Exploring Dietary Intake in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
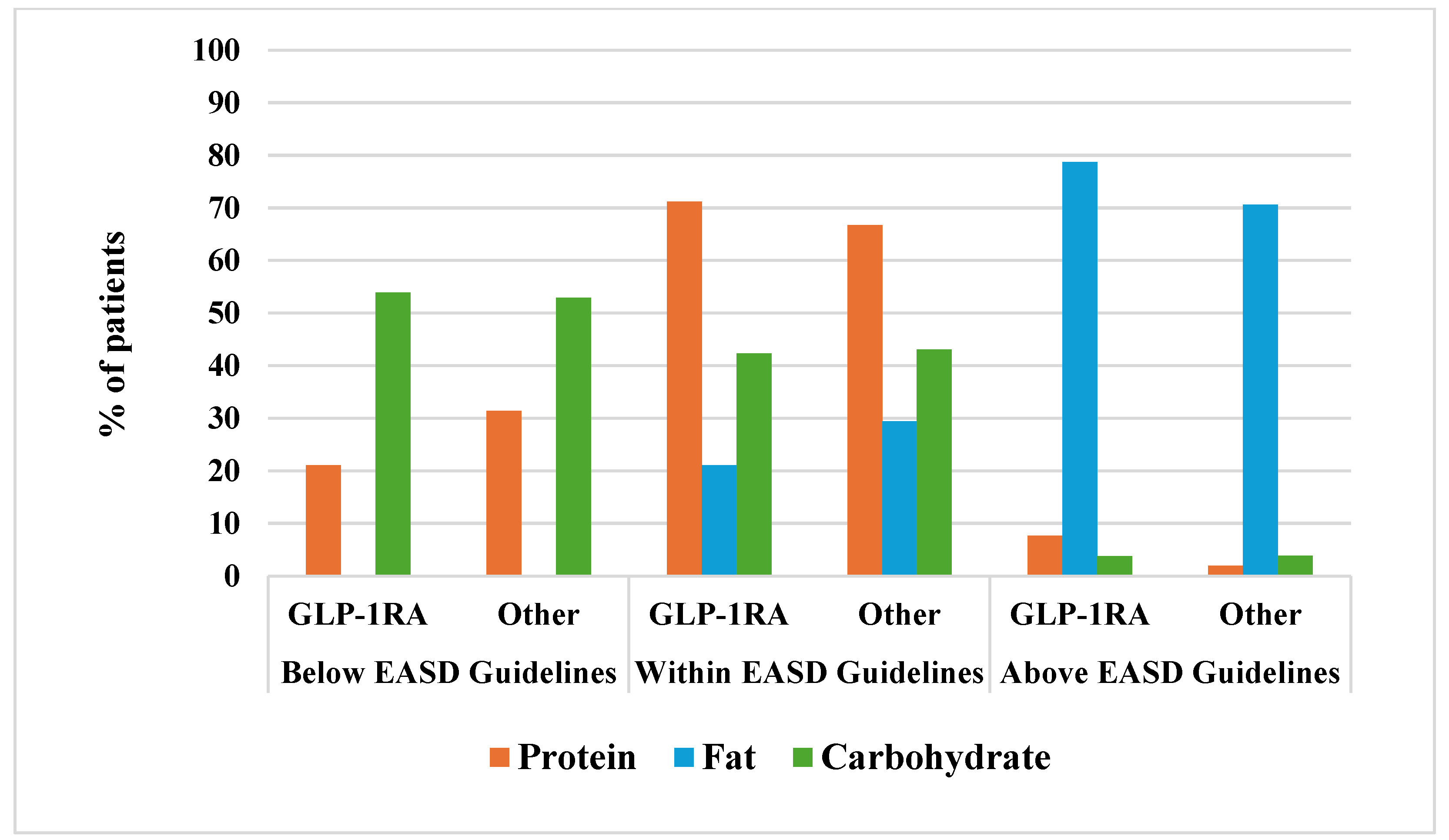
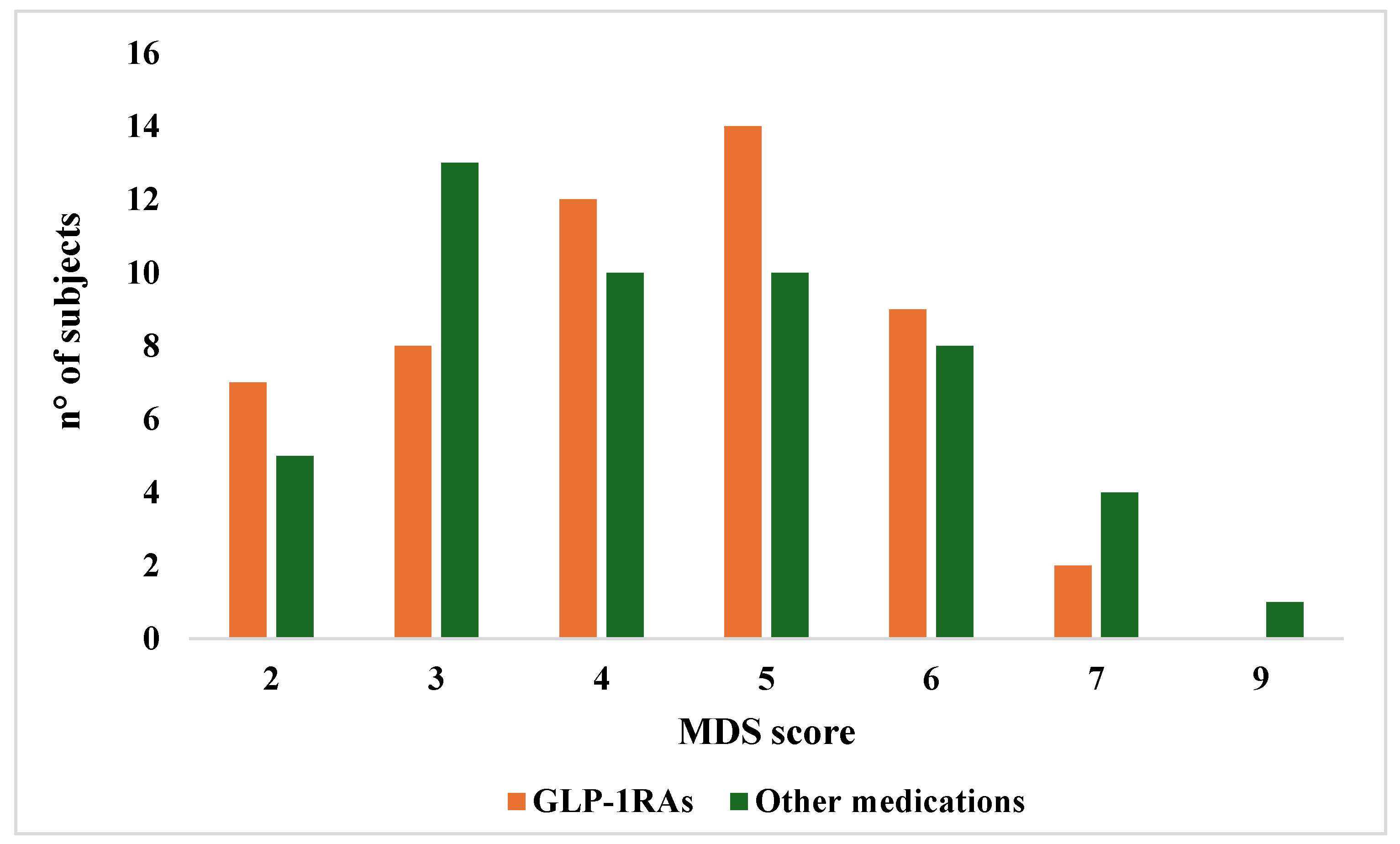
3.1. Comparison of Nutrient Intake and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Score Between Patients Taking GLP-1RAs Versus Those Under Other Medications
3.2. Correlations Between MDS, Nutrient Intake, Age and Anthropometric Variables
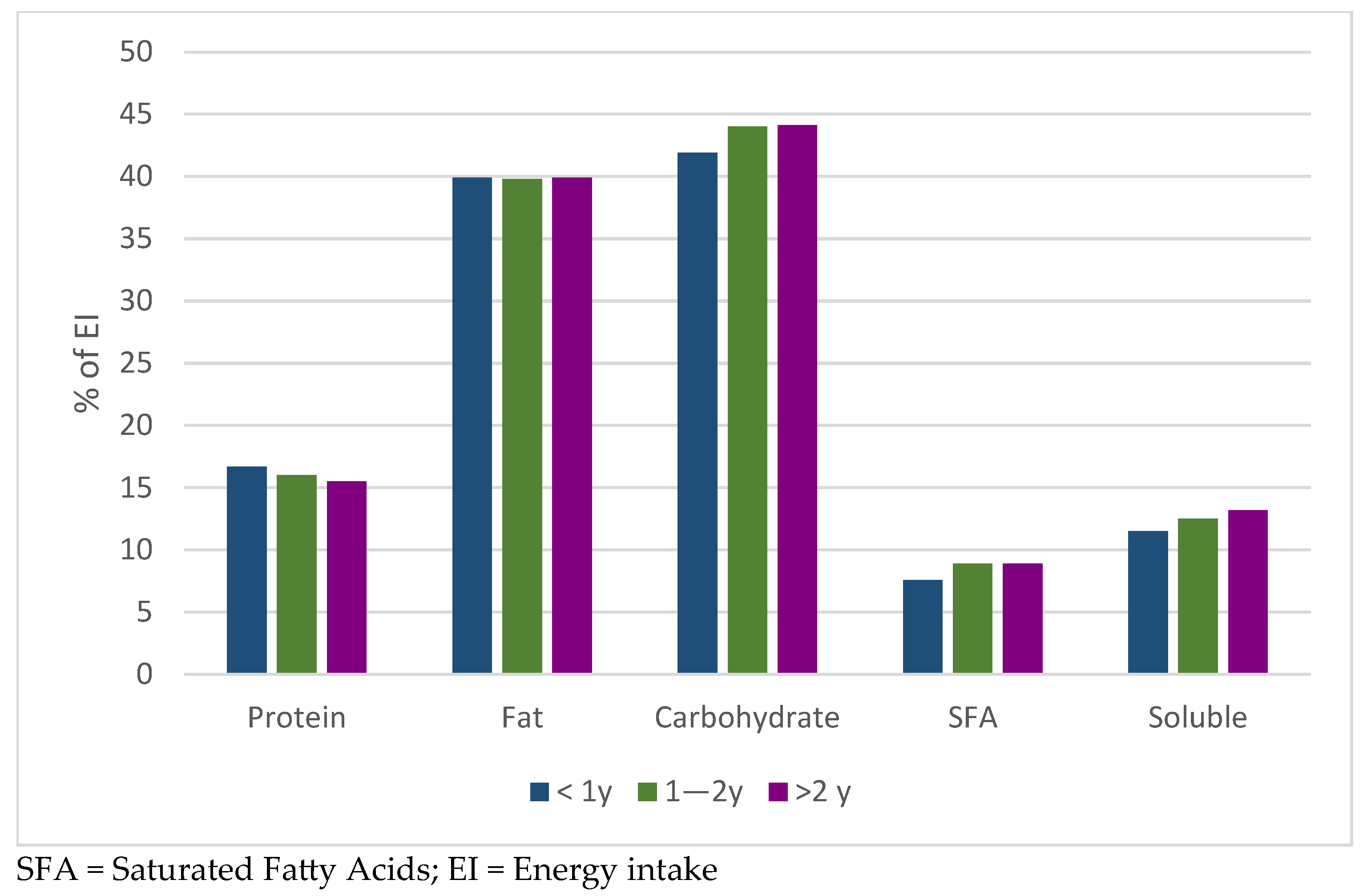
3.3. Comparison of Nutrient Intake in GLP-1RAs Users According to Treatment Duration
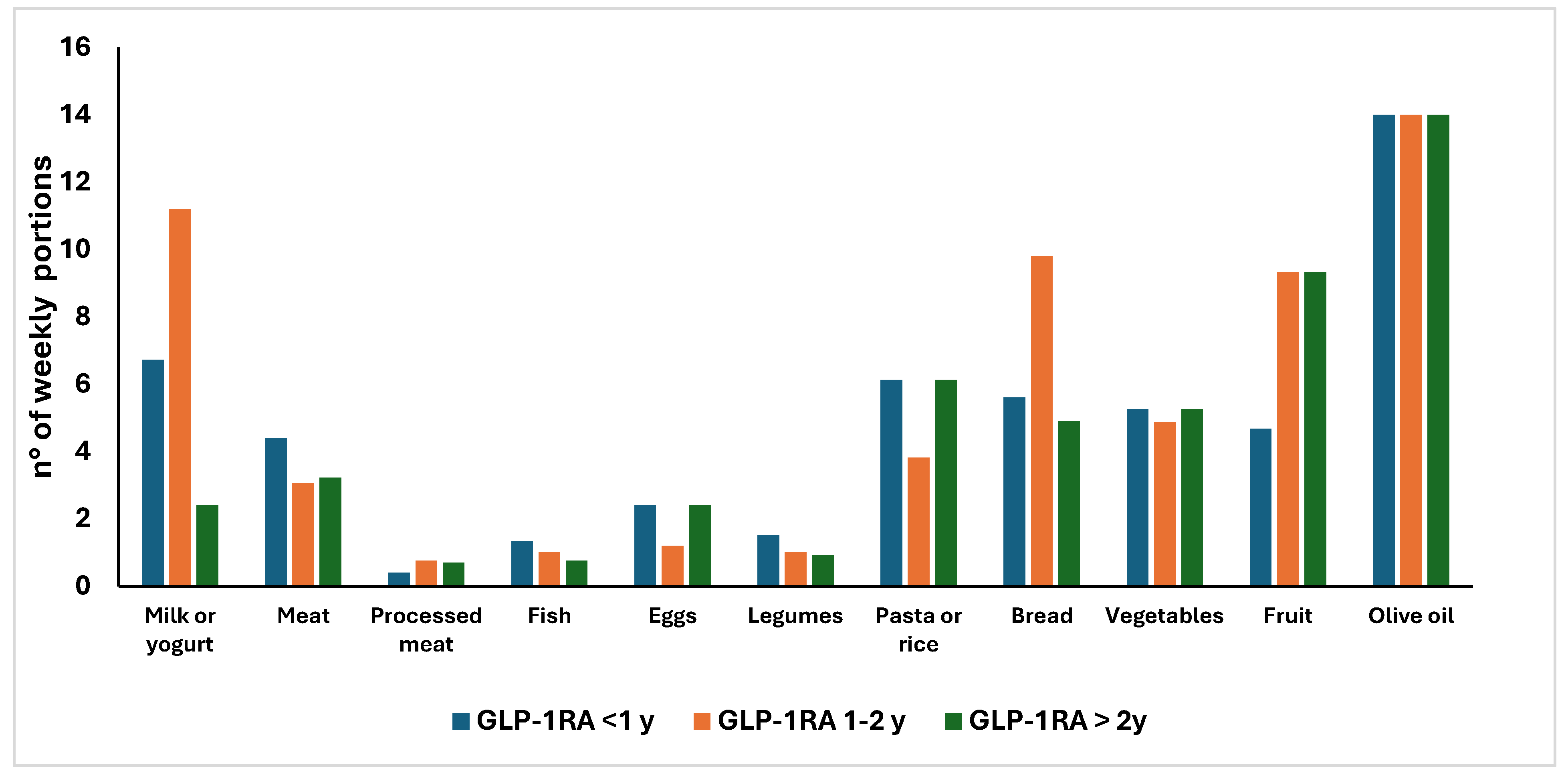
3.4. Comparison of Weekly Frequency Consumption of the Main Food Groups in GLP-1RAs Users According to Treatment Duration
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Implications
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, E.; Lim, S.; Lamptey, R.; Webb, D.R.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet 2022, 400, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.L.; Stafford, L.K.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Boyko, E.J.; Vollset, S.E.; Smith, A.E.; Dalton, B.E.; Duprey, J.; Cruz, J.A.; Hagins, H.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with Projections of Prevalence to 2050: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; Draznin, B.; Aroda, V.R.; Bakris, G.; Benson, G.; Brown, F.M.; Freeman, R.; Green, J.; Huang, E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S113–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Rosenstock, J.; Terauchi, Y.; Altuntas, Y.; Lalic, N.M.; Villegas, E.C.M.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Haluzík, M. PIONEER 1: Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Semaglutide Monotherapy in Comparison with Placebo in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.Z.; Wan, J.Y.; Yuan, C.S. Comparative Effectiveness of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Glycaemic Control, Body