Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Urolithin a Synergistically Mitigate Heat Stroke-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglial Cells
Abstract
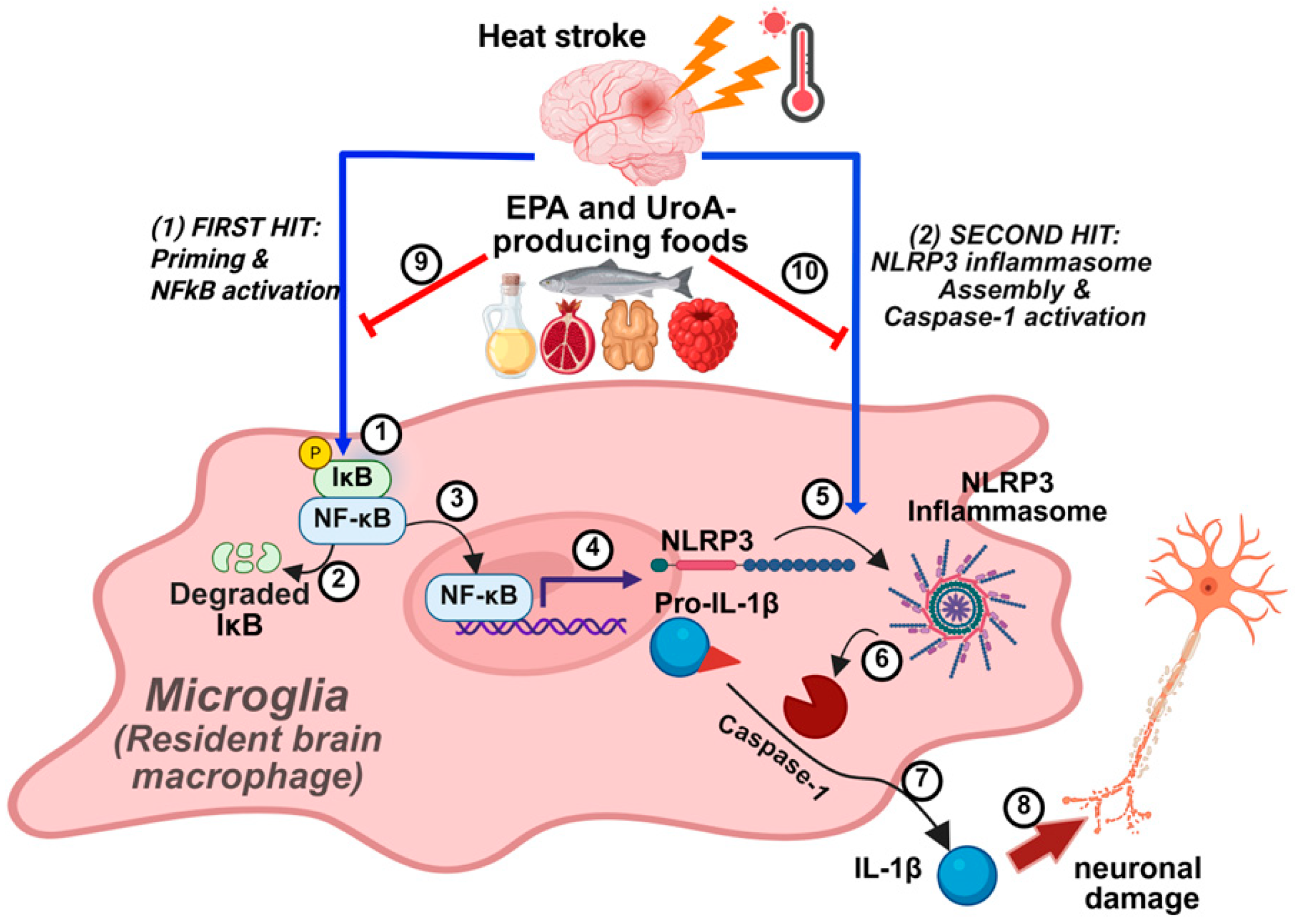
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
2.2. In Vitro Modality of Heat Stroke (HS)
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. iGLuc Reporter Assay
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.6. Western Blot Analysis and ELISA
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
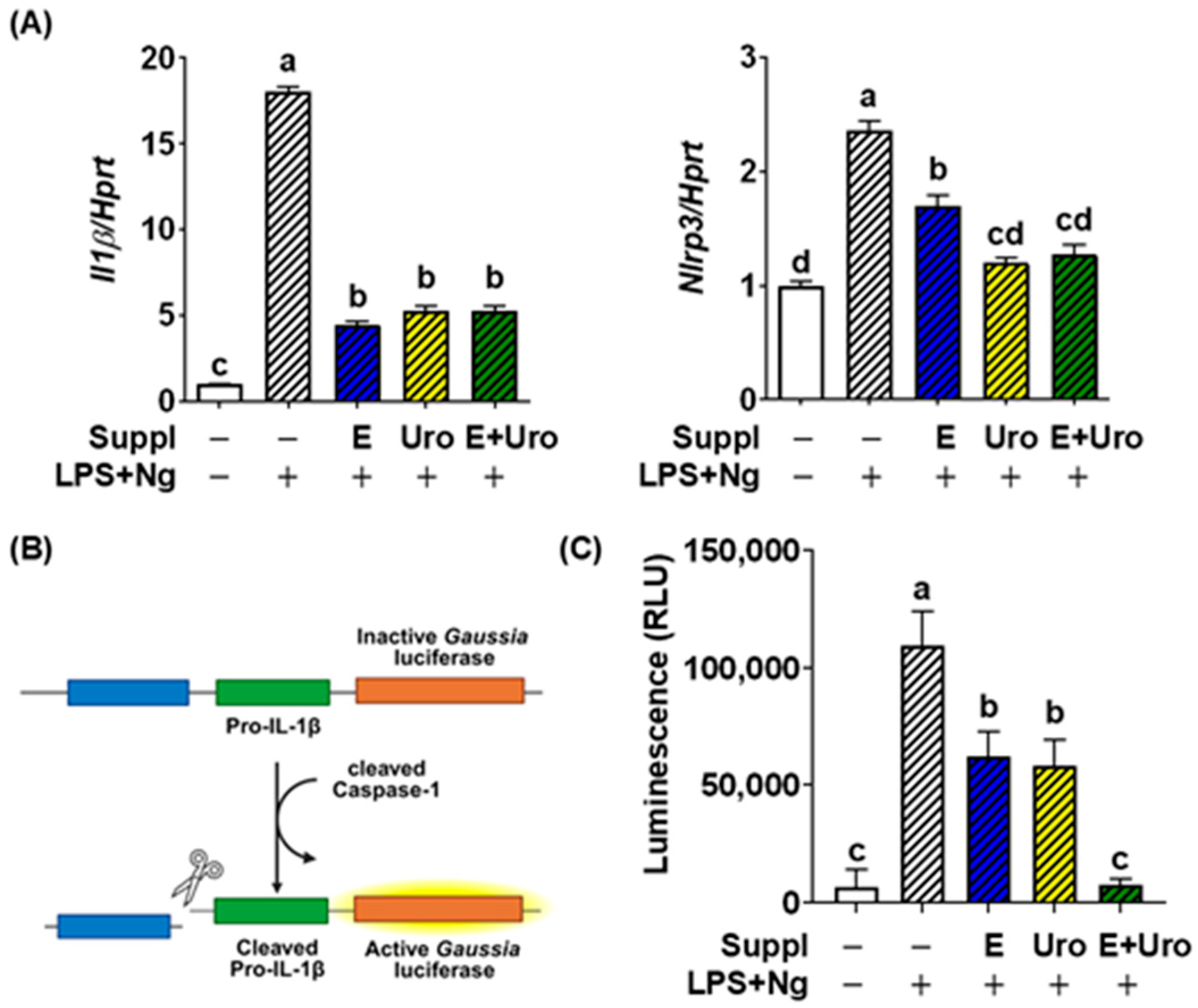
3.1. EPA and UroA Synergistically Suppressed the PAMP-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in BV2 Cells
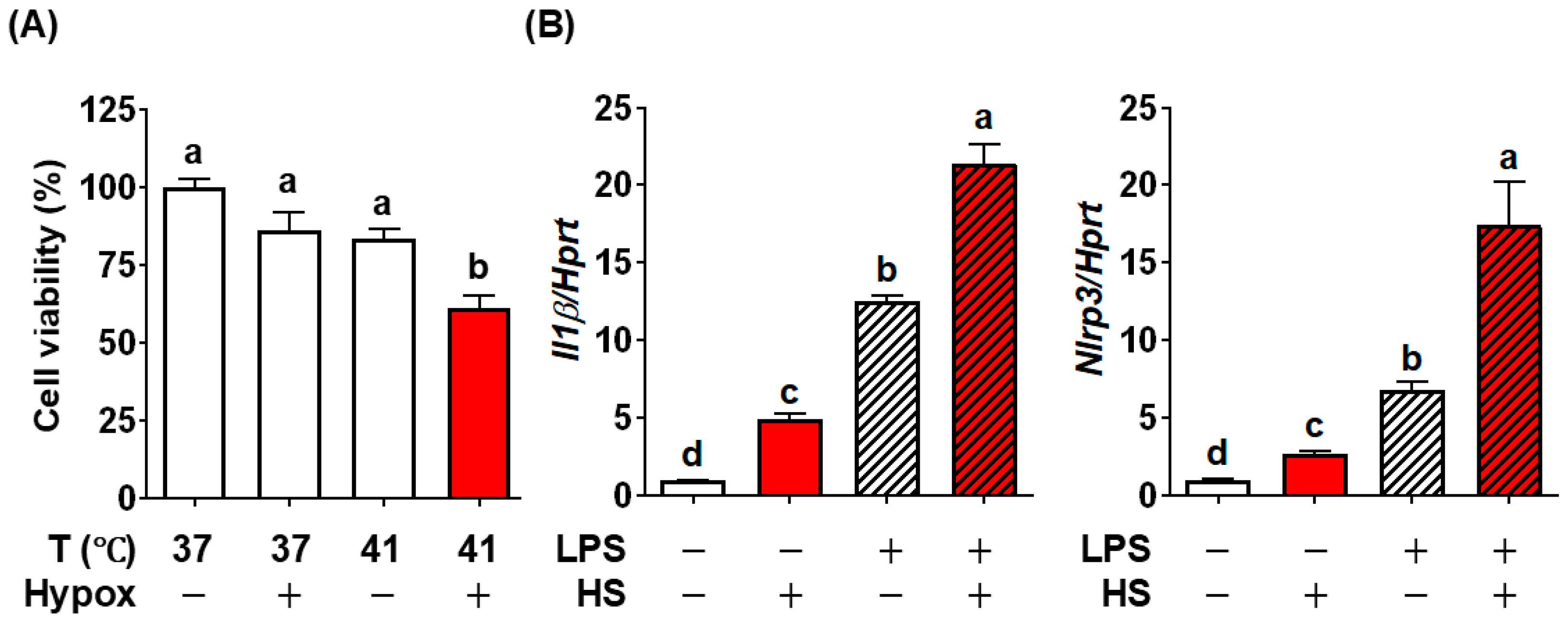
3.2. Establishment of Heat Stroke Modality In Vitro Using BV2 Microglial Cells
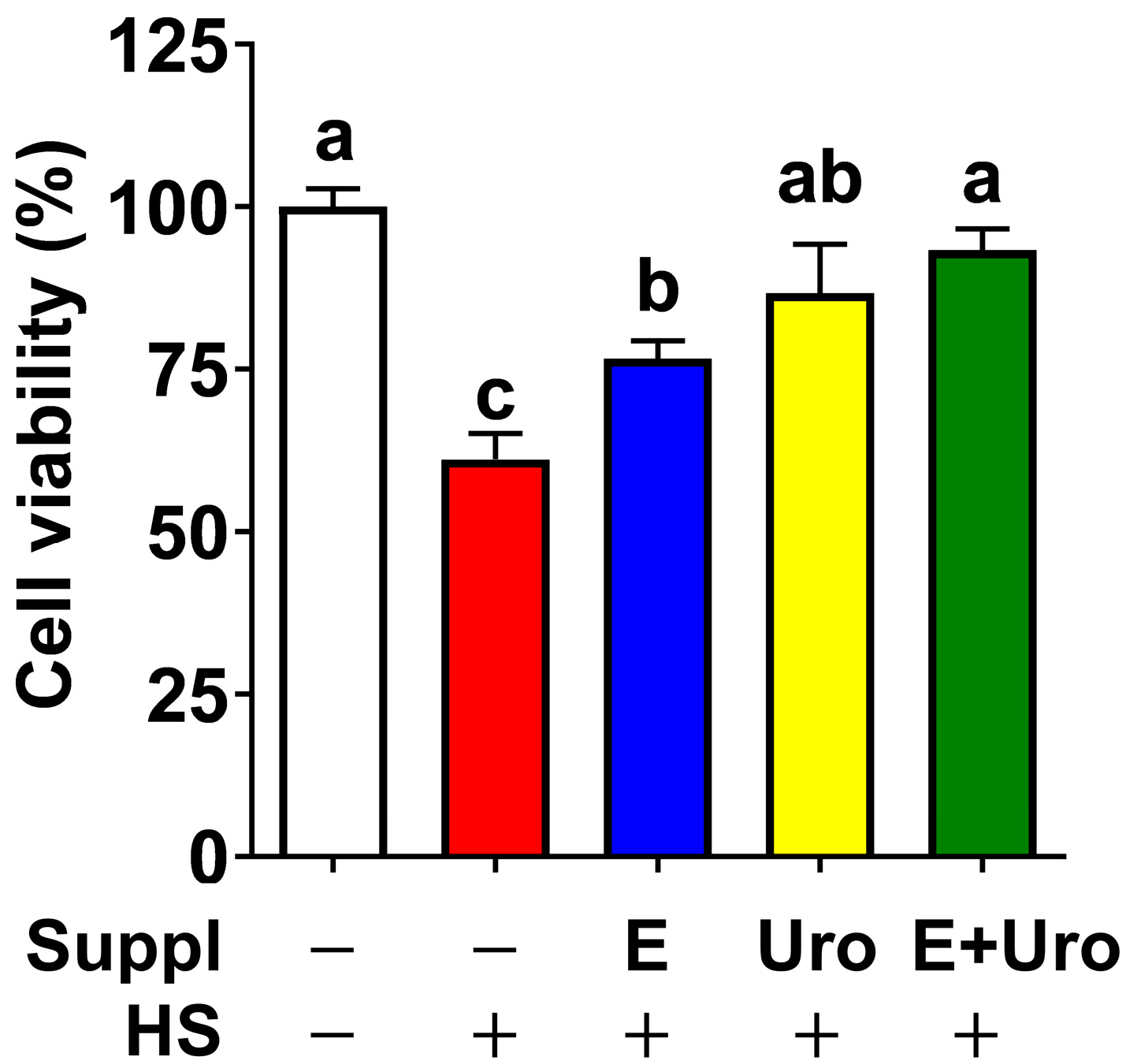
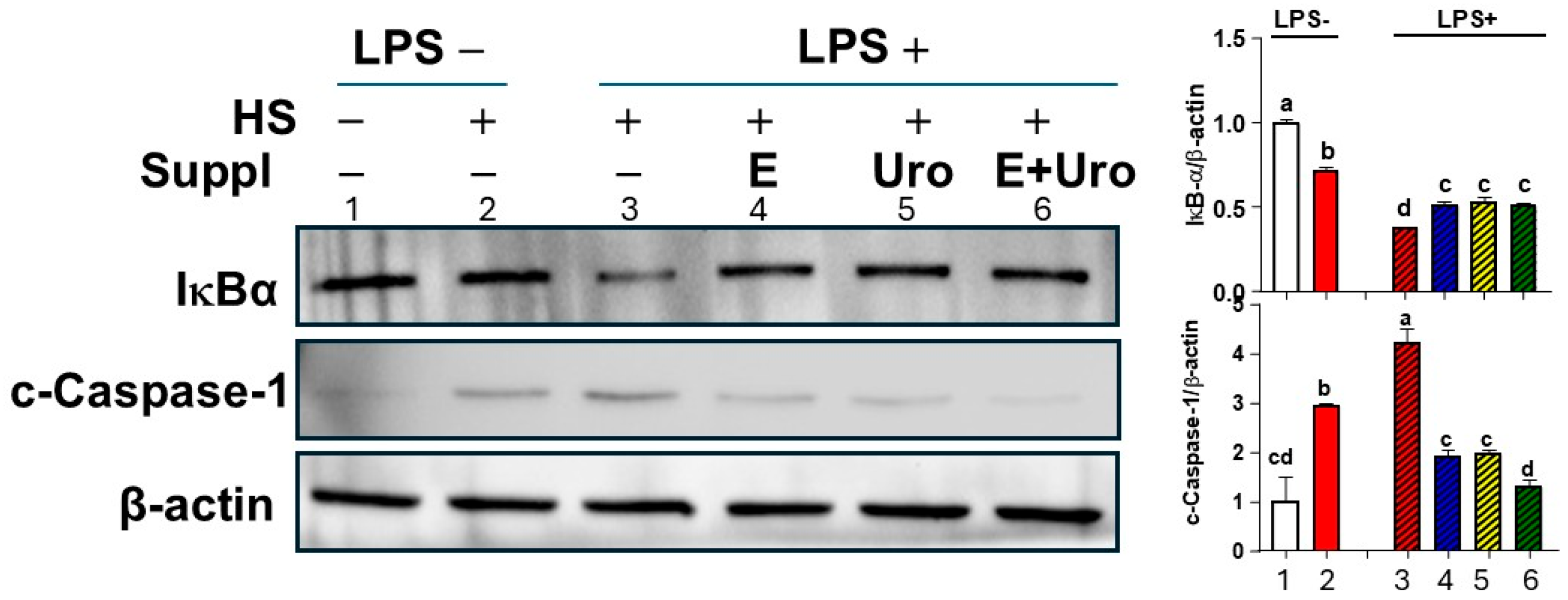
3.3. EPA, UroA, and Their Combination Were Effective in Preventing HS-Induced Cell Viability by Mitigating NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ALA | α-linolenic acid |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| Hprt | Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase |
| HS | Heat stroke |
| iGLuc | pro-IL-1β-Gaussia luciferase fusion |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccaride |
| Ng | Nigericin |
| NLRP3 | Nod-like receptor protein 3 |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| UroA | Urolithin A |
References
- World Health Organization. Heatwaves. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/heatwaves (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- World Health Organization. Heat and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-heat-and-health (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Howard, J.T.; Androne, N.; Alcover, K.C.; Santos-Lozada, A.R. Trends of Heat-Related Deaths in the US, 1999–2023. JAMA 2024, 332, 1203–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.D.; Akerman, A.P.; Notley, S.R.; McGinn, R.; Poirier, P.; Gosselin, P.; Kenny, G.P. Physiological factors characterizing heat-vulnerable older adults: A narrative review. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.G. Heat stroke and heat exhaustion: An update. Curr. Med. Issues 2018, 16, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Pei, L.; Yao, S.; Wu, Y.; Shang, Y. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Neurological Diseases, from Functions to Therapies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchama, A.; Knochel, J.P. Heat stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, D.; Lv, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z. The significant mechanism and treatments of cell death in heatstroke. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yu, H.; Bu, Z.; Wen, L.; Yan, L.; Feng, J. Focus on the Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 894298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Yang, Y.; Ou, T.; Key, C.C.; Tong, S.H.; Sequeira, R.C.; Nelson, J.M.; Nie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Boudyguina, E.; et al. Dietary PUFAs attenuate NLRP3 inflammasome activation via enhancing macrophage autophagy. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1808–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, H.; Dong, R.; Wu, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D. Effectiveness of targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome by using natural polyphenols: A systematic review of implications on health effects. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Si, Y.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Lu, L.; Wu, C.; Guan, X.; Liang, Y. Vitamin C inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and delays the development of age-related hearing loss in male C57BL/6 mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2024, 836, 137897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor Inhibits NLRP3 Activation by Impeding Its BRCC3-Mediated Deubiquitination. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Hou, Y.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Gong, T.; Jiang, W. Synthetic vitamin K analogs inhibit inflammation by targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, G.S. Riboflavin, vitamin B2, attenuates NLRP3, NLRC4, AIM2, and non-canonical inflammasomes by the inhibition of caspase-1 activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings-Almeida, B.; Castelpoggi, J.P.; Ramos-Junior, E.S.; Ferreira, E.O.; Domingues, R.; Echevarria-Lima, J.