Propolis Modulates the Gut Microbiota–Gut Hormone–Liver AMPK Axis to Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Propolis
2.2. Animal Experimental Design and Procedures
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Serum Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Histopathological Examination of Liver and Colon Tissues
2.6. Quantification of Hepatic and Colonic Gene Expression
2.7. 16S rRNA High-Throughput Sequencing
2.8. Targeted Metabolomics of SCFAs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Propolis Effect on Body Weight Gain in HFD Rats
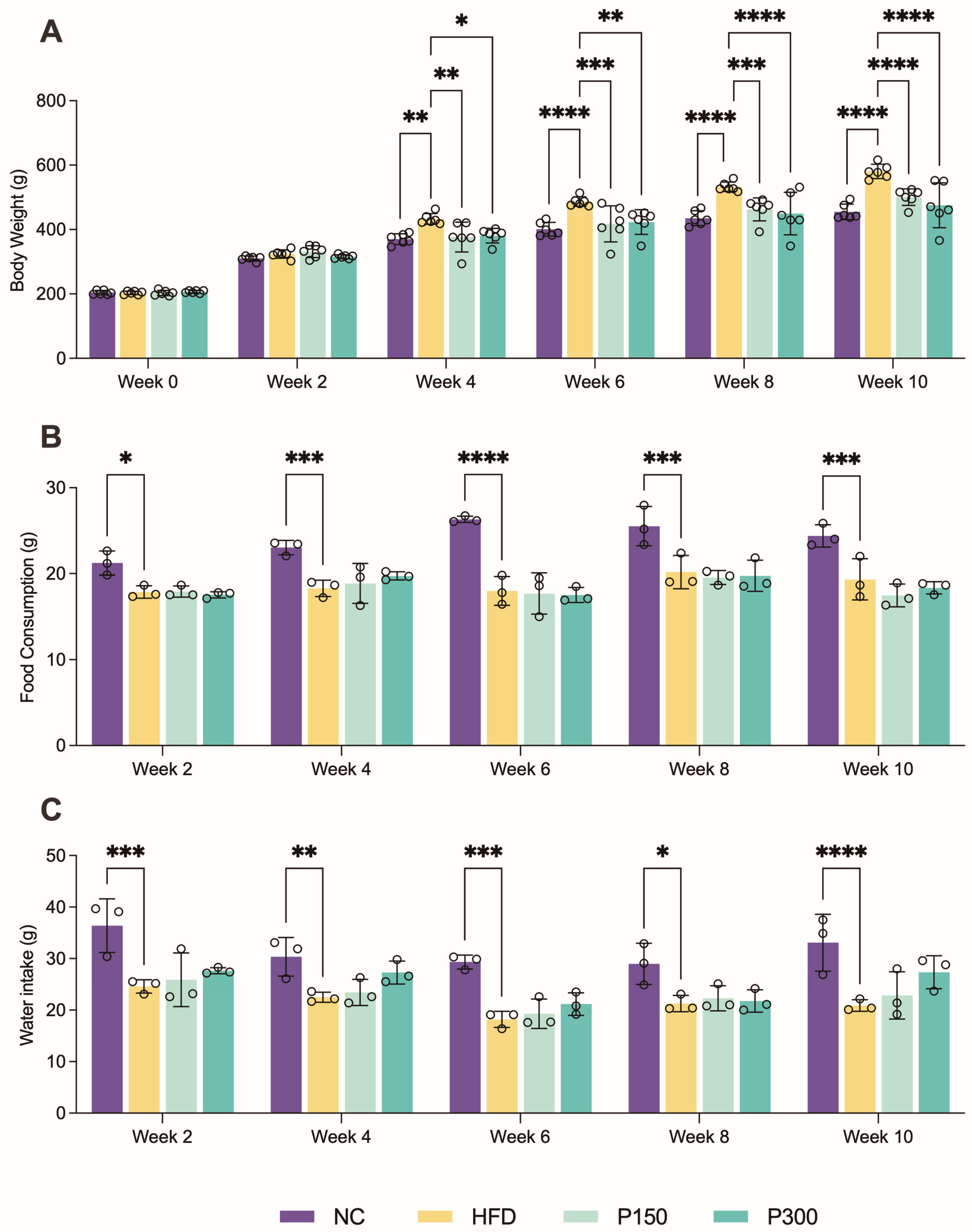
3.2. Propolis and Hepatic Steatosis in HFD Rats
3.3. Propolis and Liver Lipid Metabolism in Rats


3.4. Propolis Effect on Colonic Structure and Enteroendocrine Hormone Secretion in HFD Rats
3.5. Effects of Propolis on Gut Microbiota Diversity in HFD Rats

3.6. Propolis Effect on Gut Microbiota Composition and SCFAs in HFD Rats


3.7. The Dominant Bacteria in the Regulation of Gut Hormones and Lipid Metabolism by Propolis

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, J.; McCallin, T.; Martinez, J.; Chacko, S.; Yusuf, S. Hyperlipidemia. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 41, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, N.C.; Davies, M.J.; Lingvay, I.; Knop, F.K. Semaglutide for the treatment of overweight and obesity: A review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Function and mechanisms of enteroendocrine cells and gut hormones in metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, B.B. Srebp2: A master regulator of sterol and fatty acid synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, D.; Hegarty, B.; Bossard, P.; Ferre, P.; Foufelle, F. SREBP transcription factors: Master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 2004, 86, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Pan, J.; Qu, N.; Lei, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, D. The AMPK pathway in fatty liver disease. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 970292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janovska, A.; Hatzinikolas, G.; Staikopoulos, V.; McInerney, J.; Mano, M.; Wittert, G.A. AMPK and ACC phosphorylation: Effect of leptin, muscle fibre type and obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 284, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, I.C.; Chen, Z.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.S.; Marin, T.L.; Hsu, P.H.; Su, M.I.; Cui, X.; Pan, S.; Lytle, C.Y.; et al. Glucagon regulates ACC activity in adipocytes through the CAMKKbeta/AMPK pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1560–E1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Nian, C.; McIntosh, C.H. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in adipocytes. A role for a protein kinase B, LKB1, and AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8557–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, L.; Fu, X. Interkingdom signaling between gastrointestinal hormones and the gut microbiome. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2456592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Masujima, Y.; Ushiroda, C.; Mizushima, R.; Taira, S.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Kimura, I. Dietary short-chain fatty acid intake improves the hepatic metabolic condition via FFAR3. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, S.A.; MacSharry, J.; Casey, P.G.; Kinsella, M.; Murphy, E.F.; Shanahan, F.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Regulation of host weight gain and lipid metabolism by bacterial bile acid modification in the gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altabbal, S.; Athamnah, K.; Rahma, A.; Wali, A.F.; Eid, A.H.; Iratni, R.; Al Dhaheri, Y. Propolis: A Detailed Insight of Its Anticancer Molecular Mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Sahlabadi, A.; Chhabra, M.; Rahmani, J.; Momeni, A.; Karam, G.; Nattagh-Eshtivani, E.; Nouri, M.; Clark, C.; Salehi, P.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effect of propolis on anthropometric indices and lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, D.; Miryan, M.; Tutunchi, H.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Sadeghi, E.