietary Sources and the Effect on Appetite in Ageing Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnesen, E.K.; Thorisdottir, B.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Bärebring, L.; Nwaru, B.; Dierkes, J.; Ramel, A.; Åkesson, A. Protein Intake in Children and Growth and Risk of Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 66, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, 9th ed.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Ogilvie, A.R.; Schlussel, Y.; Sukumar, D.; Meng, L.; Shapses, S.A. Higher Protein Intake during Caloric Restriction Improves Diet Quality and Attenuates Loss of Lean Body Mass. Obesity 2022, 30, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronzato, S.; Durante, A. A Contemporary Review of the Relationship between Red Meat Consumption and Cardiovascular Risk. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, V.; Tappy, L.; Bally, L.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Lê, K.-A. Importance of Carbohydrate Quality: What Does It Mean and How to Measure It? J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, D.; Malisova, S.; Lindberg, F.A.; Karaniki, G. Glycemic Index (GI) or Glycemic Load (GL) and Dietary Interventions for Optimizing Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Patients with T2 Diabetes: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.O.; Akinnusi, E.; Ottu, P.O.; Bridget, K.; Oyubu, G.; Ajiboye, S.A.; Waheed, S.A.; Collette, A.C.; Adebimpe, H.O.; Nwokafor, C.V.; et al. The Impact of Ultra-Processed Foods on Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer: Epidemiological and Mechanistic Insights. Asp. Mol. Med. 2025, 5, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, L.A. Dietary Fiber Influence on Overall Health, with an Emphasis on CVD, Diabetes, Obesity, Colon Cancer, and Inflammation. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1510564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, M.; Rockwell, M.S.; Wentz, L.M. The Influence of Dietary and Supplemental Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Omega-3 Index: A Scoping Review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1072653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.G.; Ford, N.A.; Hu, F.B.; Zelman, K.M.; Mozaffarian, D.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. A Healthy Approach to Dietary Fats: Understanding the Science and Taking Action to Reduce Consumer Confusion. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, J.A.; Solon-Biet, S.M.; Freire, T.; Brandon, A.E. Macronutrient Determinants of Obesity, Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Health. Biology 2021, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Wu, K.; Deng, C.; Wang, S. Morning vs. Evening: The Role of Exercise Timing in Enhancing Fat Oxidation in Young Men. Front. Physiol. 2025, 16, 1574757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcour, J.A.; Aman, P.; Courtin, C.M.; Hamaker, B.R.; Verbeke, K. Prebiotics, Fermentable Dietary Fiber, and Health Claims. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.N.; Diep Pham, H.T.; Montez, J.; Mann, J. Dietary Fibre Intake in Childhood or Adolescence and Subsequent Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review of Prospective Observational Studies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Nan, F.; Liang, H.; Shu, P.; Fan, X.; Song, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, D. Excessive Intake of Sugar: An Accomplice of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 988481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L. Integrating Precision Medicine and Digital Health in Personalized Weight Management: The Central Role of Nutrition. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranić, L.; Mikolašević, I.; Milić, S. Vitamin D Deficiency: Consequence or Cause of Obesity? Medicina 2019, 55, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, B.; Godos, J.; Varrasi, S.; Roggio, F.; Castellano, S.; Musumeci, G. Physical Activity, Sun Exposure, Vitamin D Intake and Perceived Stress in Italian Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santanasto, A.J.; Newman, A.B.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Boudreau, R.M.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Glynn, N.W. Effects of Changes in Regional Body Composition on Physical Function in Older Adults: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchitomi, R.; Oyabu, M.; Kamei, Y. Vitamin D and Sarcopenia: Potential of Vitamin D Supplementation in Sarcopenia Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, I.A.; Landrier, J.