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; Moreira-Souza, A.C.A.; Marino, E.; Mackay, C.R.; et al. Dietary Fiber Drives IL-1beta-Dependent Peritonitis Induced by Bacteroides fragilis via Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszak, M.; Dobrzynska, M.; Kawka, A.; Gorna, I.; Wozniak, D.; Przyslawski, J.; Drzymala-Czyz, S. Role of Omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) as modulatory and anti-inflammatory agents in noncommunicable diet-related diseases—Reports from the last 10 years. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 63, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerec, A.H.; Lim, X.K.; Khoo, A.L.; Sandalova, E.; Guan, L.; Feng, L.; Maier, A.B. Targeting aging with urolithin A in humans: A systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.P.; Xie, J.L.; Huang, L.Y.; Wu, Q.Z.; Tang, D.F.; Jin, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, M.F. miR-29a-3p promotes the regulatory role of eicosapentaenoic acid in the NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy in microglial cells. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toney, A.M.; Albusharif, M.; Works, D.; Polenz, L.; Schlange, S.; Chaidez, V.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Chung, S. Differential Effects of Whole Red Raspberry Polyphenols and Their Gut Metabolite Urolithin A on Neuroinflammation in BV-2 Microglia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wang, W.; Okla, M.; Kang, I.; Moreau, R.; Chung, S. Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by gamma-tocotrienol ameliorates type 2 diabetes. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartok, E.; Bauernfeind, F.; Khaminets, M.G.; Jakobs, C.; Monks, B.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E.; Hornung, V. iGLuc: A luciferase-based inflammasome and protease activity reporter. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthi, S.; Fairless, C.; Fischer, E.M.; Scovronick, N.; Ben, A.; Coelho, M.; Guo, Y.L.; Guo, Y.; Honda, Y.; Huber, V.; et al. Rapid increase in the risk of heat-related mortality. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, G.P.; Yardley, J.; Brown, C.; Sigal, R.J.; Jay, O. Heat stress in older individuals and patients with common chronic diseases. CMAJ 2010, 182, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Gu, X.L.; Zhao, X.; He, X.; Shi, H.W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.M.; Su, Y.N.; Zhu, J.B.; Li, Z.W.; et al. NLRP3 ablation enhances tolerance in heat stroke pathology by inhibiting IL-1beta-mediated neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Dai, X. Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Explor. Immunol. 2022, 2, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewett, S.J.; Jackman, N.A.; Claycomb, R.J. Interleukin-1beta in Central Nervous System Injury and Repair. Eur. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 1, 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Rong, Y. Extracellular histones exacerbate heat stroke-induced liver injury by triggering hepatocyte pyroptosis and liver injury via the TLR9-NLRP3 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 126, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Tong, H.; Lou, A.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, L.; Li, X. AVE 0991 Attenuates Pyroptosis and Liver Damage after Heatstroke by Inhibiting the ROS-NLRP3 Inflammatory Signalling Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1806234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C. Extreme Heat Exposure Induced Acute Kidney Injury through NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Mice. Environ. Health 2024, 2, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Yang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhong, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Luo, E.; Ding, H.; Li, W. Heat stress induces IL-1beta and IL-18 overproduction via ROS-activated NLRP3 inflammasome: Implication in neuroinflammation in mice with heat stroke. Neuroreport 2024, 35, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighriri, I.M.; Alsubaie, A.M.; Hakami, F.M.; Hamithi, D.M.; Alshekh, M.M.; Khobrani, F.A.; Dalak, F.E.; Hakami, A.A.; Alsueaadi, E.H.; Alsaawi, L.S.; et al. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Tang, C.; Li, H.; Lei, J.; Zhu, L.; Kou, L.; Li, H.; Luo, S.; Li, C.; Chen, W.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents inflammation induced by acute cerebral infarction through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Teruyoshi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Enriched Phosphatidylcholine Mitigated Abeta1-42-Induced Neurotoxicity via Autophagy-Inflammasome Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13767–13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Y. A comparative study of EPA-enriched ethanolamine plasmalogen and