Hydration Strategies in Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. What Is Hydration, and How Does It Change with Aging?
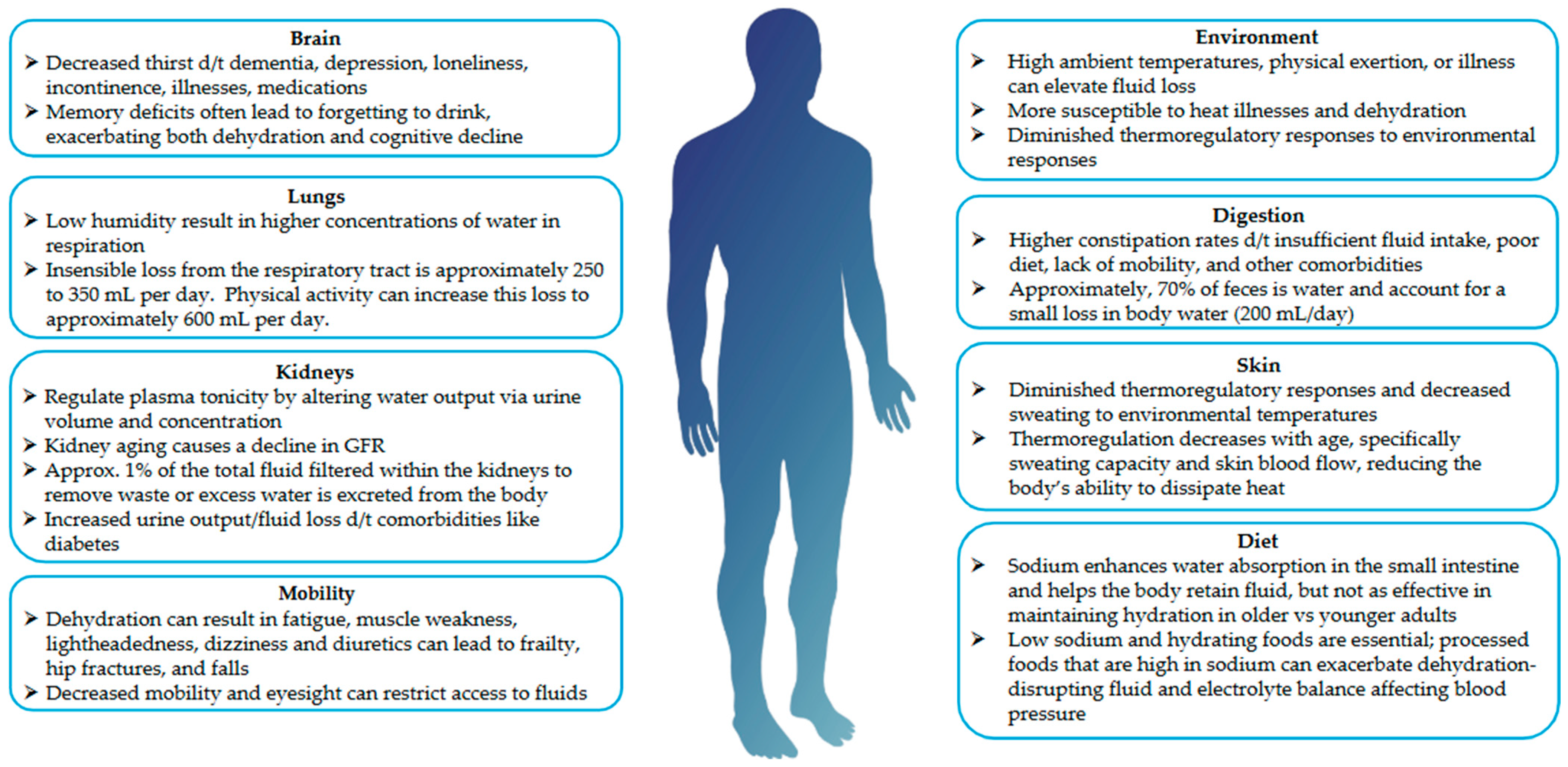
1.2. Causes and Concerns for Dehydration in Older Adults
1.3. Why Is Hydration Important?
2. What Controls Hydration?
2.1. Fluid
2.2. Food
2.3. Medications
2.4. Acute and Chronic Illness
2.5. Alteration to Thermoregulation with Age
2.6. Environment and Weather
2.7. Sweating and Activity
3. How Is Hydration Measured?
3.1. Crude Measures
3.2. Clinical and Research Measures
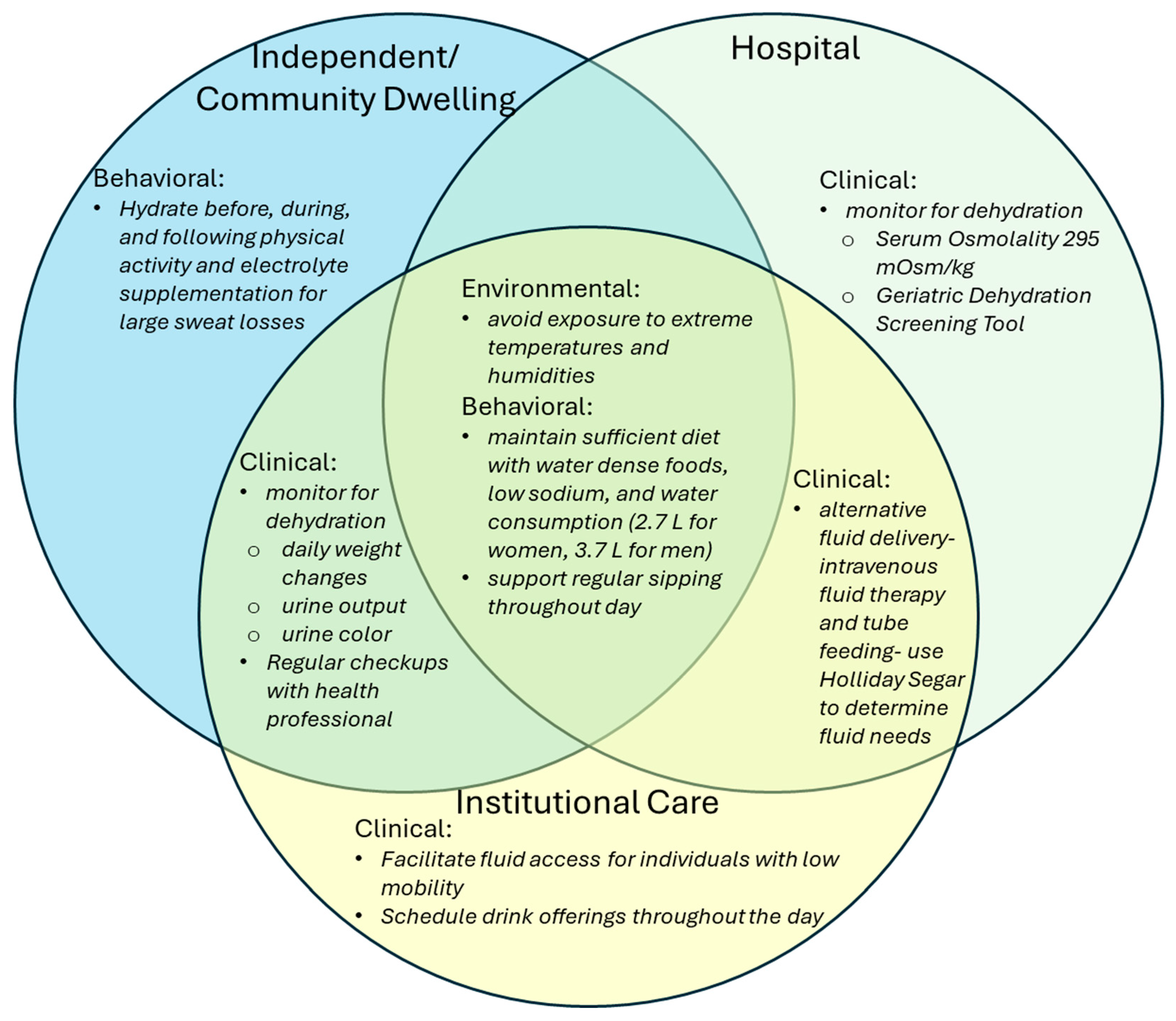
4. What Are Some Strategies to Combat Dehydration?
4.1. The Role of Food in Hydration Management
4.2. Fluid Intake
4.2.1. Oral Rehydration Solutions
4.2.2. Intravenous Fluid Therapy
4.3. Environment and Activity
5. What Are Some Strategies to Improve Hydration?
5.1. Regular Fluid Intake Throughout the Day
5.2. Fluids Before, During, and After Activity
5.3. Electrolytes
5.4. Carbohydrates
5.5. Amino Acids
5.6. Allulose
6. What Research Has Been Done on Dehydration?
6.1. Limitations
6.2. Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE inhibitors | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors |
| BASE-II | Berlin Aging Study II |
| BHI | Beverage Hydration Index |
| BIA | Bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| CDC | Center for Disease Control |
| C | Celsius |
| CES | carbohydrate-electrolyte solution |
| Cr | Creatinine |
| d/t | due to |
| D5W | Dextrose 5% in Water |
| D10W | Dextrose 10% in Water |
| F | Fahrenheit |
| g | grams |
| GDST | Geriatric Dehydration Screening Tool |
| GFR | Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| GLUT 5 | Glucose transporter 5 |
| LR | Lactated Ringers |
| L | liters |
| mL | milliliters |
| mmol/L | millimoles per liter |
| mOsm/kg | Milliosmoles per kilogram |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| ONS | Oral Nutrition Supplements |
| ORS | Oral Rehydration Solutions |
| pmol/L | picomoles per liter |
| POMS | Profile of Mood States |
| SGLT1 | Sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 |
| SLIM | Satiety Labeled Intensity Magnitude |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Ferreira-Pêgo, C.; Guelinckx, I.; Moreno, L.A.; Kavouras, S.A.; Gandy, J.; Martinez, H.; Bardosono, S.; Abdollahi, M.; Nasseri, E.; Jarosz, A.; et al. Total Fluid Intake and Its Determinants: Cross-Sectional Surveys among Adults in 13 Countries Worldwide. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.; Muñoz, C.; Armstrong, E. Distinguishing Low and High Water Consumers—A Paradigm of Disease Risk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnowski, A.; Rehm, C.D.; Constant, F. Water and Beverage Consumption among Adults in the United States: Cross-Sectional Study Using. Data from NHANES 2005–2010. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, E.; Hooper, L.; Fynn, J.; Wilsher, S.H.; Oladosu, T.; Poland, F.; Roberts, S.; Van Hout, E.; Bunn, D. Low-Intake Dehydration Prevalence in Non-Hospitalised Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, J.; Corbett, J.; Forni, L.; Hooper, L.; Hughes, F.; Minto, G.; Moss, C.; Price, S.; Whyte, G.; Woodcock, T.; et al. A Multidisciplinary Consensus on Dehydration: Definitions, Diagnostic Methods and Clinical Implications. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, C.J.; Foglia, E.; Booth, P.; Fu, C.H.Y.; Gardner, M. Dehydration in Older People: A Systematic Review of the Effects of Dehydration on Health Outcomes, Healthcare Costs and Cognitive Performance. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 95, 104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, A.M.; Sahota, O.; Lobo, D.N. Acute and Chronic Effects of Hydration Status on Health. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangeskou, M.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B.; Serra-Majem, L. Dehydration in the Elderly: A Review Focused on Economic Burden. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Barber, J.; Campbell, E.S. Economic Burden of Dehydration among Hospitalized Elderly Patients. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2004, 61, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, M.; Umegaki, H.; Komiya, H.; Fujisawa, C.; Watanabe, K.; Yamada, Y.; Miyahara, S. Dehydration and Hospital-Associated Disability in Acute Hospitalized Older Adults. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 14, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Abdelhamid, A.; Ajabnoor, S.M.; Esio-Bassey, C.; Brainard, J.; Brown, T.J.; Bunn, D.; Foster, E.; Hammer, C.C.; Hanson, S.; et al. Effects of Fluid and Drinking on Pneumonia Mortality in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jéquier, E.; Constant, F. Water as an Essential Nutrient: The Physiological Basis of Hydration. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ayers, E.; Patel, P.; Mattoo, T.K. Body Water Percentage from Childhood to Old Age. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 42, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liska, D.; Mah, E.; Brisbois, T.; Barrios, P.L.; Baker, L.B.; Spriet, L.L. Narrative Review of Hydration and Selected Health Outcomes in the General Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, I.; Serra-Prat, M.; Yébenes, J.C. The Role of Water Homeostasis in Muscle Function and Frailty: A Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanovic, K.; Skjøde Damsgaard, E.M.; Gregersen, M. Preoperative Dehydration Identified by Serum Calculated Osmolarity Is Associated with Severe Frailty in Patients with Hip Fracture. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 52, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, C.; Collier, A.; Holyday, M.; Lambert, K. Interventions to Improve Hydration in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, M.; Angez, M.; Musavi, N.B.; Rehman, S.T.; Kataria, D.; Farhan, R.; Jamshed, N. How Dietary Habits and Nutritional Deficiencies Relate to Hyponatremia in Older Adults. J. Ageing Longev. 2024, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, N.I.; Boehm, M.; Yancey, P.H.; Enhörning, S. Long-Term Health Outcomes Associated with Hydration Status. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, E.T.; Armstrong, L.E.; Bottin, J.H.; Clark, W.F.; Dolci, A.; Guelinckx, I.; Iroz, A.; Kavouras, S.A.; Lang, F.; Lieberman, H.R.; et al. Hydration for Health Hypothesis: A Narrative Review of Supporting Evidence. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriola, M.; Mangiacotti, A.; D’Onofrio, G.; Cascavilla, L.; Paris, F.; Paroni, G.; Seripa, D.; Greco, A.; Sancarlo, D. Neurocognitive Disorders and Dehydration in Older Patients: Clinical Experience Supports the Hydromolecular Hypothesis of Dementia. Nutrients 2018, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, O.M.; Li, C.R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Central Nervous System Regulation of Eating: Insights from Human Brain Imaging. Metabolism 2016, 65, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Heart Association. Are You Drinking Enough Water During Winter Months? Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/12/19/are-you-drinking-enough-water-during-winter-months (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Dmitrieva, N.I.; Burg, M.B. Increased Insensible Water Loss Contributes to Aging Related Dehydration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebl, S.K.; Davy, B.M. The Hydration Equation: Update on Water Balance and Cognitive Performance. ACSMs Health Fit. J. 2013, 17, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondon-Berrios, H.; Berl, T. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Water Homeostasis. In Frontiers of Hormone Research; Peri, A., Thompson, C.J., Verbalis, J.G., Eds.; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 52, pp. 8–23. ISBN 978-3-318-06382-0. [Google Scholar]
- Noronha, I.L.; Santa-Catharina, G.P.; Andrade, L.; Coelho, V.A.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Elias, R.M. Glomerular Filtration in the Aging Population. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 769329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajah, J.R.; Verkman, A.S. Water Transport in the Gastrointestinal Tract. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, 6th ed.; Said, H.M., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1249–1272. ISBN 978-0-12-809954-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hoen, L.; Pfeffer, D.; Zapf, R.; Raabe, A.; Hildebrand, J.; Kraft, J.; Kalkhof, S. Association of Drug Application and Hydration Status in Elderly Patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.M.; Tolos, C. Empowering Fall Prevention Through Integrated Lifestyle Medicine Strategies—From Recognition of Fall Risks to Implementation of Prevention of Falls for All in Practice. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2025, 15598276251316830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, I.; Norton, D.; Birstler, J.; Chen, G.; Cruz, L.; Hanrahan, L. Association Between Dehydration and Falls. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 4, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.D.; Akerman, A.P.; Notley, S.R.; McGinn, R.; Poirier, P.; Gosselin, P.; Kenny, G.P. Physiological Factors Characterizing Heat-Vulnerable Older Adults: A Narrative Review. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; D’Anci, K.E.; Rosenberg, I.H. Water, Hydration, and Health. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.B. Physiology of Sweat Gland Function: The Roles of Sweating and Sweat Composition in Human Health. Temperature 2019, 6, 211–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millyard, A.; Layden, J.D.; Pyne, D.B.; Edwards, A.M.; Bloxham, S.R. Impairments to Thermoregulation in the Elderly During Heat Exposure Events. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 6, 2333721420932432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmain, B.N.; Sabapathy, S.; Louis, M.; Morris, N.R. Aging and Thermoregulatory Control: The Clinical Implications of Exercising under Heat Stress in Older Individuals. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8306154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.L. Role of Whole Foods in Promoting Hydration after Exercise in Humans. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 592S–596S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, N.; Galloway, S.D.R. A Randomised Trial to Assess Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Responses Following Ingestion of Different Beverages in Young and Older Men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 123, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.M.; Stanhewicz, A.E.; Wolf, S.T.; Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W.; Kenney, W.L. A Randomized Trial to Assess Beverage Hydration Index in Healthy Older Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, S.G. Nutrition Essentials for Nursing Practice, 7th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4511-8612-3. [Google Scholar]
- How to Stay Hydrated for Better Health. Available online: https://www.ncoa.org/article/how-to-stay-hydrated-for-better-health/ (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Li, S.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X. Hydration Status in Older Adults: Current Knowledge and Future Challenges. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, J.B. Fate of Ingested Fluids: Factors Affecting Gastric Emptying and Intestinal Absorption of Beverages in Humans. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73 (Suppl. S2), 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossingham, M.J.; Carnell, N.S.; Campbell, W.W. Water Balance, Hydration Status, and Fat-Free Mass Hydration in Younger and Older Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péronnet, F.; Mignault, D.; Du Souich, P.; Vergne, S.; Le Bellego, L.; Jimenez, L.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Absorption, Distribution and Disappearance of Ingested Water Labeled with D2O in Humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémond, D.; Shahar, D.R.; Gille, D.; Pinto, P.; Kachal, J.; Peyron, M.-A.; Dos Santos, C.N.; Walther, B.; Bordoni, A.; Dupont, D.; et al. Understanding the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Elderly to Develop Dietary Solutions That Prevent Malnutrition. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13858–13898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.; Kerndt, C.C.; Moore, R.A. Physiology, Baroreceptors. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chapleau, M.W. Baroreceptor Reflexes. In Primer on the Autonomic Nervous System; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 161–165. ISBN 978-0-12-386525-0. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, L.E. Assessing Hydration Status: The Elusive Gold Standard. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 575S–584S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, G.; Goswami, N.; Reichmuth, J.; De Santo, N.G.; Valenti, G. Aquaporins, Vasopressin, and Aging: Current Perspectives. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R. Rehydration Strategies–Balancing Substrate, Fluid, and Electrolyte Provision. Int. J. Sports Med. 1998, 19 (Suppl. S2), S133–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Torres, O.; Rodríguez-Longobardo, C.; Escribano-Tabernero, R.; Fernández-Elías, V.E. Hydration, Hyperthermia, Glycogen, and Recovery: Crucial Factors in Exercise Performance-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convertino, V.A.; Armstrong, L.E.; Coyle, E.F.; Mack, G.W.; Sawka, M.N.; Senay, L.C.; Sherman, W.M. ACSM Position Stand: Exercise and Fluid Replacement. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, i–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, M. Strategies for Ensuring Good Hydration in the Elderly. Nutr. Rev. 2005, 63, S22–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Science of Hydration: How Water Impacts the Body. Available online: https://www.physiology.org/publications/news/the-physiologist-magazine/2021/july/the-science-of-hydration (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Bech, C.B.; Svendsen, J.A.; Knudsen, A.W.; Munk, T.; Beck, A.M. The Association between Malnutrition and Dehydration in Older Adults Admitted to a Geriatric Unit: An Observational Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuendorff, N.R.; Wirth, R.; Stoev, K.; Schnepper, M.; Levermann, I.; Wang, B.; Giehl, C.; Trampisch, U.S.; Funk, L.; Pourhassan, M. Dehydration and Malnutrition—Similar Yet Different: Data from a Prospective Observational Study in Older Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furoscix: Dosing, Contraindications, Side Effects, and Pill Pictures—Epocrates Online. Available online: https://www.epocrates.com/online/contextuallink/drugs/11020#safety-monitoring (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Ernstmeyer, K.; Christman, E. Chapter 6 Cardiovascular & Renal Systems. In Nursing Pharmacology [Internet], 2nd ed.; Chippewa Valley Technical College: Eau Claire, WI, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Protecting Older Adults from the Effects of Natural Disasters and Extreme Weather. Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/protecting-older-adults-effects-natural-disasters-and-extreme-weather (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Layton, J.B.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.; Gilman, J.P.; Horton, D.B.; Setoguchi, S. Heatwaves, Medications, and Heat-Related Hospitalization in Older Medicare Beneficiaries with Chronic Conditions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.M.; Lopez-Oliva, S.; Trives, C.; Partearroyo, T.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Effects of Drugs and Excipients on Hydration Status. Nutrients 2019, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schols, J.M.G.A.; De Groot, C.P.G.M.; Van Der Cammen, T.J.M.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.M. Preventing and Treating Dehydration in the Elderly during Periods of Illness and Warm Weather. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watso, J.C.; Farquhar, W.B. Hydration Status and Cardiovascular Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briongos Figuero, S.; Jiménez-Mena, M.; Ortega Marcos, J.; Camino López, A.; Fernández Santos, S.; De La Cal Segura, T.; Cortés, M.; Sanmartín Fernández, M.; Zamorano Gómez, J.L. Dehydration and Serum Hyperosmolarity as New Predictors of Mortality after Acute Coronary Syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 172, e472–e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.; Hunt, B.J.; Lewis, R.R.; Swaminathan, R.; Moody, A.; Seed, P.T.; Rudd, A. Dehydration and Venous Thromboembolism after Acute Stroke. QJM Int. J. Med. 2004, 97, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittczak, A.; Ślot, M.; Bielecka-Dabrowa, A. The Importance of Optimal Hydration in Patients with Heart Failure—Not Always Too Much Fluid. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Guelinckx, I.; Lemetais, G.; Melander, O. Two Liters a Day Keep the Doctor Away? Considerations on the Pathophysiology of Suboptimal Fluid Intake in the Common Population. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, M.; Marchese-Ragona, R.; Masiero, S.; Restivo, D.A. Dysphagia in Neurological Diseases: A Literature Review. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3067–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amella, E.J. Feeding and Hydration Issues for Older Adults with Dementia. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 39, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, R.; Duraisamy, R.; Kumar, M.P.S. Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Drug Invent. Today 2019, 12, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, B.; Britton, M.E. Hypoglycaemia in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Risk Factors, Consequences and Prevention. Pharm. Pract. Res. 2015, 45, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagalingam, S.; Kulinski, A.E.; Thorsteinsdottir, B.; Shindelar, K.L.; Takahashi, P.Y. Dysphagia in Older Adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smukalla, S.M.; Dimitrova, I.; Feintuch, J.M.; Khan, A. Dysphagia in the Elderly. Curr. Treat. Options Gastro 2017, 15, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, C.P.; Goode, P.S.; Burgio, K.L.; Markland, A.D. Urinary Incontinence in Older Adults. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2011, 78, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, T.T.; Campbell, J.M.; Jones, J.A. Fluid Intake and Urinary Incontinence in Older Community-Dwelling Women. J. Community Health Nurs. 1996, 13, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, D.; Jimoh, F.; Wilsher, S.H.; Hooper, L. Increasing Fluid Intake and Reducing Dehydration Risk in Older People Living in Long-Term Care: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsey, A.R.; McElhaney, J.E. Influenza Burden in Frail Elderly. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeny, O.; Solomon, S.D. Influenza and Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, N.G.; Delles, C.; D’Haese, P.; Layton, A.T.; Martínez-Salgado, C.; Vervaet, B.A.; López-Hernández, F.J. Haemodynamic Frailty—A Risk Factor for Acute Kidney Injury in the Elderly. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncal-Jimenez, C.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Jensen, T.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Johnson, R.J. Mechanisms by Which Dehydration May Lead to Chronic Kidney Disease. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, C.G.; Oreopoulos, D.G. Renal Changes in the Elderly. In Cardiothoracic Surgery in the Elderly; Katlic, M.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 293–299. ISBN 978-1-4419-0891-9. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes Insipidus—NIDDK. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/diabetes-insipidus (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Osilla, E.V.; Marsidi, J.L.; Shumway, K.R.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Temperature Regulation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hutton, A.; Maud, K.; Giggins, H.; Skipp, M.; Verdon-Kidd, D. Are We Adequately Promoting Climate Change Adaptation to Address the Increasing Heatwaves Affecting the Elderly? Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2025, 16, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-H.; Park, M.-S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y.-C. Effects of Cold and Hot Temperature on Dehydration: A Mechanism of Cardiovascular Burden. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, E.A.; Johnson, C.D. Recent Advances in Thermoregulation. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2015, 39, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Fernie, G.; Roshan Fekr, A. Fluid Intake Monitoring Systems for the Elderly: A Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.; Tripathi, A.K. Adult Dehydration. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Alsanie, S.; Lim, S.; Wootton, S.A. Detecting Low-Intake Dehydration Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Older Adults in Acute Care Settings: A Systematic Review. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frith, J. New Horizons in the Diagnosis and Management of Dehydration. Age Ageing 2023, 52, afad193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, B.R.; Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W.; Sawka, M.N. Limitations of Salivary Osmolality as a Marker of Hydration Status. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, M.B.; Owen, J.A.; Raymond-Barker, P.; Bishop, C.; Elghenzai, S.; Oliver, S.J.; Walsh, N.P. Is This Elderly Patient Dehydrated? Diagnostic Accuracy of Hydration Assessment Using Physical Signs, Urine, and Saliva Markers. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.M.; Seemer, J.; Knudsen, A.W.; Munk, T. Narrative Review of Low-Intake Dehydration in Older Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Dimassi, S.; Gautier, J.; Zalc, V.; Boudaoud, S.; Istrate, D. Body Water Volume Estimation Using Bio Impedance Analysis: Where Are We? IRBM 2024, 45, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, I.M.; Milos, R.; Cortinovis, I.; Laquintana, D.; Bonetti, L. Sensitivity and Specificity of the New Geriatric Dehydration Screening Tool: An Observational Diagnostic Study. Nutrition 2022, 101, 111695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Watson, P.; Cordery, P.A.; Walsh, N.P.; Oliver, S.J.; Dolci, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, N.; Galloway, S.D. A Randomized Trial to Assess the Potential of Different Beverages to Affect Hydration Status: Development of a Beverage Hydration Index1. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hew-Butler, T.D.; Eskin, C.; Bickham, J.; Rusnak, M.; VanderMeulen, M. Dehydration Is How You Define It: Comparison of 318 Blood and Urine Athlete Spot Checks. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2018, 4, e000297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Abdelhamid, A.; Attreed, N.J.; Campbell, W.W.; Channell, A.M.; Chassagne, P.; Culp, K.R.; Fletcher, S.J.; Fortes, M.B.; Fuller, N.; et al. Clinical Symptoms, Signs and Tests for Identification of Impending and Current Water-Loss Dehydration in Older People. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD009647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, N.I.; Gagarin, A.; Liu, D.; Wu, C.O.; Boehm, M. Middle-Age High Normal Serum Sodium as a Risk Factor for Accelerated Biological Aging, Chronic Diseases, and Premature Mortality. eBioMedicine 2023, 87, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atjo, N.M.; Soraya, G.V.; Natzir, R.; Kasyim, H.; Rasyid, H.; Chana, G.; Erlichster, M.; Skafidas, E.; Hardjo, M. Point-of-Care Saliva Osmolarity Testing for the Screening of Hydration in Older Adults with Hypertension. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, e1984.e9–e1984.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; Willshire, C. Tear Osmolarity in the Diagnosis of Systemic Dehydration and Dry Eye Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Bunn, D.; Jimoh, F.O.; Fairweather-Tait, S.J. Water-Loss Dehydration and Aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.; Sobotka, L.; et al. ESPEN Practical Guideline: Clinical Nutrition and Hydration in Geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 958–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, G.; Botero-Rodríguez, F.; Misas, J.D.; Garcia-Cifuentes, E.; Sulo, S.; Brunton, C.; Venegas-Sanabria, L.C.; Gracia, D.A.; Cano Gutierrez, C.A. A Nutritionally Focused Program for Community-Living Older Adults Resulted in Improved Health and Well-Being. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Velasco, R.; John, S.; Kaufman, R.S.; Melzer, E. An Innovative Approach to Adequate Oral Hydration in an Inpatient Geriatric Psychiatry Unit. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2019, 57, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.R.; Pritchard, M.W.; Evans, D.J.; Butler, A.R.; Alderson, P.; Smith, A.F.; Roberts, I. Colloids versus Crystalloids for Fluid Resuscitation in Critically III People. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD000567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, R.W. The Maintenance Need for Water in Parenteral Fluid Therapy, by Malcolm A. Holliday, MD, and William E. Segar, MD, Pediatrics, 1957;19:823–832. Pediatrics 1998, 102, 229–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, L.M. Fluid Needs in the Older Adult Receiving Tube Feedings. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, S.F.; Alessi, C.; Schnelle, J.F. An Intervention to Increase Fluid Intake in Nursing Home Residents: Prompting and Preference Compliance. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Bak, A.; Tingle, A.; Greene, C.; Tsiami, A.; Canning, D.; Myron, R.; Loveday, H. Improving Hydration of Care Home Residents by Increasing Choice and Opportunity to Drink: A Quality Improvement Study. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, A.M.; Watson, P.; Neal, K.R.; Ljungqvist, O.; Maughan, R.J.; Sahota, O.; Lobo, D.N. Hydration and Outcome in Older Patients Admitted to Hospital (The HOOP Prospective Cohort Study). Age Ageing 2015, 44, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, A.M.; Sahota, O.; Maughan, R.J.; Lobo, D.N. The Pathophysiology of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance in the Older Adult Surgical Patient. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, M.J.; Chivers, L.; Karagiannis, T.C. Effects of Oral Intake of Water in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. BMC Geriatr. 2011, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Miller, M.; Doeltgen, S.; Scholten, I. Intake of Thickened Liquids by Hospitalized Adults with Dysphagia after Stroke. Int. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2014, 16, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-309-09169-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sollanek, K.J.; Kenefick, R.W.; Cheuvront, S.N. Osmolality of Commercially Available Oral Rehydration Solutions: Impact of Brand, Storage Time, and Temperature. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera Marcolin, L.; Cuñé Castellana, J.; Martí Melero, L.; de Lecea, C.; Tintoré Gazulla, M. Synergistic Effect of Postbiotic Yeast ABB C22® on Gut Inflammation, Barrier Function, and Protection from Rotavirus Infection in In Vitro Models. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, M.R.; Borhade, M.B. Fluid Management. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- IV Fluids (Intravenous Fluids): Types & Uses. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/21635-iv-fluids (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Omid Manoochehri, M.D.; Sean, M.; Hickey, M.D. Critical Care Alert: Crystalloids vs. Colloids for Fluid Resuscitation in the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Available online: https://www.emra.org/emresident/article/critcare-alert-crystalloids-vs-colloids (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- CDC. Older Adults: Adding Activity Recommendations. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/physical-activity-basics/adding-older-adults/index.html (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Department of Health and Human Services. Heat Stress Hydration; Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Armstrong, L.E. Rehydration during Endurance Exercise: Challenges, Research, Options, Methods. Nutrients 2021, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Shirreffs, S.M.; Watson, P. Exercise, Heat, Hydration and the Brain. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 604S–612S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S. Hydrate to Stay Active—International Council on Active Aging®. Available online: https://www.icaa.cc/blog/2019-10/Hydrate-to-stay-active.htm (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- Mentes, J.C.; DeVost, M.A.; Nandy, K. Salivary Osmolality, Function, and Hydration Habits in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. SAGE Open Nurs. 2019, 5, 2377960819826253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.B.; Phillips, M.D.; Mercer, S.P.; Baylies, H.L.; Pizza, F.X. Postexercise Rehydration: Effect of Na+ and Volume on Restoration of Fluid Spaces and Cardiovascular Function. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawka, M.N.; Eichner, E.R.; Maughan, R.J.; Montain, S.J.; Stachenfeld, N.S. Exercise and Fluid Replacement. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staying Hydrated, Staying Healthy. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/fitness/fitness-basics/staying-hydrated-staying-healthy (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Pence, J.; Bloomer, R.J. Impact of Nuun Electrolyte Tablets on Fluid Balance in Active Men and Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, R.J.; Pence, J.; Hellenbrand, J.; Davis, A.; Davis, S.; Stockton, M.; Martin, K.R. Randomized Trial to Assess the Safety and Tolerability of Daily Intake of an Allulose Amino Acid-Based Hydration Beverage in Men and Women. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizel, R.; Coqueiro, A.Y.; Bonvini, A.; Tirapegui, J. 1—Sports and Energy Drinks: Aspects to Consider. In Sports and Energy Drinks; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 1–37. ISBN 978-0-12-815851-7. [Google Scholar]
