Sex Differences in Vitamin Metabolism and Their Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
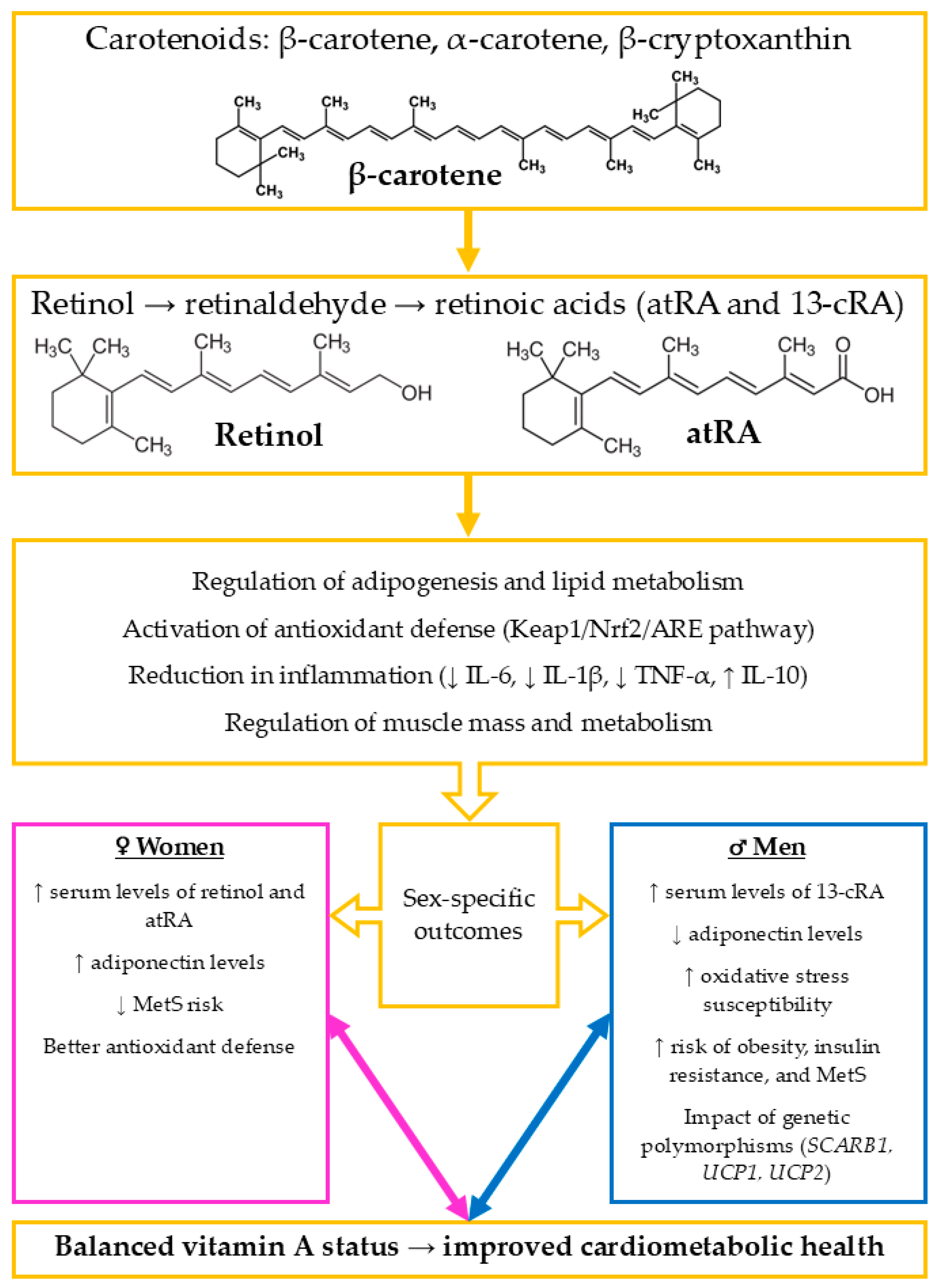
2. The Impact of Vitamin A on Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health
3. Sex Differences in the Effects of Selected B Vitamins (B2 and B12) on Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Health
4. The Role of Vitamin C in Metabolic Health and the Cardiovascular System: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Significance
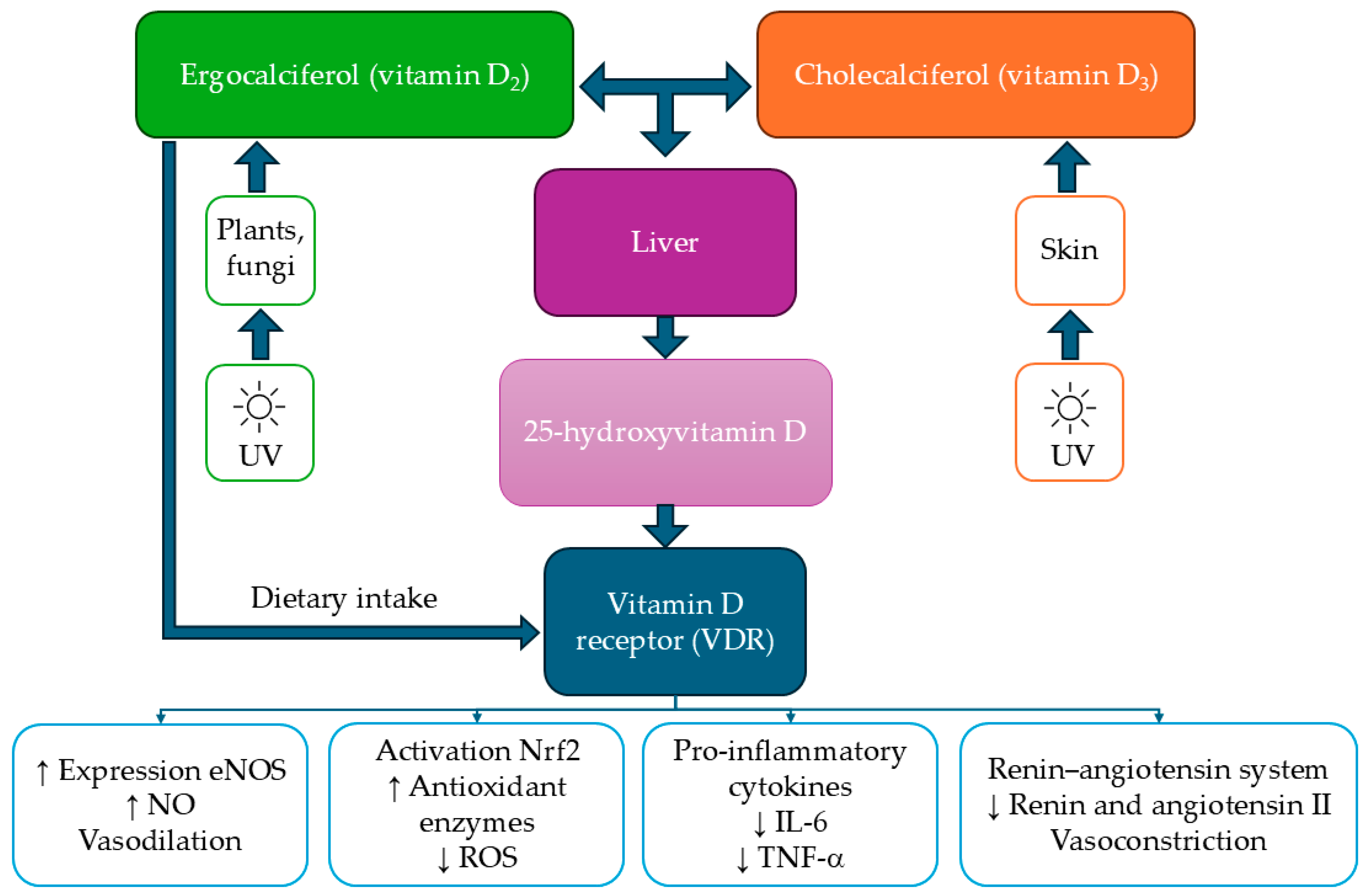
5. The Impact of Vitamin D on Cardiometabolic Health and Oxidative Stress in the Context of Sex Differences
6. Sex Differences in the Effect of Vitamin E on Oxidative Stress and Cardiometabolic Health
7. The Role of Vitamin K in Cardiometabolic Health, Its Associations with Oxidative Stress, and Sex Differences
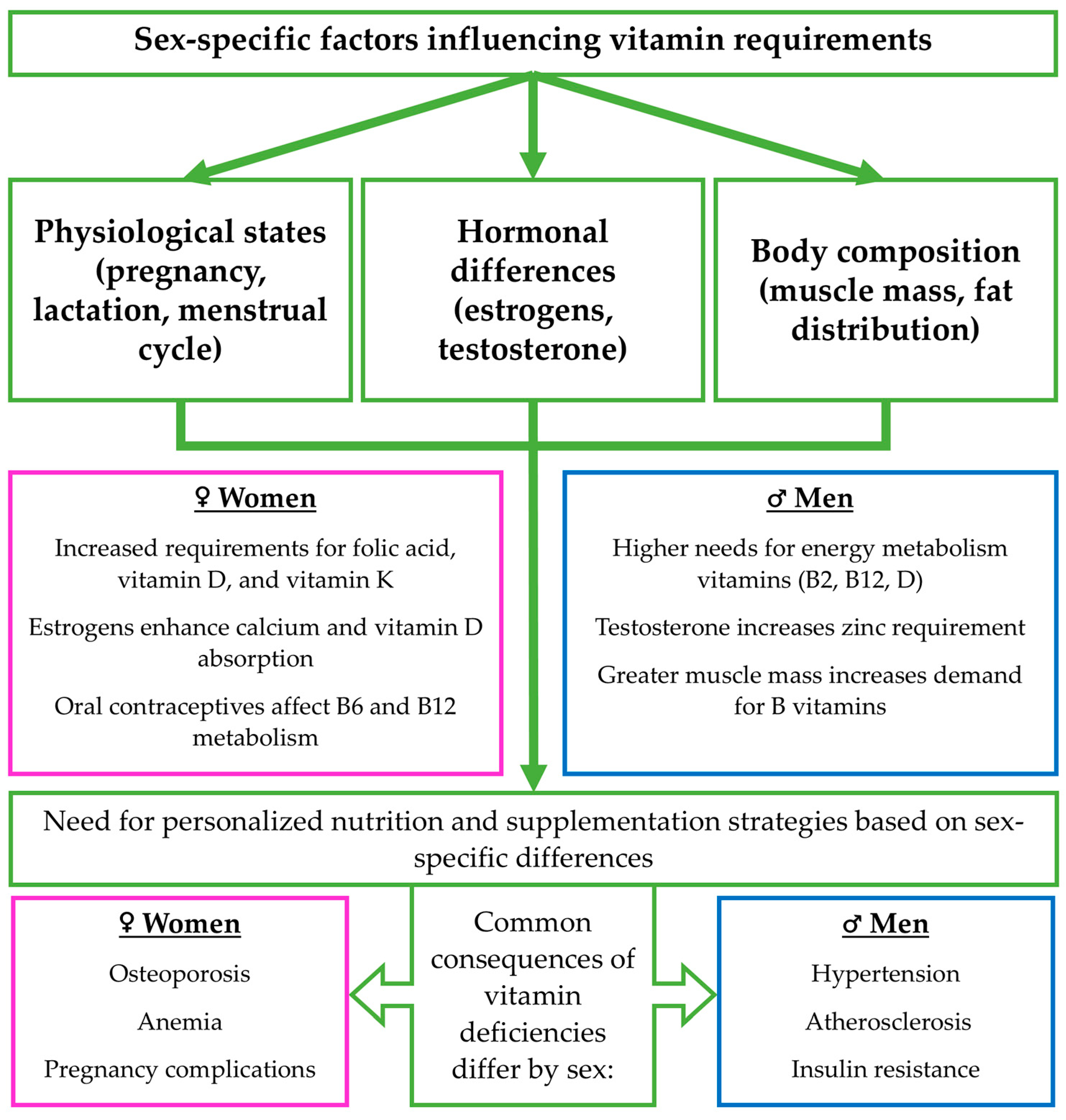
8. Sex Differences in the Requirements, Bioavailability, and Absorption of Vitamins A, D, E, K, B2, B12, C, and Their Natural Sources in the Diet
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8-iso-PGF2α | 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α |
| 13-cRA | 13-cis-retinoic acid |
| 25(OH)D | 25-hydroxyvitamin D |
| AAA | Abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| AI | Adequate Intake |
| atRA | all-trans-retinoic acid |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment Insulin Resistance |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| Keap1/Nrf2/ARE | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1/nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2/antioxidant response element |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MetS | Metabolic syndrome |
| NIZP-PZH | National Institute of Public Health-National Institute of Hygiene |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 |
| PA | Prealbumin |
| PRI | Population Reference Intake |
| RDA | Recommended Daily Allowance |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RBP | Retinol-binding protein |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SCARB1 | Scavenger receptor class B member 1 |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid-reacting substances |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling Protein 1 |
| UCP2 | Uncoupling Protein 2 |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| VDBP | Vitamin D-binding protein |
| VDR | Vitamin D receptor |
References
- Kim, D.H.; Meza, C.A.; Clarke, H.; Kim, J.S.; Hickner, R.C. Vitamin D and endothelial function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, A.B.; Brandão, I.A. The relationship between vitamin D deficiency and oxidative stress can be independent of age and gender. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2021, 91, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, C.P.; Bruno, R.M.; Rahimi, K.; Touyz, R.M.; McEvoy, J.W. What Is New and Different in the 2024 European Society of Cardiology Guidelines for the Management of Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension? Hypertension 2024, 82, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, M.; Wallert, M.; Lorkowski, S.; Peter, K. Cardiovascular and metabolic protection by vitamin E: A matter of treatment strategy? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reckelhoff, J.F.; Romero, D.G.; Yanes Cardozo, L.L. Sex, Oxidative Stress, and Hypertension: Insights From Animal Models. Physiology 2019, 34, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.F.; Rogers, G. A beneficial cardiometabolic health profile associated with dietary supplement use: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2023, 93, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarska, E.; Biskup, L.; Możdżan, M.; Grygorcewicz, O.; Możdżan, Z.; Semeradt, J.; Uramowski, M.