EPA-enriched phosphatidylethanolamine on Abeta(42) induced cognitive deficiency in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3008–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, M. DHA and EPA Prevent Seizure and Depression-Like Behavior by Inhibiting Ferroptosis and Neuroinflammation via Different Mode-of-Actions in a Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Kindling Model in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2200275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toney, A.M.; Fox, D.; Chaidez, V.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Chung, S. Immunomodulatory Role of Urolithin A on Metabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, D.; Yu, S.; Lou, H. Urolithin A promotes mitophagy and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Neuropharmacology 2022, 207, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, W.; Kishi, H.; Uchiyama, K.; Ohhira, S.; Kobashi, G. Urolithin A suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting the generation of reactive oxygen species and prevents monosodium urate crystal-induced peritonitis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2024, 88, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Yin, J.; Bai, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Urolithin A suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and postmenopausal osteoporosis by, suppresses inflammation and downstream NF-kappaB activated pyroptosis pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Lei, J.; Zhou, B. Methylated urolithin A, mitigates cognitive impairment by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction in aging mice. Neuropharmacology 2024, 252, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misrani, A.; Tabassum, S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Tan, S.H.; Long, C. Urolithin A Prevents Sleep-deprivation-induced Neuroinflammation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Young and Aged Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 1448–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, D.; Fang, L.; Leng, Y.; Min, W. Therapeutic effects of a walnut-derived peptide on NLRP3 inflammasome activation, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive dysfunction in T2DM mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, Y.Y.; Hong, Z.S.; Xie, J.; Tian, Y. Isolation, Identification, Activity