Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Depression: A Longitudinal Analysis in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Highlights
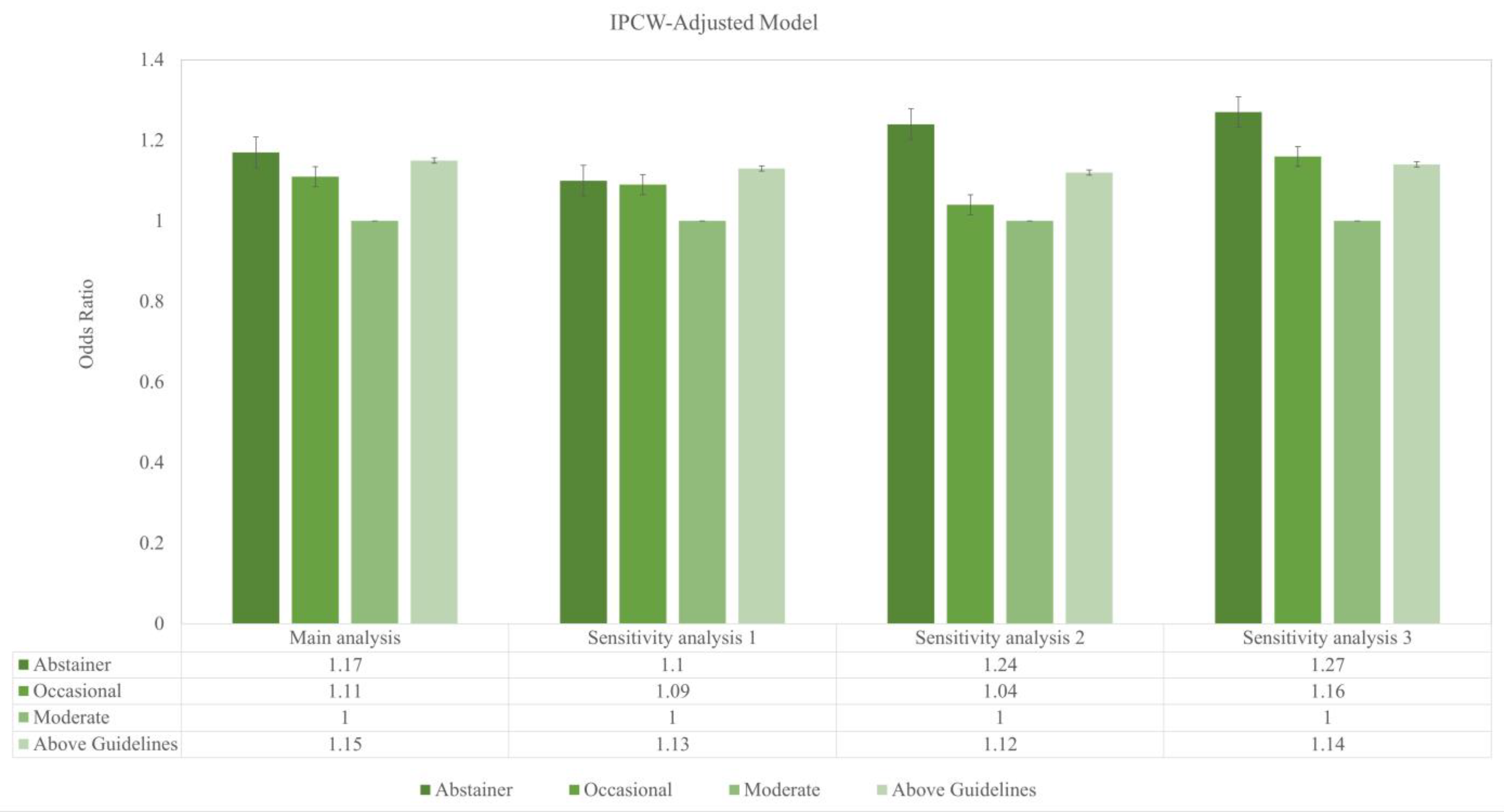
- In a prospective cohort of community-dwelling older adults from Australia and the United States—free of major physical illnesses and severe psychiatric conditions at baseline—depressive symptoms showed a J-shaped pattern with alcohol use. Compared with moderate drinkers, abstinent, occasional, and above-guideline drinkers had higher odds of depression.
