A Comprehensive Perspective on the Biological Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Periodic Short-Term Fasting: A Promising Strategy for Optimizing Metabolic Health
Highlights
- Fasting exerts multidimensional effects, including triggering metabolic switching and improving immune function, redox balance, the adipokine profile, and mTOR pathway regulation, among others.
- The modulation of the mTOR pathway through fasting shows promise, but there is a lack of consensus regarding its implementation; context-dependent regulation is crucial to avoid adverse effects and ensure safe clinical implementation.
- Despite its documented metabolic benefits, prolonged short-term fasting (PSTF) remains under-researched and may be associated with mild, self-limiting symptoms that require appropriate monitoring.
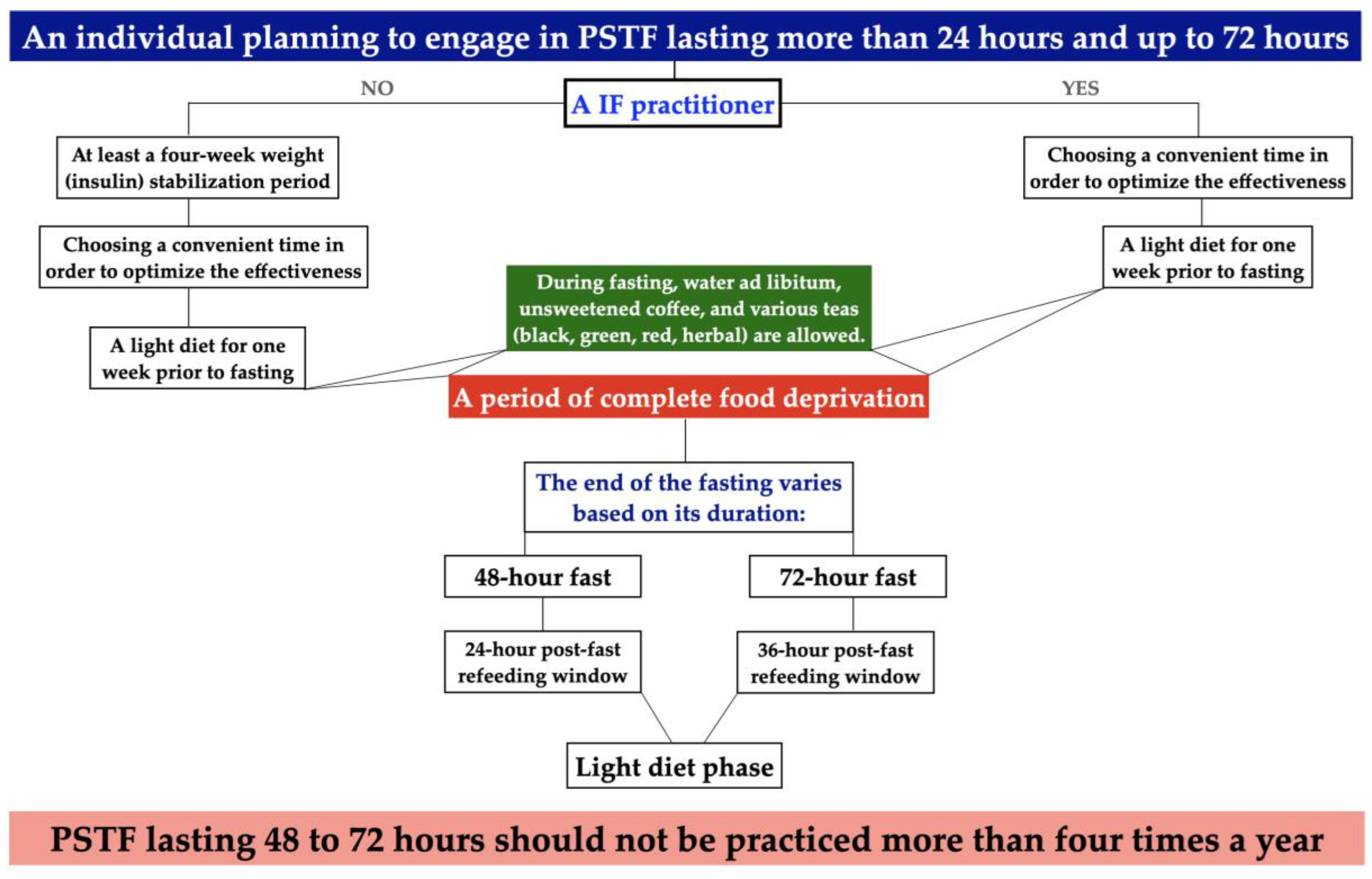
- A novel algorithm and protocol were developed to prepare healthy individuals for PSTF that lasted more than 24 hours and up to 72 hours.