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Hypertension: The Insight into Antihypertensive Properties of Vitamins A, C and E. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Beulens, J.W. The Role of Vitamin K Status in Cardiovascular Health: Evidence from Observational and Clinical Studies. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2017, 6, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuccia, R.; Cheung, M.; Ramadoss, R.; Aljahdali, A.; Sukumar, D. The Endocrine Role of Bone in Cardiometabolic Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2019, 8, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Jenkins, A.J.; Greenlaw, N.; Dudman, K.; Fernandes, T.; Carty, D.M.; Hughes, A.D.; Januszewski, A.S.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Petrie, J.R. Cardiometabolic risk factors, peripheral arterial tonometry and metformin in adults with type 1 diabetes participating in the REducing with MetfOrmin Vascular Adverse Lesions trial. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2023, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, C.M.; Koulman, A.; Forouhi, N.G.; Imamura, F.; Assah, F.; Mbanya, J.C.; Wareham, N.J. Associations of serum folate and holotranscobalamin with cardiometabolic risk factors in rural and urban cameroon. Nutrients 2022, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiidus, P.M.; Bombardier, E.; Hidiroglou, N.; Masere, R. Gender and exercise influence on tissue antioxidant vitamin status in rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1999, 45, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokgalaboni, K.; Nkambule, B.B.; Ntamo, Y.; Ziqubu, K.; Nyambuya, T.M.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Gabuza, K.B.; Chellan, N.; Cirilli, I.; Tiano, L.; et al. Vitamin K: A vital micronutrient with the cardioprotective potential against diabetes-associated complications. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, M.; Ward, M.; Sonko, B.; Muhammad, A.K.; Danso, E.; McNulty, H.; Prentice, A.M. Effect of riboflavin supplementation on blood pressure and possible effect modification by the MTHFR C677T polymorphism: A randomised trial in rural Gambia. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, F.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Qiao, G. Association between dietary vitamin A intake and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyter, J.D.; Camargo, C.A.; Stewart, A.W.; Waayer, D.; Lawes, C.M.M.; Toop, L.; Khaw, K.T.; Thom, S.A.M.G.; Hametner, B.; Wassertheurer, S.; et al. Effect of monthly, high-dose, long-term vitamin D supplementation on central blood pressure parameters: A randomized controlled trial substudy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.E.; Tangpricha, V. Vitamin D deficiency and risk for cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 338, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątkiewicz, I.; Wróblewski, M.; Nuszkiewicz, J.; Sutkowy, P.; Wróblewska, J.; Woźniak, A. The Role of Oxidative Stress Enhanced by Adiposity in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billups, K.L.; Miner, M.M.; Wierzbicki, A.S.; Jackson, G. Gender-based cardiometabolic risk evaluation in minority and non-minority men grading the evidence of non-traditional determinants of cardiovascular risk. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2011, 65, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, A. Sex differences in requirements for micronutrients across the lifecourse. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chungchunlam, S.M.S.; Moughan, P.J. Comparative bioavailability of vitamins in human foods sourced from animals and plants. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 11590–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.O.; Tang, H.M.; Petocz, P.; Samman, S. Biological variability and impact of oral contraceptives on vitamins B6, B12 and folate status in women of reproductive age. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3634–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussana, F.; Zighetti, M.L.; Bucciarelli, P.; Cugno, M.; Cattaneo, M. Blood levels of homocysteine, folate, vitamin B6 and B 12 in women using oral contraceptives compared to non-users. Thromb. Res. 2003, 112, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychlik, E.; Stoś, K.; Woźniak, A.; Mojska, H. Normy Żywienia dla Populacji Polski; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego PZH—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Warszawa, Poland, 2024; ISBN 9788365870780. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; World Health Organization. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition, 2nd ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; ISBN 9241546123. [Google Scholar]
- European Food and Safety Authority. Dietary Reference Values. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/dietary-reference-values (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Ilić, I.; Oršolić, N.; Rođak, E.; Odeh, D.; Lovrić, M.; Mujkić, R.; Aždajić, M.D.; Grgić, A.; Levak, M.T.; Vargek, M.; et al. The effect of high-fat diet and 13-cis retinoic acid application on lipid profile, glycemic response and oxidative stress in female Lewis rats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.S.; Isoherranen, N.; Rubinow, K.B. Vitamin A homeostasis and cardiometabolic disease in humans: Lost in translation? J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 69, R95–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvant, P.; Cansell, M.; Atgié, C. Vitamin A and lipid metabolism: Relationship between hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and adipocytes. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 67, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forga, L.; Bolado, F.; Goñi, M.J.; Tamayo, I.; Ibáñez, B.; Prieto, C. Low serum levels of prealbumin, retinol binding protein, and retinol are frequent in adult type 1 diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2532108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Beltrán-De-miguel, B.; Estévez-Santiago, R. Dietary β-cryptoxanthin and α-carotene have greater apparent bioavailability than β-carotene in subjects from countries with different dietary patterns. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koós, N.; Vahid, F.; Bohn, T. Protective effect of provitamin A dietary carotenoid intake on overweight/obesity and their relation to inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers—A case-control study. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 5510–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, E.C.; Schramm-Sapyta, N.L. Race differences in the relation of vitamins A, C, E, and β-carotene to metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiborn, C.; Weber, D.; Grune, T.; Biemann, R.; Jäger, S.; Neu, N.; Müller Von Blumencron, M.; Fritsche, A.; Weikert, C.; Schulze, M.B.; et al. Retinol and Retinol Binding Protein 4 Levels and Cardiometabolic Disease Risk. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmés, S.; Palou, A.; Serra, F. Increased risk of high body fat and altered lipid metabolism associated to suboptimal consumption of vitamin a is modulated by genetic variants rs5888 (Scarb1), rs1800629 (ucp1) and rs659366 (ucp2). Nutrients 2020, 12, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Castell, M.; Le Coroller, G.; Landrier, J.F.; Kerkour, D.; Weber, B.; Fagherazzi, G.