Mediterranean Diet Adherence and One-Year Metabolic Changes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: An Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Clinical and Metabolic Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Participants
3.2. Metabolic Changes at One Year Post Diagnosis
3.3. Subgroup Analysis for BMI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| K-MEDAS | Korean Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| HOMA-β | Homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function |
| MD | Mediterranean diet |
| MDS | Mediterranean dietary adherence score |
| METS-IR | Metabolic score for insulin resistance |
| PTC | Papillary thyroid cancer |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| TyG | Triglyceride-glucose |
References
- Kim, S.; Keum, N. Global trends in early-onset and late-onset cancer incidence. J. Public Health 2025, fdaf088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Devesa, S.S.; Sosa, J.A.; Check, D.; Kitahara, C.M. Trends in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, 1974-2013. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2017, 317, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanipour, S.; Zare, R.; Shahedi, A.; Delam, H. Survival rate of thyroid cancer in the Asian countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis study. Endocrine 2023, 82, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.G.; Alhashemi, A.; Fazelzad, R.; Goldberg, A.S.; Goldstein, D.P.; Sawka, A.M. A Systematic Review of Unmet Information and Psychosocial Support Needs of Adults Diagnosed with Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid Off. J. Am. Thyroid Assoc. 2016, 26, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Nan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H. Cause of Death Among Patients With Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 852347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Han, K.; Kim, M.K.; Baek, K.H.; Song, K.H.; Kwon, H.S. Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: A population-based cohort study. Korean J Intern Med 2023, 38, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.S.; Wilson, J.R.; Bernet, V.J. Links between Thyroid Disorders and Glucose Homeostasis. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Song, Y.M. Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Cancer Survivors and Family Members: A Study in a Health Promotion Center. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Willett, W.C. The Mediterranean diet and health: A comprehensive overview. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglione, S.; Di Chiara, T.; Daidone, M.; Tuttolomondo, A. Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome Concerning the Cardiometabolic Risk. Nutrients 2025, 17, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Cao, X.; Gong, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liao, L. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with lower cancer-related fatigue: A cross-sectional analysis from NHANES 2017–2020. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1506055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Tolia, M.; Mentzelou, M.; Tsoukalas, N.; Alexatou, O.; Tsiouda, T.; Tsourouflis, G.; Psara, E.; Bikos, V.; et al. Association of Mediterranean Diet Adherence with Disease Progression Characteristics, Lifestyle Factors and Overall Survival in Gastric Cancer Patients. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.K.; Bychkov, A.; Kakudo, K. Update from the 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Thyroid Tumors: A Standardized Diagnostic Approach. Endocrinol Metab 2022, 37, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, H.M.; Chu, S.H.; Lee, J.W. Development and Validation of a Questionnaire to Measure Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Korean Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Esquivel, A.; Gómez-Bernal, F.; García-González, M.; Hernández-Diaz, M.; Heras-Recuero, E.; de Vera-González, A.; González-Delgado, A.; Quevedo-Rodríguez, A.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; Castañeda, S.; et al. The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR), a Predictor of Cardiovascular Events, Relates to Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, R.; Shetty, S.P. Chapter 29—Assessment of Insulin Resistance: From the Bench to Bedside. In Metabolic Syndrome; Mukhopadhyay, S., Mondal, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 351–365. ISBN 9780323857321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, S.P.; Juvanhol, L.L.; Bressan, J.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M. Triglyceride glucose index: A new biomarker in predicting cardiovascular risk. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 29, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.S.; Kim, S.M.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Cho, G.J.; Han, J.H.; Kim, S.R.; Park, C.Y.; et al. Cut-off points of waist circumference for defining abdominal obesity in the Korean population. Korean J. Obes. 2006, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [CrossRef]
- Mardas, M.; Jamka, M.; Mądry, R.; Walkowiak, J.; Krótkopad, M.; Stelmach-Mardas, M. Dietary habits changes and quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy for epithelial ovarian cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2015, 23, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Shin, D.W.; Shin, J.; Cho, B.; Song, Y.-M. Factors Associated with Dietary Habit Changes in Korean Stomach Cancer Survivors after Cancer Treatment. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coro, D.G.; Hutchinson, A.D.; Banks, S.; Coates, A.M. Dietary Drivers and Challenges of Australian Breast Cancer Survivors: A Qualitative Study. Women’s Health Rep. 2022, 3, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-León, D.; Gómez-Abril, S.Á.; Monzó-Beltrán, L.; Estañ-Capell, N.; Arroyo-Montañés, R.; Bañuls, C.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Sáez, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Has a Protective Role against Metabolic and DNA Damage Markers in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, R.M.; Barbalace, M.C.; Croce, L.; Malaguti, M.; Campennì, A.; Rotondi, M.; Cannavò, S.; Hrelia, S. Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders: The Mediterranean Diet as a Protective Choice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelfi, F.; Tieri, M.; Gori, S.; Nicolis, F.; Petrella, M.C.; Filiberti, A.; Apolone, G.; Titta, L. Do cancer patients change their diet in the e-health information era? A review of the literature and a survey as a proposal for the Italian population. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, G.; Tieri, M.; Fabi, A.; Guarneri, V.; Falci, C.; Dieci, M.V.; Turazza, M.; Ballardini, B.; Bin, A.; Cinieri, S.; et al. Results of the ECHO (Eating habits CHanges in Oncologic patients) Survey: An Italian Cross-Sectional Multicentric Study to Explore Dietary Changes and Dietary Supplement Use, in Breast Cancer Survivors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 705927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bours, M.J.; Beijer, S.; Winkels, R.M.; Van Duijnhoven, F.J.; Mols, F.; Breedveld-Peters, J.J.; Kampman, E.; Weijenberg, M.P.; Van De Poll-Franse, L.V. Dietary changes and dietary supplement use, and underlying motives for these habits reported by colorectal cancer survivors of the Patient Reported Outcomes Following Initial Treatment and Long-Term Evaluation of Survivorship (PROFILES) registry. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keaver, L.; McGough, A.M.; Du, M.; Chang, W.; Chomitz, V.; Allen, J.D.; Attai, D.J.; Gualtieri, L.; Zhang, F.F. Self-Reported Changes and Perceived Barriers to Healthy Eating and Physical Activity among Global Breast Cancer Survivors: Results from an Exploratory Online Novel Survey. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 233–241.e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Zhu, J.; Velazquez, J.; Bernardo, R.; Garcia, J.; Rovito, M.; Hines, R.B. Evaluation of Diet Quality Among American Adult Cancer Survivors: Results From 2005-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaki, I.; Linos, D.; Linos, A. The influence of dietary patterns on the development of thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylik-Mazurek, E.