-F.; Suliburska, J. Interrelationship between Vitamin D and Calcium in Obesity and Its Comorbid Conditions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratos, I.; Li, Z.; Herlyn, P.; Rotter, R.; Behrendt, A.-K.; Mittlmeier, T.; Vollmar, B. Vitamin D Increases Cellular Turnover and Functionally Restores the Skeletal Muscle after Crush Injury in Rats. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S. Vitamin D Deficiency Impairs Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion and Increases Insulin Resistance by Reducing PPAR-γ Expression in Nonobese Type 2 Diabetic Rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Hong, K.-W.; Han, K.; Park, Y.C.; Park, J.-M.; Kim, K.; Kim, B.-T. Longitudinal Observation of Muscle Mass over 10 Years According to Serum Calcium Levels and Calcium Intake among Korean Adults Aged 50 and Older: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moum, B.; Lindgren, S. Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in Chronic Disease-Common, Important, and Treatable. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotardo, É.M.F.; Dos Santos, A.N.; Miyashiro, R.A.; Gambero, S.; Rocha, T.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Gambero, A. Mice That Are Fed a High-Fat Diet Display Increased Hepcidin Expression in Adipose Tissue. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Sulejczak, D.; Kleczkowska, P.; Bukowska-Ośko, I.; Kucia, M.; Popiel, M.; Wietrak, E.; Kramkowski, K.; Wrzosek, K.; Kaczyńska, K. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress-A Causative Factor and Therapeutic Target in Many Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, V.S.; Vishnoi, A.; Sharma, M.; Jaison, A.; Singh, N. Unveiling the Role of Magnesium: Insights into Insulin Resistance and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. EJIFCC 2024, 35, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Dudley, S.C. Magnesium, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piuri, G.; Zocchi, M.; Della Porta, M.; Ficara, V.; Manoni, M.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Pinotti, L.; Maier, J.A.; Cazzola, R. Magnesium in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Hawthorne, K.M. Magnesium Metabolism in 4-Year-Old to 8-Year-Old Children. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, I.J.; Lynch, M.F.; Hawthorne, K.M.; Chen, Z.; Hamzo, M.; Abrams, S.A. Magnesium Retention in 12 to 48 Month-Old Children. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2008, 27, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiouri, D.P.; Tsoupra, E.; Peana, M.; Perlepes, S.P.; Stefanidou, M.E.; Chasapis, C.T. Multifunctional Role of Zinc in Human Health: An Update. EXCLI J. 2023, 22, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, I.J.; Lynch, M.F.; Hawthorne, K.M.; Chen, Z.; Hamzo, M.G.; Abrams, S.A. Zinc Homeostasis in 1–4 Year Olds Consuming Diets Typical of US Children. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, J.E.; Brown, K.H. Zinc Intake of US Preschool Children Exceeds New Dietary Reference Intakes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, P.; Strippoli, V.; Fang, B.; Cimmino, L. B Vitamins and One-Carbon Metabolism: Implications in Human Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, K.V.Q.; Nguyen, L.T.H. The Impact of Thiamine Treatment in the Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2012, 4, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boachie, J.; Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Samavat, J.; Saravanan, P. Low Vitamin B12 and Lipid Metabolism: Evidence from Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska, K.; Rachoń, D.; Berg, A.; Rybka, J.; Kapczyńska, K.; Bolanowski, M.; Daroszewski, J. Alteration of Branched-Chain and Aromatic Amino Acid Profile as a Novel Approach in Studying Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Pathogenesis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cai, M.; Shi, M. Wearable Sensing in Eating Episode Monitoring: An Updated Systematic Review Protocol. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e092175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attas, O.; Al-Daghri, N.; Bamakhramah, A.; Shaun Sabico, S.; McTernan, P.; Huang, T. Telomere Length in Relation to Insulin Resistance, Inflammation and Obesity among Arab Youth. