Abstract
Background: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is characterised by chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland. The impact of a health-promoting diet and probiotics on health and quality of life, as well as on the anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody (anti-TPO), is increasingly being researched. However, the relevance of these factors to the course of HT is yet to be fully established. Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the impact of a 12-week nutritional intervention, comprising a rational, health-promoting diet supplemented with the probiotic strain Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v (Lp299v), on eating habits, nutritional status, health and quality of life in patients diagnosed with HT. Methods: The 12-week study involved 64 female patients with HT, divided into two groups: the NE+Lp299v group, which received nutritional education and Lp299v (n = 32); and the NE+placebo group, which received nutritional education and placebo (n = 32). Before and after the intervention, anthropometric parameters, body composition analysis, blood pressure, blood anti-TPO levels, dietary habits, quality of life, and gastrointestinal symptoms were assessed. Results: The NE+Lp299v intervention improved overall quality of life (60.94 pts. vs. 35.94 pts.), including 12 of 14 domains, and the diet quality index (11.03 pts. vs. 18.50 pts.). The NE+placebo group improved overall quality of life (54.69 pts. vs. 39.84 pts.), including 3 of 14 domains, and the diet quality index (12.34 pts. vs. 19.18 pts.). Anti-TPO blood levels and body mass index did not improve in either group. Conclusions: Lp299v can enhance the efficacy of nutritional education in improving the quality of life of individuals diagnosed with HT. However, these benefits appear to be independent of anti-TPO levels.
1. Introduction
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases that gradually destroys the thyroid parenchyma and negatively affects the quality of life in patients [1]. The disease manifests more frequently in women than in men (4:1 ratio) [2]. It is not fully understood why women are more often affected than men, although the cause is believed to be the role of female sex hormones or X chromosome inactivation [3]. The diagnosis is made by the physician following the identification of elevated levels of antibodies against thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) and thyroglobulin (anti-TG). The presence of anti-TPO can be detected in 95% of patients, while anti-TG is observed in 60–80% of cases [1,3]. Also important in diagnosis are the occurrence of clinical symptoms [1,3] and an ultrasound examination, which can observe the infiltration of T and B lymphocytes into the thyroid tissues [3]. The infiltration leads to the atrophy of thyroid cells, which results in the development of subclinical or overt hypothyroidism [4]. Inflammation in HT has also been demonstrated to have a detrimental effect on quality of life [5,6], particularly in the neuropsychiatric domain [6,7]. The treatment regimen involves the administration of levothyroxine (LT4), which improves hormone levels in hypothyroidism coexisting with HT. The treatment of Hashimoto’s disease represents a significant financial burden to both patients and the state. According to the National Health Fund, over PLN 114 million was spent on levothyroxine treatment in Poland in 2023; of this amount, the state reimbursed less than PLN 62 million [8].
It is increasingly recognised that diet is a necessary element of HT treatment. Previous studies, with varying results, have examined elimination diets (e.g., gluten-free, lactose-free, iodine-restricted, or restricted to selected foods), energy deficits, and the supplementation of black cumin [9,10]. The following dietary regimens have been employed: an autoimmune protocol [11,12], a low-carb diet [13], and a Mediterranean diet [10,14,15]. The anti-inflammatory nature of the Mediterranean diet, which is comparable to a rational, balanced diet, may result in a reduction in inflammation. Consequently, the Mediterranean diet could be considered a dedicated dietary strategy in HT [10,14,16]. Such a diet contains many food products with health-promoting effects and is therefore varied and provides nutrients with an anti-inflammatory effect on anti-TPO and/or anti-TG antibodies. These nutrients include, but are not limited to, vitamin D [17,18], selenium [19], iron [20,21,22], vitamin C [23], magnesium, zinc [24], iodine [25], and eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids [26]. Nevertheless, given the variety of intervention strategies and their duration, as well as the differing group sizes, it is still challenging to determine the most suitable diet for HT [9].
The impact of microbiota and probiotics on autoimmune diseases, including HT, is a subject that is being discussed with increasing frequency. In a ten-week supplementation study, the administration of a synbiotic containing Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium longum, Streptococcus thermophilus, and fructo-oligosaccharide resulted in improvements in blood pressure and quality of life in patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism. However, the study observed no significant impact on depression and TSH levels [27]. AkbariRad et al. [28] reported beneficial effects for synbiotics (a blend of bacteria, including Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactobacillus gasseri, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium longum, and Streptococcus thermophilus, along with fructooligosaccharides) supplementation on fatigue and thyroid function in hypothyroid patients. However, two meta-analyses examining the effect of probiotics and/or prebiotics on the course of various thyroid diseases concluded that probiotics did not significantly improve anti-TPO or anti-TG activity in HT [29,30].
To the best of our knowledge, no study yet has been conducted with the Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v strain (Lp299v) among patients with HT. A growing body of research is indicating its immunological effects, e.g., it improves inflammation in studies on animal models of inflammatory bowel disease [31], and in humans it reduces the concentration of IL-8 and IL-12 [32,33]. Lp299v may improve iron metabolism [34,35], the course of irritable bowel syndrome [36], and cognitive function in patients with depression [37]. Therefore, it may be posited that Lp299v could have therapeutic use in patients with HT as an adjunct to pharmacological and dietary treatment.
The objective of the present study was to evaluate the impact of a 12-week nutritional intervention, characterised by an anti-inflammatory, Mediterranean-style diet, augmented by the probiotic strain Lp299v, on the dietary habits, nutritional status, health, and quality of life of female patients diagnosed with HT. It is hypothesised that Lp299v, when incorporated into a balanced, healthy diet, may yield additional health benefits, particularly in terms of quality of life. In order to enhance the study’s validity, a randomised, double-blind design was employed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
The study design comprised 12 weeks of individualised nutritional education, provided by a dietitian, and the administration of the probiotic Lp299v (the “NE+Lp299v” or probiotic group) or a placebo (the “NE+placebo” or placebo group). The study was a single-centre, double-blind dietary intervention in which the probiotic and placebo capsules appeared identical. All measurements were collected during visits to the Dietetics Clinic at the Department of Dietetics, Warsaw University of Life Sciences (SGGW). The data collection process was executed through the utilisation of CAWI (Computer-Assisted Online Interviewing) and PAPI (Paper-and-Pen-In-Person Interviewing) methodologies. Nutrition education was conducted either online or at the Dietetics Clinic, depending on the participant’s preferences or capabilities. The personal results obtained were provided to participants free of charge. Prior to the commencement of the study, participants were furnished with comprehensive information regarding its objectives, scope, and the option of withdrawing at any stage without the need to provide a justification.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Human Nutrition, Warsaw University of Life Sciences WULS, Poland (Resolutions No. 22/2021, 18 June 2021 and No. 21/2022, 18 July 2022) for studies involving humans. Participation in the study was voluntary, and informed consent was obtained from all subjects. The participants did not receive any form of financial compensation or reimbursement for their involvement in the study.
