Chrononutrition and Energy Balance: How Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms Shape Weight Regulation and Metabolic Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Foundations of Chronobiology and Circadian Rhythms
2.1. The Interplay Between Hormonal Modulation and Circadian Rhythms
2.2. Synchronization of Biological Clocks: Entrainment Mechanisms
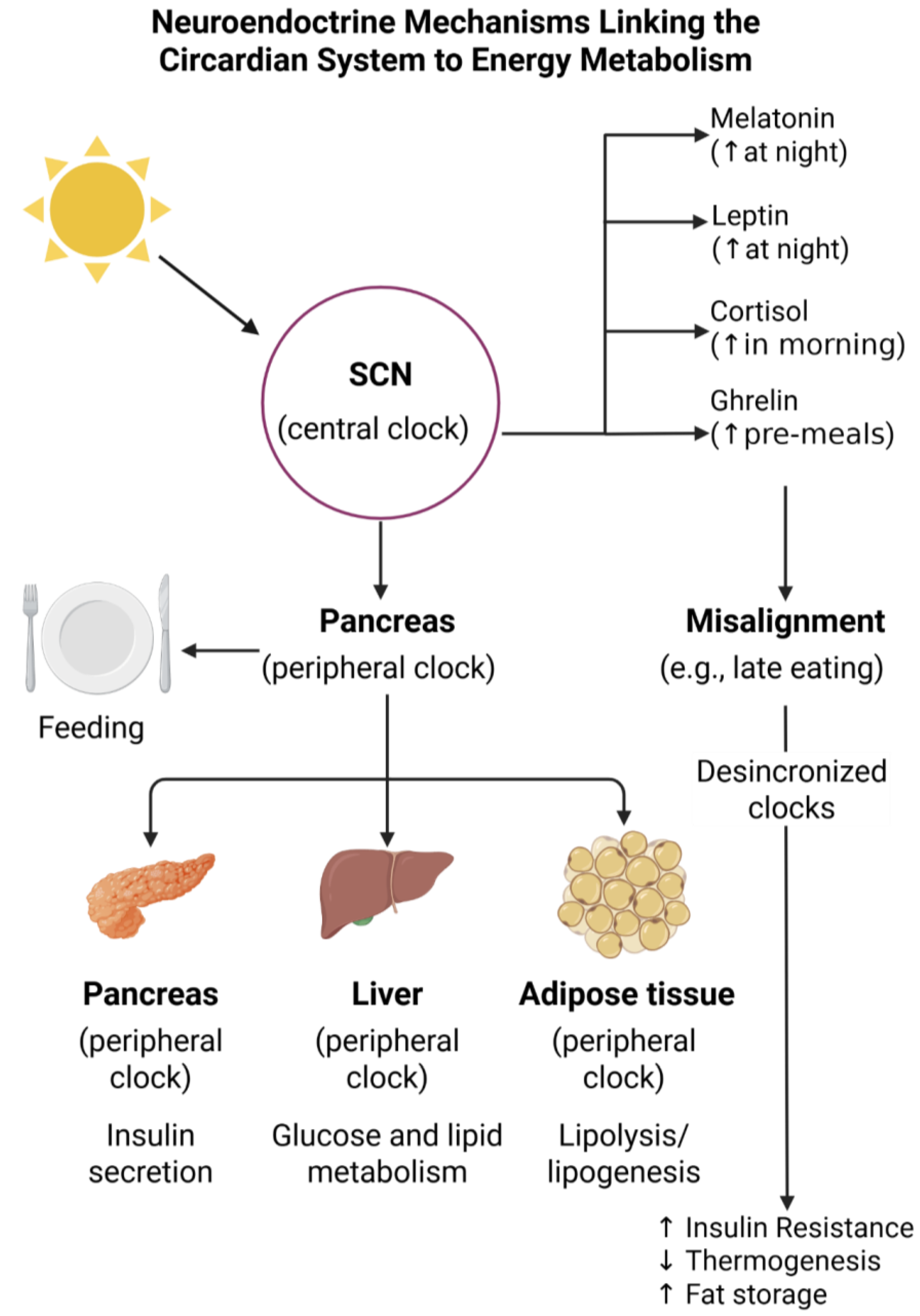
3. Mechanisms Linking Circadian Rhythms to Energy Metabolism
3.1. Regulation of Appetite and Satiety
3.2. Impact on Insulin Sensitivity, Glucose Metabolism, and Lipid Storage
3.3. Thermogenesis and Diurnal Variations in Energy Expenditure
3.4. Hypothalamic Integration of Peripheral and Central Signals
4. Meal Timing and Metabolic Outcomes
4.1. Early Versus Late Eating Patterns: Insights from Human and Animal Studies
4.2. Effects of Breakfast Skipping, Late-Night Eating, and TRE Impact on Weight Regulation, Fat Distribution, and Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors
4.3. Macronutrient Timing
4.4. Carbohydrate Timing
4.5. Protein Timing
5. TRE and Intermittent Fasting
5.1. Evidence from Clinical Trials
5.2. Mechanistic Insights: Autophagy, Insulin Sensitivity, and Mitochondrial Function
5.3. Benefits and Challenges in Long-Term Adherence
6. Chrononutrition in Special Populations
6.1. Shift Workers and Metabolic Disruption
6.2. Adolescents and Meal-Timing Irregularities
6.3. Elderly Individuals and Altered Circadian Rhythms
6.4. Gender-Specific Considerations
7. Influence of Lifestyle Factors on Circadian Health
7.1. Sleep Quality and Quantity
7.2. Physical Activity Timing
7.3. Stress and Social Rhythms
7.4. Light Exposure (Natural vs. Artificial)
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Román-Galeano, N.M.; Verde, L.; Annunziata, G.; Marchetti, M.; Matos, A.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Reytor-González, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; et al. Targeting Cytokine Dysregulation in Psoriasis: The Role of Dietary Interventions in Modulating the Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reytor-González, C.; Annunziata, G.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Morales-López, T.; Basantes-Tituaña, C.; Fascì-Spurio, F.; Verde, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; et al. Endocrinologist’s crucial role in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A comprehensive review. Minerva Endocrinol. 2025, 50, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Pugliese, G.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; Carignano, M.D.L.A.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Vitamin D in obesity and obesity-related diseases: An overview. Minerva Endocrinol. 2021, 46, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias-Toral, E.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; de Los Angeles Carignano, M.; Rodriguez-Veintimilla, D.; Alvarado-Aguilera, I.; Bautista-Litardo, N. Polycystic ovary syndrome and obesity: Clinical aspects and nutritional management. Minerva Endocrinol. 2022, 47, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias-Toral, E.; Ceriani, F.; Carriel-Mancilla, J.; Ramos, A. Editorial: Understanding obesity to determine the best therapeutic option: From lifestyle interventions to therapies. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1560942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Annunziata, G.; Verde, L.; Fascì-Spurio, F.; Reytor-González, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L. Nutritional Strategies for Battling Obesity-Linked Liver Disease: The Role of Medical Nutritional Therapy in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2025, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cardenas, D. Editorial: Environmental factors implicated in obesity. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1171507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, R.; Chapela, S.P.; Álvarez-Córdova, L.; Bautista-Valarezo, E.; Sarmiento-Andrade, Y.; Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Sarno, G. Epigenetics in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus: New Insights. Nutrients 2023, 15, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reytor-González, C.; Zambrano, A.K.; Frias-Toral, E.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Simancas-Racines, D. Mediterranean diet and breast cancer: A narrative review. Medwave 2025, 25, e3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism. 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, S.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Stierman, B.; Ogden, C.L. Obesity and Severe Obesity Prevalence in Adults: United States, August 2021-August 2023. NCHS Data Brief 2024, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Zanata, I.; Barrea, L.; Cozzolino, A.; Filice, E.; Messina, E.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A. A practical nutritional guideline to manage neuroendocrine neoplasms through chronotype and sleep. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 7546–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docimo, A.; Verde, L.; Barrea, L.; Vetrani, C.; Memoli, P.; Accardo, G.; Colella, C.; Nosso, G.; Orio, M.; Renzullo, A.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes: Also a “Clock Matter”? Nutrients 2023, 15, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reytor-González, C.; Zambrano, A.K.; Montalvan, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Simancas-Racines, A.; Simancas-Racines, D. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and its association with gastric cancer: Health benefits from a Planeterranean perspective. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, A.K.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Frias-Toral, E.; Simancas-Racines, D. Impact of fundamental components of the Mediterranean diet on the microbiota composition in blood pressure regulation. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet: Any Association with NAFLD? Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrani, C.; Verde, L.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G. The Mediterranean Diet: Effects on Insulin Resistance and Secretion in Individuals with Overweight or Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Scazzina, F.; Paternò Castello, C.; Giampieri, F.; Quiles, J.L.; Briones Urbano, M.; Battino, M.; Galvano, F.; Iacoviello, L.; de Gaetano, G.; et al. Underrated aspects of a true Mediterranean diet: Understanding traditional features for worldwide application of a “Planeterranean” diet. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Sulu, C.; Katsiki, N.; Hassapidou, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cucalón, G.; Pazderska, A.; Yumuk, V.D.; Colao, A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-related Disorders: What is the Evidence? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, R.; Bautista-Valarezo, E.; Matos, A.; Calderón, P.; Fascì-Spurio, F.; Castano-Jimenez, J.; Zambrano-Villacres, R.; Sarno, G.; Frias-Toral, E. Obesity and nutritional strategies: Advancing prevention and management through evidence-based approaches. Food Agric. Immunol. 