l-Carnitine and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Fail to Improve Anaerobic and Aerobic Performance in Trained Cyclists Despite a Reduction in Blood Lactate Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
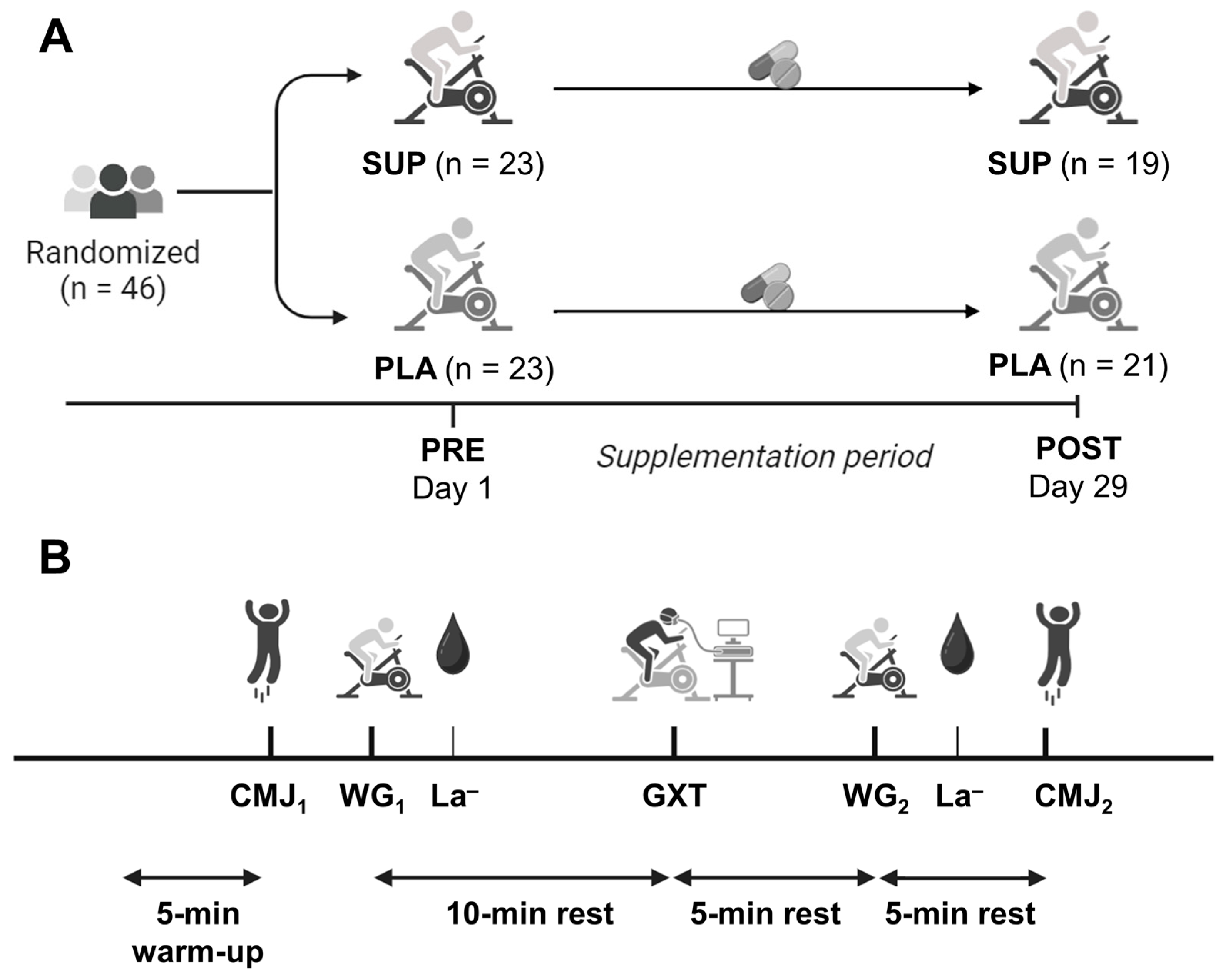
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
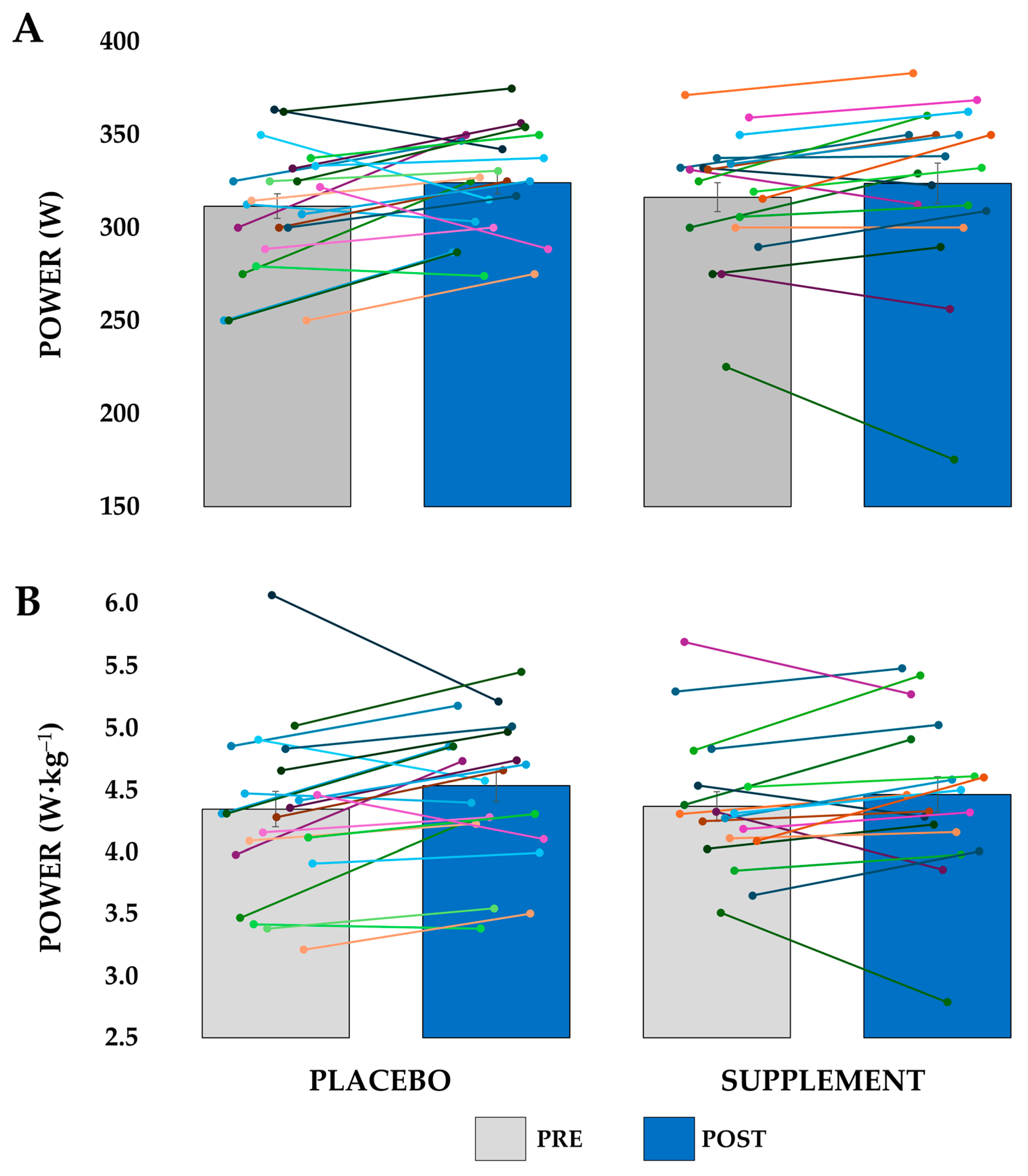
3.1. Anaerobic Performance
3.2. Aerobic Performance
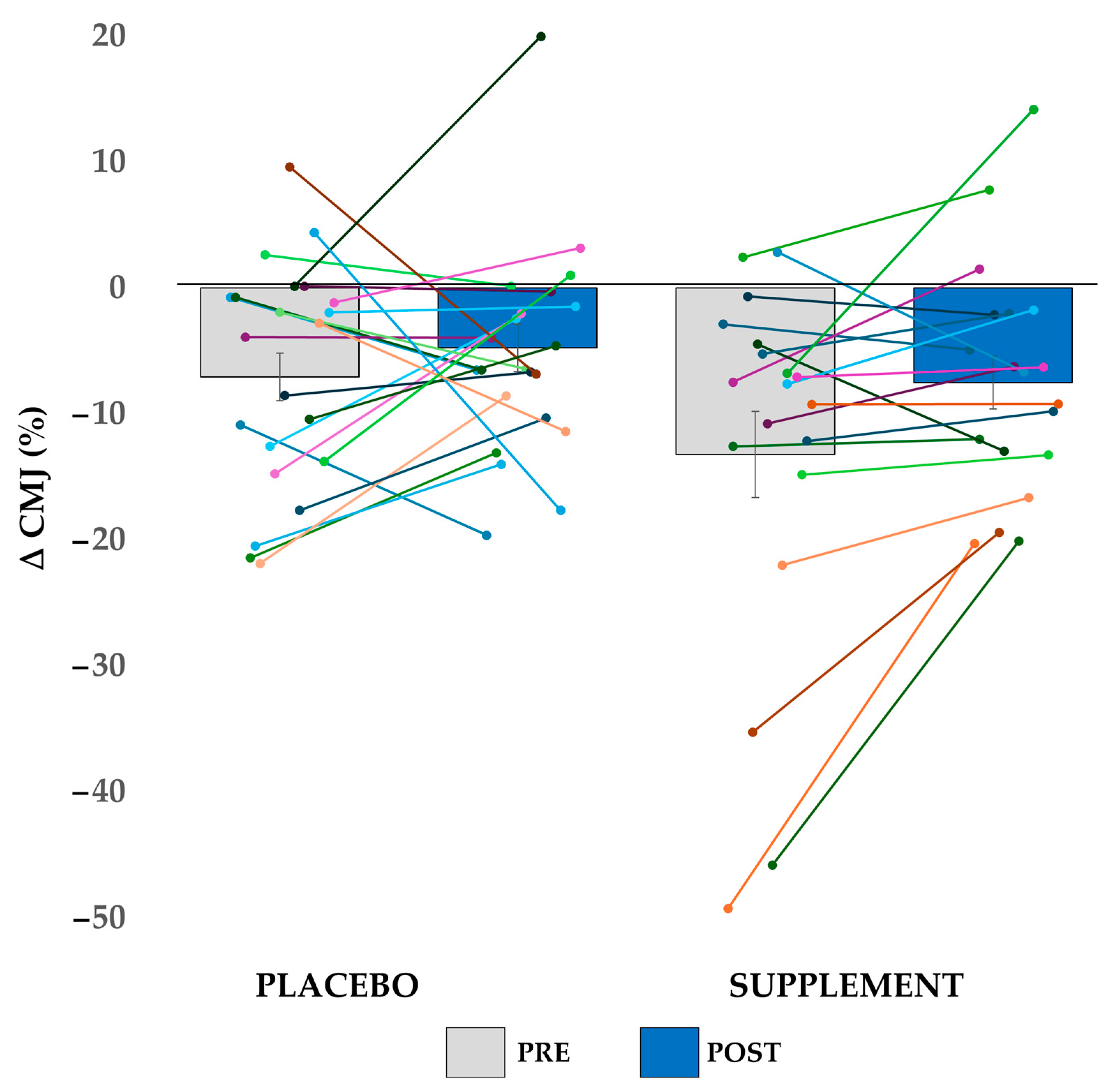
3.3. Performance Decline
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Group | Participant | PRE SESSION | POST SESSION | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wingate 1 | Wingate 2 | Wingate 1 | Wingate 2 | ||||||
| PMAX | PAVG | PMAX | PAVG | PMAX | PAVG | PMAX | PAVG | ||
| SUP | 1 | 1225 | 693 | 1244 | 620 | 1154 | 659 | 1162 | 572 |
| 4 | 1269 | 753 | 1391 | 784 | 1421 | 791 | 1479 | 792 | |
| 6 | 978 | 657 | 1105 | 656 | 1036 | 643 | 1113 | 629 | |
| 9 | 890 | 585 | 972 | 599 | 990 | 611 | 1025 | 600 | |
| 12 | 791 | 538 | 879 | 568 | 764 | 534 | 806 | 514 | |
| 15 | 873 | 648 | 997 | 653 | 802 | 581 | 947 | 586 | |
| 16 | 1443 | 831 | 1410 | 772 | 1425 | 843 | 1514 | 850 | |
| 17 | 971 | 620 | 1082 | 589 | 1014 | 591 | 1149 | 637 | |
| 19 | 1005 | 728 | 1067 | 719 | 1041 | 709 | 963 | 640 | |
| 24 | 848 | 536 | 966 | 533 | 885 | 556 | 1000 | 538 | |
| 30 | 1115 | 648 | 1241 | 643 | 1107 | 622 | 1251 | 620 | |
| 32 | 1255 | 737 | 1325 | 688 | 1221 | 758 | 1323 | 629 | |
| 33 | 1074 | 729 | 1102 | 645 | 1197 | 719 | 1184 | 696 | |
| 35 | 1262 | 781 | 1286 | 763 | 1391 | 837 | 1371 | 784 | |
| 38 | 1154 | 739 | 1228 | 739 | 1138 | 766 | 1142 | 735 | |
| 40 | 995 | 656 | 1048 | 581 | 1082 | 670 | 1086 | 637 | |
| 41 | 884 | 533 | 846 | 416 | 993 | 550 | 928 | 441 | |
| 43 | 1297 | 864 | 1242 | 739 | 1399 | 878 | 1375 | 737 | |
| 46 | 1099 | 697 | 1233 | 747 | 1136 | 706 | 1101 | 650 | |
| Mean ± SD | 1075 ± 182 | 683 ± 95 | 1140 ± 165 | 655 ± 95 | 1116 ± 196 | 685 ± 105 | 1154 ± 193 | 647 ± 101 | |
| PLA | 2 | 971 | 622 | 1017 | 615 | 954 | 597 | 1043 | 621 |
| 3 | 1047 | 618 | 1027 | 570 | 1100 | 617 | 1098 | 618 | |
| 5 | 1055 | 717 | 1138 | 658 | 1057 | 670 | 1102 | 598 | |
| 8 | 759 | 471 | 848 | 492 | 810 | 493 | 867 | 468 | |
| 10 | 1212 | 783 | 1346 | 823 | 1252 | 792 | 1241 | 790 | |