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Ostadrahimi, A. A systematic review of preclinical studies on the efficacy of propolis for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koya-Miyata, S.; Arai, N.; Mizote, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Ushio, S.; Iwaki, K.; Fukuda, S. Propolis prevents diet-induced hyperlipidemia and mitigates weight gain in diet-induced obesity in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichi, I.; Hori, H.; Takashima, Y.; Adachi, N.; Kataoka, R.; Okihara, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Kojo, S. The beneficial effect of propolis on fat accumulation and lipid metabolism in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, H127–H131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.W. Taiwanese green propolis ameliorates metabolic syndrome via remodeling of white adipose tissue and modulation of gut microbiota in diet-induced obese mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H. Propolis modulates the gut microbiota and improves the intestinal mucosal barrier function in diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, X.L.; Shen, X.G.; Sun, L.P.; Wu, L.M.; Wei, J.Q.; Marcucci, M.C.; Hu, F.L.; Liu, J.X. Effects of Chinese Propolis in Protecting Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells against Mastitis Pathogens-Induced Cell Damage. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8028291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.Y.; Aihara, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Kanazawa, K.; Mizuno, M. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces secretion of anorexigenic gut hormones. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 57, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, T.S.; Lima, P.R.; Carvalho, K.M.; Fontenele, T.M.; Solon, F.R.; Tome, A.R.; de Lemos, T.L.; da Cruz Fonseca, S.G.; Santos, F.A.; Rao, V.S.; et al. Ferulic acid lowers body weight and visceral fat accumulation via modulation of enzymatic, hormonal and inflammatory changes in a mouse model of high-fat diet-induced obesity. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.C.; Pinheiro, D.; de la Rosa, T.; de Almeida, A.G.; Scorza, F.A.; Scorza, C.A. Propolis as A Potential Disease-Modifying Strategy in Parkinson’s Disease: Cardioprotective and Neuroprotective Effects in the 6-OHDA Rat Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tao, L.; Chen, X.; Jones, T.J.; Wang, K.; Hu, F. Chinese Propolis Prevents Obesity and Metabolism Syndromes Induced by a High Fat Diet and Accompanied by an Altered Gut Microbiota Structure in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Han, M.; Shen, Z.; Huang, H.; Miao, X. Anti-hypertensive and cardioprotective effects of a novel apitherapy formulation via upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and -gamma in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Di, Y.; Li, N.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Chicoric Acid Differentially Ameliorates Circadian Rhythm Disorder-Induced Liver Glucose Homeostasis Dysregulation in Mice Depending on Intervention Time. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 15596–15609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Jia, Y.; Shi, J.; Tong, Z.; Fang, D.; Yang, B.; Su, C.; Li, R.; Xiao, X.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in high-fat-diet-fed mice are associated with antibiotic tolerance. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.J.; Gross, R.; Bittinger, K.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Lewis, J.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Power and sample-size estimation for microbiome studies using pairwise distances and PERMANOVA. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Hu, M.; Huang, X.; Yu, D.; Jia, L.; Zhi, W.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Saponins from Panax japonicus Enhance Lipolysis via Acting on FGF21-beta-Klotho/FGFR1 in Obese Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 15624–15636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Meng, Y.; Deng, Z.; Bu, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, A.; Wu, S.; Kan, X. Fruit Phenotype Analysis of SlSAHH2-CRISPR Tomato and Methylation Mechanism of SlSAHH2 Promoting Fruit Ripening. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 18691–18705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Pan, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, M.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Qi, J. CXCL5 Promotes Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Activating Kupffer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Piao, X.; Mahfuz, S.; Long, S.; Wang, J. The interaction among gut microbes, the intestinal barrier and short chain fatty acids. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Artis, D.; Becker, C. The intestinal barrier: A pivotal role in health, inflammation, and cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 10, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L.; Moron, R.; Sanchez, M.; Zarzuelo, A.; Galisteo, M. Quercetin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and improves the inflammatory status in obese Zucker rats. Obesity 2008, 16, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.; Lee, E.S.; Huh, J.H.; Chung, C.H. Caffeic acid ameliorates hepatic steatosis and reduces ER stress in high fat diet-induced obese mice by regulating autophagy. Nutrition 2018, 55–56, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Shi, W.; Zeng, Z. Kaempferitrin: A Flavonoid Marker to Distinguish Camellia oleifera Honey. Nutrients 2023, 15, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yin, L.; Shang, J.; Liang, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Qiang, G.; Du, G.; Yang, X. Kaempferol attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic mice via the Sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergstrom, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G.M.; Schutte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodriguez-Pineiro, A.M.; Nystrom, E.E.; et al. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: The good, the bad and the future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Chien, Y.W.; Chang, M.L.; Hou, C.C.; Chan, C.H.; Tang, H.W.; Huang, H.Y. Taiwanese Green Propolis Ethanol Extract Delays the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. Phenolic Compounds of Propolis Alleviate Lipid Metabolism Disorder. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2021, 2021, 7615830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Qian, K.; Jiang, N.; Zheng, X.L.; Cayabyab, F.S.; Tang, C.K. ABCG5/ABCG8 in cholesterol excretion and atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 428, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; You, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, X. Wild Lonicera caerulea berry polyphenol extract reduces cholesterol accumulation and enhances antioxidant capacity in vitro and in vivo. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, B. The Effects of Polyphenol-Rich Black Elderberry on Oxidative Stress and Hepatic Cholesterol Metabolism. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, X.; Heiyan-Perhat, S.U.; Yang, P.; Han, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; He, E.; Li, Y. Therapeutic Role of Polyphenol Extract from Prunus cerasifera Ehrhart on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver. Plants 2024, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, X. Apple Polyphenol Extract Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Regulating Bile Acid Synthesis and Gut Microbiota in C57BL/6 Male Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6829–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.G.; Bloom, S.R. Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Nature 2006, 444, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.V.; Hamr, S.C.; Duca, F.A. Regulation of energy balance by a gut-brain axis and involvement of the gut microbiota. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, N.; Montgomery, I.A.; O’Harte, F.P.; Frizelle, P.; Flatt, P.R. Comparison of the independent and combined metabolic effects of subchronic modulation of CCK and GIP receptor action in obesity-related diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Yao, J.; Gu, H.; Liu, L. Leptin Induced TLR4 Expression via the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway in Obesity-Related Osteoarthritis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 7385160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ru, F.; He, Y. Leptin promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in benign prostatic hyperplasia through downregulation of BAMBI. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 387, 111754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, C.L.; Garthwaite, M.A.; Cross, W.; Hinley, J.; Trejdosiewicz, L.K.; Southgate, J. PPARgamma-regulated tight junction development during human urothelial cytodifferentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 208, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation promotes intestinal barrier function by improving mucus and tight junctions in a mouse colitis model. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Ma, N.; Liu, G.; Wu, Q.; Su, S.; Wang, J.; Geng, Y. Ethanol extract of propolis regulates type 2 diabetes in mice via metabolism and gut microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 310, 116385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottman, N.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Aalvink, S.; de Vos, W.M.; Belzer, C. Action and function of Akkermansia muciniphila in microbiome ecology, health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Zhao, W.; Wu, L.; Tian, W.; Xue, X. Comprehensive study of volatile compounds of rare Leucosceptrum canum Smith honey: Aroma profiling and characteristic compound screening via GC–MS and GC–MS/MS. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanai-Shacoori, Z.; Smida, I.; Bousarghin, L.; Loreal, O.; Meuric, V.; Fong, S.B.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A. Roseburia spp.: A marker of health? Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Tao, H.; Zhao, H.; Cui, B. Butyrate Regulates Intestinal DNA Virome and Lipopolysaccharide Levels to Prevent High-Fat Diet-Related Liver Damage in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 8277–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.H. Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Lee, M.S.; Bae, J.W. An increase in the Akkermansia spp. population induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice. Gut 2014, 63, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tengeler, A.C.; Gart, E.; Wiesmann, M.; Arnoldussen, I.A.C.; van Duyvenvoorde, W.; Hoogstad, M.; Dederen, P.J.; Verweij, V.; Geenen, B.; Kozicz, T.; et al. Propionic acid and not caproic acid, attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and improves (cerebro) vascular functions in obese Ldlr-/-.Leiden mice. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9575–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.P.; Martin, J.C.; Campbell, G.; Mayer, C.D.; Flint, H.J. Whole-genome transcription profiling reveals genes up-regulated by growth on fucose in the human gut bacterium “Roseburia inulinivorans”. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 4340–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Belzer, C.; Goossens, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Thas, O.; De Weirdt, R.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Van de Wiele, T. Butyrate-producing Clostridium cluster XIVa species specifically colonize mucins in an in vitro gut model. ISME J. 2013, 7, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolhurst, G.; Heffron, H.; Lam, Y.S.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Diakogiannaki, E.; Cameron, J.; Grosse, J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012, 61, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Luan, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Cordycepin reduces weight through regulating gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriz, B.A.; Castro, A.P.; Almeida, J.A.; Gomes, C.P.; Fernandes, G.R.; Kruger, R.H.; Pereira, R.W.; Franco, O.L. Exercise induction of gut microbiota modifications in obese, non-obese and hypertensive rats. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Huang, W.; Shang, Y.; Sharaf El-Din, M.G.; Hang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, K. Propolis Modulates the Gut Microbiota–Gut Hormone–Liver AMPK Axis to Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders in Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193114
Sun Y, Huang W, Shang Y, Sharaf El-Din MG, Hang H, Wang P, Zhang C, Huang Y, Wang K. Propolis Modulates the Gut Microbiota–Gut Hormone–Liver AMPK Axis to Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders in Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193114
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yanru, Wanwan Huang, Yingying Shang, Mohamed G. Sharaf El-Din, Hua Hang, Peng Wang, Cuiping Zhang, Yuan Huang, and Kai Wang. 2025. "Propolis Modulates the Gut Microbiota–Gut Hormone–Liver AMPK Axis to Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders in Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193114
APA StyleSun, Y., Huang, W., Shang, Y., Sharaf El-Din, M. G., Hang, H., Wang, P., Zhang, C., Huang, Y., & Wang, K. (2025). Propolis Modulates the Gut Microbiota–Gut Hormone–Liver AMPK Axis to Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders in Rats. Nutrients, 17(19), 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193114