2025, 36, 2491597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reytor-González, C.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Castano Jimenez, J.; Román-Galeano, N.M.; Sarno, G.; Frias-Toral, E. Harnessing nutrition to combat MASLD: A comprehensive guide to food-based therapeutic strategies. Food Agric. Immunol. 2025, 36, 2496499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela, S.; Locatelli, J.; Saettone, F.; Forte, C.A.; Memoli, P.; Cucalon, G.; Ceriani, F.; Sarno, G.; Coppola, L.; Frias-Toral, E. The role of nutrition in cancer prevention: The effect of dietary patterns, bioactive compounds, and metabolic pathways on cancer development. Food Agric. Immunol. 2025, 36, 2490003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, A.K.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Frias-Toral, E.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Chapela, S.; Montalván, M.; Sarno, G.; et al. The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapela, S.P.; Simancas-Racines, A.; Ceriani, F.; Martinuzzi, A.L.N.; Russo, M.P.; Zambrano, A.K.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Verde, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Katsanos, C.S.; et al. Obesity and Obesity-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Any Potential Role for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD)? Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Camajani, E.; Verde, L.; Elce, A.; Frias-Toral, E.; Ceriani, F.; Cucalón, G.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; El Ghoch, M.; et al. Clinical and nutritional management of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in patients with psoriasis and obesity: A practical guide for the nutritionist. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10775–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Tuccinardi, D.; Moriconi, E.; Di Renzo, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Could ketogenic diet “starve” cancer? Emerging evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Farooqi, I.S.; Friedman, J.M.; Klein, S.; Loos, R.J.F.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M.; Ryan, D.H.; et al. The energy balance model of obesity: Beyond calories in, calories out. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Kreouzi, M.; Pappas, A.; Nikolaou, M. Beyond Calories: Individual Metabolic and Hormonal Adaptations Driving Variability in Weight Management—A State-of-the-Art Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, F.; Al-Najim, W.; le Roux, C.W. Health Benefits Beyond the Scale: The Role of Diet and Nutrition During Weight Loss Programmes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneiri, L.L.; Adams, C.G.; Garcia-Jackson, B.; Koecher, K.; Wilcox, M.L.; Maki, K.C. Effects of Varying Protein Amounts and Types on Diet-Induced Thermogenesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, A.; Egorova, E.S.; Dzitkowska-Zabielska, M.; Ahmetov, I.I. Genetics of Exercise and Diet-Induced Fat Loss Efficiency: A Systematic Review. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2024, 23, 236–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, O.E.; Kyeremah, E.B.; Sears, D.D.; St-Onge, M.P.; Makarem, N. Chrononutrition and Cardiometabolic Health: An Overview of Epidemiological Evidence and Key Future Research Directions. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verde, L.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G. Chrononutrition in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: A narrative review. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2024, 40, e3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G. The timing of energy intake. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2024, 83, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Docimo, A.; Chirico, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G. How Fast Do “Owls” and “Larks” Eat? Nutrients 2023, 15, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiani, F.; Di Marino, D.; Romagnoli, A.; Travelli, C.; Voltan, D.; Mannelli, L.D.C.; Racchi, M.; Govoni, S.; Lanni, C. Molecular regulations of circadian rhythm and implications for physiology and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, T.; Smith, J.G.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P.; Benitah, S.A. Circadian clock communication during homeostasis and ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2025, 26, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, C.; Docimo, A.; Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Cernea, S.; Sojat, A.S.; Marina, L.V.; Docimo, G.; Colao, A.; Dentice, M.; et al. “Time” for obesity-related cancer: The role of the circadian rhythm in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 91, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzelou, M.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Psara, E.; Voulgaridou, G.; Pavlidou, E.; Androutsos, O.; Giaginis, C. Chrononutrition in the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Disorders: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinna, L.; Verde, L.; Di Tolla, M.F.; Barrea, L.; Parascandolo, A.; D’Alterio, F.; Colao, A.; Formisano, P.; D’Esposito, V.; Muscogiuri, G. Chronodisruption enhances inflammatory cytokine release from visceral adipose tissue in obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Vahlhaus, J.; Pivovarova-Ramich, O. Meal timing and its role in obesity and associated diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Currenti, W.; Ferri, R.; Lanza, G.; Caraci, F.; Frias-Toral, E.; Guglielmetti, M.; Ferraris, C.; Lipari, V.; Carvajal Altamiranda, S.; et al. Chronotype and Cancer: Emerging Relation Between Chrononutrition and Oncology from Human Studies. Nutrients 2025, 17, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, J.; Vitet, H.; Truong, V.H.; Ananthasubramaniam, B. The role of the multiplicity of circadian clocks in mammalian systems. Sleep Med. 2025, 131, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.; Silver, R. The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and the Circadian Timekeeping System of the Body; Pfaff, D.W., Volkow, N.D., Rubenstein, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–49. ISBN 978-1-4614-6434-1. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.J. Gastrointestinal vagal afferents and food intake: Relevance of circadian rhythms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reick, M.; Garcia, J.A.; Dudley, C.; McKnight, S.L. NPAS2: An analog of clock operative in the mammalian forebrain. Science 2001, 293, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gekakis, N.; Staknis, D.; Nguyen, H.B.; Davis, F.C.; Wilsbacher, L.D.; King, D.P.; Takahashi, J.S.; Weitz, C.J. Role of the CLOCK Protein in the Mammalian Circadian Mechanism. Science 1998, 280, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunger, M.K.; Wilsbacher, L.D.; Moran, S.M.; Clendenin, C.; Radcliffe, L.A.