Abstract
Objective: To examine the association between the composite dietary antioxidant index (CDAI) and gastric cancer (GC) risk among adults in Southeast China, and to provide evidence for region-specific nutritional interventions. Methods: In this case–control study (July 2023–November 2024), 336 newly diagnosed GC patients were recruited from a hospital in Southeast China, and 336 sex-matched healthy controls were selected from local communities. Dietary data from a validated food frequency questionnaire were used to calculate CDAI scores. Results: A total of 672 participants (56.5% male) were included. The mean CDAI value was 0.47 ± 4.23 in cases versus −0.04 ± 4.61 in controls (p = 0.134), but CDAI quartile distribution differed significantly (p = 0.009). In multivariable analysis of individual CDAI components, vitamin C intake demonstrated a significant inverse association with GC risk, with the strongest protective effect observed in the highest quartile (OR = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.30–0.77, p = 0.002). Selenium intake also showed significant protective effects in the second (OR = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.32–0.83, p = 0.006) and third quartiles (OR = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.30–0.82, p = 0.006). Compared with the lowest quartile, adjusted odds ratios (95% CI) for GC in the second, third, and fourth CDAI quartiles were 0.56 (0.36–0.87), 0.59 (0.38–0.90), and 0.60 (0.39–0.92), respectively. The inverse association was stronger in participants aged >55 years, unmarried, and nonsmokers. Restricted cubic spline analysis revealed a significant nonlinear dose–response relationship. Conclusions: Higher dietary antioxidant intake is associated with lower GC risk. Personalized dietary strategies to enhance antioxidant intake may be particularly beneficial in high-risk populations.
1. Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is a major global public health challenge, ranking as the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide [1]. By 2050, the global burden of GC is projected to reach 2.5 million new cases and 1.9 million deaths annually [2]. China accounts for nearly 40% of the global GC burden, with 358,000 new cases and 187,000 deaths reported in 2022 [3]. In Fujian Province, the GC incidence rate in 2019 was 28.31 per 100,000 population, accounting for 9.3% of all malignancies and ranking fifth among cancer types, while the mortality rate was 20.88 per 100,000, accounting for 12.5% of all cancer deaths and ranking third [4].
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), generated under oxidative stress, are recognized as important contributors to the initiation and progression of GC [5]. Dietary factors can increase oxidative stress, leading to ROS accumulation, DNA damage, and ultimately carcinogenesis [6,7]. Unhealthy dietary patterns have been significantly associated with an elevated risk of GC [8,9], whereas foods rich in antioxidants—such as vitamin C and carotenoids—can modulate metabolic pathways, attenuate the genotoxic effects of ROS, and exert protective effects against GC [10,11,12]. Multiple studies have suggested that adequate dietary antioxidant intake may reduce GC incidence and prevalence [13,14,15]. Evidence from meta-analyses confirms that dietary intake of antioxidant vitamins, including vitamin C, vitamin E, and carotenoids, is associated with a reduced risk of gastric cancer [16,17]. However, the associations for blood levels of these antioxidants remain inconsistent, underscoring the complexity of assessing antioxidant exposure and its relationship with cancer risk. Moreover, adequate dietary antioxidant intake is not only associated with a reduced risk of specific cancers, such as gastric cancer, but also plays a crucial role in maintaining immune homeostasis and promoting overall health [18].
Given the complex etiology of GC, preventive measures can substantially reduce its mortality [19,20]. Among these, dietary factors have become an important target for primary prevention due to their clear etiological role and modifiability. However, most existing studies have focused on single nutrients or individual food components, without adequately addressing the synergistic effects of multiple dietary antioxidants.