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Vaillant, M.; Bohn, T. Micronutrients and markers of oxidative stress and inflammation related to cardiometabolic health: Results from the ehes-lux study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berggren Söderlund, M.; Sjöberg, A.; Svärd, G.; Fex, G.; Nilsson-Ehle, P. Biological variation of retinoids in man. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2002, 62, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Azemi, M.K.; Omu, A.E.; Fatinikun, T.; Mannazhath, N.; Abraham, S. Factors contributing to gender differences in serum retinol and α-tocopherol in infertile couples. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2009, 19, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagasabai, T.; Alkhalaqi, K.; Churilla, J.R.; Ardern, C.I. The Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Serum Concentrations of Micronutrients, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress Outside of the Clinical Reference Ranges: A Cross-Sectional Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Mu, D.; Fan, J.; Song, J.; Zhong, Y.; Li, D.; Xia, M. Circulating retinoic acid levels and the development of metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmés, S.; Palou, A.; Serra, F. Dietary Sources, Sex, and rs5888 (SCARB1) as Modulators of Vitamin A’s Effect on Cardiometabolic Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, S.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Acosta, S.; Gottsäter, A.; Memon, A.A. Oxidative stress–related genetic variation and antioxidant vitamin intake in intact and ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: A Swedish population-based retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 31, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Dietary antioxidant intake increases ankle brachial pressure index in men but not in women: A cross-sectional study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1343135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O. B vitamins and the brain: Mechanisms, dose and efficacy—A review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazar, N.; Jurdana, M. Hyperhomocysteinemia and the role of B vitamins in cancer. Radiol. Oncol. 2010, 44, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D. Associations of dietary vitamin B1, vitamin B2, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and folate equivalent intakes with metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, F.C. Fitting homocysteine to disease models, as well as adjusting the models to the disease. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschirow, L.; Khalaf, K.; Al-Aubaidy, H.A.; Jelinek, H.F. Inflammation, coagulation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in prediabetes—Biomarkers as a possible tool for early disease detection for rural screening. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, N.A.; Milan, A.M.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Mumme, K.D.; Conlon, C.A.; von Hurst, P.R.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; Jones, B.; Roy, N.C.; Coad, J.; et al. Vitamin B and One-Carbon Metabolite Profiles Show Divergent Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Markers but not Cognitive Function in Older New Zealand Adults: A Secondary Analysis of the REACH Study. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 3529–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayhan, S.; Kirnap, N.G.; Tastemur, M. Increased monocyte to HDL cholesterol ratio in vitamin B12 deficiency: Is it related to cardiometabolic risk? Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2021, 91, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boachie, J.; Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Samavat, J.; Saravanan, P. Low Vitamin B12 and Lipid Metabolism: Evidence from Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Effect of B vitamins supplementation on cardio-metabolic factors in patients with stable coronary artery disease: A randomized double-blind trial. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 29, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.-Y.; Kim, J.-H. Low riboflavin intake is associated with cardiometabolic risks in Korean women. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 28, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Morimoto, K.; Yu, J.; Bao, W.; Okita, Y.; Okada, K. Endogenous superoxide dismutase activation by oral administration of riboflavin reduces abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in rats. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikke, G.; Grooten, I.; Vrijkotte, T.; van Eijsden, M.; Roseboom, T.; Painter, R. Vitamin B 12 and folate status in early pregnancy and cardiometabolic risk factors in the offspring at age 5–6 years: Findings from the ABCD multi-ethnic birth cohort. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 123, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manapurath, R.; Strand, T.A.; Chowdhury, R.; Kvestad, I.; Yajnik, C.S.; Bhandari, N.; Taneja, S. Daily Folic Acid and/or Vitamin B12 Supplementation Between 6 and 30 Months of Age and Cardiometabolic Risk Markers After 6–7 Years: A Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.S. Obesity, cardiovascular disease, and role of vitamin C on inflammation: A review of facts and underlying mechanisms. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykkesfeldt, J.; Carr, A.C. Vitamin C—A scoping review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashor, A.W.; Lara, J.; Mathers, J.C.; Siervo, M. Effect of vitamin C on endothelial function in health and disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Atherosclerosis 2014, 235, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Park, S. A Causal Relationship between Vitamin C Intake with Hyperglycemia and Metabolic Syndrome Risk: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasiuk, E.; Zawari, M.; Whitehead, R.; Williman, J.; Carr, A.C. A High Vitamin C Micronutrient Supplement Is Unable to Attenuate Inflammation in People with Metabolic Syndrome but May Improve Metabolic Health Indices: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Spencer, E.; Heenan, H.; Lunt, H.; Vollebregt, M.; Prickett, T.C.R. Vitamin C Status in People with Types 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Varying Degrees of Renal Dysfunction: Relationship to Body Weight. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, B.K.; Ahn, J. A healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin c is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome risk in korean adults from the knhanes 2013–2017. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Keum, N.N.; Giovannucci, E.; Fadnes, L.T.; Boffetta, P.; Greenwood, D.C.; Tonstad, S.; Vatten, L.J.; Riboli, E.; Norat, T. Dietary intake and blood concentrations of antioxidants and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 1069–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasabai, T.; Ardern, C.I. Contribution of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants to the Relationship between Sleep Duration and Cardiometabolic Health. Sleep 2015, 38, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Guallar, E.; Appel, L.J.; Miller, E.R. Effects of vitamin c supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Dai, P.; Wang, H. Effects of vitamin C supplementation on essential hypertension. Medicine 2020, 99, e19274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Sasaki, S.; Sasazuki, S.; Okubo, S.; Hayashi, M.; Tsugane, S. Lack of long-term effect of vitamin C supplementation on blood pressure. Hypertension 2002, 40, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osganian, S.K.