| 14 | 1025 | 662 | 1110 | 658 | 1069 | 687 | 1101 | 655 | |
| 18 | 976 | 625 | 1047 | 541 | 989 | 585 | 1039 | 528 | |
| 20 | 1172 | 695 | 1109 | 609 | 1159 | 686 | 1157 | 662 | |
| 21 | 1137 | 729 | 1186 | 715 | 1209 | 733 | 1144 | 698 | |
| 23 | 1197 | 690 | 1379 | 720 | 1283 | 701 | 1397 | 742 | |
| 26 | 1123 | 692 | 1136 | 681 | 1049 | 654 | 1198 | 678 | |
| 27 | 1317 | 867 | 1373 | 850 | 1292 | 881 | 1421 | 866 | |
| 28 | 1069 | 721 | 1209 | 615 | 1174 | 650 | 1173 | 633 | |
| 29 | 1058 | 656 | 1209 | 700 | 986 | 614 | 1185 | 660 | |
| 31 | 1027 | 640 | 1036 | 613 | 1000 | 628 | 1043 | 604 | |
| 34 | 1246 | 791 | 1164 | 618 | 1354 | 720 | 1094 | 594 | |
| 36 | 1337 | 815 | 1455 | 852 | 1375 | 838 | 1297 | 851 | |
| 37 | 1218 | 767 | 1233 | 752 | 1314 | 797 | 1264 | 760 | |
| 39 | 1525 | 954 | 1596 | 945 | 1578 | 939 | 1710 | 907 | |
| 42 | 1018 | 753 | 988 | 718 | 1024 | 727 | 1064 | 708 | |
| 44 | 778 | 489 | 802 | 526 | 779 | 481 | 827 | 513 | |
| 45 | 1015 | 662 | 954 | 604 | 1141 | 679 | 1127 | 595 | |
| Mean ± SD | 1104 ± 174 | 701 ± 110 | 1153 ± 193 | 676 ± 115 | 1134 ± 190 | 690 ± 113 | 1163 ± 186 | 670 ± 114 | |
References
- Lopez-Maldonado, A.; Pastoriza, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Assessing the Antioxidant and Metabolic Effect of an Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Acetyl-l-Carnitine Nutraceutical. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, R.; Riede, L.; Lugo, J.P.; Bellamine, A. l-Carnitine Supplementation in Recovery after Exercise. Nutrients 2018, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Pietrantonio, L.; Viribay, A.; Calleja-González, J.; González-Bernal, J.; Fernández-Lázaro, D. Effect of Acute and Chronic Oral l-Carnitine Supplementation on Exercise Performance Based on the Exercise Intensity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnoni, A.; Longo, S.; Gnoni, G.V.; Giudetti, A.M. Carnitine in Human Muscle Bioenergetics: Can Carnitine Supplementation Improve Physical Exercise? Molecules 2020, 25, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orer, G.E.; Guzel, N.A. The Effects of Acute l-Carnitine Supplementation on Endurance Performance of Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.L.; Goldstein, E.R.; Blackburn, W.; Orem, I.; Hughes, J.J. Glycine Propionyl-l-Carnitine Produces Enhanced Anaerobic Work Capacity with Reduced Lactate Accumulation in Resistance Trained Males. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2009, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koozehchian, M.S.; Daneshfar, A.; Fallah, E.; Agha-Alinejad, H.; Samadi, M.; Kaviani, M.; Kaveh, B.M.; Jung, Y.P.; Sablouei, M.H.; Moradi, N.; et al. Effects of Nine Weeks l-Carnitine Supplementation on Exercise Performance, Anaerobic Power, and Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress in Resistance-Trained Males. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 22, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, B.T.; Stephens, F.B.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Marimuthu, K.; Macdonald, I.A.; Greenhaff, P.L. Chronic Oral Ingestion of l-Carnitine and Carbohydrate Increases Muscle Carnitine Content and Alters Muscle Fuel Metabolism during Exercise in Humans. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Insights on the Use of α-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajdi, M.; Mahmoudi-Nezhad, M.; Farhangi, M.A. An Updated Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of the Randomized Controlled Trials on the Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid Supplementation on Inflammatory Biomarkers. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2021, 93, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembron-Lacny, A.; Slowinska-Lisowska, M.; Szygula, Z.; Witkowski, K.; Stefaniak, T.; Dziubek, W. Assessment of the Antioxidant Effectiveness of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Healthy Men Exposed to Muscle-Damaging Exercise. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zembron-Lacny, A.; Gajewski, M.; Naczk, M.; Dziewiecka, H.; Siatkowski, I. Physical Activity and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Modulate Inflammatory Response through Changes in Thiol Redox Status. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 69, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.A.; Trewin, A.J.; Parker, L.; Wadley, G.D. Antioxidant Supplements and Endurance Exercise: Current Evidence and Mechanistic Insights. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soczynska, J.K.; Kennedy, S.H.; Chow, C.S.M.; Woldeyohannes, H.O.; Konarski, J.Z.; McIntyre, R.S. Acetyl-l-Carnitine and α-Lipoic Acid: Possible Neurotherapeutic Agents for Mood Disorders? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, B.P.; Jensen, J.E.; Hudson, J.I.; Coit, C.E.; Beaulieu, A.; Pope, H.G.J.; Renshaw, P.F.; Cohen, B.M. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Acetyl-l-Carnitine and α-Lipoic Acid in the Treatment of Bipolar Depression. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 33, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinicola, S.; Fuso, A.; Cucina, A.; Santiago-Reyes, M.; Verna, R.; Unfer, V.; Monastra, G.; Bizzarri, M. Natural Products—Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Acetyl-l-Carnitine—in the Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4739–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantle, D.; Hargreaves, I.P. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Role of Nutritional Supplementation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, T.M.; Liu, J.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Wehr, C.M.; Ingersoll, R.T.; Vinarsky, V.; Bartholomew, J.C.; Ames, B.N. Feeding Acetyl-l-Carnitine and Lipoic Acid to Old Rats Significantly Improves Metabolic Function While Decreasing Oxidative Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Montoro, J.-A.; Mateo-March, M.; Sánchez-Muñoz, C.; Zabala, M. Determination of Second Lactate Threshold Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Elite Cyclists. Int. J. Sports Med. 2022, 43, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Ghasemi, R.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Stephens, F.B. Increasing Skeletal Muscle Carnitine Availability Does Not Alter the Adaptations to High-Intensity Interval Training. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.A.; Fry, A.C.; Tschume, L.C.; Bloomer, R.J. Effect of Glycine Propionyl-l-Carnitine on Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercise Performance. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2008, 18, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broad, E.M.; Maughan, R.J.; Galloway, S.D.R. Effects of Four Weeks l-Carnitine L-Tartrate Ingestion on Substrate Utilization during Prolonged Exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2005, 15, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, S.W.; Costill, D.L.; Goodpaster, B.; Vukovich, M.D.; Fink, W.J. The Effects of l-Carnitine Supplementation on Performance During Interval Swimming. Int. J. Sports Med. 1994, 15, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, C.; Costill, D.L.; Vukovich, M.D.; Cole, K.J.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Trappe, S.W.; Fink, W.J. Effect of l-Carnitine Supplementation on Muscle and Blood Carnitine Content and Lactate Accumulation during High-Intensity Sprint Cycling. Int. J. Sport Nutr. 1994, 4, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, F.B.; Evans, C.E.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Greenhaff, P.L. Carbohydrate Ingestion Augments l-Carnitine Retention in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Millán, I.; Brooks, G.A. Assessment of Metabolic Flexibility by Means of Measuring Blood Lactate, Fat, and Carbohydrate Oxidation Responses to Exercise in Professional Endurance Athletes and Less-Fit Individuals. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Cederblad, G.; Hultman, E. PDC Activity and Acetyl Group Accumulation in Skeletal Muscle during Prolonged Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Carlin, J.I.; Cederblad, G.; Harrist, R.C.; Hultman, E. Acetyl Group Accumulation and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Activity in Human Muscle during Incremental Exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1991, 143, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucía, A.; Hoyos, J.; Pardo, J.; Chicharro, J.L. Metabolic and Neuromuscular Adaptations to Endurance Training in Professional Cyclists: A Longitudinal Study. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2000, 50, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| All Participants | Supplement Group | Placebo Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y.o.) | 36 ± 12 | 38 ± 10 | 35 ± 13 |
| Body Mass (kg) | 72.9 ± 8.7 | 73.0 ± 8.0 | 72.8 ± 9.4 |
| Height (cm) | 177.6 ± 7.1 | 176.7 ± 8.3 | 178.5 ± 6.0 |
| Body Mass Index (kg·m−2) | 23.1 ± 2.6 | 23.4 ± 2.6 | 22.9 ± 2.6 |