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, J.L.; Walters, R.G.; Visvikis-Siest, S.; Meyre, D.; Froguel, P.; Blakemore, A.I.F. Childhood Obesity Is Associated with Shorter Leukocyte Telomere Length. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.J. Does Work-Induced Fatigue Accumulate across Three Compressed 12 Hour Shifts in Hospital Nurses and Aides? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calzón, S.; Moleres, A.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Martínez, J.A.; Zalba, G.; Marti, A. GENOI members Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity Is Associated with Leukocyte Telomere Length in a Children and Adolescent Population. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bhagatwala, J.; Pollock, N.K.; Parikh, S.; Gutin, B.; Stallmann-Jorgensen, I.; Thomas, J.; Harshfield, G.A.; Dong, Y. High Sodium Intake Is Associated with Short Leukocyte Telomere Length in Overweight and Obese Adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calzón, S.; Moleres, A.; Gómez-Martinez, S.; Diaz, L.E.; Bueno, G.; Campoy, C.; Martinez, J.A.; Marcos, A.; Azcona-Sanjulián, M.C.; Zalba, G.; et al. Association of Telomere Length with IL-6 Levels during an Obesity Treatment in Adolescents: Interaction with the-174G/C Polymorphism in the IL-6gene. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaer, T.W.; Faurholt-Jepsen, D.; Mehta, K.M.; Christensen, V.B.; Epel, E.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.; Wojcicki, J.M. Shorter Preschool, Leukocyte Telomere Length Is Associated with Obesity at Age 9 in Latino Children. Clin. Obes. 2018, 8, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, D.B.P.; Maitre, L.; Bustamante, M.; Chatzi, L.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Fossati, S.; Grazuleviciene, R.; Gützkow, K.B.; Lepeule, J.; Martens, D.S.; et al. Obesity Is Associated with Shorter Telomeres in 8 Year-Old Children. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramura, S.; Yamagishi, K.; Umesawa, M.; Hayama-Terada, M.; Muraki, I.; Maruyama, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kishida, R.; Kihara, T.; Takada, M.; et al. Risk Factors for Hyperuricemia or Gout in Men and Women: The Circulatory Risk in Communities Study (CIRCS). J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2023, 30, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Amrousy, D.; El-Afify, D.; Salah, S. Insulin Resistance, Leptin and Adiponectin in Lean and Hypothyroid Children and Adolescents with Obesity. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga-Venegas, L.; Saracini, C.; Pancetti, F.; Muñoz-Quezada, M.T.; Lucero, B.; Foerster, C.; Cortés, S. Pesticide Exposure in Chile and Population Health: Urgency for Decision Making. Gac. Sanit. 2021, 35, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, V.; Orbak, Z.; Selimoglu, M.A.; Yildiz, L. Serum Leptin Levels in Childhood Celiac Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Leboffe, L.; Ascenzi, P. Human Plasma Lipocalins and Serum Albumin: Plasma Alternative Carriers? J. Control. Release 2016, 228, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; di Masi, A.; Ascenzi, P. Serum Albumin: A Multifaced Enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-A.; Lee, I.-K.; Kim, J.-G.; Park, K.-G.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Jeon, J.-H.; Shin, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-H. Effect of a Brown Rice Based Vegan Diet and Conventional Diabetic Diet on Glycemic Control of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A 12-Week Randomized Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Vazquez, I.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Krämer, D.K.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Garcia-Guerra, L.; Lorenzo, M. Insulin Resistance Associated to Obesity: The Link TNF-Alpha. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Kreis, N.-N.; Louwen, F.; Yuan, J. Obesity and COVID-19: Molecular Mechanisms Linking Both Pandemics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ye, S.; Lian, H.; Wang, H.; Ye, J. Obesity and COVID-19: Mechanistic Insights From Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korakas, E.; Ikonomidis, I.; Kousathana, F.; Balampanis, K.; Kountouri, A.; Raptis, A.; Palaiodimou, L.; Kokkinos, A.; Lambadiari, V. Obesity and COVID-19: Immune and Metabolic Derangement as a Possible Link to Adverse Clinical Outcomes. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E105–E109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bandt, J.