- Millard-Stafford, M.; Snow, T.K.; Jones, M.L.; Suh, H. The Beverage Hydration Index: Influence of Electrolytes, Carbohydrate and Protein. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, M.C.; Ruple, B.A.; Kontos, N.J.; Mattingly, M.L.; Lockwood, C.M.; Roberts, M.D. The Effects of a Sugar-Free Amino Acid-Containing Electrolyte Beverage on 5-Kilometer Performance, Blood Electrolytes, and Post-Exercise Cramping versus a Conventional Carbohydrate-Electrolyte Sports Beverage and Water. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2024, 21, 2296888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gou, Y.; Tsuzuki, T.; Yamada, T.; Iida, T.; Wang, S.; Banno, R.; Toyoda, Y.; Koike, T. D-Allulose Improves Endurance and Recovery from Exhaustion in Male C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayabyab, K.B.; Shin, M.J.; Heimuli, M.S.; Kim, I.J.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Johnson, R.J.; Koutnik, A.P.; Bellissimo, N.; Diamond, D.M.; Norwitz, N.G.; et al. The Metabolic and Endocrine Effects of a 12-Week Allulose-Rich Diet. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaoikonomou, G.; Apergi, K.; Malisova, O. Children, Adolescents and Urine Hydration Indices—A Systematic Literature Review on Athletes and Non-Athletes. Children 2025, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.; Kavouras, S.A. Water Intake and Hydration State in Children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, R.; Ozols, A.; Nadeau, W.J.; Braid-Forbes, M.J. Hospital Inpatient Admissions with Dehydration and/or Malnutrition in Medicare Beneficiaries Receiving Enteral Nutrition: A Cohort Study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masot, O.; Lavedán, A.; Nuin, C.; Escobar-Bravo, M.A.; Miranda, J.; Botigué, T. Risk Factors Associated with Dehydration in Older People Living in Nursing Homes: Scoping Review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2018, 82, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, A.; Gouws, C.; Breukelman, G. Effects of Hypohydration and Fluid Balance in Athletes’ Cognitive Performance: A Systematic Review. Afr. Health Sci. 2022, 22, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccio, R.P.; Barnes, K.A.; Carter, J.M.; Baker, L.B. Fluid Balance in Team Sport Athletes and the Effect of Hypohydration on Cognitive, Technical, and Physical Performance. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1951–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenefick, R.W.; Sawka, M.N. Hydration at the Work Site. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 597S–603S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luippold, A.J.; Charkoudian, N.; Kenefick, R.W.; Montain, S.J.; Lee, J.K.W.; Teo, Y.S.; Cheuvront, S.N. Update: Efficacy of Military Fluid Intake Guidance. Mil. Med. 2018, 183, e338–e342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.; Pope, R.; Orr, R.M. The Impact of Fire Suppression Tasks on Firefighter Hydration: A Critical Review with Consideration of the Utility of Reported Hydration Measures. Ann. Occup. Env. Med. 2016, 28, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périard, J.D.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Daanen, H.A.M. Exercise under Heat Stress: Thermoregulation, Hydration, Performance Implications, and Mitigation Strategies. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1873–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenefick, R.W.; Cheuvront, S.N. Hydration for Recreational Sport and Physical Activity. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, S137–S142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Périard, J.D.; DeGroot, D.; Jay, O. Exertional Heat Stroke in Sport and the Military: Epidemiology and Mitigation. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 107, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miescher, E.; Fortney, S.M. Responses to Dehydration and Rehydration during Heat Exposure in Young and Older Men. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1989, 257, R1050–R1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, G.W.; Weseman, C.A.; Langhans, G.W.; Scherzer, H.; Gillen, C.M.; Nadel, E.R. Body Fluid Balance in Dehydrated Healthy Older Men: Thirst and Renal Osmoregulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 76, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, O.; Morris, N.; Epstein, Y.; Gass, G. Comparison of Thermoregulatory Responses to Exercise in Dry Heat among Prepubertal Boys, Young Adults and Older Males. Exp. Physiol. 2004, 89, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masento, N.A.; Golightly, M.; Field, D.T.; Butler, L.T.; van Reekum, C.M. Effects of Hydration Status on Cognitive Performance and Mood. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, H.R. Hydration and Cognition: A Critical Review and Recommendations for Future Research. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 555S–561S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.J.; Campos, M.J.; Rosado, F.; Rama, L.