The composite dietary antioxidant index (CDAI) is a novel measure that integrates the intake of various antioxidants—including vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals—to provide a comprehensive assessment of overall dietary antioxidant exposure [21]. This integrated approach offers a key advantage over single-nutrient analyses by capturing the cumulative and potentially synergistic biological effects of dietary antioxidants, which may be overlooked when components are examined in isolation. In recent years, several studies have explored the association between CDAI and cancer risk. For instance, a case–control study in Iran found a significant inverse association between the dietary antioxidant index (DAI) and GC risk (OR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.43–0.95), although the association was no longer statistically significant when analyzed in subgroups [22]. In lung cancer research, individuals in the highest quartile of a food-based CDAI had a significantly lower risk compared with those in the lowest quartile (HR_Q4 vs. Q1 = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.52–0.79) [23]. Similarly, a prospective population-based cohort study reported that participants in the highest quartile had a 20% lower risk of colorectal cancer compared with the lowest quartile (HR_Q4 vs. Q1 = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.66–0.98) [24], and higher CDAI scores were also associated with a significant reduction in cancer-related mortality (HR = 0.84, 95% CI: 0.82–0.88) [25]. An Italian study further indicated an inverse trend between CDAI and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, though this did not reach statistical significance [26].
Although evidence suggests that CDAI may be associated with the risk of various cancers, studies specifically addressing its relationship with GC are limited, particularly in high-incidence regions such as southeastern China. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the association between CDAI and GC risk in a Chinese population and to explore its potential role in primary prevention, thereby providing a scientific basis for developing region-specific nutritional intervention strategies.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Participants
This 1:1 sex-matched case–control study was carried out in Fujian Province, China. The case group comprised 336 individuals with a new histopathological or cytological diagnosis of gastric cancer (GC), recruited from Fujian Medical University Union Hospital between July 2023 and November 2024. The control group consisted of 336 healthy residents, matched by sex and recruited from nine prefecture-level cities in Fujian during the same period. All participants (cases and controls) were required to be between 18 and 75 years of age and be local residents, defined as having lived in Fujian for a minimum of six months in the year prior to enrollment. Additionally, all participants had to be capable of effective communication and provide written informed consent. Key exclusion criteria for both groups encompassed a history of malignancy (with controls also excluding other major conditions like stroke or psychiatric disorders) and extremes of daily energy intake (females: <500 or >3600 kcal; males: <600 or >4200 kcal).
2.2. Questionnaire
2.2.1. Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ)
Dietary intake information was collected using a validated structured semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire (FFQ), the details of which have been described in our previous publication [27].
2.2.2. Demographics and Lifestyles
We systematically collected comprehensive covariate data beyond dietary intake. This encompassed general demographics (age, sex, height, weight, household income, education, occupation, and perceived daily stress), from which body mass index (BMI) was derived. Additionally, we documented key lifestyle habits, specifically smoking and alcohol consumption over the preceding year. Smoking status was ascertained based on a history of either smoking ≥1 cigarette daily for over six consecutive months or a cumulative lifetime consumption of ≥150 cigarettes. Similarly, alcohol drinking was defined as consuming alcoholic beverages at least weekly for a duration exceeding six months.
2.3. Calculation of the Composite Dietary Antioxidant Index (CDAI)
We adapted the CDAI proposed by Wright et al. [28]. Prior to calculating the CDAI, nutrient intakes were not energy-adjusted, with the aim of ensuring direct comparability with existing CDAI literature. Specifically, this method includes seven dietary antioxidants: vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, selenium, manganese, and β-carotene. Consistent with existing calculation methods, the CDAI was obtained by summing the Z-scores of the dietary intakes of these seven antioxidants. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables with a normal distribution were described using the mean and standard deviation (SD), whereas those not conforming to a normal distribution were expressed as the median (M) and interquartile range (P25, P75). Categorical variables were presented as frequency and percentage (N, %). The chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables between groups, while the t-test or analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied for continuous variables. Dietary antioxidants and CDAI were categorized into quartiles according to their distribution in the control group. Logistic regression models were employed to assess the associations between individual dietary antioxidants, CDAI, and GC risk, estimating odds ratios (ORs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). In addition, a linear trend test was conducted to evaluate the dose–response relationship of GC risk across CDAI quartiles. To further explore the effect of CDAI on GC risk in subpopulations with different characteristics, stratified analyses were performed. Stratification variables were selected from demographic characteristics that were statistically significant in the univariate analysis and associated with GC risk. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression was applied to visualize potential nonlinear relationships between CDAI and GC risk. All p-values were derived from two-sided tests, and a significance level of 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 26.0 (SPSS 26.0).