-P.; Monin, C. Obesity, Nutrients and the Immune System in the Era of COVID-19. Nutrients 2021, 13, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, R.; Sebastian, P.; Namdeo, M.; Devender, M.; Gertler, A. COVID-19 Severity in Obesity: Leptin and Inflammatory Cytokine Interplay in the Link Between High Morbidity and Mortality. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 649359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskiet, F.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Pruimboom, L.; Lucia, A.; Furman, D. Obesity and Leptin Resistance in the Regulation of the Type I Interferon Early Response and the Increased Risk for Severe COVID-19. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Reyes, A.; Martinez-Armenta, C.; Espinosa-Velázquez, R.; Vázquez-Cárdenas, P.; Cruz-Ramos, M.; Palacios-Gonzalez, B.; Gomez-Quiroz, L.E.; Martínez-Nava, G.A. NLRP3 Inflammasome: The Stormy Link Between Obesity and COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 570251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperberg, S.J.; Navetta-Modrov, B. The Role of Obesity in the Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 Respiratory Disease and Critical Illness. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 65, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquarelli-do-Nascimento, G.; Braz-de-Melo, H.A.; Faria, S.S.; Santos, I.d.O.; Kobinger, G.P.; Magalhães, K.G. Hypercoagulopathy and Adipose Tissue Exacerbated Inflammation May Explain Higher Mortality in COVID-19 Patients With Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, T.; Oba, S.; Komiya, Y.; Kawata, D.; Kamiya, M.; Iwai, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Kataoka, M.; Tobiume, M.; Kanno, T.; et al. Apple-Shaped Obesity: A Risky Soil for Cytokine-Accelerated Severity in COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2300155120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghili, S.M.M.; Ebrahimpur, M.; Arjmand, B.; Shadman, Z.; Pejman Sani, M.; Qorbani, M.; Larijani, B.; Payab, M. Obesity in COVID-19 Era, Implications for Mechanisms, Comorbidities, and Prognosis: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Jin, B.; Xu, X.; Zuo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. The Effects of Delivery Mode on the Gut Microbiota and Health: State of Art. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 724449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, L.H.; Schork, N.J. Personalized Medicine: Motivation, Challenges, and Progress. Fertil. Steril. 2018, 109, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors Affecting the Composition of the Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; England, E. Nutrition: Macronutrients. FP Essent. 2024, 539, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Blaser, M.J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Jansson, J.K.; Lynch, S.V.; Knight, R. Current Understanding of the Human Microbiome. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBurney, M.I.; Cho, C.E. Understanding the Role of the Human Gut Microbiome in Overweight and Obesity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2024, 1540, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aja, E.; Zeng, A.; Gray, W.; Connelley, K.; Chaganti, A.; Jacobs, J.P. Health Effects and Therapeutic Potential of the Gut Microbe Akkermansia Muciniphila. Nutrients 2025, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, M.; Lv, L.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Human Microbiota in Health and Disease. Engineering 2017, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Rufty, T.; Shi, W. Soil Microbial Diversity and Composition: Links to Soil Texture and Associated Properties. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanage, W.P.; Fraser, C.; Spratt, B.G. Sequences, Sequence Clusters and Bacterial Species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Ilhan, Z.-E.; Kang, D.-W.; DiBaise, J.K. Effects of Gut Microbes on Nutrient Absorption and Energy Regulation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Interplay between Gut Microbiota and Diet in Cardio-Metabolic Health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, K.J.; Collins, M.K.; Moloney, G.M.; Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Fülling, C.; Morley, S.J.; Clarke, G.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Short Chain Fatty Acids: Microbial Metabolites for Gut-Brain Axis Signalling. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2022, 546, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Flores, L.P.; Moreno-Terrazas Casildo, R.; Fuentes-Cabrera, J.; Pérez-Vicente, H.A.; de Anda-Jáuregui, G.; Neri-Torres, E.E. The Role of Carbohydrate Intake on the Gut Microbiome: A Weight of Evidence Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuntini, E.B.; Sardá, F.A.H.; de Menezes, E.W. The Effects of Soluble Dietary Fibers on Glycemic Response: An Overview and Futures Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, E.B.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Devkota, S. Our Extended Microbiome: The Human-Relevant Metabolites and Biology of Fermented Foods. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Gupta, S.K.; Kundu, A.; Grover, M.; Saha, S. Role of Fructooligosaccharides in Promoting Beneficial Gut Bacteria: A Prebiotic Perspective. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.N.; Wallace, M.A.; Tomilov, A.A.; Zhou, Z.; Marcotte, G.R.; Tran, D.; Perez, G.; Gutierrez-Casado, E.; Koike, S.; Knotts, T.A.; et al. A Ketogenic Diet Extends Longevity and Healthspan in Adult Mice. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 539–546.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, I.; Maslennikov, R.; Poluektova, E.; Vasilieva, E.; Zharikov, Y.; Suslov, A.; Letyagina, Y.; Kozlov, E.; Levshina, A.; Ivashkin, V. Epidemiology of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 3400–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behounek, M.; Cochran, D.; Motta-Romero, H.A.; Yang, Q.; Ding, W.; Morton, M.; Majumder, K.; Powers, R.; Rose, D.J. In Vitro Fermentation of Animal and Plant Protein Isolates by the Human Gut Microbiota Under High and Low Carbohydrate Conditions. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chu, J.; Feng, S.; Guo, C.; Xue, B.; He, K.; Li, L. Immunological Mechanisms of Inflammatory Diseases Caused by Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meigui, H.; Xu, L.; Assadpour, E.; Tan, C.; Jafari, S.M. Application of Nano/Micro-Encapsulated Bioactive Compounds in 3D Printed Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 158, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, V.; Pisanu, S.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Loviselli, A.; Manzin, A.; et al. Gut Microbiota Markers Associated with Obesity and Overweight in Italian Adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, D.M.; Kwon, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Bang, W.J.; Choi, H.G. Differences in Nutritional Intake, Total Body Fat, and BMI Score between Twins. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftei, N.-M.; Raileanu, C.R.; Balta, A.A.; Ambrose, L.; Boev, M.; Marin, D.B.; Lisa, E.L. The Potential Impact of Probiotics on Human Health: An Update on Their Health-Promoting Properties. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damms-Machado, A.; Weser, G.; Bischoff, S.C. Micronutrient Deficiency in Obese Subjects Undergoing Low Calorie Diet. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelli, M.; Franza, L.; Pignataro, G.; Ojetti, V.; Covino, M.; Piccioni, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F. Interaction between Lipopolysaccharide and Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.J.; Ghosh, S. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, LPS Translocation, and Disease Development. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikha, S.R.J.; Lee, D.M.; Ecton, K.E.; Wrigley, S.D.; Vazquez, A.R.; Litwin, N.S.; Thomas, K.N.; Wei, Y.; Battson, M.L.; Johnson, S.A.; et al. Transplantation of an Obesity-Associated Human Gut Microbiota to Mice Induces Vascular Dysfunction and Glucose Intolerance. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1940791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, D.; Bernardino, T.; Geraghty, F.; Carrion Rodriguez, A.; Fiani, B.; Chadhaury, A.; Pierre-Louis, M. Bariatric Surgery With Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass or Sleeve Gastrectomy for Treatment of Obesity and Comorbidities: Current Evidence and Practice. Cureus 2022, 14, e25762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley-Evans, S.C.; Pearce, J.; Ellis, S. Overweight, Obesity and Excessive Weight Gain in Pregnancy as Risk Factors for Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: A Narrative Review. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 35, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacruz, A.; Collado, M.C.; García-Valdés, L.; Segura, M.T.; Martín-Lagos, J.A.; Anjos, T.; Martí-Romero, M.; Lopez, R.M.; Florido, J.; Campoy, C.