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Kuźniarz-Rymarz, S.; Kieć-Klimczak, M.; Skalniak, A.; Sowa-Staszczak, A.; Gołkowski, F.; Kostecka-Matyja, M.; Pach, D. Dietary patterns as risk factors of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Postep. Hig. I Med. Dosw. 2012, 66, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Arar, Y.; Shilo, M.; Bilenko, N.; Friger, M.; Marsha, H.; Fisher, D.; Fraenkel, M.; Yoel, U. Are Higher Body Mass Index and Worse Metabolic Parameters Associated with More Aggressive Differentiated Thyroid Cancer? A Retrospective Cohort Study. Healthcare 2024, 12, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seib, C.D.; Sosa, J.A. Evolving Understanding of the Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yao, J.; Liao, L.; Dong, J. High prevalence of thyroid carcinoma in patients with insulin resistance: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Aging 2021, 13, 22232–22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shi, L.; Xing, Y.-L. The mediating role of health awareness in the relationship between health information behavior and health outcomes among the older adults. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1492472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Panza, F.; Lampignano, L.; Murro, I.; Di Noia, C.; Triggiani, V.; Giannelli, G.; Sardone, R.; De Pergola, G. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Thyroid Function in Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Apulian Survey. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Overall (n = 345) | Low (n = 107) | Mid (n = 119) | High (n = 119) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 44.4 ± 11.9 | 39.4 ± 9.6 | 45.0 ± 12.2 | 48.3 ± 11.9 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.943 | ||||
| Male | 99 (28.7%) | 32 (29.9%) | 34 (28.6%) | 33 (27.7%) | |
| Female | 246 (71.3%) | 75 (70.1%) | 85 (71.4%) | 86 (72.3%) | |
| SBP (mmHg) | 120.6 ± 15.5 | 118.7 ± 19.4 | 121.5 ± 12.9 | 121.3 ± 13.8 | 0.415 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 77.2 ± 9.9 | 76.7 ± 10.2 | 77.1 ± 9.4 | 77.8 ± 10.1 | 0.751 |
| BMI classification | 0.411 | ||||
| Underweight | 11 (3.2%) | 3 (2.8%) | 1 (0.8%) | 7 (5.9%) | |
| Normal | 132 (38.4%) | 39 (36.4%) | 50 (42.0%) | 43 (36.4%) | |
| Overweight | 64 (18.6%) | 22 (20.6%) | 19 (16.0%) | 23 (19.5%) | |
| Obese | 137 (39.8%) | 43 (40.2%) | 49 (41.2%) | 45 (38.1%) | |
| Alcohol consumption, yes (%) | 164 (47.5%) | 63 (58.9%) | 61 (51.3%) | 40 (33.6%) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status, yes (%) | 16 (4.6%) | 9 (8.4%) | 4 (3.4%) | 3 (2.5%) | 0.100 |
| Physical activity, yes (%) | 143 (42.6%) | 35 (34.7%) | 50 (43.1%) | 58 (48.7%) | 0.110 |
| HTN, yes (%) | 107 (31.0%) | 28 (26.2%) | 34 (28.6%) | 45 (37.8%) | 0.134 |