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Martinho, D.; Teixeira, A.; Massart, A. Analysis of Hydration Habits Before and During a Specific Training Session in Male Padel Athletes Aged over 65: Physiological and Psychological Implications. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.B.; Munce, T.A.; Kenney, W.L. Sex Differences in Voluntary Fluid Intake by Older Adults during Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belval, L.N.; Hosokawa, Y.; Casa, D.J.; Adams, W.M.; Armstrong, L.E.; Baker, L.B.; Burke, L.; Cheuvront, S.; Chiampas, G.; González-Alonso, J.; et al. Practical Hydration Solutions for Sports. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.T.; Stanhewicz, A.E.; Clarke, M.M.; Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W.; Kenney, W.L. Age-Related Differences in Water and Sodium Handling after Commercial Hydration Beverage Ingestion. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, J.D.; Kavouras, S.A.; Suh, H.; Lang, F. Underhydration Is Associated with Obesity, Chronic Diseases, and Death Within 3 to 6 Years in the U.S. Population Aged 51–70 Years. Nutrients 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantantzis, K.; Drewelies, J.; Duezel, S.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Demuth, I.; Wagner, G.G.; Lindenberger, U.; Gerstorf, D. Dehydration Predicts Longitudinal Decline in Cognitive Functioning and Well-Being among Older Adults. Psychol. Aging 2020, 35, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Comorbidity | Pathway to Dehydration | Study |
|---|---|---|
| Acute coronary syndrome | Hyperosmolality leads to increased risk of renal injury, cerebral ischemic events, and increased cardiovascular mortality | [5,64,65] |
| Arterial/Venous thrombosis | Increased blood viscosity and hematocrit | [5,11,66] |
| Cardiovascular disease | Fluid buildup leading to fluid restriction | [24,67,68] |
| Dementia | Impaired memory | [21,69,70] |
| Lack of proper care or support | ||
| Impaired ability to detect hunger and thirst | ||
| Dysphagia | ||
| Diabetes | Increased thirst | [29,71,72] |
| Increased urine output | ||
| Dysphagia | Difficulty swallowing | [42,73,74] |
| Incontinence | Fluid restriction to control frequency | [75,76,77] |
| Influenza | Diarrhea | [63,78,79] |
| Vomiting | ||
| Fever | ||
| Increased sweating | ||
| Kidney disease | Increased fluid loss due to urine output | [80,81,82] |
| Measure | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) | Estimates body water Not accurate in disease population | [90,94,99] |
| Blood Properties | ||
| BUN/Creatinine Ratio | >20 non-specific, but may indicate isotonic dehydration | [93] |
| Plasma Copeptin | >6.79 pmol/L or >10.6 pmol/L for men and >6.5 pmol/L for women | [19,20] |
| Plasma Osmolality | >300 mOsm/kg | [42] |
| Serum Osmolality | >295 mOsm/kg, not accurate for isotonic | [5,10,42,49,89] |
| Serum Sodium | >142 or >144 mmol/L | [19,100] |
| Cardiovascular | ||
| Heart Rate | >90–100 beats per minute, not sensitive in older adults | [5,93] |
| Systolic Blood Pressure | <100 mmHg | [5,93] |
| Peripheral Venous Filling | Non-invasive clinical indicator | [93] |
| Geriatric Dehydration Screening Tool (GDST) | Utilizes a combination of clinical examination and hydration questions for patient | [96] |
| Eyes | Non-invasive clinical indicator Appear sunken | [93] |
| Mass | ||
| Body Water loss | ≥2% | [20,89] |
| Total Body Mass | ≥3% | [99] |
| Mucosal Dryness | Non-invasive clinical indicator | [93] |
| Saliva | ||
| Osmolality | >93 mOsm/kg or | [91,92,93,101] |
| >94–97 mOsm/kg in Emergency Department | ||
| Flowrate | Poor indicator | [93] |
| Skin Turgor | Non-invasive clinical indicator | [93] |
| Tears | ||
| Osmolality | Not accurate measure, may require waiting a period with eyelids closed | [99,102] |
| Volume | Not accurate measure | [99] |
| Thirst | Poor indicator in older adults | [8,12,50] |
| Tracers | Includes D2O, used mainly in research to determine hydration rates | [5,42,45] |
| Urine | ||
| Color | (dark yellow), >6 on 8-point scale, simplistic, but unreliable | [20,49] |
| Frequency | Not accurate | [99] |
| Specific Gravity | 1.020 | [20,98] |
| Osmolality | 700 mOsm/kg | [20,98] |
| Volume | 0.5 L/24 h | [20,103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pence, J.; Davis, A.; Allen-Gregory, E.; Bloomer, R.J. Hydration Strategies in Older Adults. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142256
Pence J, Davis A, Allen-Gregory E, Bloomer RJ. Hydration Strategies in Older Adults. Nutrients. 2025; 17(14):2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142256
Chicago/Turabian StylePence, Jacquelyn, Allyson Davis, Ebonie Allen-Gregory, and Richard J. Bloomer. 2025. "Hydration Strategies in Older Adults" Nutrients 17, no. 14: 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142256
APA StylePence, J., Davis, A., Allen-Gregory, E., & Bloomer, R. J. (2025). Hydration Strategies in Older Adults. Nutrients, 17(14), 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142256