Weight, and Lipid Profile for Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2024, 384, e076410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.; Robinson, K.; Thomas, S.; Williams, D.R. Dietary Intake by Patients Taking GLP-1 and Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Narrative Review and Discussion of Research Needs. Obes. Pillars 2024, 11, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, X. Pharmacovigilance Study of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Metabolic and Nutritional Adverse Events. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1416985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.; Milstead, M.; Thomas, O.; McGlasson, T.; Green, L.; Kreider, R.; Jones, R. Investigating Nutrient Intake During Use of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1566498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsbøll, T.; Lindahl, C.; Nielsen, N.F.; Tikkanen, C.K. Real-World Impact of Once-Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide after 2 Years of Follow-up: Results from a Nationwide Observational Study in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegland, T.A.; Fang, Z.; Bucher, K. GLP-1 Medication Use for Type 2 Diabetes Has Soared. JAMA 2024, 332, 952–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najim, W.; Raposo, A.; BinMowyna, M.N.; le Roux, C.W. Unintended Consequences of Obesity Pharmacotherapy: A Nutritional Approach to Ensuring Better Patient Outcomes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscemi, S.; Rosafio, G.; Vasto, S.; Massenti, F.M.; Grosso, G.; Galvano, F.; Rini, N.; Barile, A.M.; Maniaci, V.; Cosentino, L.; et al. Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Use in Italian Adults Living in Sicily. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Survival in a Greek Population. N. Eng. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostchega, Y.; Seu, R.; Sarafrazi, N.; Zhang, G.; Hughes, J.P.; Miller, I. Waist Circumference Measurement Methodology Study: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016. Vital Health Stat. 2019, 2, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, D.A.; Lera, L.; Márquez, C.; Valenzuela, A.; Saguez, R.; Weisstaub, G.; Albala, C. Neck Circumference Cut-Off Points for Identifying Adiposity: Association with Chronic Metabolic Diseases in Older People. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italian Society of Human Nutrition (SINU). LARN—Reference Intake Levels of Nutrients and Energy for the Italian Population; 5th Revision; SICS Publisher: Milan, Italy, 2023; Available online: https://sinu.it/larn/ (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Vitale, M.; Masulli, M.; Cocozza, S.; Anichini, R.; Babini, A.C.; Boemi, M.; Bonora, E.; Buzzetti, R.; Carpinteri, R.; Caselli, C.; et al. Sex Differences in Food Choices, Adherence to Dietary Recommendations and Plasma Lipid Profile in Type 2 Diabetes—The TOSCA.IT Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzo, V.; Rosato, R.; Tarsia, E.; Goitre, I.; De Michieli, F.; Fadda, M.; Monge, T.; Pezzana, A.; Broglio, F.; Bo, S. Self-Reported Adherence to Diet and Preferences towards Type of Meal Plan in Patient with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, C.; Ryan, M.; McNulty, B.; Gibney, M.J.; Canavan, R.; O’Shea, D. High Saturated-Fat and Low-Fibre Intake: A Comparative Analysis of Nutrient Intake in Individuals with and without Type 2 Diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimino, E.; Izzo, A.; Castaldo, C.; Amoroso, A.P.; Rivellese, A.A.; Capaldo, B.; Della Pepa, G. Dietary Micronutrient Adequacies and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in a Population of Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, M.S.; Rodríguez-Caldero, M.C.; Martín-Pérez, M.P.; Mira-Solves, J.J.; Vitaller-Burillo, J.; Carratalá-Munuera, M.C. Impact of Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and/or Drug Treatment on Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: DM2-CUMCYL Study. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, T.; Ozeki, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Miyamoto, S.; Gotoh, K.; Shibata, H. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Semaglutide Improves Eating Behavior and Glycemic Control in Japanese Obese Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Metabolites 2022, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.B.K.; Janus, C.; Lundgren, J.R.; Juhl, C.R.; Sandsdal, R.M.; Olsen, L.M.; Andresen, A.; Borg, S.A.; Jacobsen, I.C.; Finlayson, G.; et al. Exploratory Analysis of Eating- and Physical Activity-Related Outcomes from a Randomized Controlled Trial for Weight Loss Maintenance with Exercise and Liraglutide Single or Combination Treatment. Nat. Commun 2022, 13, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Agarwal, M.; Aggarwal, M.; Alexander, L.; Apovian, C.M.; Bindlish, S.; Bonnet, J.; Butsch, W.S.; Christensen, S.; Gianos, E.; et al. Nutritional Priorities to Support GLP-1 Therapy for Obesity: A Joint Advisory from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, the American Society for Nutrition, the Obesity Medicine Association, and the Obesity Society. Obes. Pillars 2025, 15, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, M.; Almadani, F.A.; Almuhammadi, N.; Algabsani, S.; Alamro, Y.; Aldhwayan, M. The Efficacy of GLP-1 Analogues on Appetite Parameters, Gastric Emptying, Food Preference and Taste Among Adults with Obesity: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hironaka, J.; Ushigome, E.; Kondo, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Osaka, T.; Majima, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Okada, H.; Senmaru, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; et al. Changes in Food Preferences after Oral Semaglutide Administration in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: KAMOGAWA-DM Cohort. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2025, 22, 14791641251318309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadouh, H.; Chedid, V.; Halawi, H.; Burton, D.D.; Clark, M.M.; Khemani, D.; Vella, A.; Acosta, A.; Camilleri, M. GLP-1 Analog Modulates Appetite, Taste Preference, Gut Hormones, and Regional Body Fat Stores in Adults with Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.V.B.; Milstead, M.; Green, L.; Kreider, R.; Jones, R. Diet quality and nutrient distribution while using glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonist: A secondary cross-sectional analysis. Obes. Pillars 2025, 16, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Medicines for Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1873–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S181–S206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, I.; Morino, K.; Fuse, K.; Kondo, K.; Ohi, A.; Nishida, K.; Kurihara, M.; Yasuhara, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Nishida, Y.; et al. Impact of Obesity on Underreporting of Energy Intake in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: Clinical Evaluation of Energy Requirements in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (CLEVER-DM) Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 39, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgojo-Martínez, J.J.; Mezquita-Raya, P.; Carretero-Gómez, J.; Castro, A.; Cebrián-Cuenca, A.; de Torres-Sánchez, A.; García-de-Lucas, M.D.; Núñez, J.; Obaya, J.C.; Soler, M.J.; et al. Clinical Recommendations to Manage Gastrointestinal Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Glp-1 Receptor Agonists: A Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott Butsch, W.; Sulo, S.; Chang, A.T.; Kim, J.A.; Kerr, K.W.; Williams, D.R.; Hegazi, R.; Panchalingam, T.; Goates, S.; Heymsfield, S.B. Nutritional Deficiencies and Muscle Loss in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Retrospective Observational Study. Obes. Pillars 2025, 15, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelli, M.N.; Schoeller, D.A. Traditional Self-Reported Dietary Instruments Are Prone to Inaccuracies and New Approaches Are Needed. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Overall Sample (n = 103) | GLP-1RAs (n = 52) | Other Drugs (n = 51) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 65.8 ± 7.9 | 65.0 ± 7.9 | 66.7 ± 7.8 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Males | 67 (65%) | 35 (67%) | 32 (63%) |
| Females | 36 (35%) | 17 (33%) | 19 (37%) |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 12 (11.7%) | 7 (13.5%) | 5 (9.8%) |
| No | 91 (88.3%) | 45 (86.5%) | 46 (90.2%) |
| Education, n (%) | |||
| Primary school | 9 (8.7%) | 2 (3.8%) | 7 (13.7%) |
| Secondary school | 40 (38.8%) | 21 (40.4%) | 19 (37.2%) |
| High school | 43 (41.7%) | 22 (42.3%) | 21 (41.2%) |
| University | 11 (10.7%) | 7 (13.5%) | 4 (7.9%) |
| Marital status, n (%) | |||
| Single | 13 (12.6%) | 7 (13.5%) | 6 (11.8%) |
| Married | 70 (68%) | 38 (73%) | 32 (62.8%) |
| Widow | 11 (10.7) | 2 (3.8%) | 9 (17.6%) |
| Divorces | 9 (8.7%) | 5 (9.6%) | 4 (7.8%) |
| Weight, kg | 79.5 ± 18.3 | 85.2 ± 20.0 | 73.6 ± 14.0 ** |
| Height, m | 1.68 ± 0.09 | 1.68 ± 0.09 | 1.68 ± 0.08 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.1 ± 5.5 | 30.0 ± 5.9 | 26.1 ± 4.4 ** |
| BMI categories, n (%) | |||
| Normal | 31 (30.1%) | 9 (17.3%) | 22 (43.1%) |
| Overweight | 41 (39.8%) | 20 (38.5%) | 21 (41.2%) |
| Obesity | 31 (30.1%) | 23 (44.2%) | 8 (15.7%) |
| Waist circumference, cm | 103.1 ± 13.8 | 107 ± 13 | 99 ± 13 ** |