2.5. Ethical Considerations
This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fujian Medical University (FJMU No. 2020[53]). Before participation, the purpose and content of the study were fully explained to the patients, and informed consent was obtained. Participants were free to withdraw from the study at any time if they experienced any discomfort, and refusal to participate had no impact on their medical care. All personal information of the participants was kept strictly confidential at all times.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics
Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of the study population (N = 672). Compared with controls, GC cases were older (mean age: 56.76 ± 10.34 vs. 53.86 ± 11.13 years, p < 0.001) and more likely to be married (p = 0.011), current smokers (p = 0.019), and to report low or no daily life stress (p < 0.001). No significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of sex distribution, education level, occupation, household income, alcohol consumption, or BMI. The mean CDAI value was slightly higher in the case group (0.47 ± 4.23) than in the control group (−0.04 ± 4.61), but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.134). In the distribution of CDAI quartiles, participants in the case group were more likely to be in the lowest quartile (Q1, <−1.95) compared with controls (36.9% vs. 25.0%), while a higher proportion of controls were in the second, third, and fourth quartiles (each 25.0%) compared with cases (19.6%, 20.8%, and 22.6%, respectively). The difference in CDAI distribution between the two groups was statistically significant (p = 0.009).

Table 1.
General demographic information and distribution of CDAI scores of the study population (N = 672).
3.2. Association Between CDAI Components and Gastric Cancer Risk
Table 2 shows the associations between individual CDAI components and GC risk. In multivariable logistic regression models adjusted for vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, manganese, age group, marital status, smoking, and daily life stress level, higher intakes of vitamin C and selenium were significantly associated with a reduced risk of GC. Compared with the lowest quartile, participants in the highest quartile of vitamin C intake had a 52% lower risk of GC (OR = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.30–0.77, p = 0.002), while those in the second and third quartiles of selenium intake had ORs of 0.52 (95% CI: 0.32–0.83, p = 0.006) and 0.50 (95% CI: 0.30–0.82, p = 0.006), respectively. No significant associations were observed for vitamin A, vitamin E, zinc, manganese, or β-carotene after adjustment.

Table 2.
Association between CDAI components and risk of gastric cancer.
3.3. Association Between CDAI Score and Gastric Cancer Risk
Table 3 summarizes the association between CDAI quartiles and GC risk. In the unadjusted model, higher CDAI scores were significantly associated with a lower risk of GC, with ORs (95% CIs) of 0.53 (0.35–0.81), 0.57 (0.37–0.86), and 0.61 (0.40–0.93) for the second, third, and fourth quartiles, respectively, compared with the lowest quartile (p for trend = 0.020). Similar inverse associations were observed after adjusting for age group, marital status, daily life stress level, and smoking, with adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of 0.56 (0.36–0.87), 0.59 (0.38–0.90), and 0.60 (0.39–0.92) for the second, third, and fourth quartiles, respectively (p for trend = 0.019).

Table 3.
Association between CDAI score and risk of gastric cancer.
Table 4 presents the stratified analysis of the association between CDAI scores and GC risk. In participants aged >55 years, higher CDAI scores were significantly associated with reduced GC risk, with adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of 0.48 (0.26–0.90) and 0.42 (0.23–0.76) for the second and third quartiles, respectively (p for trend = 0.044). Among married individuals, CDAI scores in the third quartile were associated with a borderline significant risk reduction (OR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.41–1.00, p = 0.046). In the subgroup of participants with low or no daily life stress, the third quartile of CDAI was associated with a significantly lower GC risk (OR = 0.49, 95% CI: 0.28–0.85, p = 0.019). Similarly, among participants with moderate or high stress levels, those in the second quartile had a significantly reduced GC risk (OR = 0.37, 95% CI: 0.18–0.75, p < 0.050). No statistically significant associations were observed in other subgroups.

Table 4.
Stratified analysis of the association between CDAI scores and gastric cancer risk.