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Associated with Body Weight, Weight Gain and Biochemical Parameters in Pregnant Women. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Isolauri, E.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S. Distinct Composition of Gut Microbiota during Pregnancy in Overweight and Normal-Weight Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorczyca, K.; Obuchowska, A.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Wierzchowska-Opoka, M.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Changes in the Gut Microbiome and Pathologies in Pregnancy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, N.H.; Haddad, E.N.; Kerver, J.M.; Cassidy-Bushrow, A.E.; Comstock, S.S. Maternal Body Mass Index Associates with Prenatal Characteristics and Fecal Microbial Communities. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tun, H.M.; Bridgman, S.L.; Chari, R.; Field, C.J.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Sears, M.R.; et al. Roles of Birth Mode and Infant Gut Microbiota in Intergenerational Transmission of Overweight and Obesity From Mother to Offspring. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, K.Y.; Paneth, N.; Comstock, S.S. Michigan Cohorts to Determine Associations of Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index with Pregnancy and Infant Gastrointestinal Microbial Communities: Late Pregnancy and Early Infancy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, K.F.; Flanagan, J.P.; Sones, J.L. Microbiome and Pregnancy: Focus on Microbial Dysbiosis Coupled with Maternal Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Duarte, R.; Černáková, L.; Kadam, S.; Kaushik, K.S.; Salehi, B.; Bevilacqua, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Antolak, H.; Dybka-Stępień, K.; Leszczewicz, M.; et al. Advances in Chemical and Biological Methods to Identify Microorganisms-From Past to Present. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Interaction with Food Components. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Wei, L.; Bartlett, A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Rajender, S.; Ro, S. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Dysmotility and Metabolic Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asad, A.; Kirk, M.; Zhu, S.; Dong, X.; Gao, M. Effects of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety in Clinically Diagnosed Samples: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, e1504–e1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burén, J.; Ericsson, M.; Damasceno, N.R.T.; Sjödin, A. A Ketogenic Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet Increases LDL Cholesterol in Healthy, Young, Normal-Weight Women: A Randomized Controlled Feeding Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.S.; Koller, K.R.; Ramaboli, M.C.; Nesengani, L.T.; Ocvirk, S.; Chen, C.; Flanagan, C.A.; Sapp, F.R.; Merritt, Z.T.; Bhatti, F.; et al. Diet and the Human Gut Microbiome: An International Review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bloch, N.; Chang, A.Y.; Bhavsar, R.; Wang, Q.; Crawford, A.; DiLillo, D.J.; Vazzana, K.; Mohrs, K.; Dudgeon, D.; et al. A PD-1-Targeted, Receptor-Masked IL-2 Immunocytokine That Engages IL-2Rα Strengthens T Cell-Mediated Anti-Tumor Therapies. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková, N.; Laursen, M.F.; La Barbera, G.; Tsekitsidi, E.; Jørgensen, M.S.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Raes, J.; Licht, T.R.; Dragsted, L.O.; Roager, H.M. Gut Physiology and Environment Explain Variations in Human Gut Microbiome Composition and Metabolism. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 3210–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Malik, V.S.; Hu, F.B. Cardiovascular Disease Prevention by Diet Modification: JACC Health Promotion Series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, D.-K.; Trinh, K.T.L. Emerging Biomarkers in Metabolomics: Advancements in Precision Health and Disease Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, T.A.H.; Van Every, D.W.; Phillips, S.M. The Impact and Utility of Very Low-Calorie Diets: The Role of Exercise and Protein in Preserving Skeletal Muscle Mass. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2023, 26, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkeren, E.; Piskovsky, V.; Foster, K.R. Metabolic Ecology of Microbiomes: Nutrient Competition, Host Benefits, and Community Engineering. Cell Host Microbe 2025, 33, 790–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, O.M.; Ramos, M.C.; Calisto, R.; Almeida, E.; Vasconcelos, V.; Vicente, F. Current Screening Methodologies in Drug Discovery for Selected Human Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, T.; Nakamura, S.; Nishiyama, M.; Narimatsu, H. Holistic Evaluation of the Gut Microbiota through Data Envelopment Analysis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Dossus, L.; Barquera, S.; Blottière, H.M.; Franks, P.W.; Gunter, M.; Hwalla, N.; Hursting, S.D.; Leitzmann, M.; Margetts, B.; et al. Energy Balance and Obesity: What Are the Main Drivers? Cancer Causes Control 2017, 28, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Cristobal, R.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ordovas, J.M.; Martínez, J.A. Contribution of Macronutrients to Obesity: Implications for Precision Nutrition. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, P.; Joyce, S.A.; O’Toole, P.W.; O’Connor, E.M. Dietary Fibre Modulates the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Updates Guidelines on Fats and Carbohydrates; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Simpson, S.J.; Raubenheimer, D. Obesity: The Protein Leverage Hypothesis. Obes. Rev. 2005, 6, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, S.I.S.; Kaur, G. Nutrition, Food and Diet in Health and Longevity: We Eat What We Are. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylińska, M.; Antosik, K.; Decyk, A.; Kurowska, K. Malnutrition in Obesity: Is It Possible? Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, G.; Maffeis, C.; Saggese, G.; Ambruzzi, M.A.; Balsamo, A.; Bellone, S.; Bergamini, M.; Bernasconi, S.; Bona, G.; Calcaterra, V.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Pediatric Obesity: Consensus Position Statement of the Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology and the Italian Society of Pediatrics. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biltoft-Jensen, A.; Matthiessen, J.; Hess Ygil, K.; Christensen, T. Defining Energy-Dense, Nutrient-Poor Food and Drinks and Estimating the Amount of Discretionary Energy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramati, F.; Leijte, G.P.; Bruse, N.; Grondman, I.; Habibi, E.; Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Megchelenbrink, W.; Peters van Ton, A.M.; Heesakkers, H.; Bremmers, M.E.; et al. Systemic Inflammation Impairs Myelopoiesis and Interferon Type I Responses in Humans. Nat. Immunol. 2025, 26, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.M.; Corkins, M.R.; Lyman, B.; Malone, A.; Goday, P.S.; Carney, L.; Monczka, J.L.; Plogsted, S.W.; Schwenk, W.F. Defining Pediatric Malnutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37, 460–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; Rababa, M.; Alsuwayl, H.; Alsubail, A.; Alenizi, W. Diagnostic Challenges and Patient Safety: The Critical Role of Accuracy—A Systematic Review. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2025, 18, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Jin, W.; Liu, S.; Jiao, Z.; Li, X. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Postbiotics in Health and Disease. MedComm 2023, 4, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, R.J.; Hoekstra, T.; Jager, K.J.; Zoccali, C.; Tripepi, G.; Dekker, F.W.; van Diepen, M. Conducting Correlation Analysis: Important Limitations and Pitfalls. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2332–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarita, B.; Samadhan, D.; Hassan, M.Z.; Kovaleva, E.G. A Comprehensive Review of Probiotics and Human Health-Current Prospective and Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1487641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Form of Malnutrition | Definition (WHO Criteria) | Primary Causes and Risk Factors | Major Clinical Consequences | Global Prevalence/Epidemiological Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wasting (acute undernutrition) | BMI-for-age or weight-for-height > 3 SD below WHO median |
|
| ~45 million children < 5 years [23] |
| Stunting (chronic undernutrition) | Height-for-age > 2 SD below WHO median |
|
| ~149 million children < 5 years [23] |
| Underweight | Weight-for-age > 2 SD below WHO median |
|
| Predominant in low- and middle-income countries [5] |
| Overweight/Obesity (overnutrition) | Excessive body fat accumulation impairing health |
|
| >340 million children and adolescents globally [1] |
