Beyond Weight Loss: Comparative Effects of Tirzepatide Plus Low-Energy Ketogenic Versus Low-Calorie Diet on Hepatic Steatosis and Stiffness in MASLD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. TZP Protocol and LEKT and LCD Characteristics
2.3. Assessment of BW, CAP, LSM, and Laboratory Parameters
2.4. Evaluation of Treatment Adherence and Side Effects
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Groups at Baseline
3.2. Impact of TZP + LEKT vs. TZP + LCD on BW, LSM, and CAP
3.3. Impact of TZP + LEKT vs. TZP + LCD on Clinical Status
3.4. Effects of TZP + LEKT and TZP + LCD on Appetite Suppression and Tolerability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.Q.; Wong, V.W.S.; Rinella, M.E.; Boursier, J.; Lazarus, J.V.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Loomba, R. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in adults. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Heterogeneous pathomechanisms and effectiveness of metabolism-based treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Jahid Hasan, M.; Khan, M.A.S.; Alam, M.; Hasan, N. Effect of Weight Reduction on Histological Activity and Fibrosis of Lean Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Patient. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2019, 7, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Annunziata, G.; Verde, L.; Fascì-Spurio, F.; Reytor-González, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L. Nutritional Strategies for Battling Obesity-Linked Liver Disease: The Role of Medical Nutritional Therapy in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2025, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Investigators Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Wysham, C.; Frías, J.P.; Kaneko, S.; Lee, C.J.; Fernández Landó, L.; Mao, H.; Cui, X.; Karanikas, C.A.; Thieu, V.T. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K.; SURPASS-2 Investigators. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Cusi, K.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bray, R.; Brouwers, B.; Rodríguez, Á. Effect of tirzepatide versus insulin degludec on liver fat content and abdominal adipose tissue in people with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3 MRI): A substudy of the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 SURPASS-3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Hartman, M.L.; Lawitz, E.J.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Boursier, J.; Bugianesi, E.; Yoneda, M.; Behling, C.; Cummings, O.W.; Tang, Y.; et al. Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Nikooie, A.; Tang, Y.; Robins, D.A.; Brouwers, B.; Hartman, M.L. Randomised clinical trial: Design of the SYNERGY-NASH phase 2b trial to evaluate tirzepatide as a treatment for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis and modification of screening strategy to reduce screen failures. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Santella, B.; Mingo, M.; Rossetti, G.; Orio, M.; Cobellis, L.; Maurano, A.; Iannelli, A.; Pilone, V. Preliminary Evidence Suggests That a 12-Week Treatment with Tirzepatide Plus Low-Energy Ketogenic Therapy Is More Effective than Its Combination with a Low-Calorie Diet in Preserving Fat-Free Mass, Muscle Strength, and Resting Metabolic Rate in Patients with Obesity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emanuele, F.; Biondo, M.; Tomasello, L.; Arnaldi, G.; Guarnotta, V. Ketogenic Diet in Steatotic Liver Disease: A Metabolic Approach to Hepatic Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schugar, R.C.; Crawford, P.A. Low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets, glucose homeostasis, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Thompson, C.H.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Wittert, G.A.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Brinkworth, G.D. A very low-carbohydrate, low-saturated fat diet for type 2 diabetes management: A randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, M.K.; Pissios, P.; Kennedy, A.R.; Koukos, G.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brener, S. Transient Elastography for Assessment of Liver Fibrosis and Steatosis: An Evidence-Based Analysis. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2015, 15, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar Das, T.; Meng, X.; Abdallah, M.; Bilal, M.; Sarwar, R.; Shaukat, A. An Assessment of the Feasibility, Patient Acceptance, and Performance of Point-of-Care Transient Elastography for Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taru, M.G.; Neamti, L.; Taru, V.; Procopciuc, L.M.; Procopet, B.; Lupsor-Platon, M. How to Identify Advanced Fibrosis in Adult Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Using Ultrasound Elastography—A Review of the Literature and Proposed Multistep Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Frias, J.P.; Jastreboff, A.M.