Association of Parental Feeding Styles with Body Composition Among Children in Two Regions in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Questionnaire Data Collection
2.3. Anthropometric and Body Composition Measurements
2.4. Study Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Characteristics of Parental Feeding Practices and Body Composition
3.3. Multivariate Analysis Between Parental Feeding Practices and Body Composition
3.4. Analysis of Factors Influencing Children’s Body Composition
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| FMI | Fat mass index |
| FFMI | Fat free mass index |
| WHtR | Waist to height ratio |
| MN | Monitoring |
| PE | Pressure to eat |
| RST | Restriction |
| PCW | Perceived child weight |
| CN | Concern about child weight |
| PPW | Perceived parent weight |
| FR | Food as reward |
References
- Myette, R.L.; Flynn, J.T. The ongoing impact of obesity on childhood hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathirana, H.P.D.T.H.; Wijesekara, I.; Yalegama, L.L.W.C.; Garusinghe, C.; Jayasinghe, M.; Waidyarathne, K.P. Comparison of blood glucose responses by cane sugar (Saccharum officinarum) versus coconut jaggery (Cocos nucifera) in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Future Foods 2022, 2, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, N.R.F. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Initiatives, D. 2018 Global Nutrition Report: Shining a Light to Spur Action on Nutrition. Available online: https://globalnutritionreport.org/reports/global-nutrition-report-2018/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Horesh, A.; Tsur, A.M.; Bardugo, A.; Twig, G. Adolescent and childhood obesity and excess morbidity and mortality in young adulthood—A systematic review. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Du, Z.; Jiang, C.; Yang, C.; et al. Therapeutic effect of ketogenic diet treatment on type 2 diabetes. J. Future Foods 2022, 2, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, C.; Kautzky, A.; Watzal, V.; Gramser, A.; Kadriu, B.; Deng, Z.D.; Bartova, L.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Lanzenberger, R.; Souery, D.; et al. Body mass index and clinical outcomes in individuals with major depressive disorder: Findings from the GSRD European Multicenter Database. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 335, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brener, A.; Waksman, Y.; Rosenfeld, T.; Levy, S.; Peleg, I.; Raviv, A.; Interator, H.; Lebenthal, Y. The heritability of body composition. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, L.; Mathew, A.; Baldini, G.; Hosch, R.; Koitka, S.; Kleesiek, J.; Rischpler, C.; Haubold, J.; Fuhrer, D.; Nensa, F.; et al. CT-derived body composition analysis could possibly replace DXA and BIA to monitor NET-patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniccola, G.D.; Castro, M.G.; Piovacari, S.M.F.; Horie, L.M.; Correa, F.G.; Barrere, A.P.N.; Toledo, D.O. Current technologies in body composition assessment: Advantages and disadvantages. Nutrition 2019, 62, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Velez, R.