Effect of a Nutritional Education Intervention on Sports Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Intake, and Body Composition in Female Athletes: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
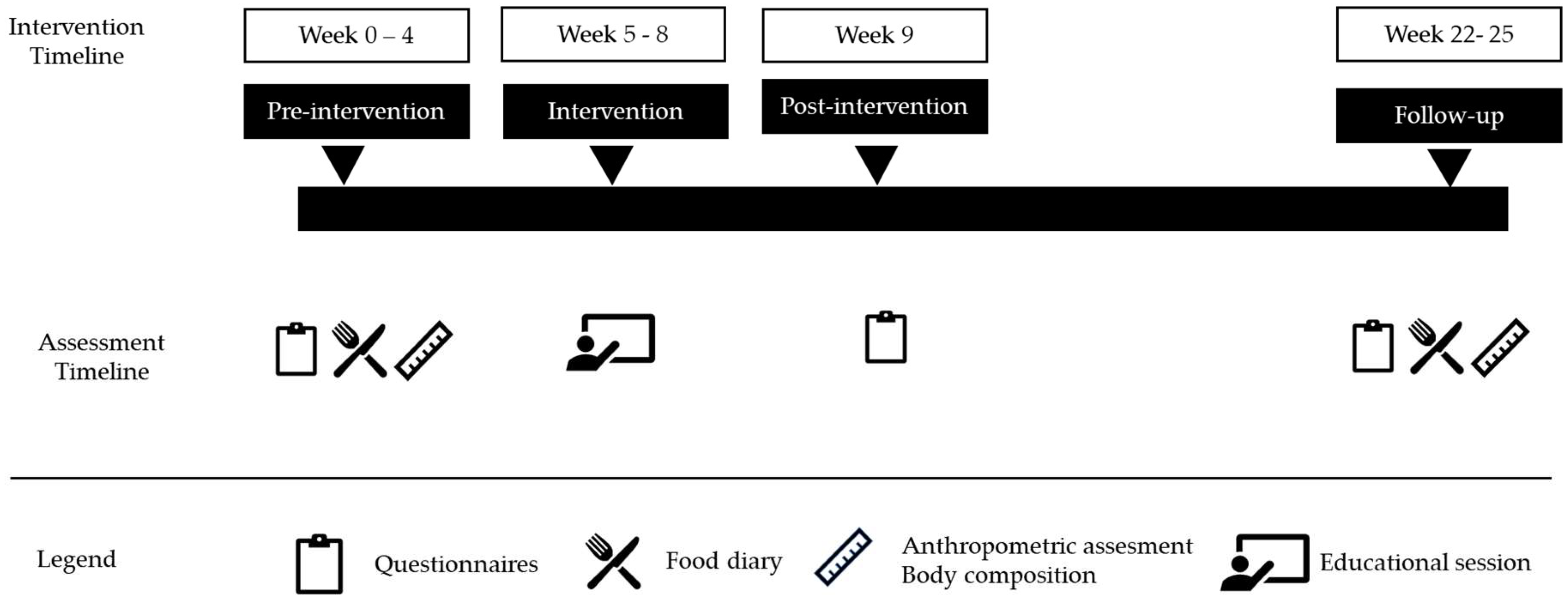
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Data Collection and Measurements
2.4.1. Questionnaires
2.4.2. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet
2.4.3. Assessment of Dietary Intake
2.4.4. Anthropometric Measurements and Body Composition
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Sports Nutritional Knowledge
3.3. Mediterranean Diet Score Adherence
3.4. Dietary Intake Assessment
3.5. Anthropometric Measurements and Body Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Sports Nutritional Knowledge
4.2. Mediterranean Diet Score Adherence
4.3. Dietary Intake
4.4. Anthropometric Measurements and Body Composition
4.5. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGAUR | Agència de Gestió d’Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca |
| MD | Mediterranean diet |
| NUKYA | Sports Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire for Young and Adult Athletes |
| EAT-26 | Eating Attitudes Test |
| BSQ | Body Shape Questionnaire |
| MLM | Mixed linear models |
| MAR | Missing at random |
References
- Janiczak, A.; Alcock, R.; Forsyth, A.; Trakman, G.L. A systematic review of interventions targeting modifiable factors that impact dietary intake in athletes. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 131, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastrich, M.D.; Quick, V.; Bachmann, G.; Moriarty, A.M. Nutritional Risks among Female Athletes. J. Women’s Health 2020, 29, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, R.; Hislop, M.; Vidgen, H.A.; Desbrow, B. Youth and Adolescent Athlete Musculoskeletal Health: Dietary and Nutritional Strategies to Optimise Injury Prevention and Support Recovery. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenhead, K.L.; Slater, G. A Review of Factors Influencing Athletes’ Food Choices. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelly, F.E.; Thurecht, R.L.; Slater, G. Determinants of Food Choice in Athletes: A Systematic Scoping Review. Sports Med.-Open 2022, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spronk, I.; Kullen, C.; Burdon, C.; O’Connor, H. Relationship between nutrition knowledge and dietary intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiczak, A.; Devlin, B.L.; Forsyth, A.; Trakman, G.L. A systematic review update of athletes’ nutrition knowledge and association with dietary intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmanus, A.M.; Armstrong, N. Physiology of Elite Young Female Athletes. In The Elite Young Athlete; Medicine and Sport Science; Armstrong, N., Mcmanus, A.M., Eds.; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, S.T.; Kerksick, C.M.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Janse de Jonge, X.A.K.; Hirsch, K.R.; Arent, S.M.; Hewlings, S.J.; Kleiner, S.M.; Bustillo, E.; Tartar, J.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Nutritional concerns of the female athlete. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2204066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso-Pulgar, M.; Farran-Codina, A.; Fernández de Arriba, R. Effects of nutrition education programs designed to improve dietary intake and nutritional knowledg. in female athletes: A systematic review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2025, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilo, A.; Lozano, L.; Tauler, P.; Nafría, M.; Colom, M.; Martínez, S. Nutritional status and implementation of a nutritional education program in young female artistic gymnasts. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektunalı Akman, C.; Gönen Aydın, C.; Ersoy, G. The effect of nutrition education sessions on energy availability, body composition, eating attitude and sports nutrition knowledge in young female endurance athletes. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1289448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condo, D.; Lohman, R.; Kelly, M.; Carr, A. Nutritional Intake, Sports Nutrition Knowledge and Energy Availability in Female Australian Rules Football Players. Nutrients 2019, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Martinez, P.; Perea-Moreno, A.-J.; Martinez-Jimenez, M.P.; Redel-Macías, M.D.; Pagliari, C.; Vaquero-Abellan, M. Social Media, Thin-Ideal, Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Attitudes: An Exploratory Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, K.E.; Baker, D.F.; Sims, S.T. Nutritional Needs of the Female Athlete: Risk and Prevention of Low Energy Availability. Strength Cond. J. 2020, 42, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, C.; Mooney, E.; Mc Cloat, A. Nutritional Intake and Dietary Knowledge of Athletes: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Espino, K.; Rodas-Font, G.; Farran-Codina, A. Sport Nutrition Knowledge, Attitudes, Sources of Information, and Dietary Habits of Sport-Team Athletes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, M.; Lehtovirta, M.; Autio, O.; Fogelholm, M.; Valve, R. The impact of nutrition education intervention with and without a mobile phone application on nutrition knowledge among young endurance athletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manore, M.M.; Patton-Lopez, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Wong, S.S. Sport nutrition knowledge, behaviors and beliefs of high school soccer players. Nutrients 2017, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lacoba, R.; Pardo-Garcia, I.; Amo-Saus, E.; Escribano-Sotos, F. Mediterranean diet and health outcomes: A systematic meta-review. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.; Matu, J.; Whyte, E.; Akin-Nibosun, P.; Clifford, T.; Stevenson, E.; Shannon, O.M. The Mediterranean dietary pattern for optimising health and performance in competitive athletes: A narrative review. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Erbasan, H.; Riso, P.; Perna, S. Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on Athletic Performance, Muscle Strength, Body Composition, and Antioxidant Markers in Both Athletes and Non-Professional Athletes: A Systematic Review of Intervention Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murimi, M.W.; Kanyi, M.; Mupfudze, T.; Amin, M.R.; Mbogori, T.; Aldubayan, K. Factors Influencing Efficacy of Nutrition Education Interventions: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Espino, K.; Fernández-Tena, C.; Lizarraga-Dallo, M.A.; Farran-Codina, A. Development and validation of a short sport nutrition knowledge questionnaire for athletes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, T.; Bersabé, R.; Jiménez, M.; Berrocal, C. The Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26): Reliability and validity in Spanish female samples. Span. J. Psychol. 2010, 13, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, J.; Henderson, L. The validity of a short version of the Body Shape Questionnaire. Psychiatry Res. 2001, 102, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean Diet Quality Index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Contreras, C.; Farran-Codina, A.; Zerón-Rugerio, M.F.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M. Relative Validity and Reliability of the Remind App as an Image-Based Method to Assess Dietary Intake and Meal Timing in Young Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casperson, S.L.; Sieling, J.; Moon, J.; Johnson, L.; Roemmich, J.N.; Whigham, L. A mobile phone food record app to digitally capture dietary intake for adolescents in a free-living environment: Usability study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2015, 3, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantos, D.; Farran-Codina, A.; Palma-Linares, I. Programa de Càlcul Nutricional PCN Pro Versió 1. 