- A key methodological strength of this study was the use of marginal structural models to account for a comprehensive list of observed confounders, complemented by reporting the E-value to assess the effects of unmeasured confounders. These novel approaches mitigated confounding bias and assessed the robustness of findings to potential unmeasured confounders.
- Among older adults free from severe psychiatric conditions, moderate drinkers were associated with lower depression risk than non-drinkers and those exceeding the US dietary guidelines for alcoholic beverages.
- The pattern underscores the clinical importance of assessing drinking habits and screening for depression, with particular attention to above-guideline intake in geriatric and psychiatric care.
- Subgroup analyses revealed no significant differences by sex or social/behavioural factors, suggesting that the observed J-shaped pattern was consistent across demographic and lifestyle groups.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Outcome Assessment
2.3. Exposure Assessment
2.4. Assessment of Potential Confounders
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Subgroup Analyses
2.7. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Primary Analyses
3.3. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moss, K.; Scogin, F.; Di Napoli, E.; Presnell, A. A self-help behavioral activation treatment for geriatric depressive symptoms. Aging Ment. Health 2012, 16, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators GMD. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Zhao, X.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Luo, L.; Yang, C.; Yang, F. Prevalence of depression in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022, 311, 114511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppa, M.; Heinrich, S.; Matschinger, H.; Sandholzer, H.; Angermeyer, M.C.; König, H.-H.; Riedel-Heller, S.G. Direct costs associated with depression in old age in Germany. J. Affect. Disord. 2008, 105, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenebe, Y.; Akele, B.; W/Selassie, M.; Necho, M. Prevalence and determinants of depression among old age: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2021, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achour, Y.; Lucas, G.; Iceta, S.; Boucekine, M.; Rahmati, M.; Berk, M.; Akbaraly, T.; Aouizerate, B.; Capuron, L.; Marx, W.; et al. Dietary Patterns and Major Depression: Results from 15,262 Participants (International ALIMENTAL Study). Nutrients 2025, 17, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, J.M.; Fergusson, D.M. Alcohol and depression. Addiction 2011, 106, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visontay, R.; Mewton, L.; Slade, T.; Aris, I.M.; Sunderland, M. Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Depression: A Marginal Structural Model Approach Promoting Causal Inference. Am. J. Psychiatry 2023, 180, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Shen, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.; Rong, X.; Peng, Y. Effect of alcohol use disorders and alcohol intake on the risk of subsequent depressive symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Addiction 2020, 115, 1224–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.E.; Zubritsky, C.; Cody, M.; Coakley, E.; Chen, H.; Ware, J.H.; Oslin, D.W.; Sanchez, H.A.; Durai, U.N.B.; Miles, K.M.; et al. Alcohol Consumption Among Older Adults in Primary Care. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2007, 22, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, K.M.; Allel, K.; Staudinger, U.M.; Ornstein, K.A.; Calvo, E. Alcohol consumption predicts incidence of depressive episodes across 10 years among older adults in 19 countries. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 148, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Greenland, S.; Mansournia, M.A.; Altman, D.G. Sparse data bias: A problem hiding in plain sight. BMJ 2016, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, T.S.; Stockwell, T.; Zhao, J.; Xuan, Z.; Dangardt, F.; Saitz, R.; Liang, W.; Chikritzhs, T. Selection biases in observational studies affect associations between ‘moderate’alcohol consumption and mortality. Addiction 2017, 112, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group AI. Study design of ASPirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE): A randomized, controlled trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2013, 36, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, J.J.; Woods, R.L.; Ward, S.A.; Britt, C.J.; Lockery, J.E.; Beilin, L.J.; Owen, A.J. Cohort Profile: The ASPREE Longitudinal Study of Older Persons (ALSOP). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1048–1049h. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrens, M.; Fonseca, F.; Mateu, G.; Farré, M. Efficacy of antidepressants in substance use disorders with and without comorbid depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2005, 78, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, M.; Nguyen, V.; McNeil, J.J.; Woods, R.L.; Nelson, M.R.; Shah, R.C.; Storey, E.; Murray, A.M.; Reid, C.M.; Kirpach, B. Psychometric properties of a short form of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D-10) scale for screening depressive symptoms in healthy community dwelling older adults. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2018, 51, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.A. Dietary guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025. Workplace Health Saf. 2021, 69, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.T.; Freak-Poli, R.; Orchard, S.G.; Wolfe, R.; Reid, C.M.; Tonkin, A.M.; Beilin, L.J.; McNeil, J.J.; Ryan, J.; Woods, R.L. Alcohol consumption and risks of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in healthy older adults. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 29, e230–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero-Calafell, J.; Burón, A.; Castells, X.; Porta, M. Intention to treat and per protocol analyses: Differences and similarities. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2024, 173, 111457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernán, M.A.; Sauer, B.C.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Platt, R.; Shrier, I. Specifying a target trial prevents immortal time bias and other self-inflicted injuries in observational analyses. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 79, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnaye, N.C.; Stel, V.S.; Tripepi, G.; Dekker, F.W.; Fu, E.L.; Zoccali, C.; Jager, K.J. An introduction to inverse probability of treatment weighting in observational research. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneuse, S.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Arterburn, D. Using the E-value to assess the potential effect of unmeasured confounding in observational studies. JAMA 2019, 321, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, J.F.; Kok, R.M.; van Marwijk, H.W.J.; van der Mast, R.C.; Naarding, P.; Oude Voshaar, R.C.; Stek, M.L.; Verhaak, P.F.M.; de Waal, M.W.M.; Comijs, H.C. Correlates of Alcohol Abstinence and At-Risk Alcohol Consumption in Older Adults with Depression: The NESDO Study. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2014, 22, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, E.V. Alcohol and the Etiology of Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2023, 180, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.; Conigrave, J.H.; Lewohl, J.; Haber, P.; Morley, K.C. Alcohol use disorder and circulating cytokines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpato, S.; Pahor, M.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Fellin, R.; Harris, T.B. Relationship of Alcohol Intake With Inflammatory Markers and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitior-1 in Well-Functioning Older Adults. Circulation 2004, 109, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, S.P. Neuroimmune interface in the comorbidity between alcohol use disorder and major depression. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 233688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruwys, T.; Dingle, G.A.; Haslam, C.; Haslam, S.A.; Jetten, J.; Morton, T.A. Social group memberships protect against future depression, alleviate depression symptoms and prevent depression relapse. Soc. Sci. Med. 2013, 98, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhinaraset, M.; Wigglesworth, C.; Takeuchi, D.T. Social and Cultural Contexts of Alcohol Use: Influences in a Social-Ecological Framework. Alcohol Res. 2016, 38, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.M.; Wang, W.; Zhornitsky, S.; Dhingra, I.