Drugs and Nutrients in Epilepsy: Vitamin B6 and the Ketogenic Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. List of Nutrients
2.2. PubMed Count and Epilepsy Association
3. Results
3.1. Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs)
3.2. Antiepileptic Drug Families and Scaffolds
3.3. Diagnostic Markers
3.4. Biomarkers for GABA-Transaminase Deficiency
3.5. Inducers of Epilepsy in Animal Models
3.6. Investigational Compounds
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AED | Antiepileptic Drug |
| AMPA | Alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic Acid |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CNQX | 6-Cyano-7-Nitroquinoxaline-2,3-Dione |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid |
| HMDB | Human Metabolome Database |
| ILAE | International League Against Epilepsy |
| KBr | Potassium Bromide |
| MPTP | 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyridine |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-D-Aspartic Acid |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PLP | Pyridoxal Phosphate |
| S/N | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SPECT | Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography |
| VNS | Vagus Nerve Stimulation |
References
- Farrell, J.S.; Wolff, M.D.; Teskey, G.C. Neurodegeneration and Pathology in Epilepsy: Clinical and Basic Perspectives. Adv. Neurobiol. 2017, 15, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, E.M.; Coulter, D.A. Mechanisms of Epileptogenesis: A Convergence on Neural Circuit Dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perucca, P.; Bahlo, M.; Berkovic, S.F. The Genetics of Epilepsy. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2020, 21, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, A.M.; Bicchi, M.M. Antiseizure Medications for Adults With Epilepsy. JAMA 2022, 327, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.; Nevitt, S.J.; Cotton, J.; Gandhi, S.; Weston, J.; Sudan, A.; Ramirez, R.; Newton, R. Surgery for Epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, CD010541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Mao, H.; Hu, T.; Xie, H.; Ye, L.; Cheng, H. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus for a Patient with Drug Resistant Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy: 1 Year Follow-Up. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 4997–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Whitney, R.; RamachandranNair, R.; Bijarnia Mahay, S.; Sharma, S. Genetic Testing in Pediatric Epilepsy: Tools, Tips, and Navigating the Traps. Pediatr. Neurol. 2024, 157, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, T.; Allan, K.; Cooper, K. The Use of Ketogenic Diets in Children Living with Drug-resistant Epilepsy, Glucose Transporter 1 Deficiency Syndrome and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Deficiency: A Scoping Review. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2024, 37, 827–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, C.; Freeman, J.M.; Pillas, D.J.; Pyzik, P.L. The Ketogenic Diet: A 3- to 6-Year Follow-Up of 150 Children Enrolled Prospectively. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.R.; Sander, J.W. The Use of Caffeine by People with Epilepsy: The Myths and the Evidence. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamerle, M.; Ghaeni, L.; Kowski, A.; Weissinger, F.; Holtkamp, M. Alcohol Use and Alcohol-Related Seizures in Patients With Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holló, A.; Clemens, Z.; Lakatos, P. Epilepsy and Vitamin D. Int. J. Neurosci. 2014, 124, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.P.; Plecko, B.; Mills, P.B.; Clayton, P.T. Disorders Affecting Vitamin B6 Metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuytten, D.; Van Hees, J.; Meulemans, A.; Carton, H. Magnesium Deficiency as a Cause of Acute Intractable Seizures. J. Neurol. 1991, 238, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julian, T.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Zis, P. Gluten Sensitivity and Epilepsy: A Systematic Review. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, S. Causal Relationship between Human Blood Omega-3 Fatty Acids and the Risk of Epilepsy: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1130439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mendalawi, M.D. Serum Levels of Zinc and Copper in Epileptic Children during Long-Term Therapy with Anticonvulsants. Neurosciences 2016, 21, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubana, S.S.; Alfishawy, M.; Singh, N.; Atkinson, S. Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Elevated Folate Levels: An Unusual Cause of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure. Am. J. Case Rep. 2015, 16, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Brigo, F.; Trinka, E. Acute Symptomatic Seizures Caused by Electrolyte Disturbances. J. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fu, B. The Research on Gene-Disease Association Based on Text-Mining of PubMed. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła, P.; Shardlow, M.; Aubin, S.; Bossy, R.; de Castilho, R.E.; Piperidis, S.; McNaught, J.; Ananiadou, S. Text Mining Resources for the Life Sciences. Database 2016, 2016, baw145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Campillos, M.; Letunic, I.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. A Side Effect Resource to Capture Phenotypic Effects of Drugs. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2010, 6, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Pallejà, A.; Tsafou, K.; Binder, J.X.; Jensen, L.J. DISEASES: Text Mining and Data Integration of Disease–Gene Associations. Methods 2015, 74, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabour, R.; Meirson, T.; Samson, A.O. Global Antibiotic Resistance Is Mostly Periodic. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 7, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzman, R.; Calfon, O.; Saha, T.; Bloch, N.; Ben Zaken, K.; Rosenfeld, A.; Samson, A.O.; Amitay, M. Resistance to Antimalarial Monotherapy Is Cyclic. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, H.; Malov, M.; Saha Detroja, T.; Ben Zaken, K.; Bloch, N.; Gal-Tanamy, M.; Avni, O.; Polis, B.; Samson, A.O. Autoimmune Disease Classification Based on PubMed Text Mining. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitan, I.; Halperin, Y.; Saha, T.; Bloch, N.; Atrahimovich, D.; Polis, B.; Samson, A.O.; Braitbard, O. Towards a Consensus on Alzheimer’s Disease Comorbidity? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.; Marshall, G.A. Primary and Secondary Prevention Trials in Alzheimer Disease: Looking Back, Moving Forward. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleyadeh, R.; Carson, R.P. Fosphenytoin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fariba, K.A.; Saadabadi, A. Topiramate. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Awosika, A.O.; Nguyen, H. Valproic Acid. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Tripp, J. Phenytoin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R.; Kumar, B.; Akhtar, M.J.; Chawla, P.A. Voltage Gated Sodium Channel Inhibitors as Anticonvulsant Drugs: A Systematic Review on Recent Developments and Structure Activity Relationship Studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, J.M.; Donnelly, A. Carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 1998, 20, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, R.L.; Kelly, K.M. Antiepileptic Drug Mechanisms of Action. Epilepsia 1995, 36, S2–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sills, G. The Mechanisms of Action of Gabapentin and Pregabalin. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisewikul, R.; Baillie, N.; Marson, A.G. Calcium Antagonists as an Add-on Therapy for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Chaisewikul, R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Winblad, B. Piracetam: A Review of Pharmacological Properties and Clinical Uses. CNS Drug Rev. 2005, 11, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Omata, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Aoyama, H.; Tanabe, Y. Potassium Bromide in the Treatment of Pediatric Refractory Epilepsy. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 34, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Marsh, E.; Friedman, D.; Thiele, E.; Laux, L.; Sullivan, J.; Miller, I.; Flamini, R.; Wilfong, A.; Filloux, F.; et al. Cannabidiol in Patients with Treatment-Resistant Epilepsy: An Open-Label Interventional Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, L. Optimal Dose of Fenfluramine in Adjuvant Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1371704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharod, S.C.; Kang, S.K.; Kadam, S.D. Off-Label Use of Bumetanide for Brain Disorders: An Overview. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.B.; Patel, P.; Adams, N. Phenobarbital. 2024 Feb 28. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trinka, E. Phenobarbital in Status Epilepticus—Rediscovery of an Effective Drug. Epilepsy Behav. 2023, 141, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermeling, D.P. Intranasal Delivery of Antiepileptic Medications for Treatment of Seizures. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo-Lavizzari, G. The Clinical Anti-Convulsant Effects of Flumazenil, a Benzodiazepine Antagonist. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. Suppl. 1988, 2, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Marchant, B.; Wray, R.; Leach, A.; Nama, M. Flumazenil Causing Convulsions and Ventricular Tachycardia. BMJ 1989, 299, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relsner-Keller, L.A.; Pham, Z. Oral Flumazenil in the Treatment of Epilepsy. Ann. Pharmacother. 1995, 29, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Elger, C.E. Induction of Partial Epileptic Seizures by Flumazenil. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolkowska, D.; Wu, C.-Y.; Rogawski, M.A. Intranasal Allopregnanolone Confers Rapid Seizure Protection: Evidence for Direct Nose-to-Brain Delivery. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Karnebeek, C.D.M.; Tiebout, S.A.; Niermeijer, J.; Poll-The, B.T.; Ghani, A.; Coughlin, C.R.; Van Hove, J.L.K.; Richter, J.W.; Christen, H.J.; Gallagher, R.; et al. Pyridoxine-Dependent Epilepsy: An Expanding Clinical Spectrum. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 59, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, A.A.; Bass, A.K.; Ahmed, M.S.; Abdelhamid, A.A.; Elshaier, Y.A.; Salman, A.M.; Aly, O.M. Design, Synthesis and Anticonvulsant Activity of New Imidazolidindione and Imidazole Derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 101, 104020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, K.; Wiklik, B.; Obniska, J. Synthesis, Anticonvulsant Properties, and SAR Analysis of Differently Substituted Pyrrolidine-2,5-diones and Piperidine-2,6-diones. Arch. Pharm. 2014, 347, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, K.; Wiklik, B.; Obniska, J. Synthesis and Anticonvulsant Activity of New N-Phenyl-2-(4-Phenylpiperazin-1-Yl)Acetamide Derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 3047–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.W.; de la Cruz, M.A.M.; Covey, D.F.; Rothman, S.M. Effects of Anticonvulsant Lactams on in Vitro Seizures in the Hippocampal Slice Preparation. Epilepsy Res. 1999, 37, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, K. Novel Hybrid Anticonvulsants Derived from Pyrrolidine-2,5-Dione Scaffold with Broad Spectrum of Activity in the Preclinical Studies. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffin, K.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Van Laere, K.; Van Paesschen, W. Neuronuclear Assessment of Patients With Epilepsy. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2008, 38, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.C.; Thomas, T.; Patel, S.; Han, V.X.; Kothur, K.; Troedson, C.; Gupta, S.; Gill, D.; Malone, S.; Waak, M.; et al. CSF Neopterin and Quinolinic Acid Are Biomarkers of Neuroinflammation and Neurotoxicity in FIRES and Other Infection-triggered Encephalopathy Syndromes. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.D.; Pappan, K.L.; Donti, T.; Delgado, M.R.; Shinawi, M.; Pearson, T.S.; Lalani, S.R.; Craigen, W.J.; Sutton, V.R.; Evans, A.M.; et al. 2-Pyrrolidinone and Succinimide as Clinical Screening Biomarkers for GABA-Transaminase Deficiency: Anti-Seizure Medications Impact Accurate Diagnosis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.X.; Brooks-Kayal, A.R. Excitation–Inhibition Epilepsies. In Neural Circuit Development and Function in the Brain; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 709–730. [Google Scholar]