| Average training volume (h/week) | 10.2 ± 3.7 | 9.0 ± 3.3 | 11.1 ± 3.9 |
| Maximal heart rate (bpm) | 185 ± 11 | 180 ± 12 | 188 ± 10 |
| Counter-movement Jump (cm) | 28.8 ± 5.4 | 28.9 ± 4.8 | 28.6 ± 6.0 |
| Peak Power (W) | 1090 ± 176 | 1075 ± 182 | 1104 ± 174 |
| Pear Power (W·kg−1) | 15.05 ± 2.41 | 14.75 ± 2.07 | 15.31 ± 2.69 |
| 30-s Average Power in Wingate (W) | 692 ± 102 | 683 ± 95 | 701 ± 110 |
| 30-s Average Power in Wingate (W·kg−1) | 9.56 ± 1.52 | 9.39 ± 1.20 | 7.73 ± 1.76 |
| Maximal Aerobic Power (W) | 314 ± 32 | 316 ± 34 | 311 ± 31 |
| Maximal Aerobic Power (W·kg−1) | 4.35 ± 0.60 | 4.36 ± 0.52 | 4.34 ± 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Rozas, A.; Pérez-Díaz, J.-J.; Muros, J.J.; Sánchez-Muñoz, C.; Rufían-Henares, J.-Á.; Zabala, M.; Salas-Montoro, J.-A. l-Carnitine and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Fail to Improve Anaerobic and Aerobic Performance in Trained Cyclists Despite a Reduction in Blood Lactate Concentration. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132227
de Rozas A, Pérez-Díaz J-J, Muros JJ, Sánchez-Muñoz C, Rufían-Henares J-Á, Zabala M, Salas-Montoro J-A. l-Carnitine and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Fail to Improve Anaerobic and Aerobic Performance in Trained Cyclists Despite a Reduction in Blood Lactate Concentration. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132227
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Rozas, Alejandro, Juan-José Pérez-Díaz, José Joaquín Muros, Cristóbal Sánchez-Muñoz, José-Ángel Rufían-Henares, Mikel Zabala, and José-Antonio Salas-Montoro. 2025. "l-Carnitine and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Fail to Improve Anaerobic and Aerobic Performance in Trained Cyclists Despite a Reduction in Blood Lactate Concentration" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132227
APA Stylede Rozas, A., Pérez-Díaz, J.-J., Muros, J. J., Sánchez-Muñoz, C., Rufían-Henares, J.-Á., Zabala, M., & Salas-Montoro, J.-A. (2025). l-Carnitine and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Fail to Improve Anaerobic and Aerobic Performance in Trained Cyclists Despite a Reduction in Blood Lactate Concentration. Nutrients, 17(13), 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132227