3.4. Dose–Response Relationship Between CDAI and Gastric Cancer Risk
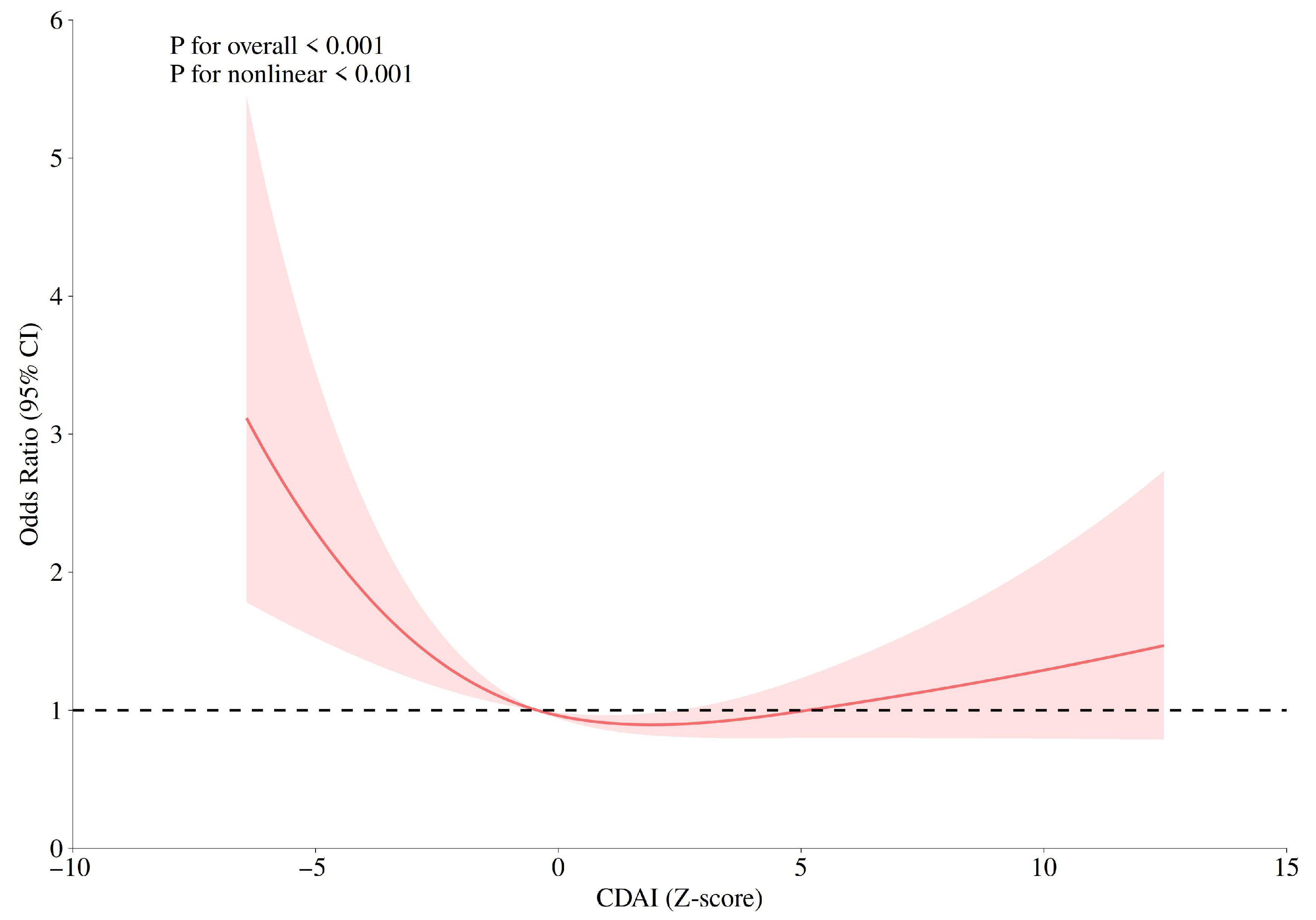
Restricted cubic spline (RCS) models were used to evaluate the dose–response relationship between CDAI and GC risk. Knots were placed at the 10th, 50th, and 90th percentiles of the CDAI distribution, with the 50th percentile as the reference. The models were adjusted for age group, marital status, daily life stress level, and smoking. As shown in Figure 1, a significant nonlinear association was observed between CDAI and GC risk (Pfor overall < 0.001, Pfor nonlinearity < 0.001), with a U-shaped curve indicating that both low and high CDAI levels were associated with higher GC risk, whereas moderate CDAI values were associated with the lowest risk.
