Psychobiotics in Depression: Sources, Metabolites, and Treatment—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
2.7. Data Synthesis
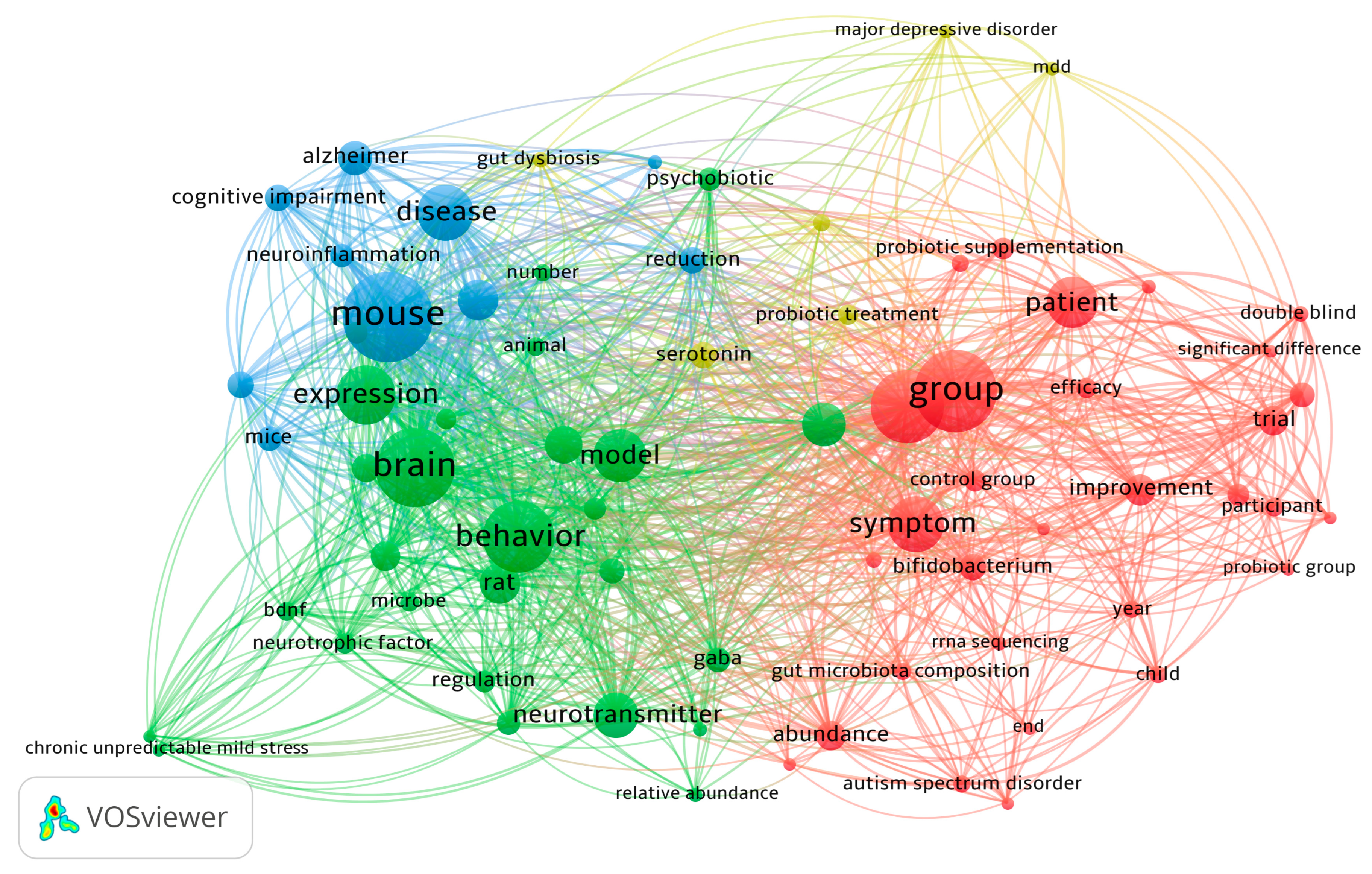
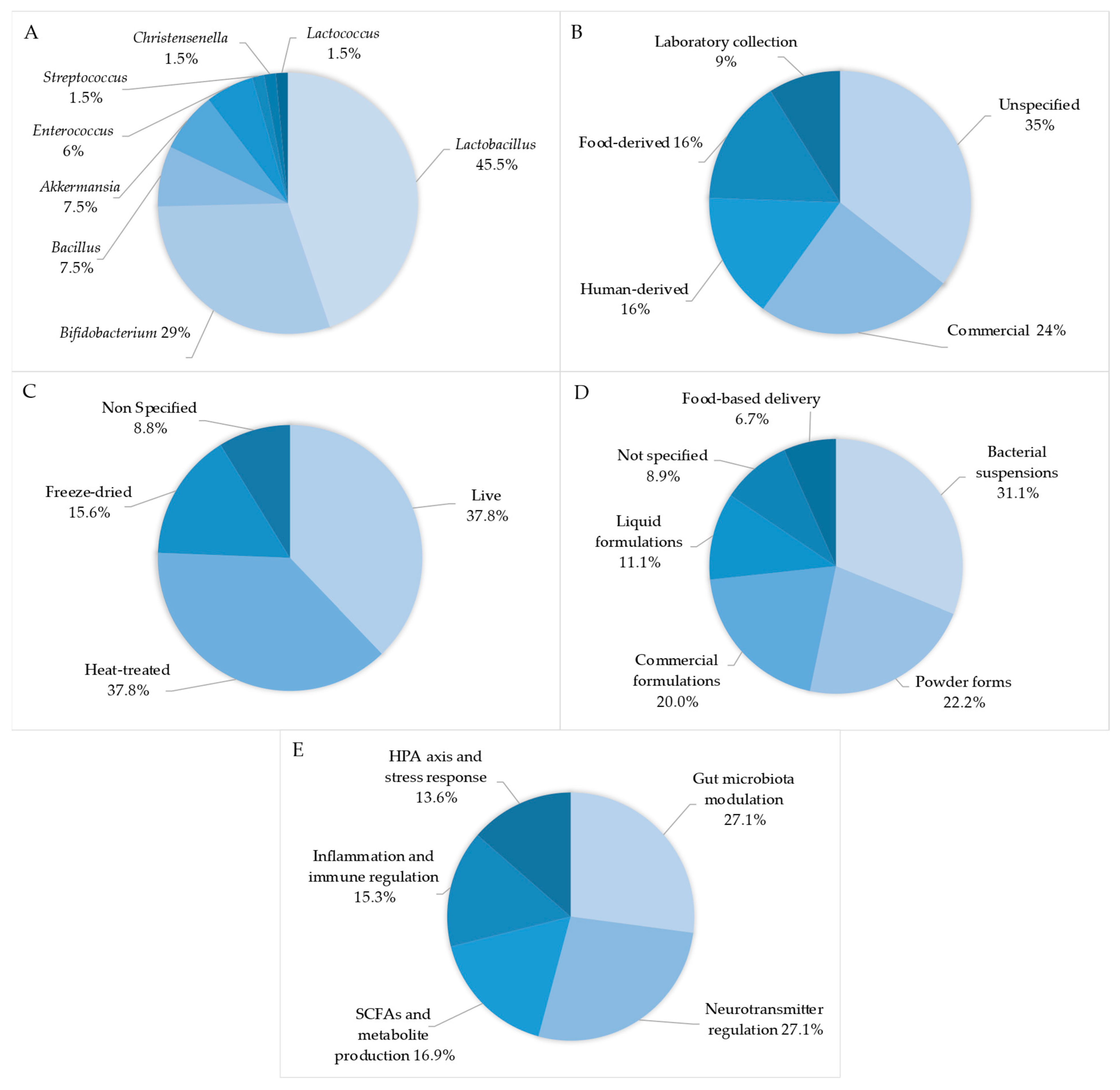
3. Results
3.1. Summary of Studies
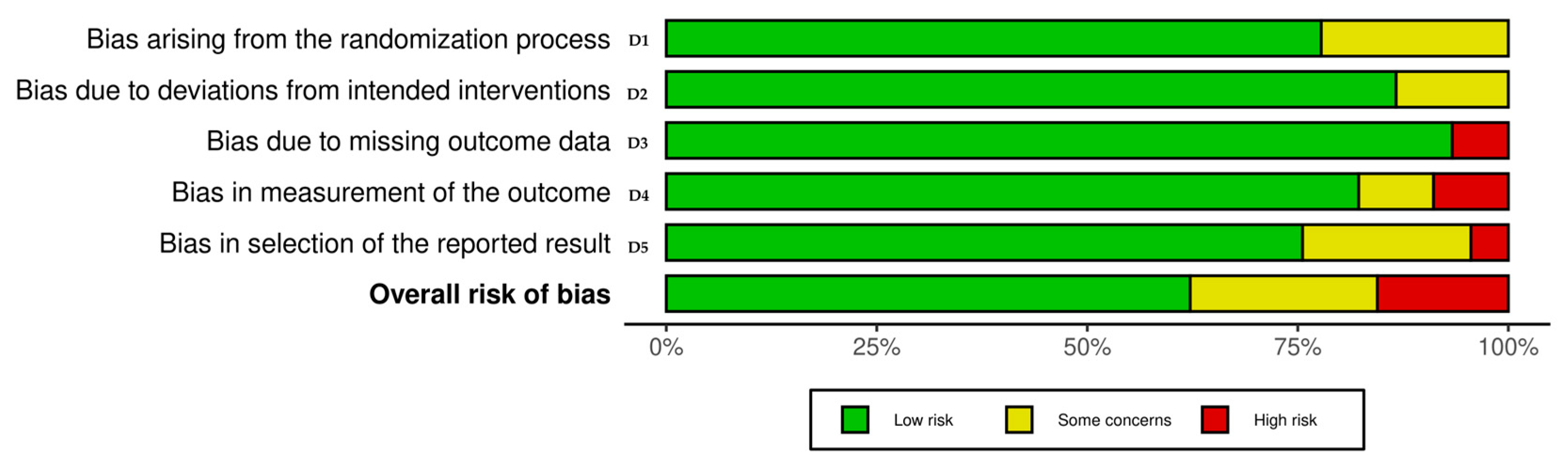
3.2. Quality Assessment—Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of the Studies Included in the Review
4.2. Implications of the Results for Practice and Policy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2022; Volume 5, ISBN 0890425752. [Google Scholar]
- Zelek-Molik, A.; Litwa, E. Trends in Research on Novel Antidepressant Treatments. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1544795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamran, M.; Bibi, F.; Rehman, A.; Morris, D.W. Major Depressive Disorder: Existing Hypotheses about Pathophysiological Mechanisms and New Genetic Findings. Genes 2022, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopwood, M. Anxiety Symptoms in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: Commentary on Prevalence and Clinical Implications. Neurol. Ther. 2023, 12, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, P.L.; Roiser, J.P.; Riedel, W.J.; Blackwell, A.D. Cognitive Impairment in Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, D.; Ingenito, A.; von Gal, A.; Francesca, M.; Piccardi, L. Relationship between Depression and Neurodegeneration: Risk Factor, Prodrome, Consequence, or Something Else? A Scoping Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinmann, T.; Wibowo, R.; Forster, F.; Gerlich, J.; Wengenroth, L.; Weinmayr, G.; Genuneit, J.; Nowak, D.; Vogelberg, C.; Radon, K.; et al. Association of Chronic Stress during Studies with Depressive Symptoms 10 Years Later. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelek-Molik, A.; Gądek-Michalska, A.; Wilczkowski, M.; Bielawski, A.; Maziarz, K.; Kreiner, G.; Nalepa, I. Restraint Stress Effects on Glutamate Signaling Protein Levels in the Rats’ Frontal Cortex: Does β1 Adrenoceptor Activity Matter? Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 15, 1451895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielawski, A.; Zelek-Molik, A.; Rafa-Zabłocka, K.; Kowalska, M.; Gruca, P.; Papp, M.; Nalepa, I. Elevated Expression of HSP72 in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus of Rats Subjected to Chronic Mild Stress and Treated with Imipramine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelek-Molik, A.; Bobula, B.; Gądek-Michalska, A.; Chorązka, K.; Bielawski, A.; Kuśmierczyk, J.; Siwiec, M.; Wilczkowski, M.; Hess, G.; Nalepa, I. Psychosocial Crowding Stress-Induced Changes in Synaptic Transmission and Glutamate Receptor Expression in the Rat Frontal Cortex. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J. Gut Microbiota Changes in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Treated with Vortioxetine. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 641491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warda, A.K.; Rea, K.; Fitzgerald, P.; Hueston, C.; Gonzalez-Tortuero, E.; Dinan, T.G.; Hill, C. Heat-Killed Lactobacilli Alter Both Microbiota Composition and Behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 362, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.-M.; Ling, Z. Short-Chain Fatty Acids-Producing Probiotics: A Novel Source of Psychobiotics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 7929–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães-Guedes, K.T. Psychobiotic Therapy: Method to Reinforce the Immune System. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2022, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casertano, M.; Fogliano, V.; Ercolini, D. Psychobiotics, Gut Microbiota and Fermented Foods Can Help Preserving Mental Health. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörkl, S.; Butler, M.I.; Wagner-Skacel, J. Gut-Brain-Crosstalk-the Vagus Nerve and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Depression. A Narrative Review. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2023, 13, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-Parabiotics: The New Horizons in Microbial Biotherapy and Functional Foods. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nain, N.; Kumari, K.G.; Haridasan, H.; Sharma, S.G. Microbes in Food and Beverage Industry. In Microbial Diversity, Interventions and Scope; Sharma, S., Sharma, N., Sharma, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 249–258. ISBN 9789811540981. [Google Scholar]
- Koubaa, M. Introduction to Conventional Fermentation Processes. In Fermentation Processes; Koubaa, M., Barba, F.J., Roohinejad, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Parletta, N.; Milte, C.M.; Meyer, B.J. Nutritional Modulation of Cognitive Function and Mental Health. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucklidge, J.J.; Johnstone, J.M.; Kaplan, B.J. Nutrition Provides the Essential Foundation for Optimizing Mental Health. Evid.-Based Pract. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2021, 6, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, A.; Cosme, F.; Inês, A. Wine and Non-Dairy Fermented Beverages: A Novel Source of Pro- and Prebiotics. Fermentation 2020, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglenius, H.; Mäkivuokko, H.; Ahonen, I.; Forssten, S.D.; Wacklin, P.; Mättö, J.; Lahtinen, S.; Lehtoranta, L.; Ouwehand, A.C. In Vitro Screen of Lactobacilli Strains for Gastrointestinal and Vaginal Benefits. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borody, T.J.; Warren, E.F.; Leis, S.M.; Surace, R.; Ashman, O.; Siarakas, S. Bacteriotherapy Using Fecal Flora. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 38, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, S.; Erginkaya, Z.; Ünal Turhan, E.; Konuray, G. Assessment of the Risk of Probiotics in Terms of the Food Safety and Human Health. In Health and Safety Aspects of Food Processing Technologies; Malik, A., Erginkaya, Z., Erten, H., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 419–443. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Mani, I. Beneficial Effects of Psychobiotic Bacteria, Cyanobacteria, Algae, and Modified Yeast in Various Food Industries. In Recent Advances in Food Biotechnology; Patruni, K., Singh, V., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 161–173. ISBN 9789811681240. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Br. Med. J. 2021, 372, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlainić, J.V.; Šuran, J.; Vlainić, T.; Vukorep, A.L. Probiotics as an Adjuvant Therapy in Major Depressive Disorder. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, I.; Rahman, M.Z.; Ad-Dab’bagh, Y.; Akhtar, M. Effect of Probiotic Interventions on Depressive Symptoms: A Narrative Review Evaluating Systematic Reviews. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, A.C.; Maurya, P.K.; Pedrini, M.; Zeni-Graiff, M.; Asevedo, E.; Mansur, R.B.; Wieck, A.; Grassi-Oliveira, R.; McIntyre, R.S.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; et al. Microbiota Abnormalities and the Therapeutic Potential of Probiotics in the Treatment of Mood Disorders. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-Of-Bias VISualization (Robvis): An R Package and Shiny Web App for Visualizing Risk-Of-Bias Assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Meng, C.; Hao, Z.; Liu, H. Bacillus licheniformis Reshapes the Gut Microbiota to Alleviate the Subhealth. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, M.; Wu, X.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Zz-1 Exerts Preventive Effects on Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depression in Mice via Regulating the Intestinal Microenvironment. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4331–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Shu, Y.; Jian, C.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, S.; Shu, X. Lactobacillus Ameliorates SD-Induced Stress Responses and Gut Dysbiosis by Increasing the Absorption of Gut-Derived GABA in Rhesus Monkeys. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 915393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jeon, S.; Kim, J.; Seol, D.; Jo, J.; Cho, S.; Kim, H. Investigation of Memory-Enhancing Effects of Streptococcus Thermophilus EG007 in Mice and Elucidating Molecular and Metagenomic Characteristics Using Nanopore Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandekar, M.P.; Palepu, M.S.K.; Satti, S.; Jaiswal, Y.; Singh, A.A.; Dash, S.P.; Gajula, S.N.R.; Sonti, R. Multi-Strain Probiotic Formulation Reverses Maternal Separation and Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Generated Anxiety- and Depression-like Phenotypes by Modulating Gut Microbiome–Brain Activity in Rats. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1948–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, K.; Moghimi, H.; Golbabaei, A.; Alijanpour, S.; Rezayof, A. Post-Weaning Treatment with Probiotic Inhibited Stress-Induced Amnesia in Adulthood Rats: The Mediation of GABAergic System and BDNF/C-Fos Signaling Pathways. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2357–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlessi, A.S.; Botelho, M.E.M.; Manosso, L.M.; Borba, L.A.; Maciel, L.R.; Andrade, N.M.; Martinello, N.S.; Padilha, A.P.Z.; Generoso, C.M.; Bencke, C.V.; et al. Sex Differences on the Response to Antidepressants and Psychobiotics Following Early Life Stress in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2022, 220, 173468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, D.; Chitrakar, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Tian, H.; Luo, Y. Study on Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum R6-3 from Sayram Ketteki to Prevent Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depression in Mice through the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3304–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, P.; Liao, A.; Pan, L.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; He, W.; Ou, X. Fermented Wheat Germ Alleviates Depression-like Behavior in Rats with Chronic and Unpredictable Mild Stress. Foods 2023, 12, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, E.-J.; Park, G.-S.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.-E.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.; Kang, J.; Koo, J.W.; Choi, T.-Y. Lactobacillus Reuteri ATG-F4 Alleviates Chronic Stress-Induced Anhedonia by Modulating the Prefrontal Serotonergic System. Exp. Neurobiol. 2023, 32, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Meng, C.; Liu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Z. Bacillus licheniformis Prevents and Reduces Anxiety-like and Depression-like Behaviours. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 4355–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Dong, Y. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CR12 Attenuates Chronic Unforeseeable Mild Stress Induced Anxiety and Depression-like Behaviors by Modulating the Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 107, 105710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; King, M.K.; Rajasekera, T.A.; Batabyal, A.; Woodke, S.T.; Gur, T.L. Gestational Administration of Bifidobacterium Dentium Results in Intergenerational Modulation of Inflammatory, Metabolic, and Social Behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 122, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Tian, P.; Guo, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Determining the Emotional Regulation Function of Bifidobacterium breve: The Role of Gut Metabolite Regulation over Colonization Capability. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1598–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, J.; Fabius, S.; Fernández-Ciganda, S.; Urbanavicius, J.; Piccini, C.; Scorza, C.; Zunino, P. Beneficial Effect of GABA-Producing Lactiplantibacillus Strain LPB145 Isolated from Cheese Starters Evaluated in Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviours in Rats. Benef. Microbes 2024, 15, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusti, A.; Molina-Mendoza, G.V.; Tamayo, M.; Rossini, V.; Cenit, M.C.; Frances-Cuesta, C.; Tolosa-Enguis, V.; Pulgar, D.; Flor-Duro, A.; Sanz, Y. Christensenella minuta Mitigates Behavioral and Cardiometabolic Hallmarks of Social Defeat Stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Akkermansia muciniphila Improves Depressive-like Symptoms by Modulating the Level of 5-HT Neurotransmitters in the Gut and Brain of Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 61, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, X.; Li, D.; Xu, L.; Zhou, G.; Xu, M.; Peng, L.; Sun, G.; Pan, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Sleep Deprivation-Induced Anxiety-like Behaviors Are Associated with Alterations in the Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0143723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yin, W.; Huang, Y. Exertional Heat Stroke-Induced Changes in Gut Microbiota Cause Cognitive Impairment in Mice. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Qian, X.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Probiotics Administration Alleviates Cognitive Impairment and Circadian Rhythm Disturbance Induced by Sleep Deprivation. Deleted J. 2024, 13, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; An, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Y. Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila Ameliorates Diabetic Cognitive Impairment by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Db/Db Mice. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 378, 114823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, K.; Fan, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, S. Prophylactic Effects of Supplementation of a Combination of Lactobacillus Lactis WHH2078 and Saffron on Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice Exposed to Chronic Stress. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 5912–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.J.; Cha, M.-G.; Kwon, G.-H.; Han, S.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, S.K.; Ahn, M.E.; Won, S.-M.; Ahn, E.H.; Suk, K.T. Akkermansia muciniphila Improve Cognitive Dysfunction by Regulating BDNF and Serotonin Pathway in Gut-Liver-Brain Axis. Microbiome 2024, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Baek, J.-S.; Shin, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-H. Alleviation of Immobilization Stress or Fecal Microbiota-Induced Insomnia and Depression-like Behaviors in Mice by Lactobacillus plantarum and Its Supplement. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, L.; Lin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Song, L. The Co-Fermentation of Whole Grain Black Barley and Quinoa Improves Murine Cognitive Impairment Induced by a High-Fat Diet via Altering Gut Microbial Ecology and Suppressing Neuroinflammation. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 11667–11685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bu, F.; Chen, T.; Shi, G.; Yuan, X.; Feng, Z.; Duan, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; et al. A Next-Generation Probiotic: Akkermansia muciniphila Ameliorates Chronic Stress–Induced Depressive-like Behavior in Mice by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8411–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, N.R.; Kent, M.; Fox, N.; Vavra, D.; Lambert, K. Neurobiological Effects of a Probiotic-Supplemented Diet in Chronically Stressed Male Long-Evans Rats: Evidence of Enhanced Resilience. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 11, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, S.; Caracci, F.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Q.; Frolinger, T.; Simon, J.; Pasinetti, G.M. Microbiota Metabolites Modulate the T Helper 17 to Regulatory T Cell (Th17/Treg) Imbalance Promoting Resilience to Stress-Induced Anxiety- and Depressive-like Behaviors. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, S.; Xin, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, N.; Li, L.; Ni, X.; Zeng, D.; Ma, H.; Bai, Y. Psychoactive Effects of Lactobacillus johnsonii against Restraint Stress-Induced Memory Dysfunction in Mice through Modulating Intestinal Inflammation and Permeability-a Study Based on the Gut-Brain Axis Hypothesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 662148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Steinhausen, K.; Bharwani, A.; Mian, M.F.; McVey Neufeld, K.