2.2. Participant Selection
Recruitment of the study sample was based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, conducted using snowball sampling, using social media platforms, primarily social media groups for residents of Warsaw and the surrounding area and dedicated to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The study was also promoted at a partner medical facility and pharmacy.
The following inclusion criteria were employed: (1) a diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis based on the presence of anti-TPO and anti-TG antibodies, or characteristic ultrasound images indicative of HT; (2) thyroid function assessed for euthyroidism based on the results of tests performed by the patient; (3) female gender; (4) age between 18 and 64 years; (5) normal body weight (BMI 18.50–24.99 kg/m2) or excessive body weight (BMI ≥ 25.00 kg/m2); and/or a low-quality diet (low pHDI-10) [38]; (6) informed consent to participate in the study. The following criteria were used to determine exclusion from the study: (1) thyroid diseases other than HT, cancer, coeliac disease, Dühring’s disease or gluten allergy; (2) pregnancy, lactation; (3) administration of Lp299v or weight loss medications.
To calculate the minimum number of participants in both groups, a 50% improvement in overall quality of life after the intervention was presumed (assuming a 5% significance level and 80% power). Based on this, each group should have 47 participants. A minimum of 100 patients was assumed to be eligible for the study, to account for potential dropout.
2.3. Randomisation and Blinding
Patients were randomly assigned to a probiotic group (nutrition education with Lp299v) or a placebo group (nutrition education with placebo) according to a computer-generated randomisation list created by an investigator not involved in the study. The study was double-blind, meaning that neither the patient nor the investigator conducting the experiment knew which group had received the probiotic until the end of the nutritional intervention.
2.4. Intervention Procedure
A 12-week individual nutritional education programme was conducted in two groups. Additionally, one group received the Lp299v strain (NE+Lp299v group) and the other received a placebo (NE+P group). Prior to and after the education programme, dietary habits were evaluated using a three-day food and beverage intake questionnaire. Patients were also asked to complete questionnaires to assess: (1) dietary habits (FFQ-6 and KomPAN® questionnaire [38,39]); (2) quality of life with thyroid disease (ThyPROpl) [40]; (3) the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) [41]. Anthropometric measurements (body weight and height, waist and hip circumference), body composition analysis, peripheral blood pressure, and measurement of anti-TPO antibody concentration in blood were also performed. All parameters were measured at the baseline and after a 12-week period of intervention in order to assess the difference, and if possible, to compare to reference values. The study design is presented below (Figure 1).
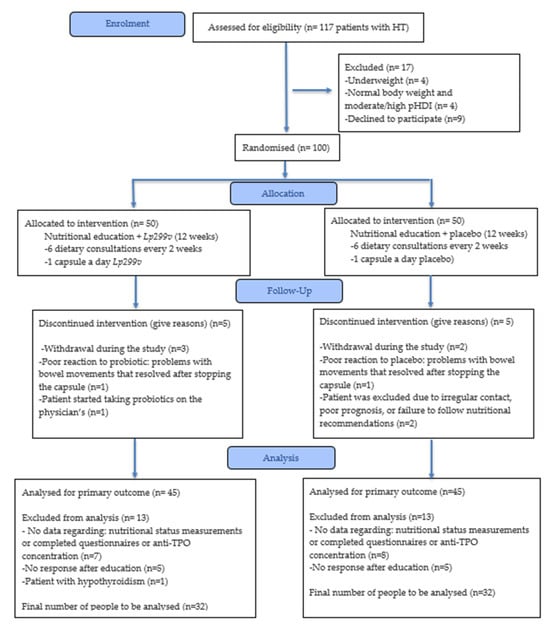
Figure 1.
The study diagram. HT—Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; pHDI-10—Pro-Healthy Diet Index 10; NE+Lp299v—nutrition education + Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v; NE+P—nutrition education + placebo; anti-TPO-antibodies against thyroid peroxidase.
2.5. Nutrient Intake and Diet Quality
The estimation of energy and nutrient intake at the baseline and after the intervention was assessed using a three-day food and beverage intake questionnaire recommended by the Polish Society of Dietetics and the National Consultant for Family Medicine [42]. Patients were asked to record all food and drink consumed, including spices, particularly salt, for two typical days, e.g., weekdays, and one non-typical day (e.g., weekends). The estimation of energy and nutrient intake was assessed using the “DietetykPro®” dietary programme (Wrocław, Poland). The programme incorporates a Polish nutrient database for food products and dishes [43], and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) nutrient database [44]. In instances where food items were not present in the database, the most similar product was selected for the purpose of nutrient calculation. Nutrient intake was compared with Polish dietary standards and recommendations from 2020 [45]. Energy intake was compared to the individual’s total energy requirement, which was estimated by multiplying their basal metabolic rate, calculated using the Mifflin-St-Jeor equation [46], by their physical activity index (PAL) based on the interview: 1.4–1.69—for a sedentary or lightly active lifestyle; 1.7–1.99—for an active or moderately active lifestyle; and 2.00–2.40—for a very active lifestyle [47].
The Polish-validated Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ-6) was used to assess the frequency of consumption of selected food products and dietary habits. Participants were asked to select one of six categories indicating the frequency of food consumption in the past 12 months: (1) never or almost never (0 times/day); (2) once a month or less often (0.025 times/day); (3) several times a month (0.1 times/day); (4) several times a week (0.571 times/day); (5) daily (1 time/day); (6) several times a day (2 times/day) [39].
The quality of the diet was evaluated using two validated questionnaires: the Healthy Diet Index (pHDI-10) and the Unhealthy Diet Index (nHDI-14) [38]. The pHDI-10 contains 10 questions pertaining to the frequency of consuming health-promoting foods, while the nHDI-14 comprises 14 questions regarding the frequency of consumption unhealthy foods. The cafeteria of answers, with designated daily frequencies assigned to each option were as follows: (1) never (0 times/day); (2) 1–3 times a month (0.06 times/day); (3) once a week (0.14 times/day); (4) few times a week (0.5 times/day); (5) once a day (1 time/day); (6) few times a day (2 times/day). The ranges for both the pHDI-10 and nHDI-14 were as follows: scores of 0–33 points indicate a low index; 34–66 points indicate a moderate index, and 67–100 points indicate a high index. The DQI (Diet-Quality Index) was also estimated, with the calculation based on the sum of the positive pHDI-10 and negative nHDI-14 scores. The DQI scale used was as follows: (1) −100 to −26 points–a high intensity of non-healthy dietary characteristics; (2) −25 to 25 points-a low intensity of non-healthy and pro-healthy dietary characteristics; (3) 26 to 100 points-a high intensity of pro-healthy dietary characteristics [38].
2.6. Selected Lifestyle and Health Factors
All participants were questioned about their medical care, medications, dietary supplements, and herbal remedies. Patients were requested to refrain from modifying their supplementation regimen (with the exception of vitamin D supplementation) and to report any alterations to their medication.