| T2DM, yes (%) | 35 (10.1%) | 4 (3.7%) | 11 (9.2%) | 20 (16.8%) | 0.004 |
| Dyslipidemia, yes (%) | 141 (40.9%) | 38 (35.5%) | 45 (37.8%) | 58 (48.7%) | 0.095 |
| Metabolic syndrome, yes (%) | 102 (30.9%) | 28 (27.2%) | 27 (24.1%) | 47 (40.9%) | 0.016 |
| Abdominal obesity | 214 (62.2%) | 68 (63.6%) | 74 (62.2%) | 72 (61.0%) | 0.922 |
| Increased blood pressure | 113 (32.8%) | 31 (29.2%) | 38 (31.9%) | 44 (37.0%) | 0.473 |
| Increased fasting glucose | 133 (38.9%) | 33 (30.8%) | 40 (34.5%) | 60 (50.4%) | 0.006 |
| Decreased HDL-C | 84 (25.1%) | 22 (21.0%) | 24 (20.9%) | 38 (33.0%) | 0.061 |
| Increased triglycerides | 91 (28.4%) | 30 (30.6%) | 24 (21.8%) | 37 (33.0%) | 0.147 |
| Thyroidectomy | 0.063 | ||||
| Partial | 234 (67.8%) | 77 (72.0%) | 84 (70.6%) | 73 (61.3%) | |
| Total | 111 (32.2%) | 30 (28.0%) | 35 (29.4%) | 46 (38.7%) | |
| Radioactive iodine therapy | 81 (23.5%) | 21 (19.6%) | 26 (21.8%) | 34 (28.6%) | 0.251 |
| Levothyroxine replacement | 336 (97.4%) | 102 (95.3%) | 115 (96.6%) | 119 (100.0%) | 0.047 |
| Variable | At Diagnosis | Post-Diagnosis for One Year | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (n = 345) | Low (n = 107) | Mid (n = 119) | High (n = 119) | p-Value | Overall (n = 345) | Low (n = 107) | Mid (n = 119) | High (n = 119) | p-Value | |
| BMI | 24.5 ± 4.1 | 24.5 ± 4.3 | 24.4 ± 3.8 | 24.5 ± 4.3 | 0.987 | 24.3 ± 4.0 | 24.5 ± 4.1 | 24.5 ± 3.9 | 23.9 ± 3.9 | 0.671 |
| Glucose | 99.9 ± 12.8 | 97.4 ± 9.0 | 99.3 ± 13.4 | 102.8 ± 14.5 | 0.005 | 100.1 ± 13.2 | 99.1 ± 14.7 | 99.5 ± 11.7 | 101.8 ± 13.1 | 0.29 |
| HbA1c | 6.1 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 6.0 ± 0.7 | 6.4 ± 0.8 | 0.021 | 5.6 ± 0.4 | 5.6 ± 0.3 | 5.6 ± 0.4 | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 0.178 |
| Insulin | 10.8 ± 7.9 | 10.3 ± 5.5 | 10.9 ± 9.3 | 11.2 ± 8.2 | 0.705 | 9.4 ± 9.0 | 11.3 ± 13.6 | 8.2 ± 6.2 | 8.9 ± 4.9 | 0.219 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.7 ± 2.2 | 2.5 ± 1.4 | 2.7 ± 2.7 | 2.9 ± 2.2 | 0.412 | 2.4 ± 2.5 | 2.9 ± 3.9 | 2.1 ± 1.6 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 0.288 |
| METS-IR | 36.1 ± 9.7 | 35.8 ± 8.5 | 36.2 ± 11.8 | 36.3 ± 8.5 | 0.928 | 34.6 ± 7.6 | 34.3 ± 8.3 | 35.0 ± 7.8 | 34.4 ± 6.7 | 0.885 |
| HOMA-β | 110.3 ± 86.5 | 110.5 ± 60.1 | 112.8 ± 102.1 | 107.6 ± 90.1 | 0.903 | 94.3 ± 70.4 | 112.9 ± 95.3 | 80.4 ± 55.6 | 91.0 ± 51.5 | 0.072 |
| Total Cholesterol | 190.7 ± 38.2 | 192.0 ± 36.5 | 191.6 ± 39.3 | 188.7 ± 38.9 | 0.784 | 190.3 ± 37.4 | 191.8 ± 31.8 | 188.5 ± 38.6 | 190.8 ± 40.8 | 0.818 |
| Triglycerides | 129.8 ± 81.9 | 131.1 ± 93.8 | 122.4 ± 78.1 | 136.0 ± 74.1 | 0.457 | 113.7 ± 73.4 | 115.6 ± 66.2 | 108.6 ± 65.1 | 117.9 ± 88.5 | 0.743 |
| HDL-C | 56.1 ± 14.9 | 58.2 ± 14.8 | 56.3 ± 14.9 | 53.9 ± 14.7 | 0.106 | 59.7 ± 15.0 | 60.5 ± 14.2 | 59.1 ± 16.3 | 59.7 ± 14.3 | 0.871 |