- Combining fasting with individualized physical activity is essential to preserve skeletal muscle mass and enhance overall metabolic outcomes.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Impact of Various Fasting Regimens on Metabolic and Cellular Signaling Pathways
2.1. Overview of Different Intermittent Fasting Patterns
2.2. Effect of Various TRE Schemes on Metabolic and Signaling Pathways
2.3. Effect of Various PSTF Schemes on Metabolic and Signaling Pathways
| Fasting Time Frame | Duration | Study Design | Study Population | Positive Metabolic Outcomes | Negative Metabolic Outcomes | First Author/[Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 10 weeks | Single-center, randomized controlled trial | 88 females overweight females | ↓ glucose, ↓ insulin, ↓ HOMA-IR, ↑ BHB | ↓ insulin sensitivity, ↑ AST | Hutchison et al., 2019 [58] |
| 24 h | Single protocol | Randomized controlled crossover trial | 30 healthy cases (20 women and 10 men) | ↑ GH, the observed changes in GH levels occurred independently of any associated weight loss | Not reported | Horne et al., 2025 [60] |
| 24 h | 26 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 38 adults | ↓ HOMA-IR, ↓ insulin, ↓ fasting glucose, ↓ metabolic syndrome score, ↓ diastolic blood pressure, ↑ HDL-C | Not reported | Bartholomew et al., 2021 [61] |
| 24 h | 26 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 68 adults | ↓ HOMA-IR, ↓ insulin, ↓ fasting glucose | ↔ body weight | Horne et al., 2024 [62] |
| 24 h | 4 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 28 metabolically healthy, non-obese adults | ↓ body weight, ↑ BHB, ↓ sICAM-1, ↓ systolic blood pressure, ↓ diastolic blood pressure, ↓ HR, ↓ fat: lean ratios, improved lipide profile | ↓ T3 | Stekovic et al., 2019 [63] |
| 24 h | 8 weeks | Randomized parallel-arm trial | 8 healthy adults (4 male and 4 female) | ↓ body weight, ↓ BMI, ↓ FFM | ↓ SMM | Herz et al., 2024 [51] |
| 36 h | Single protocol | Randomized crossover study | 20 healthy adults (11 male and 9 female) | ↑ BHB, ↓insulin, ↑ glucagon, ↓ insulin/glucagon ratio | Not reported | Deru et al., 2021 [64] |
| 36 h | Single protocol | Controlled pilot study | 20 healthy adults (10 male and 10 female) | ↓ TGs, ↓glucose, ↑ circulating ketone bodies, ↑ total antioxidant capacity | Not reported | Rhodes et al., 2023 [15] |
| 48 h | Single protocol | Randomized crossover study | 11 overweight/obese women (mean age: 68.8 ± 6.4 years) | ↓ body mass, ↓ BMI, ↓ FFM, ↓ glucose, ↑ ketone bodies | ↑ salivary cortisol concentration, ↑ hunger, ↑ fatigue, ↑ tension, ↓ reaction time | Solianik et al., 2020 [65] |
| 48 h | Single protocol | Paired within-subject design | 16 healthy females | ↓ body mass, ↓ BMI, ↔ in cortisol levels | Not reported | Mazurak et al., 2013 [66] |
| 48 h | Single protocol | Paired within-subject design | 9 healthy male participants | ↓ body mass, ↓ BMI, ↓glucose, ↓ systolic blood pressure, ↓ heart rate, ↓ oxygenated hemoglobin | ↑ anger, ↓ reaction time | Solianik et al., 2016 [67] |
| 59 h | Single protocol | Controlled human study | 15 young, healthy, non-obese subjects (11 men and 4 women) | ↓ glucose, ↓ insulin, ↑ GH, ↑ lipolytic rate | Not reported | Goldenberg et al., 2022 [68] |
| 60 h | Separated by a period of minimally 2 weeks. | Randomized controlled crossover study | 12 healthy male participants | ↓ body weight, ↓ RER, ↓ energy expenditure | Not reported | Andriessen et al., 2023 [69] |
| 60 h | 2 experimental periods | Randomized controlled crossover study | 12 healthy male participants | ↑ FFA, ↓ insulin, ↓ glucose, ↑ β-oxidation of FFA | ↓ skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity | Hoeks et al., 2010 [70] |
| 60 h | 2 experimental periods | Randomized crossover study | 10 healthy male participants | ↓ leptin, ↓ chemerin, ↑ VEGF | ↔ in Il-1, Il-6, TNF-α,IL-8, hs-CR, adiponectin levels | van Herpen et al., 2013 [71] |
| 72 h | Single protocol | FAST*BRAIN study | 15 healthy females | ↓ body weight, ↓ glucose, ↑ ketone bodies | ↑ BDI-2 score | Ding et al., 2018 [59] |
| 72 h | Two analyses were conducted | Randomized crossover study | 8 healthy males | ↓ insulin, ↓ C-peptide, ↓ glucose, ↓ mTOR, ↑ FFA, ↑ glucagon, ↑ blood flow | ↓ free and total T3 | Vendelbo et al., 2014 [72] |
| 72 h | Single protocol | Controlled metabolic study (lean vs. obese, pre–post design) | 18 healthy men, subjects (9 normal-weight and 9 obese) | ↓ insulin, ↓ C-peptide, ↓ glucose, ↑ FFA, ↑ glucagon,↔ in cortisol levels, ↓ mTOR, ↑ p62 | Not reported | Bak et al., 2016 [73] |
3. Algorithm and Protocol for Preparing Healthy Individuals for PSTF Lasting More than 24 h and up to 72 h
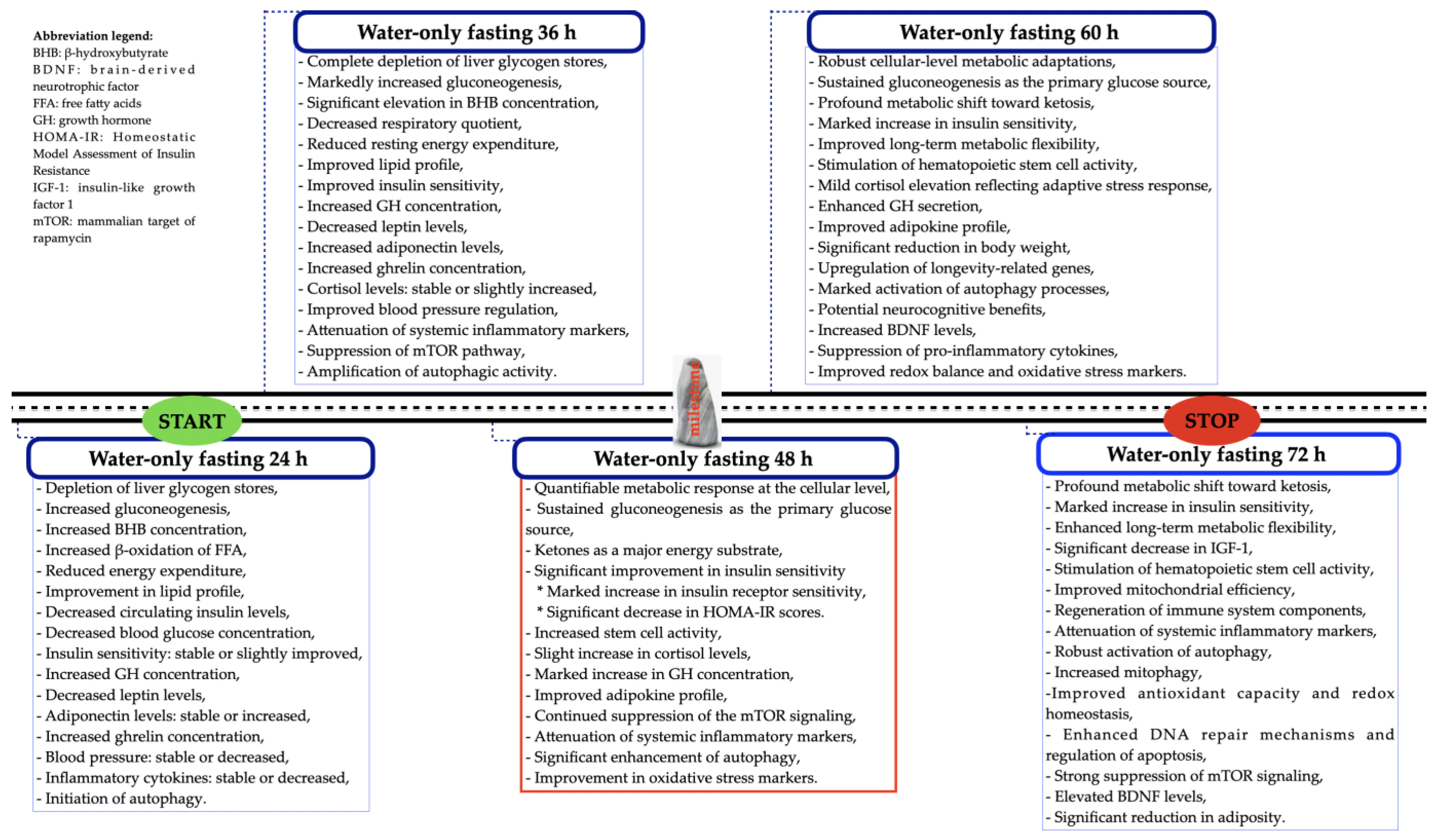
4. A Graphical Summary of the Effects of PSTF Lasting More than 24 h and up to 72 h
5. General Discussion and Future Directions
6. Methodology
- Cross-sectional, case–control, and randomized control trials, and retrospective, prospective cohort or cohort epidemiological studies were included.
- Only studies conducted in humans were included.
- Only full-text articles in English were included.
- Non-human experimental models were excluded.
- Non-English papers were excluded because of the structural language barrier.
- Articles that were not peer-reviewed were excluded.
- Studies involving fasting periods for religious reasons or those exceeding 72 h were also omitted.
- Studies classified as meta-analyses or systematic reviews were excluded.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADF | Alternate-day fasting |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| BDI-2 | Beck Depression Inventory-2 |