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Simon, M.C.; Takahashi, J.S.; Bradfield, C.A. Mop3 Is an Essential Component of the Master Circadian Pacemaker in Mammals. Cell 2000, 103, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, V.G. Rhythms in Remodeling: Posttranslational Regulation of Bone by the Circadian Clock. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnocchi, D.; Bruscalupi, G. Circadian Rhythms and Hormonal Homeostasis: Pathophysiological Implications. Biology 2017, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.-M.; Schmidt, C.X.; Brockmann, R.M.; Oster, H. Circadian regulation of endocrine systems. Auton. Neurosci. 2019, 216, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Fernández, O.H.; Liu, J.A.; Nelson, R.J. Circadian Rhythms Disrupted by Light at Night and Mistimed Food Intake Alter Hormonal Rhythms and Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykan, U.; Güvel, M.C.; Paykal, G.; Uluoglu, C. Neuropharmacologic modulation of the melatonergic system. Explor. Neurosci. 2023, 2, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, F.G.D.; Cipolla-Neto, J. A brief review about melatonin, a pineal hormone. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 62, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadi, A.; Andreadi, S.; Todaro, F.; Ippoliti, L.; Bellia, A.; Magrini, A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Lauro, D. Modified Cortisol Circadian Rhythm: The Hidden Toll of Night-Shift Work. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, R.L.; Chun, L.E.; Hartsock, M.J.; Woodruff, E.R. Glucocorticoid hormones are both a major circadian signal and major stress signal. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2017, 49, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Debono, M. Replication of cortisol circadian rhythm: New advances in hydrocortisone replacement therapy. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 1, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Wang, X.; Geng, Z.; Wan, M.; Hao, J.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, Z. Long non-coding RNA LncCplx2 regulates glucose homeostasis and pancreatic β cell function. Mol. Metab. 2024, 80, 101878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, N.; Doucette, C.A. Circadian Regulation of the Pancreatic Beta Cell. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. Circadian System and Glucose Metabolism: Implications for Physiology and Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Jung, I.; Park, S.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, N.H.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, K.M.; et al. Attention to Innate Circadian Rhythm and the Impact of Its Disruption on Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick-Collins, L.C.; Morgan, P.J.; Johnstone, A.M. Mealtime: A circadian disruptor and determinant of energy balance? J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 32, e12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadipour, M.; Depoortere, I. The function of gastrointestinal hormones in obesity—Implications for the regulation of energy intake. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.D. Appetite Regulation: Hormones, Peptides, and Neurotransmitters and Their Role in Obesity. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2019, 13, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.M.; Arnaldo, L.; Milhomem, L.P.; Aguiar, S.S.; Franco, O.L. The intricate relationship between circadian rhythms and gastrointestinal peptides in obesity. Peptides 2025, 185, 171356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Drunen, R.; Eckel-Mahan, K. Circadian Rhythms of the Hypothalamus: From Function to Physiology. Clocks Sleep 2021, 3, 189–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmal, C.; Herzel, H.; Myung, J. Clocks in the Wild: Entrainment to Natural Light. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zele, A.J.; Feigl, B.; Smith, S.S.; Markwell, E.L.; Dryer, S. The circadian response of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.G.; Hughes, S.; Peirson, S.N. Circadian Photoentrainment in Mice and Humans. Biology 2020, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, A.L.; Bechtold, D.A. The metabolic significance of peripheral tissue clocks. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.G.F.; de Araujo, L.D.; Roa, S.L.R.; Bueno, A.C.; Uchoa, E.T.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Moreira, A.C.; Elias, L.L.K.; de Castro, M.; Martins, C.S. Restricted feeding modulates peripheral clocks and nutrient sensing pathways in rats. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 65, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manella, G.; Sabath, E.; Aviram, R.; Dandavate, V.; Ezagouri, S.; Golik, M.; Adamovich, Y.; Asher, G. The liver-clock coordinates rhythmicity of peripheral tissues in response to feeding. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmers, C.; Gill, S.; DiTacchio, L.; Pulivarthy, S.R.; Le, H.D.; Panda, S. Time of feeding and the intrinsic circadian clock drive rhythms in hepatic gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21453–21458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.; Mangini, C.; Domenie, E.D.; Zarantonello, L.; Montagnese, S. Circadian rhythms and the liver. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickel, L.; Sung, H.-K. Feeding Rhythms and the Circadian Regulation of Metabolism. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Tang, Q.; Chen, G.; Xie, M.; Yu, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L. New insights into the circadian rhythm and its related diseases. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Tahara, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Haraguchi, A.; Shibata, S. Entrainment of mouse peripheral circadian clocks to <24 h feeding/fasting cycles under 24 h light/dark conditions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Noya, S.B.; Sehgal, A. The microbiome interacts with the circadian clock and dietary composition to regulate metabolite cycling in the gut. BioExiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rios, A.; Ordovas, J.M. Chronodisruption and cardiovascular disease. Clin. Investig. Arterioscler. Publ. Of. Soc. Esp. Arterioscler. 2022, 34 (Suppl. S1), S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiz Erim, S.; Sert, H. The relationship between chronotype and obesity: A systematic review. Chronobiol. Int. 2023, 40, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Ceriani, F.; Chavez, A.O.; El Ghoch, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Mehta, R.J.; Mendez, V.; Paschou, S.A.; et al. Nutritional guidelines for the management of insulin resistance. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6947–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, A.; Gundlach, A.L.; Hess, G.; Lewandowski, M.H. Interactions of circadian rhythmicity, stress and orexigenic neuropeptide systems: Implications for food intake control. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.P.; Bagnasco, M.; Otukonyong, E.E.; Dube, M.G.; Kalra, P.S. Rhythmic, reciprocal ghrelin and leptin signaling: New insight in the development of obesity. Regul. Pept. 2003, 111, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosjean, E.; Simonneaux, V.; Challet, E. Reciprocal Interactions between Circadian Clocks, Food Intake, and Energy Metabolism. Biology 2023, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blancas-Velazquez, A.; Mendoza, J.; Garcia, A.N.; la Fleur, S.E. Diet-induced obesity and circadian disruption of feeding behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallop, M.R.; Tobin, S.Y.; Chaix, A. Finding balance: Understanding the energetics of time-restricted feeding in mice. Obesity 2023, 31 (Suppl. S1), 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begemann, K.; Heyde, I.; Witt, P.; Inderhees, J.; Leinweber, B.; Koch, C.E.; Jöhren, O.; Oelkrug, R.; Liskiewicz, A.; Müller, T.D.; et al. Rest phase snacking increases energy resorption and weight gain in male mice. Mol. Metab. 2023, 69, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arble, D.M.; Bass, J.; Laposky, A.D.; Vitaterna, M.H.; Turek, F.W. Circadian timing of food intake contributes to weight gain. Obesity 2009, 17, 2100–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M. The Human Energy Balance: Uncovering the Hidden Variables of Obesity. Diseases 2025, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggiogalle, E.; Jamshed, H.; Peterson, C.M. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans. Metabolism 2018, 84, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Tait, C.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Catalano, C.; Rustgi, V.K. Circadian Rhythms, the Gut Microbiome, and Metabolic Disorders. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, L. Circadian rhythm, glucose metabolism and diabetic complications: The role of glucokinase and the enlightenment on future treatment. Front. Physiol. 2025, 16, 1537231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Bonham, M.P.; Nguo, K.; Huggins, C.E. Glycaemic response at night is improved after eating a high protein meal compared with a standard meal: A cross-over study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, G.K.W.; Huggins, C.E.; Ware, R.S.; Bonham, M.P. Time of day difference in postprandial glucose and insulin responses: Systematic review and meta-analysis of acute postprandial studies. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, I.C.; Qian, J.; Adler, G.K.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. Impact of circadian disruption on glucose metabolism: Implications for type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Wong, F.S.; Pearson, J.A. Circadian rhythms and pancreas physiology: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 920261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudet, V. Nuclear receptors: At the heart of the biological crosstalk between metabolism and circadian rhythm. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 3, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, A.L.; Ray, D.W. Circadian Clock Regulation of Hepatic Energy Metabolism Regulatory Circuits. Biology 2019, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Feng, T.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, X. Circadian clock and lipid metabolism disorders: A potential therapeutic strategy for cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1292011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A. The Influence of Physical Exercise, Ketogenic Diet, and Time-Restricted Eating on De Novo Lipogenesis: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Shen, M.; Kuang, L.; Yang, K.; Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. SIRT1/SREBPs-mediated regulation of lipid metabolism. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Livelo, C.; Melkani, G.C. Time-restricted feeding regulates lipid metabolism under metabolic challenges. Bioessays 2023, 45, e2300157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrenko, V.; Sinturel, F.; Riezman, H.; Dibner, C. Lipid metabolism around the body clocks. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 91, 101235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovich, Y.; Rousso-Noori, L.; Zwighaft, Z.; Neufeld-Cohen, A.; Golik, M.; Kraut-Cohen, J.; Wang, M.; Han, X.; Asher, G. Circadian clocks and feeding time regulate the oscillations and levels of hepatic triglycerides. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Rust, B.M.; Palmer, D.G. Time-restricted feeding restores metabolic flexibility in adult mice with excess adiposity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1340735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena, C.; Flavia, L.; Davide, M.; Mariaignazia, C.; Chandra, M.; Orietta, G.; Elena, G.; Mikiko, W.; Stefania, M.; Lucio, G.; et al. Eating behavior patterns, metabolic parameters and circulating oxytocin levels in patients with obesity: An exploratory study. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2025, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, N.B.; Teixeira, G.P.; Rinaldi, A.E.M.; Azeredo, C.M.; Crispim, C.A. Late meal intake is associated with abdominal obesity and metabolic disorders related to metabolic syndrome: A chrononutrition approach using data from NHANES 2015–2018. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.T.; Batterham, A.M.; Atkinson, G.; Thompson, D. Perspective: Is the Response of Human Energy Expenditure to Increased Physical Activity Additive or Constrained? Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Careau, V.; Halsey, L.G.; Pontzer, H.; Ainslie, P.N.; Andersen, L.F.; Anderson, L.J.; Arab, L.; Baddou, I.; Bedu-Addo, K.; Blaak, E.E.; et al. Energy compensation and adiposity in humans. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 4659–4666.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp, K.R. Diet induced thermogenesis. Nutr. Metab. 2004, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitting, K.-M.; Vujovic, N.; Yuan, R.K.; Isherwood, C.M.; Medina, J.E.; Wang, W.; Buxton, O.M.; Williams, J.S.; Czeisler, C.A.; Duffy, J.F. Human Resting Energy Expenditure Varies with Circadian Phase. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3685–3690.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.; Leung, G.K.W.; Jong, J.; Coates, A.M.; Davis, R.; Blair, M.; Huggins, C.E.; Dorrian, J.; Banks, S.; Kellow, N.J.; et al. The Impact of Time of Day on Energy Expenditure: Implications for Long-Term Energy Balance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refinetti, R. Circadian rhythmicity of body temperature and metabolism. Temperature 2020, 7, 321–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Herzog, N.; Janka, S.; Baumann, T.; Kistenmacher, A.; Oltmanns, K.M. Twice as High Diet-Induced Thermogenesis After Breakfast vs Dinner on High-Calorie as Well as Low-Calorie Meals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e211–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.D.M.; Cade, J.E.; Grant, P.J.; Hardie, L.J. Nutrition and the circadian system. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Matz, Y.; Landau, Z.; Rosenblum, R.C.; Twito, O.; Wainstein, J.; Tsameret, S. Interaction Between Early Meals (Big-Breakfast Diet), Clock Gene mRNA Expression, and Gut Microbiome to Regulate Weight Loss and Glucose Metabolism in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, M.; Phillips, C.J.C.; Shi, B. Thermogenesis and Energy Metabolism in Brown Adipose Tissue in Animals Experiencing Cold Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuko, O.O.; Saito, M. Brown fat as a regulator of systemic metabolism beyond thermogenesis. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Okamatsu-Ogura, Y. Thermogenic Brown Fat in Humans: Implications in Energy Homeostasis, Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. World J. Mens Health 2023, 41, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, R.; Flak, J.N. Hypothalamic neural circuits regulating energy expenditure. Vitam. Horm. 2025, 127, 79–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.T.; Park, S.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.W.; Kwon, O. Hypothalamic control of energy expenditure and thermogenesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Lee, N.J.; Ip, C.K.; Enriquez, R.; Tasan, R.; Zhang, L.; Herzog, H. Agrp-negative arcuate NPY neurons drive feeding under positive energy balance via altering leptin responsiveness in POMC neurons. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 979–995.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, M.S.; Benchoula, K.; Serpell, C.J.; Hwa, W.E. AgRP/NPY and POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus and their potential role in treatment of obesity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 915, 174611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jais, A.; Brüning, J.C. Arcuate Nucleus-Dependent Regulation of Metabolism-Pathways to Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begemann, K.; Rawashdeh, O.; Olejniczak, I.; Pilorz, V.; de Assis, L.V.M.; Osorio-Mendoza, J.; Oster, H. Endocrine regulation of circadian rhythms. npj Biol. Timing Sleep 2025, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsbeek, A.; Scheer, F.A.; Perreau-Lenz, S.; La Fleur, S.E.; Yi, C.-X.; Fliers, E.; Buijs, R.M. Circadian disruption and SCN control of energy metabolism. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1412–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starnes, A.N.; Jones, J.R. Inputs and Outputs of the Mammalian Circadian Clock. Biology 2023, 12, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaHammam, A.S.; Pirzada, A. Timing Matters: The Interplay between Early Mealtime, Circadian Rhythms, Gene Expression, Circadian Hormones, and Metabolism—A Narrative Review. Clocks Sleep 2023, 5, 507–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis, L.V.M.; Oster, H. The circadian clock and metabolic homeostasis: Entangled networks. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4563–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.M.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Circadian blueprint of metabolic pathways in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plano, S.A.; Casiraghi, L.P.; García Moro, P.; Paladino, N.; Golombek, D.A.; Chiesa, J.J. Circadian and Metabolic Effects of Light: Implications in Weight Homeostasis and Health. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yi, P.; Liu, F. The Effect of Early Time-Restricted Eating vs Later Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss and Metabolic Health. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Ueda, T. Early Time-Restricted Eating Improves Weight Loss While Preserving Muscle: An 8-Week Trial in Young Women. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshed, H.; Steger, F.L.; Bryan, D.R.; Richman, J.S.; Warriner, A.H.; Hanick, C.J.; Martin, C.K.; Salvy, S.-J.; Peterson, C.M. Effectiveness of Early Time-Restricted Eating for Weight Loss, Fat Loss, and Cardiometabolic Health in Adults With Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Goede, P.; Foppen, E.; Ritsema, W.I.G.R.; Korpel, N.L.; Yi, C.-X.; Kalsbeek, A. Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Glucose Tolerance in Rats, but Only When in Line With the Circadian Timing System. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, D. Impacts of time-restricted feeding on middle-aged and old mice with obesity. J. Physiol. 2024, 22, 6109–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibney, M.J.; Barr, S.I.; Bellisle, F.; Drewnowski, A.; Fagt, S.; Livingstone, B.; Masset, G.; Varela Moreiras, G.; Moreno, L.A.; Smith, J.; et al. Breakfast in Human Nutrition: The International Breakfast Research Initiative. Nutrients 2018, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtgil, S.; Pekcan, A.G. Determination of breakfast habits, food pattern and quality among adults. Med. J. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 16, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Zhong, Y.; Peng, Y.; Qian, C. Breakfast skipping and traits of cardiometabolic health: A mendelian randomization study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 59, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscemi, C.; Randazzo, C.; Barile, A.M.; Caldarella, R.; Murro, I.; Caruso, R.; Colombrita, P.; Lombardo, M.; De Pergola, G.; Buscemi, S. The impact of breakfast skipping on plasma glucose levels in non-diabetic individuals: Gender-based differences and implications. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 76, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Aprano, S.; Castellucci, B.; Pugliese, G.; Rodriguez-Veintimilla, D.; Vitale, G.; Gentilini, D.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S.; et al. The clock diet: A practical nutritional guide to manage obesity through chrononutrition. Minerva Med. 2022, 113, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballon, A.; Neuenschwander, M.; Schlesinger, S. Breakfast Skipping Is Associated with Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes among Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofori-Asenso, R.; Owen, A.J.; Liew, D. Skipping Breakfast and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Death: A Systematic Review of Prospective Cohort Studies in Primary Prevention Settings. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujović, N.; Piron, M.J.; Qian, J.; Chellappa, S.L.; Nedeltcheva, A.; Barr, D.; Heng, S.W.; Kerlin, K.; Srivastav, S.; Wang, W.; et al. Late isocaloric eating increases hunger, decreases energy expenditure, and modifies metabolic pathways in adults with overweight and obesity. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1486–1498.