2013. Available online: https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/handle/2445/44329?locale=es (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Codina, A.F.; de Arriba, R.F.; González, A.G.; Almiñana, S.J. Tablas Estándar de Composición de Los Alimentos–TECA: Taules Estàndard de Composició Dels Aliments-TECA; McGraw Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2022; ISBN 9788448634872. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-López, M.D.; Reyes Artacho, M.L. Guía para Estudios Dietéticos. In Álbum Fotográfico de Alimentos, 1st ed.; Editorial Universidad de Granada: Granada, Spain, 2011; ISBN 978-84-338-5167-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-López, M.D. Martínez de Victoria Muñoz, E; Gil Hernández, A. Guía Fotográfica de Porciones de Alimentos Consumidos en España, 1st ed.; Ruiz-López, M.D., Martínez de Victoria Muñoz, E., Gil Hernández, A., Eds.; Fundación Iberoamericana de Nutrición: Granada, Spain, 2019; ISBN 978-84-09-08860-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wiita, B.G.; Stombaugh, I.A. Nutrition Knowledge, Eating Practices, and Health of Adolescent Female Runners: A 3-Year Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Sport Nutr. 1996, 6, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davar, V. Nutritional Knowledge and Attitudes Towards Healthy Eating of College-going Women Hockey Players. J. Hum. Ecol. 2012, 37, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abood, D.A.; Black, D.R.; Birnbaum, R.D. Nutrition education intervention for college female athletes. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2004, 36, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.; Toma, R.B.; Tuveson, R.V.; Jacob, M. Nutrition Knowledge among Adolescent High School Female Athletes. Adolescence 1997, 32, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.B.; Nogueira, J.A.D.; da Costa, T.H.M. The Food Pyramid Adapted to Physically Active Adolescents as a nutrition education tool. Rev. Bras. Ciências Esporte 2014, 36, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton-Lopez, M.M.; Manore, M.M.; Branscum, A.; Meng, Y.; Wong, S.S. Changes in sport nutrition knowledge, attitudes/beliefs and behaviors following a two-year sport nutrition education and life-skills intervention among high school soccer players. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-McGehee, T.M.; Green, J.M.; Leaver-Dunn, D.; Leeper, J.D.; Bishop, P.A.; Richardson, M.T. Attitude and Knowledge Changes in Collegiate Dancers following a Short-Term, Team-Centered Prevention Program on Eating Disorders. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2011, 112, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collison, S.B. Impact of Nutrition Education on Female Athletes. Am. J. Health Behav. 1996, 20, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, N.V.S.; Jürgensen, L.P.; Padovani, R.D.C.; Juzwiak, C.R. Impact of an interdisciplinary food, nutrition and health education program for adolescent Brazilian volleyball players. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 29, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, M.E.; Bell, L.B.; Luccia, B.H.D. Peer Nutrition Education Program to Improve Nutrition Knowledge of Female Collegiate Athletes. J. Nutr. Educ. 2001, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laramée, C.; Drapeau, V.; Valois, P.; Goulet, C.; Jacob, R.; Provencher, V.; Lamarche, B. Evaluation of a Theory-Based Intervention Aimed at Reducing Intention to Use Restrictive Dietary Behaviors Among Adolescent Female Athletes. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 497–504.