Standardized Hibiscus–Inulin Shot Lowers Lipid–Glucose Indices in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: 8-Week Randomized Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Participants
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Intervention and Adherence
2.5. Beverage Preparation and Composition
2.6. Sample Size Determination
2.7. Measurements and Outcomes
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Chemical Composition and Bioactive Properties
3.3. Cardiometabolic Effects of the Intervention
3.4. Metabolic Response and Responder Profile
3.5. Physio-Metabolic Profile and Response Variability
3.6. Baseline Risk and Metabolic Response
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebrahimpur, M.; Mohammadi-Vajari, E.; Sharifi, Y.; Ghotbi, L.; Sarvari, M.; Ayati, A.; Hashemi, B.; Shadman, Z.; Khashayar, P.; Ostovar, A.; et al. Evaluation of the Prevalence of Cardiometabolic Disorders (Diabetes, Hypertension, and Hyperlipidemia) Diagnosed, Undiagnosed, Treated, and Treatment Goal in the Elderly: Bushehr Elderly Health Program (BEH). BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, D.; Catal, C.; Tekinerdogan, B. Precision Nutrition: A Systematic Literature Review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.; He, Y. Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Risk, Severity, and Prognosis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Andrade, J.C.d.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Emerging Perspectives on Analytical Techniques and Machine Learning for Food Metabolomics in the Era of Industry 4.0: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 6045–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Cui, M. Triglyceride–Glucose Index and the Incidence of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee Rad, M.; Ghasempour Dabaghi, G.; Darouei, B.; Amani-Beni, R. The Association of Atherogenic Index of Plasma with Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liang, J.; Xue, Z.; Meng, X.; Jia, L. Effect of Dietary Anthocyanins on the Risk Factors Related to Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0315504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.L.; Alvarado, D.