2.7. Quality of Life
The quality of life of study participants at the baseline and after the intervention was assessed using two instruments: (1) the Thyroid Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire (ThyPROpl) [40]; and (2) the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) [41]. ThyPROpl is a thyroid-specific questionnaire validated for the Polish population by Sawicka-Gutaj et al. [40]. It captures both physical and psychological dimensions of disease impact, including symptoms, emotional functioning, cognitive complaints, fatigue, and social participation. The questionnaire consists of a 13-point scale including questions regarding: (1) goitrogen symptoms; (2) hyperthyroid symptoms; (3) hypothyroid symptoms; (4) eye symptoms; (5) tiredness; (6) cognitive complaints; (7) anxiety; (8) depressivity; (9) emotional susceptibility; (10) impaired social life; (11) impaired daily life; (12) impaired sexual life; (13) cosmetic complaints; and (14) overall quality of life. The ThyPROpl questionnaire uses a 5-point Likert scale, where respondents indicate the frequency or intensity of specific symptoms and experiences (e.g., from “not at all” to “very much”) [40]. The score range is 0 to 100, with higher scores reflecting greater symptom burden or lower quality of life.
The validated Polish version of the GSRS consists of 15 test items grouped into five symptom groups (reflux, abdominal pain, indigestion, diarrhoea, and constipation). The response scale is 7-point, where 1 indicates no bothersome symptoms and 7 indicates very bothersome symptoms [41].
2.8. Nutritional and Health Status
All anthropometric measurements were performed in accordance with the Anthropometry Procedures Manual by a trained dietitian using standardised equipment [48]. Body weight (BW, kg) was measured to the nearest 0.1 kg using an electronic digital scale (ACCUNIQ BC720, SELVAS Healthcare, Korea), with participants wearing light indoor clothing and no shoes. Height (H, cm) was assessed in the Frankfort horizontal plane, barefoot, with a precision of 0.1 cm. Waist circumference (WC, cm) and hip circumference (HC, cm) were measured with an inelastic measuring tape (SECA 201, Hamburg, Germany) to the nearest 0.1 cm, following standardised procedures [49]. Central obesity was defined as waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) > 0.8 [50] and/or waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) ≥ 0.5 [51]. Overweight was defined as a body mass index (BMI) between 25.00 and 29.99 kg/m2, while obesity was defined as a BMI ≥ 30.00 kg/m2 [52]. Body composition (body fat, muscle mass, and total body water) was analysed with the bioelectrical impedance (BIA) method using the body composition analyser (ACCUNIQ BC-720, SELVAS Healthcare, Korea). This BIA method was omitted in patients with contraindications to the procedure, including those with metal parts in their bodies. Detailed measurement procedures are described in the previously published protocol (Section 3.8.) [53].
Peripheral blood pressure was examined with the subject in a sitting position, after a minimum of 5 min of rest, with the ACCUNIQ BC-250. Detailed measurement procedures are described in the previously published protocol (Section 3.9.) [53].
The anti-TPO titter was assessed in venous blood samples obtained from a cubital vein of the forearm by qualified medical laboratory personnel. Serum concentrations were measured using immunochemistry on the “Alinity I” analyser (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, IL, USA) and compared with the reference value of <5.61 IU/mL. Detailed measurement procedures are described in the previously published protocol (Section 3.10.) [53].
2.9. Nutrition Education
The nutritional education programme (6 individual meetings spaced about 2 weeks apart, a total of 6 h of education) is described in detail in the protocol in Section 3.11. [53]. All educational materials were based on scientific literature and standards of the Polish Society of Dietetics and the National Institute of Public Health–National Institute of Hygiene. Each patient received not only educational materials, but also a sample menu based on individual energy needs, illustrating appropriate meals and portion sizes. Throughout the intervention, patients were provided with an access to a dietitian support, and this was not limited to meetings.
2.10. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v
The experimental group received 1 × 1010 CFU (colony-forming units) of Lp299v contained in Sanprobi IBS®. The carrier was potato starch and magnesium salts of fatty acids (capsule shell: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose). The control group received a placebo capsule containing granulated potato starch and magnesium stearate (capsule shell: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose). Patients were instructed to take one capsule (probiotic in the experimental group and placebo capsule in the control group) once daily with a meal. Side effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v are rare and do not pose a threat to the patient. Detailed information regarding the Lp299v capsules and placebo intake can be found in the protocol in Section 3.12. [53].
2.11. Statistical Analyses
All statistical analyses were performed using Statistica 13.1 PL (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA; StatSoft, Krakow, Poland). Descriptive statistics were generated for all variables of interest. Normality of the variables was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test before statistical analysis. The student t-test was used for quantitative data with a normal distribution, and the Mann–Whitney test for non-normally distributed data. The Wilcoxon test was used for ordinal dependent variables within groups (before vs. after education). The two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post hoc tests was performed to assess the effectiveness of the nutritional intervention and to observe differences between the probiotic and placebo groups. A Bonferroni post hoc analysis was then used to determine which group showed significance. The differences in categorical variables between groups were tested using the Pearson chi-square test, and the McNemar test was used for comparisons within the group (before vs. after intervention). The average treatment effect (ATE) was calculated as the mean difference in the obtained value between the probiotic group and the placebo group. A p value of ≤0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Group
A total of 64 women with HT completed the study, 32 of whom were assigned to the probiotic group (NE+Lp299v), and the remaining 32 were assigned to the placebo group (NE+P). All participants had euthyroid thyroid function. The average age in the probiotic group was 41.53 ± 11.77 years, and in the placebo group, 39.28 ± 8.97 years. Levothyroxine administration was reported by 84% of the probiotic group and 78% of the placebo group. Neither age nor the levothyroxine usage differed between the groups (Table 1).

Table 1.
Group characteristics (SD, standard deviation; Me, median; Min—minimum, Max—maximum).
3.2. Effect of the Intervention on Nutritional Status and Health Parameters
Prior to the intervention, the mean BMI in both groups indicated that the subjects were overweight. The mean WHR and WHtR scores indicated the risk of metabolic diseases, respectively. The mean blood pressure scores indicated no hypertension among studied individuals. The probiotic group showed a decrease in hip circumference, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure after the intervention. However, the nutritional intervention with Lp299v or placebo had no effect on other anthropometric measurements, body composition, pulse rate, and the anti-PRO concentration. The magnitude of change over time showed a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure in the probiotic group. However, in the case of WHR and muscle mass, the placebo group demonstrated favourable outcomes (Table 2).

Table 2.
Effect of the intervention on nutritional status and health parameters among the studied women. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
The body weight status and other health risk indicators examined, based on the waist circumference, WHR, and WHtR (e.g., metabolic risk, abdominal obesity), did not differentiate between groups, either before or after the intervention. The intervention, in the form of nutritional education with the administration of probiotics or a placebo, resulted in a higher percentage of people with normal body weight in the probiotic group and a lower percentage of people with “no abdominal obesity” according to the WHR index (Supplementary Materials: Table S1).
