Human Breast Milk Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Endothelial Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
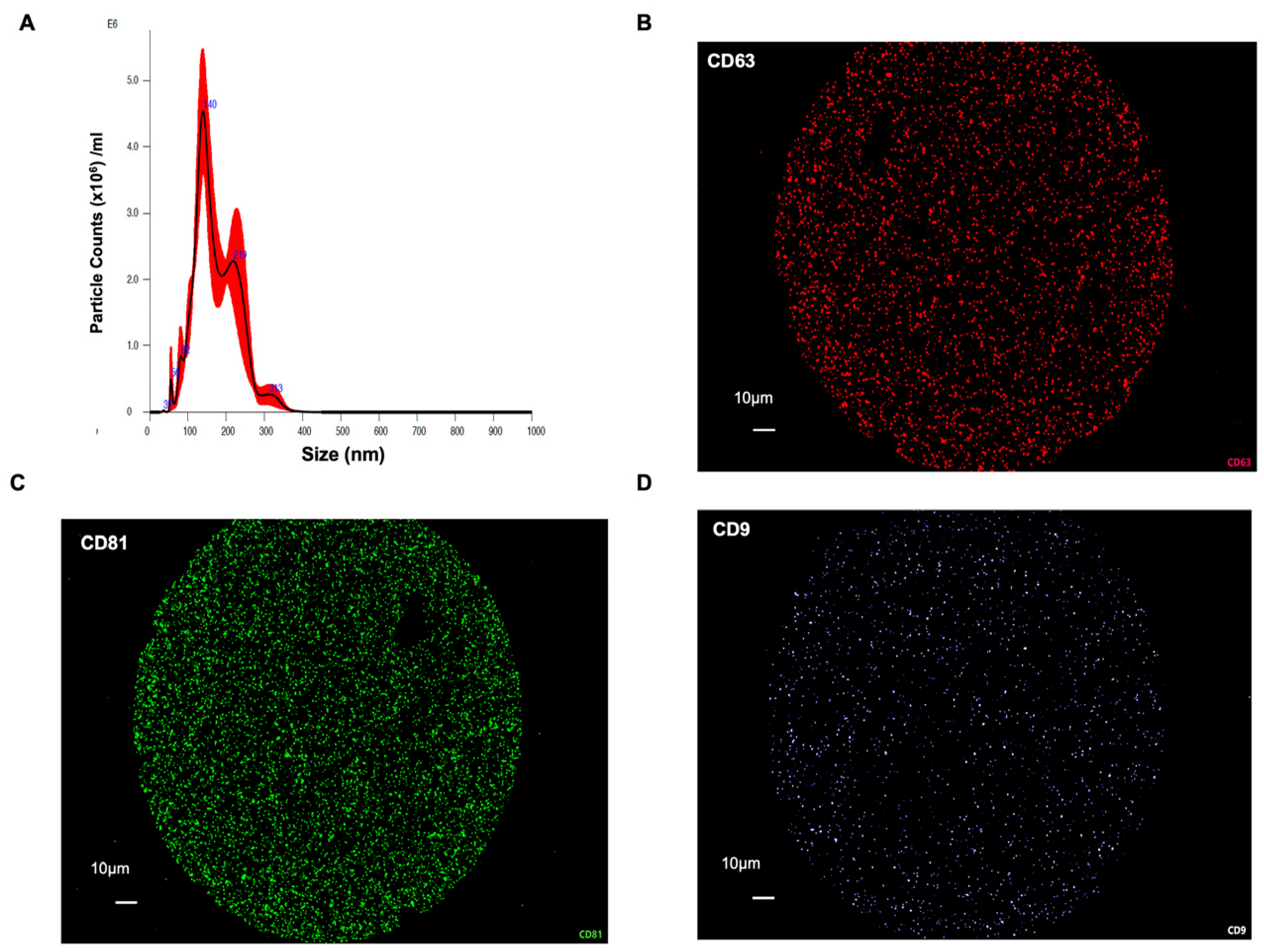
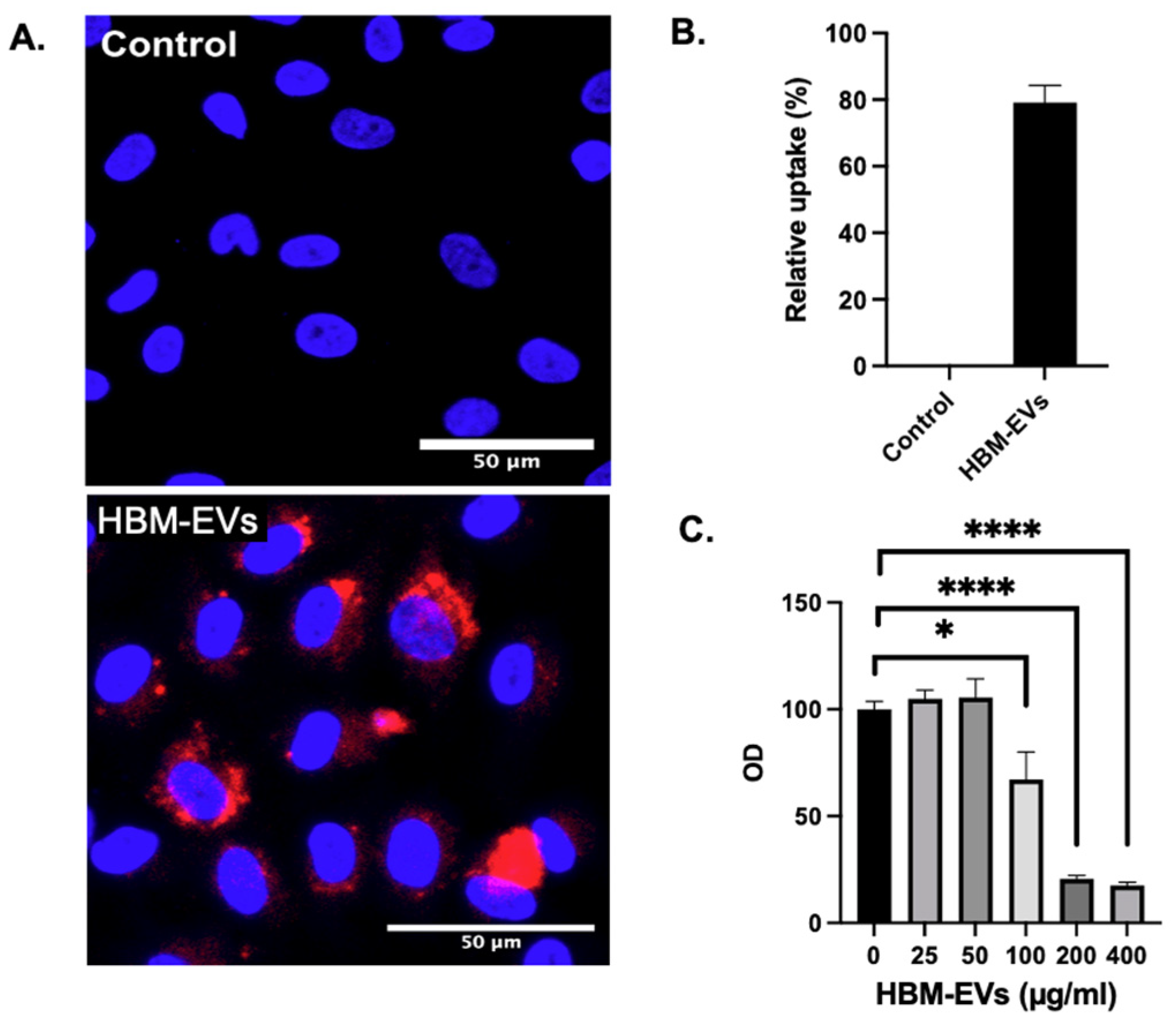
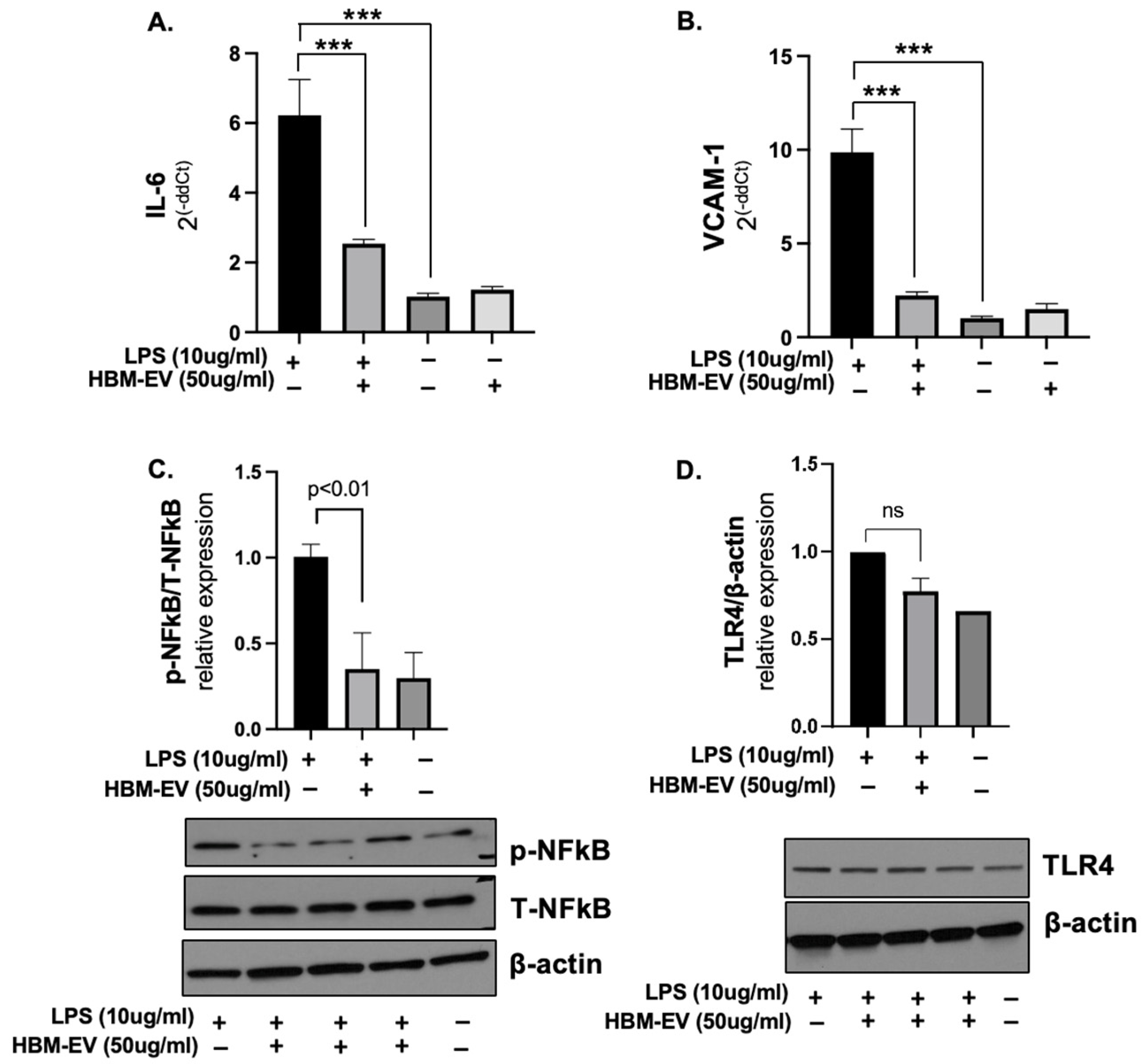
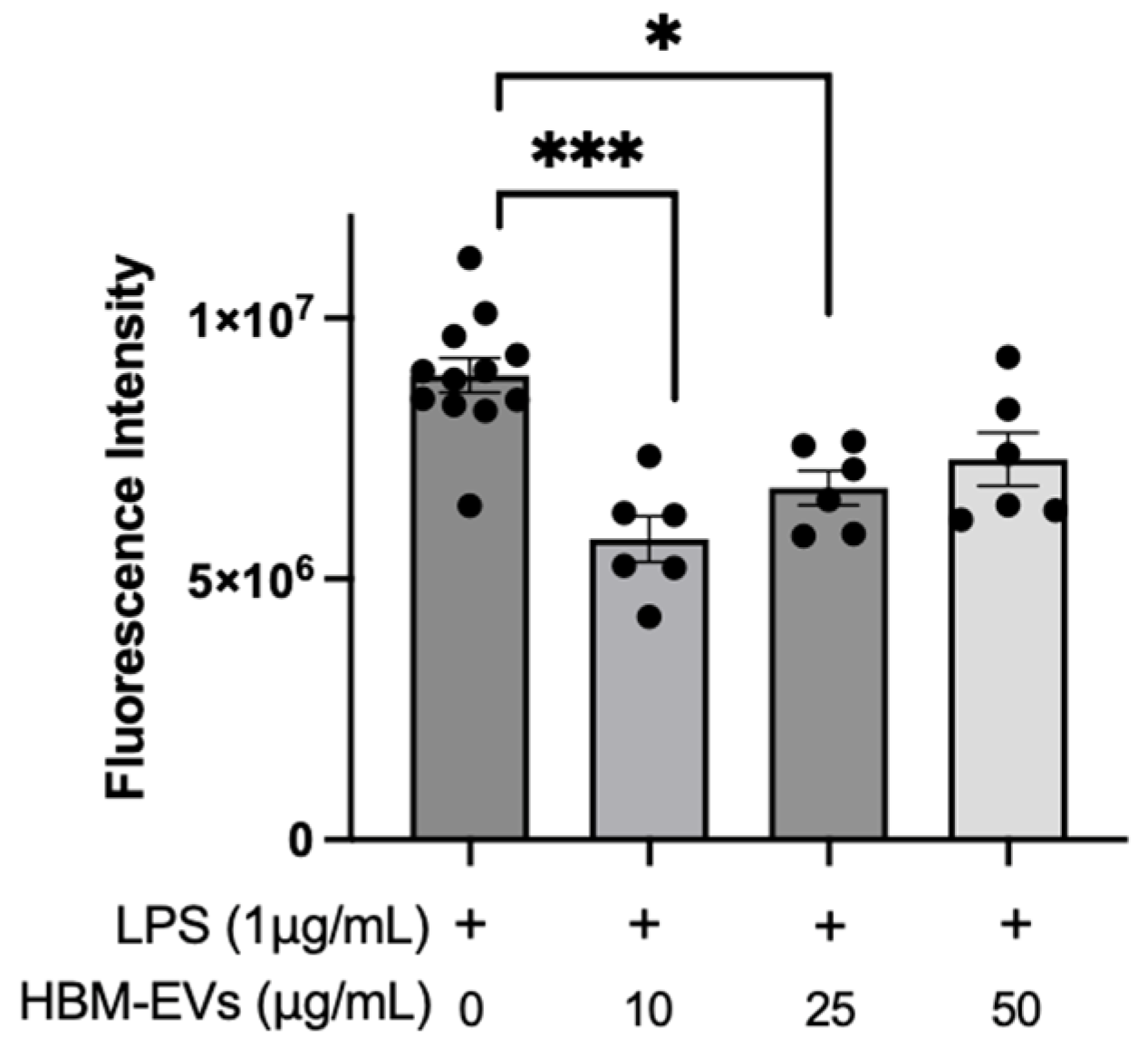
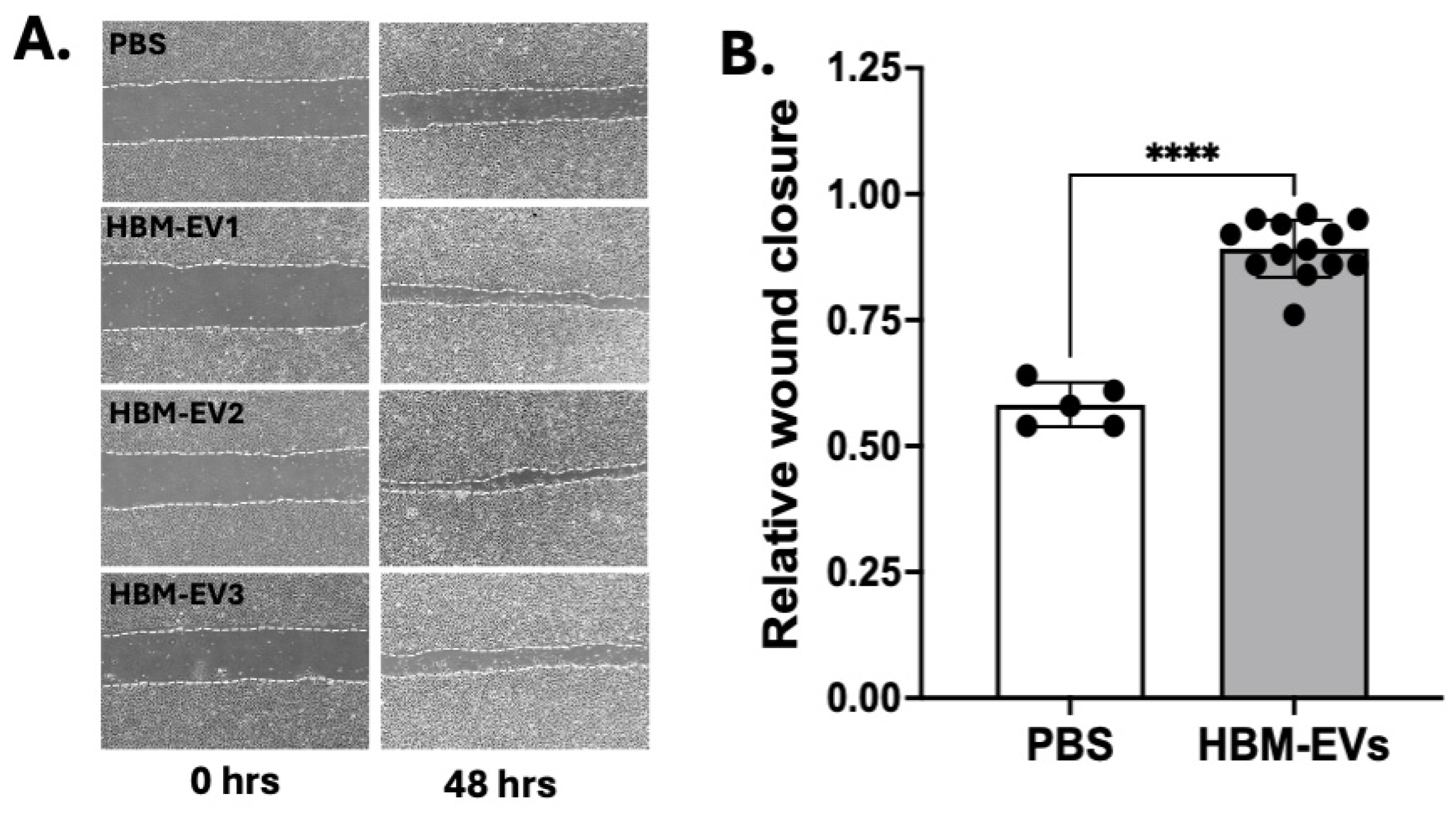
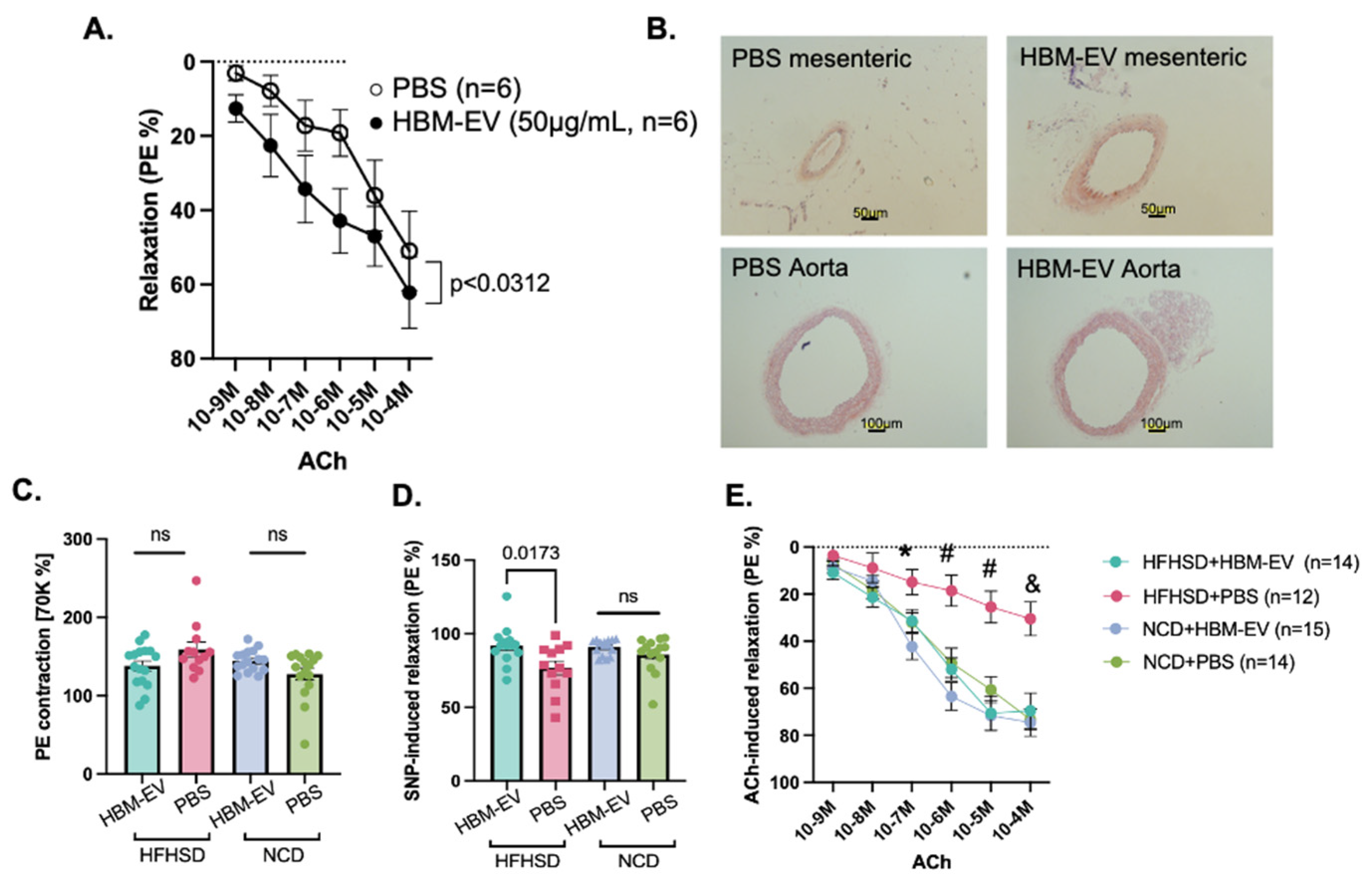
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Galis, Z.S. Exploring the Role of Endothelial Cell Resilience in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsis, V.; Stabouli, S.; Papakatsika, S.; Rizos, Z.; Parati, G. Mechanisms of obesity-induced hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasut, A.; Lama, E.; Van Craenenbroeck, A.H.; Kroon, J.; Carmeliet, P. Endothelial cell metabolism in cardiovascular physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernanz, R.; Martinez-Revelles, S.; Palacios, R.; Martin, A.; Cachofeiro, V.; Aguado, A.; Garcia-Redondo, L.; Barrus, M.T.; de Batista, P.R.; Briones, A.M.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to vascular remodelling and endothelial dysfunction in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3159–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, K.P.; de Oliveira, A.A.; Lima, V.V.; Webb, R.C. Toll-Like Receptor 4 and Blood Pressure: Lessons From Animal Studies. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.O.; He, M. Unlocking the Power of Exosomes for Crossing Biological Barriers in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.E.; Chen, S.; Crouch, K.; Yun, J.; Klingelhutz, A. Impact of Aging and a High-Fat Diet on Adipose-Tissue-Derived Extracellular Vesicle miRNA Profiles in Mice. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Qazi, K.R.; Filen, J.J.; Lahesmaa, R.; Norman, M.; Neve, E.P.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnik, B.C.; Stremmel, W.; Weiskirchen, R.; John, S.M.; Schmitz, G. Exosome-Derived MicroRNAs of Human Milk and Their Effects on Infant Health and Development. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.N.; Hu, H.; Wen, P.C.; Lian, S.; Xie, X.L.; Song, H.L.; Yang, Z.N.; Ren, F.Z. Yak milk-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammation by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/C3 pathway activation. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8411–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T.; Gong, P.; Zhang, L.; Cao, F.; et al. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate ulcerative colitis by regulating the gut immunity and reshaping the gut microbiota. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8570–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.Y.; Hou, L.J.; Sun, J.J.; Zeng, B.; Xi, Q.Y.; Luo, J.Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.L. Porcine Milk Exosome MiRNAs Attenuate LPS-Induced Apoptosis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB and p53 Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9477–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, M.; Sodhi, C.P.; Egan, C.E.; Afrazi, A.; Jia, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Lu, P.; Branca, M.F.; Ma, C.; Prindle, T., Jr.; et al. Breast milk protects against the development of necrotizing enterocolitis through inhibition of Toll-like receptor 4 in the intestinal epithelium via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1166–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betker, J.L.; Angle, B.M.; Graner, M.W.; Anchordoquy, T.J. The