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Holscher, H.D. The Prebiotic Potential of Inulin-Type Fructans: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 492–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assempoor, R.; Daneshvar, M.S.; Taghvaei, A.; Abroy, A.S.; Azimi, A.; Nelson, J.R.; Hosseini, K. Atherogenic Index of Plasma and Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.R.; Zulfiqar, S.; Holmes, M.; Marshall, L.; Dye, L.; Boesch, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa on Blood Pressure and Cardiometabolic Markers. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz-López, M.; Olivares-Vicente, M.; Boix-Castejón, M.; Caturla, N.; Roche, E.; Micol, V. Differential Effects of a Combination of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora Polyphenols in Overweight/Obese Subjects: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, E.; Gharagozlian, S.; Birkeland, K.I.; Valeur, J.; Måge, I.; Rud, I.; Aas, A.M. Prebiotic Effect of Inulin-Type Fructans on Faecal Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3325–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce-Reynoso, A.; Mateos, R.; Mendivil, E.J.; Zamora-Gasga, V.M.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G. Bioavailability of Bioactive Compounds in Hibiscus sabdariffa Beverage as a Potential Anti-Inflammatory. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Venema, K.; Tabernero, M.; Sarriá, B.; Bravo, L.; Mateos, R. Bioconversion of Polyphenols and Organic Acids by Gut Microbiota of Predigested Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Calyces and Agave (A. Tequilana Weber) Fructans Assessed in a Dynamic in Vitro Model (TIM-2) of the Human Colon. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; Chen, B. Association of Atherogenic Index of Plasma with Cardiovascular Disease Mortality and All-Cause Mortality in the General US Adult Population: Results from NHANES 2005–2018. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, A.; Marhuenda, J.; Arcusa, R.; Pérez-Piñero, S.; Sánchez-Macarro, M.; García-Muñoz, A.M.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; Cánovas, F.; López-Román, F.J. Effectiveness of a Polyphenolic Extract (Lippia citriodora and Hibiscus sabdariffa) on Appetite Regulation in Overweight and Obese Grade I Population: An 8-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Cross-over, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebas, P.; Patel, A.; Agnes, J.T.; Parzych, E.M.; Baer, A.; Caturla, M.; Ghosh, S.; Purwar, M.; Bedanova, N.; Tsang, C.; et al. Safety and Pharmacokinetics of SARS-CoV-2 DNA-Encoded Monoclonal Antibodies in Healthy Adults: A Phase 1 Trial. Nat. Med. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosqvist, F.; Cedernaes, J.; Martínez Mora, A.; Fridén, M.; Johansson, H.E.; Iggman, D.; Larsson, A.; Ahlström, H.; Kullberg, J.; Risérus, U. Overfeeding Polyunsaturated Fat Compared with Saturated Fat Does Not Differentially Influence Lean Tissue Accumulation in Individuals with Overweight: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçalı, Ç.; Uçar, A.; Atay, K. A Randomized Trial of Inulin for Bowel Symptoms, Depression and Quality of Life in Constipation Predominant IBS. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 34252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Romero, E.; Izaola, O.; Primo, D.; Aller, R. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Insulin Resistance After Two Hypocaloric Diets with Different Fat Distribution in Obese Subjects: Effect of the Rs10767664 Gene Variant in Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Lifestyle Genom. 2017, 10, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, F.; Tutunchi, H.; Vaghef-Mehrabani, E.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. The Effect of Prebiotic Supplementation on Serum Levels of Tryptophan and Kynurenine in Obese Women with Major Depressive Disorder: A Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. BMC Res. Notes 2024, 17, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Yu, L.; Li, J.; Huang, L.; Xue, T.; Yang, D.; Huang, X.; Meng, C. Multiple Triglyceride-Derived Metabolic Indices and Incident Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Heart Disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubalová, K.; Porvazník, I.; Majherová, M.; Demková, L.; Piotrowska, A.; Mydlárová Blaščáková, M. Lipid Levels and Atherogenic Indices as Important Predictive Parameters in the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis—Slovak Pilot Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürdeniz, G.; Uusitupa, M.; Hermansen, K.; Savolainen, M.J.; Schwab, U.; Kolehmainen, M.; Brader, L.; Cloetens, L.; Herzig, K.H.; Hukkanen, J.; et al. Analysis of the SYSDIET Healthy Nordic Diet Randomized Trial Based on Metabolic Profiling Reveal Beneficial Effects on Glucose Metabolism and Blood Lipids. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, T. A Review of Statistical Methods for Dietary Pattern Analysis. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Costa-Rocha, I.; Bonnlaender, B.; Sievers, H.; Pischel, I.; Heinrich, M. Hibiscus sabdariffa L.—A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Determination of Anthocyanins, Organic Acids, and Phenolic Acids in Hibiscus Market Products Using LC/UV/MS. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 1098–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Madrigal, M.; Quintero-Ramos, A.; Amaya-Guerra, C.A.; Meléndez-Pizarro, C.O.; Castillo-Hernández, S.L.; Aguilera-González, C.J. Effect of Agave Fructans as Carrier on the Encapsulation of Blue Corn Anthocyanins by Spray Drying. Foods 2019, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda-Miramontes, J.P.; González-Frías, S.E.; Padlon-Manjarrez, S.; García-Cayuela, T.; Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E. Obtaining a Fiber-Rich Ingredient from Blueberry Pomace Through Convective Drying: Process Modeling and Its Impact on Techno-Functional and Bioactive Properties. LWT 2024, 210, 116862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda-Miramontes, J.P.; Espinoza-Paredes, B.C.; Zatarain-Palffy, A.; García-Cayuela, T.; Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E. Process Modeling and Convective Drying Optimization of Raspberry Pomace as a Fiber-Rich Functional Ingredient: Effect on Techno-Functional and Bioactive Properties. Foods 2024, 13, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Luo, J.; Zhu, Y.; An, P.; Luo, Y.; Xing, Q. The Effect of Antioxidant Polyphenol Supplementation on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhuenda, J.; Perez, S.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; Abellán, M.S.; Caturla, N.; Jones, J.; López-Román, J. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial to Determine the Effectiveness a Polyphenolic Extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora) in the Reduction of Body Fat Mass in Healthy Subjects. Foods 2020, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvo-González, E.; Villagrán, Z.; González-Torres, S.; Iñiguez-Muñoz, L.E.; Isiordia-Espinoza, M.A.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Arteaga-Garibay, R.I.; Acosta, J.L.; González-Silva, N.