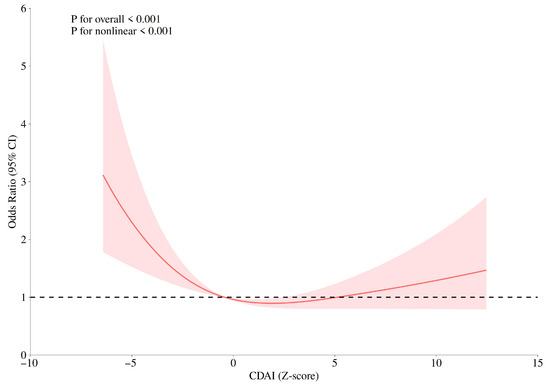
Figure 1.
Restricted cubic spline (RCS) plots for the correlations between CDAI and gastric cancer risk.
4. Discussion
The present case–control study aimed to investigate the association between the composite dietary antioxidant index (CDAI) and the risk of gastric cancer (GC). Our findings indicate that higher CDAI scores, reflecting diets rich in antioxidant nutrients, were significantly associated with a lower risk of GC, and this relationship remained robust after adjustment for multiple potential confounders. In addition, higher intakes of vitamin C and selenium were independently associated with reduced GC risk. Stratified analyses suggested that the inverse association between CDAI and GC risk was more pronounced among participants aged >55 years, those not currently married, and nonsmokers. Furthermore, RCS analysis revealed a significant nonlinear dose–response relationship between CDAI and GC risk, characterized by a U-shaped curve. These results highlight the potential role of dietary antioxidant status in GC prevention and underscore the importance of dietary interventions targeting oxidative stress in high-risk populations.
4.1. Association of CDAI Components with Gastric Cancer
GC development is influenced by genetic, infectious, environmental, and lifestyle factors, among which dietary nutrition plays a particularly important and modifiable role. In the present study, vitamin C and selenium intake were inversely associated with GC risk.
Biologically, vitamin C is a major water-soluble antioxidant that scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitigates oxidative DNA damage in the gastric mucosa [29]. It also competitively inhibits the reaction between nitrite and amines in the stomach, thereby blocking the endogenous formation of carcinogenic N-nitroso compounds [30]. Our findings are consistent with previous epidemiological evidence. A meta-analysis of 32 prospective studies reported that high vitamin C intake reduced GC risk by 19% (OR = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.68–0.95), with dose–response analysis suggesting an optimal protective effect at 65 mg/day [17]. Similarly, a Korean case–control study observed significantly lower vitamin C intake among GC patients, with an inverse association between intake and GC risk (OR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.46–0.88) [31].
Selenium intake was also significantly inversely associated with GC risk in our study, particularly in the third quartile, where the strongest protective effect was observed. Selenium’s anticancer effects are primarily mediated through its role as an essential component of selenoproteins [32]. These selenium-dependent antioxidant enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidases (GPx) and thioredoxin reductases (TrxR), protect gastric mucosal DNA from oxidative damage and modulate tumor-related signaling pathways, including NF-κB and p53 [33]. The attenuated and nonsignificant protective effect observed in the highest quartile may reflect selenium’s biphasic dose–response, whereby excessive intake could induce pro-oxidant effects [34,35]. Evidence from a dose–response meta-analysis on prostate cancer supports this phenomenon [36]. Specifically, the protective effect was observed at plasma/serum selenium concentrations up to ~170 ng/mL and toenail selenium levels between 0.85–0.94 μg/g, respectively, beyond which the benefit diminished. Furthermore, the protective association of CDAI may extend beyond essential vitamins and minerals to include non-vitamin antioxidants. Polyphenols such as resveratrol, for instance, contribute to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory defense through distinct mechanisms like Nrf2 pathway activation, and may synergize with other lifestyle factors for broader health benefits [37].
4.2. Association Between CDAI and Gastric Cancer
CDAI, an integrative measure of dietary antioxidant capacity, was constructed in this study from seven key antioxidant nutrients. In multivariable-adjusted models, participants in the highest CDAI quartile had a significantly lower risk of GC compared with those in the lowest quartile, suggesting that antioxidant-rich dietary patterns may protect against GC.