3.3. Effect of the Intervention on Quality of Life
Prior to the intervention, subjects in both groups reported fatigue as the most bothersome symptom, followed closely by decreased overall quality of life and depression. Following the intervention, fatigue was reported as the most bothersome symptom, with depression ranking second. In the placebo group, the overall quality of life dropped to third place, and in the probiotic group, it dropped to fourth place. The least bothersome symptom prior to the intervention in the probiotic group was impaired social life. In contrast, the least bothersome symptom in the placebo group was goitre symptoms (Table 3). The implemented nutritional intervention with probiotics or placebo significantly improved quality of life measured by the ThyPROpl questionnaire over time in almost all aspects of life, except for goitrogenic symptoms. Subsequent post hoc analyses indicated more favourable outcomes in the probiotic group in comparison to the placebo group (significant change for 12 of the 14 categories vs. 3 of the 14 categories, respectively). The ATE value indicated that the addition of probiotics to nutritional education improved the women’s quality of life in all areas except hyperthyroid symptoms. In the probiotic group, the overall quality of life score decreased significantly from baseline (mean difference = −25.0 points, 95% CI: −42.3 to −7.7; t(31) = −2.95; p = 0.006), with an estimated statistical power of approximately 85%. In the placebo group, the overall quality of life score also decreased significantly (mean difference = −14.9 points, 95% CI: −29.2 to −0.5; t(31) = −2.11; p = 0.043), although the statistical power of this comparison was limited (≈57%).

Table 3.
Effect of the intervention on quality of life among the studied women. Results are presented as mean and standard deviation.
With regard to the GSRS, the most troublesome reported symptom in both groups was indigestion, both prior to and following the intervention. The least problematic symptom in all individuals was found to be reflux (and diarrhoea in the probiotic group prior to the intervention). The nutritional intervention was found to have a beneficial effect on all symptoms. In post hoc analyses, a beneficial effect was detected in three out of five domains, while for the placebo group, this effect was observed in two out of five domains, respectively. The ATE value indicated that the addition of probiotics to nutritional education improved the symptoms in three domains: constipation, abdominal pain and reflux (Table 3).
3.4. Effect of the Nutritional Education on Diet Quality and Dietary Intake
Examined diet quality index categories (pHDI-10, nHDI-14, DQI) did not differ between the groups before and after the intervention. Following the intervention, there was a significant decrease in the frequency of low-intensity unhealthy traits and a significant increase in the frequency of high-intensity health-promoting traits in the placebo group (Table 4). Higher percentage of better dietary quality according to the DQI and moderate pHDI levels were also observed in the placebo and probiotic groups. (Supplementary Table S2). The intervention had a significant impact on dietary quality indicators, with positive scores increasing and negative scores decreasing. Post hoc analyses confirmed a significant effect of time for both groups on the DQI and nHDI-14 (Table 4).

Table 4.
Effect of the nutritional education on diet quality among the studied women. Results are presented as mean and standard deviation.
Nutrition education increased the frequency of consumption of some of the healthy foods listed in the pHDI-10 index, including whole-wheat bread in the probiotic group and buckwheat, oatmeal and whole-grain pasta in the placebo group. In both groups, the frequency of fish consumption showed an increase following the intervention (Supplementary Materials, Table S3). Consequently, the educational programme led to a decline in the frequency of consumption of selected products from the n-HDI-14 index. These products were: fast food, cheese and alcohol in the probiotic group; fried foods, butter and sweetened beverages in the placebo group, and cold cuts, sausages and sweets in both groups. The frequency of tomato consumption increased significantly in the probiotic group after the education programme.
Following the nutritional education programme, several beneficial changes were observed in energy and nutrient intake. The intake of energy, carbohydrates, sucrose, total fat, and saturated fat decreased, while the intake of alpha-linolenic acid, omega 3, and vitamin D increased. In post hoc analyses, the significant effect remained for the probiotic group for the majority of the analysed components. In this group, the beneficial effect of education was found to be significantly greater for EPA+DHA and vitamin B12 (Table 5).

Table 5.
Effect of the nutritional education on dietary intake among the studied women (n = 49). Results are presented as mean and standard deviation.
However, nutrition education did not result in an increase in the number of people meeting dietary guidelines for vitamins and minerals (with the exception of vitamin B12 in the placebo group). In this context, no significant differences were observed between the two groups, either before or after the educational intervention (Supplementary Materials, Table S4).
4. Discussion
Nutrition education has been shown to improve diet quality, which can in turn enhance various aspects of quality of life. Furthermore, it has been observed to reduce symptoms of hyperthyroidism, fatigue, and abdominal pain. The Lp299v supplementation enhanced the improvement in quality of life across almost all domains. The probiotic group also experienced greater improvements in blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) and hip circumference. However, the study found that nutrition education with probiotics or placebo did not reduce anti-TPO titres, BMI, waist circumference, or body composition.
In our study, the mean BMI remained unchanged, although the percentage of individuals with a normal body weight increased. Other studies have observed a reduction in BMI following a Mediterranean diet [14,54] or a combined diet (Mediterranean + gluten-free) [14]. Regarding other parametric and body composition characteristics, our study observed a reduction in hip circumference but also a higher percentage of individuals with abdominal obesity according to WHR. In the Ülker study, the Mediterranean diet and the Mediterranean + gluten-free diet demonstrated reduced waist and hip circumference [14]. Probiotics may also affect obesity by modifying the gut microbiota, enriching and increasing its diversity. This modification also reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, as well as endotoxemia, which is associated with the development of obesity [55]. Regarding the effect of probiotics on body weight, one candidate may be Akkermansia muciniphila. According to a meta-analysis conducted by Liu et al., involving animal studies, A. muciniphila significantly reduced body weight gain by approximately 10% [55,56]. The number of studies examining the effect of Lp299v on obesity is limited. In a human study, a probiotic mixture (Lp299v + Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii) with octacosanol did not change BMI [57].
The nutritional education programme incorporating probiotics resulted in a marked improvement in blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) compared to the education programme with a placebo. It is well-documented that dietary patterns have a significant impact on blood pressure, with certain diets, notably the Mediterranean diet, having demonstrated both preventive and therapeutic benefits [58,59,60]. However, the effect of probiotics in this regard remains unclear. In a study with Lp299v supplementation, no reduction in blood pressure was observed [32], while in another study, systolic blood pressure increased [33] after the use of this probiotic. However, the study by Naruszewicz demonstrated a decrease in systolic blood pressure in patients supplementing with Lp299v [61].