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M. Physiological Effects and Human Health Benefits of Hibiscus sabdariffa: A Review of Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Yang, K.; Li, S.; Dai, M.; Chen, G. Effect of Green Tea Consumption on Blood Lipids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Xu, A.; Tian, J.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yang, B.; Li, B.; Sun, Y. Anthocyanins as Natural Bioactives with Anti-Hypertensive and Atherosclerotic Potential: Health Benefits and Recent Advances. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Campaniello, D.; Speranza, B.; Racioppo, A.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. An Update on Prebiotics and on Their Health Effects. Foods 2024, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z.; Yao, C. Association Between TyG Index and Long-Term Prognosis of Patients with ST-Segment Elevated Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e079279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, J. Correlations of the Triglyceride−Glucose Index and Modified Indices with Arterial Stiffness in Overweight or Obese Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1499120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheilifard, S.; Faramarzi, E.; Mahdavi, R. Relationship Between Dietary Intake and Atherogenic Index of Plasma in Cardiometabolic Phenotypes: A Cross-Sectional Study from the Azar Cohort Population. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2025, 44, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Gan, W.; Mao, H.; Nie, S.; Zeng, X.; Chen, W. Association Between the Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3–4. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiezzi, M.; Vieceli Dalla Sega, F.; Gentileschi, P.; Campanelli, M.; Benavoli, D.; Tremoli, E. Effects of Weight Loss on Endothelium and Vascular Homeostasis: Impact on Cardiovascular Risk. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorfer, B.; Kayser, B.D.; Yoshino, M.; Yoshino, J.; Watrous, J.D.; Jain, M.; Eagon, J.C.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Heterogeneity in the Effect of Marked Weight Loss on Metabolic Function in Women with Obesity. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e169541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teparak, C.; Uriyapongson, J.; Phoemsapthawee, J.; Tunkamnerdthai, O.; Aneknan, P.; Tong-un, T.; Panthongviriyakul, C.; Leelayuwat, N.; Alkhatib, A. Diabetes Therapeutics of Prebiotic Soluble Dietary Fibre and Antioxidant Anthocyanin Supplement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Randomised Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiel, S.