Pro-Cognitive Effect of Royal Jelly Is Linked with Increased Burst Activity of Mesocorticolimbic Dopaminergic Neurons
Abstract
1. Introduction
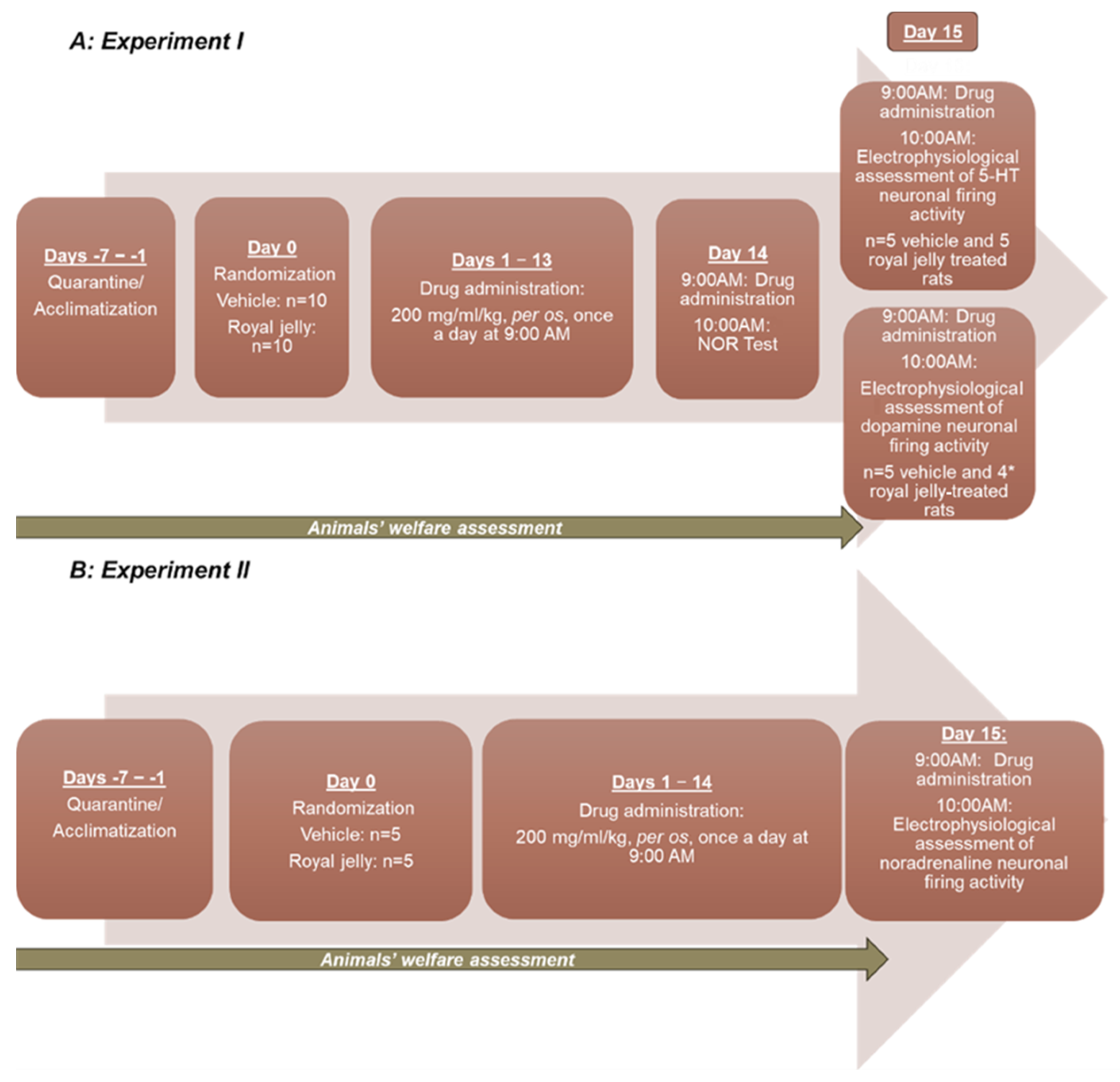
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Royal Jelly Preparation
2.2. Animals
2.3. Repeated Administration of the Royal Jelly
2.4. NOR Test
2.5. In Vivo Electrophysiology
2.6. Electrophysiological Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Repeated Treatment with Royal Jelly Improved Cognitive Performance in the NOR Test
3.2. Royal Jelly Did Not Alter the Excitability of 5-HT Neurons of the DRN
3.3. Royal Jelly Did Not Alter the Excitability of Noradrenergic Neurons of the LC
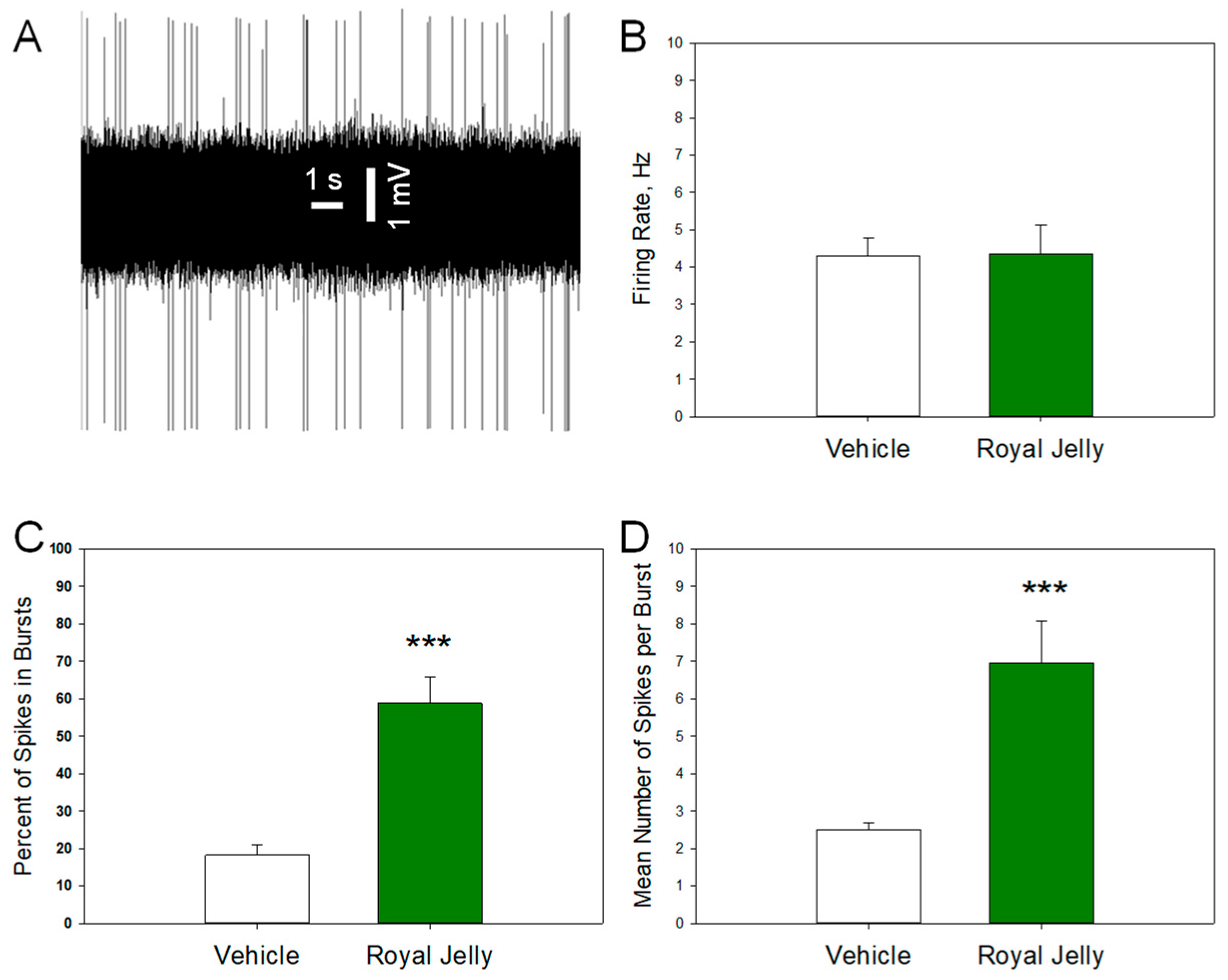
3.4. Royal Jelly Enhanced the Burst Firing of Dopamine Neurons of the VTA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| BDNF | Brain derived neurotrophic factor |
| DRN | Dorsal raphe nucleus |
| ISI | Interspike interval |
| LC | Locus coeruleus |
| MRJP | Major royal jelly protein |
| NOR | Novel object recognition |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| VTA | Ventral tegmental area |
References
- Sabatini, A.G.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Caboni, M.F.; Bogdanov, S.; Bicudo, L.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Quality and standardisation of Royal Jelly. J. ApiProduct ApiMedical Sci. 2009, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, G.M.; Robinson, G.E.; Bilikova, K.; Simuth, J. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature 2006, 443, 931–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitzová, J.; Klaudiny, J.; Albert, S.; Schröder, W.; Schreckengost, W.; Hanes, J.; Júdová, J.; Simúth, J. A family of major royal jelly proteins of the honeybee Apis mellifera L. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1998, 54, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimúth, J. Some properties of the main protein of honeybee (Apis mellifera) royal jelly. Apidologie 2001, 32, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, R.; Maleszka, R.; Hayward, D.C.; Ball, E.E. A royal jelly protein is expressed in a subset of Kenyon cells in the mushroom bodies of the honey bee brain. Naturwissenschaften 1998, 85, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, J.; Šimuth, J. Identification and partial characterization of the major royal jelly protein of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.). J. Apic. Res. 1992, 31, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Sasaki, M.; Nakamura, J.; Sasagawa, H.; Ohashi, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Natori, S. Change in the expression of hypopharyngeal-gland proteins of the worker honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) with age and/or role. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.D.; Wheeler, D.E. Differential gene expression between developing queens and workers in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5575–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleszka, R. Epigenetic integration of environmental and genomic signals in honey bees: The critical interplay of nutritional, brain and reproductive networks. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oršolić, N.; Jazvinšćak Jembrek, M. Royal Jelly: Biological Action and Health Benefits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Campos, M.G.; Fratini, F.; Altaye, S.Z.; Li, J. New Insights into the Biological and Pharmaceutical Properties of Royal Jelly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.F.; Al-Ghamdi, A. Bioactive compounds and health-promoting properties of royal jelly: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimúth, J.; Bíliková, K.; Kováčová, E.; Kuzmová, Z.; Schroder, W. Immunochemical Approach to Detection of Adulteration in Honey: Physiologically Active Royal Jelly Protein Stimulating TNF-α Release Is a Regular Component of Honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2154–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simuth, J.; Bilikova, K. Potential contribution of royal jelly proteins for health. Honeybee Sci.-Tamagawa Univ. 2004, 25, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bilikova, K.; Kristof Krakova, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamaguchi, Y. Major royal jelly proteins as markers of authenticity and quality of honey. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2015, 66, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanpour, A.M.; Saboor, M.; Panahizadeh, R.; Saadati, H.; Dadkhah, M. Combined effects of royal jelly and environmental enrichment against stress-induced cognitive and behavioral alterations in male rats: Behavioral and molecular studies. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licznerski, P.; Duman, R.S. Remodeling of axo-spinous synapses in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Neuroscience 2013, 251, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.M. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Applications, 5th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, D.C. The significance of action potential bursting in the brain reward circuit. Neurochem. Int. 2002, 41, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavacova, N.; Chmelova, M.; Danevova, V.; Csanova, A.; Jezova, D. Inhibition of fatty-acid amide hydrolyse (FAAH) exerts cognitive improvements in male but not female rats. Endocr. Regul. 2015, 49, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremencov, E.; Oravcova, H.; Grinchii, D.; Romanova, Z.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Lacinova, L.; Jezova, D. Maternal treatment with a selective delta-opioid receptor agonist during gestation has a sex-specific pro-cognitive action in offspring: Mechanisms involved. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1357575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliokha, R.; Vinas-Noguera, M.; Bukatova, S.; Grinchii, D.; Gaburjakova, J.; Gaburjakova, M.; Ozbasak, H.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Khoury, T.; Lacinová, Ľ.; et al. Effects of pre-gestational exposure to the stressors and perinatal mirtazapine administration on the excitability of hippocampal glutamate and brainstem monoaminergic neurons, hippocampal neuroplasticity, and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. Paxino’s and Watson’s the Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Vandermaelen, C.P.; Aghajanian, G.K. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1983, 289, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.A.; Bunney, B.S. Intracellular and extracellular electrophysiology of nigral dopaminergic neurons—1. Identification and characterization. Neuroscience 1983, 10, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.; Bunney, B. The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: Burst firing. J. Neurosci. 1984, 4, 2877–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, G.S.; Huff, K.D.; Vandergriff, J.L.; Sharp, T.; O’Neill, M.J.; Rasmussen, K. Olanzapine activates the rat locus coeruleus: In vivo electrophysiology and c-Fos immunoreactivity. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajós, M.; Allers, K.A.; Jennings, K.; Sharp, T.; Charette, G.; Sík, A.; Kocsis, B. Neurochemical identification of stereotypic burst-firing neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus using juxtacellular labelling methods. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrzanowska, J.; Piechal, A.; Blecharz-Klin, K.; Joniec-Maciejak, I.; Graikou, K.; Chinou, I.; Widy-Tyszkiewicz, E. Long-term administration of Greek Royal Jelly improves spatial memory and influences the concentration of brain neurotransmitters in naturally aged Wistar male rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfan Saeed Alwali Alkindi, F.; El–Keblawy, A.; Lamghari Ridouane, F.; Bano Mirza, S. Factors influencing the quality of Royal jelly and its components: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2348253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, H.M.; Du, G.H. Protections of pinocembrin on brain mitochondria contribute to cognitive improvement in chronic cerebral hypoperfused rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 542, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K. Nutrition and dopamine: An intake of tyrosine in royal jelly can affect the brain levels of dopamine in male honeybees (Apis mellifera L.). J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 87, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmawla, A.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zeng, Z.; He, X. Roles of DNA Methylation in Color Alternation of Eastern Honey Bees (Apis cerana) Induced by the Royal Jelly of Western Honey Bees (Apis mellifera). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, S.; Nagao, T.; Sasaki, K. Consumption of tyrosine in royal jelly increases brain levels of dopamine and tyramine and promotes transition from normal to reproductive workers in queenless honey bee colonies. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 211, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, S.; Kolaric, R.; Espera, J.; Ha, Q.; Tomaio, J.; Gether, U.; Sørensen, A.T.; Mingote, S. Role of dopamine neurons in familiarity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 59, 2522–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, K.; Gomes, F.V.; Rincón-Cortés, M.; Grace, A.A. Female rats are resistant to the long-lasting neurobehavioral changes induced by adolescent stress exposure. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Heo, H.I.; Kim, D.H.; Ko, I.G.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, T.W.; Ji, E.S.; Kim, J.D.; et al. Treadmill exercise and methylphenidate ameliorate symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder through enhancing dopamine synthesis and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 504, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinchii, D.; Hoener, M.C.; Khoury, T.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Nejati Bervanlou, R.; Jezova, D.; Dremencov, E. Effects of acute and chronic administration of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) ligands on in vivo excitability of central monoamine-secreting neurons in rats. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4861–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dremencov, E.; Grinchii, D.; Romanova, Z.; Chomanic, P.; Lacinova, L.; Jezova, D. Effects of chronic delta-opioid receptor agonist on the excitability of hippocampal glutamate and brainstem monoamine neurons, anxiety, locomotion, and habituation in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliokha, R.; Grinchii, D.; Khoury, T.; Nejati Bervanlou, R.; Dremencov, E. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 with proadifen alters the excitability of brain catecholamine-secreting neurons. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2022, 41, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, R.R.; de Souza, A.V.; Peixoto, L.G.; Machado, H.L.; Caixeta, D.C.; Vilela, D.D.; Baptista, N.B.; Franci, C.R.; Espindola, F.S. Royal jelly decreases corticosterone levels and improves the brain antioxidant system in restraint and cold stressed rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 655, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bíliková, K.; Jezova, D.; Grinchii, D.; Oravcová, H.; Krištof Kraková, T.; Paliokha, R.; Özbaşak, H.; Račický, M.; Dremencov, E. Pro-Cognitive Effect of Royal Jelly Is Linked with Increased Burst Activity of Mesocorticolimbic Dopaminergic Neurons. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223593
Bíliková K, Jezova D, Grinchii D, Oravcová H, Krištof Kraková T, Paliokha R, Özbaşak H, Račický M, Dremencov E. Pro-Cognitive Effect of Royal Jelly Is Linked with Increased Burst Activity of Mesocorticolimbic Dopaminergic Neurons. Nutrients. 2025; 17(22):3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223593
Chicago/Turabian StyleBíliková, Katarína, Daniela Jezova, Daniil Grinchii, Henrieta Oravcová, Tatiana Krištof Kraková, Ruslan Paliokha, Hande Özbaşak, Matej Račický, and Eliyahu Dremencov. 2025. "Pro-Cognitive Effect of Royal Jelly Is Linked with Increased Burst Activity of Mesocorticolimbic Dopaminergic Neurons" Nutrients 17, no. 22: 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223593
APA StyleBíliková, K., Jezova, D., Grinchii, D., Oravcová, H., Krištof Kraková, T., Paliokha, R., Özbaşak, H., Račický, M., & Dremencov, E. (2025). Pro-Cognitive Effect of Royal Jelly Is Linked with Increased Burst Activity of Mesocorticolimbic Dopaminergic Neurons. Nutrients, 17(22), 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223593