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wu, L.; Jiang, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Zheng, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, Z. Late-Night Eating-Induced Physiological Dysregulation and Circadian Misalignment Are Accompanied by Microbial Dysbiosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e900867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zou, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X.; Tan, D.; Xiang, Q.; Yu, R. mTOR-mediated nutrient sensing and oxidative stress pathways regulate autophagy: A key mechanism for traditional Chinese medicine to improve diabetic kidney disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1578400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaix, A.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Melkani, G.C.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Eating to Prevent and Manage Chronic Metabolic Diseases. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2019, 39, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes-Alves, D.; Teixeira, G.P.; Guimarães, K.C.; Crispim, C.A. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Time-Restricted Eating with and Without Caloric Restriction for Weight Loss. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adafer, R.; Messaadi, W.; Meddahi, M.; Patey, A.; Haderbache, A.; Bayen, S.; Messaadi, N. Food timing, circadian rhythm and chrononutrition: A systematic review of time-restricted eating’s effects on human health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarul Zaman, M.; Teng, N.I.M.F.; Kasim, S.S.; Juliana, N.; Alshawsh, M.A. Effects of time-restricted eating with different eating duration on anthropometrics and cardiometabolic health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Cardiol. 2023, 15, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.D.; Guimarães, K.C.; Oliveira, R.A.; Rosa, D.A.; Crispim, C.A. Time-restricted eating increases hunger in adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Nutr. Res. 2025, 138, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, H.M.; Sefidmooye Azar, P.; Kang, M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Wijayatunga, N.N. Effects of time-restricted eating with exercise on body composition in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyama, Y.; Takeshita, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Sako, S.; Kanamori, T.; Takamura, T. Distinct effects of carbohydrate ingestion timing on glucose fluctuation and energy metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled study. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Almoosawi, S.; Palla, L. Day-Time Patterns of Carbohydrate Intake in Adults by Non-Parametric Multi-Level Latent Class Analysis-Results from the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey (2008/09–2015/16). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, D.R.; Buosi, W.; Fyfe, C.L.; Horgan, G.W.; Manios, Y.; Androutsos, O.; Giannopoulou, A.; Finlayson, G.; Beaulieu, K.; Meek, C.L.; et al. Appetite control across the lifecourse: The acute impact of breakfast drink quantity and protein content. the full4health project. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, E.A.; Colenso-Semple, L.; McKellar, S.R.; Yau, T.; Ali, M.U.; Fitzpatrick-Lewis, D.; Sherifali, D.; Gaudichon, C.; Tomé, D.; Atherton, P.J.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of protein intake to support muscle mass and function in healthy adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, J.; Hillesheim, E.; Brennan, L. The Role of Protein Intake and its Timing on Body Composition and Muscle Function in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezpeleta, M.; Cienfuegos, S.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Gabel, K.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Varady, K.A. Time-restricted eating: Watching the clock to treat obesity. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, P.; O’Connor, S.G.; Heckman-Stoddard, B.M.; Sauter, E.R. Time-Restricted Feeding Studies and Possible Human Benefit. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2022, 6, pkac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, S.; Tabanelli, R.; Puca, S.; Calderone, V. Intermittent Fasting: Myths, Fakes and Truth on This Dietary Regimen Approach. Foods 2024, 13, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyildirim, C.; Uçar, A. An alternative approach to obesity treatment: Intermittent fasting. Minerva Endocrinol. 2023, 48, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K.; Pavlou, V.; Mulas, A.; Chakos, K.; McStay, M.; Wu, J.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; et al. Time-Restricted Eating Without Calorie Counting for Weight Loss in a Racially Diverse Population: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.G.; Boyd, P.; Bailey, C.P.; Shams-White, M.M.; Agurs-Collins, T.; Hall, K.; Reedy, J.; Sauter, E.R.; Czajkowski, S.M. Perspective: Time-Restricted Eating Compared with Caloric Restriction: Potential Facilitators and Barriers of Long-Term Weight Loss Maintenance. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, S.G.; Boyd, P.; Bailey, C.P.; Nebeling, L.; Reedy, J.; Czajkowski, S.M.; Shams-White, M.M. A qualitative exploration of facilitators and barriers of adherence to time-restricted eating. Appetite 2022, 178, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.L.; Hawley, N.A.; Mohr, A.E.; Hermer, J.; Ofori, E.; Yu, F.; Sears, D.D. Impact of Intermittent Fasting and/or Caloric Restriction on Aging-Related Outcomes in Adults: A Scoping Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wan, K.; Miyashita, M.; Ho, R.S.; Zheng, C.; Poon, E.T.; Wong, S.H. The Effect of Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Exercise on Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, H.S.J.; Ang, W.H.D.; Tan, Z.Y.A.; Chan, K.S.; Lau, Y. Umbrella review of time-restricted eating on weight loss, fasting blood glucose, and lipid profile. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 1180–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, X.-Y.; Gao, S.; Varady, K.A.; Forslund, S.K.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.-Y.; Cao, F.; Zou, B.-J.; Sun, M.-H.; et al. Intermittent fasting and health outcomes: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 70, 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patikorn, C.; Roubal, K.; Veettil, S.K.; Chandran, V.; Pham, T.; Lee, Y.Y.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Varady, K.A.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Intermittent Fasting and Obesity-Related Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2139558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, P.; Heilbronn, L.K. Time-Restricted Eating: Benefits, Mechanisms, and Challenges in Translation. iScience 2020, 23, 101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabkhizan, R.; Haiaty, S.; Moslehian, M.S.; Bazmani, A.; Sadeghsoltani, F.; Saghaei Bagheri, H.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Sakhinia, E. The Beneficial and Adverse Effects of Autophagic Response to Caloric Restriction and Fasting. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Persons, P.A.; Lorenzo, A.M.; Chaliki, S.S.; Bersoux, S. Time-Restricted Eating and Its Metabolic Benefits. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Laudisio, D.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Anti-Inflammatory Nutrients and Obesity-Associated Metabolic-Inflammation: State of the Art and Future Direction. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Vetrani, C.; Caprio, M.; El Ghoch, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Mehta, R.J.; Mendez, V.; Moriconi, E.; Paschou, S.A.; Pazderska, A.; et al. Nutritional management of type 2 diabetes in subjects with obesity: An international guideline for clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Guan, Y.; Wu, G.; Huang, J.; Wang, S. Time-restricted eating for patients with diabetes and prediabetes: A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1025919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, I.D.; Vassi, E.; Alvanou, M.; Angelakis, C.; Skaperda, Z.; Tekos, F.; Garikipati, V.N.S.; Spandidos, D.A.; Kouretas, D. The impact of diet upon mitochondrial physiology (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Islam, M.A.; Sehar, U.; Reddy, A.P.; Vijayan, M.; Reddy, P.H. Impact of diet and exercise on mitochondrial quality and mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 108, 102734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currenti, W.; Godos, J.; Castellano, S.; Caruso, G.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Grosso, G.; Galvano, F. Time-restricted feeding is associated with mental health in elderly Italian adults. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, M.A.; Gutierrez, N.R.; Laing, K.L.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Panda, S. Barriers to adherence in time-restricted eating clinical trials: An early preliminary review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1075744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, K.; Cherrin, C.; Meires, J. Intermittent Fasting: Exploring Approaches, Benefits, and Implications for Health and Weight Management. J. Nurse Pract. 2024, 20, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, L.A.; Ronnekleiv-Kelly, S.M.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Bradfield, C.A.; Malecki, K.M. Circadian disruption, clock genes, and metabolic health. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e170998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, M.C.B.; Senger, M.B.; Schnorr, C.C.; Ehlert, L.R.; Rodrigues, T.d.C. Effect of night-shift work on cortisol circadian rhythm and melatonin levels. Sleep Sci. 2022, 15, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, N.A.S.M.; Juliana, N.; Teng, N.I.M.F.; Azmani, S.; Das, S.; Effendy, N. Consequences of circadian disruption in shift workers on chrononutrition and their psychosocial well-being. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, B.P.; Soehner, A.M.; Clark, D.B. Sleep and circadian contributions to adolescent alcohol use disorder. Alcohol 2015, 49, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, M.; Kooij, J.J.S.; Coogan, A.N. Review: Identification and Management of Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders as a Transdiagnostic Feature in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 60, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.R.; Neves, M.E.A.; Gorgulho, B.M.; Souza, A.M.; Nogueira, P.S.; Ferreira, M.G.; Rodrigues, P.R.M. Breakfast skipping and cardiometabolic risk factors in adolescents: Systematic review. Rev. Saude Publica 2021, 55, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Barrea, L.; Vetrani, C.; Frias-Toral, E.; Chapela, S.P.; Jayawardena, R.; de Alteriis, G.; Docimo, A.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; et al. Chronotype and Sleep Quality in Obesity: How Do They Change After Menopause? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Grosso, G.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Lanza, G.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Caruso, G.; Castellano, S. Mediterranean diet, mental health, cognitive status, quality of life, and successful aging in southern Italian older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 175, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, K.; Pivovarova-Ramich, O. Meal Timing, Aging, and Metabolic Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.L.; Rosatto, N.; Marzullo, P.; Bellan, M. Circadian variations in the elderly: A scoping review. Chronobiol. Int. 2024, 41, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Barrea, L.; Docimo, A.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Chronotype as a predictor of weight loss and body composition improvements in women with overweight or obesity undergoing a very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD). Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, R.; Qian, J.; Chellappa, S.L. Sex differences in sleep, circadian rhythms, and metabolism: Implications for precision medicine. Sleep Med. Rev. 2024, 75, 101926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; He, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, G.; Gong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Liang, T.; Guo, L. Decoding Multifaceted Roles of Sleep-Related Genes as Molecular Bridges in Chronic Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Hirpara, P.; Jha, H.; Thaker, R.; Patel, J.; Momin, A.S. Exploring the Role of Circadian Rhythms in Sleep and Recovery: A Review Article. Cureus 2024, 16, e61568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Can the ketogenic diet improve our dreams? Effect of very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) on sleep quality. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, J.; Rosi, A.; Scazzina, F.; Bonifaz, M.A.T.; Giampieri, F.; Abdelkarim, O.; Ammar, A.; Aly, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Pons, J.; et al. Diet, Eating Habits, and Lifestyle Factors Associated with Adequate Sleep Duration in Children and Adolescents Living in 5 Mediterranean Countries: The DELICIOUS Project. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Pugliese, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Napolitano, B.; Laudisio, D.; Aprano, S.; Ceriani, F.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Is there a relationship between the ketogenic diet and sleep disorders? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, F.; Muurlink, O.; Reid, N. Effects of caffeine on sleep quality and daytime functioning. Risk Manag. Health Policy 2018, 11, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Weakley, J.; Burke, L.M.; Roach, G.D.; Sargent, C.; Maniar, N.; Townshend, A.; Halson, S.L. The effect of caffeine on subsequent sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2023, 69, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Weakley, J.; Burke, L.M.; Roach, G.D.; Sargent, C.; Maniar, N.; Huynh, M.; Miller, D.J.; Townshend, A.; Halson, S.L. The effect of alcohol on subsequent sleep in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2025, 80, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Pugliese, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; El Ghoch, M.; Castellucci, B.; Chapela, S.P.; Carignano, M.d.L.A.; Laudisio, D.