-A.; Forsythe, P. Increased Persistence of Avoidance Behaviour and Social Deficits with L. rhamnosus JB-1 or Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Treatment Following Social Defeat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Han, X.; Cen, S.; Duan, H.; Feng, S.; Xue, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; et al. Beneficial Effect of GABA-Rich Fermented Milk on Insomnia Involving Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 233, 126409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, J.; Watcharin, S.; Makioka-Itaya, Y.; Inoue, R.; Watanabe, G.; Yamaguchi, H.; Nagaoka, K. Heat-Killed Enterococcus fecalis (EC-12) Supplement Alters the Expression of Neurotransmitter Receptor Genes in the Prefrontal Cortex and Alleviates Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 720, 134753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, S.; Ruiz, L.; Lugli, G.A.; Tames, H.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Mancino, W.; Longhi, G.; Carnevali, L.; Sgoifo, A.; et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a Key Member of the Human Gut Microbiota in the Production of GABA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Wan, Y.; Li, N.; Luo, L.; Gou, H.; Gu, J. The Potential Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum GM11 on Rats with Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress- Induced Depression. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 27, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayan, N.A.; Aow, J.; Lim, M.G.L.; Arcego, D.M.; Ryan, R.; Nourbakhsh, N.; de Lima, R.M.S.; Craig, K.; Zhang, T.Y.; Goh, Y.T.; et al. Shared and Unique Transcriptomic Signatures of Antidepressant and Probiotics Action in the Mammalian Brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 3653–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Zou, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 Attenuates Major Depression Disorder via Regulating Gut Microbiome and Tryptophan Metabolism: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 100, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Fang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Psychobiotic Lactobacillus plantarum JYLP-326 Relieves Anxiety, Depression, and Insomnia Symptoms in Test Anxious College via Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Lu, J.; Qiao, G.; Mao, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Tian, P.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium Breve CCFM1025 Improves Sleep Quality via Regulating the Activity of the HPA Axis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; et al. Effectiveness of Psychobiotic Bifidobacterium breve BB05 in Managing Psychosomatic Diarrhea in College Students by Regulating Gut Microbiota: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Cheng, R.; He, F.; Xiao, L.Z.; et al. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve 207-1 on Regulating Lifestyle Behaviors and Mental Wellness in Healthy Adults Based on the Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 2567–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casertano, M.; Dekker, M.; Valentino, V.; De Filippis, F.; Fogliano, V.; Ercolini, D. Gaba-Producing Lactobacilli Boost Cognitive Reactivity to Negative Mood without Improving Cognitive Performance: A Human Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Cross-over Study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 122, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, K.; Birkl-Toeglhofer, A.M.; Haybaeck, J.; Reiter, A.; Dalkner, N.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Maget, A.; Platzer, M.; Seidl, M.; Mendel, L.-M.; et al. PROVIT-CLOCK: A Potential Influence of Probiotics and Vitamin B7 Add-on Treatment and Metabolites on Clock Gene Expression in Major Depression. Neuropsychobiology 2024, 83, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzien, J.; Kalaska, B.; Rudzki, L.; Barbas-Bernardos, C.; Swieton, J.; Lopez-Gonzalvez, A.; Ostrowska, L.; Szulc, A.; Waszkiewicz, N.; Ciborowski, M.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Supplementation in Patients with Major Depression in a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial: A Metabolomics Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 368, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quero, C.D.; Manonelles, P.; Fernández, M.; Abellán-Aynés, O.; López-Plaza, D.; Andreu-Caravaca, L.; Hinchado, M.D.; Gálvez, I.; Ortega, E. Differential Health Effects on Inflammatory, Immunological and Stress Parameters in Professional Soccer Players and Sedentary Individuals after Consuming a Synbiotic. A Triple-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidarzadeh-Rad, N.; Gökmen-Özel, H.; Kazemi, A.; Almasi, N.; Djafarian, K. Effects of a Psychobiotic Supplement on Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Depressive Patients: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, T.; Kerpel, R. Psychobiotics in the Treatment of Depression: A New Look at Mental Health—A Systematic Search Review. Rev. Científica Multidiscip. Núcleo Do Conhecimento 2022, 1, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Toshimitsu, T.; Okada, E.; Anzai, S.; Shiraishi, I.; Inamura, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Sashihara, T.; Hisatsune, T. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum OLL2712 on Memory Function in Older Adults with Declining Memory: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Katsumata, N.; Bernier, F.; Ohno, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Odamaki, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Ito, K.; Kaneko, T. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in Improving Cognitive Functions of Older Adults with Suspected Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 77, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, C.; Martinez, S.L.; Liscano, Y. Effectiveness of Psychobiotics in the Treatment of Psychiatric and Cognitive Disorders: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Lehto, S.M.; Harty, S.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Burnet, P.W.J. Psychobiotics and the Manipulation of Bacteria–Gut–Brain Signals. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Noorbala, A.A.; Azam, K.; Eskandari, M.H.; Djafarian, K. Effect of Probiotic and Prebiotic vs Placebo on Psychological Outcomes in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.Z.; Platzer, M.; Kohlhammer-Dohr, A.; Hamm, C.; Mörkl, S.; Bengesser, S.A.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Lahousen-Luxenberger, T.; Leitner-Afschar, B.; Schöggl, H.; et al. PROVIT: Supplementary Probiotic Treatment and Vitamin B7 in Depression—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romijn, A.R.; Rucklidge, J.J.; Kuijer, R.G.; Frampton, C. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum for the Symptoms of Depression. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2017, 51, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, G.K.; Gage, S.H.; Kemmer, D.; White, R.E. Common Measures in Mental Health: A Joint Initiative by Funders and Journals. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study ID | Population/Sample Size | Dysfunction | Intervention-Bacteria | Outcomes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal Studies | ||||||||||
| Author | Study Design | Species/Strain | Source of Origin | Form/Dose/Time of Treatment | Behavioral Tests | Bacterial Metabolites/Neurotransmitters | Mechanism | Health Benefits | ||
| Feng et al., 2022 [35] | RCEAS | Male Sprague Dawley rats, n = 68 | Subhealth state induced by chronic stress and antibiotics | B. licheniformis BL20386 | Vaginal swab | Live bacte- rial suspen- sion/1 mL, 1 × 108 CFU/mL)/ 5–8 weeks | FST, EPM | SCFAs, isobutyric acid, isovaleric acid, propionic acid, GABA, 5-HT, Glu, NE | Gut microbiota modulation; anti-inflammation; HPA axis inhibition | ↓anxiety behaviors, ↓inflammatory markers, ↓CORT ↑gut microbiota, |
| Xu J. et al., 2022 [36] | RCEAS | Male C57BL/6 mice, n = 60 | Depression induced by CUMS | L. rhamnosus zz-1 | Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China | Bacterial suspension/0.1 mL, 2 × 107–109 CFU/kg bw)/ 5 weeks | SPT, FST, OFT Body weight monitoring | 5-HT, NE, DA | HPA axis inhibition; BDNF/TrkB activation; microbiota modulation | ↓depression, ↓inflammation, ↑intestinal barrier, ↑gut microbiota, ↑neurotransmitters |
| Zhao et al., 2022 [37] | EIS | Rhesus monkeys, n = 30 | SD-induced stress responses and gut dysbiosis | Bifid Triple Viable Capsules: B. longum, L. acidophilus, and E. faecalis | - | Capsules—420 mg in water/2×/day/30 days | Paradoxical sleep disruption, light and noise response | GABA, NE | Gut microbiota modulation; GABA elevation; gut–brain axis regulation | ↓stress hormones, ↓inflammation, ↑gut microbiota |
| Kim et al., 2022 [38] | EIS | Male SPF C57BL/C mice, n = 11–12/group, 3 groups | Cognitive function and memory | S. thermophilus EG007, L. plantarum A003F7 | Fermented dairy products | Suspension in water/0.2 mL (1.08 or 3.12 × 109 CFU)/4 weeks | Y-SAT, Y-FAT, NORT, PAT | GABA | GABA production; gut microbiota modulation | ↑spatial memory, ↑learning, ↑object recognition |
| Dandekar et al., 2022 [39] | EPAS | Sprague-Dawley rats, n = 6–8/group, 3 groups | Depression and anxiety-like behaviors induced by MS and CUMS | Probiotic: B. coagulans Unique IS-2, L. plantarum UBLP-40, L. rhamnosus UBLR-58 B. lactis UBBLa-70, B. breve UBBr-01, B. infantis UBBI-01 | Commercial multi-strain probiotic (Cognisol, Unique Biotech Ltd., Telangana, India) | Freeze-dried probiotic in water/1 capsule daily/6 weeks | FST, SPT, EMP, OFT | 5-HT, DA, Acetate, Propionate, Butyrate | Gut–brain axis modulation; Trp metabolism regulation | ↓anxiety/depression, ↓neuroinflammation, ↑neurotransmitters, ↑intestinal function |
| Alizadeh et al., 2022 [40] | ECAS | Male Wistar rats, multiple groups of 7 rats | Stress-induced memory loss/amnesia | L. plantarum ATCC 8014, L. brevis ATCC 14869, B. bifidum ATCC 29521 | - | Daily suspen- sion in water/2 × 106–109 CFU/2–5 weeks | PALT, STL, EPST | GABA | GABAergic system modulation; BDNF expression regulation | ↓memory loss, ↑memory formation, ↑signaling pathways |
| Carlessi et al., 2022 [41] | EAS | Male and female Wistar rats, n = 12–15/group, 5 groups | MDD induced by maternal deprivation | B. infantis | - | Probiotic/1 × 1010 CFU in 100 mL water/10–50 days | OFT, FST, ST | - | Oxidative damage regulation; blood–brain barrier (BBB) protection | ↓depression, ↓oxidative stress markers, ↑BBB integrity |
| Zhao et al., 2023 [42] | EAS | Male C57BL/6J mice, 4 groups | Depression (CUMS-induced depression) | L. plantarum R6-3 | Sayram Ketteki (Xinjiang fermented yogurt) | Live bacteria/5 × 109 CFU in 0.9% saline/8 weeks | SPT, TST, FST Body weight measurements | SCFAs, 5-HT, DA, NE | Gut–brain axis signaling; SCFA production; BDNF/TrkB pathway activation | ↓depression, ↑weight, ↑hippocampus, ↓CORT levels, ↑BDNF |