| BDN | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BHB | Beta-hydroxybutyrate |
| DHEA | Dehydroepiandrosterone |
| FFA | Free fatty acids |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| GnRH | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| GSK | Glycogen synthase kinase |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobine A1c |
| HDL-C | High-density-lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HLD | Hyperlipidemia |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| IF | Intermittent fasting |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor type 1 |
| IGFBP-1 | Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1 |
| IGFBP-2 | Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 2 |
| IL-1 | Interleukin 1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin 8 |
| LDL-C | Low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MKP-1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| PTSF | Periodic short-term fasting |
| RER | Respiratory exchange ratio |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SHBG | Sex hormone-binding globulin |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| T3 | Triiodothyronine |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TGs | Triglycerides |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TRE | Time-restricted eating |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Thompson, S.; Madsen, L.T.; Bazzell, A. Impact of Fasting on Patients with Cancer: An Integrative Review. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2023, 14, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.D.; Shapiro, M.D.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Tilg, H.; Valenti, L.; Somers, V.K.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G.; Yang, W.; et al. Global burden of metabolic diseases, 1990–2021. Metabolism 2024, 160, 155999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.W.S.; Ng, C.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Kong, G.; Lin, C.; Chin, Y.H.; Lim, W.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Quek, J.; Fu, C.E.; et al. The global burden of metabolic disease: Data from 2000 to 2019. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 414–428.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizi, N.A.; Azhari, N.S.; Ali, A.; Zakaria, N.S.; Yusof, H.M. Outcomes of different types of intermittent fasting for practitioners in terms of nutritional status and quality of life: A systematic review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- López-Tenorio, I.I.; Aguilar-Villegas, Ó.R.; Espinoza-Palacios, Y.; Segura-Real, L.; Peña-Aparicio, B.; Amedei, A.; Aguirre-García, M.M. Primary Prevention Strategy for Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) and Their Risk Factors: The Role of Intestinal Microbiota. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, L.; Zechmeister-Koss, I.; Reinsperger, I. National Strategies for Preventing and Managing Non-communicable Diseases in Selected Countries. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 838051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G. Managing metabolic diseases: The roles and therapeutic prospects of herb-derived polysaccharides. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folin, O.; Denis, W. On starvation and obesity with special regerence to acidosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1915, 21, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Mucignat-Caretta, C.; Anile, F.; Panaite, S.A. Traditional and Medical Applications of Fasting. Nutrients 2022, 14, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, K.; Cherrin, C.; Meires, J. Intermittent Fasting: Exploring Approaches, Benefits, and Implications for Health and Weight Management. J. Nurse Pract. 2024, 20, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasheh, R.T.; Ankireddy, A.; Gabel, K.; Ezpeleta, M.; Lin, S.; Tamatam, C.M.; Reddy, S.P.; Spring, B.; Cheng, T.-Y.D.; Fontana, L.; et al. Effect of Time-Restricted Eating on Circulating Levels of IGF1 and Its Binding Proteins in Obesity: An Exploratory Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.V.; Rhodes, C.H.; Agus, J.K.; Tang, X.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, J.J.; Zivkovic, A.M. A single 36-h water-only fast vastly remodels the plasma lipidome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1251122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.D.; Di Tano, M.; Mattson, M.P.; Guidi, N. Intermittent and periodic fasting, longevity and disease. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.H.; Zhu, C.; Agus, J.; Tang, X.; Li, Q.; Engebrecht, J.; Zivkovic, A.M. Human fasting modulates macrophage function and upregulates multiple bioactive metabolites that extend lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans: A pilot clinical study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppold, D.A.; Breinlinger, C.; Hanslian, E.; Kessler, C.; Cramer, H.; Khokhar, A.R.; Peterson, C.M.; Tinsley, G.; Vernieri, C.; Bloomer, R.J.; et al. International consensus on fasting terminology. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1779–1794.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, R.; Johnston, K.L.; Collins, A.L.; Robertson, M.D. Intermittent v. continuous energy restriction: Differential effects on postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism following matched weight loss in overweight/obese participants. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruces-Sande, M.; Arcones, A.C.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Val-Blasco, A.; Sharabi, K.; Díaz-Rodríguez, D.; Puigserver, P.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Murga, C. Autophagy mediates hepatic GRK2 degradation to facilitate glucagon-induced metabolic adaptation to fasting. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xin, B.; Ma, T.; et al. Hepatic metabolite responses to 4-day complete fasting and subsequent refeeding in rats. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Pakosz, P.; Łukaniszyn-Domaszewska, K.; Mikuláková, W.; Sadowska-Krępa, E.; Anton, S. Effect of a six-week times restricted eating intervention on the body composition in early elderly men with overweight. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, A.L.; Katsilambros, N.L.; Koliaki, C.C. Intermittent Energy Restriction, Weight Loss and Cardiometabolic Risk: A Critical Appraisal of Evidence in Humans. Healthcare 2021, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Pakosz, P.; Baczkowicz, D.; Sadowska-Krępa, E. Effect of a six-week intermittent fasting intervention program on the composition of the human body in women over 60 years of age. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Rogowska, A.M. Examining Associations Between Fasting Behavior, Orthorexia Nervosa, and Eating Disorders. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Dybek, T.; Łukaniszyn-Domaszewska, K.; Anton, S.; Sadowska-Krępa, E.; Skorupska, E. Comparison of the effects of six-week time-restricted eating on weight loss, body composition, and visceral fat in overweight older men and women. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 174, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, T.; Tinsley, G.; Longo, G.; Grigoletto, D.; Bianco, A.; Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Veneto, A.; Tagliabue, A.; Marcolin, G.; et al. Time-restricted eating effects on performance, immune function, and body composition in elite cyclists: A randomized controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M.D.M.; Soares, P.S.G.; Savoi, L.A.; Silva, R.A.D. Fasting reduces satiety and increases hunger but does not affect the performance in resistance training. Biol. Sport 2024, 41, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabkhizan, R.; Haiaty, S.; Moslehian, M.S.; Bazmani, A.; Sadeghsoltani, F.; Saghaei Bagheri, H.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Sakhinia, E. The Beneficial and Adverse Effects of Autophagic Response to Caloric Restriction and Fasting. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.A.; Wu, N.; Rohdin-Bibby, L.; Moore, A.H.; Kelly, N.; Liu, Y.E.; Philip, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Olgin, J.E.; et al. Effects of Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss and Other Metabolic Parameters in Women and Men with Overweight and Obesity: The TREAT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Beyl, R.A.; Poggiogalle, E.; Hsia, D.S.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Reduces Appetite and Increases Fat Oxidation But Does Not Affect Energy Expenditure in Humans. Obesity 2019, 27, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayra, S.T.; Chondropoulos, K.; De Leon, A.; Kravat, N.; Johnston, C.S. The feasibility and preliminary efficacy of early time-restricted eating on diet quality in college students: A randomized study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 16, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, G.; Mirisola, M.G.; Longo, V.D. Intermittent and Periodic Fasting, Hormones, and Cancer Prevention. Cancers 2021, 13, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, T.; Tinsley, G.; Pacelli, F.Q.; Marcolin, G.; Bianco, A.; Paoli, A. Twelve Months of Time-restricted Eating and Resistance Training Improves Inflammatory Markers and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, T.; Tinsley, G.; Bianco, A.; Marcolin, G.; Pacelli, Q.F.; Battaglia, G.; Palma, A.; Gentil, P.; Neri, M.; Paoli, A. Effects of eight weeks of time-restricted feeding (16/8) on basal metabolism, maximal strength, body composition, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors in resistance-trained males. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cienfuegos, S.; Gabel, K.; Kalam, F.; Ezpeleta, M.; Wiseman, E.; Pavlou, V.; Lin, S.; Oliveira, M.L.; Varady, K.A. Effects of 4- and 6-h Time-Restricted Feeding on Weight and Cardiometabolic Health: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Adults with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 366–378.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.J.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Zadourian, A.; Lo, H.; Fakhouri, S.; Shoghi, A.; Wang, X.; Fleischer, J.G.; Navlakha, S.; Panda, S.; et al. Ten-Hour Time-Restricted Eating Reduces Weight, Blood Pressure, and Atherogenic Lipids in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 92–104.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Yan, C.; Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z. Time-restricted feeding improves blood glucose and insulin sensitivity in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised controlled trial. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, A.T.; Regmi, P.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Fleischer, J.G.; Wittert, G.A.; Panda, S.; Heilbronn, L.K. Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Glucose Tolerance in Men at Risk for Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Obesity 2019, 27, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, A.; Tamargo, J.A.; Golberg, L.; Haub, M.D.; Anton, S.D. The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Overweight Older Adults: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Hernández, D.R.; Jiménez-Domínguez, G.; Méndez, J.D.; Olvera-Hernández, V.; Martínez-López, M.C.; Guzmán-Priego, C.G.; Reyes-López, Z.; Ramos-García, M.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; Zavaleta-Toledo, S.S.; et al. Effect of Early Time-Restricted Eating on Metabolic Markers and Body Composition in Individuals with Overweight or Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, B.; Domin, R.; Krzywicka, M.; Laudańska-Krzemińska, I. Effect of exercise alone and in combination with time-restricted eating on cardiometabolic health in menopausal women. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, M.J.; Pigg, B.L.; Renteria, L.I.; Waldman, H.S. Time-restricted feeding improves markers of cardiometabolic health in physically active college-age men: A 4-week randomized pre-post pilot study. Nutr. Res. 2020, 75, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, K.; Hoddy, K.K.; Haggerty, N.; Song, J.; Kroeger, C.M.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Panda, S.; Varady, K.A. Effects of 8-h time restricted feeding on body weight and metabolic disease risk factors in obese adults: A pilot study. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Pavlou, V.; Chakos, K.; McStay, M.; Runchey, M.C.; Alexandria, S.J.; Varady, K.A. Effect of Time-Restricted Eating versus Daily Calorie Restriction on Mood and Quality of Life in Adults with Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejeki, P.S.; Pranoto, A.; Widiatmaja, D.M.; Utami, D.M.; Izzatunnisa, N.; Sugiharto; Lesmana, R.; Halim, S. Combined Aerobic Exercise with Intermittent Fasting Is Effective for Reducing mTOR and Bcl-2 Levels in Obese Females. Sports 2024, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshed, H.; Beyl, R.A.; Manna, D.L.D.; Yang, E.S.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves 24-Hour. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, F.; Akasheh, R.T.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ankireddy, A.; Gabel, K.; Ezpeleta, M.; Lin, S.; Tamatam, C.M.; Reddy, S.P.; Spring, B.; et al. Effect of time-restricted eating on sex hormone levels in premenopausal and postmenopausal females. Obesity 2023, 31, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stote, K.S.; Baer, D.J.; Spears, K.; Paul, D.R.; Harris, G.K.; Rumpler, W.V.; Strycula, P.; Najjar, S.S.; Ferrucci, L.; Ingram, D.K.; et al. A controlled trial of reduced meal frequency without caloric restriction in healthy, normal-weight, middle-aged adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, O.; Martin, B.; Stote, K.S.; Golden, E.; Maudsley, S.; Najjar, S.S.; Ferrucci, L.; Ingram, D.K.; Longo, D.L.; Rumpler, W.V.; et al. Impact of reduced meal frequency without caloric restriction on glucose regulation in healthy, normal-weight middle-aged men and women. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, M.R.; Lammers, N.M.; Dubbelhuis, P.F.; Ackermans, M.T.; Jonkers-Schuitema, C.F.; Fliers, E.; Sauerwein, H.P.; Aerts, J.M.; Serlie, M.J. Intermittent fasting does not affect whole-body glucose, lipid, or protein metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, D.; Karl, S.; Weiß, J.; Zimmermann, P.; Haupt, S.; Zimmer, R.T.; Schierbauer, J.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Erlmann, M.P.; Niedrist, T.; et al. Effects of Different Types of Intermittent Fasting Interventions on Metabolic Health in Healthy Individuals (EDIF): A Randomised Trial with a Controlled-Run in Phase. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, R.; Robertson, T.M.; Robertson, M.D.; Johnston, J.D. A pilot feasibility study exploring the effects of a moderate time-restricted feeding intervention on energy intake, adiposity and metabolic physiology in free-living human subjects. J. Nutr. Sci. 2018, 7, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/24-07-2024-hunger-numbers-stubbornly-high-for-three-consecutive-years-as-global-crises-deepen--un-report (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Parcha, V.; Heindl, B.; Kalra, R.; Li, P.; Gower, B.; Arora, G.; Arora, P. Insulin Resistance and Cardiometabolic Risk Profile Among Nondiabetic American Young Adults: Insights From NHANES. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e25–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, M.; Abou Jaoudeh, M.G.; Merhi, S.; Mosleh, J.M.B.; Ghadieh, R.; Al Hayek, S.; El Hayek Fares, J.E. Evaluation of risk factors for insulin resistance: A cross sectional study among employees at a private university in Lebanon. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogłodek, E.; Pilis, W. Is Water-Only Fasting Safe? Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2021, 10, 21649561211031178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmi de Toledo, F.; Grundler, F.; Bergouignan, A.; Drinda, S.; Michalsen, A. Safety, health improvement and well-being during a 4 to 21-day fasting period in an observational study including 1422 subjects. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, A.T.; Liu, B.; Wood, R.E.; Vincent, A.D.; Thompson, C.H.; O’Callaghan, N.J.; Wittert, G.A.; Heilbronn, L.K. Effects of Intermittent Versus Continuous Energy Intakes on Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Risk in Women with Overweight. Obesity 2019, 27, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.Q.; Maudsley, A.A.; Schweiger, U.; Schmitz, B.