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Sanders-Tordecilla, A.; Ojeda-Pardo, M.L.; Cobo-Mejia, E.A.; Castellanos-Vega, R.D.P.; Garcia-Hermoso, A.; Gonzalez-Jimenez, E.; Schmidt-RioValle, J.; Gonzalez-Ruiz, K. Percentage of body fat and fat mass index as a screening tool for metabolic syndrome prediction in Colombian university students. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, D.; Karssen, L.T.; Vink, J.M.; Burk, W.J.; Larsen, J.K. Food parenting practices and children’s weight outcomes: A systematic review of prospective studies. Appetite 2021, 158, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Warkentin, S.; Jansen, E.; Carnell, S. Acculturation, food-related and general parenting, and body weight in Chinese-American children. Appetite 2022, 168, 105753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Shang, L. Caregivers’ feeding behaviour, children’s eating behaviour and weight status among children of preschool age in China. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 34, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, L.; Lopes, C.; Severo, M.; Santos, S.; Real, H.; Durao, C.; Moreira, P.; Oliveira, A. Bidirectional association between parental child-feeding practices and body mass index at 4 and 7 y of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yan, N.; Shi, Z.; Ding, Y.; He, S.; Tan, Z.; Xue, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y. A 3-year longitudinal study of effects of parental feeding practices on child weight status: The childhood obesity study in China mega-cites. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, N.B.; Baur, L.A.; Felix, J.F.; Hill, A.J.; Marcus, C.; Reinehr, T.; Summerbell, C.; Wabitsch, M. Child and adolescent obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sares-Jaske, L.; Gronqvist, A.; Maki, P.; Tolonen, H.; Laatikainen, T. Family socioeconomic status and childhood adiposity in Europe—A scoping review. Prev. Med. 2022, 160, 107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.X.; Song, D.P.; Chen, C.L.; Li, F.F.; Zhu, D.Q. Reliability and validity of a Chinese version of Child Feeding Questionnaire among parents of preschoolers. Chin. J. Child Health Care 2016, 2016, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Li, C.; Nazir, N.; Choi, W.S.; Resnicow, K.; Birch, L.L.; Ahluwalia, J.S. Confirmatory factor analysis of the child-feeding questionnaire among parents of adolescents. Appetite 2006, 47, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeddine, D.; Itani, L.; Rossi, A.P.; Pellegrini, M.; El Ghoch, M. Strength and performance tests for screening reduced muscle mass in elderly lebanese males with obesity in community dwellings. Diseases 2021, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ding, Y.; Wen, X.; Gao, L.; Zhao, L.; Xue, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Parent-child resemblance in BMI and obesity status and its correlates in China. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 5400–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, L.; Jia, P.; Xue, H.; Xu, F.; Zhao, L.; Xue, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Longitudinal effects of school policies on children’s eating behaviors and weight status: Findings from the childhood obesity study in China megacities. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domaradzki, J.; Słowińska-Lisowska, M.R. Sex-moderated divergence between adult child and parental dietary behavior patterns in relation to body mass condition—Evaluating the mediating role of physical activity: A cross-sectional study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, A.; Monroe-Lord, L.; Wakefield, D.; Castor, C. Parenting styles, food parenting practices, family meals, and weight status of African American families. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Su, H.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Li, T.A.; Ma, L. Dietary and activity habits associated with hypertension in Kunming school-aged children and adolescents: A multilevel analysis of the study of hypertension risks in children and adolescents. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 46, 102854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, A.B. Unique considerations for the medical care of restrictive eating disorders in children and young adolescents. J. Eat Disord. 2023, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, R.; Baran, J.; Leszczak, J.; Bejer, A.; Wyszynska, J. Sociodemographic and socioeconomic factors influencing the body mass composition of school-age children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, R.; Wu, N.; Gao, H.; Gao, H.; Li, D. Assessment of the risk factors of duodenogastric reflux in relation to different dietary habits in a Chinese population of the Zhangjiakou area. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67, 9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.J.; Hibbs-Shipp, S.; Hobbs, S.; Boles, R.E.; Nelson, T.L.; Johnson, S.L.; Bellows, L.L. Maternal risk of cardiovascular disease is associated with higher BMI among preschool-aged children: A cross-sectional study. Child Obes. 2024, 20, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, J.; Downing, K.L.; Tang, L.; Campbell, K.J.; Hesketh, K.D. Associations between maternal concern about child’s weight and related behaviours and maternal weight-related parenting practices: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phy. 2018, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Agostino, J.; Ciszek, K.; Douglas, K.A. Parents’ perceptions of their child’s weight among children in their first year of primary school: A mixed-methods analysis of an Australian cross-sectional (complete enumeration) study. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Mendez, J.; Power, T.G.; Fisher, J.O.; O’Connor, T.M.; Hughes, S.O. Child weight status and accuracy of perceived child weight status as predictors of Latina mothers’ feeding practices and styles. Appetite 2019, 142, 104387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, J.; Meir, A.Y.; Hong, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Pearson, C.; Adams, W.G.; Wang, X.; Liang, L. Maternal pre-pregnancy BMI, offspring epigenome-wide DNA methylation, and childhood obesity: Findings from the Boston Birth Cohort. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavernier, R.L.E.; Mason, S.M.; Levy, R.L.; Seburg, E.M.; Sherwood, N.E. Association of childhood abuse with behavioral weight-loss outcomes: Examining the mediating effect of binge eating severity. Obesity 2022, 30, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Aruhan; Surenjidiin, S.; Zhang, L.-M.; Zhang, C.-H.; Li, M.-H. Yinshan Zhengyao: Exploring the power of food and inheriting healthy thoughts. Food Med. Homol. 2024, 1, 9420006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All | Sex | Region | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (678) | Female (620) | t/x2 a | p a | Yulin (650) | Shenzhen (648) | T/x2 b | p b | ||
| Age(M ± SD) | 10.65 ± 0.86 | 10.67 ± 0.03 | 10.62 ± 0.03 | 1.23 | 0.219 | 10.47 ± 0.05 | 10.82 ± 0.01 | −7.30 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.99 ± 3.87 | 19.68 ± 4.07 | 18.24 ± 3.50 | 6.77 | <0.001 | 19.24 ± 3.80 | 18.75 ± 3.94 | 2.32 | 0.021 |
| WHtR | 0.46 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.07 | 0.44 ± 0.05 | 11.03 | <0.001 | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 0.46 ± 0.06 | −3.17 | 0.002 |
| Thin (%) | 5.93 | 5.16 | 6.77 | 1.51 | 0.219 | 3.23 | 8.64 | 17.03 | <0.001 |
| Overweight (%) | 15.64 | 19.47 | 11.45 | 15.78 | <0.001 | 16.15 | 15.12 | 0.26 | 0.609 |
| Obesity (%) | 18.88 | 23.16 | 14.19 | 16.99 | <0.001 | 21.23 | 16.51 | 4.72 | 0.030 |
| Central obesity (%) | 29.51 | 39.91 | 18.15 | 73.31 | <0.001 | 27.38 | 31.67 | 2.85 | 0.091 |
| Family characteristics | |||||||||
| Paternal profession (%) | 6.57 | 0.161 | 61.85 | <0.001 | |||||
| Agriculture, forestry, fishery and animal husbandry personnel | 3.12 | 3.21 | 3.03 | 5.54 | 0.50 | ||||
| Workers, staff, and staff members | 34.43 | 35.11 | 33.67 | 33.38 | 35.56 | ||||
| Responsible person and professional and technical personnel | 13.85 | 15.73 | 11.78 | 8.62 | 19.53 | ||||
| Soldiers and others | 24.10 | 23.66 | 24.58 | 28.15 | 19.70 | ||||
| People waiting for employment | 24.50 | 22.29 | 26.94 | 24.31 | 24.71 | ||||
| Maternal profession (%) | 5.75 | 0.218 | 588.99 | <0.001 | |||||