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, R.; McCloat, A.; Mooney, E.; Kelly-Blakeney, E. Recipes for Success: Lessons learned from the implementation of a food skills and nutrition education workshop with Gaelic athletic players on the Island of Ireland (IOI). Health Educ. J. 2023, 82, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, L. The implementation and evaluation of a nutrition education programme for university elite athletes. Prog. Nutr. 2013, 15, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Valliant, M.W.; Emplaincourt, H.P.; Wenzel, R.K.; Garner, B.H. Nutrition education by a registered dietitian improves dietary intake and nutrition knowledge of a NCAA female volleyball team. Nutrients 2012, 4, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, N.N.Z.K.; Muhamad, A.S.; Jusoh, M.R.C. Knowledge, attitude, practice (KAP) and dietary intake of young university athletes following sports nutrition education. Malays. J. Nutr. 2021, 27, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannakoulia, M.; Sitara, M.; Matalas, A.L. Reported eating behavior and attitudes improvement after a nutrition intervention program in a group of young female dancers. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2002, 12, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakman, G.L.; Forsyth, A.; Hoye, R.; Belski, R. Australian team sports athletes prefer dietitians, the internet and nutritionists for sports nutrition information. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 76, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J.; Parmenter, K.; Waller, J. Nutrition knowledge and food intake. Appetite 2000, 34, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton Greg, J.; Thomson Christine, D.; Hopkins William, G. Nutrition knowledge of elite distance runners. N. Z. J. Sports Med. 1994, 22, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sofi, F.; Macchi, C.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Mediterranean diet and health status: An updated meta-analysis and a proposal for a literature-based adherence score. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, M.; Nguyen, C.; Shetty, M.; Oppezzo, M.; Barrack, M.; Fredericson, M. Popular Dietary Trends’ Impact on Athletic Performance: A Critical Analysis Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S. Polyphenols: Potential beneficial effects of these phytochemicals in athletes. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2020, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.A.; Daniels, D.; Calder, P.C.; Castell, L.M.; Pedlar, C.R. Are There Benefits from the Use of Fish Oil Supplements in Athletes? A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, M.; Cerullo, G.; Abate, M. Is the Mediterranean Diet Pattern a Good Choice for Athletes? Nutr. Today 2019, 54, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippou, E.; Middleton, N.; Pistos, C.; Andreou, E.; Petrou, M. The impact of nutrition education on nutrition knowledge and adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in adolescent competitive swimmers. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoune, R.; Bouchenak, M. Nutritional intervention promoting Mediterranean diet improves dietary intake and enhances score adherence in adolescent athletes. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 13, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso-Pulgar, M.; Arcila-Agudelo, A.M.; Ferrer-Svoboda, C.; Torres-Fernández, T.; Farran-Codina, A. Estado nutricional y adherencia a la dieta mediterránea en la población escolar de la ciudad de Mataró (Cataluña, España). Nutr. Hosp. 2024, 41, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nowacka, E.; Leszczyńska, T.; Kopeć, A.; Hojka, D. Nutritional behavior of Polish canoeist’s athletes: The interest of nutritional education. Sci. Sports 2016, 31, e79–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenz, C.; Sanders, D.J.; Brooks, S.J.; Bracken, L.; Jordan, A.; Stoner, J.; Vatne, E.; Wahler, M.; Brown, A.F. TRelationship Between Dance Training Volume, Body Composition, and Habitual Diet in Female Collegiate Dancers: The Intercollegiate Artistic Athlete Research Assessment (TIAARA) Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manore, M.M. Chronic dieting in active women: What are the health consequences? Women’s Health Issues 1996, 6, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. American College of Sports Medicine Joint Position Statement. Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 543–568. [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman, B.; Ackerman, K.E. Recommendations and Nutritional Considerations for Female Athletes: Health and Performance. Sports Med. 2021, 51 (Suppl. S1), 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrosa, M.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; González-Rodríguez, L.G.; Alférez, M.J.M.; San Juan, A.F.; Sánchez-Gómez, Á.; Calvo-Ayuso, N.; Ramos-Álvarez, J.J.; Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Lopez-Grueso, R.; et al. Nutritional Strategies for Optimizing Health, Sports Performance, and Recovery for Female Athletes and Other Physically Active Women: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, e1068–e1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Sociedad Española, G.C.; de Nutrición Comunitaria, S.E.N.C. Guías alimentarias para la población española (SENC, diciembre 2016): La nueva pirámide de la alimentación saludable. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33 (Suppl. S8), 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Barney, D.E., Jr.; Cheung, S.N.; Harris, A.R.; Berryman, C.E.; Hennigar, S.R. Dietary Intake and Diet Quality of Female and Male NCAA Division I Cross Country Runners from a Single University. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagowska, K.; Kapczuk, K.; Jeszka, J. Nine-month nutritional intervention improves restoration of menses in young female athletes and ballet dancers. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagowska, K.; Kapczuk, K.; Friebe, Z.; Bajerska, J. Effects of dietary intervention in young female athletes with menstrual disorders. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2014, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.; Lozano-Casanova, M.; Sospedra, I.; Norte, A.; Gutiérrez-Hervás, A.; Martínez-Sanz, J.M. Energy and Macronutrients Intake in Indoor Sport Team Athletes: Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeukendrup, A.E. High-carbohydrate versus high-fat diets in endurance sports. Schweiz. Z. Sportmed. Sport. 2014, 51, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, M.C.; Beavers, K.M.; Ziegenfuss, T. Essential and Nonessential Micronutrients and Sport. In Nutritional Supplements in Sports and Exercise; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 77–103. [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter, S. Sport nutrition: A review of the latest guidelines for exercise and sport nutrition from the American College of Sport Nutrition, the International Olympic Committee and the International Society for Sports Nutrition: Review article. S. Afr. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 26, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingitore, A.; Pace, G.; Lima, P.; Mastorci, F.; Quinones, A.; Iervasi, G.; Vassalle, C. Exercise and oxidative stress: Potential effects of antioxidant dietary strategies in sports. Nutrition 2015, 31, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudio ENALIA 2012–2014. Encuesta Nacional de consumo de Alimentos en población Infantil y Adolescente; Agencia Española de Consumo, Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición, Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases: Report of a Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation; WHO Technical Report Series, No. 916; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/924120916X (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; Mazzilli, M.; Gobbo, L.A.; Coratella, G. Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.E. The Impact of Feedback on Dietary Intake and Body Composition of College Women Volleyball Players Over a Competitive Season. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2220–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzio, A.; Cassera, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Pozzi, A.; Orlando, A.; Greco, A.; Palestini, P.; Cazzaniga, E. The impact of a nutritional intervention program on eating behaviors in Italian athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.K.; Valliant, M.W.; Chang, Y.; Bomba, A.K.; Lambert, L.G. Dietary Assessment and Education Improves Body Composition and Diet in NCAA Female Volleyball Players. Top. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 27, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-McGehee, T.M.; Pritchett, K.L.; Zippel, D.; Minton, D.M.; Cellamare, A.; Sibilia, M. Sports nutrition knowledge among collegiate athletes, coaches, athletic trainers, and strength and conditioning specialists. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeller, D.A.; Bandini, L.G.; Dietz, W.H. Inaccuracies in self-reported intake identified by comparison with the doubly labelled water method. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1990, 68, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, R.K.; Abram, J.K.; Brown, K.; Ziegler, P.J.; Parrott, J.S.; Steiber, A.L. Development and Validation of the Guide for Effective Nutrition Interventions and Education (GENIE): A Tool for Assessing the Quality of Proposed Nutrition Education Programs. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2015, 47, 308–316.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Session | Topic |
|---|---|
| 1 | Introduction to health and the Mediterranean diet |
| 2 | Energy and carbohydrate requirements |
| 3 | Protein and fat requirements |
| 4 | Micronutrients |
| 5 | Hydration |
| 6 | Supplementation and periodicity |
| Food Group | Foods |
|---|---|
| Fruits | Fresh fruits, canned fruits, and dried fruits |
| Vegetables | Leaf, flower, or stem vegetables, root vegetables, bulbs, and mushrooms |
| Cereals and grains | Cereals, grains and flour, pasta, baked goods, cookies, pastries, and breakfast cereals |
| Legumes | Legumes, dry legumes, legume flour, and derivatives |
| Tubers | Potatoes and other starchy tubers |
| Milk and dairy products | Milk and milkshakes, yogurt and fermented milk, dairy desserts, fresh cheese, aged cheese, processed cheese, milk ice cream, or similar |
| Meats | Pork, veal, lamb, beef, rabbit, poultry, viscera, and raw, raw-cured, and heat-treated sausages |
| Eggs | Chicken eggs and other eggs from other birds |
| Fish | Cod, hake, salmon, tuna, sole, monkfish, mackerel, sardines, etc. |
| Oils and fats | Olive oil, sunflower oil, coconut oil, lard, butter, and margarine |
| High-sugar foods | Sugar, honey, syrups, jams, chocolates, and candies |
| Nuts | Almonds, walnuts, hazelnuts, cashews, pistachios, macadamia nuts, pecans, and peanuts |
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Competition category | ||
| Cadetes | 14 | 31.1 |
| Juvenil | 14 | 31.1 |
| Senior | 17 | 37.8 |
| Team rol | ||
| Player | 39 | 86.7 |
| Goalkeeper | 6 | 13.3 |
| Training period (years) | ||
| 1–5 years | 13 | 28.9 |
| >5 years | 32 | 71.1 |
| Level of education | ||
| Basic | 16 | 35.6 |
| Intermediate | 16 | 35.6 |
| University | 13 | 28.8 |
| Currently employed | ||
| Yes | 6 | 13.3 |
| No | 39 | 86.7 |
| Mother’s highest educational level | ||
| Without studies or only compulsory education | 5 | 11.1 |
| Secondary education | 19 | 42.2 |
| University education | 21 | 46.7 |
| Attendance at sessions | ||
| Session 1 | 35 | 77.8 |
| Session 2 | 33 | 73.3 |
| Session 3 | 29 | 64.4 |
| Session 4 | 21 | 46.7 |
| Session 5 | 31 | 68.9 |
| Session 6 | 24 | 53.3 |
| Completion of questionnaire | ||
| EAT-26 | 45 | 100.0 |
| BSQ | 45 | 100.0 |
| NUKYA pre-intervention | 44 | 97.8 |
| NUKYA post-intervention | 41 | 91.1 |
| NUKYA follow-up | 35 | 77.8 |
| Kidmed Index pre-intervention | 45 | 100.0 |
| Kidmed Index follow-up | 36 | 80.0 |
| Completion of diet record | ||
| Pre-intervention | 42 | 93.3 |
| Follow-up | 37 | 82.2 |