| Hu et al., 2023 [43] | EAS | Male SD rats, n = 7/group, 6 groups | Depression (CUMS-induced depression-like behavior) | L. plantarum (M618) | Laboratory-preserved strain | Fermented wheat germ powder/ 43–60 mg GABA/kg/day/4 weeks | EPM, FST, OFT, SPT | 5-HT, 5-HIAA, ACH, GABA | Gut microbiota structure restoration; amino acid metabolism regulation | ↓depression, ↑neurotransmitters, ↑weight, ↓anhedonia |
| Lee et al., 2023 [44] | ECAS | C57BL6/N male mice, n = 50 | Chronic stress-induced anhedonia | L. reuteri ATG-F4 (F4) | Fecal samples of newborn babies in Daejeon, South Korea | Live bacteria/ 5 × 108 CFU/mL/ 250 µL daily/ 4 weeks | SPT, body weight measurements | 5-HT, Trp metabolites, 5-HTP, 5-HIAA | Trp metabolism modulation; serotonin regulation; gut microbiota modulation | ↓anhedonia, ↑weight, ↑serotonergic system |
| Feng et al., 2023 [45] | ECAS | Male Sprague Dawley rats, n = 52 | Depression and anxiety induced by CUMS | B. licheniformis CGMCC NO.0298 | Zhengchangsheng® (Liyang, China) | Live bacteria/ 1 × 108 CFU/mL/1 mL daily/ 4 weeks | FST, EMP | GABA, Trp, DA, epinephrine, SCFAs | Gut microbiota modulation; SCFA production; neurotransmitter regulation | ↓depression, ↓anxiety, ↑gut microbiota |
| Ma et al., 2023 [46] | EAS | Adult female C57BL/6J mice, n = 10/group | Depression induced by CUMS | L. plantarum CR12 | - | Live bacteria in powder form/ 1 × 109 CFU/mL/ 200 μL daily/ 3 weeks | OFT, FST, TST, SPT, MWM | SCFAs, butyrate, 5-HT, DA, NE | Gut microbiota modulation; butyrate enhancement; neuroinflammation reduction | ↑cognitive function, ↓anxiety/depression, ↑gut barrier |
| Galley et al., 2024 [47] | EIS | Female nulliparous C57Bl6/J mice and offspring, n = 82 | Prenatal stress (PNS) exposure | B. dentium 27678 | American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) | Live bacteria in 0.9% saline/3.0–9.0 × 108 CFU/150 μL daily/7 days | TCSBT, LDT, SB | KA, I3PA, 5-HT, Trp metabolites | Anti-inflammatory action; Trp metabolism modulation | ↓maternal inflammation, ↓fetal neuroinflammation, ↑social behavior |
| Qian et al., 2024 [48] | EAS | Male C57BL/6J mice, n = 69 | CUMS-induced anxiety, depression-like behavior, and memory impairment | B. breve CCFM1025 | feces of a healthy adult Tibetan man | Live bacteria in suspension/ 1 × 107–109 CFU/ oral daily/ 7–35 days | OFT, EPM, FST, LDB | CA, IAM, IAA, ILA, Trp metabolites 5-HT | Gut metabolite modulation; bile salt hydrolase activation; HPA axis regulation | ↓anxiety, ↑memory, ↓depression, ↑gut homeostasis |
| Lozano et al., 2024 [49] | ECIS | Adult male Wistar rats, n = 12/group, 2 groups | Anxiety- and depression-like behaviors | L. plantarum LPB145 | Uruguayan cheese starter isolate | Lyophilized live bacteria in skim milk/ 5 × 108 CFU/ 0.5 mL daily/ 28 days | EMP, FST, OFT | GABA | GABA production; specific microbiota enhancement | ↓depression behaviors, no effect on anxiety/locomotion |
| Agusti et al., 2024 [50] | EIS | Male C57BL/6 mice and CD-1 mice as aggressors, n = 45/group, 3 groups | SD-induced disturbances | C. minuta DSM 32891 | feces of a healthy volunteer | Live bacteria suspended in PBS with 0.05% L-cysteine + 10% glycerol/1 × 109 CFU daily/6 weeks | FST, TST, SPT, OFT, LDT, SIT | DA, NA, ADE, CORT, DOPAC, HVA, 3-MT | HPA axis modulation; dopamine metabolism regulation; receptor expression modulation | ↓depression/anxiety, ↓inflammation, ↓cardiovascular damage |
| Guo et al., 2023 [51] | EIS | Male C57BL/6J SPF mice, NIAAA: n = 12/4 groups, CUMS: n = 15/3 groups | Depression-like behaviors induced by: Chronic alcohol exposure, CUMS | A. muciniphila (ATTC BAA-835) | - | Live bacteria in 5% glycerol/ 2.5 × 109 CFU/ 200 μL daily/ 4 weeks | FST, TST, SPT, OFT, FC | 5-HT | Serotonin enhancement; SERT expression inhibition | ↓depression, ↑hedonic response, ↑liver function, ↑serotonin |
| Zhang et al., 2024 [52] | EIS | Male Sprague-Dawley rats, n = 30 rats | SD-induced anxiety-like behaviors | B. longum L. acidophilus E. faecalis B. licheniformis B. subtilis E. faecium | Commercial probiotics | Live multi-strain bacteria in saline/ 1 × 106–108 CFU per strain/daily for 14 days | OFT | LPS, serum metabolites, including uridine and Trp | LPS reduction; inflammatory bacteria reduction | ↑anxiety behaviors, ↓serum LPS |
| Xie et al., 2024 [53] | EAS | Male C57BL/6 mice, n = 30 mice | EHS-induced cognitive impairment | L. murinus, Probiotic blend: B. bifidum F-35 B. longum CCFM729, Lactobacillus species | - | Live multi-strain blend/0.02 mg/kg/daily for 28 days | OFT, EPM, TST, FST, NORT | SCFAs | Microbiota equilibrium restoration; BDNF/TrkB pathway modulation | ↑cognitive performance, ↑BDNF/TrkB, ↑cognitive recovery |
| Tian et al., 2024 [54] | EIS | C57BL/6J mice, n = 8/group, 3 groups | SDStress-induced cognitive impairment and circadian rhythm disturbance | B. breve CCFM1025 | - | Live bacteria in 10% skim milk/1 × 1010 CFU/mL/daily for 7 days | OFT, NORT, Y-maze test | Isovaleric acid GABA, serum purine metabolites, 5-HT, melatonin | Gut microbiota modulation; striatal melatonin system regulation | ↑cognitive performance, ↑weight/food intake, ↑serotonin metabolism |
| Du et al., 2024 [55] | EAS | Male db/db mice and db/m controls, n = 12/group, 4 groups | Diabetic cognitive impairment (DCI) | A. muciniphila | - | Live bacteria in PBS/ 5 × 109 CFU/mL/ oral daily/ 8 weeks | MWM, EL, PCT, TSTQ, SS | GA, Gly, Xyl, IAA | Neuroinflammation reduction; gut microbiota modulation; synaptic structure improvement | ↑cognitive function, ↑memory, ↑synapses, ↓neuroinflammation |