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Aizenberg, D.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Machineni, S.; Kushner, R.; Ard, J.; Srivastava, G.; Halpern, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide after intensive lifestyle intervention in adults with overweight or obesity: The SURMOUNT-3 phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronne, L.J.; Sattar, N.; Horn, D.B.; Bays, H.E.; Wharton, S.; Lin, W.Y.; Ahmad, N.N.; Zhang, S.; Liao, R.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Continued Treatment with Tirzepatide for Maintenance of Weight Reduction in Adults with Obesity: The SURMOUNT-4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronne, L.J.; Horn, D.B.; le Roux, C.W.; Ho, W.; Falcon, B.L.; Gomez Valderas, E.; Das, S.; Lee, C.J.; Glass, L.C.; Senyucel, C.; et al. Tirzepatide as Compared with Semaglutide for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; Pilone, V.; Rossetti, G.; Barbarisi, A.; Cesaretti, M.; Iannelli, A. A 4-Week Preoperative Ketogenic Micronutrient-Enriched Diet Is Effective in Reducing Body Weight, Left Hepatic Lobe Volume, and Micronutrient Deficiencies in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery: A Prospective Pilot Study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; Pierro, R.; Asteria, C.; Calabrese, P.; Di Biasio, A.; Coluzzi, I.; Severino, L.; Giovanelli, A.; Pilone, V.; Silecchia, G. Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure to Alleviate Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Patients with Obesity Scheduled for Bariatric/Metabolic Surgery: A Pilot, Prospective, Randomized Multicenter Comparative Study. Obes. Surg. 2022, 32, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; De Stefano, G.; Persico, F.; Gargiulo, S.; Di Spirito, F.; Griguolo, G.; Petrucciani, N.; Fontas, E.; Iannelli, A.; Pilone, V. A Randomized, Controlled Trial Comparing the Impact of a Low-Calorie Ketogenic vs a Standard Low-Calorie Diet on Fat-Free Mass in Patients Receiving an Elipse™ Intragastric Balloon Treatment. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; D’Amico, R.; Sowden, A.J.; Sakarovitch, C.; Song, F.; Petticrew, M.; Altman, D.G.; International Stroke Trial Collaborative Group; European Carotid Surgery Trial Collaborative Group. Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies. Health Technol. Assess. 2003, 7, iii–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Tsunekawa, Y.; Tanimura, D. Association between the Big Five personality traits and medication adherence in patients with cardiovascular disease: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershuni, V.M.; Yan, S.L.; Medici, V. Nutritional Ketosis for Weight Management and Reversal of Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulides, C.; Dyson, P.; Sprecher, D.; Tsintzas, K.; Karpe, F. Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists but not ketosis in man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3594–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Gan, L.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; Cai, D.; Cui, H.; Gou, L.; Deng, J.; et al. Beta-Hydroxybutyrate: A Dual Function Molecular and Immunological Barrier Function Regulator. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 805881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, S.; Götz, A.; Finan, B.; Feuchtinger, A.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Döring, Y.; Weber, C.; Tschöp, M.H.; Müller, T.D.; Hofmann, S.M. GIP receptor agonism improves dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis independently of body weight loss in preclinical mouse model for cardio-metabolic disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantó, C.; Auwerx, J. PGC-1alpha, SIRT1 and AMPK, an energy sensing network that controls energy expenditure. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2009, 20, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, M.D.; Gao, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Gromada, J. Fibroblast growth factor 21 regulates energy metabolism by activating the AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1alpha pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viollet, B.; Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Horman, S.; Dentin, R.; Bertrand, L.; Hue, L.; Andreelli, F. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver: A new strategy for the management of metabolic hepatic disorders. J. Physiol. 2006, 574 Pt 1, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


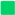 T) indicates convergence of mechanistic pathways shared by TZP and LEKT.
T) indicates convergence of mechanistic pathways shared by TZP and LEKT.
 T) indicates convergence of mechanistic pathways shared by TZP and LEKT.
T) indicates convergence of mechanistic pathways shared by TZP and LEKT.