Mechanistically, oxidative stress contributes to carcinogenesis via DNA damage, gene mutations, and dysregulated cell signaling [38]. High CDAI scores indicate diets rich in antioxidants, which can promote apoptosis of damaged cells, suppress malignant transformation, and scavenge ROS within cancer cells [39,40]. Moreover, dietary antioxidants may exert epigenetic effects by modulating DNA methylation, histone modifications, and noncoding RNAs, thereby influencing GC-related gene expression [41,42]. These mechanistic insights provide biological plausibility for the observed inverse association between CDAI and GC risk.
Previous studies have linked higher intake of individual CDAI components to reduced GC risk [43,44,45], while cohort studies in the United States have reported lower cancer mortality among individuals consuming antioxidant-rich diets [46]. Beyond cancer prevention, higher CDAI has also been associated with reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved health outcomes [47,48].
4.3. Population Heterogeneity in the CDAI–Gastric Cancer Association
Our stratified analyses revealed potential population heterogeneity in the CDAI–GC relationship. The inverse association was stronger in older adults (>55 years), possibly because endogenous antioxidant defense systems decline with age, making dietary supplementation more impactful [49]. Among unmarried individuals, the protective effect was more pronounced, whereas in married participants, social support and associated health behaviors may attenuate the relative contribution of dietary antioxidants [50]. In nonsmokers, the protective association was also more evident, potentially because tobacco smoke–induced oxidative stress and nitrosamine exposure impair antioxidant response pathways, such as Nrf2 signaling [51]. Notably, the protective effect of higher CDAI was consistent across stress-level subgroups, suggesting broad applicability of antioxidant-focused dietary interventions.
RCS analysis further demonstrated a significant nonlinear dose–response between CDAI and GC risk, with a U-shaped curve indicating the lowest risk at moderate CDAI levels. It was also demonstrated that there was no significant difference in the mean CDAI scores between the case group and the control group; however, analysis based on quartiles revealed a significant negative correlation trend. This pattern suggests that while moderate antioxidant intake may effectively neutralize excessive ROS and maintain redox homeostasis, excessive intake could disrupt physiological ROS signaling or induce pro-oxidant effects [52]. These findings emphasize the importance of determining optimal antioxidant intake levels for personalized dietary prevention strategies.
4.4. Limitations
Several limitations should be acknowledged. First, as a case–control study, dietary data were retrospectively collected using a food frequency questionnaire (FFQ), which is subject to recall bias—particularly among GC patients, who may overreport unhealthy dietary habits. Although we instructed all participants to recall their dietary habits from the year prior to diagnosis (for cases) or interview (for controls), the accuracy of recall may still differ between groups. Second, we were unable to account for Helicobacter pylori infection, an important confounder in GC risk assessment. Third, due to clinical data limitations, we could not perform subgroup analyses based on GC pathological subtypes, which may have provided additional insights into differential associations. Fourth, the generalizability of our findings may be limited. The use of community-based controls and the specific dietary patterns and antioxidant sources unique to Southeast China may restrict the direct extrapolation of our results to other populations. Finally, information on participants’ physical activity levels was not collected. Since physical activity can influence oxidative stress and overall health, future studies could benefit from incorporating such data to further clarify the independent role of dietary antioxidants.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this case–control study demonstrated that higher CDAI scores, indicative of antioxidant-rich diets, were significantly associated with lower GC risk. Increased consumption of vitamin C- and selenium-rich foods may represent effective dietary strategies for GC prevention, particularly in high-risk populations and regions with high GC incidence. These findings provide scientific evidence for dietary prevention and intervention strategies targeting oxidative stress in GC. Public health initiatives should integrate antioxidant-rich dietary guidance into chronic disease prevention frameworks, especially in GC-endemic regions. Community-level interventions, including systematic nutritional assessments, personalized dietary recommendations, and early nutritional risk screening, may enhance public awareness of the link between dietary antioxidants and cancer risk. Future randomized controlled trials are warranted to confirm the preventive effects of optimized CDAI on gastric precancerous lesions and to explore potential interactions among its components, thereby advancing precision nutrition approaches in GC prevention.