Potential of Exosomes From Cow Milk for Oral Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, S.; Upadhyaya, B.; Mutai, E.; Desaulniers, A.T.; Cederberg, R.A.; White, B.R.; Zempleni, J. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ebea, P.; Mutai, E.; Wang, H.; Sukreet, S.; Navazesh, S.; Dogan, H.; Li, W.; Cui, J.; Ji, P.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles in Milk Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier in Murine Cerebral Cortex Endothelial Cells and Promote Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus and Brain Function in C57BL/6J Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 838543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.E.; Vorn, R.; Chimenti, M.; Crouch, K.; Shaoshuai, C.; Narayanaswamy, J.; Harken, A.; Schmidt, R.; Gill, J.; Lee, H. Extracellular vesicle miRNAs in breast milk of obese mothers. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 976886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Yoon, Y.; Oh, D.J. A calpain inhibitor protects against fractalkine production in lipopolysaccharide-treated endothelial cells. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 36, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, R.J.; Choi, H.; Koch, S.R.; Fensterheim, B.A.; Lamb, F.S.; Sherwood, E.R. Endothelial cell tolerance to lipopolysaccharide challenge is induced by monophosphoryl lipid A. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKelvey, K.J.; Powell, K.L.; Ashton, A.W.; Morris, J.M.; McCracken, S.A. Exosomes: Mechanisms of Uptake. J. Circ. Biomark. 