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Portheault, D.; Leyrolle, Q.; Bindels, L.B.; Gomes da Silveira Cauduro, C.; Mulders, M.D.G.H.; Zamariola, G.; Azzi, A.S.; et al. Link Between Gut Microbiota and Health Outcomes in Inulin-Treated Obese Patients: Lessons from the Food4Gut Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3618–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, F.; Koudoufio, M.; Desjardins, Y.; Spahis, S.; Delvin, E.; Levy, E. Efficacy of Polyphenols in the Management of Dyslipidemia: A Focus on Clinical Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qiu, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, G. Associations of the Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Atherogenic Index of Plasma with the Severity of New-Onset Coronary Artery Disease in Different Glucose Metabolic States. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
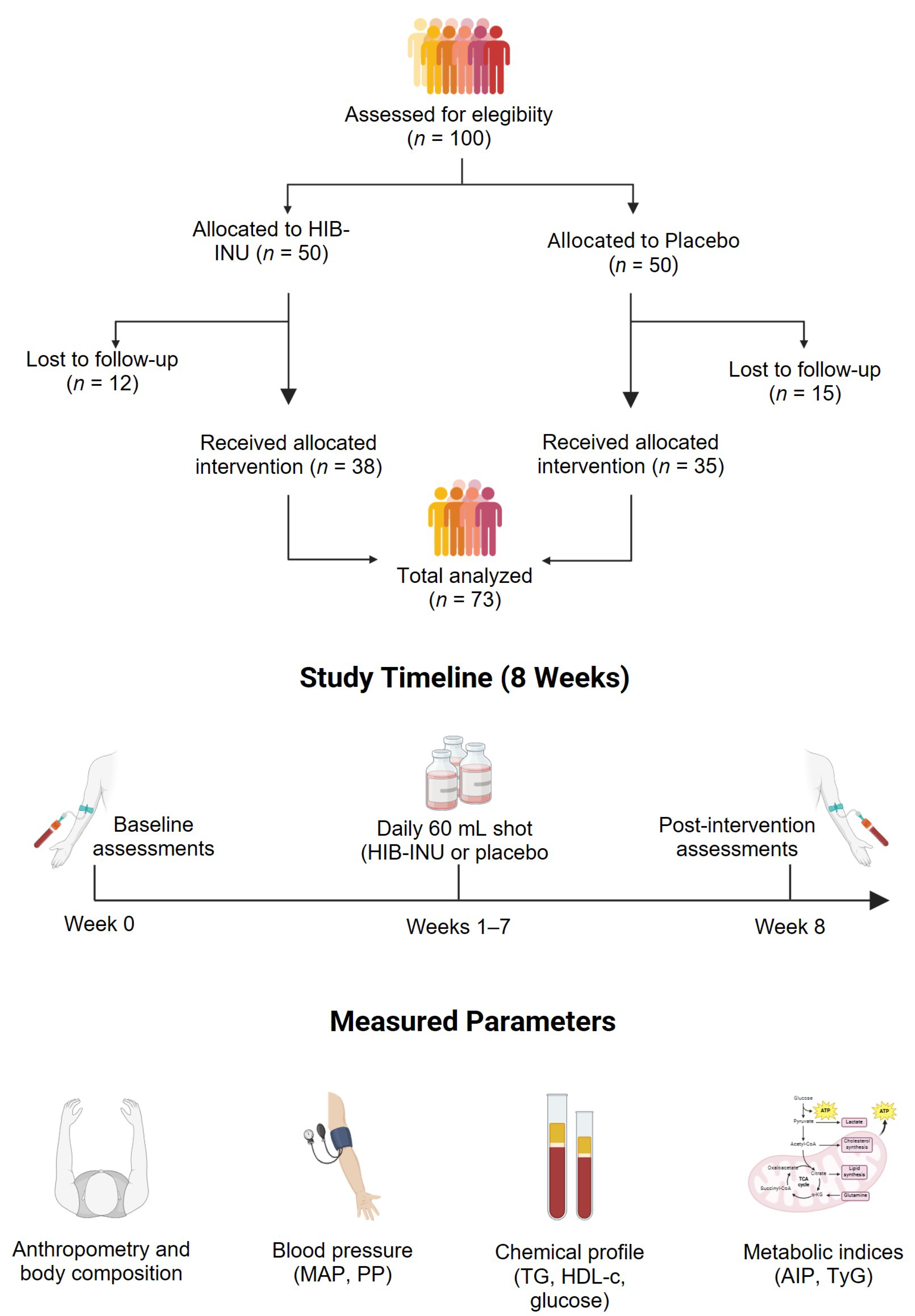
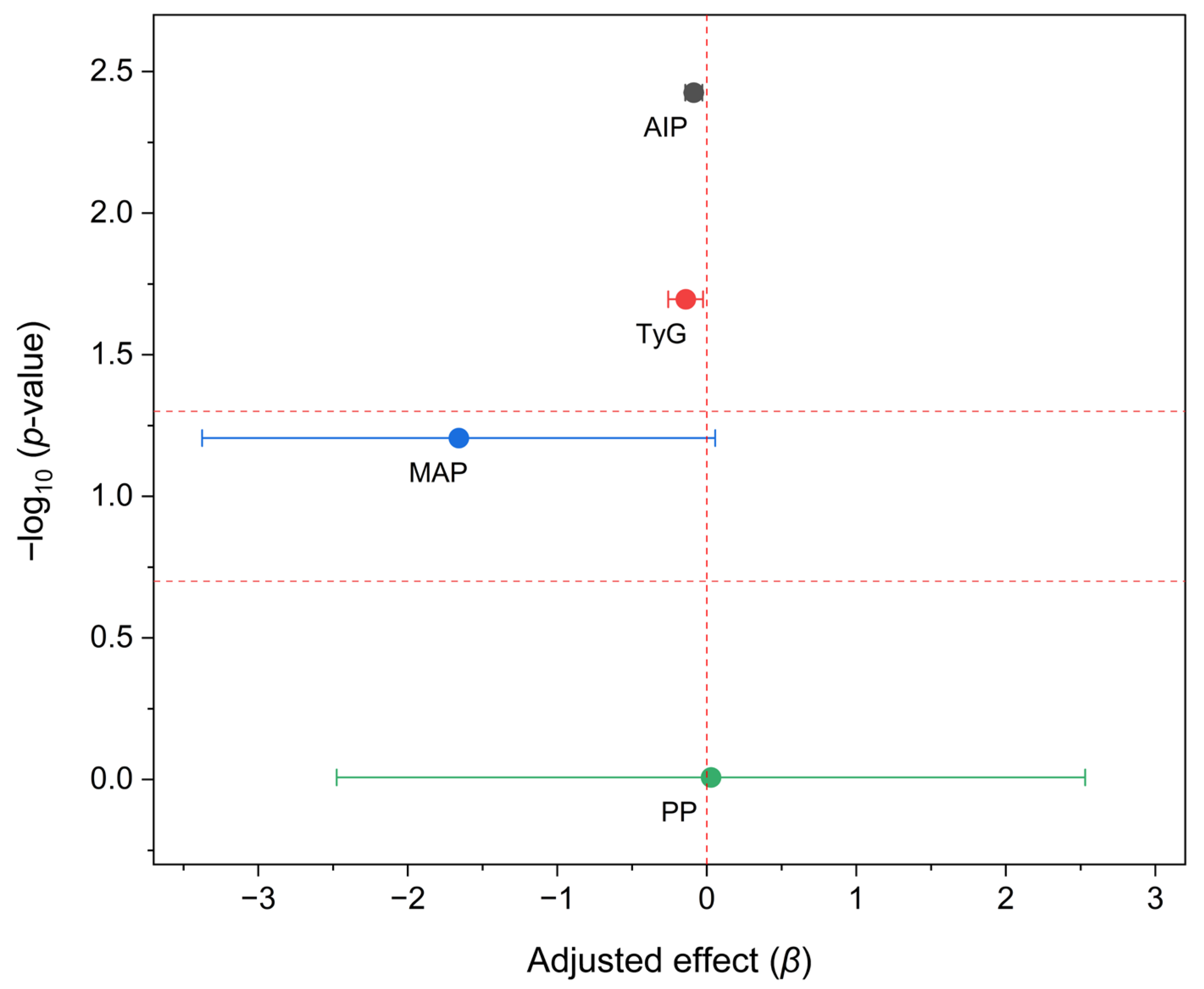
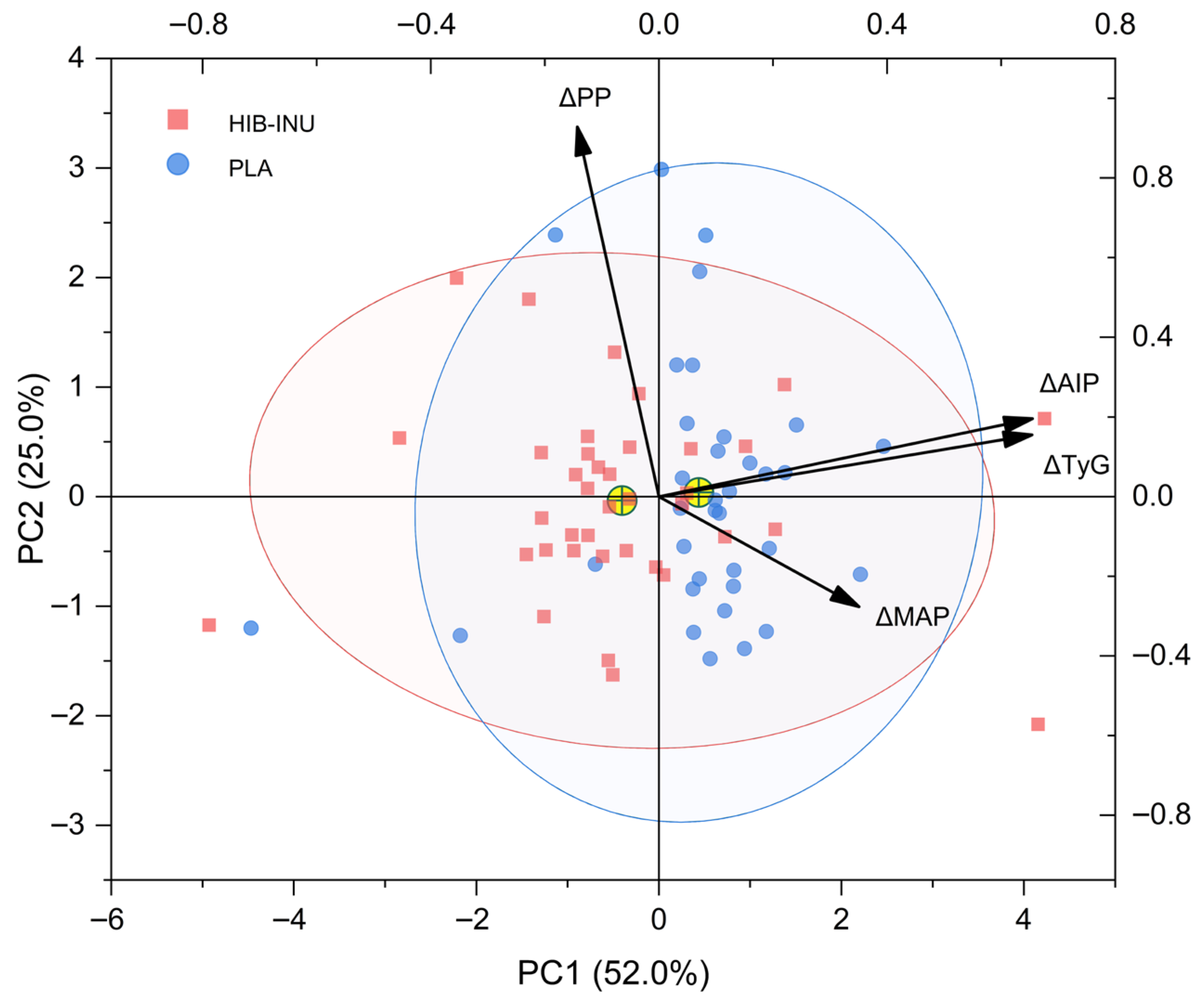
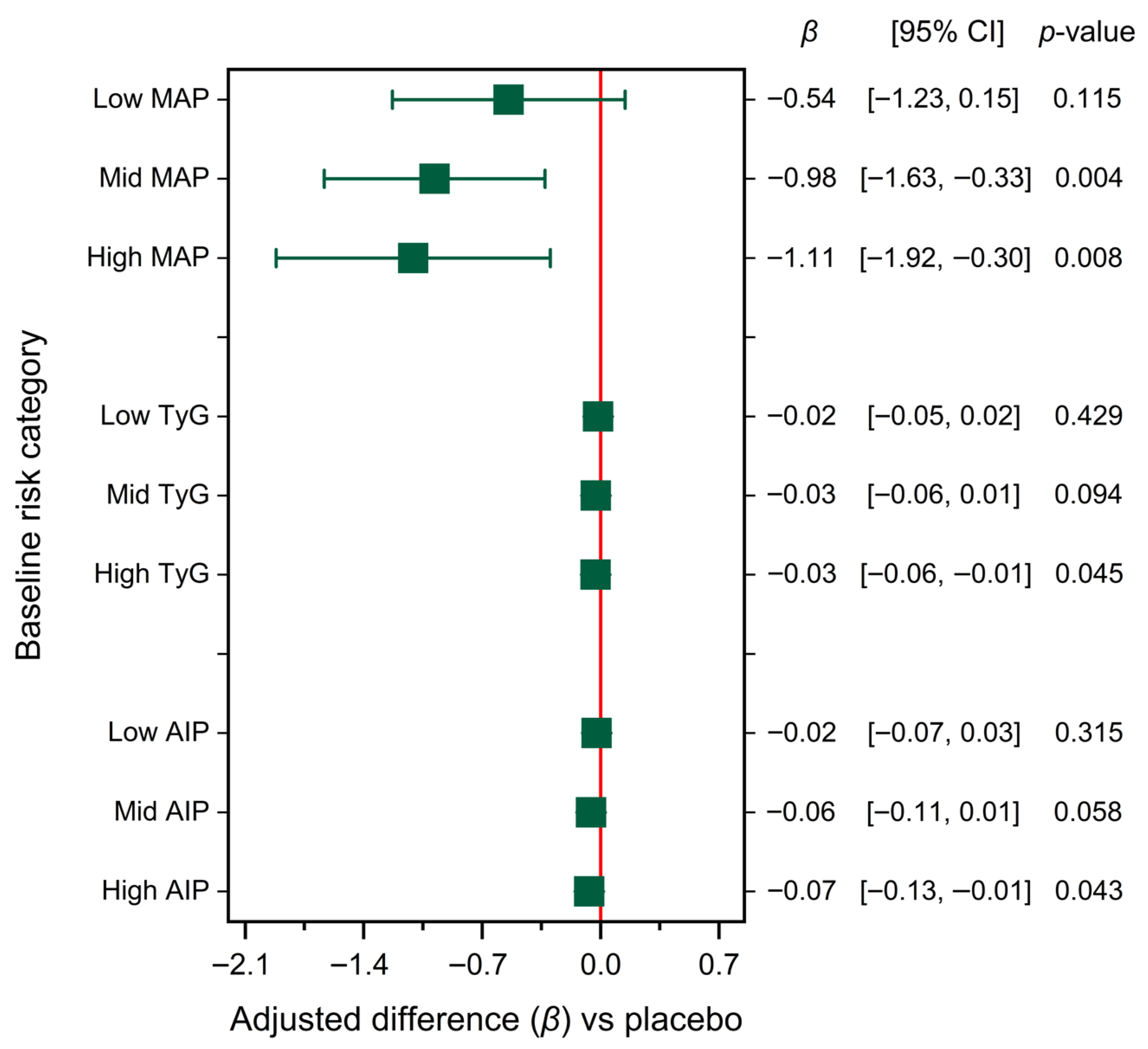
| Parameter | Placebo (n = 35) | HIB–INU (n = 38) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 39.37 ± 10.84 (40.0) | 37.89 ± 10.76 (36.5) | 0.562 |
| Weight (kg) | 71.17 ± 13.23 (74.7) | 74.17 ± 15.91 (77.2) | 0.383 |
| Height (cm) | 170.86 ± 11.22 (172.0) | 168.21 ± 10.71 (168.0) | 0.307 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 25.43 ± 2.61 (24.6) | 26.20 ± 3.39 (24.7) | 0.136 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 82.47 ± 10.98 (79.4) | 86.79 ± 13.28 (88.7) | 0.133 |
| Hip Circumference (cm) | 100.11 ± 7.25 (101.0) | 100.06 ± 9.32 (98.8) | 0.977 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 111.49 ± 11.20 (109.0) | 114.82 ± 13.16 (114.0) | 0.247 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 70.03 ± 9.17 (69.0) | 72.97 ± 9.35 (73.0) | 0.179 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 88.03 ± 13.90 (88.0) | 90.18 ± 15.38 (88.5) | 0.531 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 111.77 ± 46.74 (97.0) | 102.84 ± 39.34 (93.5) | 0.382 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 63.46 ± 7.80 (64.0) | 60.82 ± 7.93 (62.0) | 0.156 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 187.60 ± 16.48 (189.0) | 187.97 ± 18.73 (188.5) | 0.928 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 101.79 ± 13.92 (103.2) | 106.59 ± 18.35 (107.5) | 0.210 |