| Agriculture, forestry, fishery and animal husbandry personnel | 1.20 | 1.68 | 0.67 | 1.38 | 1.00 | ||||
| Workers, staff, and staff members | 29.86 | 31.10 | 28, 28 | 12.46 | 48.75 | ||||
| Responsible person and professional and technical personnel | 14.89 | 15.57 | 14.14 | 9.85 | 20.37 | ||||
| Soldiers and others | 17.13 | 16.49 | 17.85 | 8.00 | 27.05 | ||||
| People waiting for employment | 36.91 | 34.96 | 39.06 | 68.31 | 28.40 | ||||
| Paternal education (%) | 0.32 | 0.850 | 444.65 | <0.001 | |||||
| Middle school or lower | 45.88 | 25.34 | 46.46 | 72.46 | 17.03 | ||||
| High or vocational school | 26.66 | 27.33 | 25.93 | 21.23 | 32.55 | ||||
| College and above | 27.46 | 27.33 | 27.61 | 6.31 | 50.42 | ||||
| Maternal education (%) | 1.02 | 0.599 | 460.47 | <0.001 | |||||
| Middle school or lower | 43.72 | 42.60 | 44.95 | 71.08 | 14.02 | ||||
| High or vocational school | 26.98 | 28.09 | 25.76 | 20.92 | 33.56 | ||||
| College and above | 29.30 | 29.31 | 29.29 | 8.00 | 52.42 | ||||
| Income (Yuan) | 1.06 | 0.303 | 693.34 | <0.001 | |||||
| <10,000 | 59.33 | 58.63 | 60.10 | 94.46 | 21.20 | ||||
| ≥10,000 | 40.67 | 41.37 | 39.90 | 5.54 | 78.80 | ||||
| Maternal BMI (kg/m2) | 22.26 ± 4.59 | 23.81 ± 0.15 | 24.18 ± 0.19 | −1.52 | 0.130 | 23.93 ± 0.21 | 24.05 ± 0.12 | −0.52 | 0.605 |
| Paternal BMI (kg/m2) | 23.99 ± 4.38 | 22.18 ± 0.17 | 22.35 ± 0.19 | −0.68 | 0.497 | 22.61 ± 0.21 | 21.91 ± 0.14 | 2.73 | 0.006 |
| SES c | 2.29 | 0.318 | 191.83 | <0.001 | |||||
| Low | 38.83 | 37.71 | 40.07 | 70.46 | 4.51 | ||||
| Middle | 32.91 | 33.89 | 31.82 | 27.54 | 38.73 | ||||
| High | 28.26 | 28.40 | 28.11 | 13.00 | 56.76 | ||||
| Parental feeding practices (M ± SD) | |||||||||
| Monitoring | 13.73 ± 4.18 | 13.73 ± 0.15 | 13.73 ± 0.17 | −0.01 | 0.998 | 13.14 ± 0.18 | 14.32 ± 0.14 | −5.16 | <0.001 |
| Pressure to Eat | 12.63 ± 3.56 | 12.65 ± 0.13 | 12.60 ± 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.824 | 12.81 ± 0.15 | 12.45 ± 0.13 | 1.83 | 0.068 |
| Restriction | 22.08 ± 5.77 | 22.11 ± 0.22 | 22.06 ± 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.881 | 21.70 ± 0.25 | 22.48 ± 0.20 | −2.44 | 0.015 |
| Perceived Child Weight | 11.61 ± 2.16 | 11.77 ± 0.08 | 11.43 ± 0.09 | 2.85 | 0.004 | 11.44 ± 0.09 | 11.78 ± 0.08 | −2.83 | 0.005 |
| Concern about Child Weight | 6.52 ± 3.27 | 6.62 ± 0.13 | 6.41 ± 0.13 | 1.15 | 0.249 | 7.63 ± 0.13 | 5.40 ± 0.11 | 13.07 | <0.001 |
| Perceived Parent Weight | 8.52 ± 1.76 | 8.51 ± 0.07 | 8.54 ± 0.07 | −0.27 | 0.791 | 8.73 ± 0.07 | 8.31 ± 0.07 | 4.29 | <0.001 |
| Food as Reward | 6.16 ± 2.30 | 6.29 ± 0.09 | 6.02 ± 0.09 | 2.13 | 0.033 | 6.11 ± 0.09 | 6.22 ± 0.09 | −0.83 | 0.409 |
| MN | PE | RST | PCW | CN | PPW | FR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Higher | Lower | Higher | Lower | Higher | Lower | Higher | Lower | Higher | Lower | Higher | Lower | Higher | |
| Yulin | ||||||||||||||