| Chen et al., 2024 [56] | RCEAS | Male BALB/c mice, n = 10/group, 4 groups | Depression-like behaviors induced by CRS | L. lactis WHH2078 | Hangzhou Wahaha Group Co. (Hangzhou, China) | Live bacteria in saline/ 5 × 108 CFU/mL/ 0.2 mL daily/ 3 weeks | TST, OFT, FST, SPT | 5-HT CORT | Gut microbiome modulation; microbial diversity restoration | ↓depression, ↑exploration, ↑locomotion, ↑gut dysbiosis |
| Kang et al. 2024 [57] | HBCCS-AE | Cirrhosis pts ± HE; Cognitive dysfunction (n = 154); C57BL/6J mice | Hepatic encephalopathy Cognitive dysfunction Liver injury/cirrhosis | A. muciniphila | - | Live bacteria/ ~1 × 109 CFU/mL/ 200 μL/ 3×/week/ | NORT, WMT, TST, SNSB | 5-HT, BDNF | BDNF/5-HT pathway regulation; 5-HT receptor suppression | ↑cognitive function, ↓liver injury, ↓gut inflammation |
| Lee et al., 2024 [58] | EAS | Male C57BL/6 mice, multiple groups of 6–8 mice | Depression/anxiety (DA) Insomnia, Stress-induced inflammation | L. plantarum P72 | healthy human feces bacterial collection | Live bacteria (P72) in 0.1% trehalose/ 1 × 109 CFU/day/ oral daily/ 5–7 days | OFR, EPM, TST, SLT, SD | GABA, 5-HT, GABAA receptor α1, 5-HT1A receptor | GABA/GABAA receptor upregulation; serotonin/5-HT1A receptor enhancement | ↓depression, ↓anxiety, ↑sleep parameters, ↓inflammation |
| Wei et al., 2024 [59] | ECAS | C57BL/6J male mice, n = 10/group,4 groups | Cognitive impairment induced by high-fat diet | L. kisonensis (JCM15041) | State Key Lab of Bioreactor Eng. (East China Univ. of Sci.& Tech. Shanghai) | Live bacteria in fermented grain mixture/ 5 × 108 CFU/mL/ 10 mL/kg daily/ 10 weeks | NBT, OFT, EPM | DA, EPI, NE, 5-HT, ACH | Gut microbiota dysbiosis regulation; neurotransmitter pathway upregulation | ↑behavioral skills, ↑neurotransmitters, ↓synaptic damage |
| Ding et al., 2021 [60] | EAS | Male C57BL/6 mice, n = 6/group, 3 groups | Chronic restraint stress (CRS)-induced depression-like behavior | A. muciniphila (ATCC® BAA-835TM) | - | Live bacteria (5 × 108 CFU/mL, 200 µL), oral, daily/3 weeks | OFT, TST, FST | CORT, DA, 5-HT, BDNF | Hormone/neurotransmitter/BDNF regulation; gut microbiota modulation | ↓depression, ↑locomotor activity, ↑neurotransmitter levels |
| Natale et al., 2021 [61] | RCEAS | Male Long-Evans rats, n = 6/group, 4 groups | Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) | L. helveticus R0052 (5%) L. rhamnosus R0011 (95%) | Lacidofil® probiotic (Mirabel, QC, Canada) | 109 CFU/mL, in water, oral, daily/27 days | OFT, FST | CORT, DHEA | Microglia reactivity reduction; DHEA/CORT ratio improvement | ↑emotional resilience, ↓anxiety markers, ↑exploration |
| Westfall et al., 2021 [62] | EIS | Male C57BL/6J mice, n = 12–16/group, 8 groups | Chronic stress-induced anxiety and depression-like behaviors | L. plantarum ATCC 793 B. longum ATCC 15707 | - | Live bacteria in drinking water/1 × 109 CFU per strain daily/oral/6 weeks | OFT, FST | 4-HPPA, 4-HPAA, CA, 5-HT, kynurenine metabolites | AHR receptor activation; inflammatory response reduction | ↓anxiety/depression, ↓neuroinflammation, ↑immune regulation |
| Wang et al., 2021 [63] | EAS | C57BL/6J male mice, n = 36/group, 3 groups | Restraint stress-induced memory dysfunction | L. johnsonii BS15 (CCTCC M2013663) | Hongyuan Prairie yogurt (Aba, Taicang, China) | Live suspension (2 × 108 CFU in 0.2 mL PBS), oral daily, 28 days | NORT, T-maze test, Passive avoidance test | DA, 5-HT, Ach, Glu, GABA, nitric oxide (NO) | Memory-related protein enhancement; neurotransmitter level increase | ↑memory, ↓CORT, ↑gut barrier, ↑inflammation markers |
| Liu et al., 2020 [64] | EIS | Male C57BL/6 mice and CD-1 retired breeder mice, n = 74 mice | PTSD-like behavior induced by chronic social defeat (CSD) | L. rhamnosus JB-1 | Alimentary Health Ltd., Cork, Ireland | Live bacteria (1 × 109 CFU in 200 μL PBS), oral daily | 3-chamber test, Aggressor avoidance test, OFT, LDT, EMP | CRHR-1 BDNF | CRHR-1 expression reduction; BDNF expression reduction | Negative effects: ↑avoidance behavior, ↑social deficits |
| Yu et al., 2020 [65] | EAS | Male ICR mice, n = 10/group, 6 groups | Insomnia and anxiety | L. brevis DL1-11 | Traditional Chinese fermented food pao cai | Live bacteria (1 × 108 CFU/mL), oral gavage/30 days | OFT, EPM, SLD | GABA, SCFAs, Butyric acid | Beneficial bacteria abundance increase; SCFA production enhancement | ↓anxiety behavior, ↑sleep time, ↓sleep latency |
| Kambe et al., 2020 [66] | EIS | Male C57BL/6J mice, n = 8/group, 2 groups | Anxiety-like behavior | E. faecalis EC-12 | - | 0.125% heat-killed bacteria/4 weeks | OFT, EMP, FST | EC-12 | Neurotransmitter receptor gene upregulation; gut microbiota composition alteration | ↓anxiety behavior, anti-depressive trend, ↑exploration |
| Duranti et al., 2020 [67] | EAS | n = 32 Male wild-type Groningen rats | Anxiety and depression | B. adolescentis PRL2019 B. adolescentis HD17T2H | Human gut/intestine/feces | Live bacteria in solution, 1 × 109 CFU/day/5 days | - | GABA | GABA production via GAD enzyme system | ↑GABA production, potential gut–brain axis modulation |
| Ma et al., 2023 [68] | EAS | Male SPF SD rats, n = 10/group, 3 groups | Depression induced by CUMS | L. plantarum GM11 | Sichuanbroad bean paste (fermented food) | Live bacteria (2 × 109 CFU/mL), oral gavage/ 21 days | FST, SPT, EMP, OFT | 5-HT, CORT, BDNF | Serotonin and BDNF level increase; CORT reduction | ↓depression, ↓despair, ↓anhedonia |