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, X.; Luo, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, X. Interaction between mitochondrial homeostasis and barrier function in lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial cell injury. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2023, 104, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.E.; Basu, A.; Dai, A.; Heldak, M.; Makino, A. Coronary endothelial dysfunction and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in type 2 diabetic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 305, C1033–C1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dri, E.; Lampas, E.; Lazaros, G.; Lazarou, E.; Theofilis, P.; Tsioufis, C.; Tousoulis, D. Inflammatory Mediators of Endothelial Dysfunction. Life 2023, 13, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, H.O.; Chaker, H.; Leaming, R.; Johnson, A.; Brechtel, G.; Baron, A.D. Obesity/insulin resistance is associated with endothelial dysfunction. Implications for the syndrome of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zou, M.H. Molecular insights and therapeutic targets for diabetic endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 2009, 120, 1266–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, R.J.; Manca, S.; Friemel, T.; Sukreet, S.; Nguyen, C.; Zempleni, J. Human vascular endothelial cells transport foreign exosomes from cow’s milk by endocytosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C800–C807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Hu, J.; Li, P.; Yan, J.; Ling, X.; Xiao, J. Bovine Milk Exosomes Alleviate Cardiac Fibrosis via Enhancing Angiogenesis In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2022, 15, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troseid, M.; Nestvold, T.K.; Rudi, K.; Thoresen, H.; Nielsen, E.W.; Lappegard, K.T. Plasma lipopolysaccharide is closely associated with glycemic control and abdominal obesity: Evidence from bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Kopydlowski, K.M.; Vogel, S.N. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction in endotoxin-tolerized mouse macrophages: Dysregulation of cytokine, chemokine, and toll-like receptor 2 and 4 gene expression. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5564–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.C.; Xiao, T.T. Protective Effects of Human Milk-Derived Exosomes on Intestinal Stem Cells Damaged by Oxidative Stress. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720912690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Mohammed-Geba, K.; Tawfic, A.A.; El-Magd, M.A. Camel milk exosomes modulate cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and immuno-toxicity in rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7523–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Mu, S.; Xu, X.; Shen, L.; Li, P. Protective effects of bovine milk exosomes against oxidative stress in IEC-6 cells. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.H.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, Y.E.; Park, H.S.; Cho, Y.E. Human Breast Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Osteoblast Activation via BMP2/MAPK Signaling Pathways. J. Med. Food 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.E.; Han, G.; Lim, N.R.; Kim, E.H.; Jang, Y.; Cho, H.; Jang, H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Harnessing the Natural Healing Power of Colostrum: Bovine Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Colostrum