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Bleich, S.; Lanfermann, H.; Kahl, K.G. Effects of a 72 h fasting on brain metabolism in healthy women studied in vivo with magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2018, 38, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, B.D.; Anderson, J.L.; May, H.T.; Bair, T.L.; Le, V.T.; Iverson, L.; Knowlton, K.U.; Muhlestein, J.B. Weight loss-independent changes in human growth hormone during water-only fasting: A secondary evaluation of a randomized controlled trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1401780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, C.; Muhlestein, J.B.; May, H.T.; Le, V.T.; Galenko, O.; Garrett, K.D.; Brunker, C.; Hopkins, R.O.; Carlquist, J.F.; Knowlton, K.U.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of once-per-week intermittent fasting for health improvement: The WONDERFUL trial. Eur. Heart J. Open 2021, 1, oeab026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, B.D.; Anderson, J.L.; May, H.T.; Bair, T.L.; Le, V.T.; Iverson, L.; Knowlton, K.U.; Muhlestein, J.B. Insulin resistance reduction, intermittent fasting, and human growth hormone: Secondary analysis of a randomized trial. NPJ Metab. Health Dis. 2024, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekovic, S.; Hofer, S.J.; Tripolt, N.; Aon, M.A.; Royer, P.; Pein, L.; Stadler, J.T.; Pendl, T.; Prietl, B.; Url, J.; et al. Alternate Day Fasting Improves Physiological and Molecular Markers of Aging in Healthy, Non-obese Humans. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 462–476.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deru, L.S.; Bikman, B.T.; Davidson, L.E.; Tucker, L.A.; Fellingham, G.; Bartholomew, C.L.; Yuan, H.L.; Bailey, B.W. The Effects of Exercise on β-Hydroxybutyrate Concentrations over a 36-h Fast: A Randomized Crossover Study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solianik, R.; Žlibinaitė, L.; Drozdova-Statkevičienė, M.; Sujeta, A. Forty-eight-hour fasting declines mental flexibility but improves balance in overweight and obese older women. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 223, 112995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurak, N.; Günther, A.; Grau, F.S.; Muth, E.R.; Pustovoyt, M.; Bischoff, S.C.; Zipfel, S.; Enck, P. Effects of a 48-h fast on heart rate variability and cortisol levels in healthy female subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solianik, R.; Sujeta, A.; Terentjevienė, A.; Skurvydas, A. Effect of 48 h Fasting on Autonomic Function, Brain Activity, Cognition, and Mood in Amateur Weight Lifters. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1503956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, N.; Horowitz, J.F.; Gorgey, A.; Sakharova, A.; Barkan, A.L. Role of pulsatile growth hormone (GH) secretion in the regulation of lipolysis in fasting humans. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriessen, C.; Doligkeit, D.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Mensink, M.; Hesselink, M.K.C.; Hoeks, J.; Schrauwen, P. The impact of prolonged fasting on 24h energy metabolism and its 24h rhythmicity in healthy, lean males: A randomized cross-over trial. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeks, J.; van Herpen, N.A.; Mensink, M.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; van Beurden, D.; Hesselink, M.K.; Schrauwen, P. Prolonged fasting identifi es skeletal muscle mitochondrial dysfunction as consequence rather than cause of human insulin resistance. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herpen, N.A.; Sell, H.; Eckel, J.; Schrauwen, P.; Mensink, R.P. Prolonged fasting and the effects on biomarkers of inflammation and on adipokines in healthy lean men. Horm. Metab. Res. 2013, 45, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendelbo, M.H.; Møller, A.B.; Christensen, B.; Nellemann, B.; Clasen, B.F.; Nair, K.S.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Jessen, N.; Møller, N. Fasting increases human skeletal muscle net phenylalanine release and this is associated with decreased mTOR signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, A.M.; Møller, A.B.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Nielsen, T.S.; Viggers, R.; Rungby, J.; Pedersen, S.B.; Jørgensen, J.O.; Jessen, N.; Møller, N. Differential regulation of lipid and protein metabolism in obese vs. lean subjects before and after a 72-h fast. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E224–E235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attinà, A.; Leggeri, C.; Paroni, R.; Pivari, F.; Dei Cas, M.; Mingione, A.; Dri, M.; Marchetti, M.; Di Renzo, L. Fasting: How to Guide. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, E.; Gabriel, S.; Ncube, M.; Thompson, N.; Newmire, D.; Scharf, E.L.; Goldhamer, A.C.; Myers, T.R. Prolonged Water-Only Fasting Followed by a Whole-Plant-Food Diet Is a Potential Long-Term Management Strategy for Hypertension and Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarrillom, C.M.; Keirns, B.H.; Elliott, D.C.; Emerson, S.R. The effect of black coffee on fasting metabolic markers and an abbreviated fat tolerance test. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 41, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Johnson, E.C. Water Intake, Water Balance, and the Elusive DailyWater Requirement. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.D.; Mattson, M.P. Fasting: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torske, A.; Bremer, B.; Hölzel, B.K.; Maczka, A.; Koch, K. Mindfulness meditation modulates stress-eating and its neural correlates. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.H.; Rajeev, V.; Fann, D.Y.; Jo, D.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Intermittent fasting increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencioni, A.; Caffa, I.; Cortellino, S.; Longo, V.D. Fasting and cancer: Molecular mechanisms and clinical application. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 298Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlma, R.S.; Prabakaran, D.; Mantzoros, C.; Qu, D.; Lowell, B.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Flier, J.S. Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 1996, 382, 250–252. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Fernández, R.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Navarro, V.M.; Barreiro, M.L.; Castellano, J.M.; Aguilar, E.; Pinilla, L. Effects of ghrelin upon gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin secretion in adult female rats: In vivo and in vitro studies. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 82, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, V.; Singh, A.; Bhatt, M.; Tonk, R.K.; Azizov, S.; Raza, A.S.; Sengupta, S.; Kumar, D.; Garg, M. Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullur, R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Brent, G.A. Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Joo, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Choe, H.K.; Tong, Q.; Kwon, O. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on the Circulating Levels and Circadian Rhythms of Hormones. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedinger, C.J.; Kimball, K.J.; Kilgore, L.C.; Bell, C.W.; Heidel, R.E.; Boone, J.D. Water only fasting and its effect on chemotherapy administration in gynecologic malignancies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, J.; Brooks, A.; Fernando, S.; Westenberger, G.; Junkins, S.; Smith, S.; Min, K.; Lawan, A. Fasting-Induced Upregulation of MKP-1 Modulates the Hepatic Response to Feeding. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, H. Exploring the therapeutic potential of plasma from intermittent fasting and untreated rats on aging-induced liver damage. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, M.; Mao, X.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Huang, H.; et al. Alternate-day fasting protects the livers of mice against high-fat diet-induced inflammation associated with the suppression of Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor κB signaling. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijngaarden, M.A.; van der Zon, G.C.; van Dijk, K.W.; Pijl, H.; Guigas, B. Effects of prolonged fasting on AMPK signaling, gene expression, and mitochondrial respiratory chain content in skeletal muscle from lean and obese individuals. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E1012–E1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. β-hydroxybutyrate: Much more than a metabolite. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 106, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, F.; James, D.L.; Li, Y.R.; Coleman, M.F.; Kiesel, V.A.; Cespedes Feliciano, E.M.; Hursting, S.D.; Sears, D.D.; Kleckner, A.S. Intermittent fasting interventions to leverage metabolic and circadian mechanisms for cancer treatment and supportive care outcomes. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2023, 2023, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yecies, J.L.; Manning, B.D. MTOR links oncogenic signaling to tumor cell metabolism. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Hall, M.N. Making new contacts: The mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damián, J.P.; Bausero, M.; Bielli, A. Acute stress, hypothalamic-hypophyseal-gonadal axis and testicular function-a review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2015, 15, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IF Regimens | Fasting/Eating Window | Recommended Daily Schedules | Intended Population | Strengths | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRE: 16/8 | 16 h fasting/ 8 h feeding | 10 a.m.–6 p.m. 11 a.m.–7 p.m. 12 p.m.–8 p.m. | Entry-level practitioners or Intermediate-level practitioners |
|
|
| TRE: 18/6 | 18 h fasting/ 6 h feeding | 12 p.m.–6 p.m. 1 p.m.–7 p.m. 2 p.m.–8 p.m. | Intermediate-level practitioners |
|
|
| TRE: 20/4 | 20 h fasting/ 4 h feeding | 2 p.m.–6 p.m. 3 p.m.–7 p.m. 4 p.m.–8 p.m. | Advanced practitioners |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fasting/Eating Time | Duration | Study Design | Study Population | Positive Metabolic Outcomes | Negative Metabolic Outcomes | First Author, Year [Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14/10 | 12 weeks | Single-arm, paired-sample trial | 19 participants with metabolic syndrome | ↓ systolic and diastolic blood pressure, ↓ TC, ↓ LDL-C, ↓ non-HDL-C, ↓ HbA1c | Not reported | Wilkinson et al., 2020 [35] |
| 14/10 | 12 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 120 overweight adults with type 2 diabetes | ↓ HbA1c, ↓ glucose, ↑ insulin sensitivity, ↓ TGs, ↓ TC, ↓ LDL-C | Not reported | Che et al., 2021 [36] |
| 15/9 | 1 week | Randomized crossover trial | 15 adults with prediabetes | ↓ TGs, ↑ glucose responses | Not reported | Hutchison et al., 2019 [37] |