| Disease duration, years | 12.7 [0.4–47.5] | 12.7 [0.4–47.5] | 13.0 [0.7–45.5] |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| Hypertension | 53 (51.5%) | 23 (44%) | 30 (59%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 55 (53.4%) | 27 (52%) | 28 (55%) |
| CKD | 12 (11.7%) | 5 (10%) | 7 (14%) |
| MALSD | 11 (10.7%) | 6 (11%) | 5 (10%) |
| Fasting blood glucose, mg/dL | 144 ± 48 | 137 ± 49 | 151 ± 46 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.4 ± 1.7 | 7.0 ± 1.5 | 7.6 ± 1.8 * |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 159 ± 47 | 146 ± 47 | 169 ± 46 * |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 85 ± 39 | 76 ± 42 | 93 ± 36 * |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 49 ± 13 | 46 ± 11 | 51 ± 15 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 135 ± 68 | 134 ± 52 | 136 ± 80 |
| Physical activity (IPAQ), n (%) | |||
| Sedentary | 18 (17.5%) | 12 (23.1%) | 6 (11.8%) |
| Poor active | 39 (37.9%) | 16 (30.8%) | 23 (45.1%) |
| Moderately active | 37 (35.9%) | 22 (42.3%) | 15 (29.4%) |
| Active | 8 (7.7%) | 2 (3.8%) | 6 (11.8%) |
| Very active | 1 (1%) | - | 1 (2%) |
| EASD Guidelines | GLP-1 Ras (n = 52) | % of EI | Other (n = 51) | % of EI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy intake (EI), kcal/d | 1514 ± 353 | 1568 ± 294 | |||
| Protein, g | 10/15–20% ° | 60.5 ± 17.1 | 16% | 60.1± 13.9 | 15% |
| Fat, g | 20–35% EI | 67.3 ± 20.5 | 40% | 67.9 ± 18.2 | 39% |
| SFA, g | <10% EI | 14.8 ± 6.14 | 9% | 15.8 ± 7.52 | 9% |
| MUFA, g | 29.2 ± 9.42 | 17% * | 27.4 ± 7.97 | 16% | |
| PUFA, g | 7.77 ± 3.32 | 5% | 7.87 ± 3.10 | 4% | |
| n-6 PUFA, g | 5.26 ± 1.85 | 3% | 5.13 ± 1.47 | 3% | |
| n-3 PUFA, g | 0.77 ± 0.25 | 0.4% | 0.74 ± 0.22 | 0.4% | |
| Cholesterol, mg | - | 209 ± 98.6 | 183 ± 71.3 | ||
| Carbohydrate, g | 45–60% EI | 176 ± 48.5 | 44% | 183 ± 36.8 | 44% |
| Starch, g | - | 115 ± 34.2 | 116 ± 34.5 | ||
| Soluble, g | <10% EI | 51.1 ± 22.2 | 13% | 49.0 ± 21.0 | 12% |
| Fiber/1000 kcal, g | 16.7 | 11.0 ± 2.51 | 11.0 ± 2.81 | ||