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rimm, E.; Spiegelman, D.; Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.A.E.; Willett, W.C. Vitamin C and risk of coronary heart disease in women. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashor, A.W.; Shannon, O.M.; Werner, A.D.; Scialo, F.; Gilliard, C.N.; Cassel, K.S.; Seal, C.J.; Zheng, D.; Mathers, J.C.; Siervo, M. Effects of inorganic nitrate and vitamin C co-supplementation on blood pressure and vascular function in younger and older healthy adults: A randomised double-blind crossover trial. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.V.T.; Nguyen, Y.T.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.J. Vitamin A, D, E, and K as Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 Regulators That Affect Expression and Enzymatic Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bailo, B.; Da Costa, L.A.; Arora, P.; Karmali, M.; El-Sohemy, A.; Badawi, A. Plasma vitamin D and biomarkers of cardiometabolic disease risk in adult Canadians, 2007–2009. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2013, 10, E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabaşı, M.; Bardaş Özkan, E. The profound influence of nitric oxide on intercellular communication and health. Demiroglu J. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, S.; Dobnig, H.; Nijpels, G.; Heine, R.J.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Snijder, M.B.; Van Dam, R.M.; Dekker, J.M. Vitamin D and mortality in older men and women. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.M.; Iqbal, M.; Chopra, H.; Urmi, S.; Junapudi, S.; Bibi, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Pangi, V.N.; Singh, I.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Pivotal Role of Vitamin D in Mitochondrial Health, Cardiac Function, and Human Reproduction. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 967–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Liu, L.-K.; Chen, M.-J.; Lee, W.-J.; Lin, M.-H.; Peng, L.-N.; Chen, L.-K. Associations between vitamin D deficiency, musculoskeletal health, and cardiometabolic risk among community-living people in Taiwan. Medicine 2018, 97, e13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Li, W.-C.; Ke, P.-H.; Chen, I.-C.; Yu, W.; Huang, H.-Y.; Xiong, X.-J.; Chen, J.-Y. Association between metabolic body composition status and vitamin D deficiency: A cross-sectional study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 940183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, C.M.; Koulman, A.; Forouhi, N.G.; Sharp, S.J.; Imamura, F.; Jones, K.; Meadows, S.R.; Assah, F.; Mbanya, J.C.; Wareham, N.J. Association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cardiometabolic risk factors in adults in rural and urban settings. Nutr. Diabetes 2022, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H. Vitamin D status and its association with cardiometabolic risk factors in Korean adults based on a 2008-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2013, 7, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, A.; Rehman, W.; Dastani, Z.; Greenwood, C.; Timpson, N.; Langsetmo, L.; Berger, C.; Fu, L.; Wong, B.Y.L.; Malik, S.; et al. The Causal Effect of Vitamin D Binding Protein (DBP) Levels on Calcemic and Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisic, A.; Cojic, M.; Patoulias, D.; Ninic, A. Multimarker Approach as More Reliable Method Than Single Vitamin D in Relationship with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Montenegrin Postmenopausal Women. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N.; Amani, R.; Hajiani, E.; Cheraghian, B. Women may respond different from men to vitamin D supplementation regarding cardiometabolic biomarkers. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Wani, K.; Sabico, S.; Garbis, S.D.; Chrousos, G.P.; Amer, O.E.; Ansari, M.G.A.; Al-Saleh, Y.; Aljohani, N.J.; Al-Attas, O.S.; et al. Sex-specific expression of apolipoprotein levels following replenishment of vitamin D. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 180, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N.; de Courten, M.P.J.; Scragg, R.; de Courten, B. 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in a predominantly vitamin D-deficient and overweight/obese but otherwise healthy cohort. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 173, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantovic, A.; Zec, M.; Zekovic, M.; Obrenovic, R.; Stankovic, S.; Glibetic, M. Vitamin D Is Inversely Related to Obesity: Cross-Sectional Study in a Small Cohort of Serbian Adults. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghera, D.K.; Sapkota, B.R.; Aston, C.E.; Blackett, P.R. Vitamin D Status, Gender Differences, and Cardiometabolic Health Disparities. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Saleh, Y.; Aljohani, N.; Alokail, M.; Al-Attas, O.; Alnaami, A.M.; Sabico, S.; Alsulaimani, M.; Al-Harbi, M.; Alfawaz, H.; et al. Vitamin D deficiency and cardiometabolic risks: A juxtaposition of arab adolescents and adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.J.; Burrows, S.; Lucas, R.M.; Marshall, C.E.; Huang, R.-C.; Chan She Ping-Delfos, W.; Beilin, L.J.; Holt, P.G.; Hart, P.H.; Oddy, W.H.; et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and cardiometabolic risk factors in adolescents and young adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Hochner, H.; Sitlani, C.M.; Williams, M.A.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; De Boer, I.H.; Kestenbaum, B.; Siscovick, D.S.; Friedlander, Y.; Enquobahrie, D.A. Plasma vitamin D is associated with fasting insulin and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance in young adult males, but not females, of the Jerusalem Perinatal Study. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraghmeh, A.H.; Bertoia, M.L.; Al-Qadi, M.O.; Abdulbaki, A.M.; Roberts, M.B.; Eaton, C.B. Evidence for the vitamin D hypothesis: The NHANES III extended mortality follow-up. Atherosclerosis 2016, 255, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, J.; Thorsby, P.M.; Kamycheva, E.; Jorde, R. Vitamin D supplementation does not improve CVD risk factors in vitamin D-insufficient subjects. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karur, S.; Veerappa, V.; Nanjappa, M.C. Study of vitamin D deficiency prevalence in acute myocardial infarction. IJC Heart Vessel. 2014, 3, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Omage, S.O.; Börmel, L.; Kluge, S.; Schubert, M.; Wallert, M.; Lorkowski, S. Vitamin E and Metabolic Health: Relevance of Interactions with Other Micronutrients. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Ohashi, N.; Hayashidani, S.; Suematsu, N.; Tsuchihashi, M.; Tamai, H.; Takeshita, A. Greater oxidative stress in healthy young men compared with premenopausal women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, A.; Nakade, M.; Tamai, H.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; Tanaka, K. The association between vitamin E intake and hypertension: Results from the re-analysis of the national health and nutrition survey. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2014, 60, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Bruckdorfer, K.R.; Shaper, A.G.; Papacosta, O.; Lennon, L.; Whincup, P.H. Plasma vitamin C, but not vitamin E, is associated with reduced risk of heart failure in older men. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, C.U.; Albert, C.M.; Moorthy, M.V.; Lee, I.M.; Buring, J.E. Vitamin E supplementation and the risk of heart failure in women. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redberg, R.F. Vitamin E and Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA 2005, 294, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuszkiewicz, J.; Sutkowy, P.; Wróblewski, M.; Pawłowska, M.; Wesołowski, R.; Wróblewska, J.; Woźniak, A. Links between Vitamin K, Ferroptosis and SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.-N.; Huang, Y.-S.; Tsai, C.-T.; Kuo, L.; Chen, S.-J.; Tuan, T.-C.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, S.-A.; Chao, T.-F. Gender Differences in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Oral Anticoagulants. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, M.J. The challenge to reach nutritional adequacy for vitamin A: β-carotene bioavailability and conversion—Evidence in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1193S–1203S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Caillaud, D.; Cano, N.J. Vitamin D Bioavailability: State of the Art. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.B. Vitamin K Active Compounds—Study of Content and Bioavailability. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, H.J. Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F. Vitamin B 12 Sources and Bioavailability. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.H. Bioavailability of vitamin B12. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2010, 80, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoot, H.R.; Zamwar, U.M.; Chakole, S.; Anjankar, A. Dietary Sources, Bioavailability, and Functions of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Role in the Common Cold, Tissue Healing, and Iron Metabolism. Cureus 2023, 15, e49308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Concentration | HOMA-IR | Insulin Level | TG | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | Fasting Glucose Level | BMI | SBP | DBP | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma 25(OH)D levels | IR ♂ | IR ♂ | IR ♂ | IR♀ | IR ♀ | NA | NA | - | - | - | [72] |
| Serum 25(OH)D levels | IR ♀ | NA | - | - | - | - | IR ♂ | IR ♂ > ♀ | NA | NA | [86] |
| Serum 25(OH)D levels | IR ♂ > ♀ | IR ♂ > ♀ | IR ♀ > ♂ | IR ♀ > ♂ | IR ♀ > ♂ | NA | NA | IR ♂ > ♀ | NA | IR ♂ | [76] |
| Serum 25(OH)D levels | IR ♂ | IR ♂ | IR♂ | IR♀ | IR ♀ = ♂ | PR ♀ = ♂ | IR♀ | IR ♀ = ♂ | IR ♀ = ♂ | IR ♀ | [79] |
| Serum 25(OH)D levels | IR ♀ = ♂ | - | PR ♀ | NA | NA | NA | - | IR ♀ > ♂ | NA | - | [88] |
| Plasma 25(OH)D levels | IR ♂ | IR ♂ | IR ♂ > ♀ | - | NA | NA | NA | IR ♀ = ♂ | NA | NA | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wróblewska, J.; Długosz, A.; Wróblewski, M.; Nuszkiewicz, J.; Wróblewska, W.; Woźniak, A. Sex Differences in Vitamin Metabolism and Their Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162697
Wróblewska J, Długosz A, Wróblewski M, Nuszkiewicz J, Wróblewska W, Woźniak A. Sex Differences in Vitamin Metabolism and Their Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162697
Chicago/Turabian StyleWróblewska, Joanna, Anna Długosz, Marcin Wróblewski, Jarosław Nuszkiewicz, Weronika Wróblewska, and Alina Woźniak. 2025. "Sex Differences in Vitamin Metabolism and Their Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162697
APA StyleWróblewska, J., Długosz, A., Wróblewski, M., Nuszkiewicz, J., Wróblewska, W., & Woźniak, A. (2025). Sex Differences in Vitamin Metabolism and Their Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients, 17(16), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162697