| Overweight and Obesity (%) | 140 (38.90) | 94 (35.21) | 155 (42.23) | 88 (31.10) * | 116 (35.47) | 124 (39.32) | 154 (29.28) | 89 (71.77) ** | 80 (28.88) | 163 (43.70) ** | 184(34.20) | 59 (52.68) ** | 154 (43.02) | 89 (30.48) * |
| Central obesity (%) | 105 (27.42) | 73 (27.34) | 117 (31.88) | 61 (21.55) * | 86 (26.30) | 92 (28.48) | 103 (19.58) | 75 (60.48) ** | 55 (19.86) | 123 (32.98) ** | 129(23.98) | 49 (43.75) ** | 112 (31.28) | 66 (22.60) * |
| FMI (kg/m)2 | 5.60 ± 2.61 | 5.73 ± 2.89 | 5.98 ± 2.92 | 5.23 ± 2.39 ** | 5.46 ± 2.55 | 5.85 ± 2.89 | 5.10 ± 2.31 | 7.99 ± 3.09 ** | 5.02 ± 2.34 | 6.12 ± 2.90 ** | 4.70 ± 2.88 | 6.15 ± 3.47 ** | 5.84 ± 2.67 | 5.43 ± 2.78 |
| FFMI (kg/m)2 | 13.45 ± 1.43 | 13.42 ± 1.45 | 13.56 ± 1.50 | 13.27 ± 1.34 * | 13.42 ± 1.38 | 13.44 ± 1.50 | 13.22 ± 1.31 | 14.35 ± 1.58 ** | 13.16 ± 1.37 | 13.63 ± 1.46 ** | 13.88 ± 1.39 | 14.48 ± 1.45 ** | 13.56 ± 1.42 | 13.28 ± 1.45 * |
| Shenzhen | ||||||||||||||
| Overweight and Obesity (%) | 91 (30.23) | 114 (32.85) | 152 (38.00) | 53 (21.37) ** | 99 (30.46) | 106 (32.82) | 78 (17.26) | 127 (64.8) ** | 88 (19.09) | 117 (62.90) ** | 161(29.38) | 44 (44.44) * | 99 (31.83) | 106 (31.55) |
| Central obesity (%) | 90 (30.30) | 113 (32.85) | 152 (38.48) | 51 (20.73) ** | 97 (30.12) | 106 (33.23) | 91 (20.31) | 112 (58.03) ** | 96 (32.98) | 107 (58.79) ** | 159(29.28) | 44 (45.36) * | 95 (31.05) | 108 (32.34) |
| FMI (kg/m2) | 4.15 ± 3.19 | 4.27 ± 3.10 | 4.78 ± 3.41 | 3.31 ± 2.39 ** | 4.07 ± 2.83 | 4.36 ± 3.41 | 3.19 ± 2.12 | 6.58 ± 3.78 ** | 3.23 ± 2.06 | 6.65 ± 3.94 ** | 4.70 ± 2.88 | 6.15 ± 3.47 ** | 4.31 ± 3.17 | 4.13 ± 3.12 |
| FFMI (kg/m2) | 14.49 ± 1.22 | 14.56 ± 1.11 | 14.70 ± 1.09 | 14.24 ± 1.23 ** | 14.54 ± 1.10 | 14.51 ± 1.23 | 14.23 ± 1.06 | 15.21 ± 1.10 ** | 14.27 ± 1.08 | 15.14 ± 1.13 ** | 13.88 ± 1.39 | 14.48 ± 1.45 ** | 14.56 ± 1.12 | 14.49 ± 1.21 |
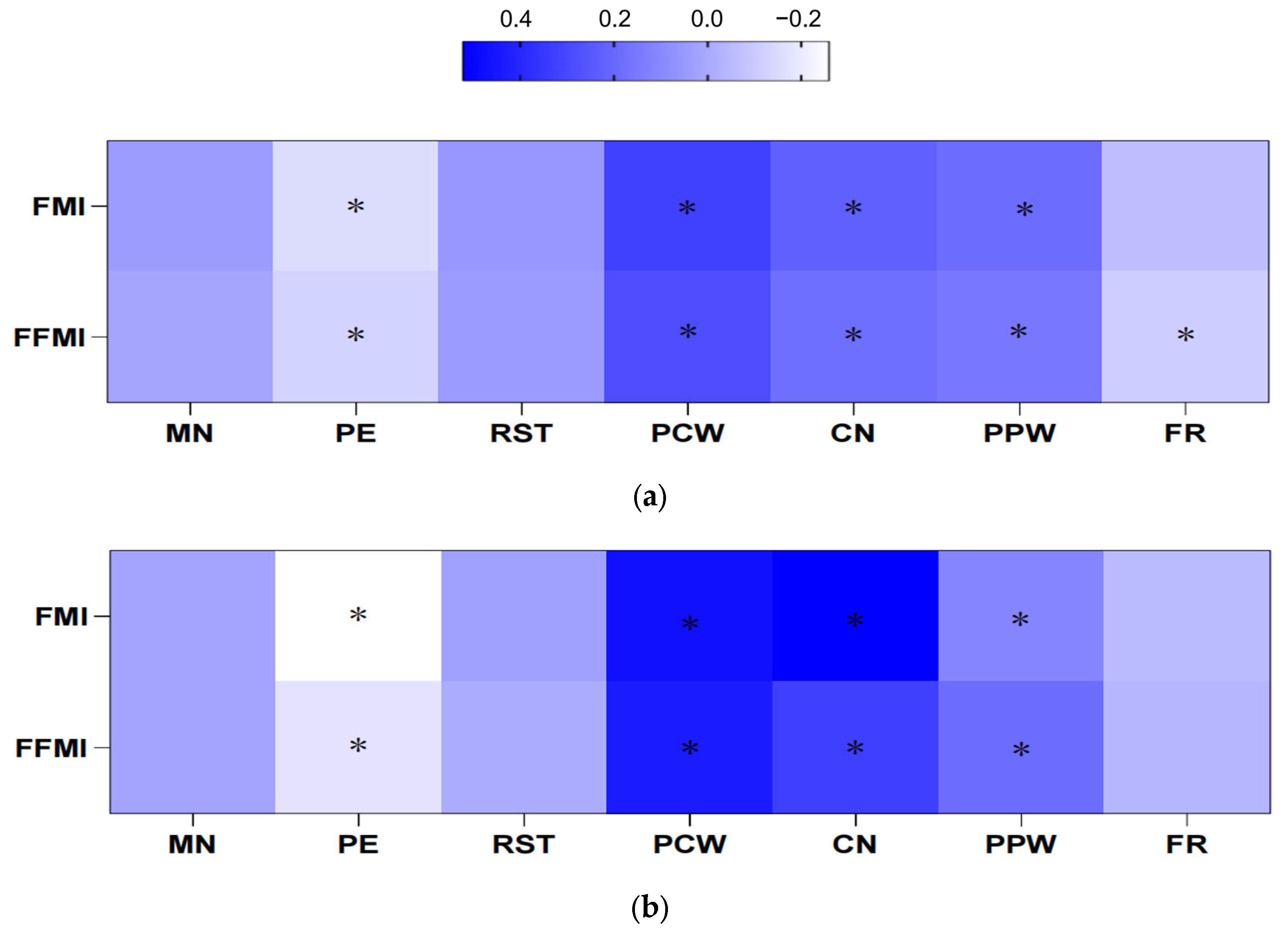
| FMI (kg/m2) [β(95% CI)] | FFMI (kg/m2) [β(95% CI)] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MN | Yulin | 0.02 (−0.02, 0.07) | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.03) |
| Shenzhen | 0.05 (−0.01, 0.12) | 0.02 (−0.01, 0.04) | |
| Region * MN | 0.02 (−0.07, 0.10) | 0.00 (−0.03, 0.04) | |
| PE | Yulin | −0.11 (−0.17, −0.06) ** | −0.04 (−0.06, −0.01) * |
| Shenzhen | −0.25 (−0.32, −0.18) ** | −0.06 (−0.08, −0.03) ** | |
| Region * PE | −0.14 (−0.22, −0.05) * | −0.02 (−0.06, 0.02) | |
| RST | Yulin | 0.03 (−0.01, 0.06) | 0.01 (−0.003, 0.03) |
| Shenzhen | 0.03 (−0.02, 0.08) | 0.00 (−0.02, 0.02) | |
| Region * RST | −0.00 (−0.06, 0.06) | −0.01 (−0.04, 0.01) | |
| PCW | Yulin | 0.39 (0.30, 0.47) ** | 0.17 (0.13, 0.22) ** |
| Shenzhen | 0.67 (0.56, 0.78) ** | 0.22 (0.18, 0.26) ** | |
| Region * PCW | 0.32 (0.18, 0.46) ** | 0.06 (−0.00, 0.11) | |
| CN | Yulin | 0.17 (0.11, 0.23) ** | 0.07 (0.04, 0.10) ** |
| Shenzhen | 0.56 (0.48, 0.64) ** | 0.12 (0.09, 0.16) ** | |
| Region * CN | 0.44 (0.34, 0.54) ** | 0.07 (0.02, 0.11) * | |