- Nieoczym, D.; Socała, K.; Zelek-Molik, A.; Pieróg, M.; Przejczowska-Pomierny, K.; Szafarz, M.; Wyska, E.; Nalepa, I.; Wlaź, P. Anticonvulsant Effect of Pterostilbene and Its Influence on the Anxiety- and Depression-like Behavior in the Pentetrazol-Kindled Mice: Behavioral, Biochemical, and Molecular Studies. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 3167–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baram, T.Z.; Snead, O.C. Bicuculline Induced Seizures in Infant Rats: Ontogeny of Behavioral and Electrocortical Phenomena. Dev. Brain Res. 1990, 57, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, A.; Moshé, S.L. Animal models. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 107, pp. 63–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ness, P.C.; Olsen, R.W.; Verity, M.A. MPTP Is Proconvulsant Acutely but Has No Long-Term Effect in Rodent Models of Seizure and Epilepsy. Brain Res. 1989, 504, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, H.; Ishikawa, R.; Saitoh, T.; Kambe, T.; Chiba, T.; Taguchi, K.; Abe, K. Preventative Effects of 1-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline Derivatives (N-Functional Group Loading) on MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism in Mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 100, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusina, E.; Bernard, C.; Williamson, A. The Kainic Acid Models of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. eNeuro 2021, 8, ENEURO.0337-20.2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, J.; Saito, M.; Yokomori, M. The Potential of Bemegride as an Activation Agent in Electroencephalography in Dogs. Animals 2022, 12, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, J.F.; Reinhard, J.F. Experimental Evaluation of Anticonvulsants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 57–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakers, G.M.J.; Peeters, B.W.M.M.; Vossen, J.M.H.; Coenen, A.M.L. CNQX, a New Non-NMDA Receptor Antagonist, Reduces Spike Wave Discharges in the WAG/Rij Rat Model of Absence Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 1991, 9, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.-N.; Li, L.; Hu, S.-H.; Yang, Y.-X.; Ma, Z.-Z.; Huang, L.; An, Y.-P.; Yuan, Y.-Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; et al. Ketogenic Diet-Produced β-Hydroxybutyric Acid Accumulates Brain GABA and Increases GABA/Glutamate Ratio to Inhibit Epilepsy. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleshin, V.A.; Graf, A.V.; Artiukhov, A.V.; Boyko, A.I.; Ksenofontov, A.L.; Maslova, M.V.; Nogués, I.; di Salvo, M.L.; Bunik, V.I. Physiological and Biochemical Markers of the Sex-Specific Sensitivity to Epileptogenic Factors, Delayed Consequences of Seizures and Their Response to Vitamins B1 and B6 in a Rat Model. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, S.J.; Schell, J.; Qian, W.; Silguero, M.; Baseviciene, A.; Chen, W.H.; Trevino, R., Jr.; Chocron, E.S.; Ogle, M.M.; Varmazyad, M.; et al. Divergent sex-specific effects on a ketogenic diet: Male, but not female, mice exhibit oxidative stress and cellular senescence. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 116026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprankle, K.W.; Knappenberger, M.A.; Locke, E.J.; Thompson, J.H.; Vinovrski, M.F.; Knapsack, K.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr. Sex- and Age-Specific Differences in Mice Fed a Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.E.; Poff, A.M.; Moss, A.; DeBlasi, J.M.; D’Agostino, D.P. From glucose to histone modification: Sex-specific metabolic responses to ketogenic therapy in VM/Dk mice. Front Nutr. 2025, 19, 1554743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Felice, F.; Malerba, S.; Nardone, V.; Salvestrini, V.; Calomino, N.; Testini, M.; Boccardi, V.; Desideri, I.; Gentili, C.; De Luca, R.; et al. Progress and Challenges in Integrating Nutritional Care into Oncology Practice: Results from a National Survey on Behalf of the NutriOnc Research Group. Nutrients 2025, 17, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Roulet Perez, E.; et al. Operational Classification of Seizure Types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnellan, E.P.; Kehoe, C.; Moran, A.; Ni Chollatain, M.; Hynes, Y.; Hennessy, M.; Reade, E.; Allen, N.M. The 2017 and 2022 ILAE Epilepsy Classification Systems Identify Needs and Opportunities in Care: A Paediatric Hospital-Based Study. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 157, 109804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riney, K.; Bogacz, A.; Somerville, E.; Hirsch, E.; Nabbout, R.; Scheffer, I.E.; Zuberi, S.M.; Alsaadi, T.; Jain, S.; French, J.; et al. International League Against Epilepsy Classification and Definition of Epilepsy Syndromes with Onset at a Variable Age: Po-sition Statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1443–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, U.B.S.; Lauxmann, S.; Wolff, M.; Synofzik, M.; Bast, T.; Binelli, A.; Serratosa, J.M.; Martínez-Ulloa, P.; Allen, N.M.; King, M.D.; et al. 4-Aminopyridine Is a Promising Treatment Option for Patients with Gain-of-Function KCNA2 -Encephalopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, S.A.; Carney, P.W.; Roten, A.; Ching, M.; Lightfoot, P.A.; Churilov, L.; Nair, U.; Li, M.; Berkovic, S.F.; Petrou, S.; et al. Precision Therapy for Epilepsy Due to KCNT1 Mutations. Neurology 2018, 90, e67–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nájera-Chávez, B.C.; Seeber, L.; Goldhahn, K.; Panzer, A. Use of Sodium Channel Blockers in the Thr226Met Pathologic Variant of SCN1A: A Case Report. Neuropediatrics 2023, 54, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
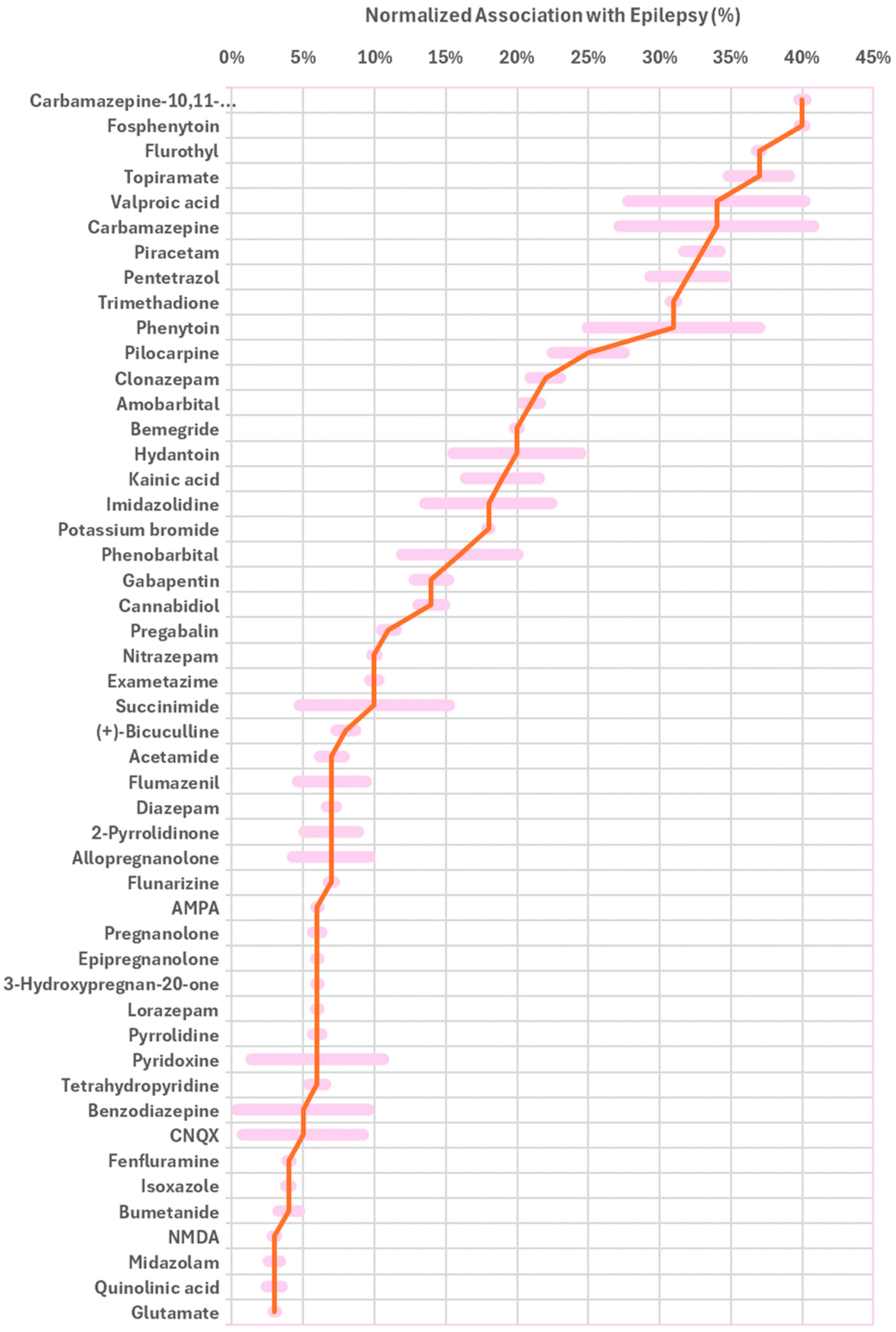

| Role in Epilepsy | Molecule |
|---|---|
| Drug | Fosphenytoin (40%), topiramate (37%), valproic acid (34%), hydantoin (20%), phenytoin (31%), carbamazepine (33%), carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide (40%), trimethadione (31%), gabapentin (14%), pregabalin (11%), flunarizine (7%), KBr (18%), cannabidiol (14%), fenfluramine (4%), bumetanide (4%), clonazepam (22%), nitrazepam (10%), diazepam (7%), lorazepam (6%), midazolam (3%), amobarbital (21%), phenobarbital (16%), *,# flumazenil (7%), allopregnanolone (7%), pregnanolone (6%), epipregnanolone (6%), 3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (6%), vitamin B6 (6%) |
| Drug families and scaffold | Imidazolidine (18%), # succinimide (10%), acetamide (7%), # 2-pyrrolidinone (7%), pyrrolidine (6%), tetrahydropyridine (6%), isoxazole (4%) |
| Diagnostic marker | Exametazime (10%), quinolinic acid (3%) |
| GABA-Transaminase Deficiency Biomarker | # Succinimide (10%), # 2-pyrrolidinone (7%) |
| Investigational | Cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (5%) |
| Inducers | Flurothyl (37%), pilocarpine (25%), (+)-bicuculline (8%), pentetrazol (32%), MPTP (6%), bemegride (20%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahalul-Yarchi, S.; Hartman, F.; Ben Zaken, K.; Sawaid, I.O.; Segev, L.; Mesfin, S.; Frankel, P.; Ezzy, R.; Samson, A.O. Drugs and Nutrients in Epilepsy: Vitamin B6 and the Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162676
Bahalul-Yarchi S, Hartman F, Ben Zaken K, Sawaid IO, Segev L, Mesfin S, Frankel P, Ezzy R, Samson AO. Drugs and Nutrients in Epilepsy: Vitamin B6 and the Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162676
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahalul-Yarchi, Shani, Feigy Hartman, Karin Ben Zaken, Ibrahim O. Sawaid, Lior Segev, Samuel Mesfin, Pnina Frankel, Rahaf Ezzy, and Abraham O. Samson. 2025. "Drugs and Nutrients in Epilepsy: Vitamin B6 and the Ketogenic Diet" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162676
APA StyleBahalul-Yarchi, S., Hartman, F., Ben Zaken, K., Sawaid, I. O., Segev, L., Mesfin, S., Frankel, P., Ezzy, R., & Samson, A. O. (2025). Drugs and Nutrients in Epilepsy: Vitamin B6 and the Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients, 17(16), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162676