| LDL-C | 116.3 ± 33.5 | 120.2 ± 34.0 | 116.6 ± 33.8 | 112.6 ± 32.7 | 0.264 | 112.5 ± 33.1 | 116.6 ± 34.0 | 111.5 ± 33.1 | 109.6 ± 32.5 | 0.487 |
| TyG | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 8.7 ± 0.6 | 0.071 | 8.5 ± 0.5 | 8.5 ± 0.6 | 8.5 ± 0.5 | 8.5 ± 0.6 | 0.855 |
| T3 | 0.94 ± 0.19 | 0.94 ± 0.15 | 0.95 ± 0.19 | 0.94 ± 0.21 | 0.883 | 1.00 ± 0.21 | 1.03 ± 0.20 | 0.98 ± 0.22 | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 0.276 |
| Free T4 | 1.01 ± 0.23 | 0.99 ± 0.10 | 1.00 ± 0.11 | 1.04 ± 0.37 | 0.418 | 1.09 ± 0.18 | 1.08 ± 0.17 | 1.08 ± 0.18 | 1.10 ± 0.19 | 0.654 |
| TSH | 1.87 ± 1.47 | 1.92 ± 1.56 | 1.74 ± 1.03 | 1.94 ± 1.74 | 0.419 | 1.85 ± 6.68 | 1.14 ± 1.26 | 1.69 ± 4.40 | 2.63 ± 10.31 | 0.149 |
| Variables | Coefficient (95% CI) for Change | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (n = 345) | Low MDS (n = 107) | Mid MDS (n = 119) | High MDS (n = 119) | Low vs. Mid | Low vs. High | Mid vs. High | |
| BMI | −0.28 (−0.53, −0.03) * | −0.34 (−0.78, 0.11) | −0.36 (−0.77, 0.06) | −0.14 (−0.57, 0.29) | 0.954 | 0.531 | 0.998 |
| Glucose | 0.02 (−1.21, 1.25) | 1.58 (−0.69, 3.86) | −0.12 (−2.20, 1.96) | −1.11 (−3.16, 0.95) | 0.279 | 0.085 | 0.303 |
| HbA1c | −0.12 (−0.21, −0.04) * | −0.05 (−0.23, 0.13) | −0.17 (−0.31, −0.03) * | −0.121 (−0.26, 0.02) | 0.313 | 0.551 | 0.272 |
| Insulin | −0.92 (−2.23, 0.39) | 1.13 (−1.21, 3.48) | −1.65 (−3.93, 0.63) | −2.03 (−4.22, 0.17) | 0.095 | 0.054 | 0.062 |
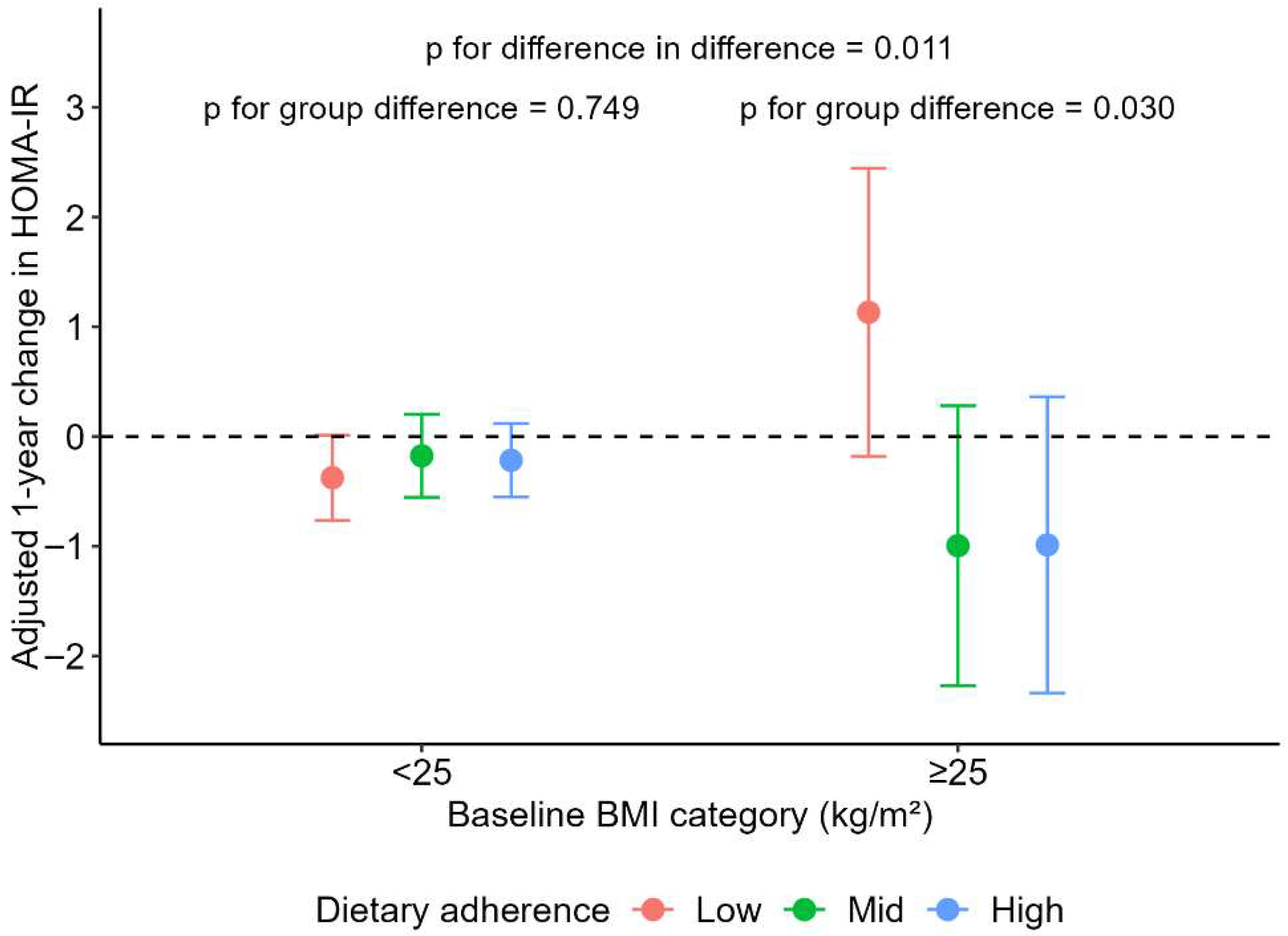
| HOMA-IR | −0.21 (−0.58, 0.17) | 0.44 (−0.22, 1.11) | −0.45 (−1.10, 0.19) | −0.53 (−1.15, 0.09) | 0.058 | 0.036 | 0.047 |
| METS-IR | −1.40 (−1.90, −0.90) * | −1.27 (−2.17, −0.36) * | −1.23 (−2.07, −0.39) * | −1.69 (−2.57, −0.82) * | 0.953 | 0.508 | 0.691 |
| HOMA-β | −10.42 (−20.76, −0.08) * | 0.27 (−18.25, 18.80) | −14.95 (−33.08, 3.18) | −15.61 (−32.94, 1.72) | 0.250 | 0.220 | 0.140 |
| Total Cholesterol | −0.82 (−5.11, 3.47) | −2.10 (−10.06, 5.85) | −3.13 (−10.40, 4.14) | 2.47 (−4.71, 9.64) | 0.852 | 0.403 | 0.869 |
| Triglycerides | −17.15 (−27.49, −6.81) * | −15.95 (−34.80, 2.89) | −15.68 (−32.85, 1.48) | −19.62 (−37.71, −1.53) * | 0.983 | 0.783 | 0.884 |
| HDL-C | 4.10 (2.80, 5.41) * | 2.51 (0.18, 4.84) * | 3.29 (1.16, 5.41) * | 6.54 (4.28, 8.80) * | 0.629 | 0.015 | 0.040 |
| LDL-C | −4.98 (−9.57, −0.39) * | −5.26 (−13.60, 3.07) | −5.05 (−12.66, 2.55) | −4.71 (−12.78, 3.35) | 0.971 | 0.926 | 0.751 |
| TyG index | −0.12 (−0.19, −0.05) * | −0.08 (−0.20, 0.05) | −0.09 (−0.20, 0.03) | −0.19 (−0.31, −0.07) * | 0.898 | 0.190 | 0.726 |
| BMI < 25 kg/m2 | p-Value | BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | p-Value | p for DID | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Mid | High | Low | Mid | High | ||||