| Anthropometric parameters | ||
| Pre-intervention | 44 | 97.8 |
| Follow-up | 35 | 77.8 |
| Pre Mean (SD) | Post Mean (SD) | Follow-Up Mean (SD) | p-Value | Effect Size (Pre/Follow-Up) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 44 | n = 41 | n = 35 | |||
| Total Score | 21.1 a (16.1) | 43.1 b (16.3) | 41.4 b (16.5) | <0.001 | 1.2 |
| Sections: | |||||
| Macronutrients | 13.4 a (10.1) | 23.1 b (10.5) | 22.7 b (9.1) | <0.001 | 0.9 |
| Micronutrients | 7.9 a (6.2) | 10.8 ab (7.1) | 11.6 b (7.1) | 0.005 | 0.4 |
| Hydration | −0.65 a (3.8) | 6.0 b (4.2) | 4.3 b (4.1) | <0.001 | 0.9 |
| Periodization | 0.42 a (2.7) | 3.2 b (2.3) | 2.7 b (3.1) | <0.001 | 0.7 |
| Before | Follow-Up | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | ||
| Energy (kcal) | 2010.4 | 455.7 | 1940.2 | 450.4 | 0.1620 |
| CHO (g/d) | 200.0 | 44.9 | 188.0 | 52.0 | 0.0802 |
| CHO (% kcal) | 40.1 | 4.8 | 38.7 | 5.7 | |
| Fiber (g/d) | 17.7 | 5.4 | 15.8 | 6.0 | 0.0169 * |
| Protein (g/d) | 99.4 | 27.6 | 100.0 | 31.2 | 0.4449 |
| Protein (% kcal) | 19.7 | 2.7 | 20.4 | 3.1 | |
| Lipids (g/d) | 90.3 | 25.3 | 87.4 | 20.5 | 0.2458 |
| Lipids (% kcal) | 40.1 | 4.6 | 40.9 | 5.3 | |
| SFA (g/d) | 30.3 | 10.1 | 30.8 | 9.9 | 0.4011 |
| SFA (% kcal) | 13.4 | 3.1 | 14.2 | 3.0 | |
| MUFA (g/d) | 36.9 | 12.1 | 37.1 | 8.6 | 0.4632 |
| MUFA (% kcal) | 16.2 | 2.9 | 17.3 | 2.3 | |
| PUFA (g/d) | 15.5 | 5.6 | 12.1 | 3.2 | 0.0006 * |
| PUFA (% kcal) | 7.1 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 1.7 | |
| Cholesterol (mg/d) | 382.5 | 161.7 | 352.2 | 131.0 | 0.1235 |
| Before | Follow-Up | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | ||
| Calcium (mg) | 856.8 | 245.0 | 934.2 | 375.3 | 0.0998 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 293.8 | 77.0 | 288.7 | 73.3 | 0.3398 |
| Iron (mg) | 13.2 | 4.5 | 11.7 | 3.8 | 0.0684 |
| Zinc (mg) | 9.7 | 2.5 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 0.2583 |
| Folates (μg) | 268.0 | 109.0 | 240.5 | 93.4 | 0.0713 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 75.8 | 45.3 | 83.1 | 42.1 | 0.2388 |
| Vitamin D (μg) | 3.0 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 2.7 | 0.5610 |
| Vitamin E (mg **) | 10.8 | 4.3 | 9.3 | 2.8 | 0.0176 * |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 2.0 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.3549 |
| Vitamin B12 (μg) | 5.7 | 3.5 | 5.4 | 2.5 | 0.2429 |
| Before | Follow-Up | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | ||
| Weight (kg) | 64.6 | 9.3 | 65.4 | 9.0 | 0.0175 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.0 | 2.8 | 23.3 | 2.9 | 0.0161 * |
| Fat mass (%) | 28.4 | 5.1 | 29.1 | 4.7 | 0.1195 |
| Fat-free mass (%) | 71.6 | 5.1 | 70.9 | 4.7 | 0.1108 |
| Muscle mass (%) | 36.2 | 3.6 | 35.5 | 3.4 | 0.0994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veloso-Pulgar, M.; Farran-Codina, A. Effect of a Nutritional Education Intervention on Sports Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Intake, and Body Composition in Female Athletes: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152560
Veloso-Pulgar M, Farran-Codina A. Effect of a Nutritional Education Intervention on Sports Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Intake, and Body Composition in Female Athletes: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152560
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeloso-Pulgar, Macarena, and Andreu Farran-Codina. 2025. "Effect of a Nutritional Education Intervention on Sports Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Intake, and Body Composition in Female Athletes: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152560
APA StyleVeloso-Pulgar, M., & Farran-Codina, A. (2025). Effect of a Nutritional Education Intervention on Sports Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Intake, and Body Composition in Female Athletes: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 17(15), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152560