| Component | Placebo | HIB–INU |
|---|---|---|
| Total bioactive compounds (mg/60 mL) | 1.22 ± 0.06 | 937.37 ± 96.31 |
| Organic acids (mg/60 mL) | 0.86 ± 0.03 | 844.39 ± 86.32 |
| Hibiscus acid | 0.80 ± 0.01 | 676.90 ± 67.10 |
| Hydroxycitric acid | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 91.35 ± 9.01 |
| Hibiscus acid dimethylester | N.D. | 62.16 ± 6.18 |
| Phenolic acids (mg/60 mL) | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 44.85 ± 20.23 |
| Methylchlorogenate I | N.D. | 14.61 ± 1.25 |
| Methylchlorogenate II | N.D. | 23.13 ± 2.14 |
| Flavonoids (mg/60 mL) | N.D. | 11.86 ± 1.21 |
| Quercetin-galloyl-hexoside | N.D. | 4.22 ± 0.00 |
| Myricetin-3-O-sambubioside | N.D. | 3.24 ± 0.31 |
| Anthocyanins (mg/60 mL) | N.D. | 36.25 ± 3.18 |
| Delphinidin-3-sambubioside | N.D. | 23.93 ± 2.35 |
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside | N.D. | 8.43 ± 0.86 |
| Delphinidin | N.D. | 3.89 ± 0.41 |
| Total non-phenolic solids (g/60 mL db) | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 17.16 ± 0.27 |
| Fructans | N.D. | 15.38 ± 0.45 |
| Fructose | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 1.04 ± 0.07 |
| Glucose | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.03 |
| Sucrose | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| Ash | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.02 |
| Variable | Group | Baseline | Week 8 | Δ Mean | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIP | Placebo | 0.21 ± 0.20 | 0.21 ± 0.21 | −0.002 | 0.007 |
| HIB–INU | 0.20 ± 0.19 | 0.12 ± 0.20 | −0.083 | ||
| TyG | Placebo | 8.41 ± 0.44 | 8.39 ± 0.42 | −0.016 | 0.049 |
| HIB–INU | 8.36 ± 0.41 | 8.21 ± 0.37 | −0.144 | ||
| MAP | Placebo | 83.85 ± 8.53 | 82.81 ± 9.46 | −1.038 | 0.092 |
| HIB–INU | 86.92 ± 9.51 | 84.46 ± 9.89 | −2.465 | ||
| PP | Placebo | 41.46 ± 10.62 | 41.26 ± 11.36 | −0.200 | 0.957 |
| HIB–INU | 41.84 ± 10.71 | 41.71 ± 10.95 | −0.132 |
| Variable |
Adjusted Effect (β [95% CI]) | p-Value | Responders HIB–INU (%) | Responders Placebo (%) |
ARD (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔAIP | −0.09 [−0.15, −0.03] | 0.004 | 73.7 | 62.9 | 10.8 [−10.4, 32.1] |