In the study, anti-TPO levels were reduced, though not to a statistically significant degree, in both groups. In another 8-week study, a synbiotic taken by patients with HT also did not affect anti-TPO levels [62]. As demonstrated by Piticchio’s meta-analysis [63], a gluten-free diet, which is a diet that has been extensively studied in the context of Hashimoto’s disease, has been shown to reduce anti-TPO levels. The Mediterranean diet, when followed for 12 weeks, has been shown to have a beneficial therapeutic effect on anti-TPO levels [14] or to have no effect [10]. The combination of a gluten-free and Mediterranean diet has been shown to bring a measurable benefit in anti-TPO concentration [14]. Levels of anti-TPO decreased after six months on a low-energy diet with selenium and zinc supplementation, with or without the elimination of selected products [64]. A similar effect was also obtained on another low-calorie diet with selenium and zinc supplementation [65] and on a low-carbohydrate diet (12–15% carbohydrates, 50–60% protein, 25–30% fat) [13,65]. A 12-week diet in compliance with the autoimmune protocol resulted in a negligible increase in anti-TPO concentration [11]. According to the literature, diets high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, salt, sodium or trans fatty acids have been shown to promote pro-inflammatory effects. Limiting the intake of the aforementioned foods and balancing the diet with health-promoting foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean meat, olive oil, fish, and whole grains, ensures the provision of nutrients (omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, magnesium, iron, iodine, selenium, protein, and vitamin B12), thus promoting anti-inflammatory effects and better thyroid function [20,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73]. It is particularly recommended to supplement with vitamin D, which effectively reduces anti-TPO titres if supplementation lasts at least 3 months [17,18,74].
In our study, the most noticeable symptoms included fatigue, depression, indigestion, and a general decrease in quality of life. This finding aligns with other studies, which identified fatigue as one of the most bothersome symptoms [7,75]. There is a possibility that it is correlated with anti-TPO and anti-TG antibodies, as observed by Li et al. [7]. Treatment with LT4 for hypothyroidism improved quality of life, although 15% of patients still reported persistent symptoms [76]. Another review revealed that, despite achieving euthyroidism with LT4, 5–10% of patients reported an unsatisfactory quality of life, mood disturbances, and symptoms of hypothyroidism [77]. The risk of a depression diagnosis in patients with hypothyroidism in autoimmune thyroiditis is 3.5 times higher than in individuals without the condition [78]. In our study, improved cognitive function was observed in the education group with probiotics. Similar results were obtained in another study, where Lp299v improved concentration in individuals with severe depression [37]. Hypothyroidism is frequently associated with indigestion and a range of other gastrointestinal disorders [79]. The Lp299v strain has a documented effect on gastrointestinal health and reduces the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome [80]. Apart from the effect of Lp299v on gastrointestinal symptoms, there is little research on its effect on other aspects of quality of life [31]. A growing body of research has consistently demonstrated the positive impact of probiotics on various aspects of quality of life. Studies have reported improvements in patients with irritable bowel syndrome [81], dyspepsia [82], and sexual function in women, particularly those receiving antidepressant treatment [83]. Additionally, probiotics have been shown to enhance the quality of life in various autoimmune diseases, such as systemic sclerosis, psoriasis, and coeliac disease. In a study on patients with hypothyroidism, a synbiotic (containing strains of the genera Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Streptococcus thermophilus) positively affected physical pain, mental health, general health perception, and vitality, but not depressive symptoms or physical functioning [27].
A diet rich in nutrients is important for perceived health [84,85,86]. With regard to the impact of diet on quality of life in cases of Hashimoto’s disease, we identified one study [87]. In this study, the most common complaints reported by patients with HT were fatigue, drowsiness, poor concentration, and dry skin. After 12 weeks of autoimmune protocol use, the number of people suffering from these symptoms decreased [11]. Among other autoimmune diseases, an anti-inflammatory diet has been shown to reduce symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis, including pain [87,88], while the Mediterranean and ketogenic diets have been found to minimise symptoms in multiple sclerosis [89]. There is also a study in which patients with HT experienced improvement in depressive symptoms after supplementation, particularly with vitamin D, but also with selenomethionine or myoinositol [79]. To summarise, both Lp299v and diet have been shown to enhance various aspects of quality of life. This may be due to modulating the gut microbiota and reducing intestinal dysbiosis [90], which occurs in people with HT [91]. Dysbiosis is particularly important in gastrointestinal symptoms [90] and neuropsychiatric disorders [92].
This probiotic/placebo nutritional education programme has several strengths. Our study has added to our understanding of the impact of diet and probiotic therapy on the course and quality of life of HT. The 12-week study of nutritional education and dietary changes was sufficient to produce measurable benefits in many aspects of quality of life. Another key strength of the programme is its educational approach, which goes beyond mere menu recommendations to provide more comprehensive dietary guidance. This educational component was found to be highly beneficial for patients, enhancing their ability to sustain healthy eating habits beyond the study’s conclusion. In addition, there was ongoing contact with a dietitian and consultations every two weeks, which allowed for gradual changes, as well as support and knowledge transfer from a specialist. Another key strength of the study is the examination of the effect of Lp299v, a potentially anti-inflammatory antibody, on the immune function of HT, which is the anti-TPO antibody.
The study also has several limitations. Firstly, the sample selection method was both purposeful and random. Secondly, the accuracy of nutrient estimates derived from the Food Register Questionnaire is contingent on the patient’s diligence and precision in providing their dietary information. Nevertheless, in order to minimise this error, all participants were provided with comprehensive instructions on how to complete the questionnaires and were able to contact the researcher at any stage. Determining nutritional biomarkers, e.g., vitamins in blood serum, would constitute an objective verification of self-assessment. However, such tests have certain limitations in terms of their use, for example, when assessing the consumption of whole grains, fruit and vegetable diversity, or legume consumption (the overall diet quality). Another confounding factor is the inclusion of individuals with both normal and excessive body weight, which may have contributed to the lack of changes in body weight in the groups during the intervention. Varying disease duration and the use (or non-use) of levothyroxine may also be confounding factors. Another limitation of the study is the limited external validity and generalisability of the findings to the broader population with HT due to the method of patient recruitment and the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The lack of inclusion of individuals with hypothyroidism may also have been a confounding factor, contributing to the lack of significance in the quality-of-life domains of goitrogen symptoms and hypothyroid symptoms. Further research is also needed to verify the impact of the placebo effect, mainly on the quality of life in people with HT. Another limitation of the study is the sample size and statistical power for the NE+placebo group in the case of overall quality of life. Finally, financial constraints limited the assessment of blood parameters to anti-TPO antibodies, precluding a more comprehensive analysis of immune and metabolic markers. This may weaken the interpretation of the mechanisms underlying the effects of Lp299v.