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; et al. Coffee consumption, health benefits and side effects: A narrative review and update for dietitians and nutritionists. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1238–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvani, M.I.; Werder, R.; Perret, C. The influence of blue light on sleep, performance and wellbeing in young adults: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 943108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlShareef, S.M. The impact of bedtime technology use on sleep quality and excessive daytime sleepiness in adults. Sleep Sci. 2022, 15, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Ma, C.; Wu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, G. Effects of exercise on circadian rhythms in humans. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1282357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Korf, H.W.; Kuffer, L.; Groß, J.V.; Erren, T.C. Exercise time cues (zeitgebers) for human circadian systems can foster health and improve performance: A systematic review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2018, 4, e000443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, K.L.; Morris, A.R.; Liu, A.C. Circadian Synchrony: Sleep, Nutrition, and Physical Activity. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2021, 1, 732243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.C.; Ungurianu, A.; Margină, D.M.; Grădinaru, D.; Dumitrescu, I.-B. Circadian Rhythms, Chrononutrition, Physical Training, and Redox Homeostasis-Molecular Mechanisms in Human Health. Cells 2024, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Ka, S.; Park, J. Effects of exercise timing and intensity on physiological circadian rhythm and sleep quality: A systematic review. Phys. Act. Nutr. 2023, 27, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.E.; Leinweber, B.; Drengberg, B.C.; Blaum, C.; Oster, H. Interaction between circadian rhythms and stress. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, C.; Garbazza, C.; Spitschan, M. Effects of light on human circadian rhythms, sleep and mood. Somnologie 2019, 23, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tähkämö, L.; Partonen, T.; Pesonen, A.-K. Systematic review of light exposure impact on human circadian rhythm. Chronobiol. Int. 2019, 36, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabuliene, L.; Milionis, C.; Koukkou, E.; Ilias, I. Exposure to artificial lighting at night: From an ecological challenge to a risk factor for glucose dysmetabolism and gestational diabetes? Narrative review. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2477304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Poggiogalle, E.; Barrea, L.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Garifalos, F.; Liccardi, A.; Pugliese, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Alviggi, C.; et al. Exposure to artificial light at night: A common link for obesity and cancer? Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 173, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Ryu, S.-H.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, E.; Choi, J. Effects of artificial light at night on human health: A literature review of observational and experimental studies applied to exposure assessment. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.K.; Bumgarner, J.R.; Nelson, R.J.; Fonken, L.K. Health Effects of Disrupted Circadian Rhythms by Artificial Light at Night. Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2023, 10, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Design and Population | TRE Intervention | Key Metabolic Outcomes | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Réda et al. (2020) [150] | Systematic review of 23 human studies | 4–12 h eating windows without caloric restriction | Average 3% reduction in body weight and fat loss; improved glucose, lipid levels, and blood pressure, independent of weight loss | Benefits attributed to circadian rhythm realignment |
| Kamarul Zaman et al. (2023) [151] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies with varying eating window durations | 8 h and >8 h windows | 8 h windows showed significant weight loss (−1.18 kg); >8 h windows showed no significant difference | Interventions longer than 12 weeks were associated with greater benefits |
| Silva et al. (2025) [152] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in overweight or obese adults | Restricted eating windows | Increased hunger; variable effects on weight loss and body composition | Highlights the need to consider adherence and impact on appetite |
| Hays et al. (2025) [153] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 studies with 338 participants combining TRE and exercise | TRE combined with exercise (aerobic, resistance, or both) | Significant reduction in fat mass (effect size: −0.20) and body fat percentage (effect size: −0.23); no significant changes in fat-free mass | TRE combined with exercise may be more effective for reducing fat while preserving muscle mass |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reytor-González, C.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Román-Galeano, N.M.; Annunziata, G.; Galasso, M.; Zambrano-Villacres, R.; Verde, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L. Chrononutrition and Energy Balance: How Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms Shape Weight Regulation and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132135
Reytor-González C, Simancas-Racines D, Román-Galeano NM, Annunziata G, Galasso M, Zambrano-Villacres R, Verde L, Muscogiuri G, Frias-Toral E, Barrea L. Chrononutrition and Energy Balance: How Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms Shape Weight Regulation and Metabolic Health. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132135
Chicago/Turabian StyleReytor-González, Claudia, Daniel Simancas-Racines, Náthaly Mercedes Román-Galeano, Giuseppe Annunziata, Martina Galasso, Raynier Zambrano-Villacres, Ludovica Verde, Giovanna Muscogiuri, Evelyn Frias-Toral, and Luigi Barrea. 2025. "Chrononutrition and Energy Balance: How Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms Shape Weight Regulation and Metabolic Health" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132135
APA StyleReytor-González, C., Simancas-Racines, D., Román-Galeano, N. M., Annunziata, G., Galasso, M., Zambrano-Villacres, R., Verde, L., Muscogiuri, G., Frias-Toral, E., & Barrea, L. (2025). Chrononutrition and Energy Balance: How Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms Shape Weight Regulation and Metabolic Health. Nutrients, 17(13), 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132135