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.-S.R. The Neural Processes Interlinking Social Isolation, Social Support, and Problem Alcohol Use. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 24, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, C.; Spanjers, K.; Patel, S.; Atherton, N.M.; Lamb, S.E. Effect of exercise on depression severity in older people: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 201, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, M.; Vancampfort, D.; Giesen, E.S.; Lundin, A.; Stubbs, B. Exercise as treatment for alcohol use disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevers, D.; Billieux, J.; de Timary, P.; Desmedt, O.; Maurage, P.; Perales, J.C.; Suárez-Suárez, S.; Bechara, A. Physical exercise to redynamize interoception in substance use disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yemiscigil, A.; Vlaev, I. The bidirectional relationship between sense of purpose in life and physical activity: A longitudinal study. J. Behav. Med. 2021, 44, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, F.G.d.M.; Gobbi, S.; Andreatto, C.A.A.; Corazza, D.I.; Pedroso, R.V.; Santos-Galduróz, R.F. Physical exercise modulates peripheral levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): A systematic review of experimental studies in the elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2013, 56, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.; Bolstad, I.; Lien, L.; Bramness, J.G. The Association Between Regular Physical Activity and Depressive Symptoms Among Patients in Treatment of Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders. Subst. Abus. 2023, 17, 11782218231175813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgülü, E.; Bieber, M.; Engeroff, T.; Zabel, K.; Etyemez, S.; Prvulovic, D.; Reif, A.; Oertel, V. Physical activity, physical self-perception and depression symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder: A mediation analysis. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, N.; Oscar-Berman, M. Chronic Pain in Relation to Depressive Disorders and Alcohol Abuse. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.R.; Lac, A.; Labrie, J.W.; Hummer, J.F.; Pham, A. Mental health, sleep quality, drinking motives, and alcohol-related consequences: A path-analytic model. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2013, 74, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Forger, D.B.; Frank, E.; Sen, S.; Goldstein, C. Day-to-day variability in sleep parameters and depression risk: A prospective cohort study of training physicians. npj Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, T.M.; Rodgers, B.; Jorm, A.F.; Christensen, H.; Jacomb, P.A.; Korten, A.E.; Lynskey, M.T. Patterns of association between alcohol consumption and symptoms of depression and anxiety in young adults. Addiction 2002, 97, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartka, E.; Johnstone, B.; Leino, E.V.; Motoyoshi, M.; Temple, M.T.; Fillmore, K.M. A meta-analysis of depressive symptomatology and alcohol consumption over time. Br. J. Addict. 1991, 86, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Abstainer (n = 3756) | Occasional (n = 4195) | Moderate (n = 5340) | Above Guidelines (n = 3272) | Total (n = 16,563) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Mean (SD) | 75.3 (5.0) | 75.2 (4.6) | 75.0 (4.4) | 75.0 (4.3) | 75.1 (4.6) | |
| Education level | Above year 12 | 1377 (36.7%) | 1779 (42.4%) | 2589 (48.5%) | 1482 (45.3%) | 7227 (43.6%) |
| Race/ethnicity | White/Caucasian | 3093 (84.3%) | 3811 (92.1%) | 5155 (96.8%) | 3215 (98.5%) | 15,274 (93.2%) |
| Other | 574 (15.7%) | 328 (7.9%) | 168 (3.2%) | 48 (1.5%) | 1118 (6.8%) | |
| Sex | Female | 2508 (66.8%) | 2616 (62.4%) | 1775 (33.2%) | 2033 (62.1%) | 8932 (53.9%) |
| Body mass index | Mean (SD) | 28.7 (5.3) | 28.5 (4.9) | 27.6 (4.1) | 27.2 (4.4) | 28.0 (4.7) |
| Positive history of smoking | 135 (3.6%) | 145 (3.5%) | 173 (3.2%) | 154 (4.7%) | 607 (3.7%) | |
| Living at home with family, friends, or spouse | Yes | 2410 (64.2%) | 2651 (63.2%) | 3902 (73.1%) | 2301 (68.9%) | 11,264 (68.0%) |