Facilitating the Transition from Inflammation to Tissue Regeneration for Accelerating Cutaneous Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, D.L.; Robinson, A.T.; Rossman, M.J.; Seals, D.R.; Edwards, D.G. Mitochondrial contributions to vascular endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H2080–H2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Dong, G.; Pang, T.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Nie, Y.; Chang, X. Emerging insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for vascular endothelial injury-associated diseases: Focus on mitochondrial dysfunction. Angiogenesis 2024, 27, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Tong, B.; Ke, W.; Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Lei, M. Extracellular vesicles as carriers for mitochondria: Biological functions and clinical applications. Mitochondrion 2024, 78, 101935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hubal, M.J.; Kraus, V.B. Immune cell extracellular vesicles and their mitochondrial content decline with ageing. Immun. Ageing 2020, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, I.; Ghosh, J.C.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Mulugu, S.; Krishn, S.R.; Vaira, V.; Qin, J.; Plow, E.F.; Languino, L.R.; Altieri, D.C. Small Extracellular Vesicle Regulation of Mitochondrial Dynamics Reprograms a Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 163–177e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. The effect of extracellular vesicles on the regulation of mitochondria under hypoxia. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Sagar, S.; Ravindran, R.; Najor, R.H.; Quiles, J.M.; Chi, L.; Diao, R.Y.; Woodall, B.P.; Leon, L.J.; Zumaya, E.; et al. Mitochondria are secreted in extracellular vesicles when lysosomal function is impaired. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.B.; Chernausek, S.D.; Garman, L.D.; Pezant, N.P.; Plows, J.F.; Kharoud, H.K.; Demerath, E.W.; Fields, D.A. Human Milk Exosomal MicroRNA: Associations with Maternal Overweight/Obesity and Infant Body Composition at 1 Month of Life. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.; Chisanga, D.; Liem, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Anand, S.; Ang, C.S.; Adda, C.G.; Versteegen, E.; Jois, M.; Mathivanan, S. Bovine milk-derived exosomes from colostrum are enriched with proteins implicated in immune response and growth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecocci, S.; Pietrucci, D.; Milanesi, M.; Capomaccio, S.; Pascucci, L.; Evangelista, C.; Basirico, L.; Bernabucci, U.; Chillemi, G.; Cappelli, K. Comparison of colostrum and milk extracellular vesicles small RNA cargo in water buffalo. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, S.C.; Xiong, Y.; Kevil, C.G.; Luo, J. Emerging role of PKA/eNOS pathway in therapeutic angiogenesis for ischaemic tissue diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italianer, M.F.; Naninck, E.F.G.; Roelants, J.A.; van der Horst, G.T.J.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Goudoever, J.B.V.; Joosten, K.F.M.; Chaves, I.; Vermeulen, M.J. Circadian Variation in Human Milk Composition, a Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caba-Flores, M.D.; Ramos-Ligonio, A.; Camacho-Morales, A.; Martinez-Valenzuela, C.; Viveros-Contreras, R.; Caba, M. Breast Milk and the Importance of Chrononutrition. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 867507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.D.; Wright, K.P., Jr.; Spencer, R.L.; Vetter, C.; Hicks, L.M.; Jenni, O.G.; LeBourgeois, M.K. Development of the circadian system in early life: Maternal and environmental factors. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2022, 41, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiszbein, K.; Koss-Mikolajczyk, I.; Martysiak-Zurowska, D. Unlocking the Secrets of Human Milk: Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Nutr. 2025, 16, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrugger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.-E.; Chen, S.; Crouch, K.; Shutt, D.; Kaufman, J.W.; Singh, B.K. Human Breast Milk Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Endothelial Dysfunction. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182953
Cho Y-E, Chen S, Crouch K, Shutt D, Kaufman JW, Singh BK. Human Breast Milk Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Endothelial Dysfunction. Nutrients. 2025; 17(18):2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182953
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Young-Eun, Shaoshuai Chen, Keith Crouch, Damon Shutt, Justin W. Kaufman, and Brajesh K. Singh. 2025. "Human Breast Milk Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Endothelial Dysfunction" Nutrients 17, no. 18: 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182953
APA StyleCho, Y.-E., Chen, S., Crouch, K., Shutt, D., Kaufman, J. W., & Singh, B. K. (2025). Human Breast Milk Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Endothelial Dysfunction. Nutrients, 17(18), 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182953