| Rayan et al., 2024 [69] | EIS | Male Long-Evans rats, 6 groups | MDD and anxiety disorders | Lacidofil® probiotic: L. rhamnosus Rosell®-11 + L. helveticus Rosell®-52) | Lallemand, Mirabel, QC, Canada | Probiotic formulation (1.5 × 109 CFU/day)/ 21 days | EPM | - | Synaptic/signaling gene upregulation; prefrontal cortex regulation | ↓anxiety, GWAS loci enrichment, ↑neurite branching |
| Human studies | ||||||||||
| Tian et al., 2022 [70] | RPDBCT | Adults, n = 45 | MDD with associated gastrointestinal symptoms | B. breve CCFM1025 | - | Freeze-dried powder in sachet/ 1010 CFU/ 1×/day/ 4 weeks | HDRS, MADRS, BPRS, GSRS | 5-HT, 5-HIAA, Trp metabolites, indole derivatives | Gut microbiome regulation; Trp metabolism modulation | ↓depression symptoms, ↑ gastrointestinal symptoms, ↑emotional regulation |
| Zhu et al., 2023 [71] | RCT | College students, n = 30/group, 3 groups | Test anxiety, depression, and insomnia | L. plantarum JYLP-326 | Fermented sticky rice (Bama, Guangxi, China) | Sachet with 1.5 × 1010 CFU live bacteria/ oral/ 3 weeks | HAMA, HDRS, AIS | Ethyl sulfate, 1,2-propanediol | Gut microbiota modulation; fecal metabolite regulation | ↓anxiety, ↓depression, ↑insomnia, ↑microbiota |
| Lan et al., 2023 [72] | RCT | Adults, n = 40/group, 2 groups | Stress-induced insomnia | B. breve CCFM1025 | - | Sachet with 1 × 109 CFU live bacteria/ 4 weeks | PSQI, AIS | - | Stress marker reduction by daidzein; serum metabolite modulation | ↓sleep quality scores, ↑subjective sleep, ↓sleep disturbance |
| Wang et al., 2024 [73] | RPDBCT | College students, 100 students | DCS with associated anxiety and depression | B. breve BB05 | China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center | Live bacteria in sachet/ 1 × 1010 CFU per dose/ 2×/day/ 2 weeks | BSS, HAMA, HDRS | 5-HT, ACH, EPI, NE | Gut microbial diversity enhancement; beneficial bacteria increase | ↓diarrhea symptoms, ↓anxiety/depression, ↑gut microbiota |
| Li et al., 2024 [74] | RPDBCT | Adults, n = 40/group, 3 groups | High mental stress, overweight, insomnia | B. breve 207-1 | Healthy Chinese infants | Live bacteria in probiotic powder drink/ 1–5 × 1010 CFU daily/28 days | SDS, SAS, PSQI | GABA, 5-HT, SCFAs: acetic, propionic, and butyric acids | Gut–brain axis modulation; GABA enhancement; HPA axis hormone suppression | ↑sleep quality, ↑diet, ↑exercise, ↓weight, ↑serotonin |
| Casertano et al., 2024 [75] | RDBPCCS | Adults, n = 43–44/group, 2 groups | Mild-moderate stress | L. brevis P30021 L. plantarum P30025 | - | Live bacteria powder stick/ 2 × 109 CFU (+ B6, D3, Zn)/daily/4 weeks | CBB | GABA Acetylcholine Choline Glutamate | Probiotic genera abundance increase | ↓depressive symptoms, ↑rumination, no effect on cognitive performance |
| Kreuzer et al., 2024 [76] | RDBPCT | Adults with MDD, n = 24 -intervention group, n = 29 (placebo group) | MDD | B. bifidum W23, B. lactis W51, W52, L. acidophilus W22, L. casei W56, L. paracasei W20, L. plantarum W62, L. salivarius W24, L. lactis W19 | OMNi-BiOTiC Stress Repair provided by AllergoSan | Live multistrain bacteria in drink/ 7.5 × 109 CFU oral daily/28 days | BDI-II, HDRS | Butyrate, various amino acids | Clock gene expression modulation; metabolite-clock gene correlation | ↑depression scores, ↑circadian rhythm influence |
| Godzien et al., 2024 [77] | RPDBCT | MDD patients on SSRIs; n = 30/group, 2 groups | MDD | L. plantarum 299v | Strain owner—Probi AB, Lund, Sweden | Live bacteria in capsule/ 1 × 1010 CFU oral daily/8 weeks | - | LCACs, NATs, OxPC, SMs, L-His, D-Val, p-cresol | LCACs reduction; sphingomyelin level enhancement | ↑cognitive functions, ↑mitochondrial function, ↓inflammatory markers |
| Quero et al., 2021 [78] | TBRPPS | n = 13 soccer players, n = 14 sedentary students | Sleep quality, depression, anxiety, stress levels | B. lactis CBP-001010 L. rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 B. longum ES1 | - | Live bacteria in synbiotic stick/ 1 × 109 CFU oral daily/4 weeks | HLPCQ, STAI, PSS, BFI, BDI | IL-1β, IL-10, immunoglobulin A, EPI, NE, DA, 5-HT, CRH, ACTH, CORT | Immunophysiological bioregulation; dopamine increase | ↑sleep efficiency, ↑perceived health, ↓stress/anxiety, ↓depression |
| Heidarzadeh-Rad et al., 2020 [79] | RDBPCT | Adults, n = 78 | MDD | L. helveticus R0052 B. longum R0175 | Lallemand Health Solutions (Mirabel, QC, Canada) | Freeze-dried live bacteria (1 × 1010 CFU/day), powder sachet/8 weeks | BDI-II | BDNF | Serum BDNF level increase | ↓depression symptoms, ↑BDNF levels, ↓BDI scores |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Śliwka, A.; Polak-Berecka, M.; Zdybel, K.; Zelek-Molik, A.; Waśko, A. Psychobiotics in Depression: Sources, Metabolites, and Treatment—A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132139
Śliwka A, Polak-Berecka M, Zdybel K, Zelek-Molik A, Waśko A. Psychobiotics in Depression: Sources, Metabolites, and Treatment—A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132139
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚliwka, Angelika, Magdalena Polak-Berecka, Kinga Zdybel, Agnieszka Zelek-Molik, and Adam Waśko. 2025. "Psychobiotics in Depression: Sources, Metabolites, and Treatment—A Systematic Review" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132139
APA StyleŚliwka, A., Polak-Berecka, M., Zdybel, K., Zelek-Molik, A., & Waśko, A. (2025). Psychobiotics in Depression: Sources, Metabolites, and Treatment—A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 17(13), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132139