| Hypertension | Yes | 2870 (76.4%) | 3110 (74.1%) | 3897 (73.0%) | 2465 (75.3%) | 12,342 (74.5%) |
| Diabetes | Yes | 553 (14.7%) | 449 (10.7%) | 500 (9.4%) | 223 (6.8%) | 1725 (10.4%) |
| Pulmonary disease | Yes | 516 (13.7%) | 566 (13.5%) | 738 (13.8%) | 484 (14.8%) | 2304 (13.9%) |
| Chronic kidney disease | Yes | 504 (13.4%) | 477 (11.4%) | 708 (13.3%) | 212 (6.5%) | 1901 (11.5%) |
| History of cancer a | Yes | 670 (18.0%) | 737 (17.6%) | 1108 (20.8%) | 640 (19.6%) | 3155 (19.1%) |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Yes | 37 (1.0%) | 39 (0.9%) | 50 (0.9%) | 24 (0.7%) | 150 (0.9%) |
| Gout | Yes | 168 (4.5%) | 200 (4.8%) | 409 (7.7%) | 273 (8.3%) | 1050 (6.3%) |
| Dyslipidemia | Yes | 2291 (61.3%) | 3586 (62.1%) | 3224 (60.9%) | 2311 (71.2%) | 10,412 (63.3%) |
| Gastro-esophageal reflux disease | Yes | 1040 (27.7%) | 1128 (26.9%) | 1391 (26.0%) | 875 (26.7%) | 4434 (26.8%) |
| Metabolic syndrome | Yes | 1480 (49.9%) | 1596 (38.9%) | 1715 (32.8%) | 1008 (31.4%) | 5789 (35.7%) |
| Number of comorbidities | Mean (SD) | 3.0 (1.7) | 2.9 (1.6) | 2.8 (1.6) | 2.9 (1.5) | 2.9 (1.6) |
| Polypharmacy | Yes | 1249 (33.3%) | 1249 (29.8%) | 1296 (24.3%) | 903 (27.6%) | 4697 (28.4%) |
| Opioids | Yes | 114 (3.0%) | 129 (3.1%) | 112 (2.1%) | 73 (2.2%) | 428 (2.6%) |
| Anti-inflammatory | Yes | 572 (15.2%) | 641 (15.3%) | 898 (16.8%) | 674 (20.6%) | 2785 (16.8%) |
| CES-D-10 | Mean (SD) | 3.1 (3.2) | 3.0 (3.2) | 2.8 (2.9) | 3.1 (3.1) | 3.0 (3.1) |
| Alcohol Categories | Unadjusted | IPCW-Adjusted Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | E-value | p-value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | E-value | p-value | ||
| Main analysis | |||||||||
| Abstainer | 1.20 | 1.10–1.30 | 1.69 | <0.001 | 1.17 | 1.08–1.26 | 1.61 | <0.001 | |
| Occasional | 1.10 | 1.02–1.19 | 1.43 | 1.11 | 1.03–1.19 | 1.46 | |||
| Moderate | Reference | Reference | |||||||
| Above Guidelines | 1.11 | 1.02–1.20 | 1.46 | 1.15 | 1.07–1.25 | 1.51 | |||
| Sensitivity analysis 1 | |||||||||
| Abstainer | 1.20 | 1.10–1.30 | 1.69 | <0.001 | 1.10 | 1.01–1.21 | 1.43 | 0.002 | |
| Occasional | 1.10 | 1.02–1.19 | 1.43 | 1.09 | 1.00–1.18 | 1.40 | |||
| Moderate | Reference | Reference | |||||||
| Above Guidelines | 1.11 | 1.02–1.20 | 1.46 | 1.13 | 1.03–1.23 | 1.51 | |||
| Sensitivity analysis 2 | |||||||||
| Abstainer | 1.42 | 1.28–1.57 | 2.19 | 1.24 | 1.11–1.38 | 1.78 | |||
| Occasional | 1.05 | 0.94–1.17 | 1.28 | 1.04 | 0.93–1.17 | 1.24 | |||
| Moderate | Reference | 0.002 | Reference | 0.002 | |||||
| Above Guidelines | 1.17 | 1.05–1.31 | 1.61 | 1.12 | 0.99–1.26 | 1.49 | |||
| Sensitivity analysis 3 | |||||||||
| Abstainer | 1.37 | 1.23–152 | 2.08 | <0.001 | 1.27 | 1.13–1.42 | 1.85 | 0.002 | |
| Occasional | 1.17 | 1.06–1.30 | 1.61 | 1.16 | 1.04–1.31 | 1.59 | |||
| Moderate | Reference | Reference | |||||||
| Above Guidelines | 1.14 | 1.02–1.27 | 1.53 | 1.14 | 1.01–1.29 | 1.53 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohebbi, M.; Davoodian, N.; Ganjali, S.; Beilin, L.J.; Berk, M.; Forbes, M.; McNeil, J.J.; Nelson, M.R.; Ryan, J.; Wolfe, R.; et al. Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Depression: A Longitudinal Analysis in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162688
Mohebbi M, Davoodian N, Ganjali S, Beilin LJ, Berk M, Forbes M, McNeil JJ, Nelson MR, Ryan J, Wolfe R, et al. Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Depression: A Longitudinal Analysis in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162688
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohebbi, Mohammadreza, Najmeh Davoodian, Shiva Ganjali, Lawrence J. Beilin, Michael Berk, Malcolm Forbes, John J. McNeil, Mark R Nelson, Joanne Ryan, Rory Wolfe, and et al. 2025. "Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Depression: A Longitudinal Analysis in Community-Dwelling Older Adults" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162688
APA StyleMohebbi, M., Davoodian, N., Ganjali, S., Beilin, L. J., Berk, M., Forbes, M., McNeil, J. J., Nelson, M. R., Ryan, J., Wolfe, R., Woods, R. L., & Lotfaliany, M. (2025). Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Depression: A Longitudinal Analysis in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Nutrients, 17(16), 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162688