Author Contributions
X.C.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Q.W.: Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—review & editing. F.Z.: Methodology, Software, Writing—review& editing. Y.W.: Methodology, Software, Writing—review & editing. S.L.: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. W.Z.: Data curation, Writing—review & editing. Y.L.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72004025). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fujian Medical University (FJMU No. 2020[53], 13 April 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Yulan Lin, upon reasonable request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all research team members and volunteers who participated in and supported this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Chen, R.; Sun, K.; Han, B.; Bray, F.; Wei, W.; et al. Global, regional, and national lifetime risks of developing and dying from gastrointestinal cancers in 185 countries: A population-based systematic analysis of GLOBOCAN. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Wu, K.; Yu, J.; Liang, Q.; Cai, X.; Shang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Pan, K.; Sun, L.; Fang, J.; et al. A global burden of gastric cancer: The major impact of China. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.B.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, L.R. Fujian Cancer Registry Annual Report 2022; Fujian Science and Technology Press: Fuzhou, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, W.L.; Krishnan, K.; Campbell, S.E.; Palau, V.E. The role of antioxidants and pro-oxidants in colon cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikara, S.; Nagaprashantha, L.D.; Singhal, J.; Horne, D.; Awasthi, S.; Singhal, S.S. Oxidative stress and dietary phytochemicals: Role in cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2018, 413, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudo, A.; Cayssials, V.; Bonet, C.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Affret, A.; Fagherazzi, G.; Katzke, V.; Schübel, R.; et al. Inflammatory potential of the diet and risk of gastric cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Ippolito, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Strazzullo, P. Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, B.; Berthon, B.S.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Starkey, M.R.; Collison, A.; Wark, P.A.B.; Wood, L.G. Effects of fruit and vegetable consumption on inflammatory biomarkers and immune cell populations: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 136–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carini, F.; Mazzola, M.; Rappa, F.; Jurjus, A.; Geagea, A.G.; Al Kattar, S.; Bou-Assi, T.; Jurjus, R.; Damiani, P.; Leone, A.; et al. Colorectal Carcinogenesis: Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4759–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetch, M.; Harandi-Zadeh, S.; Shen, K.; Lubecka, K.; Kitts, D.D.; O’Hagan, H.M.; Stefanska, B. Dietary antioxidants remodel DNA methylation patterns in chronic disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1382–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, M.C.; Fernandes, R.; Chagas, T.R.; Trindade, E. A meta-analysis of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids effects on circulating acute-phase protein and cytokines in gastric cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, F.; Soozangar, N.; Sadeghi, M.R.; Somi, M.H.; Shirmohamadi, M.; Eftekhar-Sadat, A.T.; Samadi, N. Nrf2 overexpression is associated with P-glycoprotein upregulation in gastric cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, M.; Bellocco, R.; Wolk, A.; Ekström, A.M. Total antioxidant potential of fruit and vegetables and risk of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y. Association between dietary antioxidant vitamins intake/blood level and risk of gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, P.; Zheng, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, H.; Cai, J.; Xia, D.; Wu, Y. Association between dietary vitamin C intake/blood level and risk of digestive system cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8217–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motti, M.L.; Tafuri, D.; Donini, L.; Masucci, M.T.; De Falco, V.; Mazzeo, F. The Role of Nutrients in Prevention, Treatment and Post-Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). Nutrients 2022, 14, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebbeck, T.R.; Burns-White, K.; Chan, A.T.; Emmons, K.; Freedman, M.; Hunter, D.J.; Kraft, P.; Laden, F.; Mucci, L.; Parmigiani, G.; et al. Precision Prevention and Early Detection of Cancer: Fundamental Principles. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dutson, E.; Eibl, G. Strategies to Prevent Obesity-Related Cancer. JAMA 2018, 319, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Wang, J.; He, R.; Qu, G. Composite dietary antioxidant index and sleep health: A new insight from cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahid, F.; Rahmani, D.; Davoodi, S.H. Validation of Dietary Antioxidant Index (DAI) and investigating the relationship between DAI and the odds of gastric cancer. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qian, S.; Na, X.; Zhao, A. Association between Dietary and Supplemental Antioxidants Intake and Lung Cancer Risk: Evidence from a Cancer Screening Trial. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.C.; Paragomi, P.; Wang, R.; Jin, A.; Schoen, R.E.; Sheng, L.T.; Pan, A.; Koh, W.P.; Yuan, J.M.; Luu, H.N. Composite dietary antioxidant index and the risk of colorectal cancer: Findings from the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, P.; Xiong, K.; Cao, C. Association of dietary inflammatory index, composite dietary antioxidant index and risk of death among adult cancer survivors: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2018. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1556828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Scalisi, A.; Agodi, A. Antioxidant and inflammatory potential of diet among women at risk of cervical cancer: Findings from a cross-sectional study in Italy. Public Health Nutr. 2022, 25, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Q.; Zou, F.; Lin, Y. Association between the Chinese Dietary Inflammatory Index and risk of gastric cancer: A case-control study in Southeastern China. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1653575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.E.; Mayne, S.T.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Li, Z.; Pietinen, P.; Taylor, P.R.; Virtamo, J.; Albanes, D. Development of a comprehensive dietary antioxidant index and application to lung cancer risk in a cohort of male smokers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Wilson, R.B. Pathways of Gastric Carcinogenesis, Helicobacter pylori Virulence and Interactions with Antioxidant Systems, Vitamin C and Phytochemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, B.V.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Ryu, K.W.; Kim, J. Effect of dietary vitamin C on gastric cancer risk in the Korean population. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6257–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labunskyy, V.M.; Hatfield, D.L.; Gladyshev, V.N. Selenoproteins: Molecular pathways and physiological roles. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 739–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.; Jitaru, P.; Barbante, C. Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health. Metallomics 2014, 6, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekley, C.M.; Harris, H.H. Which form is that? The importance of selenium speciation and metabolism in the prevention and treatment of disease. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8870–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.; Hooper, L.; Norat, T.; Lau, R.; Aune, D.; Greenwood, D.C.; Vieira, R.; Collings, R.; Harvey, L.J.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. Selenium and prostate cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, M.; Motti, M.L.; Meccariello, R.; Mazzeo, F. Resveratrol and Physical Activity: A Successful Combination for the Maintenance of Health and Wellbeing? Nutrients 2025, 17, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.Y.; Bostick, R.M.; Flanders, W.D.; McClellan, W.M.; Thyagarajan, B.; Gross, M.D.; Judd, S.; Goodman, M. Oxidative balance score, colorectal adenoma, and markers of oxidative stress and inflammation. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Patel, A.K.; Shah, N.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Jha, U.K.; Yadav, U.C.; Gupta, P.K.; Pakuwal, U. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in disease and cancer: A review. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4405–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakrim, S.; El Omari, N.; El Yaagoubi, O.M.; Khalid, A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Hamza, S.M.A.; Ibrahim, S.E.; Atifi, F.; Zaid, Y.; Bouyahya, A.; et al. Epi-nutrients for cancer prevention: Molecular mechanisms and emerging insights. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2025, 41, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Wang, H.; Li, G.X.; Yang, Z.; Guan, F.; Jin, H. Cancer prevention by tea: Evidence from laboratory studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 64, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.D.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.J.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, O.; Kim, J. Dietary flavonoids and gastric cancer risk in a Korean population. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4961–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, N.; Markozannes, G.; Kanellopoulou, A.; Critselis, E.; Alhardan, S.; Karafousia, V.; Kasimis, J.C.; Katsaraki, C.; Papadopoulou, A.; Zografou, M.; et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugane, S.; Sasazuki, S. Diet and the risk of gastric cancer: Review of epidemiological evidence. Gastric Cancer 2007, 10, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.Y.; Goodman, M.; Judd, S.; Bostick, R.M.; Flanders, W.D.; McClellan, W. Oxidative balance score as predictor of all-cause, cancer, and noncancer mortality in a biracial US cohort. Ann. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 256–262.e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Chen, X.; Ren, C.; Pan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Association between composite dietary antioxidant index and erectile dysfunction: A cross-sectional study from NHANES. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Tan, Z.; Duan, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Lin, X. Association between the composite dietary antioxidant index and infertility: The national health and nutrition examination survey 2013–2020. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajam, Y.A.; Rani, R.; Ganie, S.Y.; Sheikh, T.A.; Javaid, D.; Qadri, S.S.; Pramodh, S.; Alsulimani, A.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Harakeh, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robards, J.; Evandrou, M.; Falkingham, J.; Vlachantoni, A. Marital status, health and mortality. Maturitas 2012, 73, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reczek, C.R.; Chandel, N.S. ROS Promotes Cancer Cell Survival through Calcium Signaling. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).