| PPW | Yulin | 0.25 (0.13, 0.37) ** | 0.10 (0.04, 0.16) * |
| Shenzhen | 0.15 (0.01, 0.29) * | 0.12 (0.07, 0.17) ** | |
| Region * PPW | −0.05 (−0.22, 0.14) | 0.03 (−0.05, 0.10) | |
| FR | Yulin | −0.08 (−0.17, 0.01) | −0.06 (−0.10, −0.02) |
| Shenzhen | −0.09 (−0.19, 0.02) | −0.02 (−0.05, 0.02) | |
| Region * FR | 0.01 (−0.13, 0.15) | 0.04 (−0.01, 0.10) |
| Obesity [OR (95%CI)] | Central Obesity [OR (95%CI)] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MN | Yulin | 0.97 (0.92, 1.02) | 1.00 (0.96, 1.04) |
| Shenzhen | 1.01 (0.94, 1.08) | 1.04 (0.99, 1.10) | |
| Region × MN | 1.03 (0.95, 1.11) | 1.03 (0.96, 1.10) | |
| PE | Yulin | 1.00 (0.94, 1.06) | 0.92 (0.87, 0.96) * |
| Shenzhen | 0.95 (0.89, 1.02) | 0.86 (0.81, 0.92) ** | |
| Region × PE | 0.93 (0.85, 1.02) | 0.96 (0.88, 1.03) | |
| RST | Yulin | 1.01(0.98, 1.05) | 1.00 (0.97, 1.03) |
| Shenzhen | 0.99 (0.95, 1.04) | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | |
| Region × RST | 1.01(0.95, 1.06) | 1.01 (0.96, 1.06) | |
| PCW | Yulin | 1.11 (1.01, 1.23) ** | 1.31 (1.19, 1.44) ** |
| Shenzhen | 1.23 (1.08, 1.39) ** | 1.61 (1.42, 1.82) ** | |
| Region × PCW | 1.34 (1.12, 1.61) * | 1.18 (1.02, 1.38) * | |
| CN | Yulin | 1.04 (0.98, 1.11) | 1.12 (1.07, 1.19) ** |
| Shenzhen | 1.08 (0.99, 1.17) | 1.45 (1.32, 1.58) ** | |
| Region × CN | 1.37 (1.22, 1.53) ** | 1.28 (1.16, 1.41) ** | |
| PPW | Yulin | 1.07 (0.95, 1.21) | 1.15 (1.03, 1.28) |
| Shenzhen | 1.05 (0.91, 1.20) | 1.13 (1.01, 1.27) | |
| Region × PPW | 0.99(0.83, 1.18) | 0.99(0.85, 1.16) | |
| FR | Yulin | 0.93(0.85, 1.02) | 0.93(0.86, 1.00) |
| Shenzhen | 0.97(0.87, 1.07) | 0.97(0.89, 1.06) | |
| Region × FR | 1.08(0.95, 1.23) | 1.07(0.95, 1.19) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Sun, M.; You, J.; Che, B.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Association of Parental Feeding Styles with Body Composition Among Children in Two Regions in China. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132197
Li C, Liu S, Wang D, Sun M, You J, Che B, Zhang W, Wei W, Zhao Y, Wang Y. Association of Parental Feeding Styles with Body Composition Among Children in Two Regions in China. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132197
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chao, Sha Liu, Dingkang Wang, Mengzi Sun, Jie You, Bizhong Che, Wen Zhang, Wei Wei, Yaling Zhao, and Youfa Wang. 2025. "Association of Parental Feeding Styles with Body Composition Among Children in Two Regions in China" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132197
APA StyleLi, C., Liu, S., Wang, D., Sun, M., You, J., Che, B., Zhang, W., Wei, W., Zhao, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Association of Parental Feeding Styles with Body Composition Among Children in Two Regions in China. Nutrients, 17(13), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132197