| Glucose | −0.42 (−2.90, 2.07) | 0.75 (−1.46, 2.97) | −0.66 (−2.81, 1.49) | 0.638 | 3.95 (−0.09, 7.99) | −1.37 (−5.18, 2.44) | −0.99 (−4.89, 2.90) | 0.115 | 0.122 |
| Insulin | −1.53 (−3.04, −0.01) * | −0.74 (−2.22, 0.74) | −0.93 (−2.24, 0.37) | 0.753 | 3.30 (−1.18, 7.78) | −3.24 (−7.59, 1.12) | −3.87 (−8.48, 0.74) | 0.043 | 0.021 |
| METS-IR | −0.68 (−1.68, 0.33) | −0.26 (−1.28, 0.76) | −0.88 (−1.82, 0.05) | 0.659 | −2.08 (−3.54, −0.63) * | −2.37 (−3.60, −1.14) * | −3.12 (−4.60, −1.63) * | 0.575 | 0.316 |
| HOMA-β | −12.83 (−29.30, 3.64) | −7.37 (−23.44, 8.70) | −11.37 (−25.52, 2.79) | 0.893 | 10.52 (−24.02, 45.06) | −26.70 (−60.56, 7.17) | −25.95 (−61.73, 9.83) | 0.214 | 0.327 |
| Total cholesterol | 1.64 (−8.67, 11.94) | −1.79 (−10.95, 7.38) | 8.87 (−0.03, 17.77) | 0.249 | −6.46 (−18.86, 5.95) | −4.57 (−16.26, 7.13) | −7.12 (−19.09, 4.85) | 0.953 | 0.508 |
| Triglycerides | −21.78 (−44.12, 0.57) | −16.66 (−37.92, 4.61) | −12.514 (−32.88, 7.85) | 0.830 | −7.26 (−38.92, 24.40) | −18.67 (−46.25, 8.91) | −24.59 (−57.88, 8.69) | 0.731 | 0.364 |
| HDL-C | 3.16 (−0.32, 6.64) | 2.60 (−0.82, 6.03) | 5.91 (2.67, 9.14) * | 0.331 | 1.72 (−1.30, 4.73) | 4.32 (1.77, 6.87) * | 7.35 (4.18, 10.51) * | 0.039 | 0.860 |
| LDL-C | −4.40 (−15.93, 7.14) | −1.63 (−12.66, 9.40) | −0.53 (−11.09, 10.03) | 0.887 | −5.18 (−17.37, 7.01) | −9.38 (−19.99, 1.24) | −12.54 (−25.48, 0.40) | 0.698 | 0.812 |
| TyG | −0.15 (−0.30,−0.003) * | −0.11 (−0.25, 0.03) | −0.13 (−0.26, 0.01) | 0.911 | 0.03 (−0.19, 0.23) | −0.10 (−0.28, 0.08) | −0.26 (−0.48, −0.04) * | 0.165 | 0.086 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Heo, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kang, S.-W.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-W. Mediterranean Diet Adherence and One-Year Metabolic Changes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: An Observational Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213420
Shin J, Heo S-J, Lee Y-J, Kang S-W, Kwon Y-J, Lee J-W. Mediterranean Diet Adherence and One-Year Metabolic Changes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: An Observational Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213420
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jinyoung, Seok-Jae Heo, Yae-Ji Lee, Sang-Wook Kang, Yu-Jin Kwon, and Ji-Won Lee. 2025. "Mediterranean Diet Adherence and One-Year Metabolic Changes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: An Observational Study" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213420
APA StyleShin, J., Heo, S.-J., Lee, Y.-J., Kang, S.-W., Kwon, Y.-J., & Lee, J.-W. (2025). Mediterranean Diet Adherence and One-Year Metabolic Changes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: An Observational Study. Nutrients, 17(21), 3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213420