Evaluation, and Mechanism of Action of Neuroprotective Peptides from Walnuts: A Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X. Recent Studies on Protective Effects of Walnuts against Neuroinflammation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, E.O.; Oluwatowoju, I. Omega-3 index determined by gas chromatography with electron impact mass spectrometry. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 80, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.X.; Zhu, Y.F.; Wang, C.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Xue, C.H.; Huang, Q.R.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, T.T. EPA-enriched plasmalogen attenuates the cytotoxic effects of LPS-stimulated microglia on the SH-SY5Y neuronal cell line. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 186, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Spinetti, T.; Tardivel, A.; Castillo, R.; Bourquin, C.; Guarda, G.; Tian, Z.; Tschopp, J.; Zhou, R. Omega-3 fatty acids prevent inflammation and metabolic disorder through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 2013, 38, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espin, J.C.; Larrosa, M.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Tomas-Barberan, F. Biological significance of urolithins, the gut microbial ellagic Acid-derived metabolites: The evidence so far. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 270418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Sheng, S.; Li, J.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, F. Ellagic Acid Protects Dopamine Neurons via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2963540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Neuroprotective effects of walnut (Juglans regia L.) in nervous system disorders: A comprehensive review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Sheng, L.; Wu, D.; Leng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Protective effect of walnut active peptide against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice based on untargeted metabolomics. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 112998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, F.; Shan, C.; Ma, T.; Geng, S.; Ning, D. Walnut oil alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and regulating gut microbiota. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 154, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, A.; de Rosny, C.; Kieu, T.L.; Perrey, S.; Berger, H.; Fluckiger, A.; Muller, T.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Pichon, L.; Hichami, A.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits both NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and JNK-mediated mature IL-1beta secretion in 5-fluorouracil-treated MDSC: Implication in cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.M.; Ma, D.W. Are all n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids created equal? Lipids Health Dis. 2009, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertheloot, D.; Latz, E.; Franklin, B.S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Metherel, A.H.; Chen, C.T.; Shaikh, S.R.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Layé, S. Brain eicosapentaenoic acid metabolism as a lead for novel therapeutics in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, X.; Peng, X.; Hu, G. Urolithin A in Central Nervous System Disorders: Therapeutic Applications and Challenges. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Chung, S. Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Urolithin a Synergistically Mitigate Heat Stroke-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglial Cells. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193063
Cho H, Kim J, Park Y, Kim Y-C, Chung S. Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Urolithin a Synergistically Mitigate Heat Stroke-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglial Cells. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193063
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hyunji, Judy Kim, Yongsoon Park, Young-Cheul Kim, and Soonkyu Chung. 2025. "Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Urolithin a Synergistically Mitigate Heat Stroke-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglial Cells" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193063
APA StyleCho, H., Kim, J., Park, Y., Kim, Y.-C., & Chung, S. (2025). Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Urolithin a Synergistically Mitigate Heat Stroke-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglial Cells. Nutrients, 17(19), 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193063