| Total fibers, g | 35 | 16.4 ± 4.54 | 16.4 ± 4.51 |
| GLP-1RAs Treatment Duration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| <1 y (n = 11) | 1–2 y (n = 19) | >2 y (n = 22) | |
| Energy intake, kcal/d | 1511 ± 270 | 1488 ± 318 | 1538 ± 424 |
| Protein, g | 62.5± 11.3 | 59.7 ± 15.7 | 60.1 ± 20.9 |
| Fat, g | 67.5 ± 20.1 | 66.3 ± 20.5 | 68.1± 21.2 |
| SFA, g | 12.9 ± 5.73 | 15.1 ± 5.75 | 15.6 ± 6.72 |
| MUFA, g | 26.5 ± 6.52 | 29.1 ± 10.6 | 30.5 ± 9.68 |
| PUFA, g | 7.37 ± 3.62 | 7.91 ± 3.39 | 7.84 ± 3.31 |
| n-6 PUFA, g | 4.68 ± 1.31 | 5.12 ± 2.30 | 5.59 ± 1.57 |
| n-3 PUFA, g | 0.75 ± 0.16 | 0.75 ± 0.29 | 0.79 ± 0.24 |
| Cholesterol, mg | 223 ± 142 | 194 ± 61 | 212 ± 102 |
| Carbohydrate, g | 169 ± 43.4 | 173 ± 38.0 | 181 ± 59.4 |
| Starch, g | 120 ± 25.0 | 112 ± 29.4 | 115 ± 41.1 |
| Soluble, g | 49.1 ± 29.4 | 48.5 ± 13.9 | 53.9 ± 25.6 |
| Fiber/1000 kcal, g | 10.8 ± 3.0 | 11.1 ± 2.31 | 10.9 ± 2.52 |
| Total fibers, g | 16.4 ± 5.84 | 16.3± 3.50 | 16.4 ± 4.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ponzo, V.; Vitale, M.; Bo, S.; Broglio, F.; Goitre, I.; Cioffi, I. Exploring Dietary Intake in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213318
Ponzo V, Vitale M, Bo S, Broglio F, Goitre I, Cioffi I. Exploring Dietary Intake in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213318
Chicago/Turabian StylePonzo, Valentina, Marilena Vitale, Simona Bo, Fabio Broglio, Ilaria Goitre, and Iolanda Cioffi. 2025. "Exploring Dietary Intake in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Cross-Sectional Analysis" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213318
APA StylePonzo, V., Vitale, M., Bo, S., Broglio, F., Goitre, I., & Cioffi, I. (2025). Exploring Dietary Intake in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Using GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients, 17(21), 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213318