| LEKT (n = 30) | LCD (n = 30) | p (LEKT vs. LCD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female, n) | 14/16 | 13/17 | - |
| Body Weight (kg) | 121.9 ± 23.6 | 124.3 ± 23.8 | 0.70 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 44.9 ± 6.28 | 45.5 ± 7.35 | 0.73 |
| LSM (kPa) | 7.5 ± 1.1 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 0.81 |
| CAP (dB/m) | 295 ± 16 | 298 ± 17 | 0.58 |
| Clinical Parameters (Cut-Off) | Group | Baseline | 12-Week Follow-Up | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | TZP + LEKT | 87 ± 21 | 80 ± 18 | 0.17 |
| (70–100 mg/dL) | TZP + LCD | 92 ± 17 | 87 ± 13 | 0.21 |
| Insulin | TZP + LEKT | 8.5 ± 6.3 | 7.1 ± 5.2 | 0.35 |
| (<25 mU/L) | TZP + LCD | 7.7 ± 4.7 | 7.2 ± 3.1 | 0.63 |
| HOMA IR Index | TZP + LEKT | 1.83 ± 0.8 | 1.40 ± 1.1 | 0.09 * |
| (<2.5) | TZP + LCD | 1.75 ± 1.4 | 1.55 ± 0.96 | 0.52 |
| Hemoglobin A1C | TZP + LEKT | 4.7 ± 1.7 | 3.7 ± 1.1 | 0.01 * |
| (<6.1%) | TZP + LCD | 4.3 ± 0.77 | 4.0 ± 0.80 | 0.14 |
| Total cholesterol | TZP + LEKT | 194 ± 42 | 162 ± 11 | <0.001 * |
| (<200 mg/dL) | TZP + LCD | 176 ± 48 | 159 ± 23 | 0.09 |
| HDL | TZP + LEKT | 47 ± 12 | 55.5 ± 18 | 0.03 |
| (>50 mg/dL) | TZP + LCD | 49.9 ± 22 | 45.4 ± 10 | 0.31 |
| Triglycerides | TZP + LEKT | 151 ± 75 | 118 ± 28.5 | 0.03 * |
| (<150 mg/dL) | TZP + LCD | 116 ± 54 | 109 ± 18.2 | 0.50 |
| Creatine | TZP + LEKT | 0.76 ± 0.19 | 0.81 ± 0.26 | 0.40 |
| (0.55–1.02 mg/dL) | TZP + LCD | 0.79 ± 0.17 | 0.83 ± 0.15 | 0.34 |
| AST | TZP + LEKT | 23 ± 13.8 | 24 ± 8.2 | 0.73 |
| (<34 U/L) | TZP + LCD | 26 ± 22.9 | 29 ± 9.5 | 0.51 |
| ALT | TZP + LEKT | 29 ± 21.1 | 19 ± 3.7 | 0.01 |
| (<55 U/L) | TZP + LCD | 35 ± 32.4 | 29 ± 8.7 | 0.33 |
| GGT | TZP + LEKT | 32 ± 26.4 | 28 ± 6.9 | 0.42 |
| (<38 U/L) | TZP + LCD | 31 ± 21.1 | 29 ± 9.2 | 0.64 |
| Ketonemia | TZP + LEKT | 0.3 ± 0.04 | 0.82 ± 0.49 | <0.001 |
| (<0.6 mmol/L) | TZP + LCD | 0.25 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.05 | 0.21 |
| Patient-Reported Outcomes | LEKT (n = 30) | LCD (n = 30) |
|---|---|---|
| Appetite reduction (%) | 18 | 8 |
| Nausea episodes (%) | 15 | 17 |
| Vomiting episodes (%) | 6 | 7 |
| Constipation episodes (%) | 16 | 15 |
| Diarrhea episodes (%) | 4 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiavo, L.; Santella, B.; Mingo, M.; Rossetti, G.; Orio, M.; Pilone, V. Beyond Weight Loss: Comparative Effects of Tirzepatide Plus Low-Energy Ketogenic Versus Low-Calorie Diet on Hepatic Steatosis and Stiffness in MASLD. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152409
Schiavo L, Santella B, Mingo M, Rossetti G, Orio M, Pilone V. Beyond Weight Loss: Comparative Effects of Tirzepatide Plus Low-Energy Ketogenic Versus Low-Calorie Diet on Hepatic Steatosis and Stiffness in MASLD. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152409
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiavo, Luigi, Biagio Santella, Monica Mingo, Gianluca Rossetti, Marcello Orio, and Vincenzo Pilone. 2025. "Beyond Weight Loss: Comparative Effects of Tirzepatide Plus Low-Energy Ketogenic Versus Low-Calorie Diet on Hepatic Steatosis and Stiffness in MASLD" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152409
APA StyleSchiavo, L., Santella, B., Mingo, M., Rossetti, G., Orio, M., & Pilone, V. (2025). Beyond Weight Loss: Comparative Effects of Tirzepatide Plus Low-Energy Ketogenic Versus Low-Calorie Diet on Hepatic Steatosis and Stiffness in MASLD. Nutrients, 17(15), 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152409