| Double burden of malnutrition | Coexistence of undernutrition (e.g., stunting) and overweight/obesity within the same population, household, or individual |
|
| Rising prevalence in LMICs (e.g., Malaysia, Zimbabwe) [4] |
| Model/Hypothesis | Core Mechanism | Principal Dietary Driver | Clinical and Metabolic Implications | Limitations/Ongoing Debates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate–Insulin Model (CIM) [20] |
|
| Suggests benefit of ⭣-glycemic diets in weight control. |
|
| Energy Balance Model (EBM) [21] |
|
| Supports calorie ⭣ and physical activity as core interventions. |
|
| Fructose Survival Hypothesis (FSH) [20] |
|
| Links fructose overconsumption to metabolic syndrome and fatty liver. |
|
| Protein Leverage Hypothesis (PLH) [21] |
|
| Highlights importance of protein density and quality in diet. |
|
| Inflammation–Sarcopenia Axis [19] |
|
| Links chronic inflammation to muscle ⭣ and metabolic dysfunction |
|
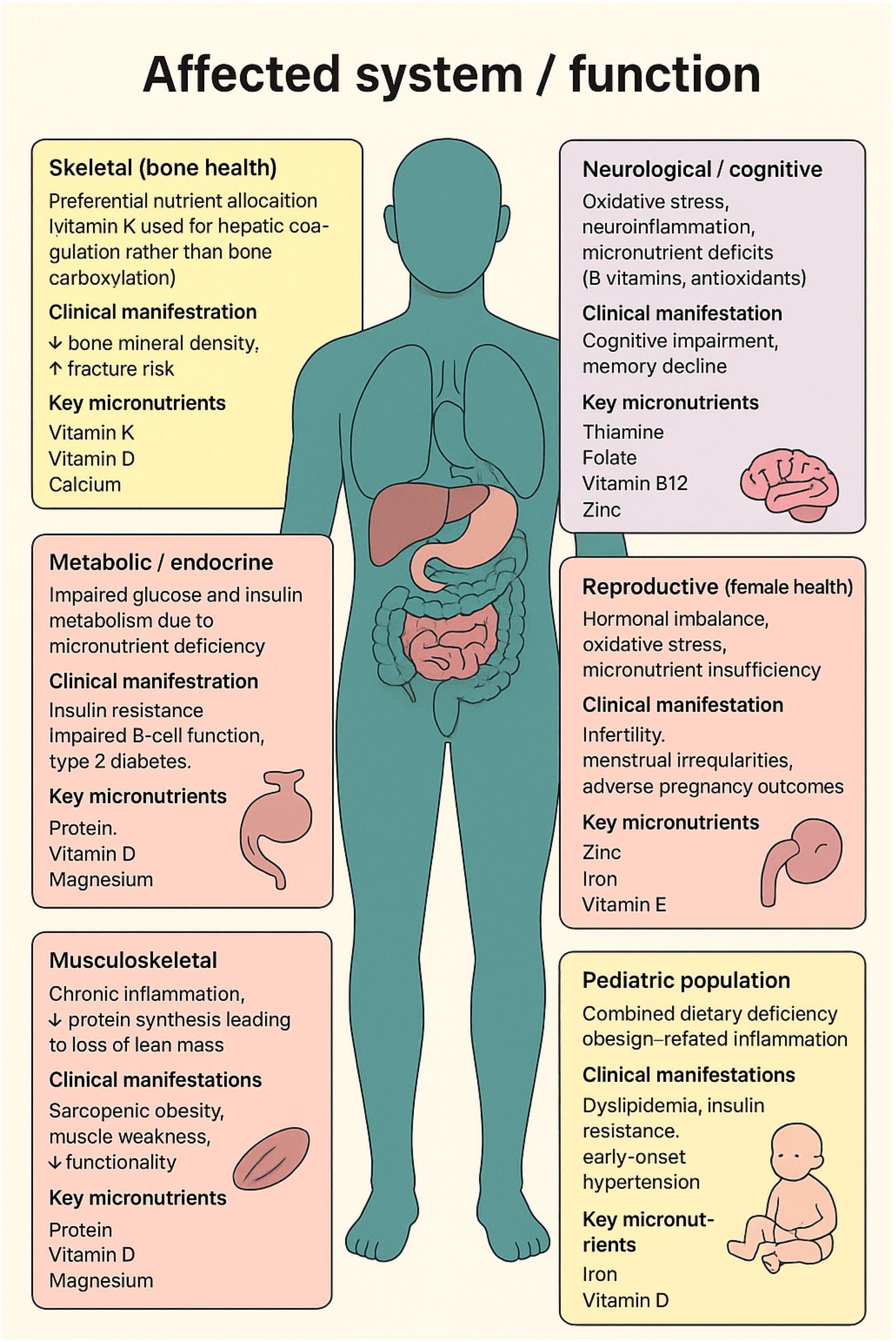
| Affected System/Function | Underlying Mechanism | Clinical Manifestation | Key Micronutrient(s) Involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skeletal (bone health) [19] |
|
|
|
| Metabolic/endocrine [38] |
|
|
|
| Musculoskeletal [41] |
|
|
|
| Neurological/cognitive [42] |
|
|
|
| Reproductive (female health) [42] |
|
|
|
| Cardiovascular [43] |
|
|
|
| Pediatric population [44] |
|
|
|
| Critical care/systemic [34] |
|
|
|
| Regulatory Mechanism/Pathway | Core principle or Function | Key Mediators/Components | Effect on Appetite, Metabolism, or Adiposity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucostatic theory | Hunger and satiety regulated by glucose availability in the brain (short-term control) |
|
|
| Lipostatic mechanism [55] | Long-term regulation of body fat through lipid feedback |
|
|
| Carbohydrate quality [56] | Influences sweetness perception, glycemic response, and satiety |
|
|
| Gut–neuroendocrine axis [57] | Coordinates short-term energy balance and appetite regulation |
|
|
| Amino acid–hormone interactions [58,59] | Amino acids regulate satiety and thermogenesis |
|
|
| Leptin signaling [57] | Endocrine link between adipose tissue and hypothalamic centers |
|
|
| “Fat-stat” hypothesis [60] | Genetic set point for adiposity maintained by feedback mechanisms |
|
|
| Reward pathway dysregulation [49] | Hyperpalatable; energy-dense foods override homeostatic control |
|
|
| Circadian regulation [61] | Synchronizes metabolism with sleep–wake cycles |
|
|
| Metabolic flexibility [62] | Ability to switch between glucose and fat oxidation |
|
|
| Gut microbiota and bile acid signaling [63,64] | Microbiota modulate energy extraction and appetite |
|
|
| Diet quality and macronutrient source | Carbohydrate and fat type exert stronger effects than total macronutrient amount |
|
|
| Macronutrient | Key Mechanisms | Clinical and Metabolic Impact | Dietary Recommendations/Preventive Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein [97,98,99,100,101] |
|
|
|
| Carbohydrates [98,102,104] |
|
|
|
| Fat [98,106,112,113] |
|
|
|
| Fiber [98,105] |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dargenio, V.N.; Sgarro, N.; Grasta, G.L.; Begucci, M.; Castellaneta, S.P.; Dargenio, C.; Paulucci, L.; Francavilla, R.; Cristofori, F. Hidden Hunger in Pediatric Obesity: Redefining Malnutrition Through Macronutrient Quality and Micronutrient Deficiency. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223601
Dargenio VN, Sgarro N, Grasta GL, Begucci M, Castellaneta SP, Dargenio C, Paulucci L, Francavilla R, Cristofori F. Hidden Hunger in Pediatric Obesity: Redefining Malnutrition Through Macronutrient Quality and Micronutrient Deficiency. Nutrients. 2025; 17(22):3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223601
Chicago/Turabian StyleDargenio, Vanessa Nadia, Nicoletta Sgarro, Giovanni La Grasta, Martina Begucci, Stefania Paola Castellaneta, Costantino Dargenio, Leonardo Paulucci, Ruggiero Francavilla, and Fernanda Cristofori. 2025. "Hidden Hunger in Pediatric Obesity: Redefining Malnutrition Through Macronutrient Quality and Micronutrient Deficiency" Nutrients 17, no. 22: 3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223601
APA StyleDargenio, V. N., Sgarro, N., Grasta, G. L., Begucci, M., Castellaneta, S. P., Dargenio, C., Paulucci, L., Francavilla, R., & Cristofori, F. (2025). Hidden Hunger in Pediatric Obesity: Redefining Malnutrition Through Macronutrient Quality and Micronutrient Deficiency. Nutrients, 17(22), 3601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223601