5. Conclusions
Nutritional education combined with the probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v has been shown to improve overall quality of life (including tiredness, depressivity, cosmetic complaints, and constipation) and blood pressure in patients suffering from Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The study found no impact on nutritional status or blood anti-TPO levels. However, the results should be treated with caution due to the limitations of the study. It is possible that a longer intervention is required or that education was not as effective in this regard compared to other diet-based interventions. Future research should employ larger, randomised trials with extended follow-up to clarify the long-term impact of integrated nutritional and probiotic interventions in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. A longer-term follow-up, for example, at 6 or 12 months post-intervention, would undoubtedly be beneficial in evaluating the sustainability of dietary changes and quality-of-life improvements observed in this study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu17213387/s1, Table S1: Body mass status and health risk parameters at the baseline and after the intervention among studied women (n = 64); Table S2. Diet quality indicators among studied women (n = 64); Table S3. The frequency of consumption of selected product groups (times per day) among the studied women (SD, standard deviation; Me, median).; Table S4. The percentage of compliance with the Polish standards according to NIZP-PZH 2020 for vitamins and minerals (n = 49).
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, K.O. and J.M.-R.; methodology, K.O., D.S. and J.M.-R.; formal analysis, K.O. and J.M.-R.; investigation, K.O.; data curation, K.O.; writing—original draft preparation, K.O.; writing—review and editing, D.S. and J.M.-R.; visualisation, K.O. and J.M.-R.; supervision, D.S. and J.M.-R.; project administration, K.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Human Nutrition, Warsaw University of Life Sciences WULS, Poland (Resolutions No. 22/2021, 18 June 2021 and No. 21/2022, 18 July 2022) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to internal regulations.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the participants for their time.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Wartofsky, L. Hashimoto thyroiditis: An evidence-based guide to etiology, diagnosis and treatment. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2022, 132, 16222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Tian, R.; Sheng, Y.; Que, H. Global prevalence and epidemiological trends of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1020709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralli, M.; Angeletti, D.; Fiore, M.; D’Aguanno, V.; Lambiase, A.; Artico, M.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: An update on pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic protocols, therapeutic strategies, and potential malignant transformation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tywanek, E.; Michalak, A.; Świrska, J.; Zwolak, A. Autoimmunity, New Potential Biomarkers and the Thyroid Gland—The Perspective of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Its Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewegen, K.L.; Mooij, C.F.; van Trotsenburg, A.S.P. Persisting symptoms in patients with Hashimoto’s disease despite normal thyroid hormone levels: Does thyroid autoimmunity play a role? A systematic review. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, M.; Christian, R.; Palokas, M. Association between anti-thyroid antibodies and quality of life in patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JBI Evid. Synth. 2021, 19, 2307–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhou, K.; Wang, X.; Pan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, Q.; Si, C.; et al. Thyroid antibodies in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients are positively associated with inflammation and multiple symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Fund in Poland. Statistics of Reimbursed Drugs Levothyroxinum Natricum in 2023 Year. Available online: https://statystyki.nfz.gov.pl/PharmacyRefund?search=true&S.Province=&S.DateFrom=2023-01&S.DateTo=2023-12&S.MedicineProduct=&S.AggregationType=G14&S.ActiveSubstance=Levothyroxinum+natricum&S.AtcName=&S.AgeGroup=&S.RefundationType=&S.Gender=&S.PrivilegesAdditional= (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Osowiecka, K.; Myszkowska-Ryciak, J. The Influence of Nutritional Intervention in the Treatment of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis—A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, M.; Piticchio, T.; Alibrandi, A.; Le Moli, R.; Pallotti, F.; Campennì, A.; Cannavò, S.; Frasca, F.; Ruggeri, R.M. Effects of Dietary Habits on Markers of Oxidative Stress in Subjects with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Comparison Between the Mediterranean Diet and a Gluten-Free Diet. Nutrients 2025, 17, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihnatowicz, P.; Gębski, J.; Drywień, M.E. Effects of Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) diet on changes in thyroid parameters in Hashimoto’s disease. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2023, 30, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.D.; Sadowski, A.; Alt, A.G. Efficacy of the Autoimmune Protocol Diet as Part of a Multi-disciplinary, Supported Lifestyle Intervention for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Cureus 2019, 11, e4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.S.; Dai, N.; Xu, J.X.; Xiang, J.Y.; Zheng, X.Z.; Ke, T.Y.; Ma, L.Y.; Shi, Q.H.; Fan, S.F. MRI quantitative assessment of the effects of low-carbohydrate therapy on Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr. Connect. 2024, 13, e230477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ülker, M.T.; Çolak, G.A.; Baş, M.; Erdem, M.G. Evaluation of the effect of gluten-free diet and Mediterranean diet on autoimmune system in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 12, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, W.; Wiśniewska, K.; Okręglicka, K.; Pazura, I.; Nitsch-Osuch, A. Lifestyle intervention towards Mediterranean Diet, physical activity adherence and anthropometric parameters in normal weight women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome or Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis—Preliminary study. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2023, 30, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, R.M.; Barbalace, M.C.; Croce, L.; Malaguti, M.; Campennì, A.; Rotondi, M.; Cannavò, S.; Hrelia, S. Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders: The Mediterranean Diet as a Protective Choice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shan, S.; Li, F.; Yun, P. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on autoantibodies and thyroid function in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e36759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Li, B.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, J. The impacts of vitamin D supplementation on serum levels of thyroid autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease: A meta-analysis. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwiler, V.V.; Maissen-Abgottspon, S.; Stanga, Z.; Mühlebach, S.; Trepp, R.; Bally, L.; Bano, A. Selenium Supplementation in Patients with Hashimoto Thyroiditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Thyroid 2024, 34, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Ren, F.; Hu, T. Inverse association between serum iron levels and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in United States females of reproductive age: Analysis of the NHANES 2007–2012. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1410538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierach, M.; Rudewicz, M.; Junik, R. Iron and ferritin deficiency in women with hypothyroidism and chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis—Systematic review. Endokrynol. Pol. 2024, 75, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, V.; Condorelli, R.A.; Cannarella, R.; Aversa, A.; Calogero, A.E.; La Vignera, S. Relationship between Iron Deficiency and Thyroid Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mao, Y.; Chen, G. Association between total vitamin C intake and hypothyroidism among Hashimoto thyroiditis: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2012. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 132, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, V.; Zakharchenko, T. Thyroid hormones and minerals in immunocorrection of disorders in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1225494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhrle, J. Selenium, Iodine and Iron–Essential Trace Elements for Thyroid Hormone Synthesis and Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczuko, M.; Zawadzka, K.; Szczuko, U.; Rudak, L.; Pobłocki, J. The Significance and Process of Inflammation Involving Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Derivatives in Hashimoto’s Disease. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, M.; Reisian, M.; Sajadi Hezaveh, Z. The effect of synbiotic supplementation on hypothyroidism: A randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AkbariRad, M.; Mazloum Khorasani, Z.; Hemmatpur, A.; Firoozi, A.; Bakhshi, A.; Ravanshad, S.; Mofatteh, A.; Mehrad-Majd, H. Effects of probiotics on thyroid function and fatigue in hypothyroid patients: A randomized placebo controlled trial. Endocrinol. Res. Pract. 2025, 29, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka, K.; Kałuzińska, K.; Świerz, M.J.; Sawiec, Z.; Antonowicz, E.; Leończyk-Spórna, M.; Abadi, A.K.; Trofimiuk-Müldner, M.; Bała, M.M. Are probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics beneficial in primary thyroid diseases? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2023, 30, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Kang, C.; Li, J.; Hou, Z.; Xiong, M.; Wang, X.; Peng, H. Effect of probiotics or prebiotics on thyroid function: A meta-analysis of eight randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, E.A.; Teixeira, C.; Montelius, C.; Jeppsson, B.; Larsson, N. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v (LP299V®): Three decades of research. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 441–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofeld, B.C.; Puppala, V.K.; Tyagi, S.; Ahn, K.W.; Anger, A.; Jia, S.; Salzman, N.H.; Hessner, M.J.; Widlansky, M.E. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v probiotic supplementation in men with stable coronary artery disease suppresses systemic inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.; Suboc, T.M.; Tyagi, S.; Salzman, N.; Wang, J.; Ying, R.; Tanner, M.J.; Kakarla, M.; Baker, J.E.; Widlansky, M.E. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Supplementation Improves Vascular Endothelial Function and Reduces Inflammatory Biomarkers in Men with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, A.; Parge, A.; Nimkar, R.; Sinha, A. Effect of probiotic and prebiotics supplementation on hemoglobin levels and iron absorption among women of reproductive age and children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nutr. 2025, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonderheid, S.C.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Park, C.; Pauls, H.; OjiNjideka Hemphill, N.; LaBomascus, B.; McLeod, A.; Koenig, M.D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Probiotic Species on Iron Absorption and Iron Status. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlicz, W.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Krynicka, P.; Łoniewski, I.; Rydzewska, G. Probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome—Is the quest for the right strain over? Rapid review of existing guidelines and recommendations. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2021, 16, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzki, L.; Ostrowska, L.; Pawlak, D.; Małus, A.; Pawlak, K.; Waszkiewicz, N.; Szulc, A. Probiotic Lactobacillus Plantarum 299v decreases kynurenine concentration and improves cognitive functions in patients with major depression: A double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 100, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezewska-Zychowicz, M.; Gawecki, J.; Wadolowska, L.; Czarnocinska, J.; Galinski, G.; Kollajtis-Dolowy, A.; Roszkowski, W.; Wawrzyniak, A.; Przybylowicz, K.; Stasiewicz, B.; et al. Dietary Habits and Nutrition Beliefs Questionnaire and the Manual for Developing of Nutritional Data, 3rd ed.; Gawęcki, J., Ed.; Polish Academy of Sciences: Warsaw, Poland, 2024; Available online: https://diettools4u.uwm.edu.pl/kompan/ (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Niedzwiedzka, E.; Wadolowska, L.; Kowalkowska, J. Reproducibility of A Non-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire (62-Item FFQ-6) and PCA-Driven Dietary Pattern Identification in 13–21-Year-Old Females. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka-Gutaj, N.; Watt, T.; Sowiński, J.; Gutaj, P.; Waligórska-Stachura, J.; Ruchała, M. ThyPROpl—The Polish version of the thyroid-specific quality of life questionnaire ThyPRO. Endokrynol. Pol. 2015, 66, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulich, K.R.; Reguła, J.; Stasiewicz, J.; Jasinski, B.; Carlsson, J.; Wiklund, I. Psychometric validation of the Polish translation of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) Questionnaire in patients with reflux disease. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2005, 113, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kostelecki, G.; Całyniuk, B.; Zajchowska, S.; Myszkowska-Ryciak, J.; Janiszewska, K.; Bronkowska, M.; Madej-Babula, M.; Lange, E.; Gajewska, D.; Pająk, R. Guidelines of the Polish Society of Dietetics and the National Consultant in the Field of Family Medicine on Providing Dietary Consultations as Part of Coordinated Care in Primary Health Care of 31/01/2023. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/zdrowie/wytyczne-dotyczace-udzielania-konsultacji-dietetycznych (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Kunachowicz, H.; Przygoda, B.; Nadolna, I.; Iwanow, K. Tables of Food Composition and Nutritional Values; PZWL: Warsaw, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Nutrient Database. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Jarosz, M.; Rychlik, E.; Stoś, K.; Charzewska, J. (Eds.) Nutrition Standards for the Polish Population and Their Application; National Institute of Public Health—National Institute of Hygiene: Warsaw, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T.; Hill, L.A.; Scott, B.J.; Daugherty, S.A.; Koh, Y.O. A New Predictive Equation for Resting Energy Expenditure in Healthy Individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutrition Division. Human Energy Requirements; Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; FAO/WHO/UNU: Rome, Italy, 2004; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/8282e44e-5197-4416-885b-250631682d14 (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (U.S.); National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.). Antropometry Procedures Manual; National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES): Washington, DC, USA, 2017. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/51795 (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio; Report of a WHO Expert Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241501491 (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Yoo, E.G. Waist-to-Height Ratio as a Screening Tool for Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-Height Ratio as an Indicator of “Early Health Risk”: Simpler and More Predictive than Using a “matrix” Based on BMI and Waist Circumference. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Healthy Lifestyle—WHO Recommendations. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/nutrition---maintaining-a-healthy-lifestyle (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Osowiecka, K.; Skrypnik, D.; Myszkowska-Ryciak, J. Assessment of the Impact of Nutritional Intervention with the Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on Nutritional Status and Quality of Life of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Patients—A Randomized Double-Blind Study Protocol. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shady, M.A.; Adly, N.N.; Ibrahim, S.; Aboelyazed, S. The Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Patients with Hashimoto Thyroiditis. QJM Int. J. Med. 2024, 117, hcae175.472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Tsilingiris, D.; Panagopoulos, F.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. The Role of Next-Generation Probiotics in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Disorders: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Ji, X.; Zhou, K. Akkermansia muciniphila for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuka, N.; Milinkovic, N.; Velickovic, K.; Polovina, S.; Sumarac-Dumanovic, M.; Minic, R.; Korčok, D.; Djordjevic, B.; Ivanovic, N.D. Beneficial effects of a new probiotic formulation on adipocytokines, appetite-regulating hormones, and metabolic parameters in obese women. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 7658–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakaloudi, D.R.; Chrysoula, L.; Leonida, I.