| ΔTyG | −0.14 [−0.26, −0.03] | 0.020 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| ΔMAP | −1.66 [−3.38, 0.06] | 0.062 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| ΔPP | 0.03 [−2.48, 2.53] | 0.983 | 73.7 | 71.4 | 2.3 [−18.2, 22.8] |
| Variables | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| ΔAIP | 0.6548 | 0.1958 |
| ΔTyG | 0.6542 | 0.1550 |
| ΔMAP | 0.3505 | −0.2761 |
| ΔPP | −0.1431 | 0.9281 |
| Response Category | Criteria | n | % of Total (n = 73) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete responders | PC1 < 0, PC2 < 0 | 19 | 26.0 |
| Partial metabolic responders | PC1 < 0, PC2 > 0 | 14 | 19.2 |
| Vascularly mixed profiles | PC1 > 0, PC2 < 0 | 17 | 23.3 |
| Non-responders | PC1 > 0, PC2 > 0 | 23 | 31.5 |
| Total | 73 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendivil, E.J.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Arellano-Gómez, L.P.; Martínez-López, E.; Hernández-Guerrero, C.; Sayago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Tejeda-Miramontes, J.P. Standardized Hibiscus–Inulin Shot Lowers Lipid–Glucose Indices in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: 8-Week Randomized Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223556
Mendivil EJ, Rivera-Iñiguez I, Arellano-Gómez LP, Martínez-López E, Hernández-Guerrero C, Sayago-Ayerdi SG, Tejeda-Miramontes JP. Standardized Hibiscus–Inulin Shot Lowers Lipid–Glucose Indices in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: 8-Week Randomized Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(22):3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223556
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendivil, Edgar J., Ingrid Rivera-Iñiguez, Laura P. Arellano-Gómez, Erika Martínez-López, César Hernández-Guerrero, Sonia G. Sayago-Ayerdi, and José P. Tejeda-Miramontes. 2025. "Standardized Hibiscus–Inulin Shot Lowers Lipid–Glucose Indices in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: 8-Week Randomized Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 22: 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223556
APA StyleMendivil, E. J., Rivera-Iñiguez, I., Arellano-Gómez, L. P., Martínez-López, E., Hernández-Guerrero, C., Sayago-Ayerdi, S. G., & Tejeda-Miramontes, J. P. (2025). Standardized Hibiscus–Inulin Shot Lowers Lipid–Glucose Indices in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: 8-Week Randomized Trial. Nutrients, 17(22), 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17223556