| 16/8 | 8 weeks | Single-blind randomized study | 34 resistance-trained males | ↑ adiponectin, ↓ total leptin, ↓ IGF-1 | ↓ testosterone, ↓ T3 | Moro et al., 2016 [33] |
| 16/8 | 12 months | Single-blind randomized study | 20 healthy resistance-trained subjects | ↓ IL-6, ↓ IL-1β, ↑ HDL-C, ↓ LDL-C, ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IGF-1 | ↓ testosterone | Moro et al., 2021 [32] |
| 16/8 | 4 weeks | Single-blind randomized study | 16 elite under-23 cyclists | ↑ adiponectin, ↓ IGF-1 | ↓ free testosterone | Moro et al., 2020 [25] |
| 16/8 | 4 weeks | Pilot, single-arm interventional study | 10 overweight older adults | ↓ IL-1β, ↓ TNF-α | Not reported | Ezzati et al., 2025 [38] |
| 16/8 | 4 weeks | Randomized crossover trial | 17 adults with obesity | Not reported | Not reported | Mena-Hernández et al., 2024 [39] |
| 16/8 | 12 weeks | Quasi-experimental trial | 62 menopausal women | ↓ glucose, ↓ insulin, ↓ HOMA-IR | Not reported | Jóźwiak et al., 2024 [40] |
| 16/8 | 4 weeks | Randomized pre-post pilot study | 22 physically active men | ↑ adiponectin, ↑ HDL-C | Not reported | McAllister et al., 2020 [41] |
| 16/8 | 12 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 46 adults with obesity | ↓ systolic blood pressure | Not reported | Gabel et al., 2018 [42] |
| 16/8 | 12 months | Randomized controlled trial | 90 adults with obesity | ↔ in total testosterone, DHEA, SHBG, estradiol, and progesterone | Not reported | Lin et al., 2023 [43] |
| 16/8 | 2 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 10 obese females | ↓ mTOR, ↓ fat mass, ↓ body weight | Not reported | Rejeki et al., 2024 [44] |
| 18/6 | 12 weeks | Randomized clinical trial | 116 adults with BMI from 27 to 43 kg/m2 | Not reported | ↔ in fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, HbA1C, TGs, TC, LDL-C or HDL-C | Lowe et al., 2020 [28] |
| 18/6 | 5 weeks | Supervised controlled feeding trial | 8 men with prediabetes | ↑ insulin sensitivity, ↑ β cell responsiveness, ↓ blood pressure, ↓ oxidative stress levels | Not reported | Sutton et al., 2018 [45] |
| 18/6 | 12 weeks | Randomized crossover trial | 11 overweight adults | ↑ glycemic control, ↓ glycemic excursions, ↑ ketone levels, ↓ cortisol levels, ↑ BDNF, ↑ sirtuine | ↑ mTOR | Jamshed et al., 2019 [46] |
| 18/6 | 4 days | Randomized crossover trial | 11 overweight adults | ↓ levels of active ghrelin, ↓ leptin, ↓ GLP-1 | Not reported | Ravussin et al., 2019 [29] |
| 18/6 | 4 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 25 healthy adults | Not reported | ↔ in systolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose and LDL-C | Mayra et al., 2022 [30] |
| 20/4 18/6 | 8 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 23 premenopausal and postmenopausal women | ↓ DHEA | ↔ in testosterone, androstenedione, SHBG, estradiol, estrone, and progesterone | Kalam et al., 2023 [47] |
| 20/4 | 8 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 15 normal-weight adults | ↑ HDL-C, ↓ cortisol | ↑ hunger, ↑ blood pressure, ↑ LDL-C | Stote et al., 2007 [48] |
| 20/4 18/6 | 8 weeks | Randomized controlled trial | 49 obese adults | ↓ fasting glucose, ↓ insulin, ↓ oxidative stress levels | ↔ in TNF-α, IL-6, TGs, TC, LDL-C or HDL-C | Cienfuegos et al., 2020 [34] |
| 20/4 | 16 weeks | Randomized crossover trial | 15 normal-weight adults | Not reported | ↑ glucose, delayed insulin response, ↑ ghrelin, ↔ differences in levels of insulin, leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and BDNF | Carlson et al., 2007 [49] |
| 20/4 | 2 weeks | Randomized crossover trial | 8 normal-weight, healthy adults | ↑ GSK, ↓ mTOR | ↔ in insulin-mediated peripheral glucose uptake, hepatic insulin sensitivity, insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue, or proteolysis | Soeters et al., 2009 [50] |
| 20/4 18/6 | 8 weeks | Randomized parallel-arm trial | 35 adults with obesity | ↓ fat mas, ↓ lean mass, ↓ visceral fat mass, ↓ waist circumference, ↓ insulin, ↓ HOMA-IR, ↓ HbA1c,↓ 8-isoprostane | ↔ in circulating levels of IGF-1, IGFBP1, and IGFBP3 | Akasheh et al., 2024 [12] |
| 20/4 18/6 | 8 weeks | Randomized parallel-arm trial | 17 healthy adults | ↓ WHR | ↑ LDL-C, ↔ in body weight or BMI | Herz et al., 2024 [51] |
| ^ | 10 weeks | Pilot feasibility study | 13 adults with obesity | ↓ fat mass, ↓ fasting glucose | Not reported | Antoni et al., 2018 [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciastek, B.; Kapłon, K.; Domaszewski, P. A Comprehensive Perspective on the Biological Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Periodic Short-Term Fasting: A Promising Strategy for Optimizing Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132061
Ciastek B, Kapłon K, Domaszewski P. A Comprehensive Perspective on the Biological Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Periodic Short-Term Fasting: A Promising Strategy for Optimizing Metabolic Health. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132061
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiastek, Barbara, Karolina Kapłon, and Przemysław Domaszewski. 2025. "A Comprehensive Perspective on the Biological Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Periodic Short-Term Fasting: A Promising Strategy for Optimizing Metabolic Health" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132061
APA StyleCiastek, B., Kapłon, K., & Domaszewski, P. (2025). A Comprehensive Perspective on the Biological Effects of Intermittent Fasting and Periodic Short-Term Fasting: A Promising Strategy for Optimizing Metabolic Health. Nutrients, 17(13), 2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132061