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Theodoridis, X.; Chourdakis, M. Impact of the level of adherence to the Mediterranean Diet on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5771–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippou, C.D.; Thomopoulos, C.G.; Kouremeti, M.M.; Sotiropoulou, L.I.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.I.; Tousoulis, D.M.; Tsioufis, C.P. Mediterranean diet and blood pressure reduction in adults with and without hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, O.R.; Mistry, N.; Deighton, K.; Matu, J.; Griffiths, A.; Minihane, A.M.; Mathers, J.C.; Shannon, O.M.; Siervo, M. Effects of a Mediterranean diet on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruszewicz, M.; Johansson, M.L.; Zapolska-Downar, D.; Bukowska, H. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v on cardiovascular disease risk factors in smokers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Karimifar, M.; Heidari, Z.; Mohammadi, H.; Askari, G. The effects of synbiotic supplementation on thyroid function and inflammation in hypothyroid patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piticchio, T.; Frasca, F.; Malandrino, P.; Trimboli, P.; Carrubba, N.; Tumminia, A.; Vinciguerra, F.; Frittitta, L. Effect of gluten-free diet on autoimmune thyroiditis progression in patients with no symptoms or histology of celiac disease: A meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1200372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska, L.; Gier, D.; Zyśk, B. The Influence of Reducing Diets on Changes in Thyroid Parameters in Women Suffering from Obesity and Hashimoto’s Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, N.; Shi, Q.H.; Zheng, L.W.; Huang, X.S.; Fan, S.F. Quantitative Multi-Parameter MRI Evaluation of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Changes After Dietary Interventions. Med. Sci. Monit. 2025, 31, e947862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danailova, Y.; Velikova, T.; Nikolaev, G.; Mitova, Z.; Shinkov, A.; Gagov, H.; Konakchieva, R. Nutritional Management of Thyroiditis of Hashimoto. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalace, M.C.; Talotta, R.; Rapisarda, F.; D’Amico, V.; Laganà, M.; Malaguti, M.; Campennì, A.; Cannavò, S.; Hrelia, S.; Ruggeri, R.M. Unlocking the Power of the Mediterranean Diet: Two in One—Dual Benefits for Rheumatic and Thyroid Autoimmune Diseases. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, S.; Ghadir, M.; Gargari, B.P. The association between dietary inflammatory index and dietary total antioxidant capacity and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: A case-control study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, R.; Beiranvand, A.; Nourooz-Zadeh, S.; Rostami, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Nourooz-Zadeh, J. Association Between Essential Trace Elements and Thyroid Antibodies in the Blood of Women with Newly Diagnosed Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 22, e145599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Ding, L.; Yu, T.; Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; et al. Severely low serum magnesium is associated with increased risks of positive anti-thyroglobulin antibody and hypothyroidism: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Celik, M.; Bulbul, B.Y.; Andac, B.; Okur, M.; Colak, S.Y.; Yekdes, A.C. Immunological harmony: The role of magnesium in the development of euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J. Elem. 2024, 29, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.Z.A.; Lungba, R.M.; Ajibawo-Aganbi, U.; Veliginti, S.; Perez Bastidas, M.V.; Saleem, S.; Cancarevic, I. Minerals: An Untapped Remedy for Autoimmune Hypothyroidism? Cureus 2020, 12, e11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Lv, X. The association between dietary sodium density and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in US adults. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1508195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, H. Effects of vitamin D on thyroid autoimmunity markers in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211060675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivaljevic, V.R.; Bukvic Bacotic, B.R.; Sipetic, S.B.; Stanisavljevic, D.M.; Maksimovic, J.M.; Diklic, A.D.; Paunovic, I.R. Quality of life improvement in patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis and other goiters after surgery: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 21, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonklaas, J. Restoration of euthyroidism with levothyroxine: Implications of etiology of hypothyroidism and the degree of residual endogenous thyroid function. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 934003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borson-Chazot, F.; Terra, J.-L.; Goichot, B.; Caron, P. What Is the Quality of Life in Patients Treated with Levothyroxine for Hypothyroidism and How Are We Measuring It? A Critical, Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmann, E.M.; Müller, H.H.O.; Luecke, C.; Philipsen, A.; Kornhuber, J.; Grömer, T.W. Association of Depression and Anxiety Disorders with Autoimmune Thyroiditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, R.; Kowalcze, K.; Szkróbka, W.; Okopień, B. Sexual Function and Depressive Symptoms in Young Women with Euthyroid Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Receiving Vitamin D, Selenomethionine and Myo-Inositol: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.M.; Hu, M.X.; Li, S.Y.; Ran, X.; Zhang, H.; Ding, X.F. Thyroid disorders and gastrointestinal dysmotility: An old association. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1389113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Morvan de Sequeira, C.; Kaeber, M.; Cekin, S.E.; Enck, P.; Mack, I. The Effect of Probiotics on Quality of Life, Depression and Anxiety in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agah, S.; Akbari, A.; Heshmati, J.; Sepidarkish, M.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Adibi, P.; Mazidi, M.; Farsi, F.; Ofori-Asenso, R.; Talley, N.J.; et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Effects of probiotic supplementation on symptoms in functional dyspepsia. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103902, ISSN 1756-4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-J.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Jin, X.; Zheng, Q.; Park, S.-J.; Yi, G.-S.; Yi, T.-H. A PRISMA Systematic Review of Sexual Dysfunction and Probiotics with Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Biology 2025, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pano, O.; Gamba, M.; Bullón-Vela, V.; Aguilera-Buenosvinos, I.; Roa-Díaz, Z.M.; Minder, B.; Kopp-Heim, D.; Laine, J.E.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martinez, A.; et al. Eating behaviors and health-related quality of life: A scoping review. Maturitas 2022, 165, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Selvamani, T.Y.; Zahra, A.; Malla, J.; Dhanoa, R.K.; Venugopal, S.; Shoukrie, S.I.; Hamouda, R.K.; Hamid, P. Association Between Dietary Habits and Depression: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e32359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Guglielmetti, M.; Ferraris, C.; Frias-Toral, E.; Domínguez Azpíroz, I.; Lipari, V.; Di Mauro, A.; Furnari, F.; Castellano, S.; Galvano, F.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Quality of Life in Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönenberger, K.A.; Schüpfer, A.-C.; Gloy, V.L.; Hasler, P.; Stanga, Z.; Kaegi-Braun, N.; Reber, E. Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Diets on Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.; Sjöblom, H.; Gjertsson, I.; Ulven, S.M.; Lindqvist, H.M.; Bärebring, L. Do Interventions with Diet or Dietary Supplements Reduce the Disease Activity Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, C.; Ignat, E.B.; Alexa, D.; Ciubotaru, A.; Leon, M.M.; Maștaleru, A.; Popescu, G.; Cumpăt, C.M.; Cucu, L.-E.; Smihor, M.I.; et al. The Role of Nutrition and Physical Activity in Modulating Disease Progression and Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garicano Vilar, E.; López Oliva, S.; Penadés, B.F.; Sánchez Niño, G.M.; Terrén Lora, A.; Sanz Rojo, S.; Mauro Martín, I.S. Mediterranean Diet Effect on the Intestinal Microbiota, Symptoms, and Markers in Patients with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Wang, C.; Meng, F.; Wang, H.; Song, B.; Yang, Y.; Shan, Z. Association Between Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 774362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Lai, X.; Li, C.; Ding, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Various Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders-An Evidence Mapping Based on Quantified Evidence. Mediators Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 5127157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).